Effects of ACLY Inhibition on Body Weight Distribution: A Drug Target Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
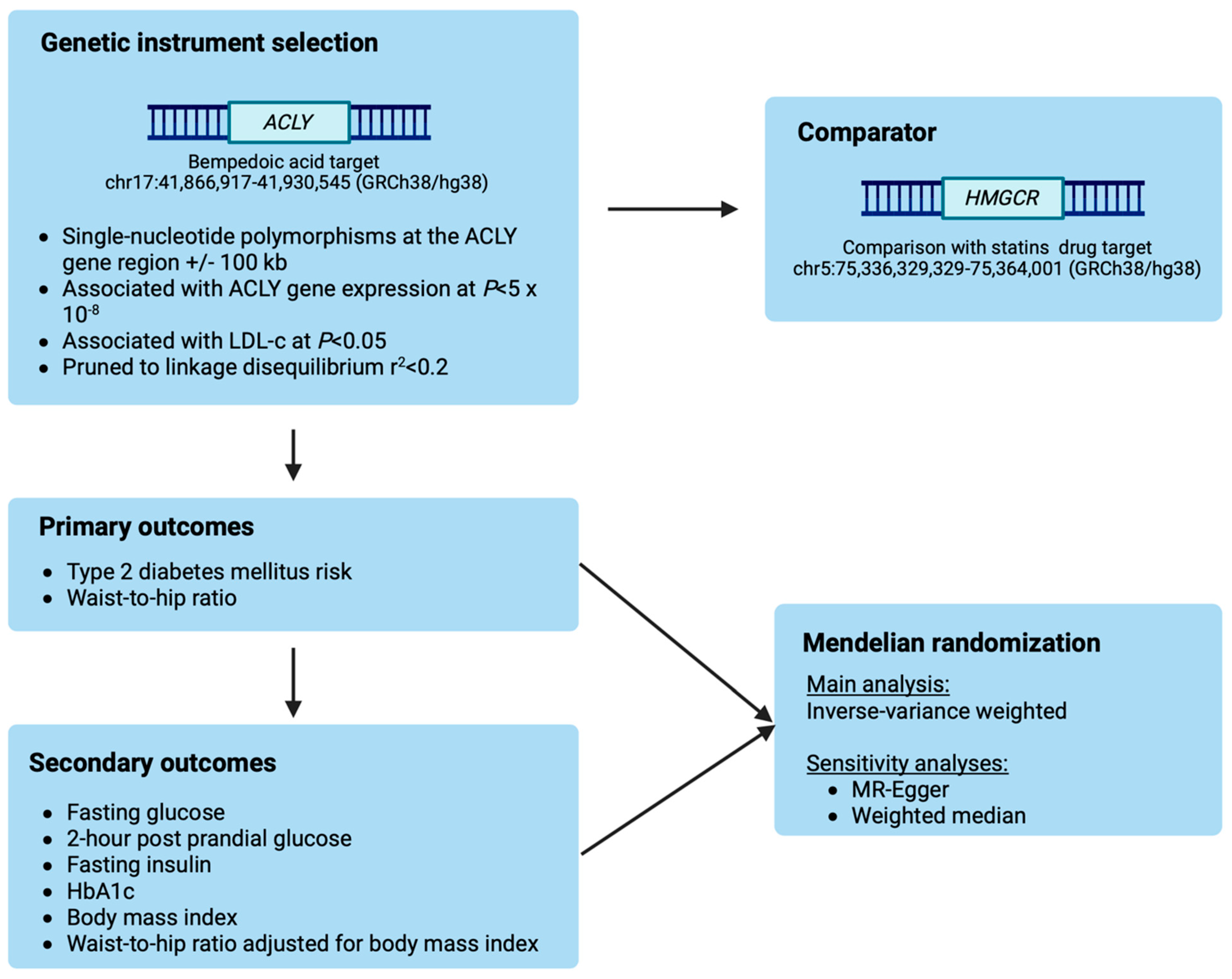
2.1. Selection of Genetic Instruments
2.2. Outcome Data Sources
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Reporting
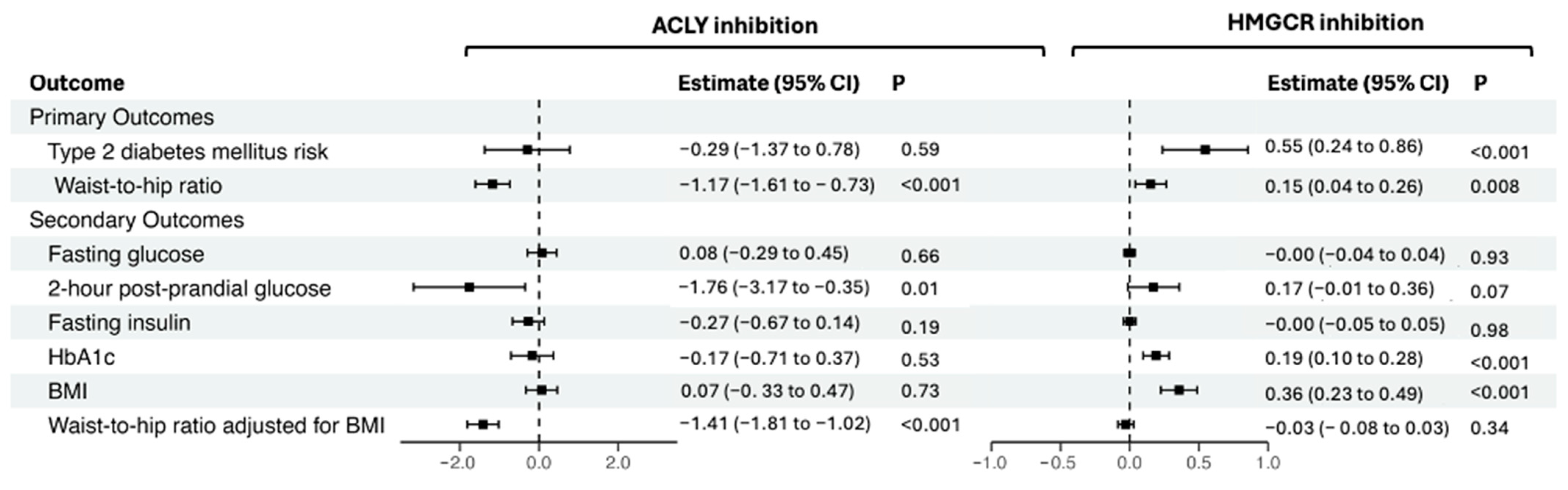
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACLY | adenosine triphosphate-citrate lyase |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| GWAS | genome-wide association study |
| HbA1c | glycated haemoglobin |
| HMGCR | 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase |
| LDL-c | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| MR | Mendelian randomization |
| OR | odds ratio |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
References
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. Metabolic syndrome—A new world-wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 16. Diabetes Care in the Hospital: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S244–S253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regufe, V.M.G.; Pinto, C.; Perez, P. Metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetic patients: A review of current evidence. Porto Biomed. J. 2020, 5, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.; Reith, C.; Emberson, J.; Armitage, J.; Baigent, C.; Blackwell, L.; Blumenthal, R.; Danesh, J.; Smith, G.D.; DeMets, D.; et al. Interpretation of the evidence for the efficacy and safety of statin therapy. Lancet 2016, 388, 2532–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chogtu, B.; Magazine, R.; Bairy, K.L. Statin use and risk of diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwala, A.; Kulkarni, S.; Maddox, T. The Association of Statin Therapy with Incident Diabetes: Evidence, Mechanisms, and Recommendations. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2018, 20, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Moon, J.Y.; Daghlas, I.; Franco, G.; Porneala, B.C.; Ahmadizar, F.; Richardson, T.G.; Isaksen, J.L.; Hindy, G.; Yao, J.; et al. Obesity Partially Mediates the Diabetogenic Effect of Lowering LDL Cholesterol. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, D.I.; Preiss, D.; Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Holmes, M.V.; Engmann, J.E.; Shah, T.; Sofat, R.; Stender, S.; Johnson, P.C.; Scott, R.A.; et al. HMG-coenzyme A reductase inhibition, type 2 diabetes, and bodyweight: Evidence from genetic analysis and randomised trials. Lancet 2015, 385, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrocola, F.; Galluzzi, L.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Madeo, F.; Kroemer, G. Acetyl coenzyme A: A central metabolite and second messenger. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 805–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmes, D.M.; Kurzbach, A.; Henke, C.; Schumann, T.; Zahn, G.; Heifetz, A.; Jordan, J.; Helfand, S.L.; Birkenfeld, A.L. The longevity gene INDY (I’m Not Dead Yet) in metabolic control: Potential as pharmacological target. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 185, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkosky, S.L.; Groot, P.H.E.; Lalwani, N.D.; Steinberg, G.R. Targeting ATP-Citrate Lyase in Hyperlipidemia and Metabolic Disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 1047–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkosky, S.L.; Newton, R.S.; Day, E.A.; Ford, R.J.; Lhotak, S.; Austin, R.C.; Birch, C.M.; Smith, B.K.; Filippov, S.; Groot, P.H.E.; et al. Liver-specific ATP-citrate lyase inhibition by bempedoic acid decreases LDL-C and attenuates atherosclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Lincoff, A.M.; Brennan, D.; Ray, K.K.; Mason, D.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Thompson, P.D.; Libby, P.; Cho, L.; Plutzky, J.; et al. Bempedoic Acid and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Statin-Intolerant Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, M.R.; Batchuluun, B.; Wu, J.; Ahmadi, E.; Leroux, J.M.; Mohammadi-Shemirani, P.; Desjardins, E.M.; Wang, Z.; Tsakiridis, E.E.; Lavoie, D.C.T.; et al. Inhibition of ATP-citrate lyase improves NASH, liver fibrosis, and dyslipidemia. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 919–936 e918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.K.; Nicholls, S.J.; Li, N.; Louie, M.J.; Brennan, D.; Lincoff, A.M.; Nissen, S.E.; Committees, C.O. Efficacy and safety of bempedoic acid among patients with and without diabetes: Prespecified analysis of the CLEAR Outcomes randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 12, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Silverio, D.; Sourlas, A.; Garcia, F.; Montan, P.D.; Guzman, E. Impact of lipid-lowering therapy on glycemic control and the risk for new-onset diabetes mellitus. Drugs Context 2018, 7, 212562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Burgess, S.; Mason, A.M.; Grant, A.J.; Slob, E.A.W.; Gkatzionis, A.; Zuber, V.; Patel, A.; Tian, H.; Liu, C.; Haynes, W.G.; et al. Using genetic association data to guide drug discovery and development: Review of methods and applications. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 110, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, D.; Georgakis, M.K.; Walker, V.M.; Schmidt, A.F.; Gkatzionis, A.; Freitag, D.F.; Finan, C.; Hingorani, A.D.; Howson, J.M.M.; Burgess, S.; et al. Mendelian randomization for studying the effects of perturbing drug targets. Wellcome Open Res. 2021, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ference, B.A.; Ray, K.K.; Catapano, A.L.; Ference, T.B.; Burgess, S.; Neff, D.R.; Oliver-Williams, C.; Wood, A.M.; Butterworth, A.S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; et al. Mendelian Randomization Study of ACLY and Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klarin, D.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Kathiresan, S. Mendelian Randomization Study of ACLY and Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, e50. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32786204/ (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Holm, H.; Sulem, P.; Helgadottir, A.; Tragante, V.; Thornorleifsson, G.; Guethbjartsson, D.; Stefansson, K. Mendelian Randomization Study of ACLY and Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, e50. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32786206/ (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Mohammadi-Shemirani, P.; Chong, M.; Perrot, N.; Pigeyre, M.; Steinberg, G.R.; Pare, G.; Krepinsky, J.C.; Lanktree, M.B. ACLY and CKD: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Spracklen, C.N.; Marenne, G.; Varshney, A.; Corbin, L.J.; Luan, J.; Willems, S.M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Horikoshi, M.; et al. The trans-ancestral genomic architecture of glycemic traits. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 840–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulit, S.L.; Stoneman, C.; Morris, A.P.; Wood, A.R.; Glastonbury, C.A.; Tyrrell, J.; Yengo, L.; Ferreira, T.; Marouli, E.; Ji, Y.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for body fat distribution in 694 649 individuals of European ancestry. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vosa, U.; Claringbould, A.; Westra, H.J.; Bonder, M.J.; Deelen, P.; Zeng, B.; Kirsten, H.; Saha, A.; Kreuzhuber, R.; Yazar, S.; et al. Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, S.E.; Clarke, S.L.; Wu, K.H.; Kanoni, S.; Zajac, G.J.M.; Ramdas, S.; Surakka, I.; Ntalla, I.; Vedantam, S.; Winkler, T.W.; et al. The power of genetic diversity in genome-wide association studies of lipids. Nature 2021, 600, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, A.; Spracklen, C.N.; Zhang, W.; Ng, M.C.Y.; Petty, L.E.; Kitajima, H.; Yu, G.Z.; Rueger, S.; Speidel, L.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Multi-ancestry genetic study of type 2 diabetes highlights the power of diverse populations for discovery and translation. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neale, B. 2018. Available online: http://www.nealelab.is/uk-biobank/ (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, N.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Davey Smith, G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: A guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ 2018, 362, k601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sola-Garcia, A.; Caliz-Molina, M.A.; Espadas, I.; Petr, M.; Panadero-Moron, C.; Gonzalez-Moran, D.; Martin-Vazquez, M.E.; Narbona-Perez, A.J.; Lopez-Noriega, L.; Martinez-Corrales, G.; et al. Metabolic reprogramming by Acly inhibition using SB-204990 alters glucoregulation and modulates molecular mechanisms associated with aging. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkosky, S.L.; Filippov, S.; Srivastava, R.A.; Hanselman, J.C.; Bradshaw, C.D.; Hurley, T.R.; Cramer, C.T.; Spahr, M.A.; Brant, A.F.; Houghton, J.L.; et al. AMP-activated protein kinase and ATP-citrate lyase are two distinct molecular targets for ETC-1002, a novel small molecule regulator of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, W.; Lobo, M.; Lavalle-Cobo, A.; Masson, G.; Molinero, G. Effect of bempedoic acid on new onset or worsening diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 168, 108369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, C.T.; Goetz, B.; Hopson, K.L.; Fici, G.J.; Ackermann, R.M.; Brown, S.C.; Bisgaier, C.L.; Rajeswaran, W.G.; Oniciu, D.C.; Pape, M.E. Effects of a novel dual lipid synthesis inhibitor and its potential utility in treating dyslipidemia and metabolic syndrome. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banach, M.; Duell, P.B.; Gotto, A.M., Jr.; Laufs, U.; Leiter, L.A.; Mancini, G.B.J.; Ray, K.K.; Flaim, J.; Ye, Z.; Catapano, A.L. Association of Bempedoic Acid Administration with Atherogenic Lipid Levels in Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trials of Patients with Hypercholesterolemia. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damask, A.; Paulding, C.; Baras, A.; Carey, D.; Abecasis, G.R. Mendelian Randomization Study of ACLY and Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, e50. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32786205/ (accessed on 5 August 2024). [PubMed]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration; Reith, C.; Preiss, D.; Blackwell, L.; Emberson, J.; Spata, E.; Davies, K.; Halls, H.; Holland, L.; Wilson, K. Effects of statin therapy on diagnoses of new-onset diabetes and worsening glycaemia in large-scale randomised blinded statin trials: An individual participant data meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 12, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandforth, A.; von Schwartzenberg, R.J.; Arreola, E.V.; Hanson, R.L.; Sancar, G.; Katzenstein, S.; Lange, K.; Preissl, H.; Dreher, S.I.; Weigert, C.; et al. Mechanisms of weight loss-induced remission in people with prediabetes: A post-hoc analysis of the randomised, controlled, multicentre Prediabetes Lifestyle Intervention Study (PLIS). Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Schulze, M.B. Metabolic health and cardiometabolic risk clusters: Implications for prediction, prevention, and treatment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, M.B.; Thorand, B.; Fritsche, A.; Haring, H.U.; Schick, F.; Zierer, A.; Rathmann, W.; Kroger, J.; Peters, A.; Boeing, H.; et al. Body adiposity index, body fat content and incidence of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despres, J.P. Body fat distribution and risk of cardiovascular disease: An update. Circulation 2012, 126, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumpertz von Schwartzenberg, R.; Vazquez Arreola, E.; Sandforth, A.; Hanson, R.L.; Birkenfeld, A.L. Role of weight loss-induced prediabetes remission in the prevention of type 2 diabetes: Time to improve diabetes prevention. Diabetologia 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkenfeld, A.L.; Mohan, V. Prediabetes remission for type 2 diabetes mellitus prevention. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 441–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakso, M.; Fernandes Silva, L. Statins and risk of type 2 diabetes: Mechanism and clinical implications. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1239335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dannecker, C.; Wagner, R.; Peter, A.; Hummel, J.; Vosseler, A.; Haring, H.U.; Fritsche, A.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Stefan, N.; Heni, M. Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Is Associated with Insulin Secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Trait and Ascertainment | N | Units | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure | ACLY gene expression in blood | 31,684 | Standard deviation | Nature Genetics. 2021 Sep; 53(9), 1300–1310 [25] |
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol | 1,231,289 | Standard deviation | Nature. 2021 Dec; 600(7890):675–679 [26] | |
| Primary outcomes | Type 2 diabetes mellitus risk | Ncases = 180,834 Ncontrols = 1,159,055 | Natural log-transformed OR | Nat Genet. 2022 May; 54(5):560–572 [27] |
| Waist-to-hip ratio | 697,734 | Standard deviation | Hum Mol Genet. 2019 Jan; 28(1):166–174 [24] | |
| Secondary outcomes | Fasting glucose—individuals without diabetes | 200,622 | mmol/L | Nat Genet. 2021 Jun; 53(6):840–860 [23] |
| 2-h post-prandial glucose—individuals without diabetes | 63,396 | mmol/L | Nat Genet. 2021 Jun; 53(6):840–860 [23] | |
| Fasting insulin—individuals without diabetes | 151,013 | Natural log-transformed pmol/L | Nat Genet. 2021 Jun; 53(6):840–860 [23] | |
| HbA1c | 344,182 | Standard deviation | UK Biobank—Neale Lab [28] | |
| Waist-to-hip ratio adjusted for body mass index | 694,649 | Standard deviation | Hum Mol Genet. 2019 Jan 1; 28(1):166–174 [24] | |
| Body mass index | 806,834 | Standard deviation |
| ACLY Gene Expression Associations | LDL-c Associations | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant | Chromosome | Position (hg19) | Effect Allele | Other Allele | Z-Score | p Value | β | Standard Error | p Value |
| rs6503666 | 17 | 39954291 | G | A | −7.663 | 1.80 × 10−14 | −0.005 | 0.002 | 0.003 |
| rs4796707 | 17 | 39964930 | C | T | −11.142 | 7.80 × 10−29 | −0.008 | 0.001 | 9.93 × 10−08 |
| rs34200091 | 17 | 40014216 | A | G | −17.964 | 3.70 × 10−72 | −0.010 | 0.002 | 9.91 × 10−07 |
| rs76162894 | 17 | 40085165 | A | C | −6.452 | 1.10 × 10−10 | −0.022 | 0.008 | 0.005 |
| rs2070106 | 17 | 40125864 | G | A | −6.442 | 1.18 × 10−10 | −0.004 | 0.002 | 0.009 |
| HMGCR Gene Expression Associations | LDL-c Associations | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant | Chromosome | Position (hg19) | Effect Allele | Other Allele | Z-Score | p Value | β | Standard Error | p Value |
| rs13356603 | 5 | 74569357 | C | T | −6.909 | 4.90 × 10−12 | −0.068 | 0.002 | <1.00 × 10−300 |
| rs114760090 | 5 | 74622241 | G | A | −7.840 | 4.50 × 10−15 | −0.017 | 0.003 | 7.53 × 10−09 |
| rs6453133 | 5 | 74692776 | A | G | −14.967 | 1.21 × 10−50 | −0.050 | 0.002 | 4.24 × 10−229 |
| rs151000110 | 5 | 74725216 | G | A | −8.659 | 4.77 × 10−18 | −0.067 | 0.003 | 1.65 × 10−103 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gill, D.; Dib, M.-J.; Gill, R.; Bornstein, S.R.; Burgess, S.; Birkenfeld, A.L. Effects of ACLY Inhibition on Body Weight Distribution: A Drug Target Mendelian Randomization Study. Genes 2024, 15, 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081059
Gill D, Dib M-J, Gill R, Bornstein SR, Burgess S, Birkenfeld AL. Effects of ACLY Inhibition on Body Weight Distribution: A Drug Target Mendelian Randomization Study. Genes. 2024; 15(8):1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081059
Chicago/Turabian StyleGill, Dipender, Marie-Joe Dib, Rubinder Gill, Stefan R. Bornstein, Stephen Burgess, and Andreas L. Birkenfeld. 2024. "Effects of ACLY Inhibition on Body Weight Distribution: A Drug Target Mendelian Randomization Study" Genes 15, no. 8: 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081059
APA StyleGill, D., Dib, M.-J., Gill, R., Bornstein, S. R., Burgess, S., & Birkenfeld, A. L. (2024). Effects of ACLY Inhibition on Body Weight Distribution: A Drug Target Mendelian Randomization Study. Genes, 15(8), 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081059





