Molecular Characterization, Recombinant Expression, and Functional Analysis of Carboxypeptidase B in Litopenaeus vannamei
Highlights
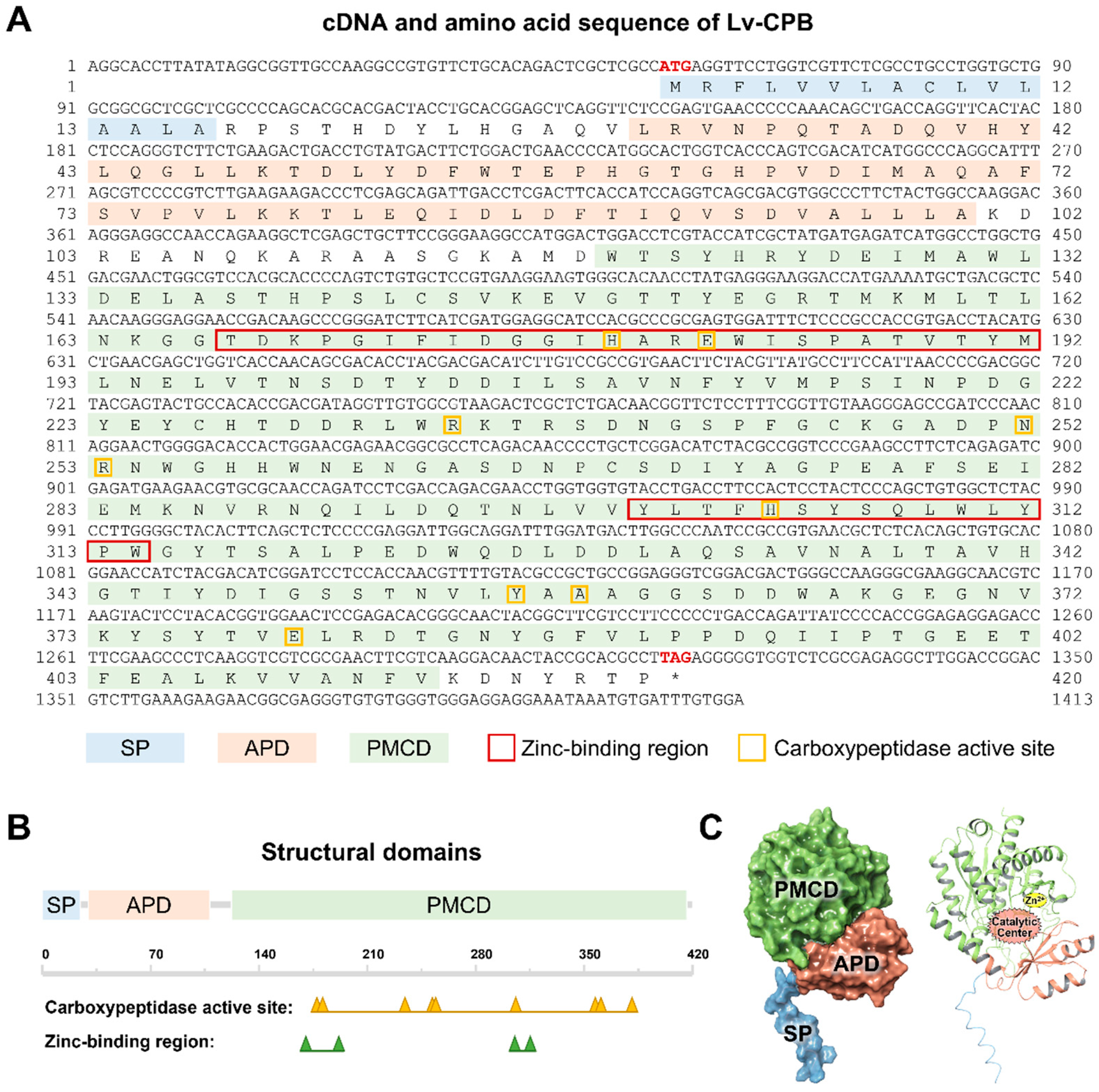
- The Lv-CPB gene in Litopenaeus vannamei was cloned and sequenced. It is 1414 bp long with a 1263 bp open reading frame (ORF) that encodes a 420-amino-acid protein. The protein is stable, hydrophilic, and contains a signal peptide, an activation peptide domain, and a functional enzymatic domain. Its 3D structure shows that the activation peptide domain shields the catalytic site, suggesting it is synthesized as an inactive precursor.
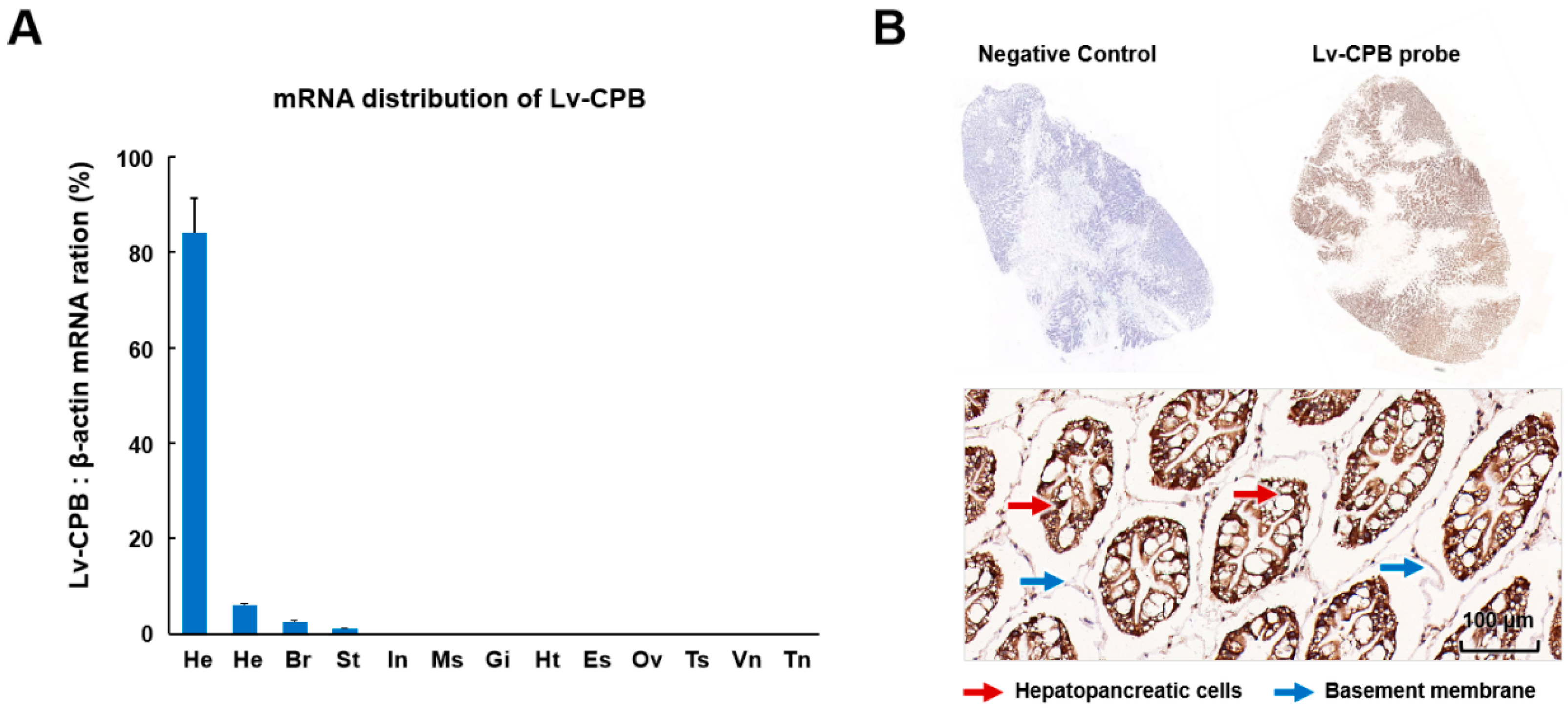
- qRT-PCR and in situ hybridization revealed that Lv-CPB is highly expressed in the hepatopancreas of Litopenaeus vannamei. It also has tissue-specific expression, with lower levels in other tissues, such as the ovary, thoracic ganglion, and abdominal ganglion.
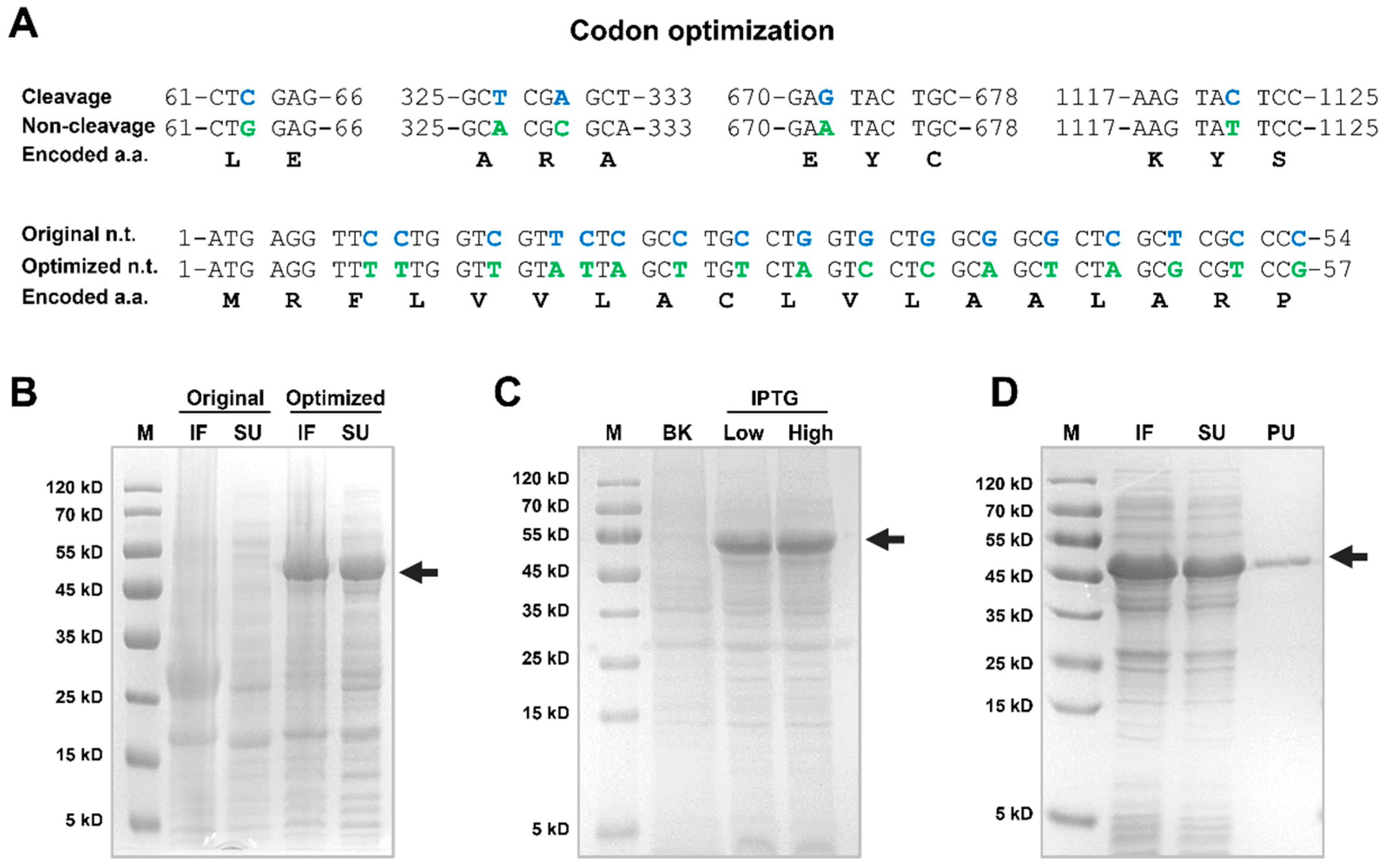
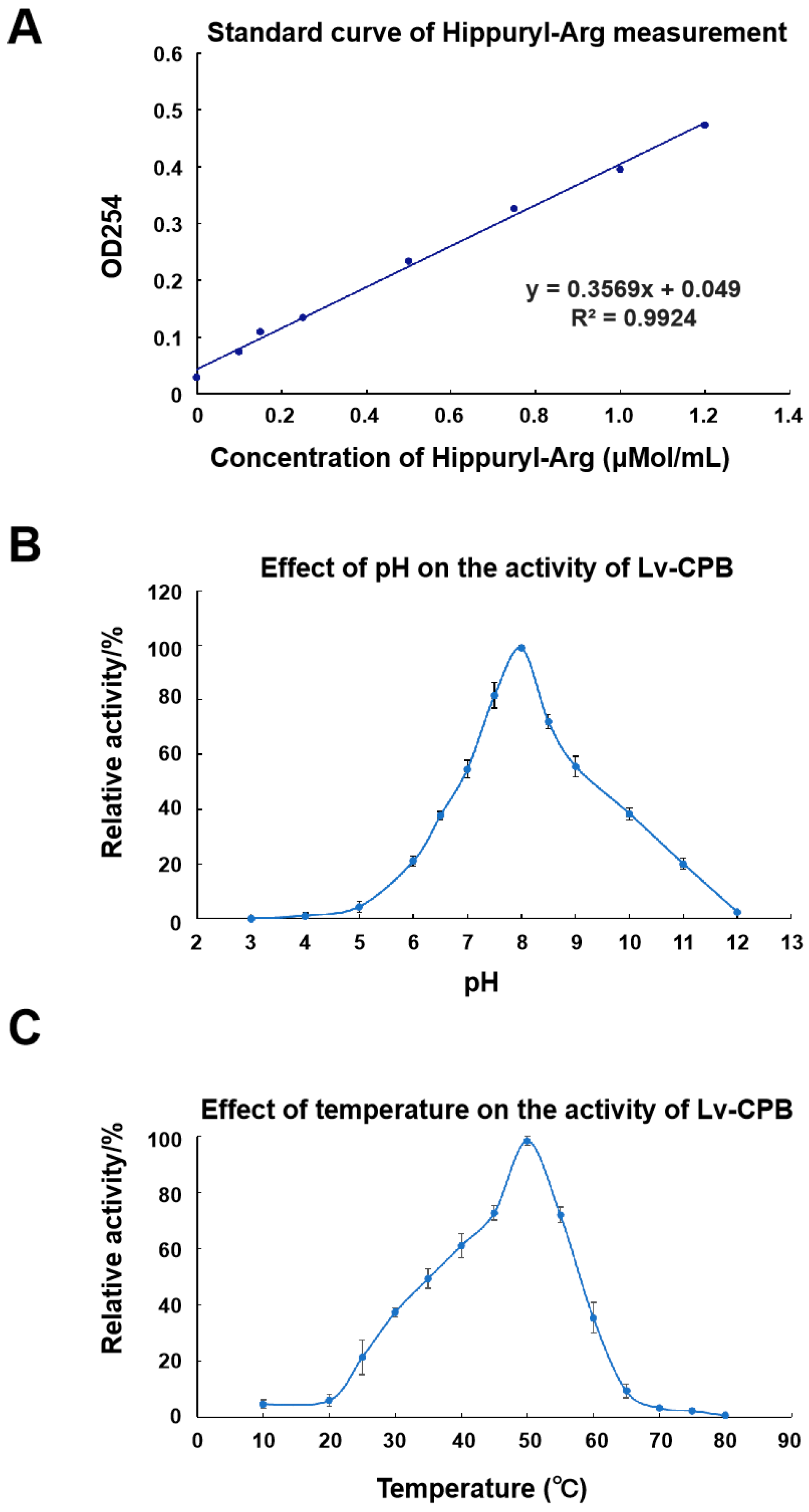
- The recombinant Lv-CPB protein was efficiently expressed in E. coli after codon optimization. The optimal pH and temperature for its activity are 8.0 and 50°C respectively. This indicates that it functions best under slightly alkaline and relatively high-temperature conditions.
- Understanding the molecular and functional characteristics of Lv-CPB provides valuable information about the digestive process in Litopenaeus vannamei. Its high expression in the hepatopancreas suggests a crucial role in protein digestion in shrimp, which is fundamental for their growth and development.
- The findings can contribute to the development of more efficient feed formulations in aquaculture. By considering the properties of Lv-CPB, such as its optimal pH and temperature, farmers can better manage the environment and feed composition to enhance the growth rate and feed conversion efficiency of Litopenaeus vannamei, ultimately improving the productivity of shrimp farming.
- The study of Lv-CPB offers important data for researching marine-sourced enzymes. It validates the use of recombinant protein production systems for studying such enzymes and deepens our understanding of proteolytic enzymes in crustaceans, which may lead to further research on other related enzymes and their functions in marine organisms.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Cloning and Sequencing of the L. vannamei CPB Gene
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Lv-CPB Gene
2.4. Tissue Distribution of Lv-CPB mRNA
2.5. In Situ Hybridization of Lv-CPB in the Hepatopancreas
2.6. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Lv-CPB
2.7. Activity Assay of Lv-CPB
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Cloning and Structural Characterization of Lv-CPB
3.2. Phylogenetic, Homology, and Structural Analysis
3.3. Expression Profiles of Lv-CPB in Different Tissues
3.4. Recombinant Expression and Optimization of Lv-CPB Protein
3.5. Enzymatic Properties of Lv-CPB
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Fernandez, D.; Boix, E.; Pallares, I.; Avilés, F.X.; Vendrell, J. Analysis of a new crystal form of procarboxypeptidase B: Further insights into the catalytic mechanism. Biopolym. Orig. Res. Biomol. 2010, 93, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Shan, Y.; Yang, C.; Sui, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Carboxypeptidase B-assisted charge-based fractional diagonal chromatography for deep screening of C-terminome. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8005–8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehfeld, J.F. Preprocholecystokinin processing in the normal human anterior pituitary. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 3019–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skidgel, R.; Davis, R.; Tan, F. Human carboxypeptidase M: Purification and characterization of a membrane-bound carboxypeptidase that cleaves peptide hormones. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 2236–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesheim, M. Fibrinolysis and the plasma carboxypeptidase. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 1998, 5, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redlitz, A.; Tan, A.K.; Eaton, D.L.; Plow, E.F. Plasma carboxypeptidases as regulators of the plasminogen system. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2534–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.J.; Hwang, I.; Cho, K.H.; Garcia, M.A.; Kim, A.J.; Wang, T.H.; Lindstrom, T.M.; Lee, A.T.; Nishimura, T.; Zhao, L. Plasma carboxypeptidase B downregulates inflammatory responses in autoimmune arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3517–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauser, E.; Gardell, S.; Craik, C.; MacDonald, R.; Rutter, W. Structural characterization of the rat carboxypeptidase A1 and B genes. Comparative analysis of the rat carboxypeptidase gene family. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 17837–17845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.F.; Zeineh, L.L.; Black, B.C.; McIvor, W.E.; Wright, T.R.; Biessmann, H. Catecholamine metabolism and in vitro induction of premature cuticle melanization in wild type and pigmentation mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. Publ. Collab. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1996, 31, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isoe, J.; Zamora, J.; Miesfeld, R.L. Molecular analysis of the Aedes aegypti carboxypeptidase gene family. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavor, E.; Choong, Y.K.; Jobichen, C.; Mok, Y.K.; Kini, R.M.; Sivaraman, J. Structure of Aedes aegypti carboxypeptidase B1-inhibitor complex uncover the disparity between mosquito and non-mosquito insect carboxypeptidase inhibition mechanism. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 2445–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, G.; Kain, W. Characterization and cDNA cloning of midgut carboxypeptidases from Trichoplusia ni. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waniek, P.J.; Araújo, C.A.; Momoli, M.M.; Azambuja, P.; Jansen, A.M.; Genta, F.A. Serine carboxypeptidases of Triatoma brasiliensis (Hemiptera, Reduviidae): Sequence characterization, expression pattern and activity localization. J. Insect Physiol. 2014, 63, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.W. Properties of the major carboxypeptidase in the larvae of the webbing clothes moth, Tineola bisselliella. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Enzymol. 1976, 429, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FishStat, F.A.O. Global Production by Production Source 1950–2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/statistics-query/en/global_production/global_production_quantity (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Zheng, X.; Duan, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J. Effects of dietary Lactobacillus plantarum on growth performance, digestive enzymes and gut morphology of Litopenaeus vannamei. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adel, M.; El-Sayed, A.-F.M.; Yeganeh, S.; Dadar, M.; Giri, S.S. Effect of potential probiotic Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, digestive enzyme activities, and disease resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Meng, Q.; Chen, T.; Ren, C.; Huang, W.; Huo, D.; Jiang, X.; Hu, C. Transcriptomic response to low pH stress in gills of the pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ruan, Y.; Chen, T.; Yu, Z.; Huo, D.; Li, X.; Wu, F.; Jiang, X.; Ren, C. First echinoderm α-amylase from a tropical sea cucumber (Holothuria leucospilota): Molecular cloning, tissue distribution, cellular localization and functional production in a heterogenous E. coli system with codon optimization. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, D.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Ren, C.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Ruan, Y.; Wen, J.; Chen, T. First echinoderm trehalase from a tropical sea cucumber (Holothuria leucospilota): Molecular cloning and mRNA expression in different tissues, embryonic and larval stages, and under a starvation challenge. Gene 2018, 665, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, L.-P.; Wong, N.-K.; Zhong, M.; Ren, C.-H.; Hu, C.-Q. Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) vitellogenesis-inhibiting hormone (VIH) is predominantly expressed in the brain and negatively regulates hepatopancreatic vitellogenin (VTG) gene expression. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folk, J.; Wolff, E.C.; Schirmer, E. The kinetics of carboxypeptidase B activity: II. Kinetic parameters of the cobalt and cadmium enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 1962, 237, 3100–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J. Evolutionary families of metallopeptidases. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 248, pp. 183–228. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, D.C.; Lewis, M.; Lipscomb, W.N. Refined crystal structure of carboxypeptidase A at 1· 54 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1983, 168, 367–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guasch, A.; Coll, M.; Avilés, F.X.; Huber, R. Three-dimensional structure of porcine pancreatic procarboxypeptidase A: A comparison of the A and B zymogens and their determinants for inhibition and activation. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 224, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Li, Q.; Peng, M.; Yang, C.; Chen, X.; Feng, P.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, D.; Zhao, Y. Biochemical indicators, cell apoptosis, and metabolomic analyses of the low-temperature stress response and cold tolerance mechanisms in Litopenaeus vannamei. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Ruiz, R.; Leyva-Carrillo, L.; Peregrino-Uriarte, A.B.; Yepiz-Plascencia, G. The combination of hypoxia and high temperature affects heat shock, anaerobic metabolism, and pentose phosphate pathway key components responses in the white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Cell Stress Chaperones 2023, 28, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Zou, J.; Fan, L. New insights into the immune regulation and tissue repair of Litopenaeus vannamei during temperature fluctuation using TMT-based proteomics. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.; Rebola, K.; Cardoso, C.; Bragatto, I.; Ribeiro, A.d.F.; Terra, W.R. Insect midgut carboxypeptidases with emphasis on S 10 hemipteran and M 14 lepidopteran carboxypeptidases. Insect Mol. Biol. 2015, 24, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavazec, C.; Bonnet, S.; Thiery, I.; Boisson, B.; Bourgouin, C. cpbAg1 encodes an active carboxypeptidase B expressed in the midgut of Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol. Biol. 2005, 14, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinkovic, D.; Marinkovic, J.; Hammon, K. Studies of human carboxypeptidase B purification and properties from human small intestine. Biochem. Med. 1979, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodrick, J.; Geokas, M.; Largman, C. Human carboxypeptidase B. II. Purification of the enzyme from pancreatic tissue and comparison with the enzymes present in pancreatic secretion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 452, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, F.; Chan, S.; Steiner, D.; Schilling, J.; Skidgel, R. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the cDNA for human membrane-bound carboxypeptidase M. Comparison with carboxypeptidases A, B, H, and N. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 13165–13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Ma, W.; Zhou, Z. The carboxypeptidase B and carbonic anhydrase genes play a reproductive regulatory role during multiple matings in Ophraella communa. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1095645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.R.; Dupart, E.; Al-Sweel, N.; Chen, A.; Cawley, N.X.; Loh, Y.P. Carboxypeptidase E promotes cancer cell survival, but inhibits migration and invasion. Cancer Lett. 2013, 341, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, M.; Forder, C.; Hennam, J.; Lee, I.; Tonge, D.; Hardern, I.; Fitton, J.; Eckersley, K.; East, S.; Shufflebotham, A. Engineered human carboxypeptidase B enzymes that hydrolyse hippuryl-L-glutamic acid: Reversed-polarity mutants. Protein Eng. 1998, 11, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Min, R.; Wu, M.C. Research progresses on the carboxypeptidase. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 31, 793–801. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Hou, Y.-M.; Tang, B.-Z. Advancement on zinc metalloproteases in insects. J. Environ. Entomol. 2021, 43, 909–921. [Google Scholar]
- Folk, J.; Schirmer, E. The porcine pancreatic carboxypeptidase A System: I. Three forms of the active enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238, 3884–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, G.; Naude, R.J.; Muramoto, K.; Yamauchi, F.; Oelofsen, W. Ostrich (Struthio camelus) carboxypeptidase A: Purification, kinetic properties and characterization of the pancreatic enzyme. Int. J. Biochem. 1994, 26, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y. Purification, Enzymatic Properties and Mechanism of Cold-adaption of Carboxypeptidase from Euphausia Superb. J. Fish. China 2020, 44, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar]
- Kishimura, H.; Hayashi, K. Isolation and characteristics of carboxypeptidase B from the pyloric ceca of the starfish Asterias amurensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2002, 133, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Lin, H.; Yang, H.; Ren, C.; He, Y.; Jiang, X.; Chen, T.; Hu, C. Molecular Characterization, Recombinant Expression, and Functional Analysis of Carboxypeptidase B in Litopenaeus vannamei. Genes 2025, 16, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010069
Li H, Lin H, Yang H, Ren C, He Y, Jiang X, Chen T, Hu C. Molecular Characterization, Recombinant Expression, and Functional Analysis of Carboxypeptidase B in Litopenaeus vannamei. Genes. 2025; 16(1):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010069
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongmei, Hai Lin, Hao Yang, Chunhua Ren, Yi He, Xiao Jiang, Ting Chen, and Chaoqun Hu. 2025. "Molecular Characterization, Recombinant Expression, and Functional Analysis of Carboxypeptidase B in Litopenaeus vannamei" Genes 16, no. 1: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010069
APA StyleLi, H., Lin, H., Yang, H., Ren, C., He, Y., Jiang, X., Chen, T., & Hu, C. (2025). Molecular Characterization, Recombinant Expression, and Functional Analysis of Carboxypeptidase B in Litopenaeus vannamei. Genes, 16(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010069




