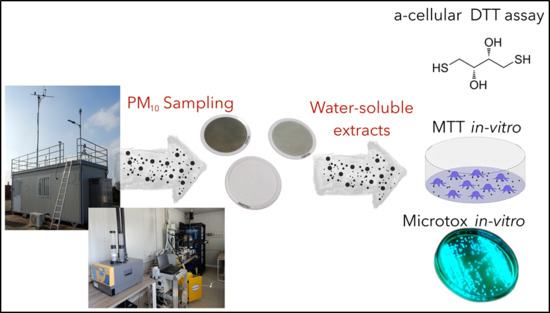
Correlation of Oxidative Potential with Ecotoxicological and Cytotoxicological Potential of PM10 at an Urban Background Site in Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
3. Results
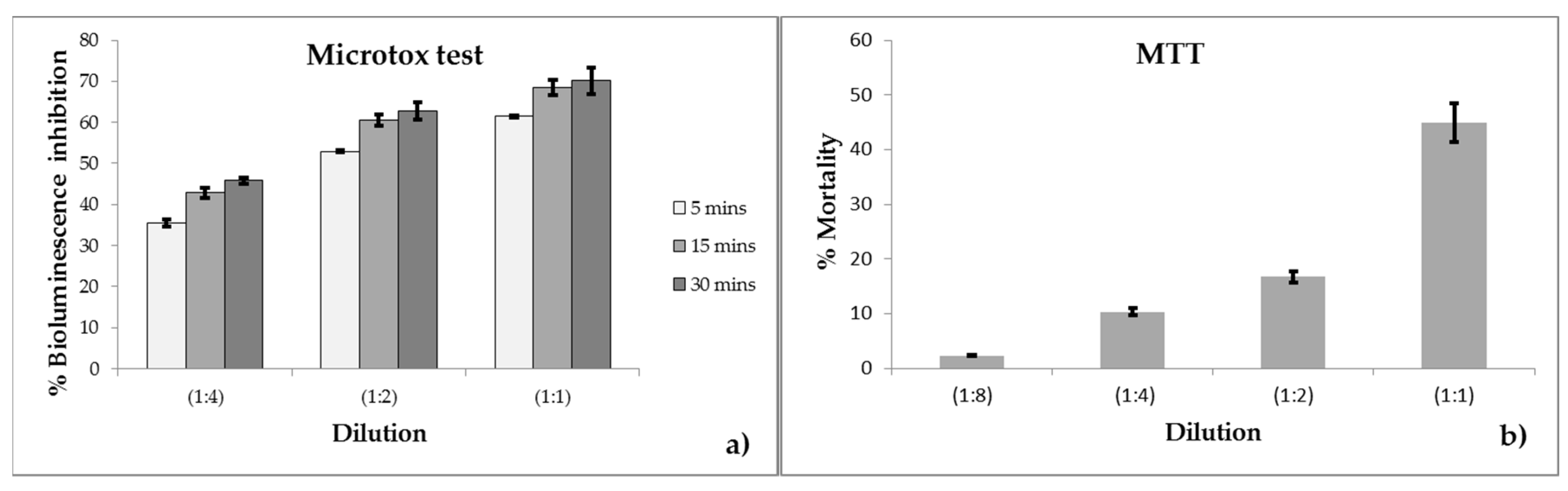
3.1. Microtox Test Results
3.2. MTT Test Results
3.3. Oxidative Potential Results
3.4. Correlation between OP and Results of Bioassays
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 50, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualtieri, M.; Longhin, E.; Mattioli, M.; Mantecca, P.; Tinaglia, V.; Mangano, E.; Proverbio, M.C.; Bestetti, G.; Camatini, M.; Battaglia, C. Gene expression profiling of A549 cells exposed to Milan PM2.5. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 209, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauderman, W.J.; Urman, R.; Avol, E.; Berhane, K.; McConnell, R.; Rappaport, E.; Chang, R.; Lurmann, F.; Gilliland, F. Association of improved air quality with lung development in children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velali, E.; Papachristou, E.; Pantazaki, A.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T.; Planou, S.; Kouras, A.; Manoli, E.; Besis, A.; Voutsa, D.; Samara, C. Redox activity and in vitro bioactivity of the water-soluble fraction of urban particulate matter in relation to particle size and chemical composition. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, M.G.; Gualtieri, M.; Ferrero, L.; Lo Porto, C.; Udisti, R.; Bolzacchini, E.; Camatini, M. Seasonal variations in chemical composition and in vitro biological effects of fine PM from Milan. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happo, M.; Markkanen, A.; Markkanen, P.; Jalava, P.; Kuuspalo, K.; Leskinen, A.; Sippula, O.; Lehtinen, K.; Jokiniemi, J.; Hirvonen, M.R. Seasonal variation in the toxicological properties of size-segregated indoor and outdoor air particulate matter. Toxicol. Vitr. 2013, 27, 1550–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, T. Toxicity Research of PM2.5 Compositions in Vitro. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sioutas, C.; Cho, A.; Schmitz, D.; Misra, C.; Sempf, J.; Wang, M.; Oberley, T.; Froines, J.; Nel, A. Ultrafine particulate pollutants induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, R.J.; Staimer, N.; Tjoa, T.; Gillen, D.L.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M. Airway inflammation and oxidative potential of air pollutant particles in a pediatric asthma panel. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, S.; Montag, M.; Dott, W. Pro-inflammatory effects and oxidative stress in lung macrophages and epithelial cells induced by ambient particulate matter. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 183, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, K.; Stone, V.; Borm, P.J.A.; Jimenez, L.A.; Gilmour, P.S.; Schins, R.P.F.; Knaapen, A.M.; Rahman, I.; Faux, S.P.; Brown, D.M. Oxidative stress and calcium signaling in the adverse effects of environmental particles (PM10). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Gonzalez-Flecha, B.; Kobzik, L. Reactive oxygen species in pulmonary inflammation by ambient particulates. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayem, A.A.; Hossain, M.K.; Cho, S.G. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in the Biological Activities of Metallic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, J.T.; Fang, T.; Verma, V.; Zeng, L.; Weber, R.J.; Tolbert, P.E.; Abrams, J.Y.; Sarnat, S.E.; Klein, M.; Mulholland, J.A.; et al. Review of acellular assays of ambient particulate matter oxidative potential: Methods and relationships with composition, sources, and health effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4003–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, J.G.; Borm, P.; Cassee, F.R.; Castranova, V.; Donaldson, K.; Ghio, A.; Harrison, R.M.; Hider, R.; Kelly, F.; Kooter, I.M.; et al. Evaluating the toxicity of airborne particulate matter and nanoparticles by measuring oxidative stress potential—A Workshop report and consensus statement. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ahmed, C.M.S.; Canchola, A.; Chen, Y.J.; Lin, Y.H. Use of Dithiothreitol Assay to Evaluate the Oxidative Potential of Atmospheric Aerosols. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Ueda, K.; Pozzer, A.; Lammel, G.; Kampf, C.J.; Fushimi, A.; Enami, S.; Arangio, A.M.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Fujitani, Y.; et al. Aerosol health effects from molecular to global scales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13545–13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øvrevik, J. Oxidative Potential Versus Biological Effects: A Review on the Relevance of Cell-Free/Abiotic Assays as Predictors of Toxicity from Airborne Particulate Matter. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Verma, V.; Bates, J.T.; Abrams, J.; Klein, M.; Strickland, M.J.; Sarnat, S.E.; Chang, H.H.; Mulholland, J.A.; Tolbert, P.E.; et al. Oxidative potential of ambient water-soluble PM2.5 in the southeastern United States: Contrasts in sources and health associations between ascorbic acid (AA) and dithiothreitol (DTT) assays. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3865–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, J.Y.; Weber, R.J.; Klein, M.; Samat, S.E.; Chang, H.H.; Strickland, M.J.; Verma, V.; Fang, T.; Bates, J.T.; Mulholland, J.A. Associations between ambient fine particulate oxidative potential and cardiorespiratory emergency department visits. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 107008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Janssen, N.A.H.; Brunekreef, B.; Cassee, F.R.; Hoek, G.; Gehring, U. Children’s respiratory health and oxidative potential of PM2.5: The PIAMA birth cohort study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 73, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, R.W.; Samoli, E.; Analitis, A.; Fuller, G.W.; Green, D.C.; Anderson, H.R.; Purdie, E.; Dunster, C.; Aitlhadj, L.; Kelly, F.J.; et al. Short-term associations between particle oxidative potential and daily mortality and hospital admissions in London. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2016, 219, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strak, M.; Janssen, N.A.; Godri, K.J.; Gosens, I.; Mudway, I.S.; Cassee, F.R.; Lebret, E.; Kelly, F.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Respiratory health effects of airborne particulate matter: The role of particle size, composition, and oxidative potential-the RAPTES project. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Heuvel, R.; Staelens, J.; Koppen, G.; Schoeters, G. Toxicity of urban PM10 and relation with tracers of biomass burning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenhof, M.; Gosens, I.; Strak, M.; Godri, K.J.; Hoek, G.; Cassee, F.R.; Mudway, I.S.; Kelly, F.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Lebret, E.; et al. In vitro toxicity of particulate matter (PM) collected at different sites in the Netherlands is associated with PM composition, size fraction and oxidative potential—The RAPTES project. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Baumgartner, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M. Oxidative potential and inflammatory impacts of source apportioned air pollution in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12920–12929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, N.A.H.; Yang, A.; Strak, M.; Steenhof, M.; Hellack, B.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Kuhlbuschc, T.; Kellyd, F.; Harrisone, R.; Brunekreefb, B.; et al. Oxidative potential of particulate matter collected at sites with different source characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, D.; De Benedetto, G.E.; Bonasoni, P.; Busetto, M.; Dinoi, A.; Merico, E.; Chirizzi, D.; Cristofanelli, P.; Donateo, A.; Grasso, F.M.; et al. Seasonal variability of PM2.5 and PM10 composition and sources in an urban background site in Southern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinoi, A.; Donateo, A.; Belosi, F.; Conte, M.; Contini, D. Comparison of atmospheric particle concentration measurements using different optical detectors: Potentiality and limits for air quality applications. Measurement 2017, 106, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinoi, A.; Cesari, D.; Marinoni, A.; Bonasoni, P.; Riccio, A.; Chianese, E.; Tirimberio, G.; Naccarato, A.; Sprovieri, F.; Andreoli, V.; et al. Inter-Comparison of Carbon Content in PM2.5 and PM10 Collected at Five Measurement Sites in Southern Italy. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Adil, S.; Ehtisham-ul-Haque, S.; Munir, B.; Yameen, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Sharc, G.A.; Tahir, M.A.; Iqbal, M. Vibrio fischeri bioluminescence inhibition assay for ecotoxicity assessment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.H.; Chao, M.R. Assessing the influence of methanol containing additive on biological characteristics of diesel exhaust emissions using microtox and mutotox assays. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 284, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, C.A.; Haritou, I.; Samaras, P.; Souboulis, A.I. Evaluation of leaching and ecotoxicological properties of sewagesludge—Fly ash mixtures. Environ. Res. 2008, 106, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voutsis, E.; Ntziachrisos, L.; Pistikopulos, P.; Samaras, Z.; Chrysikou, L.; Samara, C.; Papadimitriou, C.; Samaras, P.; Sakellaropoulos, G. An investigation on the physical, chemical and ecotoxicological charactertics of particulate matter emitted from light-duty vehicles. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2320–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roig, N.; Sierra, J.; Rovira, J.; Schumacher, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Nadal, M. In vitro tests to asses toxic effects of airborne PM10 samples. Correlation with metals and chlorinated dioxins and furans. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockert, J.C.; Blázquez-Castro, A.; Cañete, M.; Horobin, R.W.; Villanueva, A. MTT assay for cell viability: Intracellular localization of the formazan product is in lipid droplets. Acta Histochem. 2012, 114, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.A.; Oster, C.G.; Mayer, M.M.; Avery, M.L.; Audus, K.L. Characterization of the A549 cell line as a type II pulmonary epithelial cell model for drug metabolism. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 243, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.K.; Sioutas, C.; Miguel, A.H.; Kumagai, Y.; Schmitz, D.A.; Singh, M.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Froines, J.R. Redox activity of airborne particulate matter at different sites in the Los Angeles Basin. Environ. Res. 2005, 99, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirizzi, D.; Cesari, D.; Guascito, M.R.; Dinoi, A.; Giotta, L.; Donateo, A.; Contini, D. Influence of Saharan dust outbreaks and carbon content on oxidative potential of water-soluble fractions of PM2.5 and PM10. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 163, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Genga, A.; Cesari, D.; Siciliano, M.; Donateo, A.; Bove, M.C.; Guascito, M.R. Characterization and source apportionment of PM10 in an urban background site in Lecce. Atmos. Res. 2010, 95, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Cesari, D.; Donateo, A.; Chirizzi, D.; Belosi, F. Characterization of PM10 and PM2.5 and Their Metals Content in Different Typologies of Sites in South-Eastern Italy. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girotti, S.; Ferri, E.N.; Fumo, M.G.; Maiolini, E. Monitoring of environmental pollutants by bioluminescent bacteria. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 608, 2–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemmar, A.; Holme, J.A.; Rosas, I.; Schwarze, P.E.; Alfaro-Moreno, E. Recent advances in particulate matter and nanoparticle toxicology: A review of the In Vivo and In Vitro studies. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 279371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Visentin, M.; Pagnoni, A.; Sarti, E.; Pietrogrande, M.C. Urban PM2.5 oxidative potential: Importance of chemical species and comparison of two spectrophotometric cell-free assays. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Bougiatioti, A.; Stavroulas, I.; Fang, T.; Lianou, M.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Weber, R.; Nenes, A.; Mihalopoulos, N. Yearlong variability of oxidative potential of particulate matter in an urban Mediterranean environment. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, N.A.H.; Strak, M.; Yang, A.; Hellack, B.; Kelly, F.J.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Brunekreef, B.; Cassee, F.R.; Steenhof, M.; et al. Associations between three specific a-cellular measures of the oxidative potential of particulate matter and markers of acute airway and nasal inflammation in healthy volunteers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2015, 72, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, G.; Conte, E.; Perrino, C.; Canepari, S. Oxidative potential of size-segregated PM in an urban and an industrial area of Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 187, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Polidori, A.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Cassee, F.R.; Sioutas, C. Physicochemical and toxicological profiles of particulate matter in Los Angeles during the october 2007 southern California wildfires. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Verma, V.; Guo, H.; King, L.E.; Edgerton, E.S.; Weber, R.J. A semi-automated system for quantifying the oxidative potential of ambient particles in aqueous extracts using the dithiothreitol (DTT) assay: Results from the Southeastern Center for Air Pollution and Epidemiology (SCAPE). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirmohammadi, F.; Hasheminassab, S.; Wang, D.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.; Delfino, R.J.; Sioutas, C. The relative importance of tailpipe and nontailpipe emissions on the oxidative potential of ambient particles in Los Angeles, CA. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 189, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, J.T.; Weber, R.J.; Abrams, J.; Verma, V.; Fang, T.; Klein, M.; Strickland, M.J.; Sarnat, S.E.; Chang, H.H.; Mulholland, J.A.; et al. Reactive oxygen species generation linked to sources of atmospheric particulate matter and cardiorespiratory effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13605–13612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Ning, Z.; Cho, A.K.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Sioutas, C. Redox activity of urban quasi-ultrafine particles from primary and secondary sources. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 6360–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrier, J.G.; McFall, A.S.; Vu, K.K.T.; Baroi, J.; Olea, C.; Hasson, A.; Anastasio, C. A bis in the “mass-normalized” DTT response—An effect of non-linear concentration-response curves for copper and manganese. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Plewa, M.J.; Mukherjee, U.K.; Verma, V. Assessing the cytotoxicity of ambiente particulate matter (PM) using Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells and its relationship with the PM chemical composition and oxidative potential. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 179, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| PM10 (µg/m3) | Microtox (% Inhibition) | MTT (% mortality) | OPDTTV (nmol/min*m3) | OPDTTM (pmol/min*µg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (min–max) | 31.0 (11.3–53.9) | 55.4 (30.5–70.2) | 51.1 (33.7–65.8) | 0.29 (0.15–0.45) | 10.1 (6.9–15.7) |
| Median (25th–75th) | 32.1 (19.2–40.8) | 59.7 (46.2–67.7) | 52.4 (43.3–59.4) | 0.28 (0.24–0.30) | 9.0 (8.3–11.8) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lionetto, M.G.; Guascito, M.R.; Caricato, R.; Giordano, M.E.; De Bartolomeo, A.R.; Romano, M.P.; Conte, M.; Dinoi, A.; Contini, D. Correlation of Oxidative Potential with Ecotoxicological and Cytotoxicological Potential of PM10 at an Urban Background Site in Italy. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120733
Lionetto MG, Guascito MR, Caricato R, Giordano ME, De Bartolomeo AR, Romano MP, Conte M, Dinoi A, Contini D. Correlation of Oxidative Potential with Ecotoxicological and Cytotoxicological Potential of PM10 at an Urban Background Site in Italy. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(12):733. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120733
Chicago/Turabian StyleLionetto, Maria Giulia, Maria Rachele Guascito, Roberto Caricato, Maria Elena Giordano, Anna Rita De Bartolomeo, Maria Pia Romano, Marianna Conte, Adelaide Dinoi, and Daniele Contini. 2019. "Correlation of Oxidative Potential with Ecotoxicological and Cytotoxicological Potential of PM10 at an Urban Background Site in Italy" Atmosphere 10, no. 12: 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120733
APA StyleLionetto, M. G., Guascito, M. R., Caricato, R., Giordano, M. E., De Bartolomeo, A. R., Romano, M. P., Conte, M., Dinoi, A., & Contini, D. (2019). Correlation of Oxidative Potential with Ecotoxicological and Cytotoxicological Potential of PM10 at an Urban Background Site in Italy. Atmosphere, 10(12), 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120733