Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiome Community Structures in Different Populations of Asian Elephants in China and Their Correlation with Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
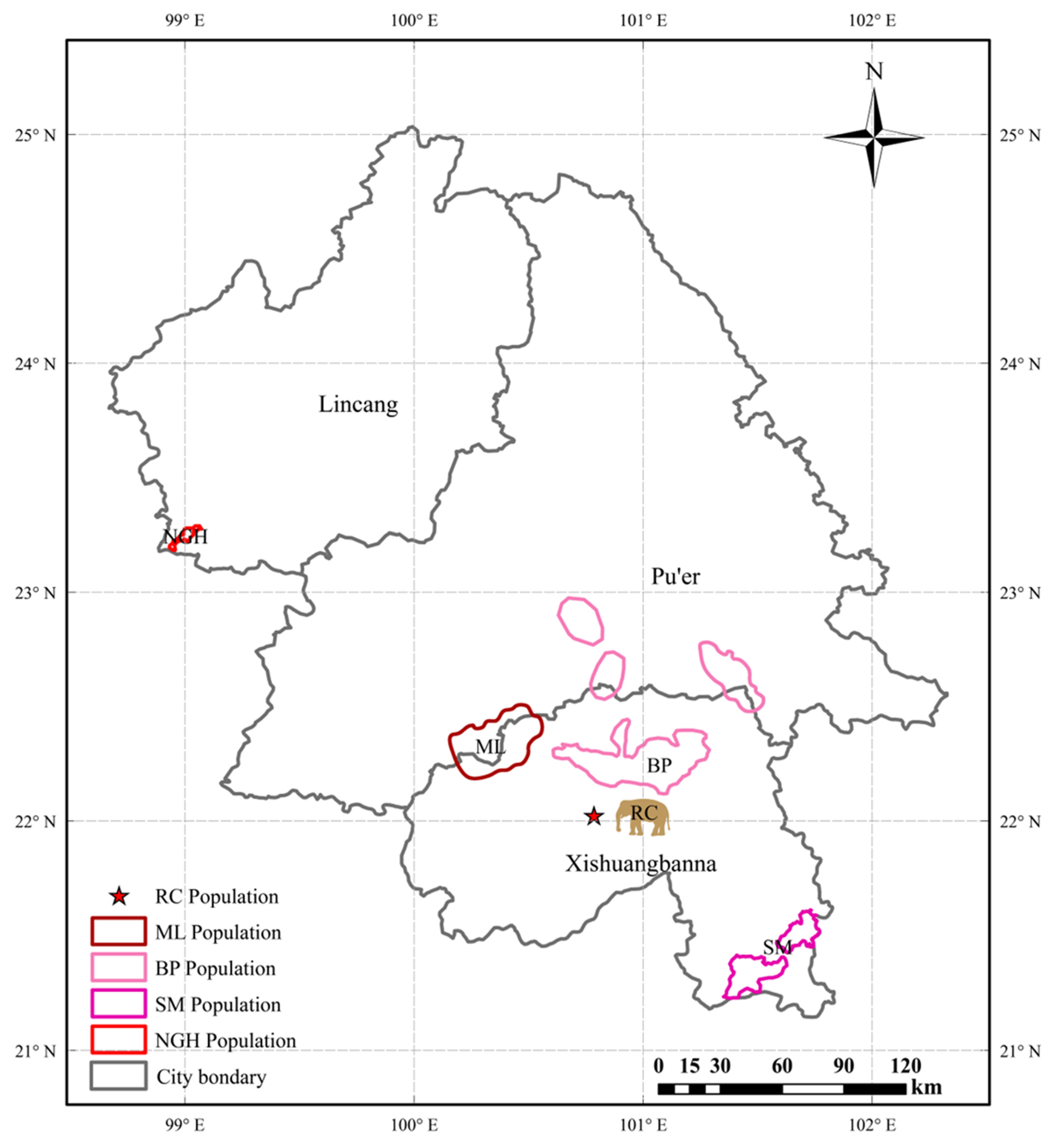
2.1. Dung Sample Collection
2.2. Microbial DNA Extraction and Metagenomic Sequencing
2.3. Metagenomic Sequence Analysis
2.4. Dietary Metabarcoding Sequencing and Analysis
2.5. Diet–Gut Microbiome Correlation Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fecal Metagenomic Sequencing and Assembly
3.2. The Gut Microbiota Profile of the Asian Elephant in China
3.3. Alpha and Beta Diversity of Gut Microbiome Across Different Populations
3.4. Interactions and Correlation Analysis of Gut Microbiome
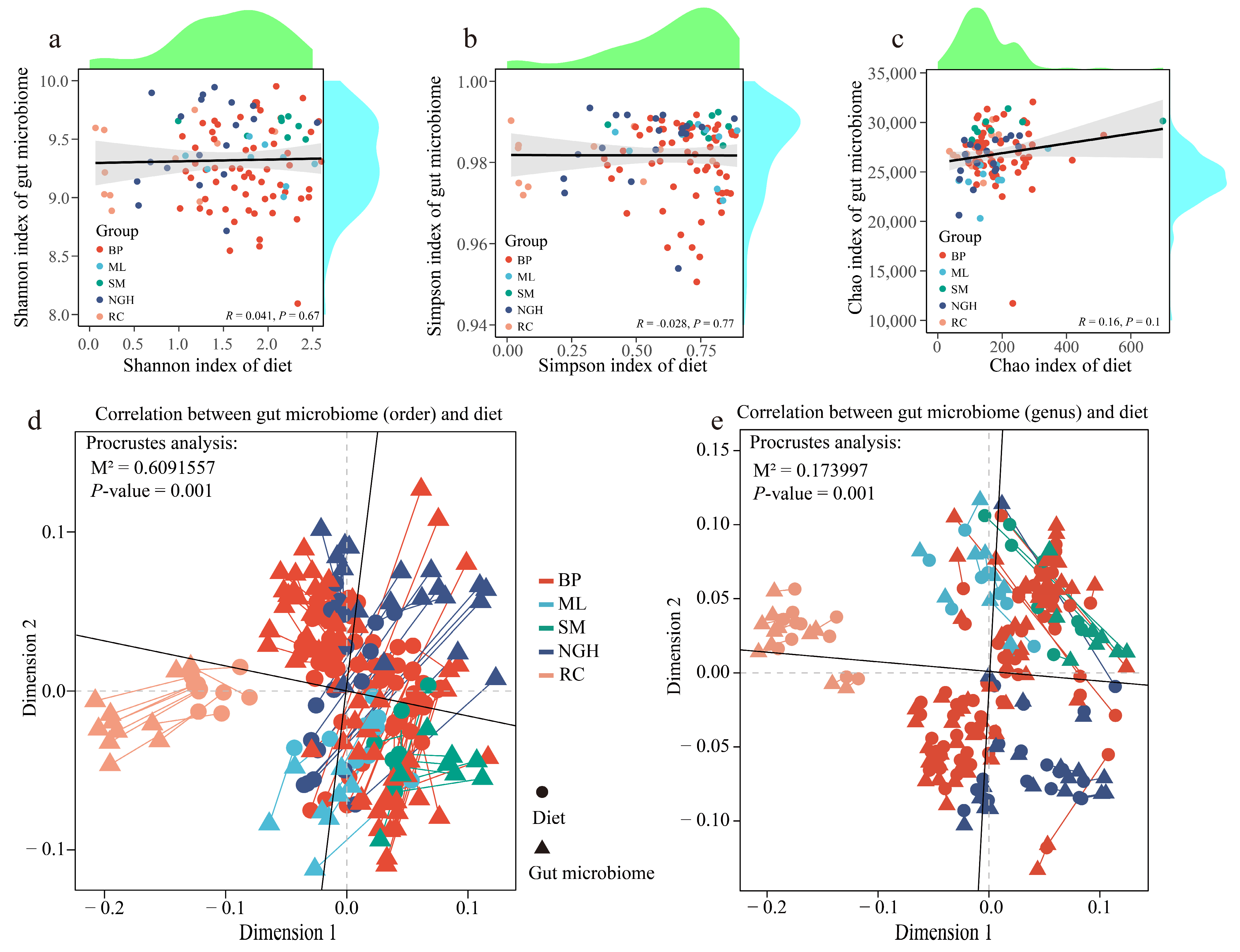
3.5. The Relationships Between Diet Diversity and Gut Microbiome Diversity
3.6. The Correlation Between Diet and the Gut Microbiome Community
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Díaz-Sacco, J.J.; Shi, K. Assessing population structure and body condition to inform conservation strategies for a small isolated Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) population in southwest China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Aliana, N.; Shi, K. Diet Analysis of Asian Elephants Using Next-Generation Sequencing. J. Resour. Ecol. 2023, 14, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, S.; Ma, L.; Su, K.; Lobora, A.; Hou, Y.; Wen, Y. Living with elephants: Analyzing commonalities and differences in human-elephant conflicts in China and Tanzania based on residents’ perspectives. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 53, e03034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, M.A.M.; Chel, H.M.; Thu, M.J.; Bawm, S.; Htun, L.L.; Win, M.M.; Oo, Z.M.; Ohsawa, N.; Lahdenpera, M.; Mohamed, W.M.A.; et al. Anthropogenic interferences lead to gut microbiome dysbiosis in Asian elephants and may alter adaptation processes to surrounding environments. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Huang, C.; Xu, T.; Onditi, K.O.; Li, X.; Jiang, X. Suitable habitats shifting toward human-dominated landscapes of Asian elephants in China. Biodivers. Conserv. 2023, 33, 685–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereswill, S.; Ilmberger, N.; Güllert, S.; Dannenberg, J.; Rabausch, U.; Torres, J.; Wemheuer, B.; Alawi, M.; Poehlein, A.; Chow, J.; et al. A Comparative Metagenome Survey of the Fecal Microbiota of a Breast- and a Plant-Fed Asian Elephant Reveals an Unexpectedly High Diversity of Glycoside Hydrolase Family Enzymes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinhom, S.; Sriwichaiin, S.; Kerdphoo, S.; Khonmee, J.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Thitaram, C. Characteristics of gut microbiota in captive Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) from infant to elderly. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 23027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, T.; Liu, H.; Liu, M.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Cong, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, B.; Pu, T.; et al. Mechanism of inulin in colic and gut microbiota of captive Asian elephant. Microbiome 2023, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Shi, W.; Wang, L.; Qu, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F.; Wei, F. PandaGUT provides new insights into bacterial diversity, function, and resistome landscapes with implications for conservation. Microbiome 2023, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.J.; Vangay, P.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Hillmann, B.M.; Ward, T.L.; Shields-Cutler, R.R.; Kim, A.D.; Shmagel, A.K.; Syed, A.N.; Personalized Microbiome Class, S.; et al. Daily Sampling Reveals Personalized Diet-Microbiome Associations in Humans. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Leng, H.; Li, J.; Li, A.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Jin, L.; Sun, K.; Feng, J. The role of host traits and geography in shaping the gut microbiome of insectivorous bats. mSphere 2024, 9, e00087-00024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, T.; Beasley, D.E.; Hedenec, P.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Lin, Q.; Li, X. Diet Diversity Is Associated with β but not α Diversity of Pika Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson, M.J.; Jeffery, I.B.; Conde, S.; Power, S.E.; O’Connor, E.M.; Cusack, S.; Harris, H.M.B.; Coakley, M.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; O’Sullivan, O.; et al. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 2012, 488, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, D.; Hu, X.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhan, J.; Bao, Z.; Guo, C.; Xu, Y. Comparison and association of winter diets and gut microbiota using trnL and 16S rRNA gene sequencing for three herbivores in Taohongling, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 53, e03041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, C.E.; Stagaman, K.; Spaan, R.S.; Combrink, H.J.; Sharpton, T.J.; Beechler, B.R.; Jolles, A.E. Diet and gut microbiome enterotype are associated at the population level in African buffalo. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.M.; Fei, H.L.; Li, Q.; Lan, L.Y.; Huang, L.N.; Fan, P.F. Eco-evolutionary dynamics of gut phageome in wild gibbons (Hoolock tianxing) with seasonal diet variations. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, T.; West, E.; Eisenhofer, R.; Stenhouse, A.; Wilson, I.; Laming, B.; Rismiller, P.; Shaw, M.; Grutzner, F. Characterising the Gut Microbiomes in Wild and Captive Short-Beaked Echidnas Reveals Diet-Associated Changes. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 687115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.-L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Guo, R.; Ni, W.; Liu, K.; Liu, Z.; Dai, J.; Xu, Y.; Abduriyim, S.; Wu, Z.; et al. Expanded catalogue of metagenome-assembled genomes reveals resistome characteristics and athletic performance-associated microbes in horse. Microbiome 2023, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Chen, L.; Ma, T.; Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Qian, X.; Xi, J.; Lu, H.; et al. EasyAmplicon: An easy-to-use, open-source, reproducible, and community-based pipeline for amplicon data analysis in microbiome research. iMeta 2023, 2, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, D.; Chen, T.; Xun, J.; Ma, C.; Luo, H.; Yang, H.; Cao, C.; Cao, X.; Cui, J.; Deng, Y.P.; et al. EasyMetagenome: A user-friendly and flexible pipeline for shotgun metagenomic analysis in microbiome research. iMeta 2025, 4, e70001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Ma, C.; Xun, J.; Luo, H.; Yang, H.; Lyu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Gai, A.; Yousuf, S.; Peng, K.; et al. MicrobiomeStatPlots: Microbiome statistics plotting gallery for meta-omics and bioinformatics. iMeta 2025, 4, e70002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lian, Z.; Xu, B.; Shen, Q.; Bao, M.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, W. Gut Microbiome Variation Along a Lifestyle Gradient Reveals Threats Faced by Asian Elephants. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2023, 21, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinhom, S.; Kunasol, C.; Sriwichaiin, S.; Kerdphoo, S.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Thitaram, C. Characteristics of gut microbiota profiles in Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) with gastrointestinal disorders. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinsawat, W.; Uthaipaisanwong, P.; Jenjaroenpun, P.; Sripiboon, S.; Wongsurawat, T.; Kusonmano, K. Microbiome variations among age classes and diets of captive Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) in Thailand using full-length 16S rRNA nanopore sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yang, X.; Dou, H.; Lyu, T.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S.; Shang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, H. Comparative Analysis of the Gut Microbiota of Mongolian Gazelle (Procapra gutturosa) Under Fragmented Habitats. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 830321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Song, P.; Jiang, F.; Cai, Z.; Gu, H.; Gao, H.; Li, B.; Liang, C.; Qin, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Large-scale metagenomic assembly provide new insights into the genetic evolution of gut microbiomes in plateau ungulates. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Yang, H.; Han, S.; Feng, L.; Wang, T.; Ge, J. Comparison of the gut microbiota composition between wild and captive sika deer (Cervus nippon hortulorum) from feces by high-throughput sequencing. AMB Express 2017, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.A.M.J.; Hesta, M.; Hollants, J.; Janssens, G.P.J.; Huys, G. Phylogenetic analysis of faecal microbiota from captive cheetahs reveals underrepresentation of Bacteroidetes and Bifidobacteriaceae. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Bao, M.; Shah, T.; Yang, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, Q.; Hou, Y.; Wang, B.; et al. Exploring the gut microbiota of healthy captive Asian elephants from various locations in Yunnan, China. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1403930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Q.; An, D.; Bao, M.; Lang, L.; Han, L.; Huang, X.; Jiang, C. Comparative and functional analyses of fecal microbiome in Asian elephants. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2022, 115, 1187–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang Jennifer, M.; Pan, C.; Cantor Rita, M.; Tang, W.H.W.; Garcia-Garcia Jose, C.; Kurtz, I.; Hazen Stanley, L.; Bergeron, N.; Krauss Ronald, M.; Lusis Aldons, J. Impact of Individual Traits, Saturated Fat, and Protein Source on the Gut Microbiome. mBio 2018, 9, 10.1128/mbio.01604-01618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ke, C.; Feng, J.; He, B.; Jiang, T. The links between dietary diversity and RNA virus diversity harbored by the great evening bat (Ia io). Microbiome 2024, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Gut Microbiome | Dietary | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | p. Value | p. Adjusted | R2 | p. Value | p. Adjusted | |
| BP vs. RC | 0.10787 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.22822 | 0.0001 | 0.00013 |
| BP vs. SM | 0.25908 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.08952 | 0.0001 | 0.00013 |
| BP vs. ML | 0.0424 | 0.0027 | 0.0030 | 0.08853 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| BP vs. NGH | 0.09079 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.09693 | 0.0001 | 0.00013 |
| RC vs. SM | 0.4531 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.63689 | 0.0001 | 0.00013 |
| RC vs. ML | 0.13787 | 0.0008 | 0.0010 | 0.60108 | 0.0001 | 0.00013 |
| RC vs. NGH | 0.18319 | 0.0001 | 0.00020 | 0.46086 | 0.0001 | 0.00013 |
| SM vs. ML | 0.46405 | 0.0002 | 0.00033 | 0.34269 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| SM vs. NGH | 0.19573 | 0.0004 | 0.00057 | 0.2844 | 0.0001 | 0.00013 |
| ML vs. NGH | 0.11923 | 0.0072 | 0.00720 | 0.26331 | 0.0001 | 0.00013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Wang, B.; Xiong, C.; Duan, W.; Luo, T.; Wang, W.; Zhou, J. Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiome Community Structures in Different Populations of Asian Elephants in China and Their Correlation with Diet. Genes 2025, 16, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050483
Guo Q, Zhang W, Xu C, Li X, Wang B, Xiong C, Duan W, Luo T, Wang W, Zhou J. Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiome Community Structures in Different Populations of Asian Elephants in China and Their Correlation with Diet. Genes. 2025; 16(5):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050483
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Qiang, Wenping Zhang, Chenyang Xu, Xu Li, Bin Wang, Chaoyong Xiong, Wenguang Duan, Tingting Luo, Weibin Wang, and Jielong Zhou. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiome Community Structures in Different Populations of Asian Elephants in China and Their Correlation with Diet" Genes 16, no. 5: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050483
APA StyleGuo, Q., Zhang, W., Xu, C., Li, X., Wang, B., Xiong, C., Duan, W., Luo, T., Wang, W., & Zhou, J. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiome Community Structures in Different Populations of Asian Elephants in China and Their Correlation with Diet. Genes, 16(5), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050483







