Raindrop Size Distribution Characteristics for Tropical Cyclones and Meiyu-Baiu Fronts Impacting Tokyo, Japan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation and Datasets
2.2. Classification of Rainfall Types
2.3. Other Data
3. Results
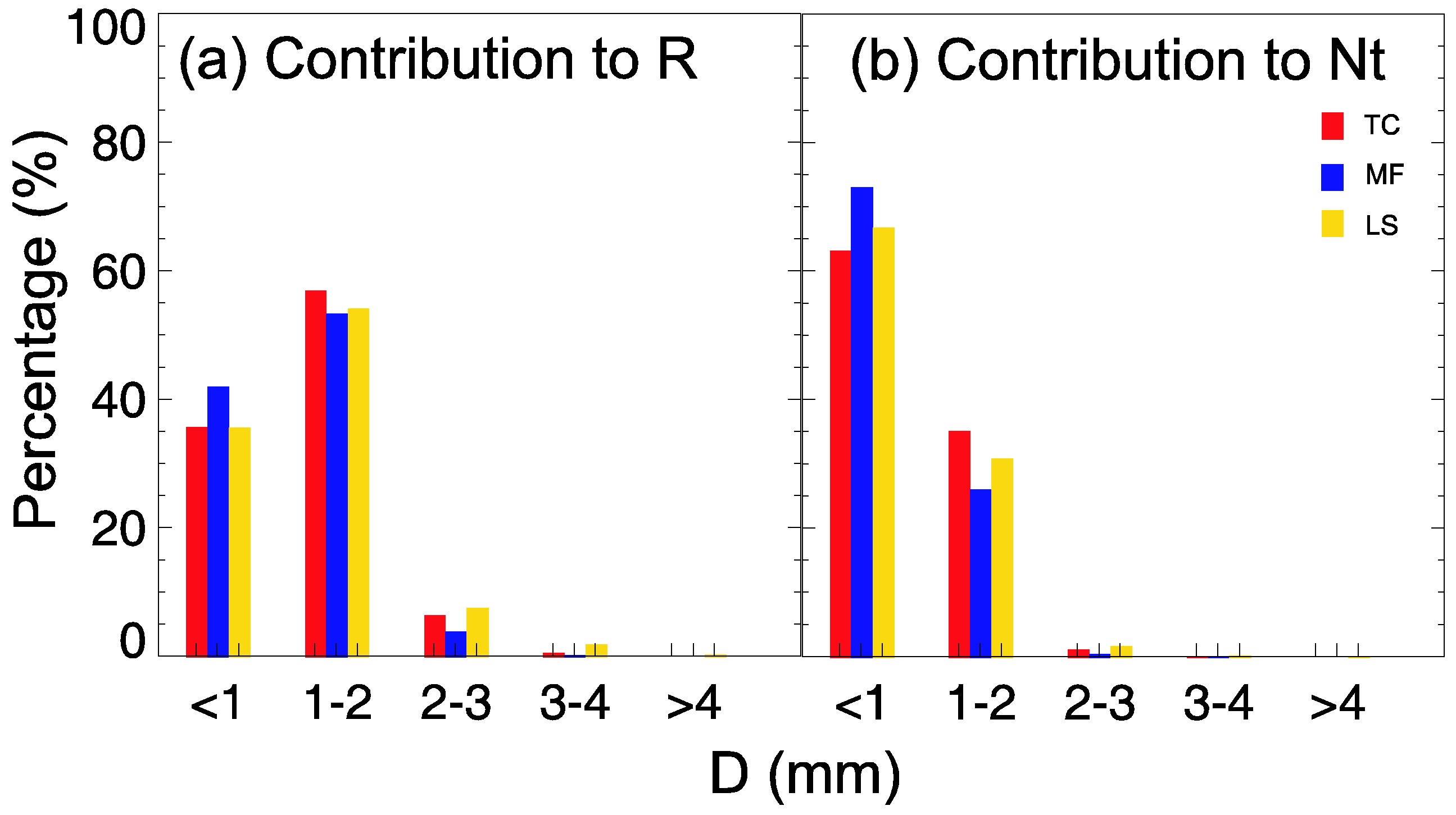
3.1. Overview of the Three Rain Types
3.2. Vertical Profiles of Mean Rain Parameters
3.3. Distributions of Dm and Nw
3.4. Composite Raindrop Spectra
3.5. Z–R Relationship
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Ding, Y.; Chan, J.C.L. The East Asian summer monsoon: an overview. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 89, 117–142. [Google Scholar]
- Sampe, T.; Xie, S.-P. Large-scale dynamics of the meiyu-baiu rainband: Environmental forcing by the westerly jet. J. Climate 2010, 23, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.S.; Xian, P.; Holben, B.N.; Hyer, E.J.; Reid, E.A.; Salinas, S.V.; Zhang, J.; Campbell, J.R.; Chew, B.N.; Holz, R.E.; et al. Aerosol meteorology of the maritime continent for the 2012 7SEAS southwest monsoon intensive study—Part 1: Regional-scale phenomena. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14041–14056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Bashor, P.G.; Habib, E.; Kasparis, T. Raindrop size distribution measurements in tropical cyclones. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2008, 136, 1669–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-Y.; Wang, T.-C.C.; Lin, P.-L. Characteristics of the raindrop size distribution and drop shape relation in typhoon systems in the Western Pacific from the 2D video disdrometer and NCU C-Band polarimetric radar. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2009, 26, 1973–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishna, B.; Narayana Rao, T. Differences in cyclonic raindrop size distribution from southwest to northeast monsoon season and from that of noncyclonic rain. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D16205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-J.; Wang, Y.; Ming, J. Microphysical characteristics of the raindrop size distribution in Typhoon Morakot (2009). J. Trop. Meteorol. 2012, 18, 162–171. [Google Scholar]
- Deo, A.; Walsh, K.J.E. Contrasting tropical cyclone and non-tropical cyclone related rainfall drop size distribution at Darwin, Australia. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, K.; Chen, G.; Wang, M.; Zhou, B.; Huang, H.; Hu, D.; Lee, W.-C.; Hu, H. Drop size distribution characteristics of seven typhoons in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6529–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Bi, S.; Wu, Z.; Shen, P.; Ao, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of dual-polarimetric radar variables and quantitative precipitation estimators for landfall typhoons and squall lines based on disdrometer data in southern China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Pu, J. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the meiyu season observed in Eastern China. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan 2013, 91, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, G.; Xue, M.; Zhou, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, X. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distributions observed in East China during the Asian summer monsoon season using 2-D video disdrometer and micro rain radar data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2265–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, A.; Harimaya, T. Characteristics of the variation of raindrop size distribution in baiu season. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan 2003, 81, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, A.; Harimaya, T. Characteristics of raindrop size distribution dependent on the life stage of a convective precipitation cloud in the baiu season. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan 2005, 83, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oue, M.; Uyeda, H.; Shusse, Y. Two types of precipitation particle distribution in convective cells accompanying a baiu frontal rainband around Okinawa Island, Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shusse, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Takahashi, N.; Satoh, S.; Iguchi, T. Characteristics of polarimetric radar variables in three types of rainfalls in a baiu front event over the East China Sea. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan 2009, 87, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, K. Characteristics of baiu front as a predominant subtropical front in the summer Northern Hemisphere. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan 1984, 62, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seela, B.K.; Janapati, J.; Lin, P.-L.; Reddy, K.K.; Shirooka, R.; Wang, P.K. A comparison study of summer season raindrop size distribution between Palau and Taiwan, two islands in Western Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 11787–11805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, K.; Wang, M.; Zhang, G. Seasonal variations of observed raindrop size distribution in East China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; An, J.-L.; Liu, H.-Z.; Duan, J. An observational study on vertical raindrop size distributions during stratiform rain in a semiarid plateau climate zone. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2016, 9, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, G.; Fischer, B.; Münster, H.; Clemens, M.; Wagner, A. Profiles of raindrop size distributions as retrieved by microrain radars. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 1930–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, E.; Kida, S.; Yoshida, S.; Morimoto, T.; Ushio, T.; Kawasaki, Z. Vertical structure of raindrop size distribution in lower atmospheric boundary layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Hartmann, P.; Battaglia, A.; Gage, K.S.; Clark, W.L.; Williams, C.R. A field study of reflectivity and Z–R relations using vertically pointing radars and disdrometers. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2009, 26, 1120–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; D’Adderio, L.P.; Campbell, J.R.; Sicard, M.; Welton, E.J.; Binci, A.; Rea, A.; Tokay, A.; Comerón, A.; Barragan, R.; et al. Vertically resolved precipitation intensity retrieved through a synergy between the ground-based NASA MPLNET Lidar network measurements, surface disdrometer datasets and an analytical model solution. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Girolamo, P.D.; Demoz, B.; Li, X.; Welton, E.J. Rain evaporation rate estimates from dual-wavelength lidar measurements and intercomparison against a model analytical solution. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2017, 34, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, J.; Waldvogel, A. Raindrop size distribution and sampling size errors. J. Atmos. Sci. 1969, 26, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Wolff, D.B.; Wolff, K.R.; Bashor, P. Rain gauge and disdrometer measurements during the Keys Area Microphysics Project (KAMP). J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2003, 20, 1460–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler-Mang, M.; Kunz, M.; Schmid, W. On the performance of a low-cost K-band Doppler radar for quantitative rain measurements. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 1999, 16, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Kruger, A.; Krajewski, W.F. Comparison of drop size distribution measurements by impact and optical disdrometers. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 2083–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tridon, F.; Van Baelen, J.; Pointin, Y. Aliasing in Micro Rain Radar data due to strong vertical winds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L02804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, T.; Kuroiwa, H.; Kojima, M.; Oikawa, K.; Kozu, T.; Kumagai, H.; Okamoto, K.I.; Okumura, M.; Nakatsuka, H.; Nishikawa, K. TRMM precipitation radar. Adv. Space Res. 2000, 25, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, T.; Kozu, T.; Meneghini, R.; Awaka, J.; Okamoto, K.I. Rain-profiling algorithm for the TRMM Precipitation Radar. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 2038–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstetter, P.-E.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Schwaller, M.; Petersen, W.; Zhang, J. Comparison of TRMM 2A25 products, version 6 and version 7, with NOAA/NSSL ground radar–based national mosaic QPE. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J.; Gorgucci, E.; Randeu, W.L.; Schoenhuber, M. Raindrop size distribution in different climatic regimes from disdrometer and dual-polarized radar analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, G.; Liu, S.; Chen, G. Impacts of instrument limitations on estimated raindrop size distribution, radar parameters, and model microphysics during meiyu season in East China. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2017, 34, 1021–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Srivastava, R.C. Evolution of raindrop size distribution by coalescence, breakup, and evaporation: Theory and observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 1761–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jash, D.; Resmi, E.A.; Unnikrishnan, C.K.; Sumesh, R.K.; Sreekanth, T.S.; Sukumar, N.; Ramachandran, K.K. Variation in rain drop size distribution and rain integral parameters during southwest monsoon over a tropical station: An inter-comparison of disdrometer and micro rain radar. Atmos. Res. 2019, 217, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Konwar, M.; Sarma, D.K.; Kalapureddy, M.C.R.; Jain, A.R. Characteristics of rain integral parameters during tropical convective, transition, and stratiform rain at Gadanki and its application in rain retrieval. J Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 1245–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lei, H.; Xie, Y.; Wen, L.; Yang, J. Characteristics of summer season raindrop size distribution in three typical regions of Western Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 4054–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifelli, R.; Williams, C.R.; Rajopadhyaya, D.K.; Avery, S.K.; Gage, K.S.; May, P.T. Drop-size distribution characteristics in tropical mesoscale convective systems. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 760–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki; Hashiguchi, H.; Shimomai, T.; Rahayu, I.; Vonnisa, M.; Afdal. Performance evaluation of micro rain radar over Sumatra through comparison with disdrometer and wind profiler. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2016, 50, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Kim, S.W.; Park, R.J.; Park, J.S.; Sang, S.P. Changes in column aerosol optical depth and ground-level particulate matter concentration over East Asia. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, R.A.; Breidenbach, J.P.; Seo, D.-J.; Miller, D.A.; O’Bannon, T. The WSR-88D rainfall algorithm. Weather Forecasting 1998, 13, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, R.; Kinzer, G.D. The terminal velocity of fall for water droplets in stagnant air. J. Meteorol. 1949, 6, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, D.; Srivastava, R.C.; Sekhon, R.S. Doppler radar characteristics of precipitation at vertical incidence. Rev. Geophys. 1973, 11, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| MRR | Value/Description |
| Frequency | 24.1 GHz |
| Power | 50 mW |
| Operation mode | FM-CW |
| Beam width | 2° |
| Antenna type | Offset parabolic |
| Height resolution | 200 m |
| Number of range gates | 30 |
| Temporal resolution | 1 min |
| Raindrop range | 0.25–5.03 mm |
| Raindrop size bin | 46 |
| JWD | Value/Description |
| Temporal resolution | 1 min |
| Raindrop range | 0.3–5.3 mm |
| Raindrop size bin | 20 |
| Type | Ty-ID 1 | Period (YYYY/MM/DD) | A MRR | b MRR | A JWD | b JWD | RG Rainfall (mm) | MRR Rainfall (mm) | JWD Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tropical cyclone | S-7 | 2005/07/25–26 | 119 | 1.12 | 154 | 1.25 | 94.1 | 64.3 | 91.5 |
| S-7 | 2006/08/08–09 | 281 | 1.21 | 295 | 1.37 | 62.5 | 55.7 | 62.7 | |
| S-4 | 2007/07/14–15 | 176 | 1.31 | 191 | 1.32 | 106.9 | 75.7 | 94.5 | |
| T-11 | 2005/08/25–26 | 189 | 1.21 | 236 | 1.38 | 87.0 | 95.1 | 82.0 | |
| Meiyu-baiu front | - | 2005/06/21–23 | 284 | 1.24 | 258 | 1.36 | 27.2 | 21.7 | 20.3 |
| - | 2005/07/03–06 | 179 | 1.34 | 179 | 1.38 | 61.8 | 48.0 | 63.5 | |
| - | 2006/06/17–19 | 159 | 1.24 | 162 | 1.25 | 24.8 | 15.9 | 25.0 | |
| - | 2006/07/17–25 | 284 | 1.14 | 262 | 1.21 | 41.9 | 32.8 | 41.2 | |
| - | 2007/07/10–12 | 206 | 1.16 | 227 | 1.21 | 26.9 | 24.8 | 23.5 | |
| - | 2008/06/11–13 | 303 | 1.32 | 299 | 1.38 | 27.4 | 25.0 | 27.5 | |
| - | 2008/06/20–23 | 205 | 1.36 | 195 | 1.40 | 56.4 | 34.8 | 52.7 | |
| - | 2008/06/28–30 | 200 | 1.28 | 188 | 1.29 | 42.2 | 30.1 | 38.5 | |
| - | 2009/06/23–25 | 309 | 1.23 | 276 | 1.32 | 27.9 | 23.8 | 26.6 | |
| - | 2009/06/28–30 | 260 | 1.42 | 250 | 1.5 | 27.2 | 24.2 | 26.9 | |
| Local storm | - | 2007/08/01–02 | 114 | 1.22 | 133 | 1.41 | 12.7 | 12.1 | 10.6 |
| - | 2008/08/10–11 | 219 | 1.20 | 235 | 1.40 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.2 |
| Region | Studies | Type/period | Dm (mm) | log10Nw (mm−1 m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tokyo, Japan | JWD—This study | Tropical cyclone | 1.25 ± 0.36 * 1 | 3.74 ± 0.47 ** 1 |
| JWD—This study | Meiyu-baiu front | 1.15 ± 0.30 * | 3.59 ± 0.48 | |
| JWD—This study | Local storm | 1.31 ± 0.48 * | 3.59 ± 0.55 | |
| JWD—This study | Summer 2005–2009 | 1.15 ± 0.36 | 3.59 ± 0.59 | |
| East China | Chen et al. [11] | Meiyu season | 1.66 | 3.42 |
| Wen et al. [35] | Meiyu season | 1.18–1.28 | 3.68–3.99 | |
| Wen et al. [19] | Summer | 1.15 | 4.09 | |
| Wen et al. [9] | Tropical cyclone | 1.13 ± 0.24 | - | |
| Eastern USA | Tokay et al. [4] | Tropical cyclone | 1.67 ± 0.30 | - |
| Region | Studies | RSD Equipment | Type/Period | A | b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tokyo, Japan | This study | MRR | Tropical cyclone | 186 | 1.20 |
| This study | MRR | Meiyu-baiu front | 243 | 1.23 | |
| This study | MRR | Local storm | 199 | 1.14 | |
| This study | JWD | Tropical cyclone | 189 | 1.38 | |
| This study | JWD | Meiyu-baiu front | 214 | 1.35 | |
| This study | JWD | Local storm | 221 | 1.37 | |
| This study | JWD | Summer 2005–2009 | 212 | 1.33 | |
| East China | Chen et al. [7] | PARSIVEL 1 | Tropical cyclone | 235 | 1.30 |
| Chen et al. [7] | PARSIVEL | Eyewall of tropical cyclone | 308 | 1.32 | |
| Chen et al. [11] | PARSIVEL | Meiyu convective | 368 | 1.21 | |
| Wen et al. [35] | 2DVD 2 | Meiyu season | 209 | 1.39 | |
| Wen et al. [9] | 2DVD | Tropical cyclone | 147 | 1.38 | |
| Wen et al. [19] | 2DVD | Summer 2014–2015 | 232 | 1.34 | |
| Taiwan, China | Chang et al. [5] | 2DVD | Tropical cyclone | 207 | 1.45 |
| Seela et al. [18] | JWD | Summer 2003–2007 | 283 | 1.35 | |
| India | Radhakrishna and Narayana Rao [6] | JWD | Southwest monsoon | 275 | 1.39 |
| Australia | Deo and Walsh [8] | JWD | Tropical cyclone | 234 | 1.30 |
| Stage | Z (dBZ) | R (mm/h) | A | b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 35.4 | 6.0 | 233 | 1.29 |
| S2 | 35.3 | 5.6 | 275 | 1.39 |
| S3 | 23.2 | 1.1 | 131 | 1.35 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Duan, J.; An, J.; Liu, H. Raindrop Size Distribution Characteristics for Tropical Cyclones and Meiyu-Baiu Fronts Impacting Tokyo, Japan. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10070391
Chen Y, Duan J, An J, Liu H. Raindrop Size Distribution Characteristics for Tropical Cyclones and Meiyu-Baiu Fronts Impacting Tokyo, Japan. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(7):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10070391
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yong, Jing Duan, Junling An, and Huizhi Liu. 2019. "Raindrop Size Distribution Characteristics for Tropical Cyclones and Meiyu-Baiu Fronts Impacting Tokyo, Japan" Atmosphere 10, no. 7: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10070391
APA StyleChen, Y., Duan, J., An, J., & Liu, H. (2019). Raindrop Size Distribution Characteristics for Tropical Cyclones and Meiyu-Baiu Fronts Impacting Tokyo, Japan. Atmosphere, 10(7), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10070391







