Spatial Particulate Fields during High Winds in the Imperial Valley, California
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Routine Data
2.2. High Resolution Data
2.2.1. IVAN
2.2.2. MAIAC
2.2.3. Sediment Supply
2.3. Method
3. Results and Discussion
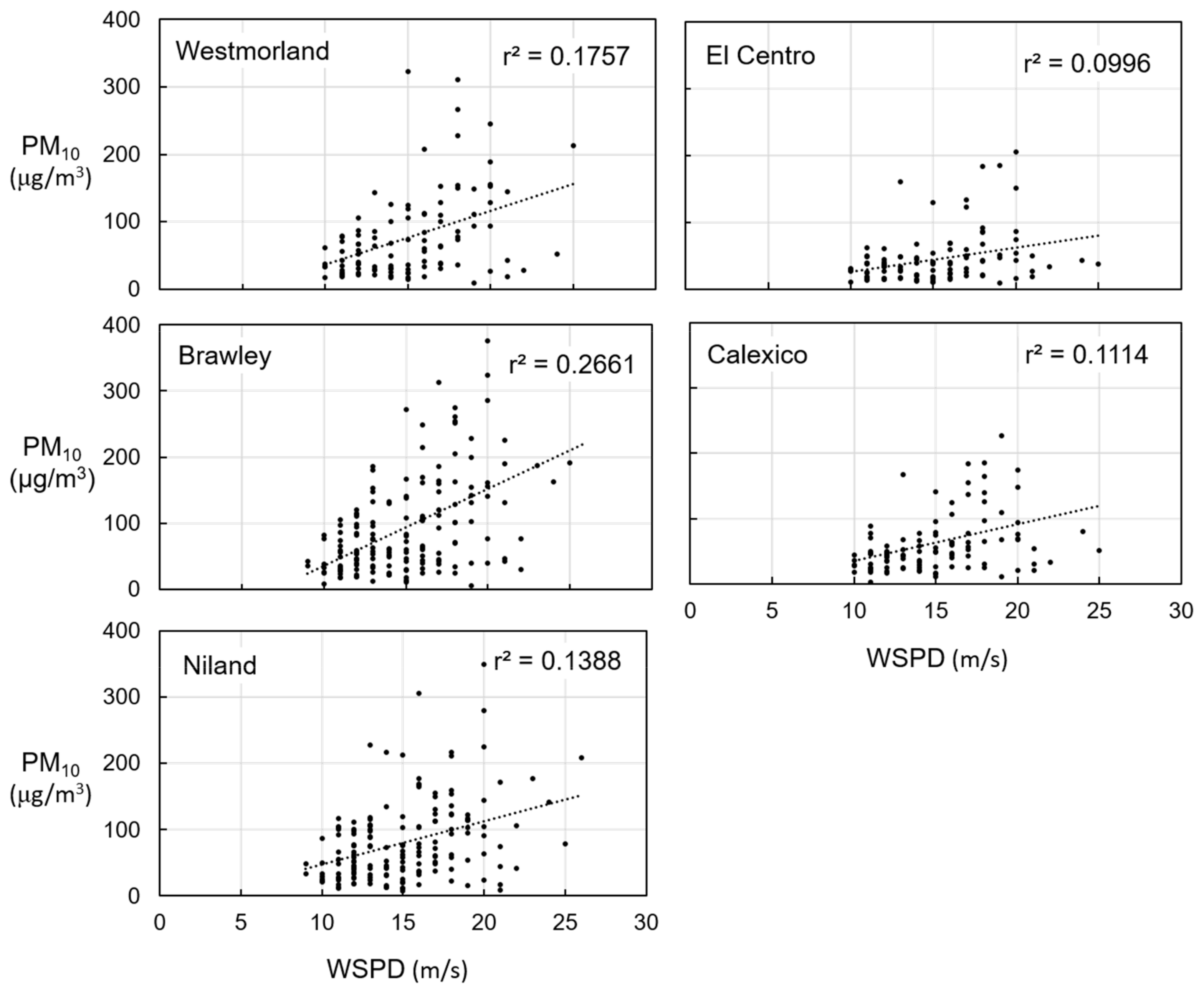
3.1. Routine Analysis
3.2. Detailed Analysis: IVAN, MAIAC, Sediment Supply
3.3. Discussion: Source Areas and Dust Emissions
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Chronology of State PM10 Designations. Available online: https://www.arb.ca.gov/desig/changes/pm10.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- Annual Report on the California Air Resources Board’s Fine Particulate Monitoring Program. Available online: https://www.arb.ca.gov/research/apr/reports/pm25-monitoring-2018.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- Tracking California, Public Health Institute. Asthma Related Emergency Department & Hospitalization data: Asthma. Available online: www.trackingcalifornia.org/asthma/query (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Wong, H.; Lau, Y. Association between air pollution and asthma admission among children in Hong Kong. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2006, 36, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adar, S.P.; Filigrana, N.; Clements, J.P. Ambient Coarse Particulate Matter and Human Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cur. Environ. Health Rep. 2014, 1, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crooks, L.J.; Cascio, E.W.; Percy, S.M.; Reyes, J.; Neas, M.L.; Hilborn, D.E. The association between dust storms and daily non-accidental mortality in the United States, 1993–2005. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, M.B.; Mittleman, M.A. Dust storms, heart attacks, and protecting those at risk. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 3209–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CDC. Increase in reported coccidioidomycosis--United States, 1998–2011. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 217. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, D.Q.; Wang, J.X.; Gill, T.E.; Lei, H.; Wang, B. Intensified dust storm activity and Valley fever infection in the southwestern United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 4304–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Green, M.C.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Bates, B.; Oslund, W.; Torres, G. Cross-border transport and spatial variability of suspended particles in Mexicali and California’s Imperial Valley. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Casuccio, G. Spectral imaging and passive sampling to investigate particle sources in urban desert regions. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.; Etyemezian, V.; Sweeney, M.; Buck, B.J.; Nikolich, G. Dust emission variability at the Salton Sea, California, USA. Aeolian Res. 2011, 3, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, B.J.; King, J.; Etyemezian, V. Effects of Salt Mineralogy on Dust Emissions, Salton Sea, California. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 71, 1971–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, M.J. Hazard’s Toll: The Cost of Inaction at the Salton Sea. Pacific Institute, September 2014. Available online: https://pacinst.org/publication/hazards-toll/ (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Frie, A.L.; Dingle, J.H.; Ying, S.C.; Bahreini, R. The Effect of a Receding Saline Lake (The Salton Sea) on Airborne Particulate Matter Composition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8283–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parajuli, S.P.; Zender, C.S. Projected changes in dust emissions and regional air quality due to the shrinking Salton Sea. Aeolian Res. 2018, 33, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.; Razafy, M.; Lugo, H.; Olmedo, L.; Farzan, S.F. The Disappearing Salton Sea: A Critical Reflection on the Emerging Environmental Threat of Disappearing Saline Lakes and Potential Impacts on Children’s Health. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICAPCD. High Wind Exceptional Event Fugitive Dust Mitigation Plan for Imperial County. 2019. Available online: https://www.co.imperial.ca.us/AirPollution/otherpdfs/MitigationPlan.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- English, P.B.; Olmedo, L.; Bejarano, E.; Lugo, H.; Murillo, E.; Seto, E.; Wong, M.; King, G.; Wilkie, A.; Meltzer, D.; et al. The Imperial County Community Air Monitoring Network: A Model for Community-based Environmental Monitoring for Public Health Action. Environ. Health Per. 2017, 125, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvlin, G.N.; Lugo, H.; Olmedo, L.; Bejarano, E.; Wilkie, A.; Meltzer, D.; Wong, M.; King, G.; Northcross, A.; Jerrett, M.; et al. Development and field validation of a community-engaged particulate matter air quality monitoring network in Imperial, California, USA. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.; Bejarano, E.; Carvlin, G.; Fellows, K.; King, G.; Lugo, H.; Jerrett, M.; Meltzer, D.; Northcross, A.; Olmedo, L.; et al. Combining Community Engagement and Scientific Approaches in Next-Generation Monitor Siting: The Case of the Imperial County Community Air Network. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Health 2018, 15, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS Collection 6 MAIAC algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parajuli, S.P.; Zender, C.S. Connecting geomorphology to dust emission through high-resolution mapping of global land cover and sediment supply. Aeolian Res. 2017, 27, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Air Resources Board, Air Quality and Meteorological Information System. Available online: https://www.arb.ca.gov/aqmis2/aqmis2.php (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- Mesowest. Available online: https://mesowest.utah.edu/ (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- LAADS DAAC, Multi-Angle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC). Available online: https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/missions-and-measurements/science-domain/maiac (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- Mesinger, F.; DiMego, G.; Kalnay, E.; Mitchell, K.; Shafran, P.C.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Jović, D.; Woollen, J.; Rogers, E.; Berbery, E.H.; et al. North American Regional Reanalysis. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2006, 87, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Hoff, R.M.; Engle-Cox, J.A. The Relation between Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Aerosol Optical Depth and PM2.5 over the United States: A Geographical Comparison by U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Regions. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 1358–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Chatfield, R.C.; Strawa, A.W. Enhancing the Applicability of Satellite Remote Sensing for PM2.5 Estimation Using MODIS Deep Blue AOD and Land Use Regression in California, United States. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2016, 50, 6546–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahangar, F.E.; Freedman, F.R.; Venkatram, A. Using Low-Cost Air Quality Sensor Networks to Improve the Spatial and Temporal Resolution of Concentration Maps. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Health 2019, 16, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kloog, I.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Lyapustin, A.; Coull, B.; Wang, Y.; Just, A.C.; Schwartz, J.; Broday, D.M. Estimating daily PM2.5 and PM10 across the complex geo-climate region of Israel using MAIAC satellite based AOD data. Atmos. Environ. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, J.G.; Zhu, T.; Chow, J.C.; Engelbrecht, J.; Fujita, E.M.; Wilson, W.E. Receptor modeling application framework for particle source apportionment. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 1093–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, P.; Doraiswamy, P.; Levy, R.; Pikelnaya, O.; Maibach, J.; Feenstra, B.; Polidori, A.; Kiros, F.; Mills, K.C. Impact of California Fires on Local and Regional Air Quality: The Role of a Low-Cost Sensor Network and Satellite Observations. Geohealth 2018, 2, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Data | Sites | Time Period |
|---|---|---|
| Routine PM10–hourly (BAMS) 1 | Niland-English Ed. | 2013–2019 |
| Westmorland | 2016–2019 | |
| Brawley | 2013–2019 | |
| El Centro | 2016–2019 | |
| Calexico | 2016–2019 | |
| Routine PM2.5–daily (Gravimetric) 1 | Brawley | 2013–2019 |
| El Centro | 2013–2019 | |
| Calexico | 2013–2019 | |
| Routine PM2.5–hourly (BAMS) 1 | Niland-English Rd. | 2016–2017 |
| Calexico | 2014–2017 | |
| IVAN PM2.5–hourly (Modified DYLOS 1700 particle counts 2) | See Figure 1 for locations | 2016 (14 sites) 2017 (29 sites) |
| WSW | ||||||
| Year | Number of Days | WSPD (mph) | WDIR (deg) | PM10 (μg/m3) | Number of AOD-PM2.5 Pairs (IVAN) | Number of AOD-PM10 Pairs (Routine) |
| 2014 | 11 | 18 | 234 | 130 | - | 19 over 2 sites |
| 2015 | 2 | 21 | 265 | 230 | - | 2 over 1 site |
| 2016 | 11 | 17 | 248 | 139 | 99 over 11 sites | 46 over 5 sites |
| 2017 | 7 | 18 | 259 | 85 | 149 over 29 sites | 32 over 5 sites |
| Total/Avg | 31 | 18 | 247 | 130 | 248 over 29 sites | 99 over 5 sites |
| SE | ||||||
| Year | Number of Days | WSPD (mph) | WDIR (deg) | PM10 (μg/m3) | Number of AOD-PM2.5 Pairs (IVAN) | Number of AOD-PM10 Pairs (Routine) |
| 2014 | 13 | 6 | 125 | 36 | - | 20 over 2 sites |
| 2015 | 12 | 7 | 100 | 29 | - | 16 over 2 sites |
| 2016 | 12 | 7 | 104 | 32 | 108 over 11 sites | 55 over 5 sites |
| 2017 | 10 | 8 | 106 | 30 | 240 over 29 sites | 49 over 5 sites |
| Total/Avg | 47 | 7 | 108 | 32 | 348 over 29 sites | 140 over 5 sites |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freedman, F.R.; English, P.; Wagner, J.; Liu, Y.; Venkatram, A.; Tong, D.Q.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Chatfield, R.; Rivera, A.; et al. Spatial Particulate Fields during High Winds in the Imperial Valley, California. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010088
Freedman FR, English P, Wagner J, Liu Y, Venkatram A, Tong DQ, Al-Hamdan MZ, Sorek-Hamer M, Chatfield R, Rivera A, et al. Spatial Particulate Fields during High Winds in the Imperial Valley, California. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(1):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010088
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreedman, Frank R., Paul English, Jeff Wagner, Yang Liu, Akula Venkatram, Daniel Q. Tong, Mohammad Z. Al-Hamdan, Meytar Sorek-Hamer, Robert Chatfield, Ana Rivera, and et al. 2020. "Spatial Particulate Fields during High Winds in the Imperial Valley, California" Atmosphere 11, no. 1: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010088
APA StyleFreedman, F. R., English, P., Wagner, J., Liu, Y., Venkatram, A., Tong, D. Q., Al-Hamdan, M. Z., Sorek-Hamer, M., Chatfield, R., Rivera, A., & Kinney, P. L. (2020). Spatial Particulate Fields during High Winds in the Imperial Valley, California. Atmosphere, 11(1), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010088








