Molecular Targets in Streptococcus pyogenes for the Development of Anti-Virulence Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Development of Antibiotic Resistance by S. pyogenes
2.1. Resistance to Macrolides
2.2. Resistance to Tetracycline
2.3. Resistance to Fluoroquinolone
2.4. Increased Subclinical Resistance to Penicillin
3. Molecular Targets for Developing Anti-Virulence Agents against S. pyogenes Infections
3.1. RopB
3.2. Mga
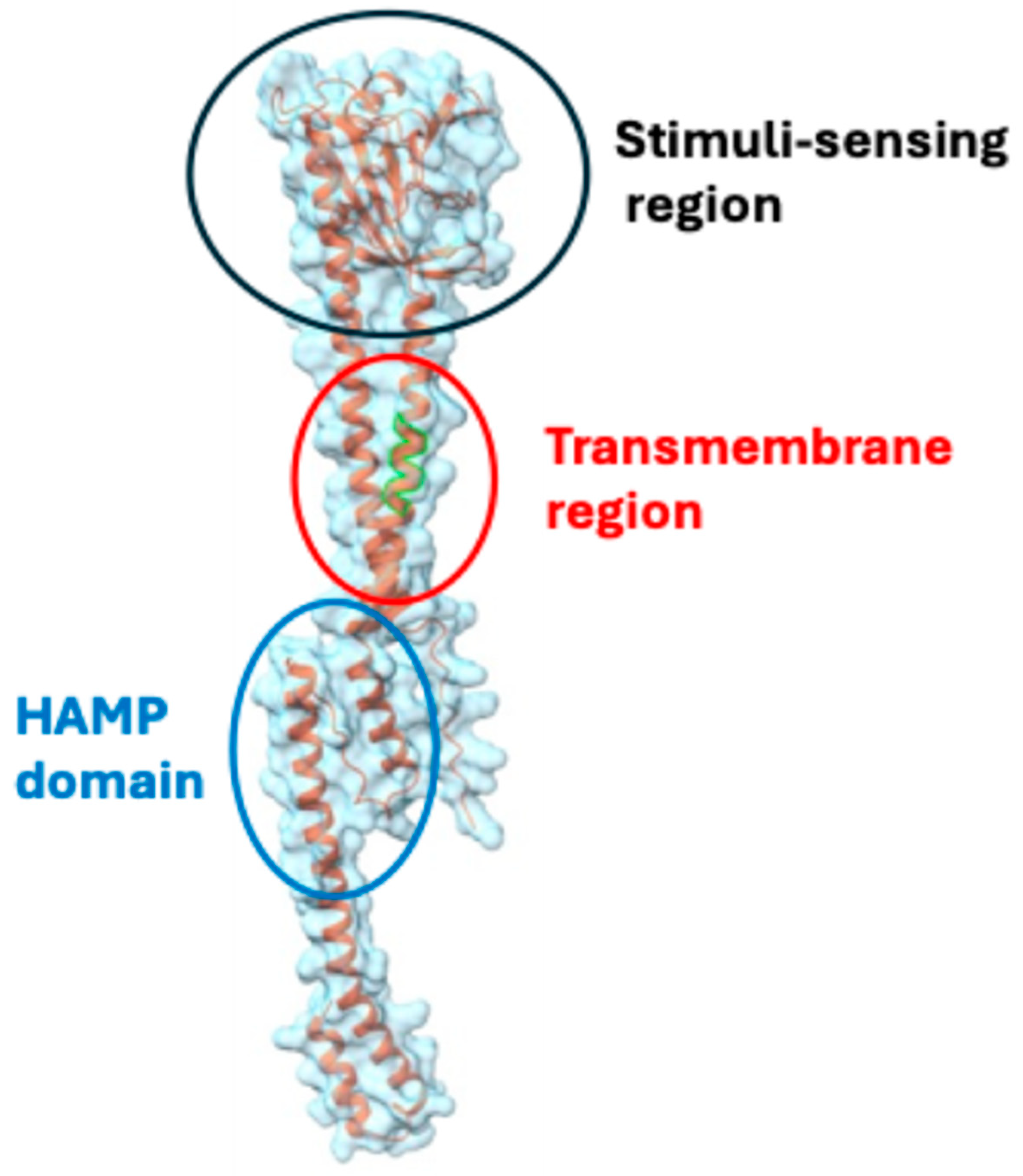
3.3. CovRS
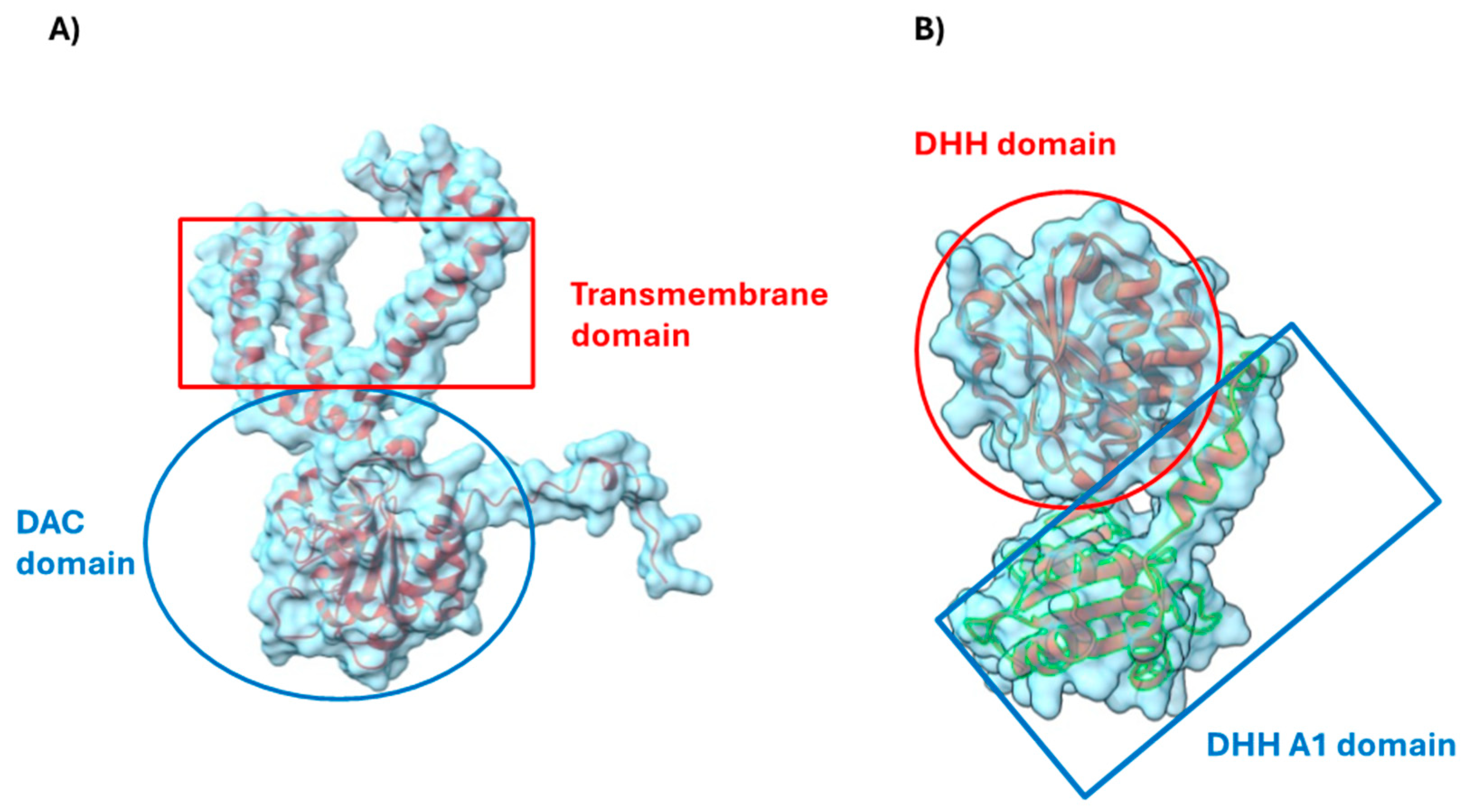
3.4. Cyclic di AMP Signaling Pathway
4. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shenoy, E.S.; Macy, E.; Rowe, T.; Blumenthal, K.G. Evaluation and Management of Penicillin Allergy: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterlund, A.; Popa, R.; Nikkila, T.; Scheynius, A.; Engstrand, L. Intracellular reservoir of Streptococcus pyogenes in vivo: A possible explanation for recurrent pharyngotonsillitis. Laryngoscope 1997, 107, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thulin, P.; Johansson, L.; Low, D.E.; Gan, B.S.; Kotb, M.; McGeer, A.; Norrby-Teglund, A. Viable group A streptococci in macrophages during acute soft tissue infection. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rasko, D.A.; Sperandio, V. Anti-virulence strategies to combat bacteria-mediated disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehbanipour, R.; Ghalavand, Z. Anti-virulence therapeutic strategies against bacterial infections: Recent advances. Germs 2022, 12, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hentzer, M.; Wu, H.; Andersen, J.B.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bagge, N.; Kumar, N.; Schembri, M.A.; Song, Z.; Kristoffersen, P.; et al. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3803–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Berbel, D.; Gonzalez-Diaz, A.; Lopez de Egea, G.; Camara, J.; Ardanuy, C. An Overview of Macrolide Resistance in Streptococci: Prevalence, Mobile Elements and Dynamics. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fyfe, C.; Grossman, T.H.; Kerstein, K.; Sutcliffe, J. Resistance to Macrolide Antibiotics in Public Health Pathogens. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brouwer, S.; Rivera-Hernandez, T.; Curren, B.F.; Harbison-Price, N.; De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Jespersen, M.G.; Davies, M.R.; Walker, M.J. Pathogenesis, epidemiology and control of Group A Streptococcus infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Clancy, J.; Petitpas, J.; Dib-Hajj, F.; Yuan, W.; Cronan, M.; Kamath, A.V.; Bergeron, J.; Retsema, J.A. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of a novel macrolide-resistance determinant, mefA, from Streptococcus pyogenes. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 22, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanetti, E.; Brenciani, A.; Morroni, G.; Tiberi, E.; Pasquaroli, S.; Mingoia, M.; Varaldo, P.E. Transduction of the Streptococcus pyogenes bacteriophage Phim46.1, carrying resistance genes mef(A) and tet(O), to other Streptococcus species. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rodriguez-Avial, I.; Rodriguez-Avial, C.; Culebras, E.; Picazo, J.J. Distribution of tetracycline resistance genes tet(M), tet(O), tet(L) and tet(K) in blood isolates of viridans group streptococci harbouring erm(B) and mef(A) genes. Susceptibility to quinupristin/dalfopristin and linezolid. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2003, 21, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, I.; Roberts, M. Tetracycline antibiotics: Mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 232–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsai, W.-C.; Shen, C.-F.; Lin, Y.-L.; Shen, F.-C.; Tsai, P.-J.; Wang, S.-Y.; Lin, Y.-S.; Wu, J.-J.; Chi, C.-Y.; Liu, C.-C. Emergence of macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pyogenes emm12 in southern Taiwan from 2000 to 2019. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.R.; Holden, M.T.; Coupland, P.; Chen, J.H.K.; Venturini, C.; Barnett, T.C.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Tse, H.; Dougan, G.; Yuen, K.-Y.; et al. Emergence of scarlet fever Streptococcus pyogenes emm12 clones in Hong Kong is associated with toxin acquisition and multidrug resistance. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, R.; Mateo, E.; Galimand, M.; Garaizar, J.; Courvalin, P.; Cisterna, R. Clonal spread of pediatric isolates of ciprofloxacin-resistant, emm type 6 Streptococcus pyogenes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2492–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brauner, A.; Fridman, O.; Gefen, O.; Balaban, N.Q. Distinguishing between resistance, tolerance and persistence to antibiotic treatment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghuysen, J.M. Serine β-lactamases and penicillin-binding proteins. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1991, 45, 37–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, R.; Neeravi, A.; Subramanian, N.; Baskar, P.; Anandhan, K.; Veeraraghavan, B. Analysis of Amino Acid Sequences of Penicillin-Binding Proteins 1a, 2b, and 2x in Invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae Nonsusceptible to Penicillin Isolated from Children in India. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerfass, I.; Hakenbeck, R.; Denapaite, D. An important site in PBP2x of penicillin-resistant clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae: Mutational analysis of Thr338. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chaguza, C.; Cornick, J.E.; Everett, D.B. Mechanisms and impact of genetic recombination in the evolution of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vannice, K.S.; Ricaldi, J.; Nanduri, S.; Fang, F.C.; Lynch, J.B.; Bryson-Cahn, C.; Wright, T.; Duchin, J.; Kay, M.; Chochua, S.; et al. Streptococcus pyogenes pbp2x Mutation Confers Reduced Susceptibility to β-Lactam Antibiotics. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Olsen, R.J.; Zhu, L.; Musser, J.M. A Single Amino Acid Replacement in Penicillin-Binding Protein 2X in Streptococcus pyogenes Significantly Increases Fitness on Subtherapeutic Benzylpenicillin Treatment in a Mouse Model of Necrotizing Myositis. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Watson, M.E., Jr.; Neely, M.N.; Caparon, M.G. Animal Models of Streptococcus pyogenes Infection. In Streptococcus pyogenes: Basic Biology to Clinical Manifestations, 2nd ed.; Ferretti, J.J., Stevens, D.L., Fischetti, V.A., Eds.; University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center: Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lyon, W.R.; Gibson, C.M.; Caparon, M.G. A role for trigger factor and an rgg-like regulator in the transcription, secretion and processing of the cysteine proteinase of Streptococcus pyogenes. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 6263–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Neely, M.N.; Lyon, W.R.; Runft, D.L.; Caparon, M. Role of RopB in growth phase expression of the SpeB cysteine protease of Streptococcus pyogenes. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 5166–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dmitriev, A.V.; McDowell, E.J.; Kappeler, K.V.; Chaussee, M.A.; Rieck, L.D.; Chaussee, M.S. The Rgg regulator of Streptococcus pyogenes influences utilization of nonglucose carbohydrates, prophage induction, and expression of the NAD-glycohydrolase virulence operon. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7230–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chaussee, M.S.; Sylva, G.L.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Smoot, L.M.; Graham, M.R.; Watson, R.O.; Musser, J.M. Rgg influences the expression of multiple regulatory loci to coregulate virulence factor expression in Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Do, H.; Makthal, N.; VanderWal, A.R.; Saavedra, M.O.; Olsen, R.J.; Musser, J.M.; Kumaraswami, M. Environmental pH and peptide signaling control virulence of Streptococcus pyogenes via a quorum-sensing pathway. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carroll, R.K.; Shelburne, S.A., 3rd; Olsen, R.J.; Suber, B.; Sahasrabhojane, P.; Kumaraswami, M.; Beres, S.B.; Shea, P.R.; Flores, A.R.; Musser, J.M. Naturally occurring single amino acid replacements in a regulatory protein alter streptococcal gene expression and virulence in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1956–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Do, H.; Makthal, N.; VanderWal, A.R.; Rettel, M.; Savitski, M.M.; Peschek, N.; Papenfort, K.; Olsen, R.J.; Musser, J.M.; Kumaraswami, M. Leaderless secreted peptide signaling molecule alters global gene expression and increases virulence of a human bacterial pathogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8498–E8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Haanes, E.J.; Heath, D.G.; Cleary, P.P. Architecture of the vir regulons of group A streptococci parallels opacity factor phenotype and M protein class. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 4967–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Podbielski, A. Three different types of organization of the vir regulon in group A streptococci. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1993, 237, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollingshead, S.K.; Arnold, J.; Readdy, T.L.; Bessen, D.E. Molecular evolution of a multigene family in group A streptococci. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1994, 11, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribardo, D.A.; McIver, K.S. Defining the Mga regulon: Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals both direct and indirect regulation by Mga in the group A streptococcus. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 491–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almengor, A.C.; Kinkel, T.L.; Day, S.J.; McIver, K.S. The catabolite control protein CcpA binds to Pmga and influences expression of the virulence regulator Mga in the Group A streptococcus. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8405–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hondorp, E.R.; Hou, S.C.; Hause, L.L.; Gera, K.; Lee, C.E.; McIver, K.S. PTS phosphorylation of Mga modulates regulon expression and virulence in the group A streptococcus. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 88, 1176–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rom, J.S.; Hart, M.T.; McIver, K.S. PRD-Containing Virulence Regulators (PCVRs) in Pathogenic Bacteria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 772874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Almengor, A.C.; McIver, K.S. Transcriptional activation of sclA by Mga requires a distal binding site in Streptococcus pyogenes. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 7847–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hause, L.L.; McIver, K.S. Nucleotides critical for the interaction of the Streptococcus pyogenes Mga virulence regulator with Mga-regulated promoter sequences. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 4904–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hondorp, E.R.; Hou, S.C.; Hempstead, A.D.; Hause, L.L.; Beckett, D.M.; McIver, K.S. Characterization of the Group A Streptococcus Mga virulence regulator reveals a role for the C-terminal region in oligomerization and transcriptional activation. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 83, 953–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sanson, M.; Makthal, N.; Gavagan, M.; Cantu, C.; Olsen, R.J.; Musser, J.M.; Kumaraswami, M. Phosphorylation events in the multiple gene regulator of group A Streptococcus significantly influence global gene expression and virulence. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 2382–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kreikemeyer, B.; McIver, K.S.; Podbielski, A. Virulence factor regulation and regulatory networks in Streptococcus pyogenes and their impact on pathogen-host interactions. Trends Microbiol. 2003, 11, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryllos, I.; Levin, J.C.; Wessels, M.R. The CsrR/CsrS two-component system of group A Streptococcus responds to environmental Mg2+. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4227–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryllos, I.; Tran-Winkler, H.J.; Cheng, M.F.; Chung, H.; Bolcome, R., III; Lu, W.; Lehrer, R.I.; Wessels, M.R. Induction of group A Streptococcus virulence by a human antimicrobial peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16755–16760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Levin, J.C.; Wessels, M.R. Identification of csrR/csrS, a genetic locus that regulates hyaluronic acid capsule synthesis in group A streptococcus. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 30, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, M.R.; Smoot, L.M.; Migliaccio, C.A.L.; Virtaneva, K.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Porcella, S.F.; Federle, M.J.; Adams, G.J.; Scott, J.R.; Musser, J.M. Virulence control in group A Streptococcus by a two-component gene regulatory system: Global expression profiling and in vivo infection modeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13855–13860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Agrahari, G.; Chandrahas, V.; Glinton, K.; Donahue, D.L.; Balsara, R.D.; Ploplis, V.A.; Castellino, F.J. A natural inactivating mutation in the CovS component of the CovRS regulatory operon in a pattern D Streptococcal pyogenes strain influences virulence-associated genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 6561–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Churchward, G. The two faces of Janus: Virulence gene regulation by CovR/S in group A streptococci. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, J.S. Signaling mechanisms of HAMP domains in chemoreceptors and sensor kinases. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faozia, S.; Fahmi, T.; Port, G.C.; Cho, K.H. c-di-AMP-Regulated K+ Importer KtrAB Affects Biofilm Formation, Stress Response, and SpeB Expression in Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commichau, F.M.; Dickmanns, A.; Gundlach, J.; Ficner, R.; Stulke, J. A jack of all trades: The multiple roles of the unique essential second messenger cyclic di-AMP. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 97, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteley, A.T.; Garelis, N.E.; Peterson, B.N.; Choi, P.H.; Tong, L.; Woodward, J.J.; Portnoy, D.A. c-di-AMP modulates Listeria monocytogenes central metabolism to regulate growth, antibiotic resistance and osmoregulation. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 104, 212–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Andrade, W.A.; Firon, A.; Schmidt, T.; Hornung, V.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Trieu-Cuot, P.; Golenbock, D.T.; Kaminski, P.-A. Group B streptococcus degrades cyclic-di-AMP to modulate STING-dependent type I interferon production. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmi, T.; Faozia, S.; Port, G.C.; Cho, K.H. The Second Messenger c-di-AMP Regulates Diverse Cellular Pathways Involved in Stress Response, Biofilm Formation, Cell Wall Homeostasis, SpeB Expression, and Virulence in Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, 147-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rivera-Galindo, M.A.; Aguirre-Garrido, F.; Garza-Ramos, U.; Villavicencio-Pulido, J.G.; Fernandez Perrino, F.J.; Lopez-Perez, M. Relevance of the Adjuvant Effect between Cellular Homeostasis and Resistance to Antibiotics in Gram-Negative Bacteria with Pathogenic Capacity: A Study of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, K.H. Molecular Targets in Streptococcus pyogenes for the Development of Anti-Virulence Agents. Genes 2024, 15, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091166
Cho KH. Molecular Targets in Streptococcus pyogenes for the Development of Anti-Virulence Agents. Genes. 2024; 15(9):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091166
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Kyu Hong. 2024. "Molecular Targets in Streptococcus pyogenes for the Development of Anti-Virulence Agents" Genes 15, no. 9: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091166
APA StyleCho, K. H. (2024). Molecular Targets in Streptococcus pyogenes for the Development of Anti-Virulence Agents. Genes, 15(9), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091166





