The Hydrometeorology Testbed–West Legacy Observing Network: Supporting Research to Applications for Atmospheric Rivers and Beyond
Abstract
:1. Introduction
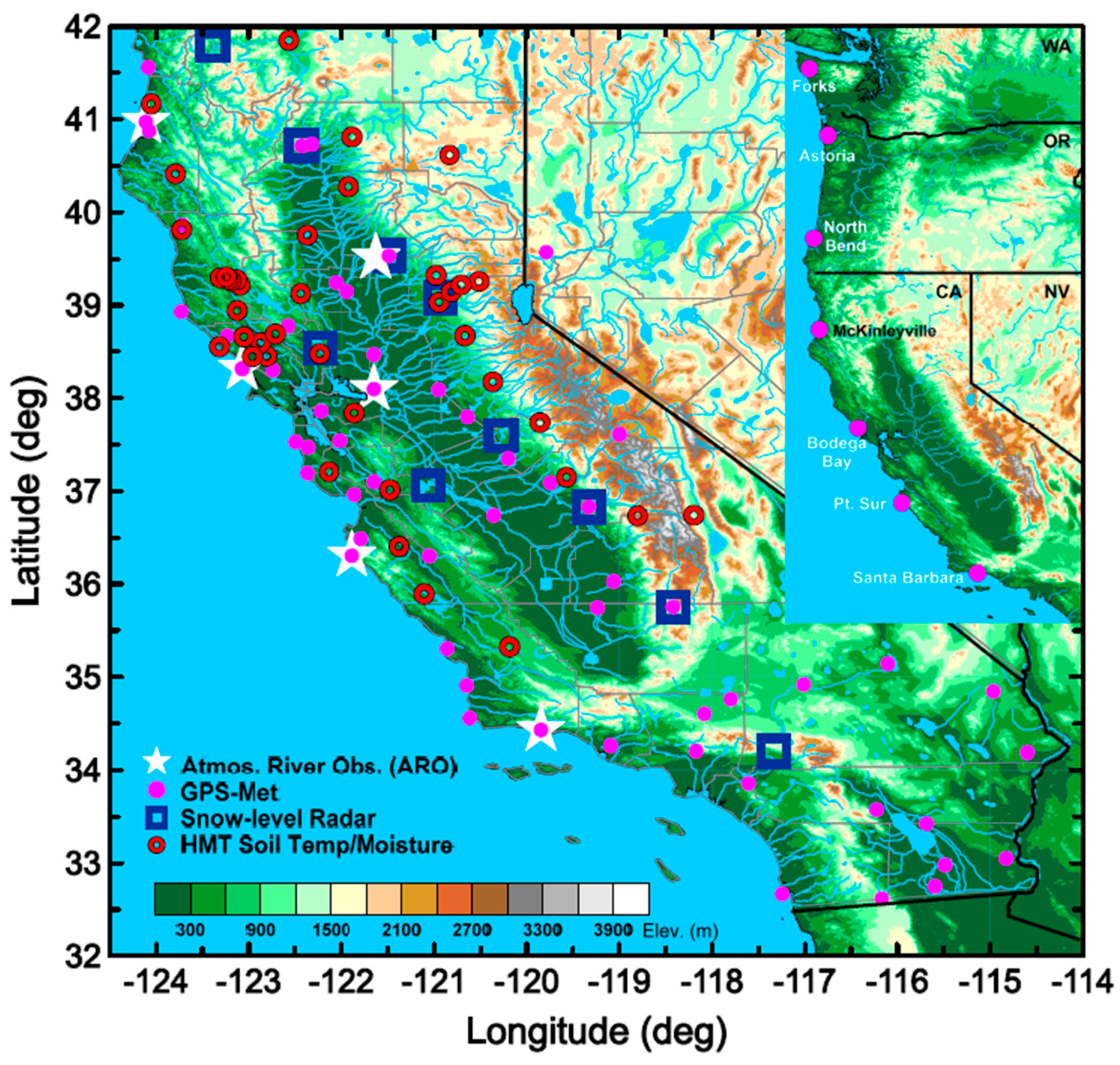
2. The HMT–West Legacy Observing Network
3. Value for the Research Community
3.1. Develop and Operate Observing Instrumentation
3.2. Serving the Data and Value-Added Products
3.3. Research on Process Understanding
3.4. Research on Model Performance and Improvement
3.5. Research Beyond ARs
3.5.1. Wind Energy Studies
3.5.2. Arctic Processes
3.5.3. Air Quality and Dispersion Studies
3.5.4. Southeastern U.S. (SEUS) Flooding and Hurricanes
3.6. Research to Operations and Applications
3.6.1. The Water Vapor Flux Tool (WVFT)
3.6.2. Snow Level Radar and Forecasting
3.6.3. WFIP2 Observation-Model Evaluation Tool
3.6.4. Wintertime Easterly Gap Flow Tool
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluate if Observations Improve Forecasts for Particular Events
4.2. Validation of Reanalyses or Reforecast Datasets
4.3. Diagnose Models for Some Key Phenomena and Places
4.4. Develop or Improve Parameterizations
4.5. Characterization of Boundary Layer Processes
4.6. Understanding Model Bias in Temperature at the Land Surface
4.7. Closing Budgets of Dynamical and Thermodynamical Properties
4.8. Understanding Cloud Properties
4.9. Vertical Air Motions in the Tropics
4.10. Understanding Arctic Winds
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, A.B.; Anderson, M.L.; Dettinger, M.D.; Ralph, F.M.; Hinojosa, A.; Cayan, D.R.; Hartman, R.K.; Reynolds, D.W.; Johnson, L.E.; Schneider, T.L.; et al. A Twenty-First-Century California Observing Network for Monitoring Extreme Weather Events. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2013, 30, 1585–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ralph, F.M.; Intrieri, J.; Andra, D.; Atlas, R.; Boukabara, S.; Bright, D.; Davidson, P.; Entwistle, B.; Gaynor, J.; Goodman, S.; et al. The Emergence of Weather-Related Test Beds Linking Research and Forecasting Operations. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1187–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; Schick, L.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Hughes, M.; Wick, G.A. Flooding in Western Washington: The Connection to Atmospheric Rivers. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 1337–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Neiman, P.J.; Wick, G.A.; Gutman, S.I.; Dettinger, M.D.; Cayan, D.R.; White, A.B. Flooding on California’s Russian River: Role of atmospheric rivers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Moore, B.J.; Gottas, D.J.; Neiman, P.J. Winter Storm Conditions Leading to Excessive Runoff above California’s Oroville Dam during January and February 2017. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettinger, M. Climate Change, Atmospheric Rivers, and Floods in California - A Multimodel Analysis of Storm Frequency and Magnitude Changes. J. Am. Water Resour. As. 2011, 47, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Molotch, N.P.; Waliser, D.E.; Fetzer, E.J.; Neiman, P.J. Extreme snowfall events linked to atmospheric rivers and surface air temperature via satellite measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, D.A.; Gage, K.S.; Ecklund, W.L.; Angevine, W.M.; Johnston, P.E.; Riddle, A.C.; Wilson, J.; Williams, C.R. Developments in Uhf Lower Tropospheric Wired Profiling at Noaas Aeronomy Laboratory. Radio. Sci. 1995, 30, 977–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Jordan, J.R.; Martner, B.E.; Ralph, F.M.; Bartram, B.W. Extending the dynamic range of an S-band radar for cloud and precipitation studies. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2000, 17, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.E.; Jordan, J.R.; White, A.B.; Carter, D.A.; Costa, D.M.; Ayers, T.E. The NOAA FM-CW Snow-Level Radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2017, 34, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, K.; Pezoa, S.; Fairall, C.; Williams, C.; Ayers, T.; Brewer, A.; de Szoeke, S.P.; Ghate, V. A Motion-Stabilized W-Band Radar for Shipboard Observations of Marine Boundary-Layer Clouds. Bound.-Lay. Meteorol. 2012, 143, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczak, J.; Finley, C.; Freedman, J.; Cline, J.; Bianco, L.; Olson, J.; Djalalova, I.; Sheridan, L.; Ahlstrom, M.; Manobianco, J.; et al. The Wind Forecast Improvement Project (WFIP) A Public-Private Partnership Addressing Wind Energy Forecast Needs. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1699–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, W.J.; Berg, L.K.; Cline, J.; Draxl, C.; Djalalova, I.; Grimit, E.P.; Lundquist, J.K.; Marquis, M.; McCaa, J.; Olson, J.B.; et al. The Second Wind Forecast Improvement Project (WFIP2): General Overview. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczak, J.M.; Stoelinga, M.; Berg, L.K.; Sharp, J.; Draxl, C.; McCaffrey, K.; Banta, R.M.; Bianco, L.; Djalalova, I.; Lundquist, J.K.; et al. The Second Wind Forecast Improvement Project (WFIP2): Observational Field Campaign. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, K.; Jackson, D.L.; Neiman, P.; Hughes, M.; Darby, L.; Wick, G.; White, A.; Sukovich, E.; Cifelli, R. Understanding the Role of Atmospheric Rivers in Heavy Precipitation in the Southeast United States. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 1617–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Mahoney, K.M.; Cifelli, R.; King, C.W. Wind Profilers to Aid with Monitoring and Forecasting of High-Impact Weather in the Southeastern and Western United States. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2039–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.W.; White, A.B.; Edson, J.B.; Hare, J.E. Integrated shipboard measurements of the marine boundary layer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 1997, 14, 338–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulou, G.; Tjernstrom, M.; Sedlar, J.; Achtert, P.; Brooks, B.J.; Brooks, I.M.; Persson, P.O.G.; Prytherch, J.; Salisbury, D.J.; Shupe, M.D.; et al. Atmospheric Conditions during the Arctic Clouds in Summer Experiment (ACSE): Contrasting Open Water and Sea Ice Surfaces during Melt and Freeze-Up Seasons. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 8721–8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persson, P.O.G.; Fairall, C.W.; Andreas, E.L.; Guest, P.S.; Perovich, D.K. Measurements near the Atmospheric Surface Flux Group tower at SHEBA: Near-surface conditions and surface energy budget. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjernström, M.; Leck, C.; Birch, C.E.; Bottenheim, J.W.; Brooks, B.J.; Brooks, I.M.; Backlin, L.; Chang, Y.W.; de Leeuw, G.; Di Liberto, L.; et al. The Arctic Summer Cloud Ocean Study (ASCOS): overview and experimental design. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2823–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tjernström, M.; Leck, C.; Persson, P.O.G.; Jensen, M.L.; Oncley, S.P.; Targino, A. The summertime Arctic atmosphere - Meteorological measurements during the Arctic Ocean experiment 2001. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; White, A.B.; Ralph, F.M.; Gottas, D.J.; Gutman, S.I. A water vapour flux tool for precipitation forecasting. P I Civil. Eng.-Wat. M 2009, 162, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Ralph, F.M.; Neiman, P.J.; Gottas, D.J.; Gutman, S.I. The NOAA coastal atmospheric river observatory. In Proceedings of the 34th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Williamsburg, VA, USA, 5–9 October 2009; p. 10B.14. [Google Scholar]
- Ralph, F.M.; Dettinger, M.; White, A.; Reynolds, D.; Cayan, D.; Schneider, T.; Cifelli, R.; Redmond, K.; Anderson, M.; Gherke, F.; et al. A Vision for Future Observations for Western U.S. Extreme Precipitation and Flooding. J. Contemp. Wat. Res. Ed. 2014, 153, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Neiman, P.J.; Creamean, J.M.; Coleman, T.; Ralph, F.M.; Prather, K.A. The Impacts of California’s San Francisco Bay Area Gap on Precipitation Observed in the Sierra Nevada during HMT and CalWater. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 1048–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; Gottas, D.J.; White, A.B.; Schneider, W.R.; Bright, D.R. A Real-Time Online Data Product that Automatically Detects Easterly Gap-Flow Events and Precipitation Type in the Columbia River Gorge. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2018, 35, 2037–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Gottas, D.J.; Strem, E.T.; Ralph, F.M.; Neiman, P.J. An automated brightband height detection algorithm for use with Doppler radar spectral moments. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2002, 19, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, L.; Gottas, D.; Wilczak, J.M. Implementation of a Gabor Transform Data Quality-Control Algorithm for UHF Wind Profiling Radars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2013, 30, 2697–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, J.K.; Wilczak, J.M.; Ashton, R.; Bianco, L.; Brewer, W.A.; Choukulkar, A.; Clifton, A.; Debnath, M.; Delgado, R.; Friedrich, K.; et al. ASSESSING STATE-OF-THE-ART CAPABILITIES FOR PROBING THE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER: The XPIA Field Campaign. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 289–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecklund, W.L.; Carter, D.A.; Balsley, B.B. A UHF Wind Profiler for the Boundary Layer: Brief Description and Initial Results. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 1988, 5, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, K.S.; Williams, C.R.; Ecklund, W.L. Uhf Wind Profilers—A New Tool for Diagnosing Tropical Convective Cloud Systems. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 75, 2289–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.R.; Ecklund, W.L.; Carter, D.A.; Gage, K.S.; Ethier, S.A. Research Applications of a Boundary-Layer Wind Profiler. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 74, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, B.J.; Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Barthold, F.E. Physical Processes Associated with Heavy Flooding Rainfall in Nashville, Tennessee, and Vicinity during 1-2 May 2010: The Role of an Atmospheric River and Mesoscale Convective Systems. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 358–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavers, D.A.; Allan, R.P.; Wood, E.F.; Villarini, G.; Brayshaw, D.J.; Wade, A.J. Winter floods in Britain are connected to atmospheric rivers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, L.R.; Qian, Y. Atmospheric rivers induced heavy precipitation and flooding in the western US simulated by the WRF regional climate model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, D.D.; Allen, D.T.; Bates, T.S.; Estes, M.; Fehsenfeld, F.C.; Feingold, G.; Ferrare, R.; Hardesty, R.M.; Meagher, J.F.; Nielsen-Gammon, J.W.; et al. Overview of the Second Texas Air Quality Study (TexAQS II) and the Gulf of Mexico Atmospheric Composition and Climate Study (GoMACCS). J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2009, 114, D00F13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, O.; Vihma, T. The atmosphere over sea ice. In Sea Ice, 3rd ed.; Thomas, D.N., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shupe, M.D.; Uttal, T.; Matrosov, S.Y. Arctic cloud microphysics retrievals from surface-based remote sensors at SHEBA. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 1544–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.R.; Riddle, A.C. TOGA COARE Integrated Sounding System Data Report—Volume IA Revised Edition, 1994. National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, June 1994. Available online: https://aspace.archives.ucar.edu/repositories/2/archival_objects/4672 (accessed on 27 August 2019).
- Webster, P.J.; Lukas, R. Toga Coare - the Coupled Ocean Atmosphere Response Experiment. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1992, 73, 1377–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, L.; Friedrich, K.; Wilczak, J.M.; Hazen, D.; Wolfe, D.; Delgado, R.; Oncley, S.P.; Lundquist, J.K. Assessing the accuracy of microwave radiometers and radio acoustic sounding systems for wind energy applications. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1707–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannon, F.; Ralph, F.M.; Wilson, A.M.; Lettenmaier, D.P. GPM Satellite Radar Measurements of Precipitation and Freezing Level in Atmospheric Rivers: Comparison With Ground-Based Radars and Reanalyses. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2017, 122, 12747–12764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifelli, R.; Chandrasekar, V.; Chen, H.N.; Johnson, L.E. High Resolution Radar Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in the San Francisco Bay Area: Rainfall Monitoring for the Urban Environment. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 96a, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartten, L.M.; Johnston, P.E.; Rodríguez Castro, V.M.; Esteban Pérez, P.S. Post-Deployment Calibration of a Tropical UHF Profiling Radar via Surface- and Satellite-Based Methods. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; Moore, B.J.; White, A.B.; Wick, G.A.; Aikins, J.; Jackson, D.L.; Spackman, J.R.; Ralph, F.M. An Airborne and Ground-Based Study of a Long-Lived and Intense Atmospheric River with Mesoscale Frontal Waves Impacting California during CalWater-2014. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 1115–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Coleman, T.; Neiman, P.J.; Zamora, R.J.; Dettinger, M.D. Observed Impacts of Duration and Seasonality of Atmospheric-River Landfalls on Soil Moisture and Runoff in Coastal Northern California. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ralph, F.M.; Neiman, P.J.; Wick, G.A. Satellite and CALJET aircraft observations of atmospheric rivers over the eastern north pacific ocean during the winter of 1997/98. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1721–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchett, B.J.; Daudert, B.; Garner, C.B.; Oakley, N.S.; Putnam, A.E.; White, A.B. Winter Snow Level Rise in the Northern Sierra Nevada from 2008 to 2017. Water 2017, 9, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Mahoney, K.; Hughes, M. High-Resolution Model-Based Investigation of Moisture Transport into the Pacific Northwest during a Strong Atmospheric River Event. In Proceedings of the 98th American Meteorological Society (AMS) Annual Meeting, Austin, TX, USA, 7–11 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczak, J.M.; Olson, J.B.; Djalalova, I.; Bianco, L.; Berg, L.K.; Shaw, W.J.; Coulter, R.L.; Eckman, R.M.; Freedman, J.; Finley, C.; et al. Data assimilation impact of in situ and remote sensing meteorological observations on wind power forecasts during the first Wind Forecast Improvement Project (WFIP). Wind Energy 2019, 22, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeira, J.M.; Ralph, F.M.; Martin, A.; Gaggggini, N.; Spackman, J.R.; Neiman, P.J.; Rutz, J.J.; Pierce, R. Forecasting Atmospheric Rivers during CalWater 2015. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.W.; Matrosov, S.Y.; Williams, C.R.; Walsh, E.J. Estimation of Rain Rate from Airborne Doppler W-Band Radar in CalWater-2. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2018, 35, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Prather, K.A.; Cayan, D.; Spackman, J.R.; DeMott, P.; Dettinger, M.; Fairall, C.; Leung, R.; Rosenfeld, D.; Rutledge, S.; et al. Calwater Field Studies Designed to Quantify the Roles of Atmospheric Rivers and Aerosols in Modulating Us West Coast Precipitation in a Changing Climate. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 1209–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsmill, D.E.; Neiman, P.J.; White, A.B. Microphysics Regime Impacts on the Relationship between Orographic Rain and Orographic Forcing in the Coastal Mountains of Northern California. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 2905–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; Cifelli, R.; Neiman, P.J.; White, A.B. Radar Rain-Rate Estimators and Their Variability due to Rainfall Type: An Assessment Based on Hydrometeorology Testbed Data from the Southeastern United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2016, 55, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; Ralph, F.M.; Neiman, P.J.; White, A.B. Quantitative Assessment of Operational Weather Radar Rainfall Estimates over California’s Northern Sonoma County Using HMT-West Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willie, D.; Chen, H.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Cifelli, R.; Campbell, C.; Reynolds, D.; Matrosov, S.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of Multisensor Quantitative Precipitation Estimation in Russian River Basin. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamean, J.M.; Ault, A.P.; White, A.B.; Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Minnis, P.; Prather, K.A. Impact of interannual variations in sources of insoluble aerosol species on orographic precipitation over California’s central Sierra Nevada. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6535–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamean, J.M.; Suski, K.J.; Rosenfeld, D.; Cazorla, A.; DeMott, P.J.; Sullivan, R.C.; White, A.B.; Ralph, F.M.; Minnis, P.; Comstock, J.M.; et al. Dust and Biological Aerosols from the Sahara and Asia Influence Precipitation in the Western U.S. Science 2013, 339, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creamean, J.M.; White, A.B.; Minnis, P.; Palikonda, R.; Spangenberg, D.A.; Prather, K.A. The relationships between insoluble precipitation residues, clouds, and precipitation over California’s southern Sierra Nevada during winter storms. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.C.; Cornwell, G.C.; Atwood, S.A.; Moore, K.A.; Rothfuss, N.E.; Taylor, H.; DeMott, P.J.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Petters, M.D.; Prather, K.A. Transport of pollution to a remote coastal site during gap flow from California’s interior: Impacts on aerosol composition, clouds, and radiative balance. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1491–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.J.; Mahoney, K.M.; Sukovich, E.M.; Cifelli, R.; Hamill, T.M. Climatology and Environmental Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation Events in the Southeastern United States. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 718–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akish, E.; Bianco, L.; Djalalova, I.V.; Wilczak, J.M.; Olson, J.B.; Freedman, J.; Finley, C.; Cline, J. Measuring the impact of additional instrumentation on the skill of numerical weather prediction models at forecasting wind ramp events during the first Wind Forecast Improvement Project (WFIP). Wind Energy 2019, 22, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djalalova, I.V.; Olson, J.; Carley, J.R.; Bianco, L.; Wilczak, J.M.; Pichugina, Y.; Banta, R.; Marquis, M.; Cline, J. The POWER Experiment: Impact of Assimilation of a Network of Coastal Wind Profiling Radars on Simulating Offshore Winds in and above the Wind Turbine Layer. Weather Forecast 2016, 31, 1071–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilczak, J.; McCaffrey, K.; Djalalova, I.V.; Bianco, L.; Olson, J.B.; Kenyon, J.; Stoelinga, M.T.; Sharp, J.; Pekour, M.; Cook, D.; et al. Identification and Analysis of Forecast Model Large Error Events During WFIP2. In Proceedings of the 98th American Meteorological Society (AMS) Annual Meeting, Austin, TX, USA, 7–11 January 2018; Available online: https://ams.confex.com/ams/98Annual/webprogram/Paper332680.html (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Bianco, L.; Djalalova, I.V.; Wilczak, J.M.; Olson, J.B.; Kenyon, J.S.; Choukulkar, A.; Berg, L.K.; Fernando, H.J.S.; Grimit, E.P.; Krishnamurthy, R.; et al. Impact of model improvements on 80-m wind speeds during the second Wind Forecast Improvement Project (WFIP2). Geosci. Model. Dev. Discuss. 2019, 2019, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, L.; White, A.B.; Gottas, D.; Coleman, T. An evaluation of integrated water vapor, wind, and precipitation forecasts using water vapor flux observations in the Western United States. Weather Forecast. 2019. in review. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczak, J.M.; McCaffrey, K.; Draxl, C.; Olson, J.B.; Stoelinga, M.T.; Berg, L.K.; Bianco, L.; Choukulkar, A.; Djalalova, I.V.; Grimit, E.P.; et al. Improved Understanding and Modeling of Key Atmospheric Phenomena during WFIP2: Cold Pools, Gap Flows, and Mountain Waves. In Proceedings of the 98th American Meteorological Society (AMS) Annual Meeting, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 6–10 January 2019; Available online: https://ams.confex.com/ams/2019Annual/meetingapp.cgi/Paper/354155 (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Olson, J.B.; Kenyon, J.S.; Djalalova, I.; Bianco, L.; Turner, D.D.; Pichugina, Y.; Choukulkar, A.; Toy, M.D.; Brown, J.M.; Angevine, W.M.; et al. Improving Wind Energy Forecasting through Numerical Weather Prediction Model Development. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankov, I.; Bao, J.W.; Neiman, P.J.; Schultz, P.J.; Yuan, H.L.; White, A.B. Evaluation and Comparison of Microphysical Algorithms in ARW-WRF Model Simulations of Atmospheric River Events Affecting the California Coast. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 847–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.R.; White, A.B.; Gage, K.S.; Ralph, F.M. Vertical structure of precipitation and related microphysics observed by NOAA profilers and TRMM during NAME 2004. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 1693–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.W.; Small, I.J.; Gutman, S.I.; Bock, Y.; Dumas, J.L.; Fang, P.; Haase, J.S.; Jackson, M.E.; Laber, J.L. National Weather Service Forecasters Use GPS Precipitable Water Vapor for Enhanced Situational Awareness during the Southern California Summer Monsoon. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaffrey, K.; Bianco, L.; Djalalova, I.V.; Wilczak, J.M.; Grimit, E.P.; Sharp, J.; Leo, L.; Friedrich, K.; Bonin, T.; Choukulkar, A. Identification and Characterization of Cold Pool Events in the Columbia River Basin during WFIP2. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Pichugina, Y.L.; Banta, R.M.; Bonin, T.; Brewer, W.A.; Choukulkar, A.; McCarty, B.J.; Baidar, S.; Draxl, C.; Fernando, H.J.S.; Kenyon, J.; et al. Spatial Variability of Winds and HRRR-NCEP Model Error Statistics at Three Doppler-Lidar Sites in the Wind-Energy Generation Region of the Columbia River Basin. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2019, 58, 1633–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxl, C.; Quon, D.; Chand, D.; Berg, L.K.; Churchfield, M.J.; Kemper, T.; Kenyon, J.; Olson, J.B.; Sharp, J. Simulated and Observed Mountain Waves and Their Implications on Wind Energy. In Proceedings of the 98th American Meteorological Society (AMS) Annual Meeting, Austin, TX USA, 7–11 January 2018; Available online: https://ams.confex.com/ams/98Annual/webprogram/Paper336065.html (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- McCaffrey, K.E.; Wilczak, J.M.; Bianco, L.; IDjalalova, I.V.; Banta, R.; Bonin, T.A.; Brewer, W.A.; Choukulkar, A.; Cook, D.; Coulter, R.L.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Cold Pool Events during WFIP2. In Proceedings of the 98th American Meteorological Society (AMS) Annual Meeting, Austin, TX, USA, 7–11 January 2018; Available online: https://ams.confex.com/ams/98Annual/webprogram/Paper331305.html (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Lund, B.; Graber, H.C.; Persson, P.O.G.; Smith, M.; Doble, M.; Thomson, J.; Wadhams, P. Arctic Sea Ice Drift Measured by Shipboard Marine Radar. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2018, 123, 4298–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, J.C.; Eleuterio, D.P.; Gallaudet, T.C.; Geernaert, G.L.; Harr, P.A.; Kaye, J.A.; McCarren, D.H.; McLean, C.N.; Sandgathe, S.A.; Toepfer, F.; et al. The National Earth System Prediction Capability: Coordinating the Giant. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, S.; Hsu, Y.K.; Andrews, A.E.; Bianco, L.; Vaca, P.; Wilczak, J.M.; Fischer, M.L. A multitower measurement network estimate of California’s methane emissions. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 11339–11351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Newman, S.; Zhang, J.S.; Andrews, A.E.; Bianco, L.; Dlugokencky, E.; Bagley, J.; Cui, X.G.; Priest, C.; Campos-Pineda, M.; et al. Inverse Estimation of an Annual Cycle of California’s Nitrous Oxide Emissions. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2018, 123, 4758–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.W.; Michelson, S.A.; Persson, P.O.G.; Djalalova, I.V.; Wilczak, J.M. Observed and WRF-simulated low-level winds in a high-ozone episode during the Central California Ozone Study. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2008, 47, 2372–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA/ESRL Physical Sciences Division. Coastal Wind Profiler Technology Evaluation: An. Integrated Ocean. Observing System Project Final Report; November 2007. Available online: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/news/2007/pdf/IOOS_Final%20Report_Nov_15_2007.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2019).
- Schwietzke, S.; Petron, G.; Conley, S.; Pickering, C.; Mielke-Maday, I.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Tans, P.P.; Vaughn, T.; Bell, C.; Zimmerle, D.; et al. Improved Mechanistic Understanding of Natural Gas Methane Emissions from Spatially Resolved Aircraft Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7286–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frost, G.J.; Trainer, M.; Allwine, G.; Buhr, M.P.; Calvert, J.G.; Cantrell, C.A.; Fehsenfeld, F.C.; Goldan, P.D.; Herwehe, J.; Hubler, G.; et al. Photochemical ozone production in the rural southeastern United States during the 1990 Rural Oxidants in the Southern Environment (ROSE) program. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1998, 103, 22491–22508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croes, B.E.; Fujita, E.M. Overview of the 1997 Southern California Ozone Study (SCOS97-NARSTO). Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, S3–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryerson, T.B.; Andrews, A.E.; Angevine, W.M.; Bates, T.S.; Brock, C.A.; Cairns, B.; Cohen, R.C.; Cooper, O.R.; de Gouw, J.A.; Fehsenfeld, F.C.; et al. The 2010 California Research at the Nexus of Air Quality and Climate Change (CalNex) field study. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 5830–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petron, G.; Karion, A.; Sweeney, C.; Miller, B.R.; Montzka, S.A.; Frost, G.J.; Trainer, M.; Tans, P.; Andrews, A.; Kofler, J.; et al. A new look at methane and nonmethane hydrocarbon emissions from oil and natural gas operations in the Colorado Denver-Julesburg Basin. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 6836–6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, W.D. The Denver Brown Cloud studies from the perspective of model assessment needs and the role of meteorology. J. Air Waste Manage. 1997, 47, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Darby, L.S.; Senff, C.J.; King, C.W.; Banta, R.M.; Koermer, J.; Wilczak, J.M.; Neiman, P.J.; Angevine, W.M.; Talbot, R. Comparing the impact of meteorological variability on surface ozone during the NEAQS (2002) and ICARTT (2004) field campaigns. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meagher, J.F.; Cowling, E.B.; Fehsenfeld, F.C.; Parkhurst, W.J. Ozone formation and transport in southeastern United States: Overview of the SOS Nashville Middle Tennessee Ozone Study. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1998, 103, 22213–22223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, L.; White, A.B.; Coleman, T. A look at winter 2015/2016 precipitation forecasts at eight locations in the western U.S. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Mountain Meteorology, Burlington, VT, USA, 27 June–1 July 2016; Available online: https://ams.confex.com/ams/17Mountain/webprogram/Paper296580.html (accessed on 27 August 2019).
- Sulek, J.P.; Krieger, L.M.; Gomez, M. Russian River Flooding Swamps Two Dozen Towns. Available online: https://www.mercurynews.com/2019/02/27/this-sonoma-county-town-got-20-inches-of-rain-in-48-hours-san-jose-averages-about-15-a-year (accessed on 29 August 2019).
- Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Moore, B.J.; Zamora, R.J. The Regional Influence of an Intense Sierra Barrier Jet and Landfalling Atmospheric River on Orographic Precipitation in Northern California: A Case Study. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Gottas, D.J.; Henkel, A.F.; Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Gutman, S.I. Developing a Performance Measure for Snow-Level Forecasts. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; Gottas, D.J.; White, A.B.; Schick, L.J.; Ralph, F.M. The Use of Snow-Level Observations Derived from Vertically Profiling Radars to Assess Hydrometeorological Characteristics and Forecasts over Washington’s Green River Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 2522–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S.Y.; Cifelli, R.; White, A.; Coleman, T. Snow-Level Estimates Using Operational Polarimetric Weather Radar Measurements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.W.A.; Sardeshmukh, P.D.; Compo, G.P.; Whitaker, J.S.; Slivinski, L.C.; McColl, C.M.; Pegion, P.J. Sensitivities of the NCEP Global Forecast System. Mon. Weather Rev. 2019, 147, 1237–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.B.; Toy, M.D.; Brown, J.M.; Angevine, W.M.; Bao, J.-W.; Jimenez, P.; Kosovic, B.; Lundquist, K.A.; Lundquist, J.K.; McCaa, J.; et al. Model Development in Support of the Second Wind Forecast improvement Project (WFIP 2). B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; van den Dool, H. Bias Correction and Forecast Skill of NCEP GFS Ensemble Week-1 and Week-2 Precipitation, 2-m Surface Air Temperature, and Soil Moisture Forecasts. Weather Forecast. 2011, 26, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomon, A.; de Boer, G.; Creamean, J.M.; McComiskey, A.; Shupe, M.D.; Maahn, M.; Cox, C. The relative impact of cloud condensation nuclei and ice nucleating particle concentrations on phase partitioning in Arctic mixed-phase stratocumulus clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 17047–17059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, M.; Sardeshmukh, P.D.; Bergman, J.W. An assessment of the NCEP, NASA, and ECMWF reanalyses over the tropical west Pacific warm pool. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.; Yamazaki, A.; Ono, J.; Dethloff, K.; Maturilli, M.; Neuber, R.; Edwards, P.; Yamaguchi, H. Additional Arctic observations improve weather and sea-ice forecasts for the Northern Sea Route. Sci. Rep.-UK 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Wind profiler observations at fine temporal and vertical scale in the boundary layer
|
Radar reflectivity and Doppler vertical velocity (S-PROF and snow-level radars)
|
Surface met tower, GPS, surface measurements (2 min. avg.)
|
Soil Moisture
|
Derived products:
|
| Project and Locations | Latitude, -Longitude (deg.), Elev (m) | Deployed (Month/Year) | Collocated Instruments |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARO/WFIP2 | |||
| Forks, WA | 47.98, −124.40, 95 | 6/2015 * | 449, GPS-met, SMet, SLR, SM, RASS |
| Astoria, OR 1 | 46.16, −123.88, 3 | 9/2015 * | 449, GPS-met, SLR, SM |
| South Bend, OR | 43.42, −124.24, 5 | 10/2015 * | 449, GPS-met, SLR, SM |
| Troutdale, OR | 45.55, −122.39, 12 | 9/2015 * | 915, GPS-met, RASS, Disd, SMet |
| ARO/HMT (CA) | |||
| McKinleyville | 40.97, −124.11, 56 | 11/2015 * | 449, GPS-met, SLR, SM |
| Bodega Bay | 38.32, −123.07, 15 | 3/2013 * | 449, GPS-met, SLR, SM |
| Pt. Sur | 36.30, −121.89, 10 | 10/2016 * | 449, 915, S-PROF, GPS-met, SLR, SM, |
| Santa Barbara | 34.43, −119.85, 2 | 8/2016 * | 449, GPS-met, SLR, SM |
| Oroville | 39.51, −121.63, 56 | 10/2017 * | 915, GPS-met, SLR, SM |
| Twitchell Island | 38.06, −121.65, 12 | 10/2017 * | 915, GPS-met SLR, SM |
| HMT- SE 2 | |||
| New Bern, NC | 35.08, −81.05, 3 | 6/2013–11/2015 | 449, S-PROF, GPS-met, Disd |
| Moss Point, MS | 30.47, −88.53, 6 | 6/2014–11/2015 | 915, GPS-met, WVF, |
| Old Fort, NC | 35.64, −82.16, 427 | 6/2013–10/2014 | 449, RASS, S-PROF, GPS-met, Parsival |
| Johns Is, SC | 32.70, −80.00, 15 | 6/2014–11/2015 | 915, GPS-met |
| Sydney, FL | 27.97, −82.23, 27 | 6/2014–11/2015 | 449, GPS-met |
| WFIP 3 | |||
| Valley City, ND | 47.03, −98.08, 378 | 6/2011–9/2012 | 449, Smet, GPS-met, WVF |
| Leeds, ND | 48.28, −99.40, 466 | 6/2011–9/2012 | 915, SODAR, Smet, WVF |
| Buffalo, SD | 44.43, −97.56, 877 | 6/2011–9/2012 | 449, SODAR, Smet |
| Ainsworth, SD | 42.58, −100.0, 793 | 6/2011–8/2012 | 915, SODAR, GPS-met, Smet, WVF |
| St James, MN | 43.98, −94.55, 324 | 6/2011–9/2012 | 915, SODAR, Smet |
| Brady, TX | 31.18, −99.33, 548 | 8/2011–9/2012 | 915, SODAR |
| Colorado City, TX | 32.47, −100.9, 665 | 7/2011–9/2012 | 915, SODAR |
| Lubbock, TX | 33.50, −102.0, 1018 | 3–12/2012 | 915, SODAR |
| Northeast & Texas Air Quality 4 | |||
| Pittsburg, PA | 40.48, −80.26, 335 | 6/2004–5/2005 | 915, SMet |
| Lunenberg, NS | 44.4, −64.3, 30 | 6/2003–5/2005 | 915, SMet |
| Plymouth, MA | 41.91, −70.73, 46 | 6/2002–5/2005 | 915, Smet |
| Beeville, TX | 28.37, −97.8, 75 | 6/2005–10.2006 | 915, Smet |
| El Paso, TX | 31.77, −106.5, 1160 | 6/2005–10/2006 | 915, SMet |
| Pacific 5 | |||
| Nauru | −0.54, 166.92, 11 | 11/1992–2/2003 | 915, SMet |
| Manus | −2.06, 147.42, 3 | 4/1992–2/2003 | 915, SMet |
| Kiritimati | 2.00, −157.40, 4 | 3/1990–8/2002 | 915 and 50-MHz WPs, SMet |
| Tarawa | 1.36, 172.92, 2 | 8/1994–2/2003 | 915, SMet |
| Arctic | |||
| R/V Oden, ACSE 2014 6 | 70–85, 19 to −156, 14 | 7–10/2014 | 449, RAOB, W-band, MWR, scanning lidar, flux tower, wave-height recorder, CTDs |
| R/V Oden, ASCOS 2008 7 | 77–90, 15 to −15, 14 | 8–9/2008 | 449, RAOB, scanning 5-mm radiometer, MMCR, MWR, flux tower, tethersondes |
| R/V Oden, AOE-2001 8 | 77–90, 10 to −150, 8 | 7–8/2001 | 915, S-PROF, RAOB, scanning 5-mm radiometer, ceilometer, on ice instruments 9 |
| Barrow, AK | 71.3, −156.6, 10 | 2–3/1997 | 449, RASS, RAOB |
| LEADEX 1992 10 | 73, −144, 0 | 3–4/1992 | 915, RAOB, RASS, surface met & energy budget, flux tower, ceilometer, SODAR |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ray, A.J.; White, A.B. The Hydrometeorology Testbed–West Legacy Observing Network: Supporting Research to Applications for Atmospheric Rivers and Beyond. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090533
Ray AJ, White AB. The Hydrometeorology Testbed–West Legacy Observing Network: Supporting Research to Applications for Atmospheric Rivers and Beyond. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(9):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090533
Chicago/Turabian StyleRay, Andrea J., and Allen B. White. 2019. "The Hydrometeorology Testbed–West Legacy Observing Network: Supporting Research to Applications for Atmospheric Rivers and Beyond" Atmosphere 10, no. 9: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090533
APA StyleRay, A. J., & White, A. B. (2019). The Hydrometeorology Testbed–West Legacy Observing Network: Supporting Research to Applications for Atmospheric Rivers and Beyond. Atmosphere, 10(9), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090533





