Summertime Aerosol over the West of Ireland Dominated by Secondary Aerosol during Long-Range Transport
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Aerosol Measurements
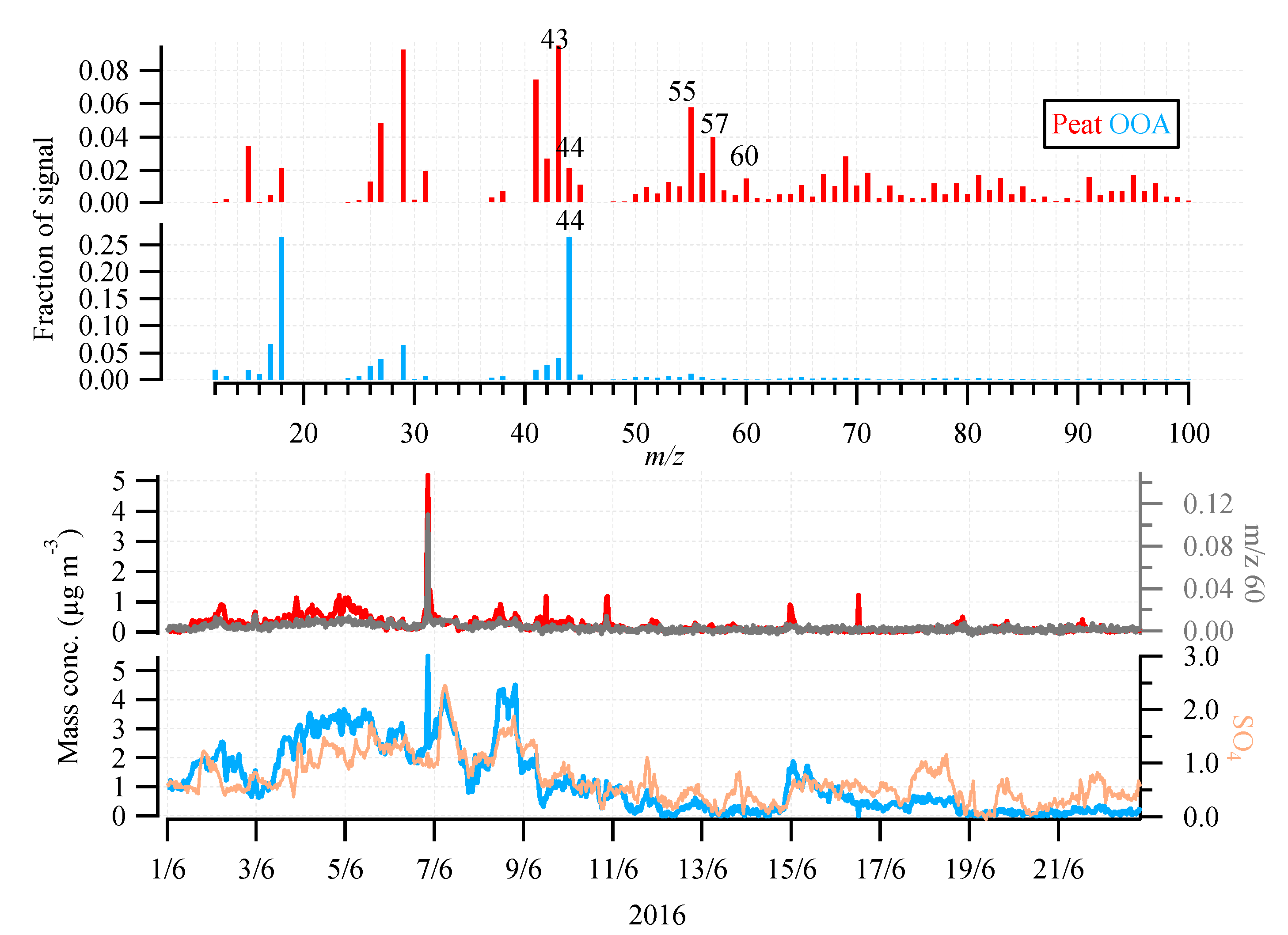
2.2. OA Source Apportionment
2.3. Back Trajectory Analysis
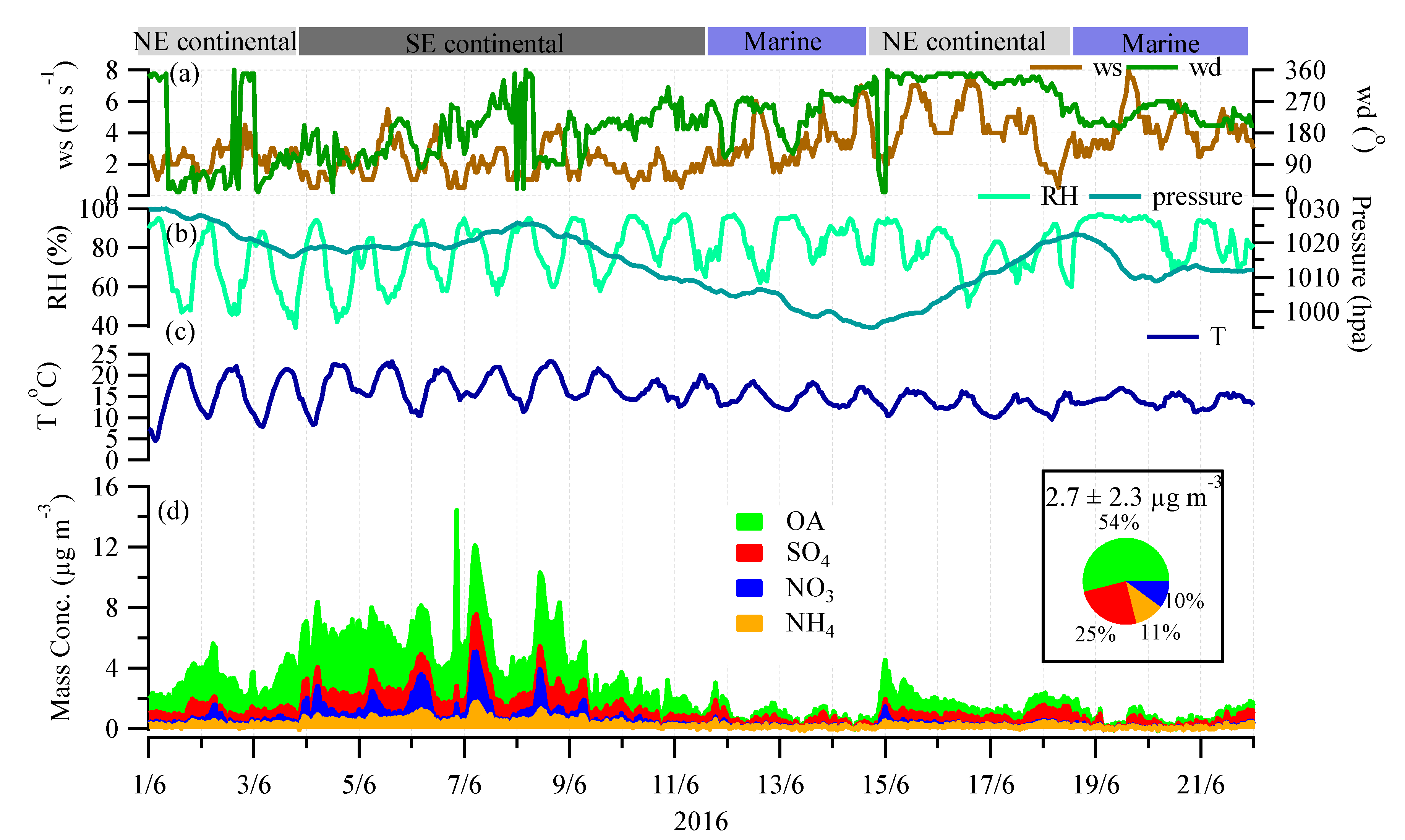
3. Results
3.1. Mass Concentration and Chemical Composition
3.2. OA Source Apportionment
3.3. Continental versus Marine Air Masses Impacts
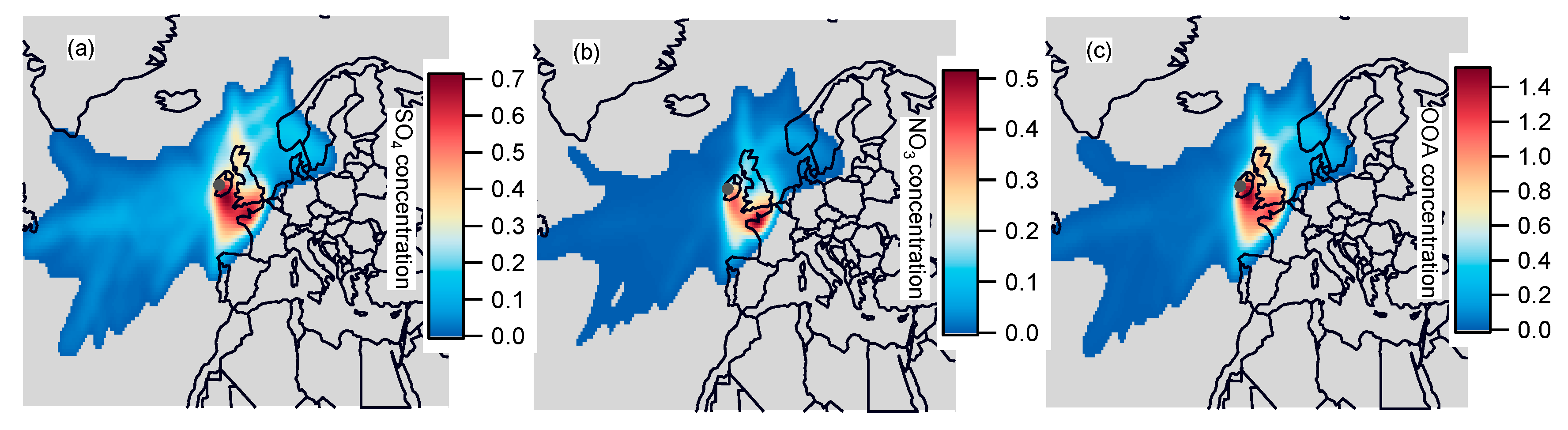
3.4. Geographic Origins of Major NR-PM1 Components
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albrecht, B.A. Aerosols, cloud microphysics, and fractional cloudiness. Science 1989, 245, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegen, I.; Lacis, A.A.; Fung, I. The influence on climate forcing of mineral aerosols from disturbed soils. Nature 1996, 380, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Tie, X.; Wu, D.; Zhou, X.; Bi, X.; Tan, H.; Li, F.; Jiang, C. Long-term trend of visibility and its characterizations in the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., III; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, L.; Goodman, P.; Sinclair, H.; Dockery, D.W. Effect of air-pollution control on death rates in Dublin, Ireland: An intervention study. Lancet 2002, 360, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A.; Ezzati, M.; Dockery, D.W. Fine-Particulate Air Pollution and Life Expectancy in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCarlo, P.F.; Kimmel, J.R.; Trimborn, A.; Northway, M.J.; Jayne, J.T.; Aiken, A.C.; Gonin, M.; Fuhrer, K.; Horvath, T.; Docherty, K.S.; et al. Field-Deployable, High-Resolution, Time-of-Flight Aerosol Mass Spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8281–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewnick, F.; Hings, S.S.; DeCarlo, P.; Jayne, J.T.; Gonin, M.; Fuhrer, K.; Weimer, S.; Jimenez, J.L.; Demerjian, K.L.; Borrmann, S.; et al. A new time-of-flight aerosol mass spectrometer (TOF-AMS)—Instrument description and first field deployment. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canagaratna, M.R.; Jayne, J.T.; Jimenez, J.L.; Allan, J.D.; Alfarra, M.R.; Zhang, Q.; Onasch, T.B.; Drewnick, F.; Coe, H.; Middlebrook, A.; et al. Chemical and microphysical characterization of ambient aerosols with the Aerodyne aerosol mass spectrometer. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2007, 26, 185–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, N.L.; Herndon, S.C.; Trimborn, A.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Croteau, P.L.; Onasch, T.B.; Sueper, D.; Worsnop, D.R.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.L.; et al. An Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor (ACSM) for routine monitoring of the composition and mass concentrations of ambient aerosol. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, R.; Cubison, M.J.; Slowik, J.G.; Bukowiecki, N.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Baltensperger, U.; Schneider, J.; Kimmel, J.R.; Gonin, M.; Rohner, U.; et al. The ToF-ACSM: A portable aerosol chemical speciation monitor with TOFMS detection. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3225–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Yang, T.; Li, J.; Pan, X.; Chen, P.; Jayne, J.T. Characterization of summer organic and inorganic aerosols in Beijing, China with an Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 51, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.E.; Favez, O.; Sciare, J.; Crenn, V.; Sarda-Estève, R.; Bonnaire, N.; Močnik, G.; Dupont, J.C.; Haeffelin, M.; Leoz-Garziandia, E. Two years of near real-time chemical composition of submicron aerosols in the region of Paris using an Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor (ACSM) and a multi-wavelength Aethalometer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2985–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Tang, L.L.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.X.; Sun, Y.L.; Liu, D.; Qin, W.; Canonaco, F.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Zhang, H.L.; et al. Insights into characteristics, sources, and evolution of submicron aerosols during harvest seasons in the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1331–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, M.; Huang, R.J.; Wolf, R.; Slowik, J.G.; Wang, Q.; Canonaco, F.; Li, G.; Bozzetti, C.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Huang, Y.; et al. New insights into PM2.5 chemical composition and sources in two major cities in China during extreme haze events using aerosol mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3207–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z.; Chan, C.K. Real-time chemical characterization of atmospheric particulate matter in China: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 158, 270–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguillón, M.C.; Ripoll, A.; Pérez, N.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Canonaco, F.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Chemical characterization of submicron regional background aerosols in the western Mediterranean using an Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6379–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovadnevaite, J.; O’Dowd, C.; Dall’Osto, M.; Ceburnis, D.; Worsnop, D.R.; Berresheim, H. Detecting high contributions of primary organic matter to marine aerosol: A case study. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ovadnevaite, J.; Ceburnis, D.; Leinert, S.; Dall’Osto, M.; Canagaratna, M.; O’Doherty, S.; Berresheim, H.; O’Dowd, C. Submicron NE Atlantic marine aerosol chemical composition and abundance: Seasonal trends and air mass categorization. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 11850–11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crenn, V.; Sciare, J.; Croteau, P.L.; Verlhac, S.; Fröhlich, R.; Belis, C.A.; Aas, W.; Äijälä, M.; Alastuey, A.; Artiñano, B.; et al. ACTRIS ACSM intercomparison—Part 1: Reproducibility of concentration and fragment results from 13 individual Quadrupole Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitors (Q-ACSM) and consistency with co-located instruments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 5063–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, R.; Crenn, V.; Setyan, A.; Belis, C.A.; Canonaco, F.; Favez, O.; Riffault, V.; Slowik, J.G.; Aas, W.; Aijälä, M.; et al. ACTRIS ACSM intercomparison—Part 2: Intercomparison of ME-2 organic source apportionment results from 15 individual, co-located aerosol mass spectrometers. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 2555–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; Canonaco, F.; Lanz, V.A.; Äijälä, M.; Allan, J.D.; Carbone, S.; Capes, G.; Ceburnis, D.; Dall’Osto, M.; Day, D.A.; et al. Organic aerosol components derived from 25 AMS data sets across Europe using a consistent ME-2 based source apportionment approach. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6159–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crippa, M.; Decarlo, P.F.; Slowik, J.G.; Mohr, C.; Heringa, M.F.; Chirico, R.; Poulain, L.; Freutel, F.; Sciare, J.; Cozic, J.; et al. Wintertime aerosol chemical composition and source apportionment of the organic fraction in the metropolitan area of Paris. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 961–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paatero, P. Least squares formulation of robust non-negative factor analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1997, 37, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonaco, F.; Crippa, M.; Slowik, J.G.; Baltensperger, U.; Prévôt, A.S.H. SoFi, an IGOR-based interface for the efficient use of the generalized multilinear engine (ME-2) for the source apportionment: ME-2 application to aerosol mass spectrometer data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3649–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canonaco, F.; Slowik, J.G.; Baltensperger, U.; Prévôt, A.S.H. Seasonal differences in oxygenated organic aerosol composition: Implications for emissions sources and factor analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6993–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Huang, R.-J.; Ceburnis, D.; Buckley, P.; Preissler, J.; Wenger, J.; Rinaldi, M.; Facchini, M.C.; O’Dowd, C.; Ovadnevaite, J. Extreme air pollution from residential solid fuel burning. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Donahue, N.M.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Zhang, Q.; Kroll, J.H.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Allan, J.D.; Coe, H.; Ng, N.L.; et al. Evolution of Organic Aerosols in the Atmosphere. Science 2009, 326, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canagaratna, M.R.; Jayne, J.T.; Ghertner, D.A.; Herndon, S.; Shi, Q.; Jimenez, J.L.; Silva, P.J.; Williams, P.; Lanni, T.; Drewnick, F.; et al. Chase Studies of Particulate Emissions from in-use New York City Vehicles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 555–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Ulbrich, I.M.; Ng, N.L.; Worsnop, D.R.; Sun, Y. Understanding atmospheric organic aerosols via factor analysis of aerosol mass spectrometry: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 3045–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Ceburnis, D.; Hellebust, S.; Buckley, P.; Wenger, J.; Canonaco, F.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Huang, R.-J.; O’Dowd, C.; Ovadnevaite, J. Characterization of primary organic aerosol from domestic wood, peat, and coal burning in Ireland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10624–10632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulbrich, I.M.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Zhang, Q.; Worsnop, D.R.; Jimenez, J.L. Interpretation of organic components from Positive Matrix Factorization of aerosol mass spectrometric data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2891–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paatero, P. The multilinear engine-a table-driven, least squares program for solving multilinear problems, including the n-way parallel factor analysis model. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1999, 8, 854–888. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, Z.L.; Monks, P.S.; Manning, A.J. Review: Untangling the influence of air-mass history in interpreting observed atmospheric composition. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104–105, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.E.; Favez, O.; Albinet, A.; Canonaco, F. A user-friendly tool for comprehensive evaluation of the geographical origins of atmospheric pollution: Wind and trajectory analyses. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 88, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, D.E.; Allan, J.D.; Williams, P.I.; Green, D.C.; Flynn, M.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Yin, J.; Gallagher, M.W.; Coe, H. Investigating the annual behaviour of submicron secondary inorganic and organic aerosols in London. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6351–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfarra, M.R.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Szidat, S.; Sandradewi, J.; Weimer, S.; Lanz, V.A.; Schreiber, D.; Mohr, M.; Baltensperger, U. Identification of the mass spectral signature of organic aerosols from wood burning emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5770–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; El Haddad, I.; Slowik, J.G.; Decarlo, P.F.; Mohr, C.; Heringa, M.F.; Chirico, R.; Marchand, N.; Sciare, J.; Baltensperger, U.; et al. Identification of marine and continental aerosol sources in Paris using high resolution aerosol mass spectrometry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 1950–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Continental (SE) | Continental (NE) | Marine | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean | Median | SD | % | N | Mean | Median | SD | % | N | Mean | Median | SD | % | |
| OA | 184 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 55 | 159 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 55 | 156 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 41 |
| SO4 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 22 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 27 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 42 | |||
| NO3 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 12 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 7 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 4 | |||
| NH4 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 11 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 11 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 13 | |||
| Total | 4.9 | 2.3 | 0.8 | ||||||||||||
| OA factors | |||||||||||||||
| Peat | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 14 | 0.1 | 0.08 | 0.2 | 14 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 28 | |||
| OOA | 2.2 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 86 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 86 | 0.20 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 72 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.; Ceburnis, D.; Huang, R.-J.; Canonaco, F.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; O'Dowd, C.; Ovadnevaite, J. Summertime Aerosol over the West of Ireland Dominated by Secondary Aerosol during Long-Range Transport. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020059
Lin C, Ceburnis D, Huang R-J, Canonaco F, Prévôt ASH, O'Dowd C, Ovadnevaite J. Summertime Aerosol over the West of Ireland Dominated by Secondary Aerosol during Long-Range Transport. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(2):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020059
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chunshui, Darius Ceburnis, Ru-Jin Huang, Francesco Canonaco, André Stephan Henry Prévôt, Colin O'Dowd, and Jurgita Ovadnevaite. 2019. "Summertime Aerosol over the West of Ireland Dominated by Secondary Aerosol during Long-Range Transport" Atmosphere 10, no. 2: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020059
APA StyleLin, C., Ceburnis, D., Huang, R.-J., Canonaco, F., Prévôt, A. S. H., O'Dowd, C., & Ovadnevaite, J. (2019). Summertime Aerosol over the West of Ireland Dominated by Secondary Aerosol during Long-Range Transport. Atmosphere, 10(2), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10020059






