Uncovering a Genetic Diagnosis in a Pediatric Patient by Whole Exome Sequencing: A Modeling Investigation in Wiedemann–Steiner Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical and Genetic Investigation
2.2. FMR1 Analysis
2.3. Karyotype
2.4. SNP-Array 850K
2.5. Exome Sequencing
Genetic Testing and Prioritization of Variants
2.6. Sanger Sequencing
2.7. In Silico Analysis and Protein Structure Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Proband Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Whole-Exome Sequencing Revealed a Mutation Responsible for Wiedemann–Steiner Syndrome
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Overlap between WSS and Other Syndromes
4.2. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miyake, N.; Tsurusaki, Y.; Koshimizu, E.; Okamoto, N.; Kosho, T.; Brown, N.J.; Tan, T.Y.; Yap, P.J.J.; Suzumura, H.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Delineation of clinical features in Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome caused by KMT2A mutations. Clin. Genet. 2016, 89, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenson, P.D.; Mort, M.; Ball, E.V.; Evans, K.; Hayden, M.; Heywood, S.; Hussain, M.; Phillips, A.D.; Cooper, D.N. The Human Gene Mutation Database: Towards a comprehensive repository of inherited mutation data for medical research, genetic diagnosis and next-generation sequencing studies. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzarides, T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 2007, 128, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fede, E.; Massa, V.; Augello, B.; Squeo, G.; Scarano, E.; Perri, A.M.; Fischetto, R.; Causio, F.A.; Zampino, G.; Piccione, M.; et al. Expanding the phenotype associated to KMT2A variants: Overlapping clinical signs between Wiedemann-Steiner and Rubinstein-Taybi syndromes. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. EJHG 2021, 29, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poreba, E.; Lesniewicz, K.; Durzynska, J. Aberrant Activity of Histone-Lysine N-Methyltransferase 2 (KMT2) Complexes in Oncogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, X.; Xie, B.; Guan, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Yi, P.; Du, R.; Mei, H.; Liu, L.; et al. Novel variants and phenotypic heterogeneity in a cohort of 11 Chinese children with Wiedemann-Steiner syn-drome. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1085210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovcevski, M.; Ruan, H.; Shen, E.Y.; Dincer, A.; Javidfar, B.; Ma, Q.; Peter, C.J.; Cheung, I.; Mitchell, A.C.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Neuronal Kmt2a/Mll1 histone methyltransferase is essential for prefrontal synaptic plasticity and working memory. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 5097–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Teng, X.; Zhang, J. Aberrant splicing caused by a novel KMT2A variant in Wiedemann–Steiner syndrome. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2024, 12, e2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Novati, G.; Pan, J.; Bycroft, C.; Žemgulytė, A.; Applebaum, T.; Pritzel, A.; Wong, L.H.; Zielinski, M.; Sargeant, T.; et al. Accurate proteome-wide missense variant effect prediction with AlphaMissense. Science 2023, 381, eadg7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, R.; Sun, S.; Weile, J.; Roth, F.P. Improved pathogenicity prediction for rare human missense variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 1891–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quang, D.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X. DANN: A deep learning approach for annotating the pathogenicity of genetic variants. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, C.; Mou, C.; Dong, Y.; Tu, Y. dbNSFP v4: A comprehensive database of transcript-specific functional predictions and annotations for human nonsynonymous and splice-site SNVs. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, N.M.; Rothstein, J.H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S.K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; et al. REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2013, 76, 7.20.1–7.20.41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, N.-L.; Kumar, P.; Hu, J.; Henikoff, S.; Schneider, G.; Ng, P.C. SIFT web server: Predicting effects of amino acid substitutions on proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W452–W457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D.M.; Jain, P.; O’Roak, B.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J. A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-Pdb Viewer: An environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yang, Q.; Simonetti, F.L.; Li, M. PremPDI estimates and interprets the effects of missense mutations on protein-DNA interactions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.H.; Pires, D.E.; Ascher, D.B. DynaMut2: Assessing changes in stability and flexibility upon single and multiple point missense mutations. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.E.V.; Ascher, D.B.; Blundell, T.L. mCSM: Predicting the effects of mutations in proteins using graph-based signatures. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobley, A.; Sadowski, M.I.; Jones, D.T. pGenTHREADER and pDomTHREADER: New methods for improved protein fold recognition and superfamily discrimination. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, J.D.; Totoo, P.; Burke, D.F.; Jänes, J.; Beltrao, P.; Martin, M.J. ProtVar: Mapping and contextualizing human missense variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W140–W147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venselaar, H.; Beek, T.A.T.; Kuipers, R.K.; Hekkelman, M.L.; Vriend, G. Protein structure analysis of mutations causing inheritable diseases. An e-Science approach with life scientist friendly interfaces. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Liu, K.; Lei, M.; Yang, A.; Li, Y.; Hughes, T.R.; Min, J. DNA Sequence Recognition of Human CXXC Domains and Their Structural Determinants. Structure 2018, 26, 85–95.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaletti, C.; Russell, P.P.S.; Hebel, K.J.; Rickard, M.M.; Boob, M.; Danksagmüller, F.; Taylor, S.A.; Pogorelov, T.V.; Gruebele, M. Hydrogen bonding heterogeneity correlates with protein folding transition state passage time as revealed by data sonification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2319094121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynisdottir, T.; Anderson, K.J.; Boukas, L.; Bjornsson, H.T. Missense variants causing Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome pref-erentially occur in the KMT2A-CXXC domain and are accurately classified using AlphaFold2. PLoS Genet. 2022, 18, e1010278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.C.; Dou, Y. Hijacked in cancer: The KMT2 (MLL) family of methyltransferases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.; Larghero, P.; Lopes, B.A.; Marschalek, R. The KMT2A/MLL consensus gene structure: A comprehensive update for research and diagnostic implications. Leukemia 2024, 38, 1403–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornsson, H.T. The Mendelian disorders of the epigenetic machinery. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Temimi, A.H.K.; Amatdjais-Groenen, H.I.V.; Reddy, Y.V.; Blaauw, R.H.; Guo, H.; Qian, P.; Mecinović, J. The nucleophilic amino group of lysine is central for histone lysine methyltransferase catalysis. Commun. Chem. 2019, 2, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, S.P.; Habib, F.; Sharma, R.; Gadewal, N.; Gupta, S.; Galande, S. HIstome—A relational knowledgebase of human histone proteins and histone modifying enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D337–D342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA Methylation and Its Basic Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Rao, C.M. Epigenetic tools (The Writers, The Readers and The Erasers) and their implications in cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 837, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroynowska-Czerwinska, A.M.; Klimczak, M.; Pastor, M.; Kazrani, A.A.; Misztal, K.; Bochtler, M. Clustered PHD domains in KMT2/MLL proteins are attracted by H3K4me3 and H3 acetylation-rich active promoters and enhancers. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górecki, M.; Kozioł, I.; Kopystecka, A.; Budzyńska, J.; Zawitkowska, J.; Lejman, M. Updates in KMT2A Gene Rearrangement in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahly, A.N.; Srour, M.; Buhas, D.; Scheffer, I.E.; Myers, K.A. The epileptology of Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome: Electroclinical findings in five patients with KMT2A pathogenic variants. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2023, 44, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramida, C.; Papoulidis, I.; Siomou, E.; Efstathiadou, C.; Gyftodimou, Y.; Pavlidou, E.; Anastasakis, E.; Garas, A.; Manolakos, E. Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome in a 2-year-old patient due to a rare nonsense KMT2A mutation of de novo origin: A case report. Int. J. Epigenet. 2024, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerimoglu, C.; Sakib, M.S.; Jain, G.; Benito, E.; Burkhardt, S.; Capece, V.; Kaurani, L.; Halder, R.; Agís-Balboa, R.C.; Stilling, R.; et al. KMT2A and KMT2B Mediate Memory Function by Affecting Distinct Genomic Regions. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fede, E.; Grazioli, P.; Lettieri, A.; Parodi, C.; Castiglioni, S.; Taci, E.; Colombo, E.A.; Ancona, S.; Priori, A.; Gervasini, C.; et al. Epigenetic disorders: Lessons from the animals–animal models in chromatinopathies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 979512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsani, K.R.; Arredondo, J.J.; Kal, A.J.; Verrijzer, C.P. A homeotic mutation in the trithorax SET domain impedes histone binding. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2197–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, S.E.; Quintero-Rivera, F. Wiedemann-Steiner Syndrome. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, H.; Chen, R. Phenotypes of Cornelia de Lange syndrome caused by non-cohesion genes: Novel variants and literature review. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 940294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiglioni, S.; Di Fede, E.; Bernardelli, C.; Lettieri, A.; Parodi, C.; Grazioli, P.; Colombo, E.A.; Ancona, S.; Milani, D.; Ottaviano, E.; et al. KMT2A: Umbrella Gene for Multiple Diseases. Genes 2022, 13, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Fahrner, J.; Bjornsson, H.T. Mendelian disorders of the epigenetic machinery: Postnatal malleability and therapeutic prospects. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, R254–R264, Erratum in Hum Mol Genet. 2020, 29, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, G.; Yu, S.; Wu, W. Wiedemann–Steiner Syndrome: Case Report and Review of Literature. Children 2022, 9, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Pal, S.; Kulshrestha, S.; Gupta, D.; Soni, A.; Saxena, R.; Bijarnia-Mahay, S.; Verma, I.C.; Puri, R.D. Role of next generation sequencing in diagnosis and management of critically ill children with suspected monogenic disorder. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2024. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


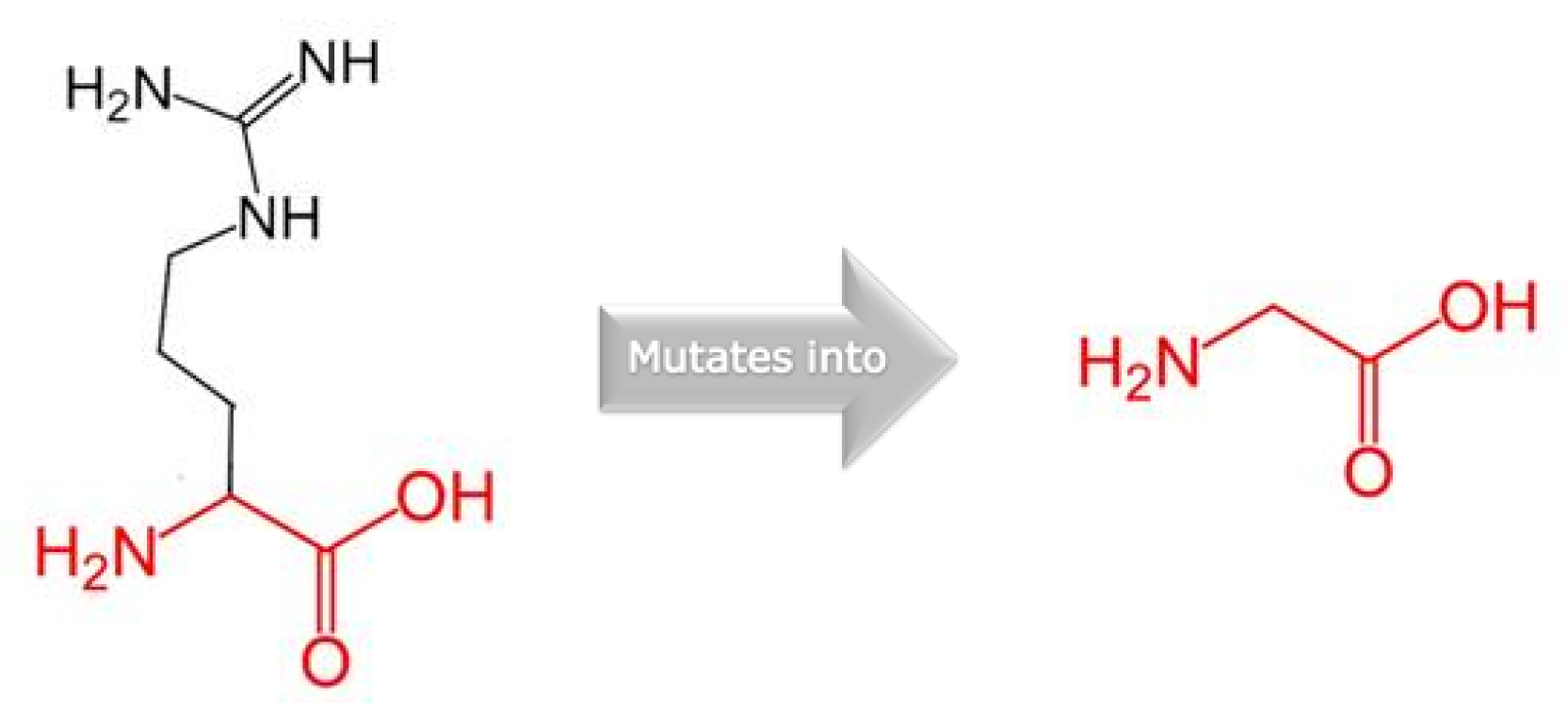

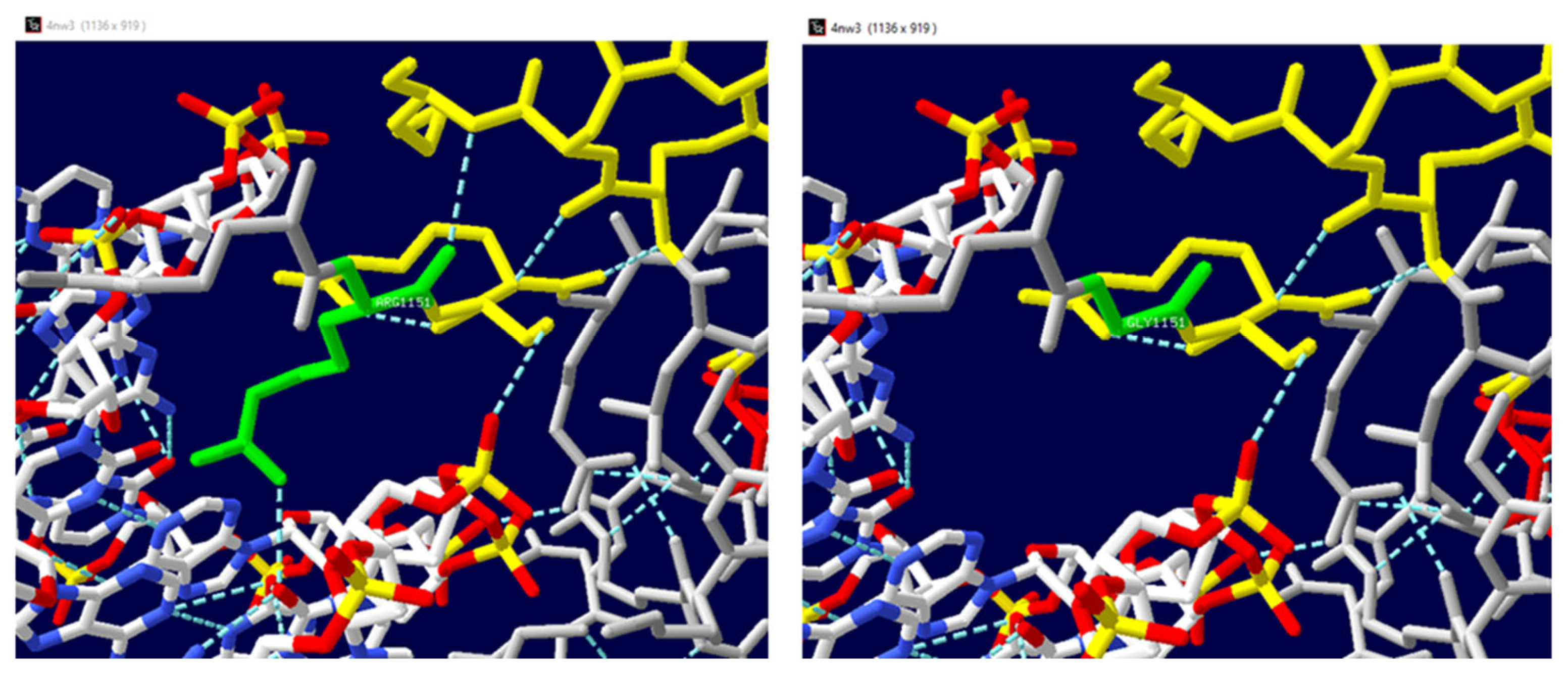
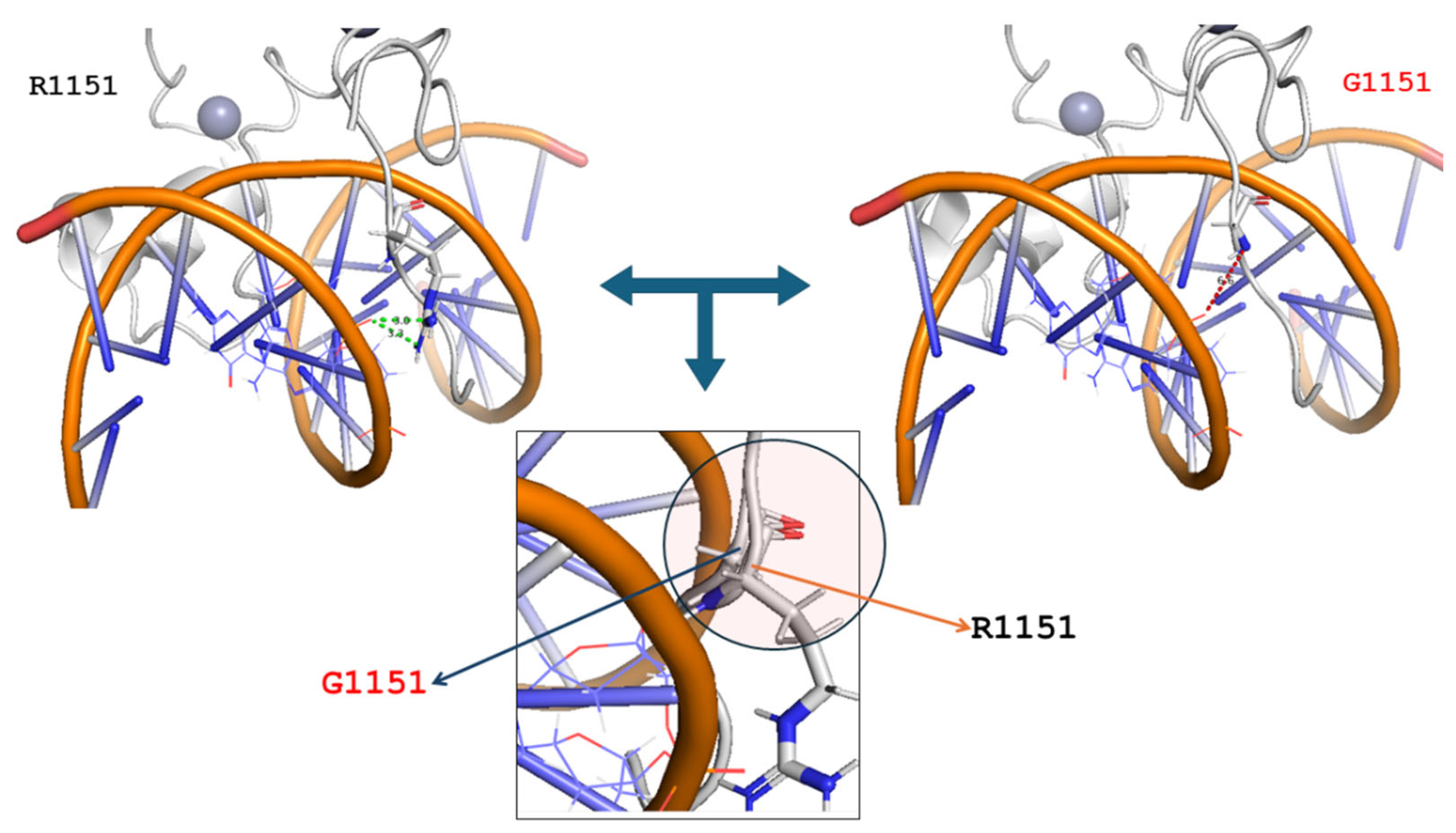
| Mutated Chain | Mutation | ΔΔG | Interface | Deleterious |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | R1151G | 1.25 | Yes | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
di Bari, I.; Ceccarini, C.; Curcetti, M.; Cesarano, C.; Croce, A.-I.; Adipietro, I.; Gallicchio, M.G.; Palladino, G.P.; Patrizio, M.P.; Frisoli, B.; et al. Uncovering a Genetic Diagnosis in a Pediatric Patient by Whole Exome Sequencing: A Modeling Investigation in Wiedemann–Steiner Syndrome. Genes 2024, 15, 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091155
di Bari I, Ceccarini C, Curcetti M, Cesarano C, Croce A-I, Adipietro I, Gallicchio MG, Palladino GP, Patrizio MP, Frisoli B, et al. Uncovering a Genetic Diagnosis in a Pediatric Patient by Whole Exome Sequencing: A Modeling Investigation in Wiedemann–Steiner Syndrome. Genes. 2024; 15(9):1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091155
Chicago/Turabian Styledi Bari, Ighli, Caterina Ceccarini, Maria Curcetti, Carla Cesarano, Anna-Irma Croce, Iolanda Adipietro, Maria Grazia Gallicchio, Grazia Pia Palladino, Maria Pia Patrizio, Benedetta Frisoli, and et al. 2024. "Uncovering a Genetic Diagnosis in a Pediatric Patient by Whole Exome Sequencing: A Modeling Investigation in Wiedemann–Steiner Syndrome" Genes 15, no. 9: 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091155
APA Styledi Bari, I., Ceccarini, C., Curcetti, M., Cesarano, C., Croce, A.-I., Adipietro, I., Gallicchio, M. G., Palladino, G. P., Patrizio, M. P., Frisoli, B., Santacroce, R., D’Apolito, M., D’Andrea, G., Castriota, O. M., Pierri, C. L., & Margaglione, M. (2024). Uncovering a Genetic Diagnosis in a Pediatric Patient by Whole Exome Sequencing: A Modeling Investigation in Wiedemann–Steiner Syndrome. Genes, 15(9), 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091155







