Genomic Characterization of Quality Wool Traits in Spanish Merino Sheep
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Animal Selection and Phenotyping
2.3. Sequencing, Alignment and Quality Control
2.4. Variant Calling
2.5. Genome-Wide Association
2.6. Identification of Candidate Genes
3. Results
3.1. Summary Statistics of Phenotype Data
3.2. Statistic of Sequencing Data
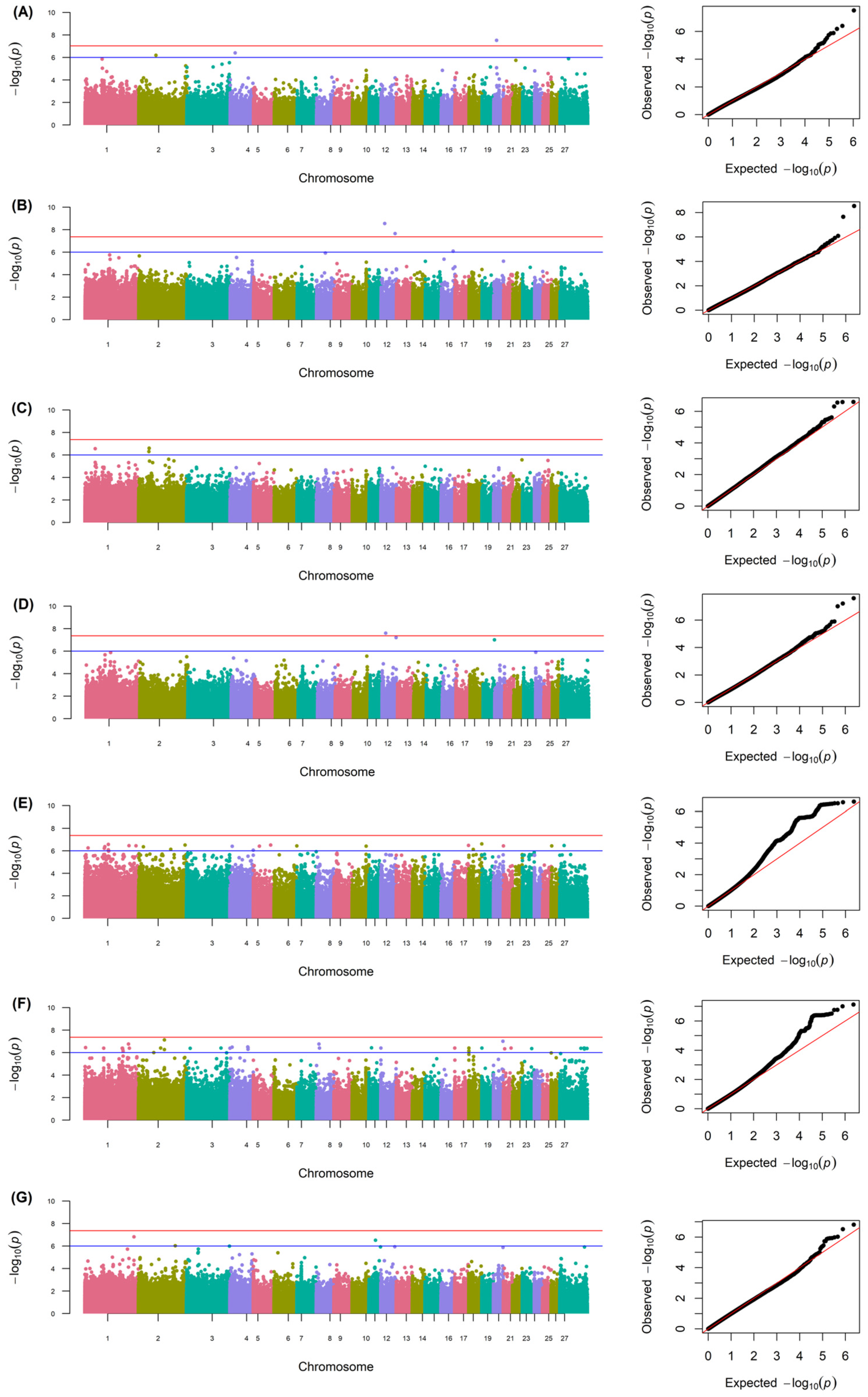
3.3. Genome-Wide Association and Identification of Candidate Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciani, E.; Lasagna, E.; D’Andrea, M.; Alloggio, I.; Marroni, F.; Ceccobelli, S.; Delgado Bermejo, J.V.; Sarti, F.M.; Kijas, J.; Lenstra, J.A.; et al. Merino and Merino-derived sheep breeds: A genome-wide intercontinental study. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2015, 47, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccobelli, S.; Landi, V.; Senczuk, G.; Mastrangelo, S.; Sardina, M.T.; Ben-Jemaa, S.; Persichilli, C.; Karsli, T.; Bâlteanu, V.-A.; Raschia, M.A. A comprehensive analysis of the genetic diversity and environmental adaptability in worldwide Merino and Merino-derived sheep breeds. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2023, 55, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belda, A.S.; Trujillano MC, S. Razas Ovinas Españolas; Ministerio de Agricultura: Madrid, Spain, 1986; p. 887. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, M. La Raza Merina y Sus Cruces en la Producción de Carne; MAPA, Ministerio de Agricultura Pesca y Alimentación del Gobierno de España: Madrid, Spain, 1994; p. 175. [Google Scholar]
- Peña Blanco, F.; Alcalde Aldea, M.J. Las Razas Ovinas Integradas en Andalucía: Merino Precoz Francés, Ille de France, Fleischscaff, Landschaff y Lacaune; Las Razas Ganaderas de Andalucía, Patrimonio Ganadero Patrimonio Ganadero Andaluz: Madrid, Spain, 2007; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Azor, P.C.I.; Valera, M.; Arranz, J.J.; Medina, C.; Gutiérrez, J.P.; Goyache, F.; Muñoz, A. Análisis preliminar de la estructura genética del Merino: Situación de las estirpes tradicionales mediante análisis genealógico y molecular. In XIV Reunión Nacional de Mejora Genética Animal; Asociación Interprofesional para el Desarrollo Agrario (AIDA): Zaragoza, Spain, 2008; Volume 104, pp. 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Granero, A.M.A.; Anaya, G.; Ziadib, C.; Alcalde, M.J. Morphometric differences based on quantitative traits between different genetic lines in the Merino Español sheep breed. ASPA 24th Congress Book of Abstract. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20 (Suppl. 1), 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granero, A.; Anaya, G.; Alcalde, M.J. Morphostructural Differences between the Historical Genetic Lines of the Spanish Merino Sheep. Animals 2023, 13, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granero, A.; Anaya, G.; Demyda-Peyrás, S.; Alcalde, M.J.; Arrebola, F.; Molina, A. Genomic Population Structure of the Main Historical Genetic Lines of Spanish Merino Sheep. Animals 2022, 12, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya, G.; Granero, A.; Alcalde, M.J. Situación genética de las principales líneas puras del merino español. ITEA-Inf. Tec. Econ. Agrar. 2024, 120, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARCA. Sistema Nacional de Información de Razas; ARCA: Barcelona, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, R.N.; Jacobs, A.; Wilder, A.P.; Therkildsen, N.O. A beginner’s guide to low-coverage whole genome sequencing for population genomics. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 5966–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. GigaScience 2015, 4, s13742-015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Stephens, M. Genome-wide efficient mixed-model analysis for association studies. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S. qqman: An R package for visualizing GWAS results using QQ and Manhattan plots. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzik, Y.; Kizilaslan, M.; Behrem, S.; White, S.N.; Piel, L.M.; Cinar, M.U. Genome-wide scan of wool production traits in Akkaraman sheep. Genes 2023, 14, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Rong, E.; Pei, W.; Li, H.; Wang, N. Genome-wide association study for wool production traits in a Chinese Merino sheep population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Guo, T.; Lu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Qiao, G.; Han, M.; Yuan, C.; Wang, T.; Li, F. Genome-wide association studies detects candidate genes for wool traits by re-sequencing in Chinese fine-wool sheep. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, M.; Li, T.; Lu, Z.; Wang, H.; Yuan, Z.; Wei, C. Whole-Genome Resequencing Reveals Selection Signal Related to Sheep Wool Fineness. Animals 2023, 13, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, F.; Rong, E.; Jing, Y.; Yang, H.; Ma, G.; Yan, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, N. Structural Characterization and Association of Ovine Dickkopf-1 Gene with Wool Production and Quality Traits in Chinese Merino. Genes 2017, 8, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolormaa, S.; Swan, A.A.; Brown, D.J.; Hatcher, S.; Moghaddar, N.; Van Der Werf, J.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Daetwyler, H.D. Multiple-trait QTL mapping and genomic prediction for wool traits in sheep. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2017, 49, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.M.; Woods, J.L.; Schauer, C.S.; Stewart, W.C.; Murdoch, B.M. Genetic association of wool quality characteristics in United States Rambouillet sheep. Front. Genet. 2023, 13, 1081175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, Z.; Garrick, D.J.; Blair, H.T.; Vera, B.; Ciappesoni, G.; Kenyon, P.R. Genomic regions associated with wool, growth and reproduction traits in Uruguayan Merino sheep. Genes 2023, 14, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaid, A.; Wang, L. Chapter 3—Identification of Australian merino wool. In The Wool Handbook; Jose, S., Thomas, S., Basu, G., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2024; pp. 75–99. [Google Scholar]
- Valera, M.; Arrebola, F.; Juárez, M.; Molina, A. Genetic improvement of wool production in Spanish Merino sheep: Genetic parameters and simulation of selection strategies. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2009, 49, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrebola, F. Caracterización Genética de la Aptitud Lanera del Merino Autóctono Español; Universidad de Córdoba: Córdoba, Colombia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cannas, A.; Nudda, A.; Pulina, G. Nutritional Strategies to Improve Lactation Persistency in Dairy Ewes; University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Pressoir, G.; Briggs, W.H.; Vroh Bi, I.; Yamasaki, M.; Doebley, J.F.; McMullen, M.D.; Gaut, B.S.; Nielsen, D.M.; Holland, J.B.; et al. A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchini, J.; Cardon, L.R.; Phillips, M.S.; Donnelly, P. The effects of human population structure on large genetic association studies. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.-J.; Zhu, W.-Y.; Wang, D.-G.; Yue, X.-Z.; Li, C.-R. Endothelin-1 combined with extracellular matrix proteins promotes the adhesion and chemotaxis of amelanotic melanocytes from human hair follicles in vitro. Cell Biol. Int. 2006, 30, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, P.; Sunkara, R.; Heitman, N.; Rangl, M.; Brown, A.; Saxena, N.; Grisanti, L.; Kohan, D.; Yanagisawa, M.; Rendl, M. Progenitor-derived endothelin controls dermal sheath contraction for hair follicle regression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2023, 25, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Jia, X.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Long, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q. An Early Diagnostic Clue for COL18A1- and LAMA1-Associated Diseases: High Myopia with Alopecia Areata in the Cranial Midline. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 644947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, M.A.; Blakeborough, L.; Harries, M.; Haslam, I.S. Cholesterol homeostasis: Links to hair follicle biology and hair disorders. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-H.; Xiang, L.-J.; Shi, H.-X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.-P.; Cai, P.-T.; Lin, Z.-L.; Lin, B.-B.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.-L.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factors Stimulate Hair Growth through β-Catenin and Shh Expression in C57BL/6 Mice. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 730139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuoka, K.; Schell, H.; Wessel, B.; Hornstein, O.P. Effects of epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, minoxidil and hydrocortisone on growth kinetics in human hair bulb papilla cells and root sheath fibroblasts cultured in vitro. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1987, 279, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Hu, R.; Li, F.; Yue, X. Five SNPs Within the FGF5 Gene Significantly Affect Both Wool Traits and Growth Performance in Fine-Wool Sheep (Ovis aries). Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 732097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chen, W.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, G.; Hu, X.; Mou, C. Comparative investigation of coarse and fine wool sheep skin indicates the early regulators for skin and wool diversity. Gene 2020, 758, 144968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzke, C.W.; Cobzaru, C.; Triantafyllopoulou, A.; Löffek, S.; Horiuchi, K.; Threadgill, D.W.; Kurz, T.; van Rooijen, N.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Blobel, C.P. Epidermal ADAM17 maintains the skin barrier by regulating EGFR ligand-dependent terminal keratinocyte differentiation. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1105–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Gordon, S.; Nixon, A.; Bawden, C.; Rogers, M.; Wildermoth, J.; Maqbool, N.; Pearson, A. Expression patterns of keratin intermediate filament and keratin associated protein genes in wool follicles. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 2009, 77, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trait | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Diameter | FD | The average fiber diameter in a staple of wool, measured in microns. Fibers do not have a uniform thickness within the staple because they grow at different rates and speeds. The differences in thickness can be up to 15 microns. |
| Standard Deviation | SD | Measurement of the variation of wool fiber diameter. Microns of variation between the average of the FD and the minimal and maximal diameter. |
| Coefficient of Variation | CV | Another measure of variability of the fiber diameter, but expressed as a percentage and relative to the average fiber diameter. This is determined mathematically using the equation: CV% = SD/AFD × 100 |
| Comfort Factor | CF | Percentage of fibers under 30 microns. Fibers wider than 30 microns are rigid and do not bend when they touch the skin, resulting in the wool having a prickly feeling and/or skin irritation. |
| Fiber under 15 microns | <15% | Percentage of extra fine fibers under 15 microns. |
| Staple Length | SL | Measurement of the length of the unstretched staple expressed in millimeters. |
| Fiber Curvature | CRV | Fiber curvature expressed in degrees/millimeters. Generally, a greater curvature is associated with a higher crimp frequency. |
| Trait (Unit) | Code | Group | Mean | Min. | Max. | CV % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber diameter (µm) | FD | Global | 22.21 | 15.2 | 28.5 | 10 |
| Male | 25.07 | 21.4 | 28.5 | 7.41 | ||
| Female | 21.92 | 15.2 | 28.2 | 9.2 | ||
| Standard deviation (µm) | SD | Global | 3.89 | 2.3 | 6.6 | 17 |
| Male | 4.40 | 2.7 | 6.4 | 17 | ||
| Female | 3.83 | 2.3 | 6.6 | 16.22 | ||
| Coefficient of variation (%) | CV | Global | 17.48 | 12 | 29 | 12 |
| Male | 17.49 | 12.5 | 25.2 | 13.93 | ||
| Female | 17.48 | 12 | 29 | 11.94 | ||
| Comfort factor (%) | CF | Global | 95.66 | 70.8 | 100 | 6 |
| Male | 87.63 | 71 | 100 | 9.38 | ||
| Female | 96.46 | 70.8 | 100 | 5.1 | ||
| Fibers under 15 microns (%) | <15% | Global | 2.74 | 0 | 44.4 | 131 |
| Male | 0.55 | 0 | 3.6 | 138 | ||
| Female | 2.96 | 0 | 44.4 | 125 | ||
| Staple length (mm) | SL | Global | 42.6 | 15 | 85 | 24 |
| Male | 50.78 | 20 | 85 | 28.62 | ||
| Female | 41.78 | 15 | 80 | 22.58 | ||
| Fiber curvature (degrees/mm) | CRV | Global | 119.14 | 69.1 | 171.8 | 13 |
| Male | 104.81 | 69.1 | 140.4 | 13.31 | ||
| Female | 120.56 | 75.1 | 171.8 | 12.75 |
| Trait | Chr | Pos. (bp) | p-Value | Nearest Gene | Distance (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FD | 2 | 89,558,512 | 6.51632 × 10−7 | LOC114112820 | −678 |
| 4 | 25,386,150 | 3.958888 × 10−7 | ENSOARG00020040429 | within | |
| 20 | 14,330,117 | 3.015784 × 10−8 | LRFN2 | within | |
| SD | 12 | 18,454,843 | 2.880708 × 10−9 | USH2A | within |
| 72,689,402 | 2.22192 × 10−8 | SYT14 | within | ||
| 16 | 61,545,925 | 8.147923 × 10−7 | CTNND2 | within | |
| CV | 1 | 52,910,619 | 2.798289 × 10−7 | ST6GALNAC3 | within |
| 2 | 53,391,808 | 4.948564 × 10−7 | FANCG | 331 | |
| 55,005,118 | 2.572812 × 10−7 | LOC121818624 | 26,374 | ||
| 55,047,205 | 2.521822 × 10−7 | ENSOARG00020031756 | within | ||
| CF | 12 | 18,454,843 | 2.542981 × 10−8 | USH2A | within |
| 72,689,402 | 6.228683 × 10−8 | SYT14 | within | ||
| 19 | 58,874,366 | 9.867142 × 10−8 | EFCC1 | within | |
| >15% | 1 | 15,993,581 | 5.558001 × 10−7 | EDN2 | 32,531 |
| 101,310,201 | 5.935847 × 10−7 | LOC114117513 | −1293 | ||
| 103,394,621 | 4.247662 × 10−7 | ENSOARG00020030884 | within | ||
| 121,546,311 | 2.677888 × 10−7 | RCAN1 | within | ||
| 121,608,994 | 8.232058 × 10−7 | RCAN1 | within | ||
| 122,856,396 | 9.882277 × 10−7 | IFNAR1 | within | ||
| 229,038,319 | 3.510156 × 10−7 | ENSOARG00020038272 | within | ||
| 265,955,164 | 3.546715 × 10−7 | COL18A1 | within | ||
| 2 | 25,569,486 | 4.394279 × 10−7 | DIRAS2 | 68,469 | |
| 16,8452,761 | 7.346249 × 10−7 | LRP1B | within | ||
| 242,826,705 | 3.103179 × 10−7 | HMGCL | 5056 | ||
| 4 | 11,699,947 | 3.954987 × 10−7 | CALCR | −28,368 | |
| 121,492,684 | 8.785249 × 10−7 | LOC114114472 | −40,923 | ||
| 5 | 31,265,184 | 3.916315 × 10−7 | ENSOARG00020027327 | within | |
| 89,990,179 | 3.08966 × 10−7 | TRNAW-CCA | −279,579 | ||
| 6 | 117,917,615 | 3.670075 × 10−7 | CTBP1 | −899 | |
| 10 | 72,536,458 | 3.864163 × 10−7 | UGGT2 | within | |
| 17 | 71,252,665 | 3.322203 × 10−7 | LOC105602956 | within | |
| 18 | 22,794,738 | 7.483516 × 10−7 | LOC114118854 | within | |
| 66,955,441 | 2.417579 × 10−7 | SIVA1 | within | ||
| 21 | 16,607 | 3.724726 × 10−7 | PANX1 | 177,023 | |
| 26 | 2,331,482 | 3.70147 × 10−7 | CSMD1 | within | |
| X | 21,855,901 | 3.363513 × 10−7 | PTCHD1 | −10,474 | |
| SL | 1 | 2,983,391 | 3.575274 × 10−7 | TRAF3IP1 | within |
| 97,859,378 | 4.074127 × 10−7 | LOC114112215 | 9239 | ||
| 194,406,396 | 4.074127 × 10−7 | LOC121816689 | 16,194 | ||
| 195,679,749 | 4.082481 × 10−7 | FGF12 | within | ||
| 196,441,630 | 5.059276 × 10−7 | ENSOARG00020027852 | within | ||
| 198,957,601 | 7.336839 × 10−7 | TPRG1 | within | ||
| 227,004,375 | 1.747904 × 10−7 | NMD3 | within | ||
| 231,145,470 | 4.074127 × 10−7 | VEPH1 | within | ||
| 2 | 115,507,582 | 3.980196 × 10−7 | LOC106990902 | −20,393 | |
| 135,022,009 | 7.476657 × 10−8 | ENSOARG00020033964 | within | ||
| 135,336,861 | 5.380042 × 10−7 | CHRNA1 | within | ||
| 3 | 18,857,597 | 4.179918 × 10−7 | ADAM17 | within | |
| 179,239,910 | 3.971237 × 10−7 | HMOX1, ENSOARG00020039035 | within | ||
| 4 | 43,547 | 4.107503 × 10−7 | LOC105605926 | 265,080 | |
| 11,316,451 | 3.296337 × 10−7 | HEPACAM2 | within | ||
| 92,353,566 | 3.143381 × 10−7 | GRM8 | within | ||
| 93,899,832 | 3.592256 × 10−7 | SND1 | within | ||
| 93,938,145 | 5.156819 × 10−7 | LRRC4 | within | ||
| 8 | 13,764,777 | 1.733298 × 10−7 | NKAIN2 | within | |
| 16,549,119 | 4.012221 × 10−7 | LOC132660198 | 102,411 | ||
| 11 | 14,111,738 | 3.757219 × 10−7 | ENSOARG00020021921 | within | |
| 12 | 192,483 | 4.012221 × 10−7 | ENSOARG00020035247 | within | |
| 17 | 37,935 | 4.012221 × 10−7 | LOC105605790 | 243,265 | |
| 18 | 221,140 | 4.012221 × 10−7 | MKRN3 | 303,877 | |
| 226,967 | 7.148295 × 10−7 | MKRN3 | 298,050 | ||
| 19 | 79,786 | 4.012221 × 10−7 | MRPS24 | 142,918 | |
| 20 | 49,080,151 | 1.000487 × 10−7 | LOC114109591 | within | |
| 21 | 6,275,544 | 4.693387 × 10−7 | GRM5, ENSOARG00020035270 | within | |
| 40,000,782 | 4.009804 × 10−7 | TIGD3 | within | ||
| 23 | 48,181,894 | 4.356746 × 10−7 | ZBTB7C | within | |
| X | 109,190,351 | 4.158501 × 10−7 | TENM1 | within | |
| 125,810,956 | 3.979989 × 10−7 | GUCY2F | within | ||
| 127,195,428 | 4.009804 × 10−7 | VSIG1 | within | ||
| 127,703,493 | 4.928113 × 10−7 | FRMPD3 | within | ||
| 141,116,984 | 4.336624 × 10−7 | TRNAC-ACA | −21,661 | ||
| CRV | 1 | 255,629,888 | 1.540812 × 10−7 | AMOTL2 | −6948 |
| 2 | 191,763,534 | 9.518238 × 10−7 | LOC101116805 | 112,736 | |
| 11 | 34,467,404 | 3.054953 × 10−7 | ENSOARG00020039760 | within |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anaya, G.; Laseca, N.; Granero, A.; Ziadi, C.; Arrebola, F.; Domingo, A.; Molina, A. Genomic Characterization of Quality Wool Traits in Spanish Merino Sheep. Genes 2024, 15, 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060795
Anaya G, Laseca N, Granero A, Ziadi C, Arrebola F, Domingo A, Molina A. Genomic Characterization of Quality Wool Traits in Spanish Merino Sheep. Genes. 2024; 15(6):795. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060795
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnaya, Gabriel, Nora Laseca, Antonio Granero, Chiraz Ziadi, Francisco Arrebola, Andrés Domingo, and Antonio Molina. 2024. "Genomic Characterization of Quality Wool Traits in Spanish Merino Sheep" Genes 15, no. 6: 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060795
APA StyleAnaya, G., Laseca, N., Granero, A., Ziadi, C., Arrebola, F., Domingo, A., & Molina, A. (2024). Genomic Characterization of Quality Wool Traits in Spanish Merino Sheep. Genes, 15(6), 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060795






