Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Transcriptional Profile of the HECT E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Gene Family in the Hard-Shelled Mussel Mytilus coruscus Gould
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of HECTs in M. coruscus
2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis of HECT Genes
2.3. Construction of Phylogenetic Tree
2.4. Collinearity Analysis
2.5. Subcellular Localization and Protein Structure Prediction
2.6. Characterization of HECT Gene Expression
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characterization of HECT Gene Family Members in Mussel
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the HECT Gene Family among Species
3.3. Analysis of Conserved Domains, Motif Discovery, and Gene Structures
3.4. Chromosomal Localization of the HECT Gene Family
3.5. Secondary Homology Modeling of HECT Protein Structures and Subcellular Localization
3.6. HECT Gene Colinearity Analysis
3.7. Analysis of HECT Gene Expression Patterns
3.8. Gene Ontology Analysis of the HECT Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rotin, D.; Kumar, S. Physiological functions of the HECT family of ubiquitin ligases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huibregtse, J.M.; Scheffner, M.; Beaudenon, S.; Howley, P.M. A family of proteins structurally and functionally related to the E6-AP ubiquitin-protein ligase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2563–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, I. Evolution of plant HECT ubiquitin ligases. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, K.I.; Nakayama, K. Ubiquitin ligases: Cell-cycle control and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Bové, X.; Sebé-Pedrós, A.; Ruiz-Trillo, I. A Genomic Survey of HECT Ubiquitin Ligases in Eukaryotes Reveals Independent Expansions of the HECT System in Several Lineages. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickart, C.M. Mechanisms Underlying Ubiquitination. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001, 70, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Bengtson, M.H.; Ulbrich, A.; Matsuda, A.; Reddy, V.A.; Orth, A.; Chanda, S.K.; Batalov, S.; Joazeiro, C.A.P. Genome-Wide and Functional Annotation of Human E3 Ubiquitin Ligases Identifies MULAN, a Mitochondrial E3 that Regulates the Organelle’s Dynamics and Signaling. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.; Klos, D.A.; Adler, A.S.; Hicke, L. The C2 domain of the Rsp5 ubiquitin ligase binds membrane phosphoinositides and directs ubiquitination of endosomal cargo. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 165, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Bai, C.; Lin, Q.; Lin, H.; Liu, M.; Ding, F.; Wang, H.R. Binding of RhoA by the C2 domain of E3 ligase Smurf1 is essential for Smurf1-regulated RhoA ubiquitination and cell protrusive activity. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, J.; Südhof, T.C. C2-domains, Structure and Function of a Universal Ca2+-binding Domain*. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 15879–15882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, F.R.; Ponstingl, H. Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange on Ran by the mitotic regulator RCC1. Nature 1991, 354, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemak, A.; Yee, A.; Bezsonova, I.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Arrowsmith, C.H. Zn-binding AZUL domain of human ubiquitin protein ligase Ube3A. J. Biomol. NMR 2011, 51, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffner, M.; Kumar, S. Mammalian HECT ubiquitin-protein ligases: Biological and pathophysiological aspects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dielen, A.-S.; Badaoui, S.; Candresse, T.; German-Retana, S. The ubiquitin/26S proteasome system in plant–pathogen interactions: A never-ending hide-and-seek game. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 11, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín, I. Animal HECT ubiquitin ligases: Evolution and functional implications. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Wu, S.; You, S.; Zhang, N.; Sun, Y. Structure and Function of HECT E3 Ubiquitin Ligases and their Role in Oxidative Stress. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 2020, 8, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Argiles-Castillo, D.; Kane, E.I.; Zhou, A.; Spratt, D.E. HECT E3 ubiquitin ligases-emerging insights into their biological roles and disease relevance. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs228072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Lin, S.-R.; Xu, L.-Z.; Ye, Y.-Y.; Qi, P.-Z.; Wang, W.-F.; Buttino, I.; Li, H.-F.; Guo, B.-Y. Comparative transcriptomic analysis revealed changes in multiple signaling pathways involved in protein degradation in the digestive gland of Mytilus coruscus during high-temperatures. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 46, 101060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, J.; Tang, R.; Li, L.; Li, D. Change in Ubiquitin Proteasome System of Grass Carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus Reared in the Different Stocking Densities. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, E.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Qin, J.G.; Chen, L. Comparative proteome analysis of the hepatopancreas from the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei under long-term low salinity stress. J. Proteom. 2017, 162, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayİr, A.; Polat, M.; Aras, N.; Nalbantoğlu, B.J.A.J.o.A.; Advances, V. Effects of high temperature stress on mRNA levels of ubiquitin-activating enzyme in ovarian tissue of goldfish, Carassius auratus. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2012, 7, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yum, S. Ubiquitin expression in soft coral (Scleronephthya gracillimum) exposed to environmental stresses. Korean J. Genet. 2006, 28, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Nie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Yan, X. Genome-wide identification and analysis of HECT E3 ubiquitin ligase gene family in Ruditapes philippinarum and their involvement in the response to heat stress and Vibrio anguillarum infection. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2022, 43, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.-L.; Li, Y.-L.; Gong, X.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, H.-Y.; Dan, C.; Gui, J.-F.; Zhang, Y.-B. A finTRIM Family Protein Acquires RNA-Binding Activity and E3 Ligase Activity to Shape the IFN Response in Fish. J. Immunol. 2022, 209, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Shi, Y.-H.; Chen, J. Characterization and immunologic functions of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor from Japanese sea bass, Lateolabrax japonicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jia, P.; Lu, X.; Liu, W.; Yi, M.; Jia, K. E3 Ubiquitin Ligase RNF114 Inhibits Innate Immune Response to Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus Infection in Sea Perch by Targeting MAVS and TRAF3 to Mediate Their Degradation. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, L. An HECT domain ubiquitin ligase CgWWP1 regulates granulocytes proliferation in oyster Crassostrea gigas. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 123, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyeong, D.; Kim, J.; Shin, Y.; Subramaniyam, S.; Kang, B.C.; Shin, E.H.; Park, E.H.; Noh, E.S.; Kim, Y.O.; Park, J.Y.; et al. Expression of Heat Shock Proteins in Thermally Challenged Pacific Abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Genes 2019, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, S.; Van Stappen, G.; Sorgeloos, P.; Vuylsteke, M.; Rombauts, S.; Bossier, P. Identification of salt stress response genes using the Artemia transcriptome. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Ye, Y.; Zhu, K.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Yao, R.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Liao, Z.; et al. Genetic Diversity, Population Structure, and Environmental Adaptation Signatures of Chinese Coastal Hard-Shell Mussel Mytilus coruscus Revealed by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, V.A.; Lyashenko, S.A.; Kolotukhina, N.K. Seasonal and interannual dynamics of larval abundance of Mytilus coruscus Gould, 1861 (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) in Amursky Bay (Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan). Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2011, 37, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Chen, Y.; Lu, W.; Wu, B.; Qi, P. Transcriptome analysis of Mytilus coruscus hemocytes in response to Vibrio alginnolyficus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, W.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Mu, C.; Song, W.; Migaud, H.; Wang, C.; Bekaert, M. The Whole-Genome Sequencing and Hybrid Assembly of Mytilus Coruscus. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zippay, M.L.; Helmuth, B. Effects of temperature change on mussel, Mytilus. Integr. Zool. 2012, 7, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burge, C.A.; Mark Eakin, C.; Friedman, C.S.; Froelich, B.; Hershberger, P.K.; Hofmann, E.E.; Petes, L.E.; Prager, K.C.; Weil, E.; Willis, B.L.; et al. Climate Change Influences on Marine Infectious Diseases: Implications for Management and Society. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 249–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyen, N.E.; Somero, G.N.; Denny, M.W. Mussel acclimatization to high, variable temperatures is lost slowly upon transfer to benign conditions. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb222893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Wang, X.-c.; Liu, H.-h.; Fan, M.-h.; Sun, J.-j.; Shen, W. Molecular characterization of a novel antimicrobial peptide from Mytilus coruscus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, G.E.; Somero, G.N. Evidence for Protein Damage at Environmental Temperatures: Seasonal Changes in Levels of Ubiquitin Conjugates and Hsp70 in the Intertidal Mussel Mytilus Trossulus. J. Exp. Biol. 1995, 198, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willer, D.F.; Aldridge, D.C. Microencapsulated diets to improve bivalve shellfish aquaculture for global food security. Glob. Food Secur. 2019, 23, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER web server: Interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER in 2013: Modeling the evolution of gene function, and other gene attributes, in the context of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D377–D386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wen, L.; Gao, X.; Jin, C.; Xue, Y.; Yao, X. DOG 1.0: Illustrator of protein domain structures. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt, C. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Bao, Z.; Wang, S. MolluscDB: An integrated functional and evolutionary genomics database for the hyper-diverse animal phylum Mollusca. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, B.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J.; Hu, S.; Chen, W.-H. Evolview v3: A webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W270–W275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.-h.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.J.; Nakai, K. WoLF PSORT: Protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. SOPMA: Significant improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by consensus prediction from multiple alignments. Bioinformatics 1995, 11, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermi, G.; Perutz, M.F.; Shaanan, B.; Fourme, R. The crystal structure of human deoxyhaemoglobin at 1.74 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1984, 175, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–w303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkert, P.; Biasini, M.; Schwede, T. Toward the estimation of the absolute quality of individual protein structure models. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. eggNOG-mapper v2: Functional Annotation, Orthology Assignments, and Domain Prediction at the Metagenomic Scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, C.; Rastogi, S.; Arvestad, L.; Dittmar, K.; Light, S.; Ekman, D.; Liberles, D.A. Evolution after gene duplication: Models, mechanisms, sequences, systems, and organisms. J. Exp. Zool. Part B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2007, 308, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, D.; Jin, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, L.; Zhang, H. Genome-Wide Identification of NAP1 and Function Analysis in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia, M.; Penny, D.; Roy, S.W. Coevolution of genomic intron number and splice sites. Trends Genet. TIG 2007, 23, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, K.F.; Kumar, S. Nedd4-like proteins: An emerging family of ubiquitin-protein ligases implicated in diverse cellular functions. Trends Cell Biol. 1999, 9, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, D.L.; Ramón, H.; Oliver, P.M. Cbl- and Nedd4-family ubiquitin ligases: Balancing tolerance and immunity. Immunol. Res. 2008, 42, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdeira-Arias, J.D.; Otero, J.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Mena RodrÍguez, A.; Nombela, M.Á. Multivariate substrate characterization: The case of shellfish harvesting areas in the Rías Altas (north-west Iberian Peninsula). Sedimentology 2021, 68, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Giri, S.S.; Jun, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, J.W.; Park, S.C. Detoxification- and Immune-Related Transcriptomic Analysis of Gills from Bay Scallops (Argopecten irradians) in Response to Algal Toxin Okadaic Acid. Toxins 2018, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo-Espinoza, R.; Ibarra, A.M.; Roberts, S.B.; Sicard-González, M.T.; Escobedo-Fregoso, C. Transcriptome profile in heat resilient Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas families under thermal challenge. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 47, 101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.M.; Kim, K.; Choi, I.Y.; Rhee, J.S. Transcriptome response of the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas susceptible to thermal stress: A comparison with the response of tolerant oyster. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Lin, F.; Fang, J.; Gao, Y.; Du, M.; Fang, J.; Li, W.; Jiang, Z. Transcriptome analysis of the Yesso scallop, Patinopecten yessoensis gills in response to water temperature fluctuations. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 80, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Ballina, N.R.; Maresca, F.; Cao, A.; Villalba, A. Bivalve Haemocyte Subpopulations: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 826255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W.X. Functional heterogeneity of immune defenses in molluscan oysters Crassostrea hongkongensis revealed by high-throughput single-cell transcriptome. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 120, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Hu, B.; Wen, C.; Mu, S. Morphology and phagocytic ability of hemocytes from Cristaria plicata. Aquaculture 2011, 310, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y. Morphological and functional characterization of clam Ruditapes philippinarum haemocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickart, C.M.; Eddins, M.J. Ubiquitin: Structures, functions, mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2004, 1695, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.-K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.C.; Yang, W.X. New insights to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (UPP) mechanism during spermatogenesis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 3213–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdol, M.; Gomez-Chiarri, M.; Castillo, M.G.; Figueras, A.; Fiorito, G.; Moreira, R.; Novoa, B.; Pallavicini, A.; Ponte, G.; Roumbedakis, K.; et al. Immunity in Molluscs: Recognition and Effector Mechanisms, with a Focus on Bivalvia. In Advances in Comparative Immunology; Cooper, E.L., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 225–341. [Google Scholar]
- Eissa, N.; Wang, H.-P. Transcriptional stress responses to environmental and husbandry stressors in aquaculture species. Rev. Aquac. 2016, 8, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furniss, J.J.; Grey, H.; Wang, Z.; Nomoto, M.; Jackson, L.; Tada, Y.; Spoel, S.H. Proteasome-associated HECT-type ubiquitin ligase activity is required for plant immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Deng, Z. Identification of GSPT1 as prognostic biomarker and promoter of malignant colon cancer cell phenotypes via the GSK-3β/CyclinD1 pathway. Aging 2021, 13, 10354–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Du, D.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, L.; Yuan, S. The structure and regulation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase HUWE1 and its biological functions in cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.Q.; Xu, W.M.; Liao, H.J.; Jiang, C.; Li, C.Q.; Zhang, W. Silencing Huwe1 reduces apoptosis of cortical neurons exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabarczyk, D.B.; Petrova, O.A.; Deszcz, L.; Kurzbauer, R.; Murphy, P.; Ahel, J.; Vogel, A.; Gogova, R.; Faas, V.; Kordic, D.; et al. HUWE1 employs a giant substrate-binding ring to feed and regulate its HECT E3 domain. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-w.; Hu, X.; Ye, M.; Lin, M.; Chu, M.; Shen, X. NEDD4 E3 ligase: Functions and mechanism in human cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 67, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-J.; Zhan, S.-K.; Ji, W.-Z.; Pan, Y.-X.; Liu, W.; Li, D.-Y.; Huang, P.; Zhang, X.-X.; Cao, C.-Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Ubiquitin-protein ligase E3C promotes glioma progression by mediating the ubiquitination and degrading of Annexin A7. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubert, J.; Barja, J.L.; Romalde, J.L. New Insights into Pathogenic Vibrios Affecting Bivalves in Hatcheries: Present and Future Prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elston, R.A.; Hasegawa, H.; Humphrey, K.L.; Polyak, I.K.; Häse, C.C. Re-emergence of Vibrio tubiashii in bivalve shellfish aquaculture: Severity, environmental drivers, geographic extent and management. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 82, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Kong, T.; Aweya, J.J.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. p53 Ubiquitination Comediated by HUWE1 and TRAF6 Contributes to White Spot Syndrome Virus Infection in Crustacean. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0202921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñaloza, C.; Gutierrez, A.P.; Eöry, L.; Wang, S.; Guo, X.; Archibald, A.L.; Bean, T.P.; Houston, R.D. A chromosome-level genome assembly for the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Nie, H.; Huo, Z.; Ding, J.; Li, Z.; Yan, L.; Jiang, L.; Mu, Z.; Wang, H.; Meng, X.; et al. Clam Genome Sequence Clarifies the Molecular Basis of Its Benthic Adaptation and Extraordinary Shell Color Diversity. iScience 2019, 19, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B.; Qi, P. Transcriptome analysis reveals tissue-specific responses of Mytilus unguiculatus to Vibrio alginolyticus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 144, 109301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


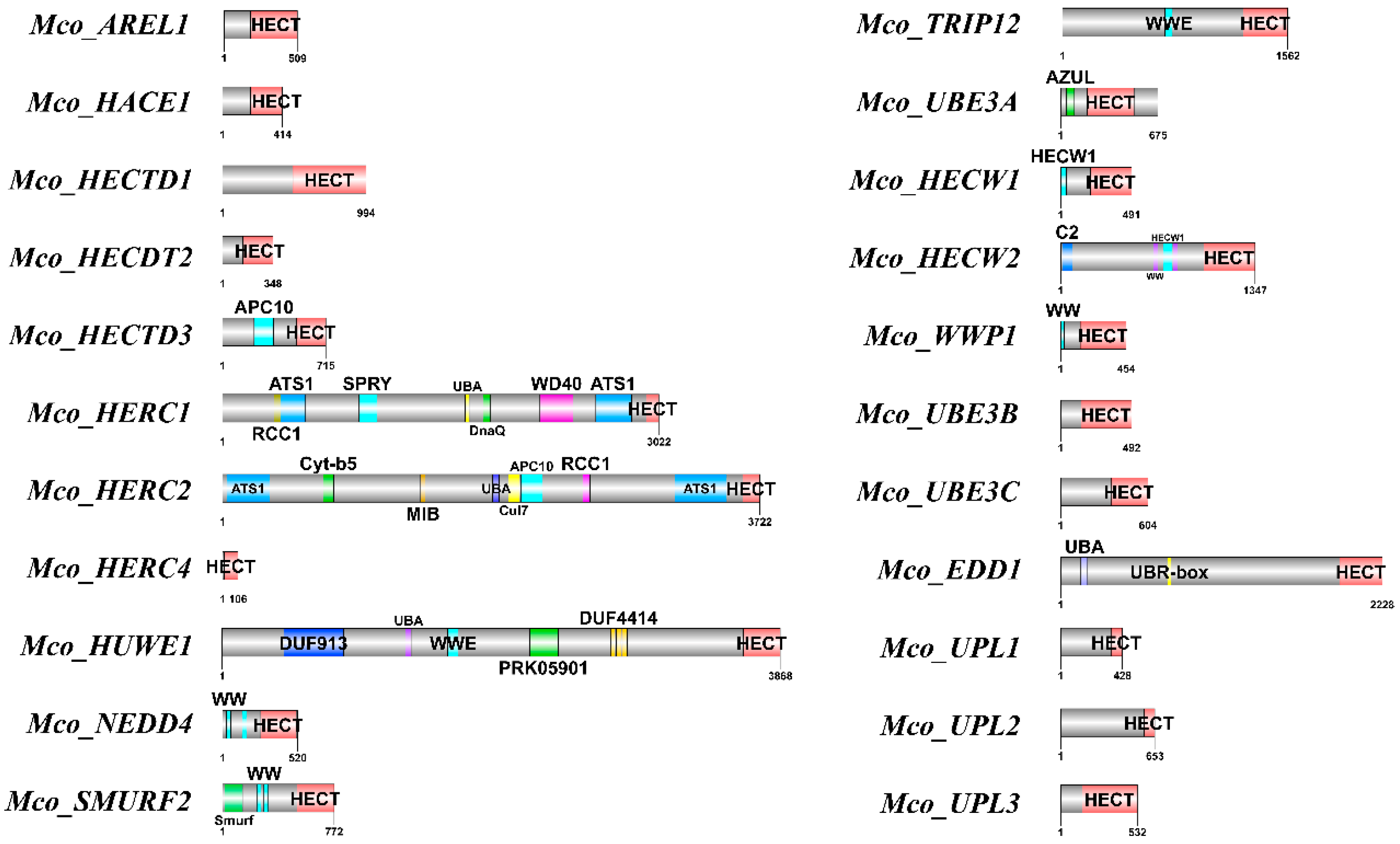
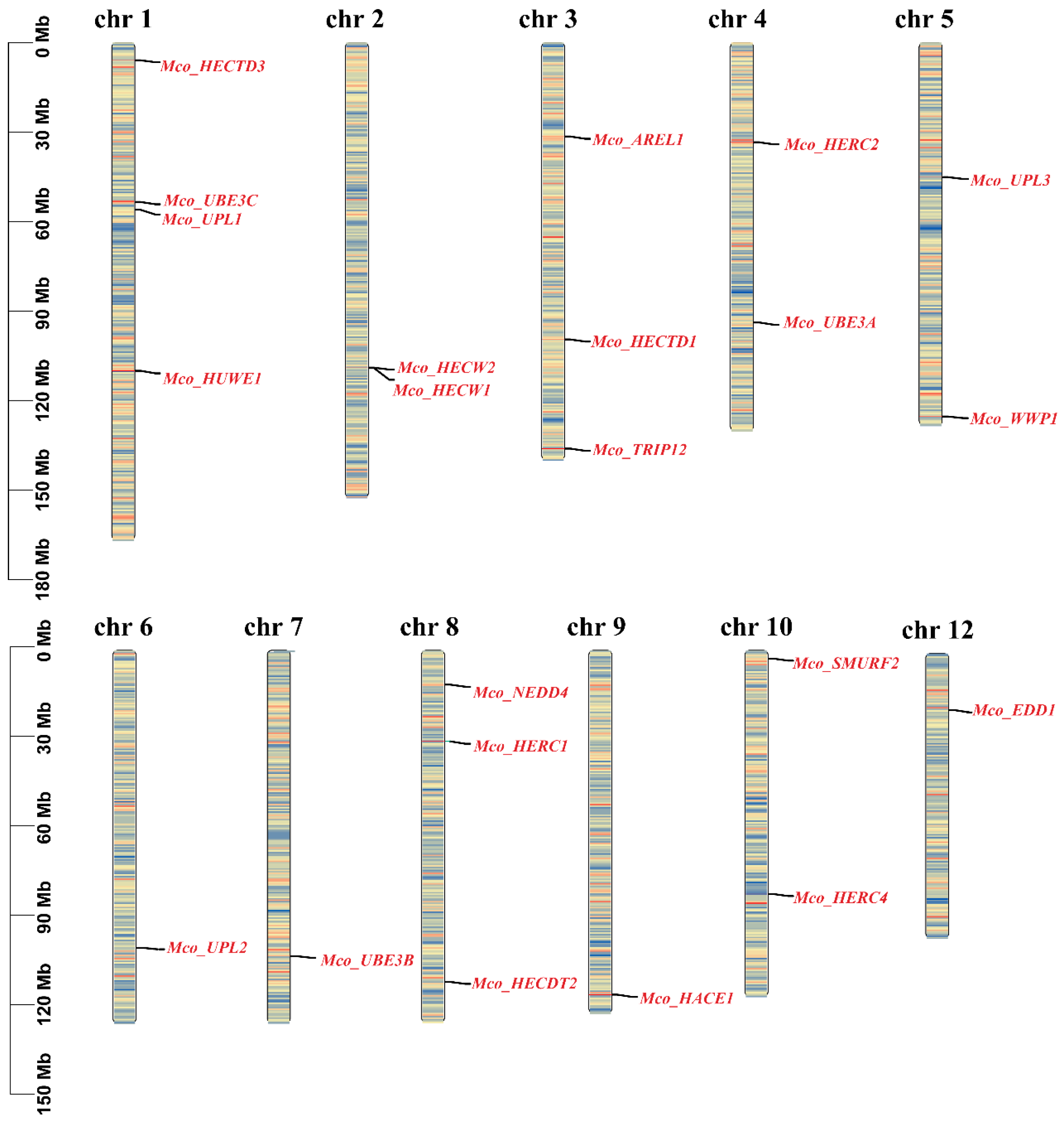
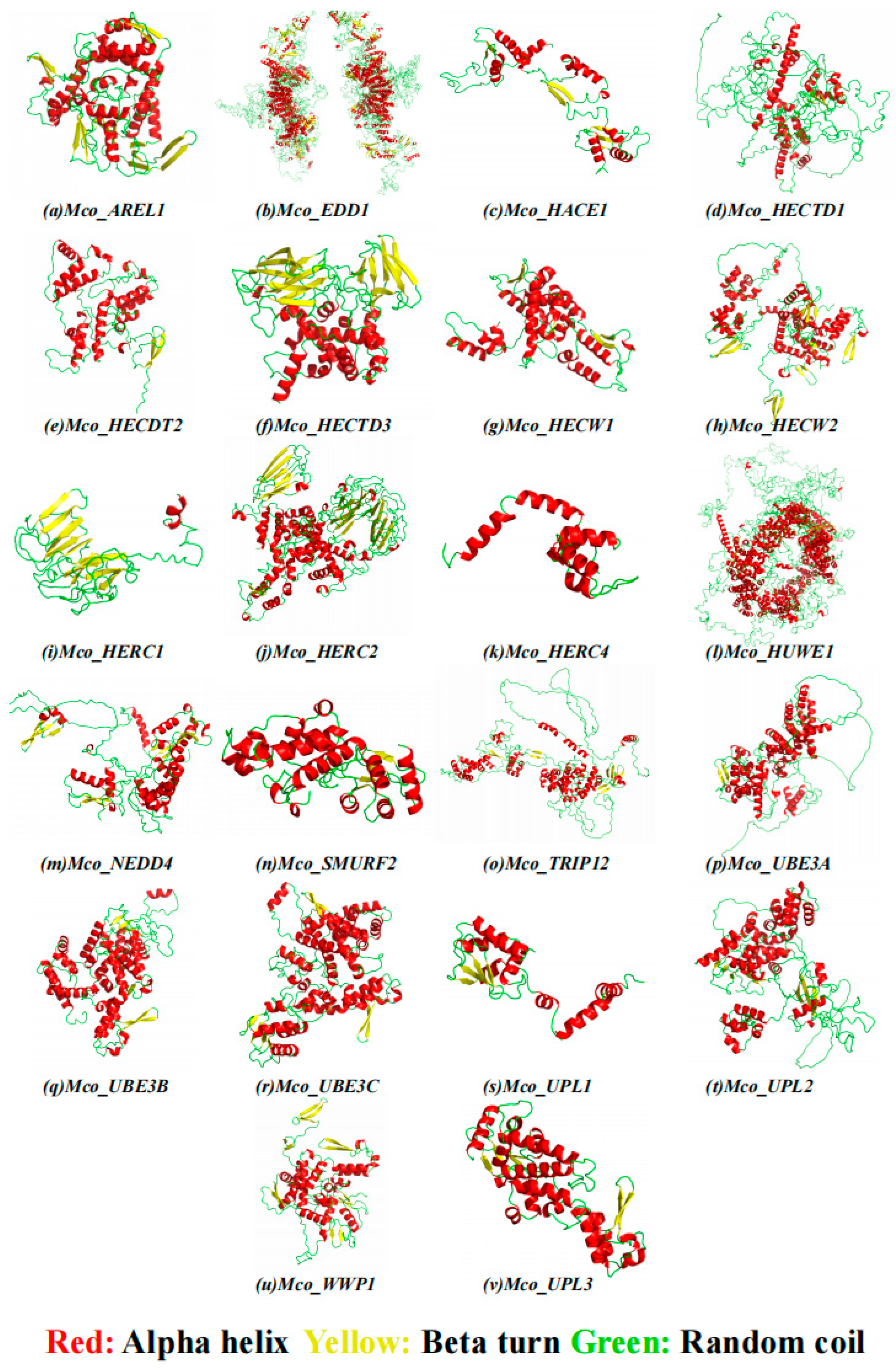



| No | Gene Name | Gene ID | CDSa Length | Protein Length | HECT Domain | Molecular Weight | Theoretical | Chromosome | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (bp) | (aa) | Location (aa) | (kDa) | pI | |||||
| 1 | Mco_NEDD4 | Maker00024065 | 1545 | 514 | 264–510 | 59,629.23 | 8.25 | chr8 | 11,448,585–11,509,784 |
| 2 | Mco_EDD1 | Maker00026964 | 6696 | 2231 | 1935–2228 | 245,120.18 | 5.43 | chr12 | 18,904,970–19,014,437 |
| 3 | Mco_UPL3 | Maker00035072 | 1608 | 535 | 450–532 | 60,513.88 | 4.62 | chr5 | 45,075,511–45,107,379 |
| 4 | Mco_HERC4 | Maker00002539 | 384 | 127 | 11–106 | 15,283.79 | 5.63 | chr10 | 81,621,876–81,717,176 |
| 5 | Mco_HERC1 | Maker00017428 | 9186 | 3061 | 2936–3022 | 338,818.36 | 5.84 | chr8 | 30,444,670–30,540,646 |
| 6 | Mco_AREL1 | Maker00023631 | 1536 | 511 | 183–509 | 58,122.03 | 5.58 | chr3 | 31,450,908–31,484,837 |
| 7 | Mco_UBE3A | Maker00027142 | 2118 | 705 | 556–675 | 79,286.27 | 5.69 | chr4 | 93,795,246–93,823,387 |
| 8 | Mco_HACE1 | Maker00030301 | 1266 | 421 | 194–414 | 47,852.62 | 5.63 | chr9 | 115,378,105–115,430,703 |
| 9 | Mco_SMURF2 | Maker00031130 | 2328 | 775 | 516–772 | 86,570.70 | 6.24 | chr10 | 2,742,196–2,791,928 |
| 10 | Mco_UPL1 | Maker00034862 | 1332 | 443 | 350–428 | 50,020.41 | 4.6 | chr1 | 56,026,608–56,033,160 |
| 11 | Mco_HUWE1 | Maker00035590 | 11,616 | 3871 | 3613–3868 | 427,315.87 | 5.16 | chr1 | 109,925,874–110,051,336 |
| 12 | Mco_UPL2 | Maker00001812 | 2172 | 723 | 578–653 | 82,200.81 | 5.26 | chr6 | 99,678,904–99,683,847 |
| 13 | Mco_UBE3C | Maker00001502 | 1821 | 606 | 350–604 | 69,595.05 | 5.36 | chr1 | 53,415,654–53,447,223 |
| 14 | Mco_HECTD1 | Maker00005002 | 2991 | 996 | 487–994 | 112,627.93 | 5.02 | chr3 | 99,488,382–99,510,834 |
| 15 | Mco_HECDT2 | Maker00005191 | 1056 | 351 | 139–348 | 39,778.40 | 9.29 | chr8 | 111,081,717–11,114,3368 |
| 16 | Mco_TRIP12 | Maker00005211 | 4692 | 1563 | 1254–1562 | 171,572.52 | 8.14 | chr3 | 135,995,715–136,168,882 |
| 17 | Mco_HECW1 | Maker00007292 | 1494 | 497 | 208–491 | 58,686.15 | 8.3 | chr2 | 109,062,131–109,097,211 |
| 18 | Mco_HECW2 | Maker00007303 | 4050 | 1349 | 992–1347 | 151,476.02 | 6.19 | chr2 | 108,953,278–108,963,278 |
| 19 | Mco_UBE3B | Maker00008133 | 1485 | 494 | 144–492 | 56,659.97 | 6.49 | chr7 | 102,429,555–102,469,658 |
| 20 | Mco_HECTD3 | Maker00011666 | 2274 | 757 | 511–715 | 87,274.83 | 5.54 | chr1 | 5,886,440–5,977,704 |
| 21 | Mco_WWP1 | Maker00013008 | 1371 | 456 | 137–454 | 54,119.19 | 6.37 | chr5 | 125,313,868–125,339,147 |
| 22 | Mco_HERC2 | Maker00015302 | 11,241 | 3746 | 3603–3722 | 412,033.61 | 5.92 | chr4 | 33,350,025–33,456,457 |
| HECT Subfamily | Gene Name | Acc. No. | Presence in Bivalvia Species * |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEDD4 | Mco_NEDD4 | Maker00024065 | M. coruscus(5), M. galloprovincialis(4), C. gigas(4), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(4) |
| Mco_SMURF2 | Maker00031130 | ||
| Mco_WWP1 | Maker00013008 | ||
| Mco_HECW1 | Maker00007292 | ||
| Mco_HECW2 | Maker00007303 | ||
| UPL1-3 | Mco_UPL1 | Maker00035072 | M. coruscus(3), M. galloprovincialis(0), C. gigas(0), R. philippinarum(2), M. yessoensis(0) |
| Mco_UPL2 | Maker00034862 | ||
| Mco_UPL3 | Maker00001812 | ||
| HACE1 | Mco_HACE1 | Maker00030301 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| HUWE1 | Mco_HUWE1 | Maker00035590 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| KIAA0317 | Mco_AREL1 | Maker00023631 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| UBE3A/E6-AP | Mco_UBE3A | Maker00027142 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| SMALL HERCs | Mco_HERC4 | Maker00002539 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| UBE3B/3C | Mco_UBE3B | Maker00008133 | M. coruscus(2), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(2), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(2) |
| Mco_UBE3C | Maker00001502 | ||
| TRIP12 | Mco_TRIP12 | Maker00005211 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(0), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| HECTD1 | Mco_HECTD1 | Maker00005002 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| HECTD2 | Mco_HECDT2 | Maker00005191 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(0), M. yessoensis(1) |
| HECTD3 | Mco_HECTD3 | Maker00011666 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| EDD/UBR5 | Mco_EDD1 | Maker00026964 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| G2E3 | Not found | Not found | M. coruscus(0), M. galloprovincialis(0), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(0), M. yessoensis(1) |
| LARGE HERCs | Mco_HERC1 | Maker00017428 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| LARGE HERCs | Mco_HERC2 | Maker00015302 | M. coruscus(1), M. galloprovincialis(0), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| Not in any subfamily | M. coruscus(0), M. galloprovincialis(1), C. gigas(1), R. philippinarum(1), M. yessoensis(1) |
| Proteins | Alpha | Beta | Random | Extended | Subcellular |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helix | Turn | Coil | Stand | Location Prediction | |
| Mco_NEDD4 | 34.82% | 6.03% | 48.83% | 10.31% | Nucleus |
| Mco_EDD1 | 34.02% | 6.28% | 42.94% | 16.76% | Cytoplasm |
| Mco_UPL3 | 50.47% | 5.05% | 35.70% | 8.79% | Nucleus |
| Mco_HERC4 | 53.54% | 5.51% | 25.98% | 14.96% | Cytoplasm |
| Mco_HERC1 | 36.92% | 8.95% | 35.41% | 18.72% | Nucleus |
| Mco_AREL1 | 40.90% | 4.89% | 34.44% | 19.77% | Cytoplasm |
| Mco_UBE3A | 42.55% | 4.82% | 40.43% | 12.20% | Cytoplasm |
| Mco_HACE1 | 44.66% | 4.51% | 35.87% | 14.96% | Cytoplasm |
| Mco_SMURF2 | 19.23% | 8.26% | 51.35% | 21.16% | Nucleus |
| Mco_UPL1 | 38.83% | 6.77% | 42.44% | 11.96% | Nucleus |
| Mco_HUWE1 | 44.33% | 4.55% | 40.02% | 11.11% | Nucleus |
| Mco_UPL2 | 41.63% | 4.98% | 40.39% | 13.00% | Plasma membrane |
| Mco_UBE3C | 48.68% | 7.10% | 28.88% | 15.35% | Plasma membrane |
| Mco_HECTD1 | 36.55% | 4.62% | 44.08% | 14.76% | Cytoplasm |
| Mco_HECDT2 | 40.17% | 6.55% | 35.90% | 17.38% | Cytoplasm |
| Mco_TRIP12 | 39.60% | 7.49% | 38.20% | 14.72% | Nucleus |
| Mco_HECW1 | 50.30% | 5.43% | 33.60% | 10.66% | Mitochondria |
| Mco_HECW2 | 28.54% | 5.86% | 51.22% | 14.38% | Nucleus |
| Mco_UBE3B | 48.38% | 5.26% | 33.00% | 13.36% | Cytoplasm |
| Mco_HECTD3 | 35.40% | 4.10% | 43.73% | 16.78% | Nucleus |
| Mco_WWP1 | 37.28% | 6.80% | 41.01% | 14.91% | Cytoplasm |
| Mco_HERC2 | 38.49% | 6.19% | 38.60% | 16.71% | Nucleus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, F.; Xin, Z.; Dong, Z.; Ye, Y. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Transcriptional Profile of the HECT E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Gene Family in the Hard-Shelled Mussel Mytilus coruscus Gould. Genes 2024, 15, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081085
Guo F, Xin Z, Dong Z, Ye Y. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Transcriptional Profile of the HECT E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Gene Family in the Hard-Shelled Mussel Mytilus coruscus Gould. Genes. 2024; 15(8):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081085
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Feng, Zhenqi Xin, Zhenyu Dong, and Yingying Ye. 2024. "Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Transcriptional Profile of the HECT E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Gene Family in the Hard-Shelled Mussel Mytilus coruscus Gould" Genes 15, no. 8: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081085
APA StyleGuo, F., Xin, Z., Dong, Z., & Ye, Y. (2024). Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Transcriptional Profile of the HECT E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Gene Family in the Hard-Shelled Mussel Mytilus coruscus Gould. Genes, 15(8), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081085






