Multiple Congenital Anomalies-Hypotonia-Seizures Syndrome 2 Caused by a Novel PIGA Variant Not Associated with a Skewed X-Inactivation Pattern
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Exome Sequencing
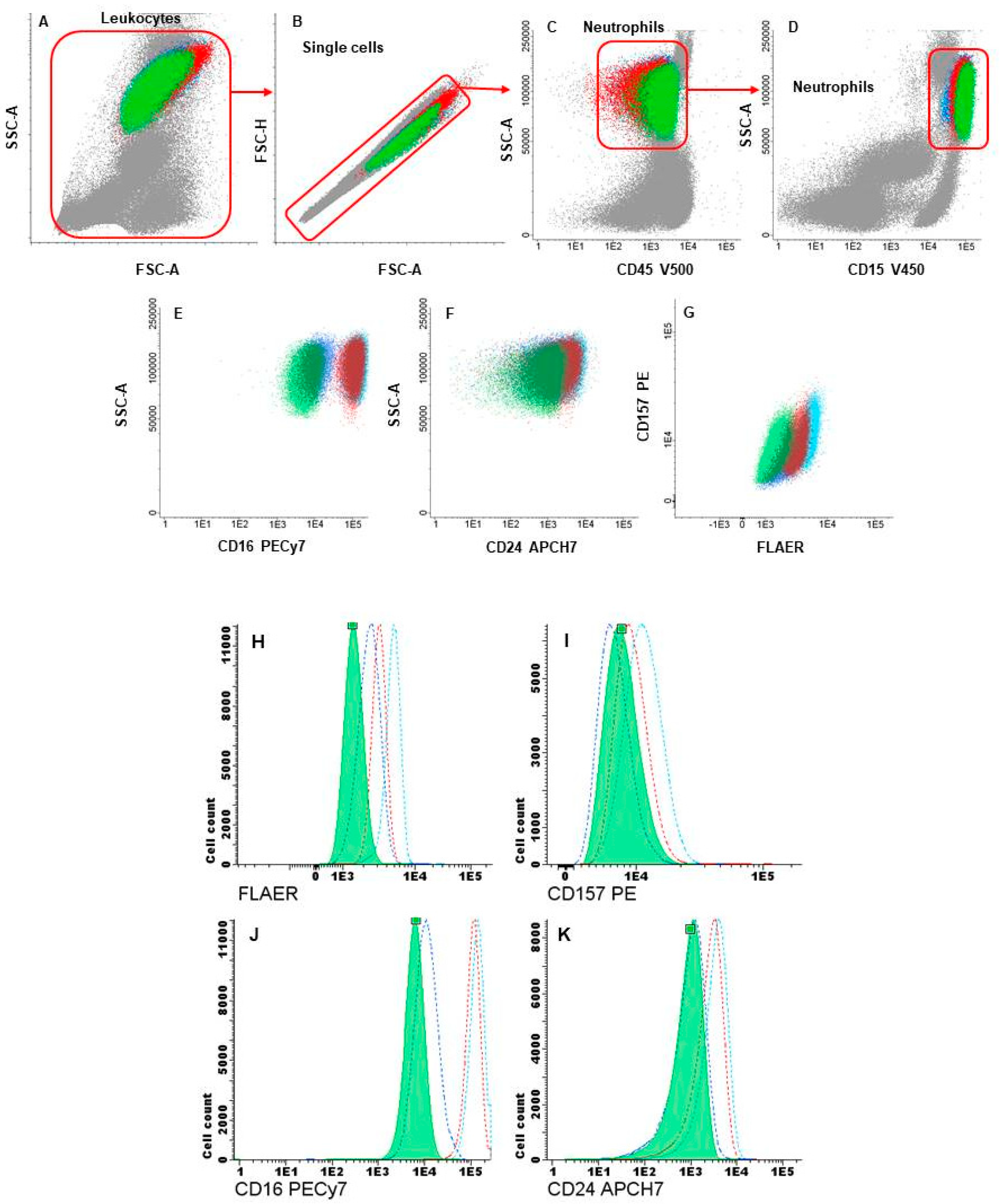
2.2. Flow-Cytometry Analysis and Cell Sorting of GPI-APs-Deficient Hematopoietic Cells
2.3. X Inactivation Studies
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Features
3.2. Identification of PIGA Variant
3.3. Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting
3.4. X Chromosome Inactivation Studies
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kinoshita, T.; Fujita, M.; Maeda, Y. Biosynthesis, remodelling and functions of mammalian GPI-anchored proteins: Recent progress. J. Biochem. 2008, 144, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, J.J.; Gropman, A.L.; Sapp, J.C.; Teer, J.K.; Martin, J.M.; Liu, C.F.; Yuan, X.; Ye, Z.; Cheng, L.; Brodsky, R.A.; et al. The phenotype of a germline mutation in PIGA: The gene somatically mutated in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swoboda, K.J.; Margraf, R.L.; Carey, J.C.; Zhou, H.; Newcomb, T.M.; Coonrod, E.; Durtschi, J.; Mallempati, K.; Kumanovics, A.; Katz, B.E.; et al. A novel germline PIGA mutation in Ferro-Cerebro-Cutaneous syndrome: A neurodegenerative X-linked epileptic encephalopathy with systemic iron-overload. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Crabben, S.N.; Harakalova, M.; Brilstra, E.H.; van Berkestijn, F.M.; Hofstede, F.C.; van Vught, A.J.; Cuppen, E.; Kloosterman, W.; van Amstel, H.K.P.; van Haaften, G.; et al. Expanding the spectrum of pheno-types associated with germline PIGA mutations: A child with developmental delay, acceler-ated linear growth, facial dysmorphisms, elevated alkaline phosphatase, and progressive CNS abnormalities. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarailo-Graovac, M.; Sinclair, G.; Stockler-Ipsiroglu, S.; Van Allen, M.; Rozmus, J.; Shyr, C.; Biancheri, R.; Oh, T.; Sayson, B.; Lafek, M.; et al. The genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of PIGA deficiency. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, G.; Galupa, R. Mechanisms of Choice in X-Chromosome Inactivation. Cells 2022, 11, 535, Erratum in Cells 2023, 12, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterova, T.B.; Johnston, C.M.; Appanah, R.; Newall, A.E.; Godwin, J.; Alexiou, M.; Brockdorff, N. Skewing X chromosome choice by modulating sense transcription across the Xist locus. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2177–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lossi, A.; Millán, J.; Villard, L.; Orellana, C.; Cardoso, C.; Prieto, F.; Fontés, M.; Martínez, F. Mutation of the XNP/ATR-X gene in a family with severe mental retardation, spastic paraplegia and skewed pattern of X inactivation: Demonstration that the mutation is involved in the inactivation bias. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 65, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, M.J.; Rangasamy, S.; Narayanan, V. Incontinentia pigmenti (Bloch-Sulzberger syndrome). Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 132, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieremans, N.; Van Esch, H.; Holvoet, M.; Van Goethem, G.; Devriendt, K.; Rosello, M.; Mayo, S.; Martinez, F.; Jhangiani, S.; Muzny, D.M.; et al. Identification of Intellectual Disability Genes in Female Patients with a Skewed X-Inactivation Pattern. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.J.; James, M.; Sharples, P.M.; Eaton, M.; Jenkinson, S.; Study, D.D.; Smithson, S.F. A novel PIGA variant associated with severe X-linked epilepsy and profound developmental delay. Seizure 2018, 56, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, F.; Caro-Llopis, A.; Roselló, M.; Oltra, S.; Mayo, S.; Monfort, S.; Orellana, C. High diagnostic yield of syndromic intellectual disability by targeted next-generation sequencing. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 54, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illingworth, A.J.; Marinov, I.; Sutherland, D.R. Sensitive and accurate identification of PNH clones based on ICCS/ESCCA PNH Consensus Guidelines—A summary. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2019, 41, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.C.; Zoghbi, H.Y.; Moseley, A.B.; Rosenblatt, H.M.; Belmont, J.W. Methylation of Hpall and Hhal Sites Near the Polymorphic CAG Repeat in the Human Androgen-Receptor Gene Correlates with X Chromosome Inactivation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1992, 51, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keller, P.; Tremml, G.; Rosti, V.; Bessler, M. X Inactivation and Somatic Cell Selection Rescue Female Mice Carrying a Piga-Null Mutation (Cre/LoxPglycosyl Phosphatidylinosi-tolXp22paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7479–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayat, A.; Knaus, A.; Pendziwiat, M.; Afenjar, A.; Barakat, T.S.; Bosch, F.; Callewaert, B.; Calvas, P.; Ceulemans, B.; Chassaing, N.; et al. Lessons learned from 40 novel PIGA patients and a review of the literature. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 1142–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.D.; Chou, I.C.; Tsai, F.J.; Hong, S.Y. A novel PIGA mutation in a Taiwanese family with early-onset epileptic encephalopathy. Seizure 2018, 58, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Saitsu, H.; Murakami, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Watanabe, S.; Iai, M.; Miya, K.; Matsuura, R.; Takayama, R.; Ohba, C.; et al. PIGA Mutations Cause Early-Onset Epileptic Encephalopathies and Distinctive Features. Neurology 2014, 82, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.; Kløvgaard, M.; Johannesen, K.M.; Barakat, T.S.; Kievit, A.; Montomoli, M.; Parrini, E.; Pietrafusa, N.; Schelhaas, J.; van Slegtenhorst, M.; et al. Deciphering the premature mortality in PIGA-CDG—An untold story. Epilepsy Res. 2021, 170, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.O.; Yang, J.H.; Park, C.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, M.K.; Shin, M.G.; Woo, Y.J. A novel PIGA mutation in a family with X-linked, early-onset epileptic encephalopathy. Brain Dev. 2016, 38, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.-L.; Song, X.-J.; Li, T.-Y.; Jiang, L. A novel germline PIGA mutation causes early-onset epileptic encephalopathies in Chinese monozygotic twins. Brain Dev. 2018, 40, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhofer, C.M.; Funke, R.; Wilken, B.; Knaus, A.; Altmüller, J.; Nürnberg, P.; Li, Y.; Wollnik, B.; Burfeind, P.; Pauli, S. A Novel Mutation in PIGA Associated with Multiple Congenital Anomalies-Hypotonia-Seizure Syndrome 2 (MCAHS2) in a Boy with a Com-bination of Severe Epilepsy and Gingival Hyperplasia. Mol. Syndromol. 2020, 11, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Reagent | Clone | Target Population | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytometry, first step | FLAER Alexa Fluor 488a | NA | Neutrophils |
| Monocytes | |||
| (GPI marker) | |||
| CD157 PEb | SY11B5 | Neutrophils Monocytes (GPI protein) | |
| CD45 PercPb | 2D1 | Leukocytes | |
| CD15 HV450b | MMA | NeutrophiIs | |
| CD64 APCb | 10.1 | Monocytes | |
| Cytometry, second step | CD16 PeCy7b (tube 1) | 3G8 | Neutrophils (GPI protein) |
| CD24 APCH7b (tube 1) | ML5 | Neutrophils (GPI protein) | |
| CD20 PerCPCy5.5b (tube 1) | L27 | B lymphocytes | |
| CD14 APCH7b (tube 2) | MP9 | Monocytes (GPI protein) | |
| CD24 PEc (tube 2) | ML5 | Neutrophils (GPI protein) | |
| Cell sorting | CD15 HV450b | MMA | Neutrophils |
| CD45 HV500b | HI30 | Leukocytes | |
| CD157 PEb | SY11B5 | Neutrophils Monocytes (GPI protein) | |
| CD16 PECy7b | 3G8 | Neutrophils (GPI protein) | |
| CD20 PerCPCy5.5b | L27 | B lymphocytes | |
| CD64 APCb | 10.1 | Monocytes | |
| FLAER Alexa Fluor 488a | NA | Neutrophils Monocytes (GPI marker) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gabaldon-Albero, A.; Cordon, L.; Sempere, A.; Pedrola, L.; Martin-Grau, C.; Oltra, S.; Monfort, S.; Caro-Llopis, A.; Dominguez-Martinez, M.; Hernandez-Muela, S.; et al. Multiple Congenital Anomalies-Hypotonia-Seizures Syndrome 2 Caused by a Novel PIGA Variant Not Associated with a Skewed X-Inactivation Pattern. Genes 2024, 15, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060802
Gabaldon-Albero A, Cordon L, Sempere A, Pedrola L, Martin-Grau C, Oltra S, Monfort S, Caro-Llopis A, Dominguez-Martinez M, Hernandez-Muela S, et al. Multiple Congenital Anomalies-Hypotonia-Seizures Syndrome 2 Caused by a Novel PIGA Variant Not Associated with a Skewed X-Inactivation Pattern. Genes. 2024; 15(6):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060802
Chicago/Turabian StyleGabaldon-Albero, Alba, Lourdes Cordon, Amparo Sempere, Laia Pedrola, Carla Martin-Grau, Silvestre Oltra, Sandra Monfort, Alfonso Caro-Llopis, Marta Dominguez-Martinez, Sara Hernandez-Muela, and et al. 2024. "Multiple Congenital Anomalies-Hypotonia-Seizures Syndrome 2 Caused by a Novel PIGA Variant Not Associated with a Skewed X-Inactivation Pattern" Genes 15, no. 6: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060802
APA StyleGabaldon-Albero, A., Cordon, L., Sempere, A., Pedrola, L., Martin-Grau, C., Oltra, S., Monfort, S., Caro-Llopis, A., Dominguez-Martinez, M., Hernandez-Muela, S., Rosello, M., Orellana, C., & Martinez, F. (2024). Multiple Congenital Anomalies-Hypotonia-Seizures Syndrome 2 Caused by a Novel PIGA Variant Not Associated with a Skewed X-Inactivation Pattern. Genes, 15(6), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060802






