The Past, Present, and Future of Plant Activators Targeting the Salicylic Acid Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification of Plant Activators
2.1. Classification by Mechanism of Action
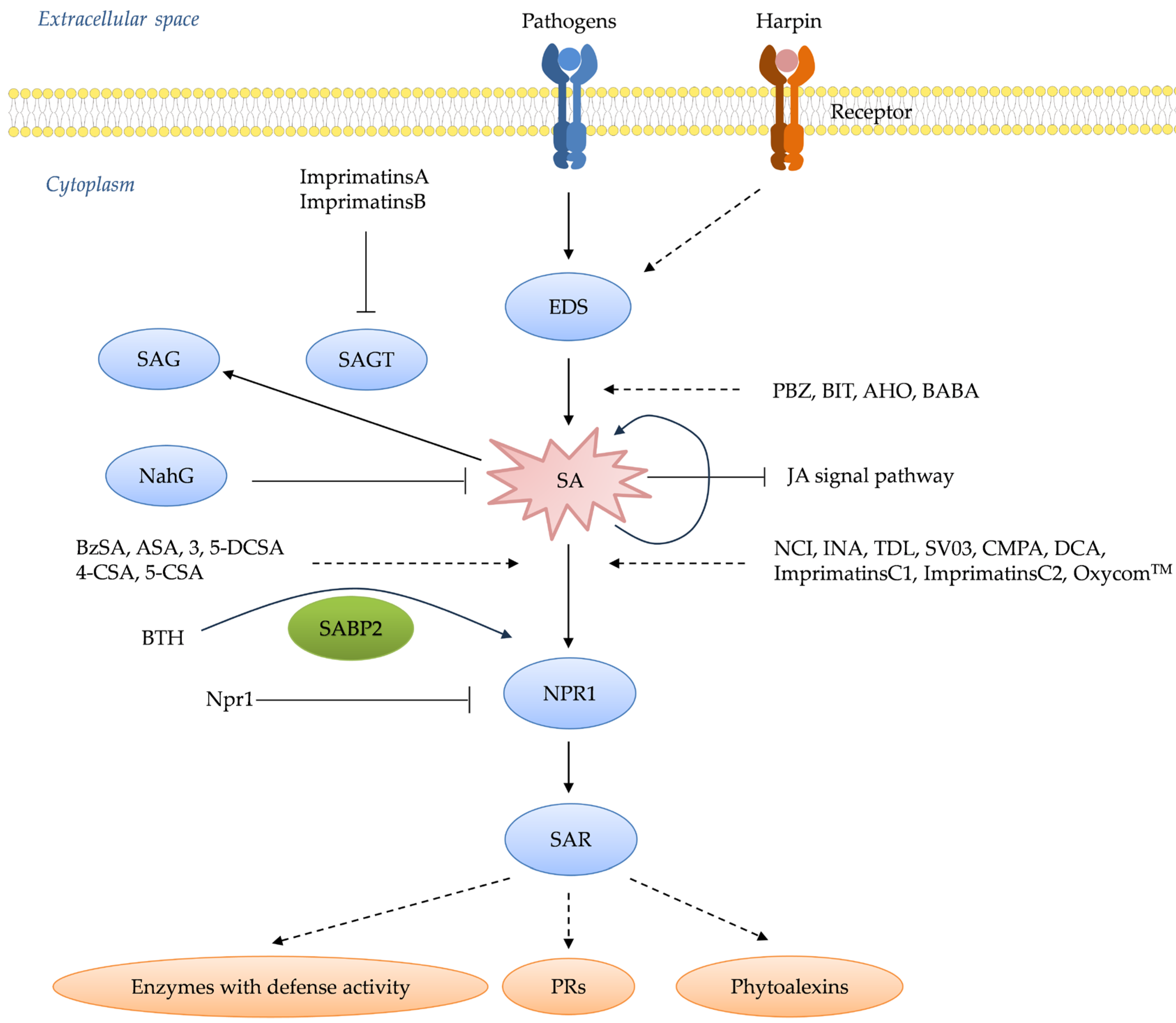
2.1.1. Upstream Activators
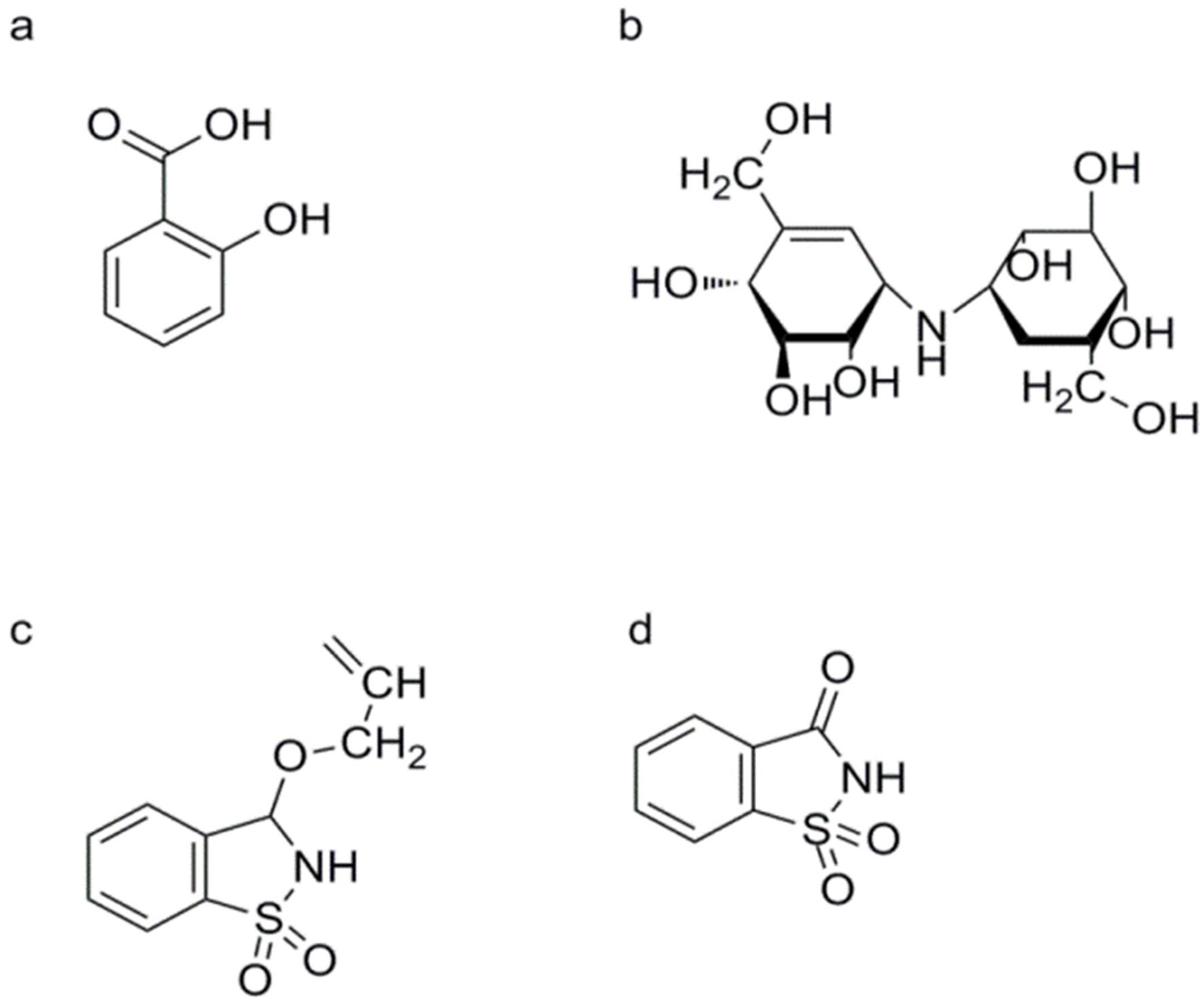
HrBP1
Validamycin A (VMA) and Validoxylamine A (VAA)
Probenazole (PBZ)
(D, L)-3-Aminobutyric Acid (BABA)
Imprimatins
Diuretics
2.1.2. Downstream Activators
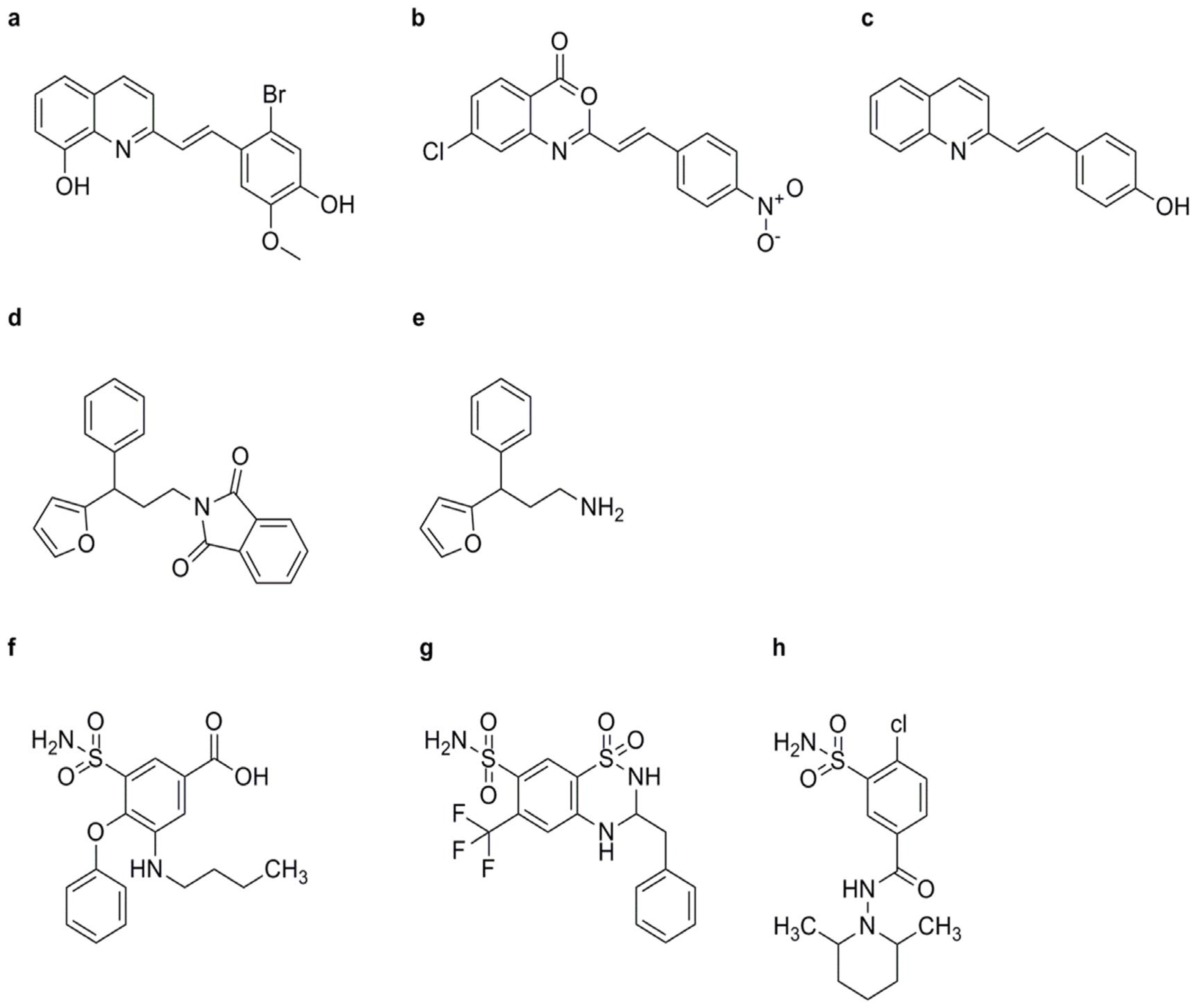
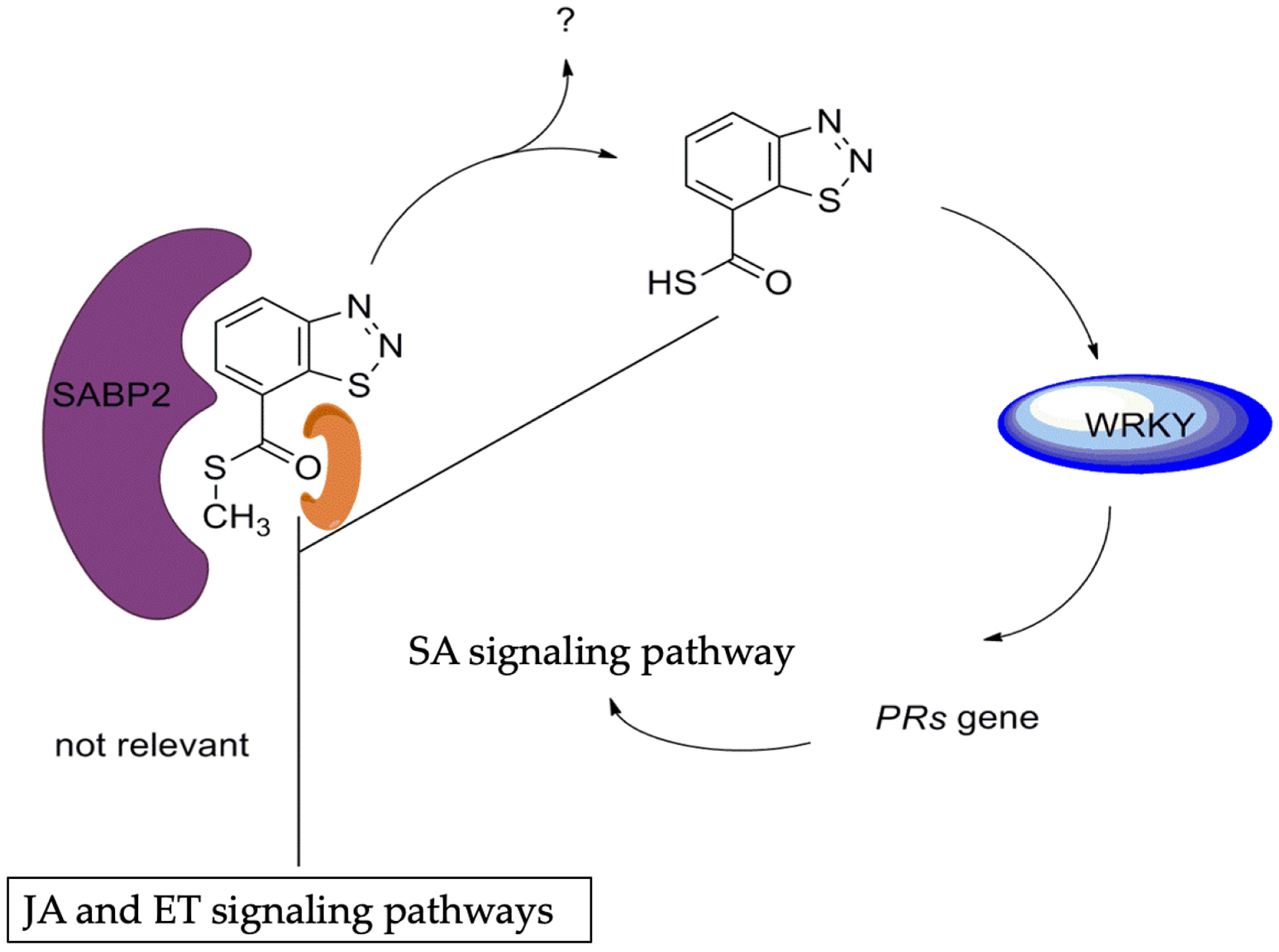
BTH
NCI
INA
TDL
CMPA
SA and Its Derivatives
DCA
Oxycom™
2.1.3. Activators with Unclear Action Sites
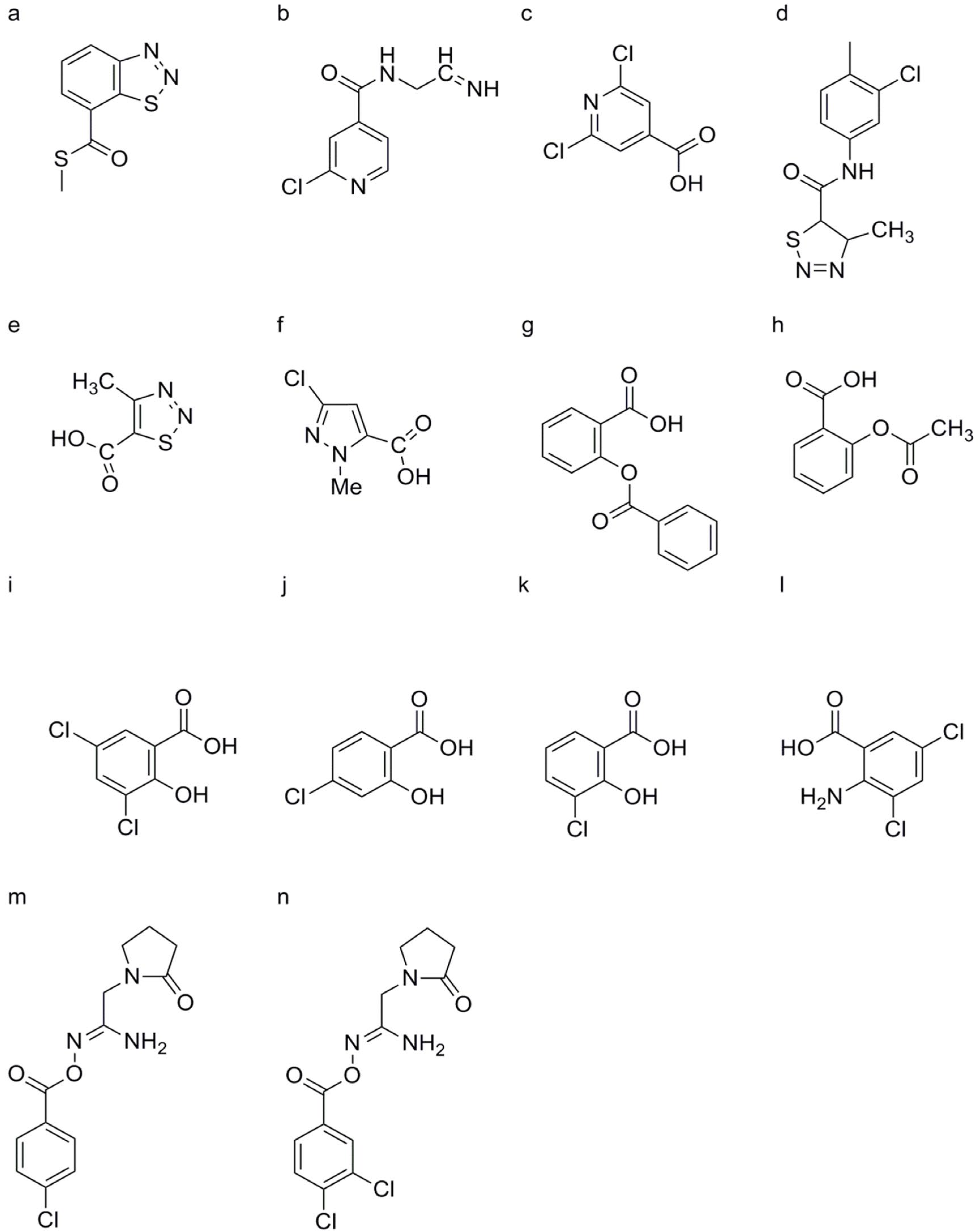
Laminarin
Chitosan
Riboflavin
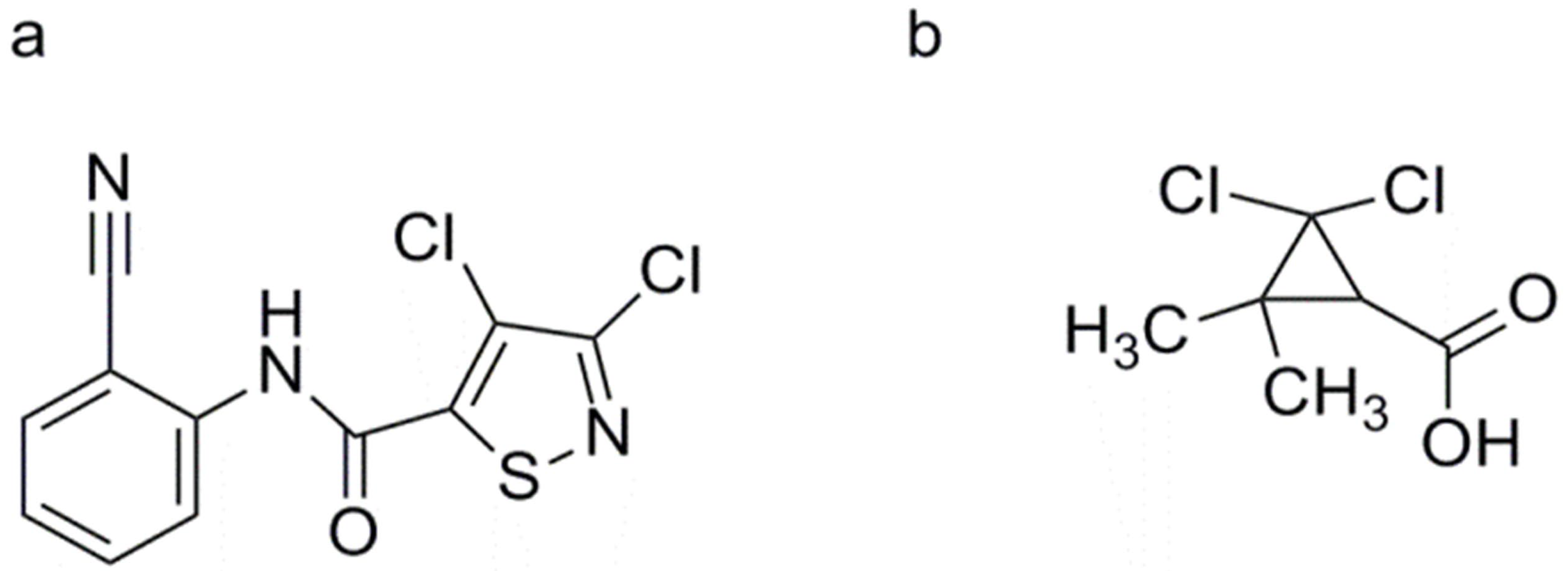
3, 4-Dichloro-2′-cyano-1, 2-thiazole-5-carboxanilide (Isotianil)
Polypeptide Product
β, γ-Methyleneadenosine 5′-triphosphate (AMP-PCP)
2, 2-Dichloro-3, 3-dimethylcyclopropane Carboxylic Acid (DDCC)
Hyaluronic Acid (HA)
Compounds Containing Indole and 4, 5-Dihydro-1H-pyrazoline Structures
Compounds Containing Pyrazole Structures
3. Classification Based on Chemical Structure
3.1. Salicylates
3.2. Benzothiadiazoles
3.3. Nicotinamide Analogs
3.4. Amino Acid Derivatives
3.5. Synthetic Chemicals with Different Structures
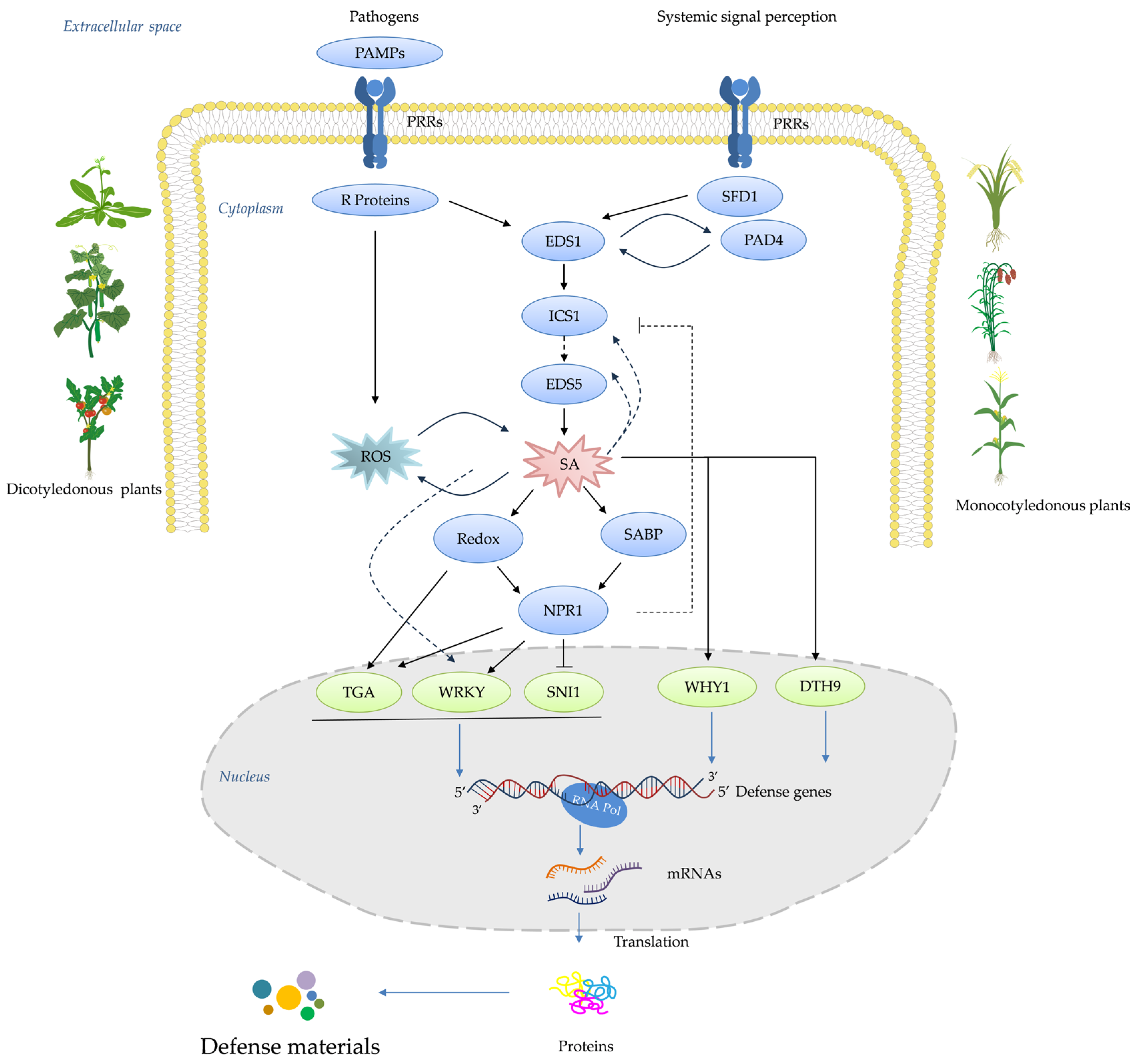
4. How Plant Receptors Trigger an Immune Response
4.1. Historical Development of Plant Activators
4.1.1. Development of Screening Methods
4.1.2. Studies of Target–Activator Interactions
4.1.3. Advancements in Understanding Target–Activator Interactions
5. Current State of Knowledge of Plant Activators against the SA Signaling Pathway
5.1. Research Trends
5.2. Challenges Facing Molecular Target Research
5.2.1. Discovery of New Targets for Plant Activators
5.2.2. Discovery of New Mechanisms for Plant Resistance Responses
5.2.3. New Research Methods for Studying the Targets of Plant Activators
5.2.4. Crosstalk between the SA and JA Signaling Pathways and Their Synergistic Role in Disease Resistance
6. Future Goals of Plant Activators
6.1. Action Mechanisms of Plant Activators
6.2. Metabolism Mechanism of Plant Activators
6.3. Screening Models of Plant Activators
6.4. Discovery of Lead Compounds Based on Novel Action Targets
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrant, W.E.; Dong, X. Systemic acquired resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004, 42, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwessinger, B.; Ronald, P.C. Plant innate immunity: Perception of conserved microbial signatures. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 451–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.M.; Kachroo, A.; Kachroo, P. Chemical inducers of systemic immunity in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Han, X.; Kahmann, R. Microbial effectors target multiple steps in the salicylic acid production and signaling pathway. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 140–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutrot, F.; Zipfel, C. Function, discovery, and exploitation of plant pattern recognition receptors for broad-spectrum disease resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M. Upscaling plant defense system through the application of plant growth-promoting fungi (PGPF). In Microbial Technology for Agro-Ecosystems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 61–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Dolatabadian, A.; Fernando, W.D. The wonderful world of intrinsic and intricate immunity responses in plants against pathogens. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 44, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentham, A.R.; de la Concepcion, J.C.; Mukhi, N.; Zdrzałek, R.; Draeger, M.; Gorenkin, D.; Hughes, R.K.; Banfield, M.J. A molecular roadmap to the plant immune system. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 14916–14935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, W.S.; Wang, T.; Meng, X.F.; Chen, T.T.; Huang, X.X.; Li, Y.J.; Hou, B.K. Methyl salicylate glucosylation regulates plant defense signaling and systemic acquired resistance. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 2167–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, M.; Xiao, X.; Kachroo, P.; Kachroo, A. Signaling mechanisms underlying systemic acquired resistance to microbial pathogens. Plant Sci. 2019, 279, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.; Sharma, G. Management of host plant resistance through immunization: An overview. J. Hill Agric. 2016, 7, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamy, J.; Carr, J.P.; Klessig, D.F.; Raskin, I. Salicylic acid: A likely endogenous signal in the resistance response of tobacco to viral infection. Science 1990, 250, 1002–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Métraux, J.; Signer, H.; Ryals, J.; Ward, E.; Wyss-Benz, M.; Gaudin, J.; Raschdorf, K.; Schmid, E.; Blum, W.; Inverardi, B. Increase in salicylic acid at the onset of systemic acquired resistance in cucumber. Science 1990, 250, 1004–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffney, T.; Friedrich, L.; Vernooij, B.; Negrotto, D.; Nye, G.; Uknes, S.; Ward, E.; Kessmann, H.; Ryals, J. Requirement of salicylic acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 1993, 261, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.R.; Uknes, S.J.; Williams, S.C.; Dincher, S.S.; Wiederhold, D.L.; Alexander, D.C.; Ahl-Goy, P.; Metraux, J.P.; Ryals, J.A. Coordinate gene activity in response to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 1991, 3, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Bowling, S.A.; Gordon, A.S.; Dong, X. Characterization of an Arabidopsis thaliana mutant that is nonresponsive to inducers of systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Kachroo, P.; Klessig, D.F. The Arabidopsis thaliana ssi1 mutation restores pathogenesis-related gene expression in npr1 plants and renders defensin gene expression salicylic acid dependent. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapin, D.; Bhandari, D.D.; Parker, J.E. Origins and immunity networking functions of EDS1 family proteins. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2020, 58, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirage, D.; Tootle, T.L.; Reuber, T.L.; Frost, L.N.; Feys, B.J.; Parker, J.E.; Ausubel, F.M.; Glazebrook, J. Arabidopsis thaliana PAD4 encodes a lipase-like gene that is important for salicylic acid signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13583–13588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulgem, T.; Somssich, I.E. Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Eulgem, T. Transcript-level expression control of plant NLR genes. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaud, M.C.; Gineste, S.; Nussaume, L.; Robaglia, C. Sucrose increases pathogenesis-related PR-2 gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana through an SA-dependent but NPR1-independent signaling pathway. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 42, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bockhaven, J.; de Vleesschauwer, D.; Höfte, M. Towards establishing broad-spectrum disease resistance in plants: Silicon leads the way. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Chen, J.; Chang, M.; Chen, H.; Hall, K.; Korin, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, D.; Fu, Z.Q. Pandemonium breaks out: Disruption of salicylic acid-mediated defense by plant pathogens. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reglinski, T.; Dann, E.; Deverall, B. Integration of induced resistance in crop production. In Induced Resistance for Plant Defence: A Sustainable Approach to Crop Protection; Walters, D., Newton, A., Lyon, G., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 201–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Chen, J.Q.; Shi, Y.X.; Sun, M.J.; Li, P.F.; Zhao, Z.J.; Zhu, W.P.; Li, H.L.; Xu, Y.F.; Li, B.J. The discovery of new scaffold of plant activators: From salicylic acid to benzotriazole. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, B.; Hu, M.; Bao, J.; Yan, W.; Han, X.; Ye, Y. Fluorescent probes for imaging and detection of plant hormones and their receptors. Adv. Agrochem. 2023, 3, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.-M.; Laby, R.J.; Zumoff, C.H.; Bauer, D.W.; He, S.Y.; Collmer, A.; Beer, S.V. Harpin, elicitor of the hypersensitive response produced by the plant pathogen Erwinia amylovora. Science 1992, 257, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.Y.; Huang, H.C.; Collmer, A. Pseudomonas syringae pv. Syringae HarpinPss: A protein that is secreted via the Hrp pathway and elicits the hypersensitive response in plants. Cell 1993, 73, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fan, P.; Yun, Z.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Y. β-aminobutyric acid priming acquisition and defense response of mango fruit to Colletotrichum gloeosporioides infection based on quantitative proteomics. Cells 2019, 8, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, W.; Schurter, R.; Maetzke, T. The chemistry of benzothiadiazole plant activators. Pestic. Sci. 1997, 50, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashita, H.; Yoshioka, K.; Yasuda, M.; Nitta, T.; Arai, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Yamaguchi, I. Probenazole induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco through salicylic acid accumulation. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2002, 61, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dann, E.; Diers, B.; Byrum, J.; Hammerschmidt, R. Effect of treating soybean with 2, 6 Dichloroisonicotinic acid (INA) and benzothiadiazole (BTH) on seed yields and the level of disease caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in field and greenhouse studies. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1998, 104, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Shao, W.-B.; Chu, P.-L.; Xiang, H.-M.; Qi, P.-Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, P.-Y.; Yang, S. 1,3,4-Oxadiazole derivatives as plant activators for controlling plant viral diseases: Preparation and assessment of the effect of auxiliaries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7929–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bektas, Y.; Eulgem, T. Synthetic plant defense elicitors. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toquin, V.; Braun, C.A.; Sirven, C.; Assmann, L.; Sawada, H. Host defense inducers. In Modern Crop Protection Compounds, 3rd ed.; Jeschke, P., Witschel, M., Kramer, W., Schirmer, U., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 9595–9978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kang, H.W. β-Aminobutyric acid and powdery mildew infection enhanced the activation of defense-related genes and salicylic acid in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Genes 2023, 14, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.; Jiang, Y.L.; Kumar, D. SABP2, a methyl salicylate esterase is required for the systemic acquired resistance induced by acibenzolar-S-methyl in plants. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3458–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yan, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Xie, X.; Li, X. Research on the interaction mechanism between α mino-phosphonate derivative QR and harpin-binding protein 1 in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plants. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 621875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoel, S.H.; Dong, X. Salicylic acid in plant immunity and beyond. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, J.R.; Collmer, A. Bacterial pathogens in plants: Life up against the wall. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1683–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvitko, B.H.; Collmer, A. Discovery of the Hrp type III secretion system in phytopathogenic bacteria: How investigation of hypersensitive cell death in plants led to a novel protein injector system and a world of inter-organismal molecular interactions within plant cells. Phytopathology 2023, 113, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Ma, W.; Li, X. Characteristics, roles and applications of proteinaceous elicitors from pathogens in plant immunity. Life 2023, 13, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Capdeville, G.; Beer, S.V.; Watkins, C.B.; Wilson, C.L.; Tedeschi, L.O.; Aist, J.R. Pre- and post-harvest harpin treatments of apples induce resistance to blue mold. Plant Dis. 2003, 87, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.H.; Leite, R.P., Jr. Lack of control of citrus canker by induced systemic resistance compounds. Plant Dis. 2004, 88, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karačić, V.; Miljaković, D.; Marinković, J.; Ignjatov, M.; Milošević, D.; Tamindžić, G.; Ivanović, M. Bacillus species: Excellent biocontrol agents against tomato diseases. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.H.; Ajaharuddin, S.M.; Rahman, S.S.; Saha, S.; Goswami, S.; Islam, S.; Barik, S.; Hossain, A.; Latef, A.A.H.A. Citrus lemon and stressful conditions. In Medicinal Plant Responses to Stressful Conditions, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 95–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlat, M.; van Gijsegem, F.; Huet, J.C.; Pernollet, J.C.; Boucher, C.A. PopA1, a protein which induces a hypersensitivity-like response on specific Petunia genotypes, is secreted via the Hrp pathway of Pseudomonas solanacearum. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, D.W.; Wei, Z.M.; Beer, S.V.; Collmer, A. Erwinia chrysanthemi harpinEch: An elicitor of the hypersensitive response that contributes to soft-rot pathogenesis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1995, 8, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Klessig, D.F.; Nürnberger, T. A harpin binding site in tobacco plasma membranes mediates activation of the pathogenesis-related gene HIN1 independent of extracellular calcium but dependent on mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Delaney, T.P.; Bauer, D.W.; Beer, S.V. Harpin induces disease resistance in Arabidopsis through the systemic acquired resistance pathway mediated by salicylic acid and the NIM1 gene. Plant J. 1999, 20, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.Q.; Liu, H.X.; Jia, Q.; Wu, X.J.; Guo, X.J.; Zhang, S.J.; Song, F.; Dong, H.S. The internal glycine-rich motif and cysteine suppress several effects of the HpaGXooc protein in plants. Phytopathology 2006, 96, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hoyos, M.E.; Stanley, C.M.; He, S.Y.; Pike, S.; Pu, X.-A.; Novacky, A. The interaction of HarpinPss with plant cell walls. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1996, 9, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Feng, S.; Tang, S.; Dong, P.; Li, Z. Biological control of potato late blight with a combination of Streptomyces strains and biochar. Biol. Control. 2023, 183, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Salicylic acid: Biosynthesis, perception, and contributions to plant immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2019, 50, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kameda, Y.; Matsui, K. Effect of validamycins on glycohydrolases of Rhizoctonia solani. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Duan, Y.; Bian, C.; Pan, X.; Yao, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M. Effects of validamycin in controlling Fusarium head blight caused by Fusarium graminearum: Inhibition of DON biosynthesis and induction of host resistance. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 153, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, R.; Fujimori, K.; Matsuura, K. Antibacterial activity of Validamycin A against Pseudomonas solanacearum and its efficacy against tomato bacterial wilt. Jpn. J. Phytopathol. 1996, 62, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shikawa, R.; Suzuki-nishimoto, M.; Fukuchi, A.; Matsuura, K. Effective control of cabbage black rot by Validamycin A and its effect on extracellular polysaccharide-production of Xanthomonas campestris pv. Campestris. J. Pestic. Sci. 2004, 29, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ishikawa, R.; Shirouzu, K.; Nakashita, H.; Lee, H.Y.; Motoyama, T.; Yamaguchi, I.; Teraoka, T.; Arie, T. Foliar spray of validamycin a or validoxylamine a controls tomato fusarium wilt. Phytopathology 2005, 95, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; Duan, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiu, Q.; Wang, J.; Hou, Y.; Song, X.; Zhou, M. Validamycin A induces broad-spectrum resistance involving salicylic acid and jasmonic acid/ethylene signaling pathways. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 1424–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Igarashi, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Seki, S.; Mase, S. The characteristics of probenazole (Oryzemate) for the control of rice blast. J. Pestic. Sci. 1977, 2, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.J.; Chun, H.J.; Choi, C.W.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, H.M.; Park, M.S.; Baek, D.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, M.C. Hostline struity, and mechanisms of novel benzofuran derivatives containing disulfide moieties. Magnaporthe oryzae and control fungal disease in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Mase, S.; Sekizawa, Y. Effect of probenazole on the activities of enzymes related to the resistant reaction in rice plant. Ann. Phytopath. Soc. Jpn. 1980, 46, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midoh, N.; Iwata, M. Cloning and characterization of a probenazoleinducible gene for an intracellular pathogenesis-related protein in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 1996, 37, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midoh, N.; Iwata, M. Expression of defense-related genes by probenazole or 1,2-benzisothiazole-3(2H)-one 1,1-dioxide. J. Pestic. Sci. 1997, 22, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, K.; Nakashita, H.; Klessig, D.F.; Yamaguchi, I. Probenazole induces systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis with a novel type of action. Plant J. 2001, 25, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y. 3-Aminobutyric acid induces systemic resistance against Peronospora tabacina. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1994, 44, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.K.; Sunwoo, J.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, B.S. Accumulation of β-1,3-glucanase and chitinase isoforms, and salicylic acid in dl-β-amino-n-butyric acid-induced resistance response of pepper stems to Phytophthora capsici. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1997, 51, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Z.; Mei, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, T.; Ye, X. β-aminobutyric acid (BABA)-induced resistance to tobacco black shank in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noutoshi, Y.; Okazaki, M.; Shirasu, K. Imprimatins A and B: Novel plant activators targeting salicylic acid metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1715–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noutoshi, Y.; Okazaki, M.; Kida, T.; Nishina, Y.; Morishita, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Suzuki, H.; Shibata, D.; Jikumaru, Y.; Hanada, A.; et al. Novel plant immune-priming compounds identified via high-throughput chemical screening target salicylic acid glucosyltransferases in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3795–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, K.; Katagiri, F. Comparing signaling mechanisms engaged in pattern-triggered and effector-triggered immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noutoshi, Y.; Jikumaru, Y.; Kamiya, Y.; Shirasu, K. ImprimatinC1, a novel plant immune-priming compound, functions as a partial agonist of salicylic acid. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noutoshi, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Shirasu, K. Diuretics prime plant immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurter, R.; Kunz, W.; Nyfelder, R. Process and a Composition for Immunizing Plants against Diseases. U.S. Patent 4,931,581, 18 August 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Molinari, S. Systemic acquired resistance activation in solanaceous crops as a management strategy against root-knot nematodes. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhamou, N.; Belanger, R.R. Benzothiadiazole-mediated induced resistance to fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicis-lycopersici in tomato. Plant Physiol. 1998, 118, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hukkanen, A.T.; Kokko, H.I.; Buchala, A.J.; McDougall, G.J.; Stewart, D.; Kärenlampi, S.O.; Karjalainen, R.O. Benzothiadiazole induces the accumulation of phenolics and improves resistance to powdery mildew in strawberries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, K.A.; Friedrich, L.; Hunt, M.; Weymann, K.; Delaney, T.; Kessmann, H.; Staub, T.; Ryals, J. Benzothiadiazole induces disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana by activation of the systemic acquired resistance signal transduction pathway. Plant J. 1996, 10, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukkanen, A.; Kokko, H.; Buchala, A.; Häyrinen, J.; Kärenlampi, S. Benzothiadiazole affects the leaf proteome in arctic bramble (Rubus arcticus). Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, B.; Guo, Q.; Shi, L.; He, M.; Qin, Z.; Li, L.; He, P.; Wang, Z.; Hu, D. A time-course proteomic analysis of rice triggered by plant activator BTH. J. Plant Growth. Regul. 2015, 34, 392–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, A.; Schwindling, S.; Conrath, U. Benzothiadiazole-induced priming for potentiated responses to pathogen infection, wounding, and infiltration of water into leaves requires the NPR1/NIM1 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimono, M.; Sugano, S.; Nakayama, A.; Jiang, C.J.; Ono, K.; Toki, S.; Takatsuji, H. Rice WRKY45 plays a crucial role in benzothiadiazole-inducible blast resistance. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Shimano, S.; Mochizuki, S.; Koike, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Konishi, K. N-Cyanoalkylisonicotinamide Derivatives. U.S. Patent US4804762A, 4 May 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H.; Konishi, K.; Koike, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Sekido, S.; Yamaguchi, I. Effect of N-Cyanomethyl-2-chloroisonicotinamide for control of rice blast. J. Pestic. Sci. 1990, 15, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Konishi, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Sekido, S.; Yamaguchi, I. Characteristics of N-phenylsulfonyl-2-chloroisonicotinamide as an anti-rice blast agent. J. Pestic. Sci. 1990, 15, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakashita, H.; Yasuda, M.; Nishioka, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Arai, Y.; Uramoto, M.; Yoshida, S.; Yamaguchi, I. Chloroisonicotinamide derivative induces a broad range of disease resistance in rice and tobacco. Plant Cell Physiol. 2002, 43, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yasuda, M.; Nakashita, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Nishioka, M.; Arai, Y.; Uramoto, M.; Yamaguchi, I.; Yoshida, S. N-cyanomethyl-2-chloroisonicotinamide induces systemic acquired resistance in arabidopsis without salicylic acid accumulation. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 2003, 67, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bektas, Y. The synthetic elicitors 2,6-dichloro-isonicotinic acid (INA) and 2,4-dichloro-6-{(E)-[(3-methoxyphenyl)imino]methyl}phenol (DPMP) enhances tomato resistance against bacterial canker disease with different molecular mechanisms. Physiol. Mol. Plant P. 2021, 116, 101740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson-Hanks, E.S.; Deverall, B.J. Effect of 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acid, its formulation materials and benzothiadiazole on systemic resistance to alternaria leaf spot in cotton. Plant Pathol. 2000, 49, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, S.; Umesha, S. 2,6-Dichloroisonicotinic acid enhances the expression of defense genes in tomato seedlings against Xanthomonas perforans. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 86, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.K.; Nielsen, J.E.; Madrid, S.M.; Mikkelsen, J.D. New antifungal proteins from sugar beet (β vulgaris L.) showing homology to non-specific lipid transfer proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 1996, 31, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Delaney, T.P. Over-expression of TGA5, which encodes a bZIP transcription factor that interacts with NIM1/NPR1, confers SAR-independent resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana to Peronospora parasitica. Plant J. 2002, 32, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.H.; Khan, I.U.; Noh, B.; Noh, Y.S. Genomic overview of INA-induced NPR1 targeting and transcriptional cascades in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 3572–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubata, K.; Kuroda, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yasokawa, N. Development of a novel plant activator for rice diseases, tiadinil. J. Pestic. Sci. 2006, 31, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yasuda, M.; Kusajima, M.; Nakajima, M.; Akutsu, K.; Kudo, T.; Yoshida, S.; Nakashita, H. Thiadiazole carboxylic acid moiety of Tiadinil, SV-03, induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco without salicylic acid cccumulation. J. Pestic. Sci. 2006, 31, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hönig, M.; Roeber, V.M.; Schmülling, T.; Cortleven, A. Chemical priming of plant defense responses to pathogen attacks. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1146577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, M.; Nakashita, H.; Yoshida, S. Tiadinil, a novel class of activator of systemic acquired resistance, induces defense gene expression and disease resistance in tobacco. J. Pestic. Sci. 2004, 29, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Ogino, A.; Ymada, K.; Sonoda, R. Induction of disease resistance in tea (Camellia sinensis L.) by plant activators. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2010, 44, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, M. Regulation mechanisms of systemic acquired resistance induced by plant activators. J. Pestic. Sci. 2007, 32, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, M.; Nishioka, M.; Nakashita, H.; Yamaguchi, I.; Yoshida, S. Pyrazolecarboxylic acid derivative induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 2614–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, M.; Nakashita, H.; Yasuda, M.; Yoshida, S.; Yamaguchi, I. Induction of resistance against rice bacterial leaf blight by 3-Chloro-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid. J. Pestic. Sci. 2005, 30, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandersson, E.; Mulugeta, T.; Lankinen, Å.; Liljeroth, E.; Andreasson, E. Plant resistance inducers against pathogens in Solanaceae species from molecular mechanisms to field application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Roychowdhury, R.; Ray, S.; Hada, A.; Kumar, A.; Sarker, U.; Aftab, T.; Das, R. Salicylic acid (SA)-mediated plant immunity against biotic stresses: An insight on molecular components and signaling mechanism. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, T.A.; Taha, N.A.; Taher, D.I.; Metwaly, M.M.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Rezk, A.A.; El-Ganainy, S.M.; Shehata, W.F.; El-Ramady, H.R.; Bayoumi, Y.A. Paclobutrazol improves the quality of tomato seedlings to be resistant to Alternaria solani blight disease: Biochemical and histological perspectives. Plants 2022, 11, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Xi, D.H.; Yuan, S.; Xu, F.; Zhang, D.W.; Lin, H.H. Salicylic acid and jasmonic acid are essential for systemic resistance against tobacco mosaic virus in Nicotiana benthamiana. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2014, 27, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mur, L.A.; Naylor, G.; Warner, S.A.; Sugars, J.M.; White, R.F.; Draper, J. Salicylic acid potentiates defence gene expression in tissue exhibiting acquired resistance to pathogen attack. Plant J. 1996, 9, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
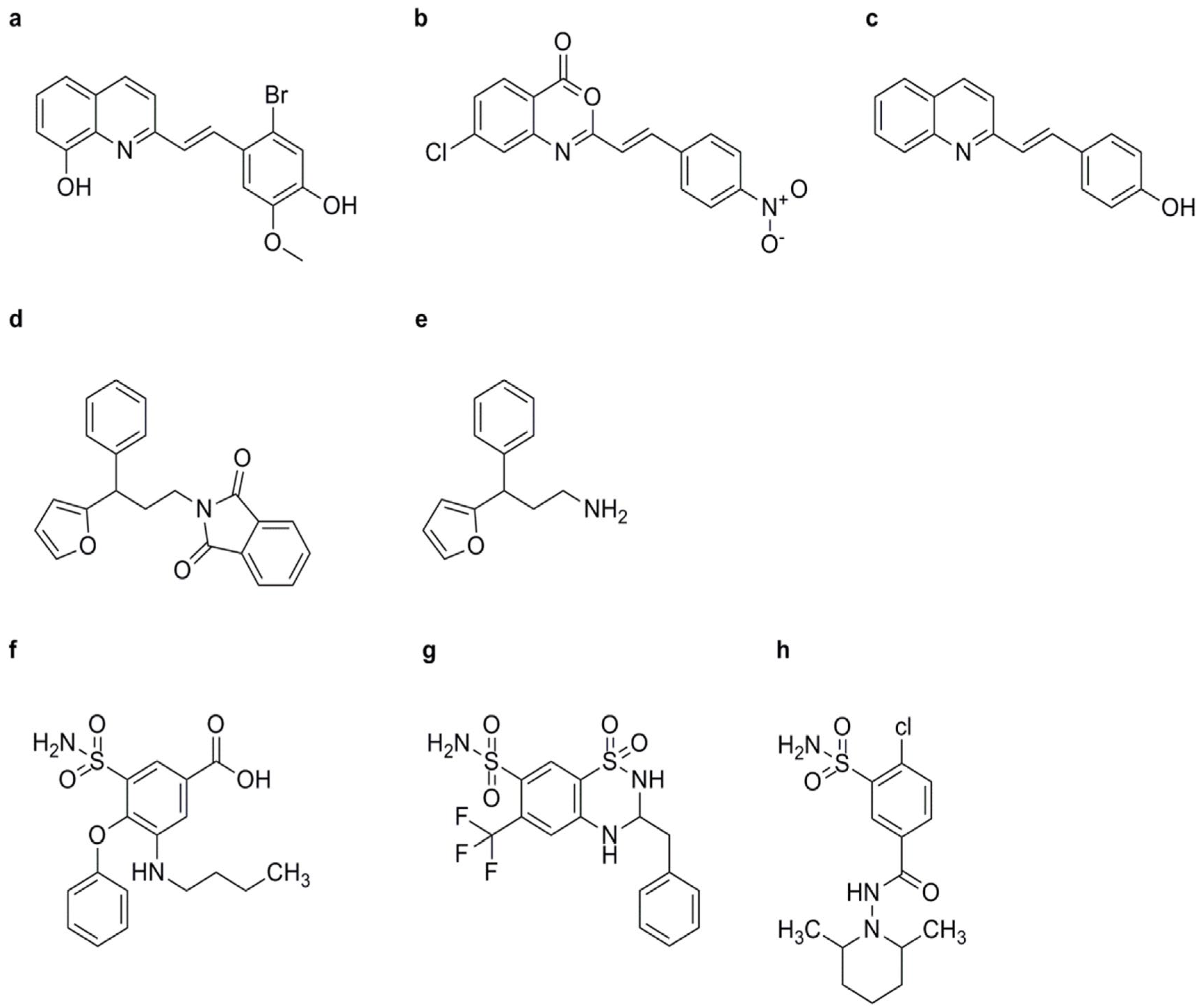
- Kamatham, S.; Neela, K.B.; Pasupulati, A.K.; Pallu, R.; Singh, S.S.; Gudipalli, P. Benzoylsalicylic acid isolated from seed coats of Givotia rottleriformis induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco and Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemist 2016, 126, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatham, S.; Pallu, R.; Pasupulati, A.K.; Singh, S.S.; Gudipalli, P. Benzoylsalicylic acid derivatives as defense activators in tobacco and Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 2017, 143, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, F.P.; Petracek, P.D.; Heiman, D.F.; Fledderman, C.M.; Warrior, P. Salicylate activity. 3. Structure relationship to systemic acquired resistance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9775–9780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath, U.; Chen, Z.; Ricigliano, J.R.; Klessig, D.F. Two inducers of plant defense responses, 2,6-dichloroisonicotinec acid and salicylic acid, inhibit catalase activity in tobacco. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7143–7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, V.A.; Thulke, O.U.; Conrath, U. A benzothiadiazole primes parsley cells for augmented elicitation of defense responses. Plant Physiol. 1998, 117, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulke, O.; Conrath, U. Salicylic acid has a dual role in the activation of defence-related genes in parsley. Plant J. 1998, 14, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath, U. Molecular aspects of defence priming. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chu, J.Y.; Boyle, P.; Wang, Y.; Brindle, I.D.; de Luca, V.; Després, C. The Arabidopsis NPR1 protein is a receptor for the plant defense hormone salicylic acid. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faize, L.; Faize, M. Functional analogues of salicylic acid and their use in crop protection. Agronomy 2018, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoth, C.; Salus, M.S.; Girke, T.; Eulgem, T. The synthetic elicitor 3, 5-dichloroanthranilic acid induces NPR1-dependent and NPR1-independent mechanisms of disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Blee, K.; Robins, J.; Anderson, A. Oxycom under field and laboratory conditions increases resistance response in plants. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2001, 107, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.Y.; Blee, K.A.; Zhang, S.; Anderson, A.J. Oxycom treatment suppresses Pseudomonas syringae infection and activates a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in tobacco. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2002, 61, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.A.; McKenry, M.V.; Yang, K.Y.; Anderson, A.J. Induction of tolerance to root-knot nematode by oxycom. J. Nematol. 2003, 35, 306–313. [Google Scholar]
- De Borba, M.C.; Velho, A.C.; de Freitas, M.B.; Holvoet, M.; Maia-Grondard, A.; Baltenweck, R.; Magnin-Robert, M.; Randoux, B.; Hilbert, J.L.; Reignault, P.; et al. A laminarin-based formulation protects wheat against Zymoseptoria tritici via direct antifungal activity and elicitation of host defense-related genes. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Yu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Shi, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Hu, D.; Song, B. Label-free quantitative proteomic analysis of chitosan oligosaccharide-treated rice infected with southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus. Viruses 2017, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Zeier, J. Long-distance communication and signal amplification in systemic acquired resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghpanah, M.; Jelodar, N.B.; Zarrini, H.N.; Pakdin-Parizi, A.; Dehestani, A. New insights into azelaic acid-induced resistance against Alternaria Solani in tomato plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.W.; Tschaplinski, T.J.; Wang, L.; Glazebrook, J.; Greenberg, J.T. Priming in systemic plant immunity. Science 2009, 324, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiadkong, K.; Fauzia, A.N.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ueda, A. Exogenous riboflavin (vitamin B2) application enhances salinity tolerance through the activation of its biosynthesis in rice seedlings under salinity stress. Plant Sci. 2024, 339, 111929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Sun, M.; Sun, F.; Deng, S.; Dong, H. Riboflavin-induced priming for pathogen defense in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2009, 51, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, R.; Yadav, M.; Varghese, S.; Singh, B.P.; Gogoi, D.K.; Kumar, R.; Arora, D.K. Role of riboflavin in induced resistance against Fusarium wilt and charcoal rot diseases of chickpea. Plant Pathol. J. 2006, 22, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.D.; He, P.; Tian, L.; Xu, S.; Yang, B.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Bai, T.; Li, X.; Li, S.; et al. Disentangling the resistant mechanism of Fusarium wilt TR4 interactions with different cultivars and its elicitor application. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1145837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuerig, B.; Binder, A.; Boller, T.; Guyer, U.; Jiménez, S.; Rentsch, C.; Tamm, L. An aqueous extract of the dry mycelium of Penicillium chrysogenum induces resistance in several crops under controlled and field conditions. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 114, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.Z.; Cohen, Y.G. Extracts of killed Pencicillium Chrysogenum induce resistance against wilt of melon. Phytoparasitica 2001, 29, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivasa, S.; Murphy, A.M.; Hamilton, J.M.; Lindsey, K.; Carr, J.P.; Slabas, A.R. Extracellular ATP is a regulator of pathogen defence in plants. Plant J. 2009, 60, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langcake, P.; Wickins, S.G.A. Studies on the action of dichlorocyclopropanes on the host-parasite relationship in the rice blast disease. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1975, 7, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, D.W.; Langcake, P.; Ride, J.P. Phytoalexin production in rice and its enhancement by a dichlorocyclopropane fungicide. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1980, 17, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langcake, P.; Cartwright, D.; Leworthy, D.P.; Ride, J.P. The dichlorocyclopropanes-fungicides with an indirect mode of action? Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1977, 83, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Paul, D.; Kim, E.; Kloepper, J.W. Hyaluronic acid of Streptococcus sp. as a potent elicitor for induction of systemic resistance against plant diseases. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wei, C.; Shen, Z.; He, H.; Yang, X.; Shi, S.; Hu, D.; Song, B. Splicing indoles and 4,5-Dihydro-1H-pyrazoline structure gave birth to novel antiviral agents: Design, synthesis, and mechanism study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 7239–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Chen, Z.; Cai, X.J.; Song, B.A.; Bhadury, P.S.; Yang, S.; Jin, L.H.; Xue, W.; Hu, D.Y.; Zeng, S. Synthesis and antiviral activity of novel pyrazole derivatives containing oxime esters group. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9699–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zu, G.; Song, B. First discovery of novel cytosine derivatives containing a sulfonamide moiety as potential antiviral agents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6026–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiu, S.H.; Bleecker, A.B. Expansion of the receptor-like kinase/Pelle gene family and receptor-like proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, S.H.; Karlowski, W.M.; Pan, R.S.; Tzeng, Y.H.; Mayer, K.F.; Li, W.H. Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, I.; Dievart, A.; Droc, G.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Chantret, N. Evolutionary dynamics of the leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase (LRR-RLK) subfamily in Angiosperms. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1595–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diévart, A.; Gilbert, N.; Droc, G.; Attard, A.; Gourgues, M.; Guiderdoni, E.; Périn, C. Leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases are sporadically distributed in eukaryotic genomes. BMC Evolut. Biol. 2011, 11, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Gilbert, N.; Droc, G.; Attard, A.; Gourgues, M.; Guiderdoni, E.; Périn, C. The tomato RLK superfamily: Phylogeny and functional predictions about the role of the LRRII-RLK subfamily in antiviral defense. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchilla, D.; Shan, L.; He, P.; de Vries, S.; Kemmerling, B. One for all: The receptor-associated kinase BAK1. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebrand, T.W.H.; van den Burg, H.A.; Joosten, M.H.A.J. Two for all: Receptor-associated kinases SOBIR1 and BAK1. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.K.; Lee, S.W.; Kwon, S.; Choi, D.I. Development of a screening system for plant defense-inducing agent using transgenic tobacco plant with PR-1a promoter and GUS gene. Plant Pathol. J. 2005, 21, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Von, R.U.; Mueller, M.J.; Durner, J. Evaluation of natural and synthetic stimulants of plant immunity by microarray technology. New Phytol. 2005, 165, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitham, S.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P.; Choi, D.; Hehl, R.; Corr, C.; Baker, B. The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: Similarity to toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell 1994, 78, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, L.; Vernooij, B.; Gaffney, T.; Morse, A.; Ryals, J. Characterization of tobacco plants expressing a bacterial salicylate hydroxylase gene. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 29, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, R.; Harvey, C.D.; Zhong, H.; Sobczyk, A.; Van Aelst, L.; Svoboda, K. Supersensitive ras activation in dendrites and spines revealed by two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, S.A.; Guo, A.; Cao, H.; Gordon, A.S.; Klessig, D.F.; Dong, X. A mutation in Arabidopsis that leads to constitutive expression of systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1845–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, L.; Lawton, K.; Ruess, W.; Masner, P.; Specker, N.; Rella, M.G.; Meier, B.; Dincher, S.; Staub, T.; Uknes, S.; et al. A benzothiadiazole derivative induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco. Plant J. 1996, 10, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, T.P.; Friedrich, L.; Ryals, J.A. Arabidopsis signal transduction mutant defective in chemically and biologically induced disease resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 6602–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uknes, S.; Winter, A.M.; Delaney, T.; Vernooij, B.; Morse, A.; Friedrich, L.; Gordon, J.N.; Potter, S.; Ward, E.; Ryals, J. Biological induction of systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1993, 6, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernooij, B.; Friedrich, L.; Ahl Goy, P.; Staub, T.; Kessmann, H.; Ryals, J. 2, 6-dichloroisonicotinic acid-induced resistance to pathogens without the accumulation of salicylic acid. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1995, 8, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ricigliano, J.W.; Klessig, D.F. Purification and characterization of a soluble salicylic acid-binding protein from tobacco. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 9533–9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitter, N.; Kazan, K.; Way, H.M.; Broekaert, W.F.; Manners, J.M. Systemic induction of an Arabidopsis plant defensin gene promoter by tobacco mosaic virus and jasmonic acid in transgenic tobacco. Plant Sci. 1998, 136, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, K.; Weymann, K.; Friedrich, L.; Vernooij, B.; Uknes, S.; Ryals, J. Systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis requires salicylic acid but not ethylene. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1995, 8, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Kwok, S.F.; Bleecker, A.B.; Meyerowitz, E.M. Arabidopsis ethylene-response gene ETR1: Similarity of product to two-component regulators. Science 1993, 262, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomma, B.P.; Eggermont, K.; Tierens, K.F.; Broekaert, W.F. Requirement of functional ethylene-insensitive 2 gene for efficient resistance of Arabidopsis to infection by Botrytis cinerea. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staswick, P.E.; Yuen, G.Y.; Lehman, C.C. Jasmonate signaling mutants of Arabidopsis are susceptible to the soil fungus Pythium irregulare. Plant J. 1998, 15, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.M.; van Wees, S.C.; van Pelt, J.A.; Knoester, M.; Laan, R.; Gerrits, H.; Weisbeek, P.J.; van Loon, L.C. A novel signaling pathway controlling induced systemic resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Klessig, D.F. Identification of a soluble salicylic acid-binding protein that may function in signal transduction in the plant disease-resistance response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 8179–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Klessig, D.F. Identification of a soluble, high-affinity salicylic acid-binding protein in tobacco. Plant Physiol. 1997, 113, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaymaker, D.H.; Navarre, D.A.; Clark, D.; del Pozo, O.; Martin, G.B.; Klessig, D.F. The tobacco salicylic acid-binding protein 3 (SABP3) is the chloroplast carbonic anhydrase, which exhibits antioxidant activity and plays a role in the hypersensitive defense response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11640–11645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, C.M.; Jun, J.H.; Nam, H.G.; Fletcher, J.C. BLADE-ON-PETIOLE1 encodes a BTB/POZ domain protein required for leaf morphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.Q.; Yan, S.P.; Saleh, A.; Wang, W.; Ruble, J.; Oka, N.; Mohan, R.; Spoel, S.H.; Tada, Y.; Zheng, N.; et al. NPR3 and NPR4 are receptors for the immune signal salicylic acid in plants. Nature 2012, 486, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durner, J.; Klessig, D.F. Inhibition of ascorbate peroxidase by salicylic acid and 2, 6-dichloroisonicotinic acid, two inducers of plant defense responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11312–11316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; von Dahl, C.C.; Liu, P.P.; Friso, G.; van Wijk, K.J.; Klessig, D.F. The combined use of photoaffinity labeling and surface plasmon resonance-based technology identifies multiple salicylic acid-binding proteins. Plant J. 2012, 72, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Jiang, Z.; Bi, G.; Nomura, K.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Cai, B.; Zhou, J.M.; He, S.Y.; Xin, X.F. Pattern-recognition receptors are required for NLR-mediated plant immunity. Nature 2021, 592, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Macho, A.P.; Han, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zipfel, C.; Zhou, J.M.; Chai, J. Structural basis for flg22-induced activation of the Arabidopsis FLS2-BAK1 immune complex. Science 2013, 342, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Qian, X.; Qian, Z.; Tian, W.; Zhong, J. Novel, unnatural benzo-1, 2, 3-thiadiazole-7-carboxylate elicitors of taxoid biosynthesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8793–8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Qian, X.; Xu, Y. Novel benzo-1,2,3-thiadiazole-7-carboxylate derivatives as plant activators and the development of their agricultural applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Hu, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, B. Synthesis and antiviral evaluation of novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole/thiadiazole-chalcone conjugates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4298–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zeng, M.; Song, B.; Hou, C.; Hu, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Fan, H.; Bi, L.; Liu, J.; et al. Dufulin activates HrBP1 to produce antiviral responses in tobacco. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Lv, M.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Jin, L.; Hu, D.; Yang, S.; et al. Screening anti-southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus drugs based on S7-1 gene expression in rice suspension cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8049–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.J.; Lu, Y.; Narusaka, M.; Shi, C.; Yang, Y.B.; Wu, J.X.; Zeng, H.Y.; Narusaka, Y.; Yao, N. A novel pyrimidin-like plant activator stimulates plant disease resistance and promotes growth. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.M.; Zhang, Z.K.; Jia, Y.T.; Shen, Y.M.; He, H.P.; Fang, R.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Hao, X.J. 3-Acetonyl-3-hydroxyoxindole: A new inducer of systemic acquired resistance in plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2008, 6, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, T.O.; Richardson, A.; Dagdas, Y.F.; Mongrand, S.; Kamoun, S.; Raffaele, S. The plant membrane-associated REMORIN1.3 accumulates in discrete perihaustorial domains and enhances susceptibility to Phytophthora infestans. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Cao, Y.; Yang, D.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Mi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ding, C. A lncRNA fine-tunes salicylic acid biosynthesis to balance plant immunity and growth. Cell Host Microbe. 2022, 30, 1124–1138.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Roles of long non-coding RNAs in plant immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Huang, H.K.; Xia, Z.Q.; Yang, Y.Q.; Jiang, X.Y.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, D.L.; Li, X.L.; Chen, Z. Sequence data, functional annotation, and relationship analysis between mRNAs and long non-coding RNAs from tea leaves during infection by the fungal pathogen Epicoccum sorghinum. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2022, 35, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.Y.; Jiang, X.Y.; Yang, Y.Q.; Jiang, S.L.; Guo, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.L.; Chen, Z. The sequence and integrated analysis of competing endogenous RNAs originating from tea leaves infected by the pathogen of tea leaf spot, Didymella segeticola. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Schmid, M.; Wang, Y. miRNA mediated regulation and interaction between plants and pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, P.K.; Sao, R.; Mondal, S.; Vishwakarma, G.; Gupta, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Singh, S.; Sharma, D.; Das, B.K. Next generation sequencing based forward genetic approaches for identification and mapping of causal mutations in crop plants: A comprehensive review. Plants 2020, 9, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, M.A.; Lee, B.R.; Park, S.H.; Muchlas, M.; Bae, D.W.; Kim, T.H. Interactive regulation of immune-related resistance genes with salicylic acid and jasmonic acid signaling in systemic acquired resistance in the Xanthomonas-Brassica pathosystem. J. Plant Physiol. 2024, 302, 154323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, J.; Dewey, R.E.; Cutt, J.R.; Klessig, D.F. Pathogen, salicylic acid and developmental dependent expression of a β-1,3-glucanase/GUS gene fusion in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant J. 1993, 4, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Plants | Plant Species | Pathogen Names | Evaluation Index | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cucumber | No mention | C. lagenarium (Paserini) Ell. & Halst | Infected leaf area | [32] |
| Tobacco | N. tabacum cv. Xanthi-nc | Tobacco mosaic virus | Lesion size | [155] |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi-nc | Oidium lycopersici | Lesion size | [89] | |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi-nc | P. syringae pv. tabaci | CFU or disease severity | [155] | |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi-nc | Cercospora nicotianae | Infected leaf area | [155] | |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi-nc | Peronospora tabacina | Infected leaf area | [155] | |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi-nc | Erwinia carotovora | Length of infected stem | [155] | |
| N. tabacum cv. Xanthi-nc | Phytophthora parasitica | Disease severity | [155] | |
| A. thaliana | Peronospora parasitica pv. Emwa | Disease severity | [156] | |
| Rice | Oryza sativa cv. Aichiasahi | M. oryzae | Lesion number | [89] |
| O. sativa cv. Aichiasahi | X. oryzae pv. oryzae | Lesion length | [89] |
| Plant | Signal Pathways | Effector/Markers | Methods | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tobacco | Salicylic acid (SA) | Salicylic acid (free SA) | Organic solvent extract coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography | [15,33,154,157] |
| SA (total SA) | Methanol extract coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography | [33] | ||
| SA (salicylic acid-glucanase) | Methanol extract coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography | [15,157] | ||
| PR-1 | Northern blotting | [16,98,155,158] | ||
| PR-1 | Western blotting | [113,121,159] | ||
| PR-2 | Northern blotting | [16,98,155,158] | ||
| PR-3 | Northern blotting | [16] | ||
| PR-4 | Northern blotting | [16] | ||
| PR-5 | Northern blotting | [16,98,155,158] | ||
| PDF1.2 | Northern blotting | [160] | ||
| Arabidopsis | SA | PR-1 | Northern blotting | [68,81] |
| SA | PR-2 | Northern blotting | [68,81] | |
| SA | PR-5 | Northern blotting | [68,81] | |
| Tomato | SA | β-1, 3-glucanase | Western blotting | [69] |
| Transgenics or Mutants | Plants | Action Sites | Signal Pathways | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NahG transgenics | Tobacco | Salicylic acid (SA) | SA | [15,152,161] |
| 161SABP2-silenced transgenic | Tobacco | SA level | SA | [39] |
| nim mutant | A. thaliana | Downstream of SA | SA | [156] |
| npr1 mutant | A. thaliana | Downstream of SA | SA | [17] |
| etr1 mutant | A. thaliana | Ethylene (ET) | [162] | |
| ein2 mutant | A. thaliana | ET | [163] | |
| jar1 mutant | A. thaliana | Jasmonic acid | [164,165] |
| Proteins Interacting with SA | Sources | Ligand Binding | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase | N. tabacum | 14C-SA | [166] |
| Methyl esterase | N. tabacum | 3H-SA | [167] |
| Carbonic anhydrase | N. tabacum | 3H-SA | [168] |
| A protein with ankyrin repeat and BTB/POZ domain | A. thaliana | Genetics/T-DNA mutant | [117,169] |
| Cullin 3/CUL3 adapter protein | A. thaliana | Genetics/NPR1 paralog | [170] |
| Cullin 3/CUL3 adapter protein | A. thaliana | Genetics/NPR1 paralog | [170] |
| Ascorbate peroxidase | N. tabacum | 3H-SA | [171] |
| E2 subunit of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase 2 | A. thaliana | 4-azido SA, SPR | [172] |
| Glutathione S-transferase 2 | A. thaliana | 4-azido SA, SPR | [172] |
| Glutathione S-transferase 8 | A. thaliana | 4-azido SA, SPR | [172] |
| Glutathione S-transferase 10 | A. thaliana | 4-azido SA, SPR | [172] |
| Glutathione S-transferase 11 | A. thaliana | 4-azido SA, SPR | [172] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naz, M.; Zhang, D.; Liao, K.; Chen, X.; Ahmed, N.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Z. The Past, Present, and Future of Plant Activators Targeting the Salicylic Acid Signaling Pathway. Genes 2024, 15, 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091237
Naz M, Zhang D, Liao K, Chen X, Ahmed N, Wang D, Zhou J, Chen Z. The Past, Present, and Future of Plant Activators Targeting the Salicylic Acid Signaling Pathway. Genes. 2024; 15(9):1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091237
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaz, Misbah, Dongqin Zhang, Kangcen Liao, Xulong Chen, Nazeer Ahmed, Delu Wang, Jingjiang Zhou, and Zhuo Chen. 2024. "The Past, Present, and Future of Plant Activators Targeting the Salicylic Acid Signaling Pathway" Genes 15, no. 9: 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091237
APA StyleNaz, M., Zhang, D., Liao, K., Chen, X., Ahmed, N., Wang, D., Zhou, J., & Chen, Z. (2024). The Past, Present, and Future of Plant Activators Targeting the Salicylic Acid Signaling Pathway. Genes, 15(9), 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091237







