Abstract
To clarify the aerosol optical properties under different pollution levels and their impacting factors, hourly organic carbon (OC), elemental carbon (EC), and water-soluble ion (WSI) concentrations in PM2.5 were observed by using monitoring for aerosols and gases (MARGA) and a semicontinuous OC/EC analyzer (Model RT-4) in Wuhan from 9 to 26 January 2018. The aerosol extinction coefficient (bext) was reconstructed using the original Interagency Monitoring of Protected Visual Environment (IMPROVE) formula with a modification to include sea salt aerosols. A good correlation was obtained between the reconstructed bext and measured bext converted from visibility. bext presented a unimodal distribution on polluted days (PM2.5 mass concentrations > 75 μg⋅m−3), peaking at 19:00. bext on clean days (PM2.5 mass concentrations < 75 μg⋅m−3) did not change much during the day, while on polluted days, it increased rapidly starting at 12:00 due to the decrease of wind speed and increase of relative humidity (RH). PM2.5 mass concentrations, the aerosol scattering coefficient (bscat), and the aerosol extinction coefficient increased with pollution levels. The value of bext was 854.72 Mm−1 on bad days, which was 4.86, 3.1, 2.29, and 1.28 times of that obtained on excellent, good, acceptable, and poor days, respectively. When RH < 95%, bext exhibited an increasing trend with RH under all pollution levels, and the higher the pollution level, the bigger the growth rate was. However, when RH > 95%, bext on acceptable, poor and bad days decreased, while bext on excellent and good days still increased. The overall bext in Wuhan in January was mainly contributed by NH4NO3 (25.2%) and organic matter (20.1%). The contributions of NH4NO3 and (NH4)2SO4 to bext increased significantly with pollution levels. On bad days, NH4NO3 and (NH4)2SO4 contributed the most to bext, accounting for 38.2% and 27.0%, respectively.
1. Introduction
In recent years, air quality deterioration and visibility impairment have occurred in many urban areas of China [1,2,3,4]. One of the key pollutants is PM2.5 (aerosol particle with aerodynamic diameter less than 2.5 μm), which has a great effect on visibility impairment, urban air quality, and human health [5,6,7]. PM2.5 is mainly composed of organic and inorganic components and is typically hygroscopic. The size of PM2.5 can increase under high relative humidity (RH) conditions, therefore influencing the aerosol optical properties and leading to an increase in the aerosol scattering coefficient (bscat) and aerosol extinction coefficient (bext) [8,9].
PM2.5 in the atmosphere can reduce visibility through light extinction (including scattering and absorption of light) and also plays an important role in the formation of haze in urban areas [10,11]. The aerosol extinction coefficient (bext) is an important parameter of atmospheric extinction and is particularly significant in aerosol optical research. bext is mainly contributed by (NH4)2SO4, NH4NO3, organic matter (OM), elemental carbon (EC), sea salt, coarse mass, and so on. Their relative contributions to bext vary with time and location. The Interagency Monitoring of Protected Visual Environment (IMPROVE) formula is a method for calculating the aerosol extinction coefficient (bext) based on the chemical composition of a substance [12,13]. Many scholars have used it to calculate the contribution of each particle component to the extinction coefficient. Existing studies have found that in urban areas, (NH4)2SO4 was the largest contributor to bext, followed by NH4NO3 and OM [14,15,16,17]. Combustion-related particles rather than wind-blown dust dominated the light extinction budget in Beijing [18]. The contributions of sulfate, ammonium, and nitrate to the PM2.5 mass concentration were 15%, 5%, and 8%, respectively. Mineral aerosol contributed 16% to the PM2.5 aerosol mass, showing that combustion-related particles rather than wind-blown dust dominated the light extinction budget [19]. The seasonally reconstructed bext was in the order of autumn (319.4 ± 207.2 Mm–1) > winter (269.6 ± 175.5 Mm–1) > summer (219.0 ± 129.3 Mm–1) > spring (193.3 ± 94.9 Mm–1) annually in Guangzhou [20]. RH is an important meteorological factor in the atmosphere and has a notable effect on the formation and optical properties of PM2.5. RH is a key factor in visibility impairment that affects light extinction through the hygroscopic growth of particles [21,22]. bext values were higher in higher humidity conditions [23,24]. High RH played an important role in the formation of PM2.5. However, when RH > 80%, PM2.5 concentrations began to decrease due to the high frequency of precipitation [25,26].
In recent years, many studies have been performed to investigate aerosol optical properties in many developed cities in China, such as Nanjing [22,27], Beijing [18,28,29], Guangzhou [20,25], and Chengdu [14,30]. In addition, many studies have been done to determine the relationship between aerosol optical properties and pollution level. The atmospheric extinction coefficient (bext) and the absorption coefficient of aerosols (babs) increased, and the single scattering albedo (SSA) decreased from excellent to polluted levels [31]. Higher aerosol optical depth (AOD) and SSAs were observed during polluted periods than during non-polluted periods [32]. However, studies in Wuhan about aerosol optical properties under different pollution levels are very limited.
As the capital of Hubei province, Wuhan covers an area of 8500 square kilometers. The permanent resident population was 10.90 million in 2017. In recent years, with the rapid development of economy and the acceleration of urbanization, haze pollution in Wuhan is increasingly serious. Therefore, many studies have been done in Wuhan. PM2.5 was the primary pollutant, and O3 was the secondary pollutant, in Wuhan as determined by calculating the value of the Individual Air Quality Index (IAQI) [33]. The major chemical compositions of PM2.5 were investigated in Wuhan, and it was found that OM was the most abundant component in PM2.5, the lowest concentrations of which were observed in summer [34]. Regional chemical transport played an important role in both short-term haze episodes and persistent haze episodes that occurred in Wuhan [35]. The physical and chemical characteristics, including chemical composition, hygroscopicity, and particle size distribution of aerosols are quite different under different pollution levels. In addition, the meteorological conditions (RH, wind speed, wind direction, and stability) are also different under different pollution levels. Therefore, the contribution of aerosol chemical components to the light extinction is different under different pollution levels. To gain a thorough knowledge of aerosol optical properties under different pollution conditions, the values of hourly concentrations of PM2.5, water-soluble ions (WSIs), organic carbon (OC), elemental carbon (EC), and meteorological parameters were observed in Wuhan during January 2018. bext was reconstructed based on the IMPROVE formula, and the reconstructed bext was used to assess the contributions of individual components of PM2.5 to the total light extinction. In this study, aerosol optical parameters under different pollution levels were compared and analyzed. The influence of meteorological factors on optical parameters was also discussed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Origins
As the central city of central China, Wuhan is located in the eastern part of Hubei province, at the intersection of the Yangtze River and Hanshui. Wuhan is covered by rivers and lakes, and water accounts for about a quarter of the total area of the city. According to the statistical bulletin of Wuhan national economic and social development in 2017, the annual GDP of Wuhan had reached 134.10 billion yuan by the end of 2017, which was an increase of 8.0% over the previous year. The annual average concentrations of ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and inhalable particulate matter (PM10) were 52 μg⋅m−3 and 87 μg⋅m−3, respectively, which were 8.8% and 5.4% lower than those of the previous year. Wuhan has a north subtropical monsoon climate and experiences abundant rainfall and sufficient heat annually. The city is relatively hot in the summer and cold in the winter. The observation time was from January 9 to January 26, 2018. All time mentioned in this passage were local time, and the time of sunset was 17:30 in January in Wuhan.
2.2. Instruments
Water-soluble ions (NO3−, SO42−, Cl−, Ca2+, and Mg2+) were measured using a model ADI 2080 monitor in ambient air (MARGA, Applikon Analytical B.V., the Netherlands) with a Teflon-coated PM2.5 sampling inlet at an hourly temporal resolution. For detailed principles of the tool, please refer to related articles [36,37,38,39,40,41].
A semicontinuous thermal-optical transmittance (TOT) carbon analyzer (Model RT-4, Sunset Laboratory Inc., Tigard, OR, USA) was used to measure the hourly concentrations of OC and EC. The affirmation of the Sunset field carbon analyzer can be found in related reference [35,36]. Each measurement cycle is composed of 45 min of sampling and 15 min of OC/EC analysis. The detailed principle of the instrument can be found in other literature [37].
Hourly concentrations of PM2.5, PM10 and NO2 were downloaded from the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE) of China website (http://106.37.208.233:20035/), Zhuankou district station (114°150 E, 30°470 N). The meteorological data (temperature, wind speed, wind direction, relative humidity) were measured from the Wuhan meteorological station (114.03° E, 30.36° N).
2.3. Data Analysis
The black carbon (BC) mass concentrations were used to calculate the babs as follows:
where α is a conversion factor. The value of α was 8.28 m2⋅g−1 based on a comparison test between the Aethalometer and the photoacoustic spectrometer in southern China [42]. BC mass concentrations were replaced by EC mass concentrations. babs is absorption coefficient of particles (unit: Mm−1).
In this study, two methods were used to calculate bext. One method used the visibility data, which were converted to bext using the Koschmeider equation [43]:
where VR represents visual range (unit: km), and bext represents the aerosol extinction coefficient (unit: Mm−1). Another method was to calculate bext using the IMPROVE formula:
where [x] represents the concentration of constituent x (unit: μg⋅m−3). [(NH4)2SO4] was replaced by 1.375 times [SO42−], [NH4NO3] was replaced by 1.29 times [NO3−], [OM] was replaced by 1.6 times [OC], [Soil] was replaced by the sum of 1.63 times [Ca+] and 1.67 times [Mg2+], and [SS] was replaced by 1.8-times [Cl−]. [CoarseMass] could be replaced by [PM10], the unit of [NO2] is 10−9, and Rayleigh Scattering was replaced by 10. f(RH) is the hygroscopic growth factor [8].
Therefore, bscat can be obtained from a difference between bext and babs:
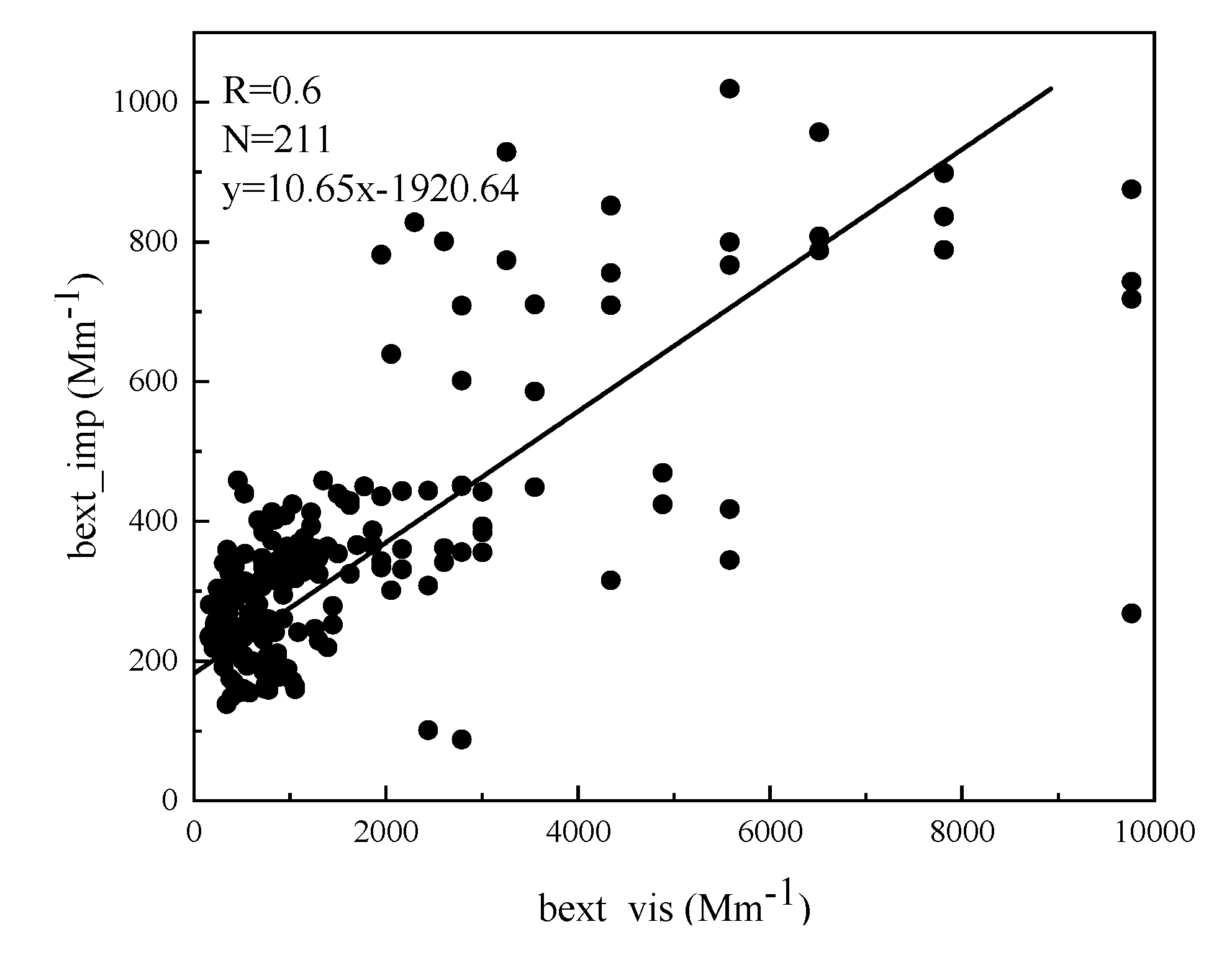
Figure 1 shows the comparison of bext between the two methods, and a fair correlation was observed between the two sets of bext, with a correlation coefficient (R) of 0.6; the number of samples (N) was 211. This finding suggests that the reconstructed bext using the IMPROVE formula can be used for later analysis.
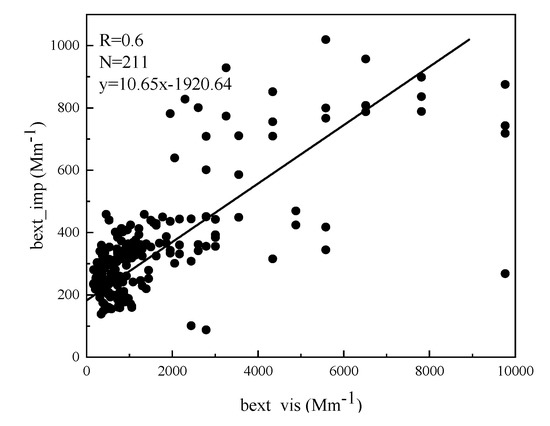
Figure 1.
Relationship of bext based on two methods.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Summary of a Haze Episode
According to newly released ambient air quality standards in 2012, in China, air quality conditions can be classified into five categories. According to PM2.5 mass concentrations from the best to worst were: excellent (PM2.5 mass concentrations < 35 μg⋅m−3), good (35 μg⋅m−3 < PM2.5 mass concentrations < 75 μg⋅m−3), acceptable (75 μg⋅m−3 < PM2.5 mass concentrations < 115 μg⋅m−3), poor (115 μg⋅m−3 < PM2.5 mass concentrations < 150 μg⋅m−3), and bad (PM2.5 mass concentrations > 150 μg⋅m−3). Wuhan experienced a severe pollution event from 18 January to 21 January, during which the hourly average mass concentration of PM2.5 was 170 μg⋅m−3, which was 1.9 times the overall average in January.
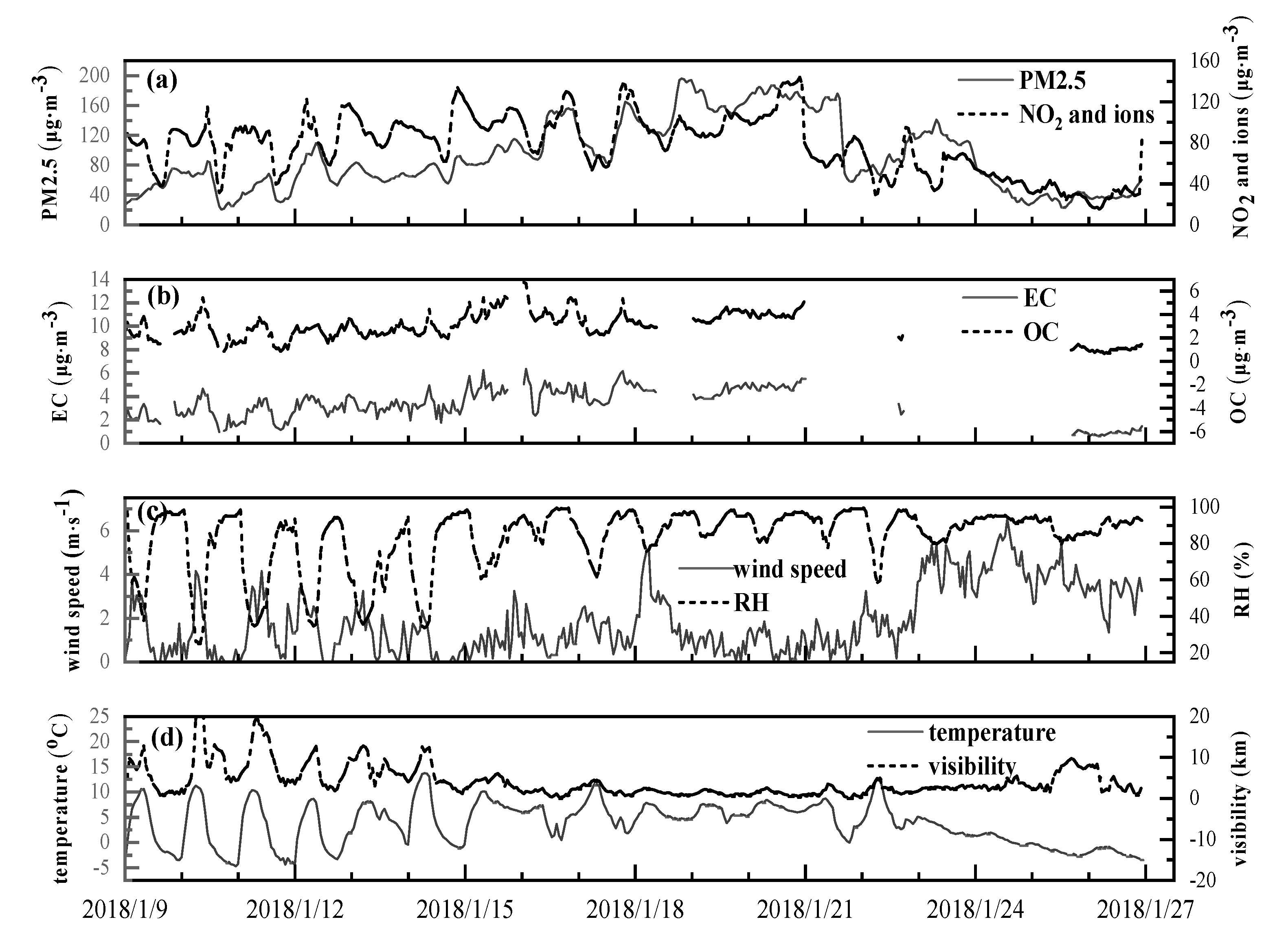
According to Figure 2, the value of PM2.5 mass concentration was moderately low, with an average of 58.9 μg⋅m−3 before 8:00 on 14 January. Excellent and good days were observed during this period. Both the visibility and RH were relatively high, and average values of 7.4 km and 68.9% were observed, respectively. The temperature was as low as 2.8 °C. The mean wind speed was 1.3 m⋅s−1 on average, and the maximum was 4.1 m⋅s−1. The mean values of light scattering components (OC, NO2, and water-soluble ions) and light absorbent components (EC) were 91.5 μg⋅m−3 and 2.7 μg⋅m−3 respectively.
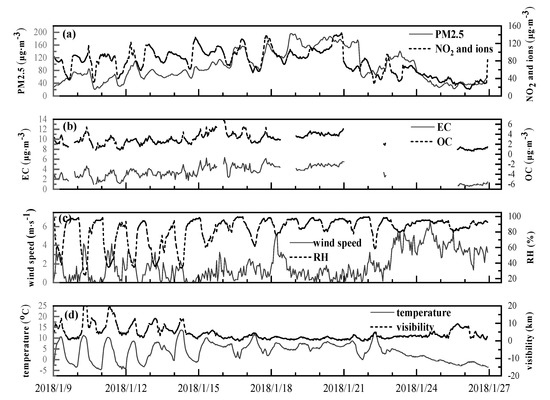
Figure 2.
Time series of meteorological elements (c,d), PM2.5 and its light scattering and absorbent components (a,b) during the observation period.
From 8:00 on 14 January to 16:00 on 18 January, both acceptable and poor days were observed, and the average concentration value of PM2.5 was 109.0 μg⋅m−3. During this period, the temperature was low, and there was a high RH, presenting mean values of 5.3 °C and 84.9%, respectively. The mean value of wind speed remained unchanged at 1.3 m⋅s−1, while the maximum reached 5.1 m⋅s−1. The mean concentration values of light scattering components and light absorbent components increased, with mean values of 108.5 μg⋅m−3 and 4.3 μg⋅m−3, respectively, resulting in a decrease in visibility to 2.5 km.
The mean value of PM2.5 mass concentration increased rapidly to 170.0 μg⋅m−3 from 16:00 on 18 January to 15:00 on 21 January. Wuhan experienced a severe pollution event composed of bad days during this period, which was related to unfavorable climate conditions such as low wind speed and high RH. On one hand, the wind speed reduced to 0.8 m⋅s−1, which is not conducive to the horizontal and vertical diffusion of PM2.5. On the other hand, the average RH reached as high as 91.7%, which was approximately 1.3 times higher than the first period. Increasing RH facilitates the aerosol hygroscopic growth and further enhances the aerosol liquid water, facilitating the secondary aerosols formation by serving as an important medium for liquid-phase and heterogeneous reactions [26]. Therefore, high RH will increase PM2.5 concentrations and worsen pollution. The temperature increased to 6.1 °C. Finally, the sum of the concentrations of light scattering components and light absorbent components reached as high as 124.3 μg⋅m−3, leading to a quick reduction of visibility, with an average of 1 km.
After this severe pollution event, due to the impact of precipitation and high wind speed (3.3 m⋅s−1), the air quality improved rapidly with an average PM2.5 mass concentration of 66.0 μg⋅m−3. The average value of temperature decreased to 1.1 °C as a result of evaporative cooling by precipitation. RH decreased slightly to 89.4%. The mean values of light scattering components and light absorbent components reduced to the same range as seen in the first period. The visibility increased to 3.0 km.
3.2. Optical Properties under Different Pollution Levels
3.2.1. Diurnal Variations of Optical Parameters on Clean and Polluted Days
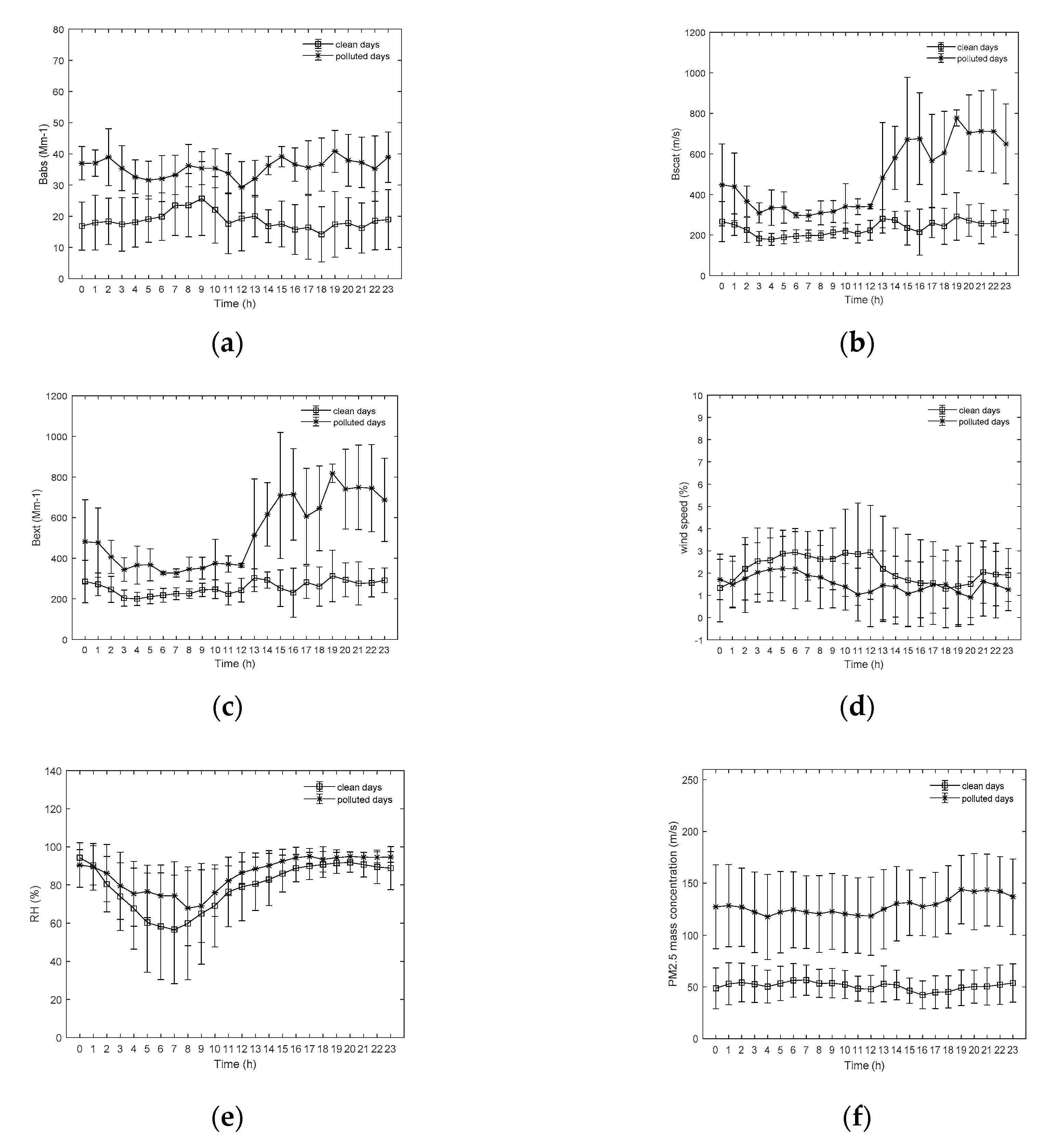
Clean days (PM2.5 mass concentrations < 75 μg⋅m−3) and polluted days (PM2.5 mass concentrations > 75 μg⋅m−3) were defined in order to analyze the influence of meteorological elements on optical properties under different pollution conditions. According to Figure 3, babs peaked at 9:00 on clean days, while it did not vary much on polluted days. bext had an identical diurnal variation to that of bscat on both clean and polluted days. bext presented a unimodal distribution that peaked at 19:00 on polluted days and it was pretty flat on clean days. Clear unimodal diurnal patterns of bext might be related to the evolution of the planetary boundary layer (PBL) and daily pollution emission trends. Since from the sunset, the height of the PBL decreased, and the turbulent mixing weakened due to the decrease of temperature. Therefore, PM2.5 accumulated in the lower atmosphere. In addition, emission from vehicles and factories increased in the evening rush hour, which led to high concentrations of PM2.5. High PM2.5 concentrations led to the increase of bext, which peaked at 19:00. As time passed and temperature increased, the turbulent mixing was enhanced, and the height of the PBL increased, leading to the decrease of PM2.5 concentration and bext values during the daytime. Besides, bscat was pretty low than babs on polluted days in the early morning hours, indicating that more absorbent particles appeared in the morning.
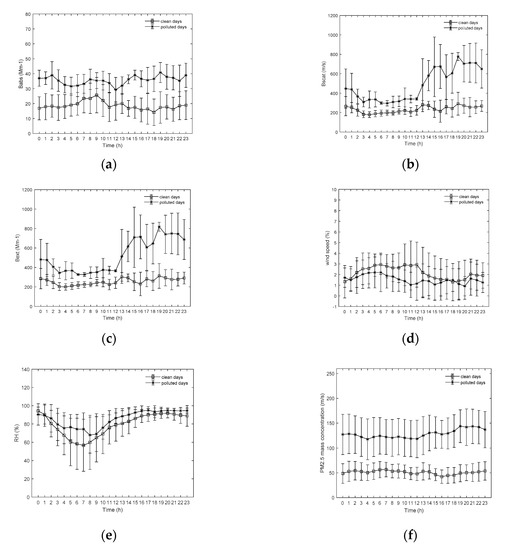
Figure 3.
Diurnal variations of babs (a), bscat (b), bext (c), wind speed (d), relative humidity (RH) (e), and PM2.5 (f) on clean and polluted days.
The diurnal variation of optical parameters on polluted days was quite different from that on clean days. As shown in Figure 3, the values of babs, bscat, and bext on polluted days were higher than those on clean days because the concentration of PM2.5 was higher on polluted days, which means there will be more particles in the atmosphere absorbing and scattering light. Furthermore, according to Figure 3c, bext increased rapidly starting at 12:00 and peaked at 19:00, with a value of 818.1 Mm−1 on polluted days. The value of bext did not change much during the day on clean days. The peak of bext on polluted days was related to meteorological conditions. According to Figure 3, the wind speed decreased significantly starting at 6:00 and continuously decreased from 2.2 m⋅s−1 to 1.0 m⋅s−1 over the next 6 h. Therefore, PM2.5 began to accumulate due to the low wind speeds, leading to a significant increase in PM2.5 concentration at 12:00. RH began increasing at 8:00 and reached 95% at 17:00, after which it remained almost unchanged. With high RH, aerosol liquid water not only augments particle sizes, which enhances aerosol scattering, but also substantially enhances secondary aerosol formation. Therefore, these two factors together led to the rapid increase of PM2.5 concentrations at 12:00.
3.2.2. Analysis of Optical Parameters under Different Pollution Levels
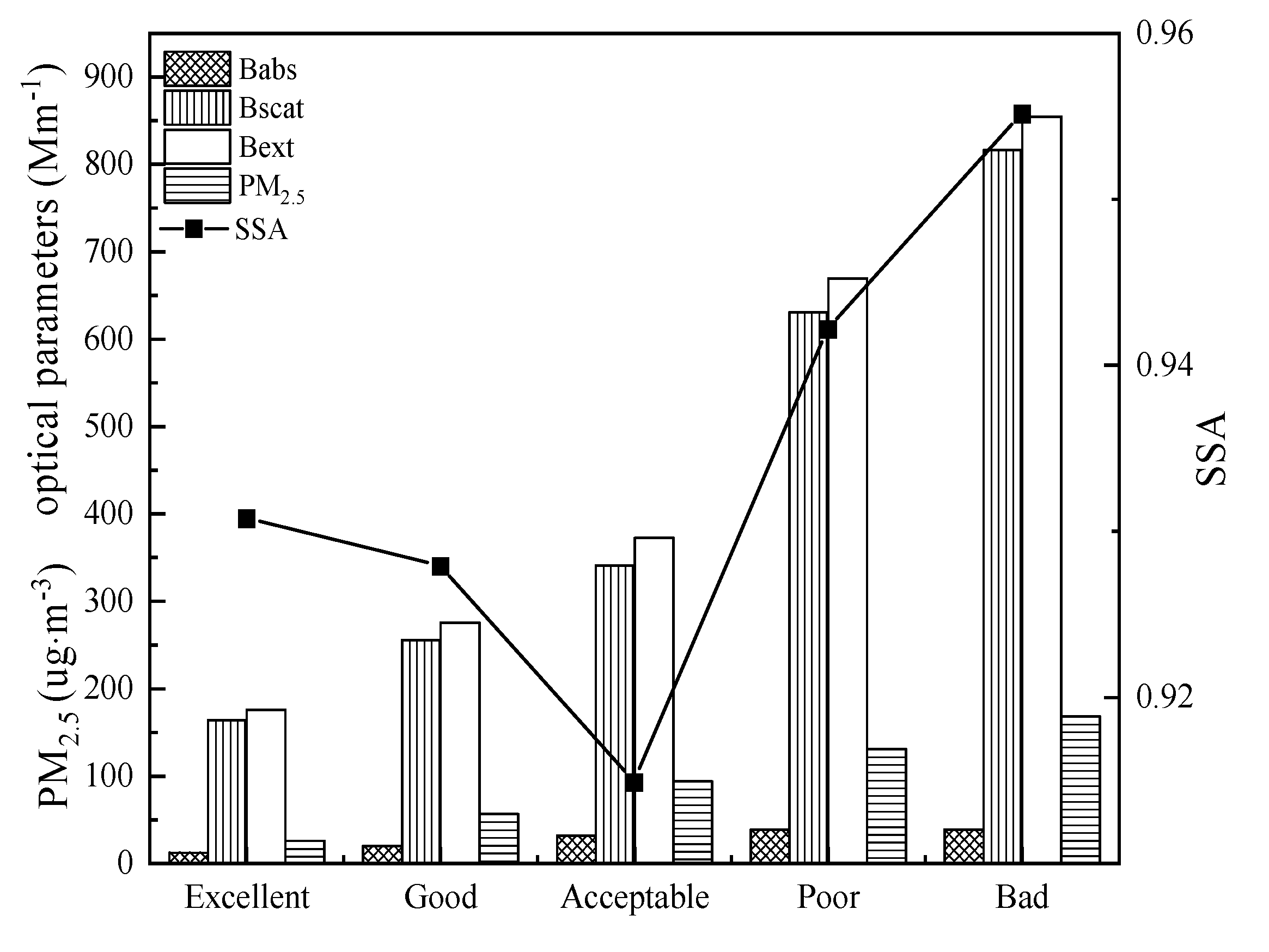
According to Figure 4, PM2.5 mass concentrations increased with pollution levels. The average mass concentrations of PM2.5 were 25.95 μg⋅m−3, 56.53 μg⋅m−3, 93.83 μg⋅m−3, 130.9 3μg⋅m−3, and 168.43 μg⋅m−3 on excellent, good, acceptable, poor, and bad days, respectively. The high levels of PM2.5 led to a rapid increase of bext, the value of which was 854.72 Mm−1 on bad days, which was 4.86, 3.1, 2.29, and 1.28 times that on excellent, good, acceptable, and poor days, respectively. The value of bscat was 816.36 Mm−1 on bad days and was 4.98, 3.19, 2.19, and 1.29 times that on excellent, good, acceptable, and poor days, respectively. The value of babs was 31.72 Mm−1 on acceptable days, which was 1.6 times that on good days. However, as pollution levels continued to increase, the value of babs did not change substantially and was 38.74 Mm−1 and 38.36 Mm−1 on poor and bad days, respectively.
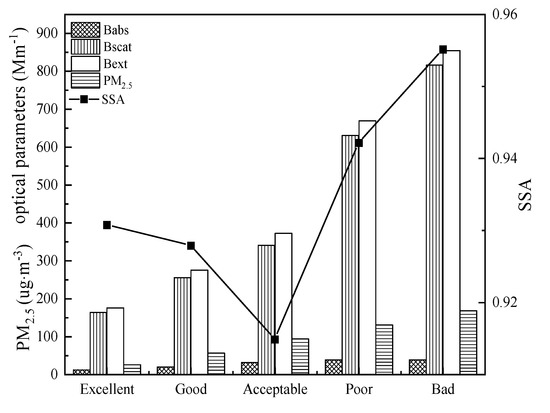
Figure 4.
Evolution of the average values of babs, bscat, bext, PM2.5, and single scattering albedo (SSA) under different pollution levels.
The single scattering albedo (SSA) is the ratio between the aerosol scattering coefficient and the aerosol extinction coefficient, reflecting the relative importance of aerosol scattering and absorption, and it is an important factor affecting global climate change. As shown in Figure 4, the value of SSA varied from 91.5% to 95.5%. The minimum value appeared on acceptable days, indicating an enhancement of absorption ability. SSA value increased with pollution levels on polluted days (including acceptable, poor, and bad days) and reached a maximum of 95.5% on bad days, showing that the contribution of scattering to light extinction was greater for higher pollution levels on polluted days.
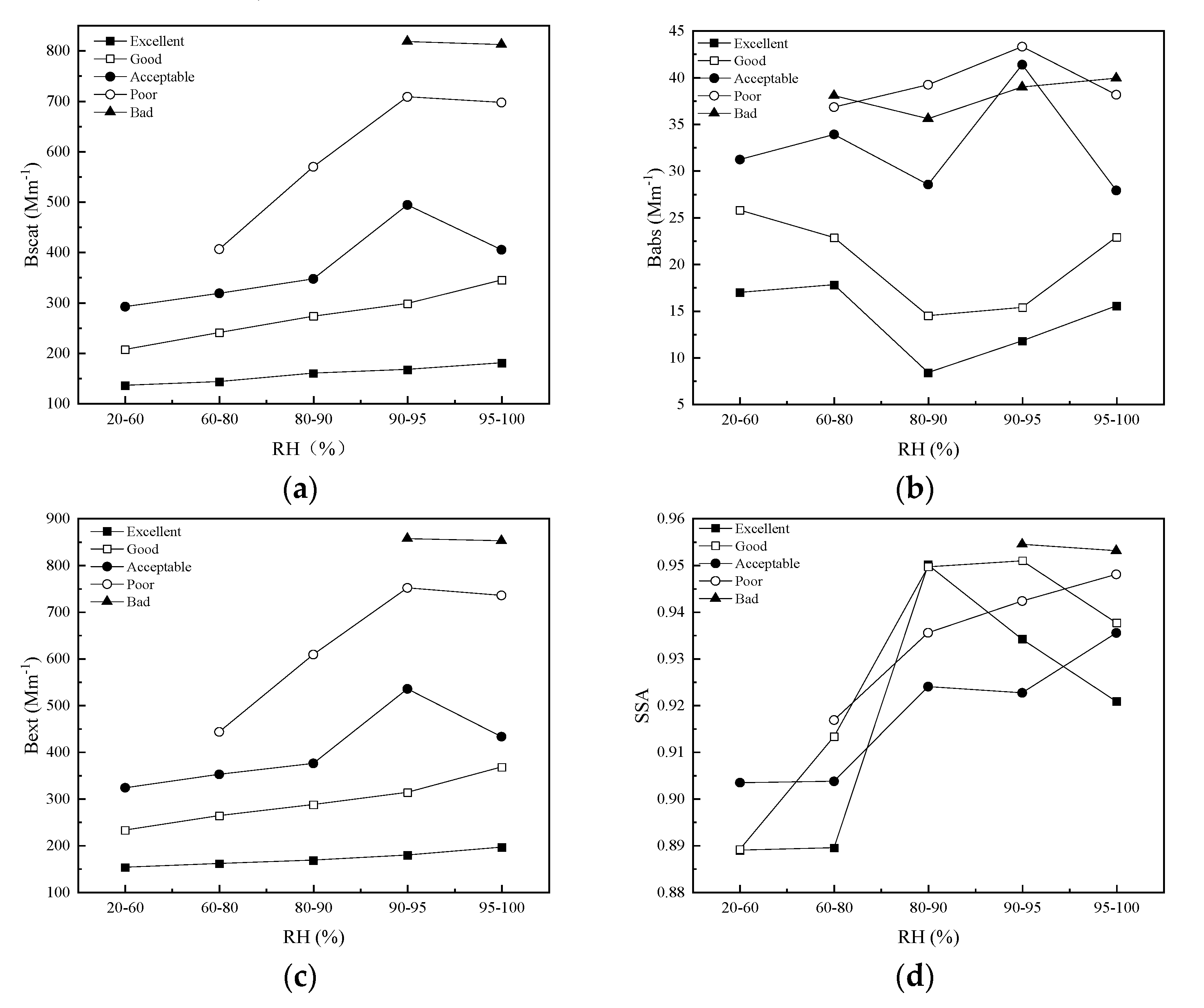
RH is an important factor affecting the optical properties of PM2.5. RH was divided into five sections: 20–60%, 60–80%, 80–90%, 90–95% and 95–100%, in order to analyze the effect of RH on optical properties. According to Figure 5, bscat showed a similar trend as bext. The values of bscat and bext at the same RH range value increased with pollution levels. The growth rate of bscat and bext grew with increasing pollution levels. In addition, bscat and bext under all pollution levels increased with the increase of RH when RH was less than 95%. Many components of atmospheric aerosols are hygroscopic, meaning that they take up water as RH increases, and the sizes and effective radius of particles will be augmented, therefore, aerosol light scattering and extinction will be enhanced [26]. However, bscat and bext began to decrease when RH exceeded 95%.
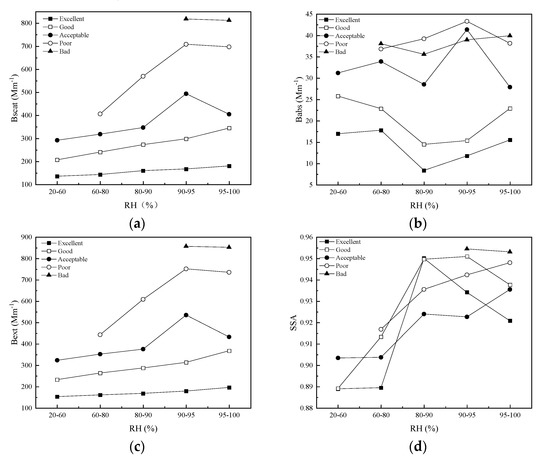
Figure 5.
Variation of bscat (a), babs (b), bext (c), and SSA (d) with RH under different pollution levels.
The babs showed a clear relationship with RH only on excellent and good days (Figure 5b). On excellent and good days, babs decreased with the increase of RH when RH was less than 90% but grew with the increase of RH when RH was more than 90%. The values of SSA under all pollution levels were low when RH was less than 80%, which means the contribution of scattering to light extinction was low (Figure 5d). The maximum of SSA on excellent and good days appeared at the RH range value of 80–90%, while the maximum on acceptable and poor days appeared at 95–100%.
3.2.3. Contribution of PM2.5 Chemical Components to Light Extinction under Different Pollution Levels
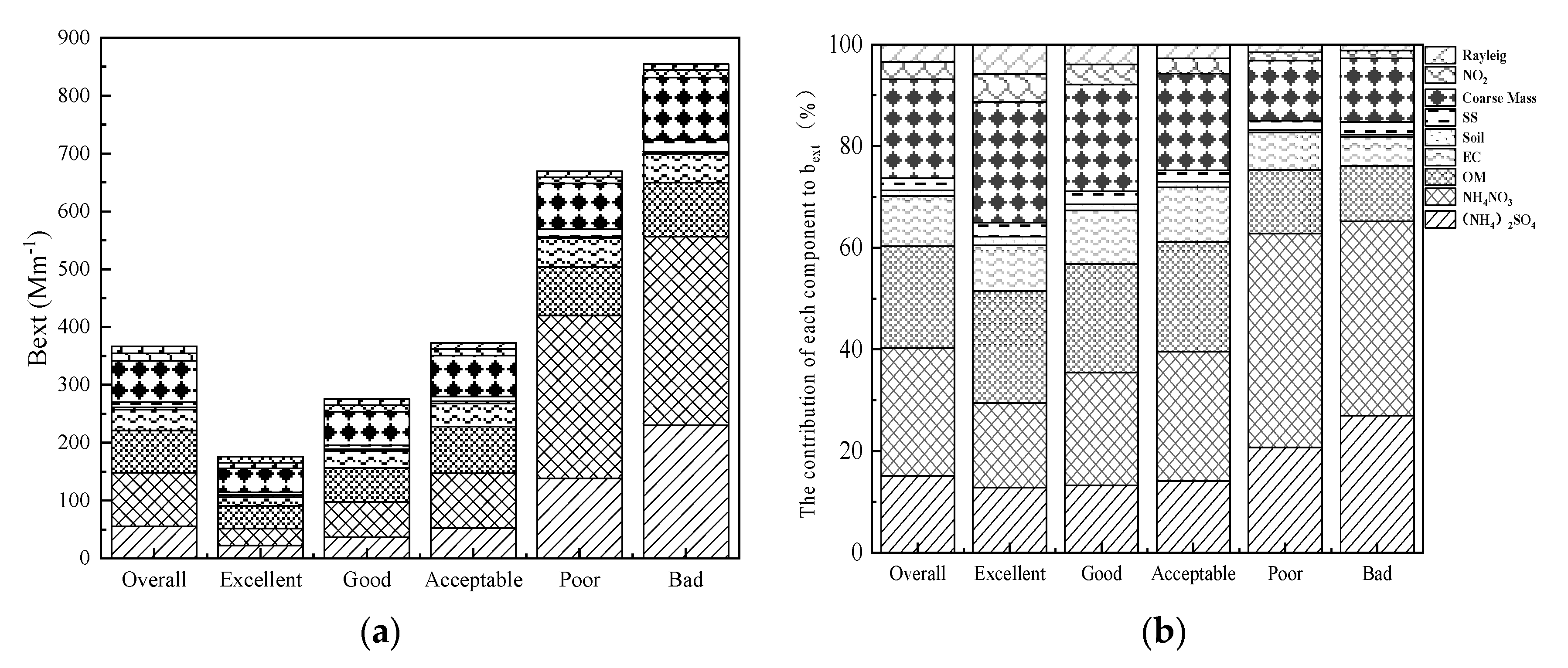
The values of bext and contributions of aerosol chemical components to bext were calculated in order to determine the effect of chemical components on visibility impairment (Figure 6). During the entire study period, the average value of bext was 366.8 Mm−1, and NH4NO3 was the largest contributor to bext, accounting for 25.2%, followed by OM (20.1%), coarse mass (19.4%), (NH4)2SO4 (15.1%), and soil made the smallest contribution, accounting for only 1.1%.
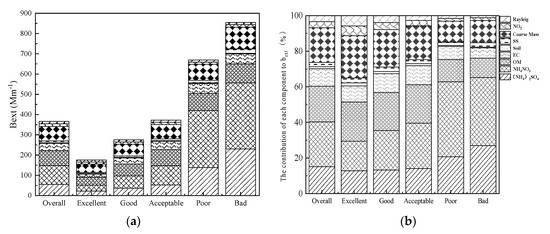
Figure 6.
Variation of bext (a) and relative contributions of each species to bext (b) under different pollution levels.
According to Figure 6a, the value of bext increased with the level of pollution. The value of bext was 854.7 Mm−1 on bad days and was 4.9 and 2.3 times that on excellent days and overall, respectively. In addition, the contribution rate of each chemical component to bext changed as the pollution level increased. OM was the largest contributor to bext on excellent days, accounting for 22.1%, and NH4NO3 and (NH4)2SO4 accounted for 16.7% and 12.8%, respectively. The contribution of NH4NO3 and (NH4)2SO4 to bext increased with pollution level. NH4NO3 contributed the most to bext on poor days, accounting for 42.1%. It was followed by (NH4)2SO4, which accounted for 20.7%. The contribution of OM decreased to 12.5%. The contribution of NH4NO3 to bext decreased slightly from poor days to bad days, but it was still the largest contributor. NH4NO3 was the largest contributor to bext on bad days, accounting for 38.2%, followed by (NH4)2SO4 (27.0%), and the contribution of OM to bext decreased to 10.9%. EC, sea salt, soil, coarse mass, NO2, and Rayleigh made a minor contribution, together accounting for 23.9%.
NH4NO3 and (NH4)2SO4 were the major components of light extinction in Wuhan, indicating that NH4NO3 and (NH4)2SO4 played an important role in visibility impairment. The other chemical components, such as OM, EC, sea salt, coarse mass, and so on, were not the major factors affecting visibility on polluted days since their contribution decreased significantly on poor and bad days.
4. Conclusions
The optical properties of PM2.5 and the influence of meteorological parameters under different pollution levels were studied in Wuhan in January 2018. Wuhan experienced a severe pollution event from 18 January to 21 January, during which time the average concentration value of PM2.5 was 170 μg⋅m−3, which was 1.9 times the overall average in January. bext showed a unimodal distribution on polluted days, peaking at 19:00. bext was larger on polluted days than on clean days for the whole day. bext on clean days did not change much during the day. On polluted days, bext increased significantly starting at 12:00 and occurred along with adverse meteorological factors, including a decrease in wind speed and an increase in RH. The value of bext increased with pollution level and was 854.72 Mm−1 on bad days, which was 4.86, 3.1, 2.29, and 1.28 times that on excellent, good, acceptable, and poor days, respectively. The value of SSA varied from 91.5% to 95.5%, increasing with pollution levels on polluted days. bext and bscat under all pollution levels increased with RH when RH was less than 95%. When RH exceeded 95%, bext and bscat began to decrease on acceptable, poor and bad days, but they still increased on excellent and good days. NH4NO3 was the largest contributor to overall bext, accounting for 25.2%, followed by OM (20.1%), while the contribution of soil was the lowest, accounting only for 1.1%. It is apparent that the contribution of (NH4)2SO4 and NH4NO3 to bext was much higher with increasing pollution levels. NH4NO3 contributed the most to bext on bad days, accounting for 38.2%, followed by (NH4)2SO4 (27.0%), and the contribution of OM to bext reduced to 10.9%.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.W.; Methodology, Y.T., Y.Y., and D.B.; Visualization, Z.W., J.W., and D.B.; Investigation, D.B., X.K., and L.S.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, D.B. and S.G.; and Writing—Review and Editing, D.B., B.Z., L.S., and H.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91644224, 41805096 and 41905026), the special fund of State Key Joint Laboratory of Environment Simulation and Pollution Control (19K03ESPCP), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20180801) and the Natural Science Research Project for Universities of Jiangsu Province, China (18KJB170011).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fu, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Qi, J.; Dang, E.; Wang, M.; Dong, J. Long-Term Atmospheric Visibility Trends and Characteristics of 31 Provincial Capital Cities in China during 1957–2016. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Hu, B.; Tang, G.; Xin, J.; Song, T.; Wen, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Analysis of heavy pollution episodes in selected cities of northern China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, G.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Song, T.; Ji, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Variability and reduction of atmospheric pollutants in Beijing and its surrounding area during the Beijing 2008 Olympic Games. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ji, D.; Wang, Y. The influence of climate factors, meteorological conditions, and boundary-layer structure on severe haze pollution in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during January 2013. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014, 685971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.F.; Xu, Y.H.; Shi, M.H.; Lian, Y.X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Jing, J.; Tao, J.; Hsu, S.C.; Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Lee, C.S.L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing: Seasonal perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7053–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L. Haze in China: Current and future challenges. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 189, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, C.C.; Day, D.E. Estimates of aerosol species scattering characteristics as a function of relative humidity. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 35, 2845–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysel, M.; Crosier, J.; Topping, D.O.; Whitehead, J.D.; Bower, K.N.; Cubison, M.J.; Williams, P.I.; Flynn, M.J.; McFiggans, G.B.; Coe, H. Closure study between chemical composition and hygroscopic growth of aerosol particles during TORCH2. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 6131–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Cai, T.; Fang, D.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y. Concentrations and chemical compositions of fine particles (PM2.5) during haze and non-haze days in Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2016, 174, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waggoner, A.P.; Weiss, R.E.; Ahlquist, N.C.; Covert, D.S.; Will, S.; Charlson, R.J. Optical characteristics of atmospheric aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 1981, 15, 1891–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitchford, M.; Malm, W.; Schichtel, B.; Kumar, N.; Lowenthal, D.; Hand, J. Revised Algorithm for Estimating Light Extinction from IMPROVE Particle Speciation Data. J. Air Waste Manag. 2012, 57, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Song, I.H.; Park, J.S.; Oh, J.; Moon, K.J.; Shin, H.J.; Ahn, J.Y.; Lee, M.D.; Kim, J.; Lee, J. Variation of PM2.5 Chemical Compositions and their Contributions to Light Extinction in Seoul. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, G.; Tian, M.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Cao, X. Aerosol optical properties and chemical composition apportionment in Sichuan Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Du, W.; Chen, J. Optical properties of PM2.5 and the impacts of chemical compositions in the coastal city Xiamen in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Yan, P. Impacts of aerosol chemical compositions on optical properties in urban Beijing, China. Particuology 2015, 18, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Ho, K.; Zhang, R.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, M.; Cao, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, G. Impact of PM2.5 chemical compositions on aerosol light scattering in Guangzhou—The largest megacity in South China. Atmos. Res. 2014, 135, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, M.H.; Cass, G.R.; Xu, J.; Fang, C.; Zeng, L.M.; Yu, T.; Salmon, L.G.; Kiang, C.S.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; et al. Aerosol radiative, physical, and chemical properties in Beijing during June 1999. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 17969–17980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tian, M.; Li, X.; Chang, Q.; Cao, J.; Yang, F.; Ma, Y.; He, K. Chemical Composition and Light Extinction Contribution of PM2.5 in Urban Beijing for a 1-Year Period. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 2200–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lai, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, D.; Zheng, J.; Zhong, L.; Lee, S.C.; Chen, B. Reconstructed Light Extinction Coefficients of Fine Particulate Matter in Rural Guangzhou, Southern China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Wiedensohler, A.; Eichler, H.; Su, H.; Gnauk, T.; Brüggemann, E.; Heintzenberg, J.; Slanina, J.; Tuch, T.; Hu, M.; et al. Aerosol optical properties and related chemical apportionment at Xinken in Pearl River Delta of China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6351–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Qi, L.; Wang, L. An intensive study on aerosol optical properties and affecting factors in Nanjing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 40, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Shu, Z. The effect of relative humidity on the tropospheric aerosol extinction coefficient with typical underlying surfaces based on CALIPSO data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 39, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skupin, A.; Ansmann, A.; Engelmann, R.; Seifert, P.; Müller, T. Four-year long-path monitoring of ambient aerosol extinction at a central European urban site: Dependence on relative humidity. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1863–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y. Control of PM2.5 in Guangzhou during the 16th Asian Games period: Implication for hazy weather prevention. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bei, N.; Hu, B.; Liu, S.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Feng, T.; et al. Is water vapor a key player of the wintertime haze in North China Plain? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8721–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Zhu, B.; Su, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F. Analysis of a long-lasting haze episode in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Res. 2013, 120, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Kumar, K.R.; Lu, R.; Ma, J. Changes in column aerosol optical properties during extreme haze-fog episodes in January 2013 over urban Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Wu, Y.; Tao, J.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhang, X.; Yan, P.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, L. Observation and analysis of near-surface atmospheric aerosol optical properties in urban Beijing. Particuology 2015, 18, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Hsu, S.C.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, R. Characterization and source apportionment of aerosol light extinction in Chengdu, southwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Hu, M.; Tan, Q.; Feng, M.; Qu, Y.; An, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cheng, N. Aerosol optical properties under different pollution levels in the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region of China. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 87, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Estelles, V.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; et al. Column aerosol optical properties and aerosol radiative forcing during a serious haze-fog month over North China Plain in 2013 based on ground-based sunphotometer measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.Y.; Wang, X.L. Analysis of the Characteristics of Haze and its Pollutants in Wuhan. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1073, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.W.; Cheng, H.R.; Lv, X.P.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.M.; Zhang, G. Seasonal variations and chemical characteristics of PM2.5 in Wuhan, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Tang, X.; Wang, Z.; Gbaguidi, A.; Liang, S.; Hu, K.; Wu, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, Z.; Shen, L. Source tagging modeling study of heavy haze episodes under complex regional transport processes over Wuhan megacity, Central China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231 Pt 1, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongejan, P.A.C.; Bai, Y.; Veltkamp, A.C.; Wyers, G.P.; Slanina, J. An automated field instrument for the determination of acidic gases in air. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1997, 66, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, B.; Mo, H.; Yan, Z.; Chong, S.L.; Heng, A.K.; Webster, R.D. Simultaneous online monitoring of inorganic compounds in aerosols and gases in an industrialized area. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. Guideline on Speciated Particulate Monitoring; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; Volume 3–7, pp. 4–37. [Google Scholar]
- Rumsey, I.C.; Cowen, K.A.; Walker, J.T.; Kelly, T.J.; Hanft, E.A.; Mishoe, K.; Rogers, C.; Proost, R.; Beachley, G.M.; Lear, G.; et al. An assessment of the performance of the Monitor for AeRosols and GAses in ambient air (MARGA): A semi-continuous method for soluble compounds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5639–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.S.; Schauer, J.J.; DeMinter, J.T.; Turner, J.R.; Smith, D.; Cary, R.A. Validation of a semi-continuous instrument for elemental carbon and organic carbon using a thermal-optical method. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.J.; Yu, X.Y.; Cary, R.; Laulainen, N.; Berkowitz, C. Characterization of the sunset semi-continuous carbon aerosol analyzer. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 59, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, O.; Chand, D.; Andreae, M.O. Aerosol optical properties in urban Guangzhou. In Proceedings of the PRD Workshop, Beijing, China, 13–14 January 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Koschmieder, H. Theorie der horizontalen Sichtweite. Beitrage zur Physik der freien Atmosphare 1924, 1924, 33–53. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).