Genomic Patterns of Homozygosity and Genetic Diversity in the Rhenish German Draught Horse
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Sample Collection and Genotype Data
2.3. Runs of Homozygosity and Fixation Index
2.4. Pedigree Based Inbreeding Coefficients
2.5. Effective Population Size
2.6. ROH Islands, Consensus ROH and Gene Onotolgy Enrichment
3. Results
3.1. ROH and Inbreeding Coefficients
3.2. Effective Population Size
3.3. Consensus ROH and ROH Islands
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aberle, K.S.; Hamann, H.; Drögemüller, C.; Distl, O. Genetic diversity in German draught horse breeds compared with a group of primitive, riding and wild horses by means of microsatellite DNA markers. Anim. Genet. 2004, 35, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharnhölz, R. Kaltblutpferde—Made in Germany Handbuch der Deutschen Kaltblutzucht; Starke Pferde-Verl.: Lemgo, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Landesamt für Umwelt, Landwirtschaft und Geologie. Das Rheinisch-Deutsche Kaltblut. Available online: https://publikationen.sachsen.de/bdb/artikel/ (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Aberle, K.S. Untersuchung der Verwandtschaftsverhältnisse, Inzucht und Genetischen Distanzen bei den Deutschen Kaltblutpferderassen. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierarztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsche Reiterliche Vereinigung e.V. (FN). Jahresbericht 2023: Anlage Zuchtstatistiken. Available online: https://www.pferd-aktuell.de/shop/broschuren-formulare-vertrage-unterrichtsmaterial/jahresberichte-fn-dokr/jahresbericht-2023-anlage-zuchtstatistiken-download.html (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Bundesanstalt für Landwirtschaft und Ernährung (BLE). Einheimische Nutztierrassen in Deutschland und Rote Liste gefährdeter Nutztierrassen 2023. Available online: https://www.genres.de/fileadmin/SITE_MASTER/content/Publikationen/TGR/Rote_Liste__Listen_einheimischer_Nutztierrassen/TGR_buch_roteliste_2023_barrierefrei.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Biedermann, G.; Clar, U.; Finke, A.; Bickel, M. Analyse der Population des Rheinisch-Deutschen Kaltbluts. Züchtungskunde 2002, 74, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Aberle, K.; Wrede, J.; Distl, O. Analyse der Populationsstruktur des Süddeutschen Kaltbluts in Bayern. Analysis of the population structure of the South German Coldblood in Bavaria. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2004, 117, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ducro, B.; Windig, J.; Hellinga, I.; Bovenhuis, H. Genetic diversity and measures to reduce inbreeding in Friesian Horses. In Proceedings of the 10th World Congress of Genetics Applied to Livestock Production, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–22 August 2014; p. 797. [Google Scholar]
- Druml, T.; Baumung, R.; Sölkner, J. Pedigree analysis in the Austrian Noriker draught horse: Genetic diversity and the impact of breeding for coat colour on population structure. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2009, 126, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, M.C.; Visscher, P.M.; Goddard, M.E. Quantification of inbreeding due to distant ancestors and its detection using dense single nucleotide polymorphism data. Genetics 2011, 189, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peripolli, E.; Munari, D.; Silva, M.; Lima, A.; Irgang, R.; Baldi, F. Runs of homozygosity: Current knowledge and applications in livestock. Anim. Genet. 2017, 48, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelsma, K.; Veerkamp, R.; Calus, M.; Bijma, P.; Windig, J. Pedigree-and marker-based methods in the estimation of genetic diversity in small groups of Holstein cattle. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2012, 129, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.T.; Pryce, J.E.; Baes, C.; Maltecca, C. Invited review: Inbreeding in the genomics era: Inbreeding, inbreeding depression, and management of genomic variability. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 6009–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druml, T.; Neuditschko, M.; Grilz-Seger, G.; Horna, M.; Ricard, A.; Mesarič, M.; Cotman, M.; Pausch, H.; Brem, G. Population networks associated with runs of homozygosity reveal new insights into the breeding history of the Haflinger horse. J. Hered. 2018, 109, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilz-Seger, G.; Neuditschko, M.; Ricard, A.; Velie, B.; Lindgren, G.; Mesarič, M.; Cotman, M.; Horna, M.; Dobretsberger, M.; Brem, G. Genome-wide homozygosity patterns and evidence for selection in a set of European and near eastern horse breeds. Genes 2019, 10, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasarda, R.; Moravčíková, N.; Kadlečík, O.; Trakovická, A.; Halo, M.; Candrák, J. Level of inbreeding in Norik of Muran horse: Pedigree vs. genomic data. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2019, 67, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancin, E.; Ablondi, M.; Mantovani, R.; Pigozzi, G.; Sabbioni, A.; Sartori, C. Genetic variability in the Italian heavy draught horse from pedigree data and genomic information. Animals 2020, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gmel, A.I.; Mikko, S.; Ricard, A.; Velie, B.D.; Gerber, V.; Hamilton, N.A.; Neuditschko, M. Using high-density SNP data to unravel the origin of the Franches-Montagnes horse breed. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2024, 56, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurink, A.; Shrestha, M.; Eriksson, S.; Bosse, M.; Bovenhuis, H.; Back, W.; Johansson, A.M.; Ducro, B.J. The genomic makeup of nine horse populations sampled in the Netherlands. Genes 2019, 10, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, J.; Morton, N.E.; Collins, A. Extended tracts of homozygosity in outbred human populations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, F.C.; Joshi, P.K.; Clark, D.W.; Ramsay, M.; Wilson, J.F. Runs of homozygosity: Windows into population history and trait architecture. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilz-Seger, G.; Druml, T.; Neuditschko, M.; Dobretsberger, M.; Horna, M.; Brem, G. High-resolution population structure and runs of homozygosity reveal the genetic architecture of complex traits in the Lipizzan horse. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curik, I.; Ferenčaković, M.; Sölkner, J. Inbreeding and runs of homozygosity: A possible solution to an old problem. Livest. Sci. 2014, 166, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablondi, M.; Dadousis, C.; Vasini, M.; Eriksson, S.; Mikko, S.; Sabbioni, A. Genetic diversity and signatures of selection in a native italian horse breed based on SNP data. Animals 2020, 10, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemberton, T.J.; Absher, D.; Feldman, M.W.; Myers, R.M.; Rosenberg, N.A.; Li, J.Z. Genomic patterns of homozygosity in worldwide human populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilz-Seger, G.; Druml, T.; Neuditschko, M.; Mesarič, M.; Cotman, M.; Brem, G. Analysis of ROH patterns in the Noriker horse breed reveals signatures of selection for coat color and body size. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, J.; Karwath, M.; Tonda, R.; Beltran, S.; Águeda, L.; Gut, M.; Gut, I.G.; Distl, O. Runs of homozygosity reveal signatures of positive selection for reproduction traits in breed and non-breed horses. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurðardóttir, H.; Ablondi, M.; Kristjansson, T.; Lindgren, G.; Eriksson, S. Genetic diversity and signatures of selection in Icelandic horses and Exmoor ponies. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 772. [Google Scholar]
- Ablondi, M.; Viklund, Å.; Lindgren, G.; Eriksson, S.; Mikko, S. Signatures of selection in the genome of Swedish warmblood horses selected for sport performance. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, W.; Thaller, G.; Kuehn, C. Selection signatures in four German warmblood horse breeds: Tracing breeding history in the modern sport horse. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, J.; Distl, O. Prevalence of Chronic Progressive Lymphedema in the Rhenish German Draught Horse. Animals 2023, 13, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, J.; Distl, O. The Estimation of Genetic Parameters for Chronic Progressive Lymphedema and Body Traits in the Rhenish German Draught Horse. Animals 2024, 14, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 2015, 4, s13742-015-0047-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyermans, R.; Gorssen, W.; Buys, N.; Janssens, S. How to study runs of homozygosity using PLINK? A guide for analyzing medium density SNP data in livestock and pet species. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencz, T.; Lambert, C.; DeRosse, P.; Burdick, K.E.; Morgan, T.V.; Kane, J.M.; Kucherlapati, R.; Malhotra, A.K. Runs of homozygosity reveal highly penetrant recessive loci in schizophrenia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19942–19947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purfield, D.C.; Berry, D.P.; McParland, S.; Bradley, D.G. Runs of homozygosity and population history in cattle. BMC Genet. 2012, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lee, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuillan, R.; Leutenegger, A.-L.; Abdel-Rahman, R.; Franklin, C.S.; Pericic, M.; Barac-Lauc, L.; Smolej-Narancic, N.; Janicijevic, B.; Polasek, O.; Tenesa, A. Runs of homozygosity in European populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuwissen, T.H.E.; Luo, Z. Computing inbreeding coefficients in large populations. Genet. Sel. Evol. 1992, 24, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boichard, D. Pedig: A Fortran package for pedigree analysis suited for large populations. In Proceedings of the 7th World Congress Genetics Applied Livestock Production, Montpellier, France, 19–23 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, J.; Cervantes, I.; Goyache, F. Improving the estimation of realized effective population sizes in farm animals. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2009, 126, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballou, J. Ancestral inbreeding only minimally affects inbreeding depression in mammalian populations. J. Hered. 1997, 88, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, S.T.; Hedrick, P.W.; Miller, P.S. Inbreeding depression in the Speke’s gazelle captive breeding program. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doekes, H.P.; Curik, I.; Nagy, I.; Farkas, J.; Kövér, G.; Windig, J.J. Revised calculation of Kalinowski’s ancestral and new inbreeding coefficients. Diversity 2020, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumung, R.; Farkas, J.; Boichard, D.; Mészáros, G.; Sölkner, J.; Curik, I. GRAIN: A computer program to calculate ancestral and partial inbreeding coefficients using a gene dropping approach. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2015, 132, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justinski, C.; Wilkens, J.; Distl, O. Genetic Diversity and Trends of Ancestral and New Inbreeding in German Sheep Breeds by Pedigree Data. Animals 2023, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, A.; Duda, J.; Distl, O. Genetic Diversity and the Impact of the Breed Proportions of US Brown Swiss in German Brown Cattle. Animals 2021, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sved, J. Linkage disequilibrium and homozygosity of chromosome segments in finite populations. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1971, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.W.; Amode, M.R.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barba, M.; Barnes, I.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Berry, A.; Bhai, J. Ensembl 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D891–D899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.D.; Ebert, D.; Muruganujan, A.; Mushayahama, T.; Albou, L.P.; Mi, H. PANTHER: Making genome-scale phylogenetics accessible to all. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Huang, X.; Ebert, D.; Mills, C.; Guo, X.; Thomas, P.D. Protocol Update for large-scale genome and gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system (v.14.0). Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 703–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.-L.; Park, C.A.; Reecy, J.M. Building a livestock genetic and genomic information knowledgebase through integrative developments of Animal QTLdb and CorrDB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D701–D710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-L.; Park, C.A.; Reecy, J.M. A combinatorial approach implementing new database structures to facilitate practical data curation management of QTL, association, correlation and heritability data on trait variants. Database 2023, 2023, baad024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, G.; Gurgul, A.; Jasielczuk, I.; Szmatoła, T.; Krupiński, J.; Bugno-Poniewierska, M. Suitability of pedigree information and genomic methods for analyzing inbreeding of Polish cold-blooded horses covered by conservation programs. Genes 2021, 12, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenčaković, M.; Hamzić, E.; Gredler, B.; Solberg, T.; Klemetsdal, G.; Curik, I.; Sölkner, J. Estimates of autozygosity derived from runs of homozygosity: Empirical evidence from selected cattle populations. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2013, 130, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druml, T.; Curik, I.; Baumung, R.; Aberle, K.; Distl, O.; Sölkner, J. Individual-based assessment of population structure and admixture in Austrian, Croatian and German draught horses. Heredity 2007, 98, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, R.; Barrowclough, G.F. Effective population size, genetic variation, and their use in population management. Viable Popul. Conserv. 1987, 87, 87–124. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, J.C.; Lemons, D.; McGinnis, W. Modulating HOX gene functions during animal body patterning. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dementieva, N.; Nikitkina, E.; Shcherbakov, Y.; Nikolaeva, O.; Mitrofanova, O.; Ryabova, A.; Atroshchenko, M.; Makhmutova, O.; Zaitsev, A. The Genetic Diversity of Stallions of Different Breeds in Russia. Genes 2023, 14, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmel, A.I.; Druml, T.; von Niederhäusern, R.; Leeb, T.; Neuditschko, M. Genome-wide association studies based on equine joint angle measurements reveal new QTL affecting the conformation of horses. Genes 2019, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, M.; Stout, T.A.; Cristarella, S.; Quartuccio, M.; Kops, G.J.; De Ruijter-Villani, M. Compromised MPS1 activity induces multipolar spindle formation in oocytes from aged mares: Establishing the horse as a natural animal model to study age-induced oocyte meiotic spindle instability. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 657366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesecke, K.; Sieme, H.; Distl, O. Infertility and candidate gene markers for fertility in stallions: A review. Vet. J. 2010, 185, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmatoła, T.; Gurgul, A.; Jasielczuk, I.; Oclon, E.; Ropka-Molik, K.; Stefaniuk-Szmukier, M.; Polak, G.; Tomczyk-Wrona, I.; Bugno-Poniewierska, M. Assessment and distribution of runs of homozygosity in horse breeds representing different utility types. Animals 2022, 12, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, A.; Almarzook, S.; Besseboua, O.; Aissanou, S.; Piórkowska, K.; Musiał, A.D.; Stefaniuk-Szmukier, M.; Ropka-Molik, K. Investigation of cerebellar abiotrophy (CA), lavender foal syndrome (LFS), and severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) variants in a cohort of three MENA region horse breeds. Genes 2021, 12, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomer, A.; Gottschalk, M.; Christmann, A.; Naccache, F.; Jung, K.; Hewicker-Trautwein, M.; Distl, O.; Metzger, J. An epistatic effect of KRT25 on SP6 is involved in curly coat in horses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, F.; Seyedabadi, H.-R.; Noshary, A.; Emamjomeh-Kashan, N.; Banabazi, M.-H. A Genome-Wide Scan for Signatures of Selection in Kurdish Horse Breed. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2022, 113, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallraf, A. Populationsgenetische Untersuchung zum Auftreten von Mauke bei den Deutschen Kaltblutpferderassen. Ph.D. Thesis, Tierarztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wallraf, A.; Hamann, H.; Ohnesorge, B.; Deegen, E.; Distl, O. Populationsgenetische Untersuchung zum Auftreten von Mauke beim Süddeutschen Kaltblut. Züchtungskunde 2004, 76, 246–261. [Google Scholar]
- De Cock, H.E.; Affolter, V.K.; Wisner, E.R.; Ferraro, G.L.; MacLachlan, N.J. Progressive swelling, hyperkeratosis, and fibrosis of distal limbs in Clydesdales, Shires, and Belgian draft horses, suggestive of primary lymphedema. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2003, 1, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Keyser, K.; Janssens, S.; Buys, N. Chronic progressive lymphoedema in draught horses. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brys, M.; Claerebout, E.; Chiers, K. Chronic Progressive Lymphedema in Belgian Draft Horses: Understanding and Managing a Challenging Disease. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, C.; Xiao, W.; Yan, N. Unravelling the role of NFE2L1 in stress responses and related diseases. Redox Biol. 2023, 65, 102819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, A.; Evseenko, D.; Brennecke, S.; Keelan, J.A.; Kalionis, B.; Murthi, P. Homeobox gene Distal-less 3 (DLX3) is a regulator of villous cytotrophoblast differentiation. Placenta 2011, 32, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mestre, A.M.; Miller, D.; Roberson, M.S.; Liford, J.; Chizmar, L.C.; McLaughlin, K.E.; Antczak, D.F. Glial Cells Missing Homologue 1 Is Induced in Differentiating Equine Chorionic Girdle Trophoblast Cells1. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 80, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-J.C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Tang, T.K. Dynamic localization and functional implications of Aurora-C kinase during male mouse meiosis. Dev. Biol. 2006, 290, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, P.D.; Knatko, E.; Moore, W.J.; Swedlow, J.R. Mitotic mechanics: The auroras come into view. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003, 15, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, K.; Katayama, H.; Stenoien, D.L.; Fujii, S.; Honda, R.; Kimura, M.; Okano, Y.; Tatsuka, M.; Suzuki, F.; Nigg, E.A. Aurora-C kinase is a novel chromosomal passenger protein that can complement Aurora-B kinase function in mitotic cells. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 2004, 59, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, S.I.; Hassold, T.J.; Hunt, P.A. Human aneuploidy: Mechanisms and new insights into an age-old problem. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi-Nejad, S.; Hoffman, G.E.; Allen, J.J.; Chu, E.; Gu, E.; Chandler, A.M.; Loredo, A.I.; Bellone, R.R.; Mezey, J.G.; Brooks, S.A. Four loci explain 83% of size variation in the horse. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junior, A.B.; Quirino, C.R.; Vega, W.H.O.; Rua, M.A.S.; David, C.M.G.; Jardim, J.G. Polymorphisms in the LASP1 gene allow selection for smaller stature in ponies. Livest. Sci. 2018, 216, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skujina, I.; Winton, C.L.; Hegarty, M.J.; McMahon, R.; Nash, D.M.; Davies Morel, M.C.; McEwan, N.R. Detecting genetic regions associated with height in the native ponies of the British Isles by using high density SNP genotyping. Genome 2018, 61, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetens, J.; Widmann, P.; Kühn, C.; Thaller, G. A genome-wide association study indicates LCORL/NCAPG as a candidate locus for withers height in German Warmblood horses. Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Pascal, G.; Monget, P. Evolution and functional divergence of NLRP genes in mammalian reproductive systems. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Z.-B.; Gold, L.; Pfeifer, K.E.; Dorward, H.; Lee, E.; Bondy, C.A.; Dean, J.; Nelson, L.M. Mater, a maternal effect gene required for early embryonic development in mice. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Liu, F.; Li, W.; Zhang, W. Knockdown of NLRP5 arrests early embryogenesis in sows. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 163, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romar, R.; De Santis, T.; Papillier, P.; Perreau, C.; Thélie, A.; Dell’Aquila, M.E.; Mermillod, P.; Dalbiès-Tran, R. Expression of maternal transcripts during bovine oocyte in vitro maturation is affected by donor age. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2011, 46, e23–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsuksili, S.; Brunner, R.M.; Goldammer, T.; Kühn, C.; Walz, C.; Chomdej, S.; Tesfaye, D.; Schellander, K.; Wimmers, K.; Schwerin, M. Bovine NALP5, NALP8, and NALP9 genes: Assignment to a QTL region and the expression in adult tissues, oocytes, and preimplantation embryos. Biol. Reprod. 2006, 74, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laseca, N.; Demyda-Peyrás, S.; Valera, M.; Ramón, M.; Escribano, B.; Perdomo-González, D.I.; Molina, A. A genome-wide association study of mare fertility in the Pura Raza Español horse. Animal 2022, 16, 100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassandri, M.; Smirnov, A.; Novelli, F.; Pitolli, C.; Agostini, M.; Malewicz, M.; Melino, G.; Raschellà, G. Zinc-finger proteins in health and disease. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, R.O.; Thomas, J.H. Adaptive evolution in zinc finger transcription factors. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
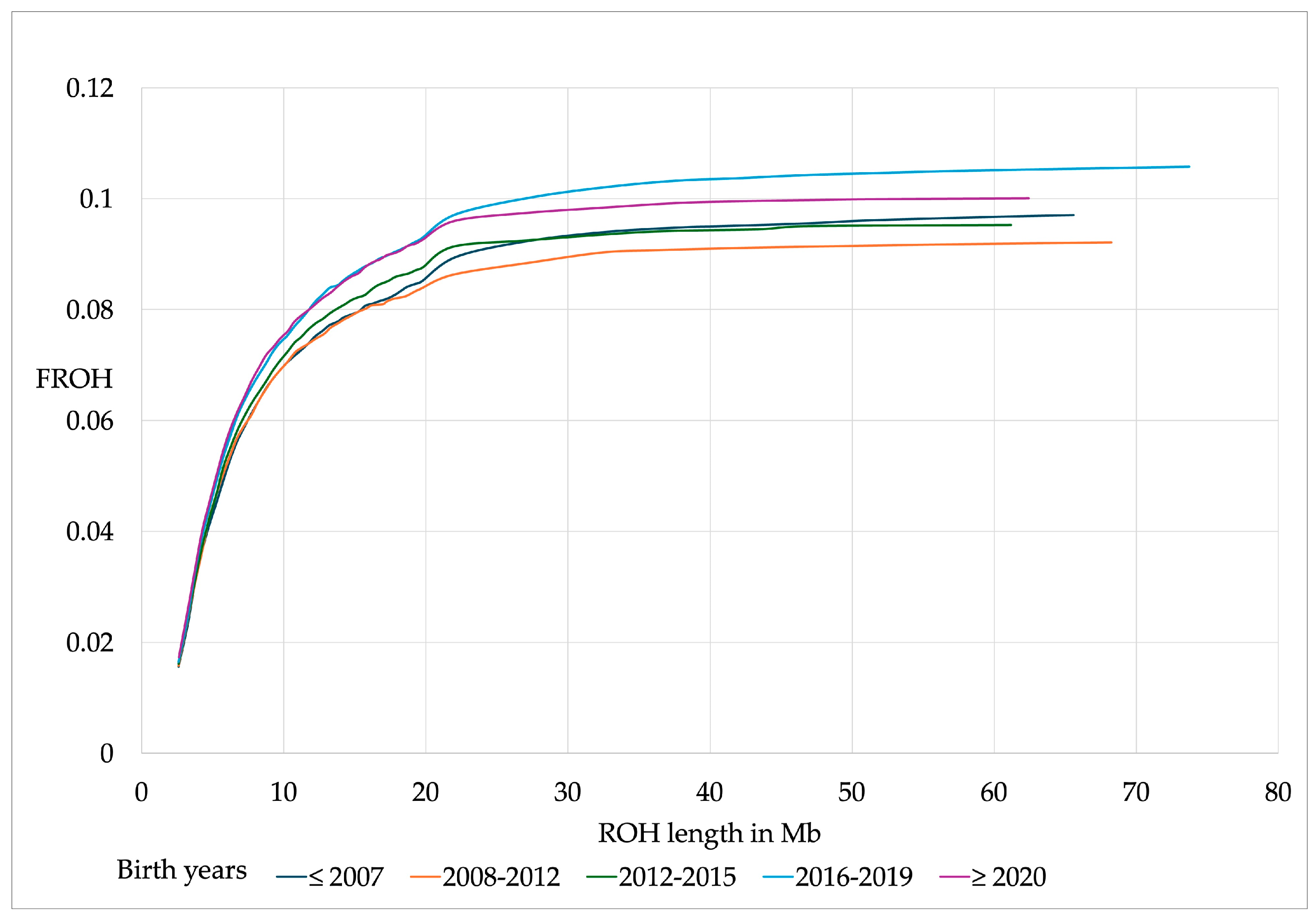
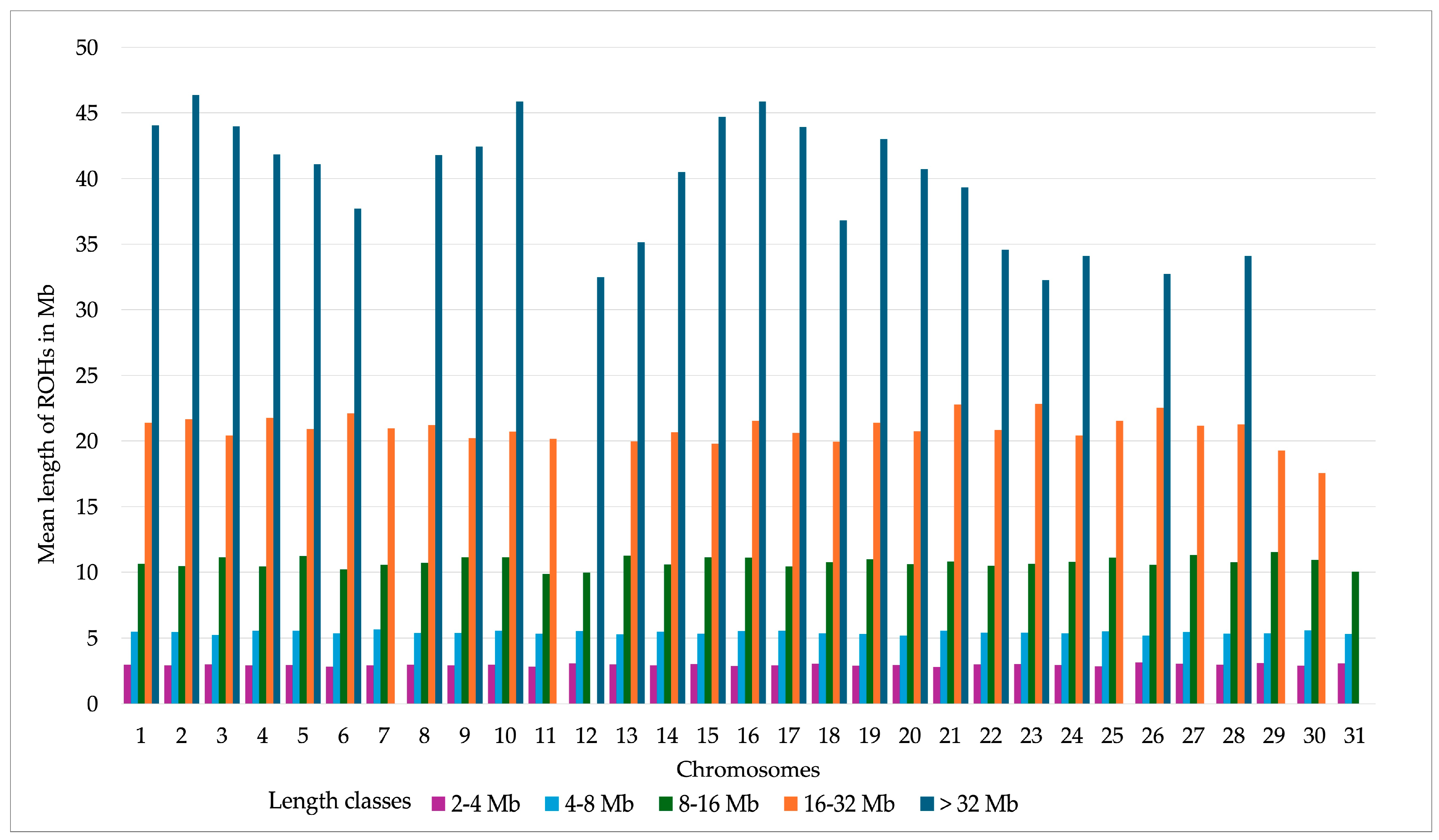
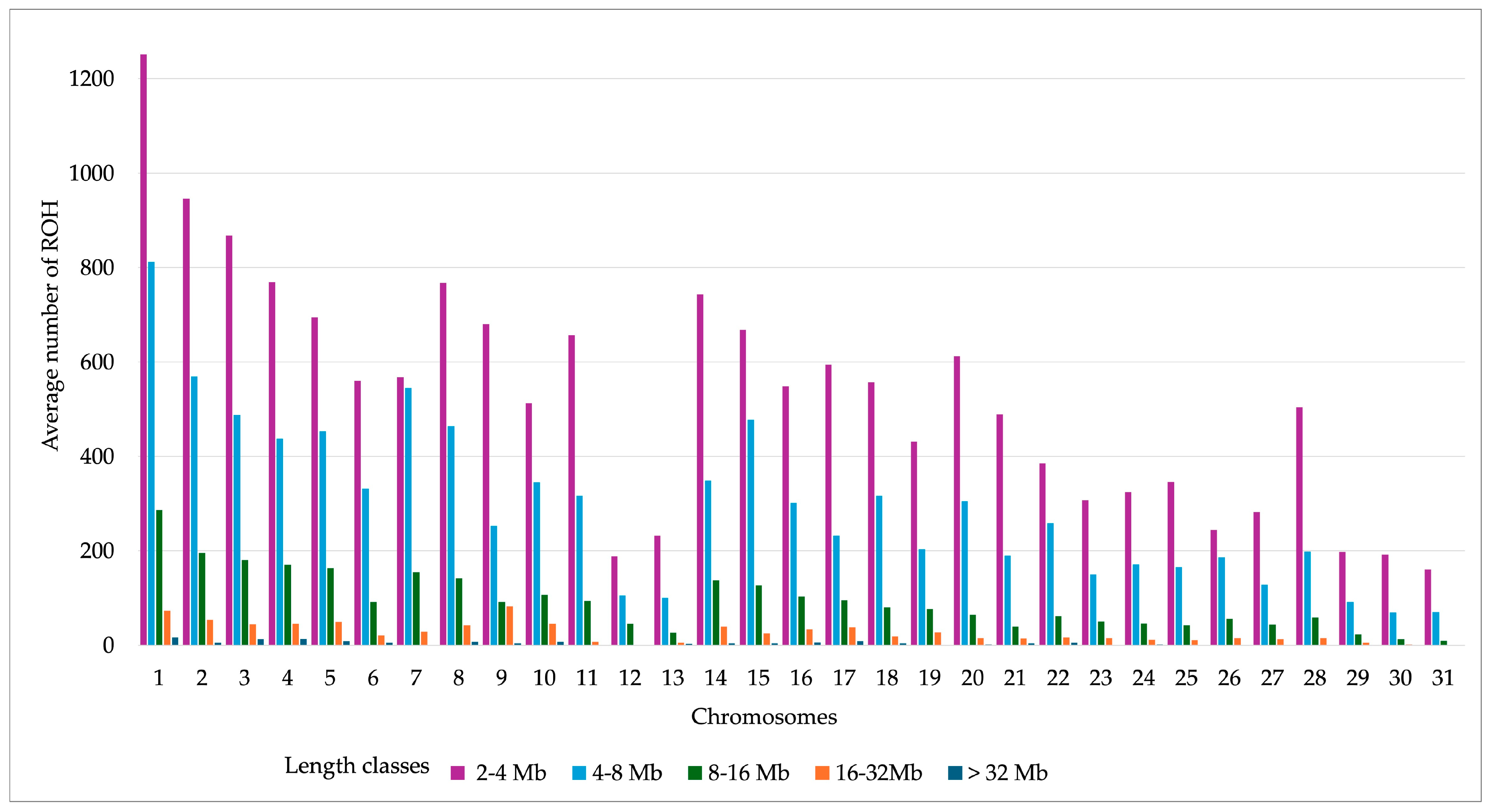

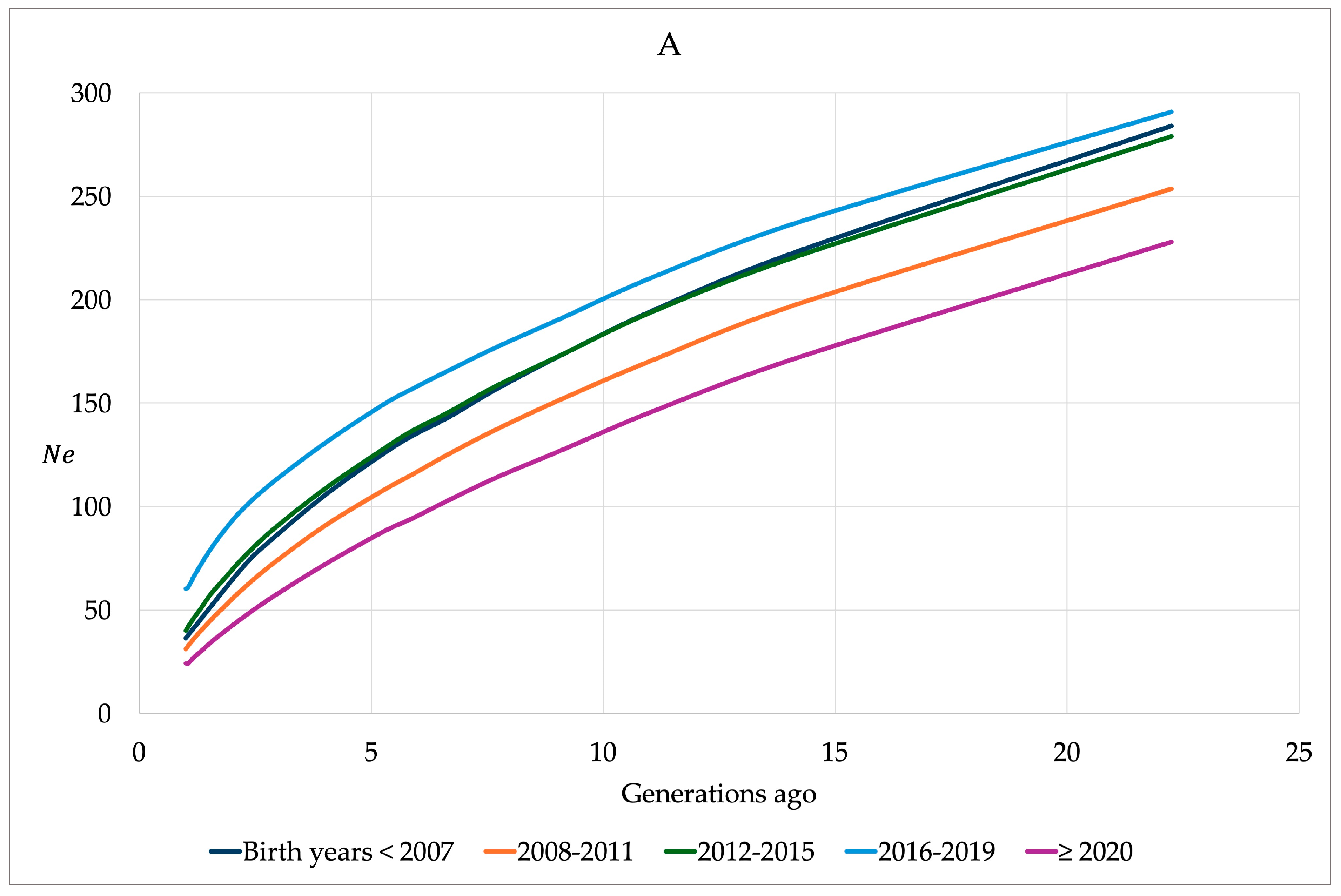

| ROH Items | Mean | SD | 95% CI | 75% CI | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average number of ROH | 43.17 | 9.459 | 32–56 | 38–48 | 0 | 164 |
| Average ROH length (Mb) | 5.087 | 1.030 | 3.954–6.804 | 4.500–5.480 | 0 | 10.858 |
| Combined ROH length (Mb) | 222.487 | 67.804 | 139.036–337.123 | 179.984–257.994 | 0 | 630.724 |
| Inbreeding Coefficients | Mean | SD | Median | Mode | 95% CI | 75% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPED | 0.016 | 0.021 | 0.038 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.058 | 0.000–0.022 |
| ΔFPED | 0.0031 | 0.0035 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.0101 | 0.0009–0.0040 |
| Fa_Bal | 0.047 | 0.036 | 0.049 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.108 | 0.004–0.074 |
| Ahc | 0.051 | 0.040 | 0.052 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.147 | 0.000–0.079 |
| Fa_Kal | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.084 | 0.000–0.015 |
| FNew | 0.012 | 0.018 | 0.012 | 0.000 | 0.001–0.051 | 0.019–0.034 |
| FIS | 0.006 | 0.069 | 0.005 | −0.028 | −0.056–0.126 | −0.013–0.025 |
| FHAT1 | 0.029 | 2.128 | −0.126 | −0.149 | −0.243–−0.846 | −0.172–−0.064 |
| FHAT2 | 0.025 | 0.635 | 0.094 | −0.149 | −0.107–0.206 | 0.041–0.134 |
| FHAT3 | 0.046 | 0.935 | −0.001 | 0.000 | −0.027–0.048 | −0.012–0.016 |
| FHOM | 0.727 | 0.019 | 0.726 | 0.722 | 0.714–0.742 | 0.721–0.732 |
| FROH | 0.099 | 0.030 | 0.095 | 0.000 | 0.062–0.150 | 0.080–0.115 |
| FROH>4 | 0.068 | 0.028 | 0.063 | 0.000 | 0.032–0.119 | 0.050–0.081 |
| FROH>6.739 | 0.041 | 0.026 | 0.036 | 0.000 | 0.011–0.088 | 0.025–0.053 |
| FROH>8 | 0.035 | 0.024 | 0.030 | 0.000 | 0.006–0.077 | 0.019–0.046 |
| FROH>16 | 0.015 | 0.019 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.048 | 0.000–0.020 |
| FROH>32 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.021 | 0.000–0.000 |
| FROH-2–4 | 0.032 | 0.008 | 0.032 | 0.000 | 0.016–0.043 | 0.027–0.036 |
| FROH-4–8 | 0.033 | 0.010 | 0.032 | 0.000 | 0.017–0.049 | 0.026–0.039 |
| FROH-8–16 | 0.020 | 0.011 | 0.019 | 0.000 | 0.004–0.042 | 0.013–0.028 |
| FROH-16–32 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.035 | 0.000–0.018 |
| ΔFPED | FIS | FROH | FROH>4 | FROH>8 | FROH>16 | FROH>32 | FROH-2–4 | FROH-4–8 | FROH-8–16 | FROH-16–32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPED | 0.981 | 0.315 | 0.591 | 0.624 | 0.654 | 0.646 | 0.565 | 0.029 | 0.144 | 0.353 | 0.469 |
| ΔFPED | 0.359 | 0.719 | 0.756 | 0.783 | 0.763 | 0.602 | 0.072 | 0.183 | 0.436 | 0.607 | |
| FIS | 0.695 | 0.593 | 0.468 | 0.382 | 0.248 | 0.526 | 0.501 | 0.384 | 0.346 | ||
| FROH | 0.962 | 0.871 | 0.759 | 0.513 | 0.386 | 0.551 | 0.634 | 0.672 | |||
| FROH>4 | 0.931 | 0.822 | 0.561 | 0.120 | 0.510 | 0.662 | 0.723 | ||||
| FROH>8 | 0.898 | 0.653 | 0.019 | 0.162 | 0.686 | 0.758 | |||||
| FROH>16 | 0.727 | −0.016 | 0.107 | 0.295 | 0.845 | ||||||
| FROH>32 | −0.029 | −0.023 | 0.216 | 0.247 | |||||||
| FROH-2–4 | 0.282 | 0.067 | 0.001 | ||||||||
| FROH-4–8 | 0.175 | 0.169 | |||||||||
| FROH-8–16 | 0.248 |
| Length Classes in Mb | Number of ROH | Percent | Mean Length | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2–4 | 16,276 | 55.85 | 2.950 | 0.489 | 2.230 | 4.000 |
| 4–8 | 9074 | 31.14 | 5.437 | 1.074 | 4.000 | 7.998 |
| 8–16 | 2862 | 9.82 | 10.740 | 2.154 | 8.002 | 15.999 |
| 16–32 | 804 | 2.76 | 21.026 | 3.984 | 16.007 | 31.996 |
| >32 | 124 | 0.43 | 41.802 | 10.350 | 32.127 | 84.829 |
| ECA | Start Position (bp) | End Position (bp) | Number of SNPs | Number of Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 90,811,943 | 93,383,936 | 75 | 16 |
| 3 | 103,264,491 | 106,074,186 | 70 | 6 |
| 5 | 48,051,957 | 53,299,414 | 274 | 48 |
| 7 | 43,493,098 | 49,256,338 | 66 | 71 |
| 9 | 34,324,099 | 38,862,009 | 63 | 13 |
| 10 | 24,466,886 | 26,947,180 | 127 | 71 |
| 11 | 23,118,264 | 29,557,882 | 175 | 99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sievers, J.; Distl, O. Genomic Patterns of Homozygosity and Genetic Diversity in the Rhenish German Draught Horse. Genes 2025, 16, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030327
Sievers J, Distl O. Genomic Patterns of Homozygosity and Genetic Diversity in the Rhenish German Draught Horse. Genes. 2025; 16(3):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030327
Chicago/Turabian StyleSievers, Johanna, and Ottmar Distl. 2025. "Genomic Patterns of Homozygosity and Genetic Diversity in the Rhenish German Draught Horse" Genes 16, no. 3: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030327
APA StyleSievers, J., & Distl, O. (2025). Genomic Patterns of Homozygosity and Genetic Diversity in the Rhenish German Draught Horse. Genes, 16(3), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030327





