Rainwater Chemistry Reveals Air Pollution in a Karst Forest: Temporal Variations, Source Apportionment, and Implications for the Forest
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
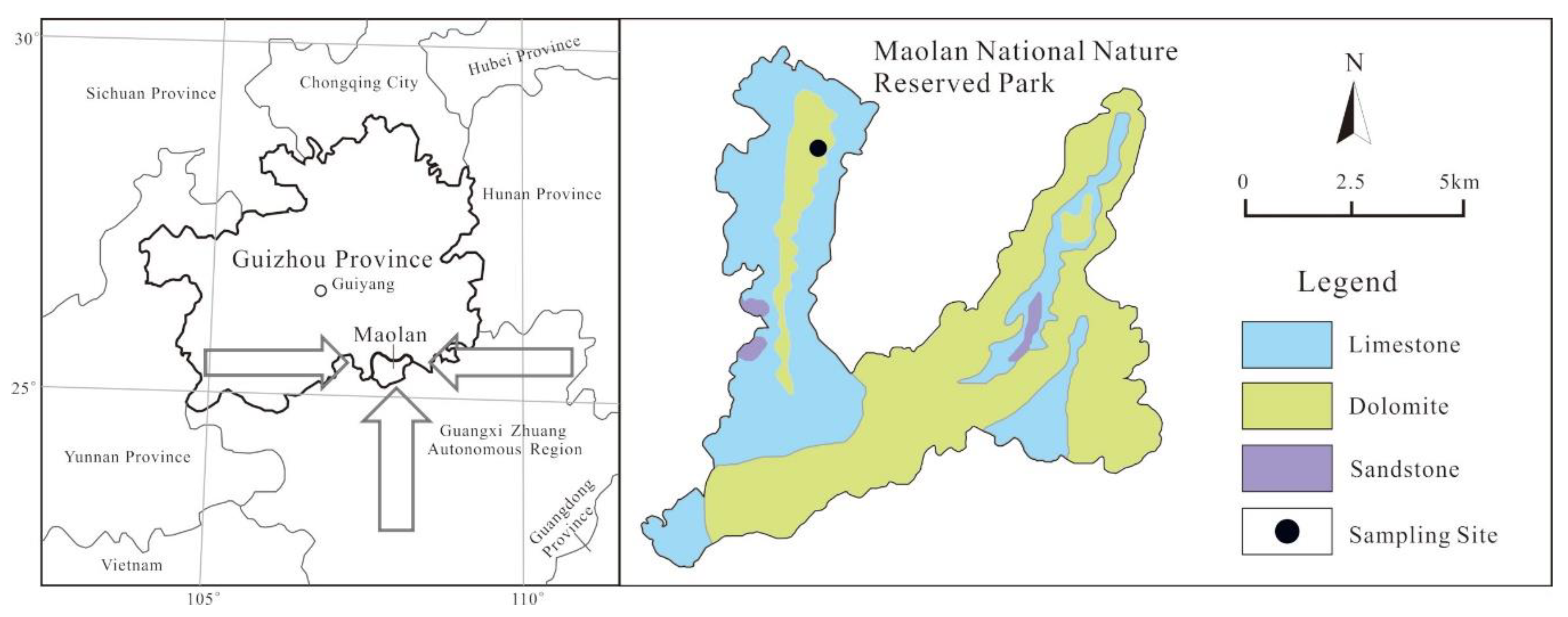
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Measurement and Quality Control
2.3. Data Processing Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rainfall Amount and pH Distribution
3.2. Ion Compositions and Temporal Variations
3.2.1. Overview of Ion Compositions
3.2.2. Temporal Variations
3.3. Source of the Rainwater Ions
3.3.1. Source Identification
3.3.2. Source Contributions
3.4. Trends in Acidifying and Neutralizing Potential
3.5. Ions Deposition Flux and Potential Environmental Effects
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Sun, L.; Huang, W.; Xue, W.; Fan, T.; Cribb, M. Satellite-Derived 1-km-Resolution PM1 Concentrations from 2014 to 2018 across China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13265–13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, E.H.; Nogarotto, D.C.; Mortatti, J.; Pozza, S.A. Chemical composition of rainwater in an urban area of the southeast of Brazil. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Han, G.; Tao, F.; Tang, Y. Chemical composition of rainwater in a karstic agricultural area, Southwest China: The impact of urbanization. Atmos. Res. 2012, 111, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szép, R.; Mateescu, E.; Niță, I.-A.; Birsan, M.-V.; Bodor, Z.; Keresztesi, Á. Effects of the Eastern Carpathians on atmospheric circulations and precipitation chemistry from 2006 to 2016 at four monitoring stations (Eastern Carpathians, Romania). Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.; Ramos, A.; Freitas, S.; Silva Dias, M.A.; Massambani, O. In-cloud and below-cloud numerical simulation of scavenging processes at Serra Do Mar region, SE Brazil. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5245–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.W.; Xiao, H.Y.; Long, A.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, C.Q. Chemical composition and source apportionment of rainwater at Guiyang, SW China. J. Atmos. Chem. 2013, 70, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larssen, T.; Lydersen, E.; Tang, D.; He, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, H.; Duan, L.; Seip, H.M.; Vogt, R.D.; Mulder, J.; et al. Acid Rain in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Y. Effects of agricultural alkaline substances on reducing the rainwater acidification: Insight from chemical compositions and calcium isotopes in a karst forests area. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 290, 106782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchini Cerqueira, M.R.; Pinto, M.F.; DeRossi, I.N.; Esteves, W.T.; Rachid Santos, M.D.; Costa Matos, M.A.; Lowinsohn, D.; Matos, R.C. Chemical characteristics of rainwater at a southeastern site of Brazil. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keresztesi, Á.; Nita, I.-A.; Birsan, M.-V.; Bodor, Z.; Szép, R. The risk of cross-border pollution and the influence of regional climate on the rainwater chemistry in the Southern Carpathians, Romania. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 9382–9402. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cereceda-Balic, F.; De La Gala-Morales, M.; Palomo-Marín, R.; Fadic, X.; Vidal, V.; Funes, M.; Rueda-Holgado, F.; Pinilla-Gil, E. Spatial distribution, sources, and risk assessment of major ions ad trace elements in rainwater at Puchuncaví Valley, Chile: The impact of industrial activities. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-M.; Seo, B.-K.; Lee, G.; Kahng, S.-H.; Jang, Y.W. Chemical Composition of Water Soluble Inorganic Species in Precipitation at Shihwa Basin, Korea. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 732–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liang, C.-S.; Ji, J.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X. Chemical composition of rainwater and the acid neutralizing effect at Beijing and Chizhou city, China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 164, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.D.; Madhavan, B.L.; Ratnam, M.V. Source apportionment of rainwater chemical composition to investigate the transport of lower atmospheric pollutants to the UTLS region. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Kang, S.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cong, Z. Wet precipitation chemistry at a high-altitude site (3,326 m a.s.l.) in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5013–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yue, F.-J.; Wang, Z.-J.; Wu, Q.; Qin, C.-Q.; Li, S.-L. Quantifying depression trapping effect on rainwater chemical composition during the rainy season in karst agricultural area, southwestern China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 218, 116998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, E.; Deng, Y. Trace Elements in Atmospheric Wet Precipitation in the Detroit Metropolitan Area: Levels and Possible Sources. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yue, F.-J.; Li, S.-L.; Wang, Z.-J.; Wu, Q.; Qin, C.-Q.; Yan, Z.-L. Determining rainwater chemistry to reveal alkaline rain trend in Southwest China: Evidence from a frequent-rainy karst area with extensive agricultural production. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, G.; Zhang, Q. Effects of agricultural abandonment on soil aggregation, soil organic carbon storage and stabilization: Results from observation in a small karst catchment, Southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 288, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Tang, Y.; Liu, M.; Van Zwieten, L.; Yang, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Song, Z. Carbon-nitrogen isotope coupling of soil organic matter in a karst region under land use change, Southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 301, 107027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G. Tracing zinc sources with Zn isotope of fluvial suspended particulate matter in Zhujiang River, southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Han, X.; Lang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Li, S. The abatement of acid rain in Guizhou province, southwestern China: Implication from sulfur and oxygen isotopes. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Li, S.-L.; Yue, F.-J.; Qin, C.-Q.; Buckerfield, S.; Zeng, J. Rainfall driven nitrate transport in agricultural karst surface river system: Insight from high resolution hydrochemistry and nitrate isotopes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 291, 106787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Li, S.; Waldron, S.; Yue, F.-J.; Wang, Z.-J.; Zhong, J.; Ding, H.; Liu, C.-Q. High-frequency monitoring reveals how hydrochemistry and dissolved carbon respond to rainstorms at a karstic critical zone, Southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, S.; Zhong, J.; Li, C. Spatial scale effects of the variable relationships between landscape pattern and water quality: Example from an agricultural karst river basin, Southwestern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 300, 106999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, F.-J.; Li, S.-L.; Waldron, S.; Wang, Z.-J.; Oliver, D.M.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.-Q. Rainfall and conduit drainage combine to accelerate nitrate loss from a karst agroecosystem: Insights from stable isotope tracing and high-frequency nitrate sensing. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G. Preliminary copper isotope study on particulate matter in Zhujiang River, southwest China: Application for source identification. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, P.; Han, G.; Wu, Q. Chemical characteristics of rainwater in karst rural areas, Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Acta Geochim. 2017, 36, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yang, T.; Tian, J. Atmospheric wet deposition of nitrogen in a subtropical watershed in China: Characteristics of and impacts on surface water quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8489–8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siudek, P.; Frankowski, M.; Siepak, J. Seasonal variations of dissolved organic carbon in precipitation over urban and forest sites in central Poland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11087–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeon, J.; Gautam, M.K.; Kim, I.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Perlman, D.H.J.; Lees, K.S. Isotopic composition of throughfall nitrates in suburban forests with different vegetations. Geosci. J. 2014, 19, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, H.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Pavuluri, C.M.; Wan, X.; Wu, G.; Li, P.; Cao, F.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Kang, S.; et al. Nitrogen Speciation and Isotopic Composition of Aerosols Collected at Himalayan Forest (3326 m a.s.l.): Seasonality, Sources, and Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12247–12256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioda, A.; Mayol-Bracero, O.L.; Scatena, F.N.; Weathers, K.C.; Mateus, V.L.; McDowell, W.H. Chemical constituents in clouds and rainwater in the Puerto Rican rainforest: Potential sources and seasonal drivers. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mulder, J. Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen at five subtropical forested sites in South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 378, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durka, W.; Schulze, E.-D.; Gebauer, G.; Voerkeliust, S. Effects of forest decline on uptake and leaching of deposited nitrate determined from 15N and 18O measurements. Nat. Cell Biol. 1994, 372, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, G.G.; Tang, C.; Fang, H.; Duan, J.; Yu, X. Effects of One-Year Simulated Nitrogen and Acid Deposition on Soil Respiration in a Subtropical Plantation in China. Forests 2020, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amiro, B.D.; Barr, A.G.; Barr, J.G.; Black, T.A.; Bracho, R.; Brown, M.; Chen, J.; Clark, K.L.; Davis, K.J.; Desai, A.R.; et al. Ecosystem carbon dioxide fluxes after disturbance in forests of North America. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Tan, Q. Chemical and strontium isotope characterization of rainwater in karst virgin forest, Southwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Chen, F. Monthly variations in nitrogen isotopes of ammonium and nitrate in wet deposition at Guangzhou, south China. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2309–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Song, Z.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z. Ca and Sr isotope compositions of rainwater from Guiyang city, Southwest China: Implication for the sources of atmospheric aerosols and their seasonal variations. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathee, L.; Guo, J.; Kang, S.; Paudyal, R.; Sharma, C.M.; Huang, J.; Chen, P.; Sharma Ghimire, P.; Sigdel, M.; Sillanpää, M. Measurement of mercury, other trace elements and major ions in wet deposition at Jomsom: The semi-arid mountain valley of the Central Himalaya. Atmos. Res. 2020, 234, 104691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yue, F.-J.; Xiao, M.; Wang, Z.J.; Wu, Q.; Qin, C.-Q. Dissolved organic carbon in rainwater from a karst agricultural area of Southwest China: Variations, sources, and wet deposition fluxes. Atmos. Res. 2020, 245, 105140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y. Chemical composition of precipitation in Shenzhen, a coastal mega-city in South China: Influence of urbanization and anthropogenic activities on acidity and ionic composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiuppa, A.; Bonfanti, P.; D’Alessandro, W. Rainwater Chemistry at Mt. Etna (Italy): Natural and Anthropogenic Sources of Major Ions. J. Atmos. Chem. 2003, 46, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lee, X.; Cao, F.; Huang, D. Seasonal variation and sources of low molecular weight organic acids in precipitation in the rural area of Anshun. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Tan, J.; Shi, Z.; Cai, Y.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Duan, F.; Okuda, T.; Tanaka, S.; Chen, G. Five-year record of atmospheric precipitation chemistry in urban Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2012, 12, 2025–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keresztesi, Á.; Birsan, M.-V.; Nita, I.-A.; Bodor, Z.; Szép, R. Assessing the neutralisation, wet deposition and source contributions of the precipitation chemistry over Europe during 2000–2017. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, F.-J.; Li, S.-L.; Liu, C.-Q.; Lang, Y.; Ding, H. Sources and transport of nitrate constrained by the isotopic technique in a karst catchment: An example from Southwest China. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, R.; Chen, B.; Wang, W. The Concentrations, Formations, Relationships and Modeling of Sulfate, Nitrate and Ammonium (SNA) Aerosols over China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Y. Acid rain and alkalization in southwestern China: Chemical and strontium isotope evidence in rainwater from Guiyang. J. Atmos. Chem. 2011, 68, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špičková, J.; Dobešová, I.; Vach, M.; Skrivan, P.; Mihaljevič, M.; Burian, M. The influence of the limestone-quarry Čertovy schody (Czech Republic) on the precipitation chemistry and atmospheric deposition. Geochemistry 2008, 68, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-S.; Lee, D.-S.; Lim, S.-S.; Kwak, J.-H.; Jeon, B.-J.; Lee, S.-I.; Lee, S.-M.; Choi, W.-J. Nitrogen isotope ratios of dissolved organic nitrogen in wet precipitation in a metropolis surrounded by agricultural areas in southern Korea. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 159, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Han, G.; Tan, H.; Jin, K.; Wang, S.; Chen, T. Chemical and Sr isotopic characteristics of rainwater on the Alxa Desert Plateau, North China: Implication for air quality and ion sources. Atmos. Res. 2017, 193, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Tian, L.; Fischer, E.; Li, Z.; Jiao, K. Study of chemical composition of precipitation at an alpine site and a rural site in the Urumqi River Valley, Eastern Tien Shan, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8934–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.-W.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Wang, Y.-L.; Long, A.-M.; Liu, C.Q. Chemical characteristics and source apportionment of atmospheric precipitation in Yongxing Island. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 3237–3244. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Yue, F.-J.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.-J.; Qin, C.-Q.; Wu, Q.-X.; Xu, S. Agriculture driven nitrogen wet deposition in a karst catchment in southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 294, 106883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.-Y.; Liu, C.-Q. Sources of nitrogen and sulfur in wet deposition at Guiyang, southwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5121–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szép, R.; Bodor, Z.; Miklóssy, I.; Niță, I.-A.; Oprea, O.A.; Keresztesi, Á. Influence of peat fires on the rainwater chemistry in intra-mountain basins with specific atmospheric circulations (Eastern Carpathians, Romania). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmala, M.; Petäjä, T.; Ehn, M.; Thornton, J.; Sipilä, M.; Worsnop, D.R.; Kerminen, V.-M. Chemistry of Atmospheric Nucleation: On the Recent Advances on Precursor Characterization and Atmospheric Cluster Composition in Connection with Atmospheric New Particle Formation. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2014, 65, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.P.R.; Gonçalves, F.L.T.; Freitas, S.R. Two case studies of sulfate scavenging processes in the Amazon region (Rondônia). Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.; Alastuey, A.; Cuevas, E.; Querol, X.; Avila, A. Quantifying Dry and Wet Deposition Fluxes in Two Regions of Contrasting African Influence: The NE Iberian Peninsula and the Canary Islands. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-C.; Zhang, M.; Shu, M.; Ho, S.S.H.; Liu, Z.-F.; Wang, X.-X.; Zhao, X.-Q. Chemical characteristics of rainwater in Sichuan basin, a case study of Ya’an. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13088–13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.-L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W. Bulk/wet deposition of trace metals to rural, industrial, and urban areas in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlasov, D.; Kasimov, N.; Eremina, I.; Shinkareva, G.; Chubarova, N. Partitioning and solubilities of metals and metalloids in spring rains in Moscow megacity. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, K. Atmospheric wet and dry deposition of trace elements at 10 sites in Northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 951–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhungel, S.; Kathayat, B.; Mahata, K.; Panday, A. Transport of regional pollutants through a remote trans-Himalayan valley in Nepal. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vet, R.; Artz, R.S.; Carou, S.; Shaw, M.; Ro, C.-U.; Aas, W.; Baker, A.; Bowersox, V.C.; Dentener, F.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; et al. A global assessment of precipitation chemistry and deposition of sulfur, nitrogen, sea salt, base cations, organic acids, acidity and pH, and phosphorus. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 93, 3–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, E.K.; Berner, R.A. Global Water Cycle: Geochemistry and Environment; Prentice-Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1987; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- Arimoto, R.; Duce, R.A.; Savoie, D.L.; Prospero, J.M.; Talbot, R.; Cullen, J.D.; Tomza, U.; Lewis, N.F.; Ray, B.J. Relationships among aerosol constituents from Asia and the North Pacific during PEM-West A. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1996, 101, 2011–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, S.-L.; Yue, F.-J.; He, S.-N.; Shi, Z.-B.; Di, C.-L.; Liu, C.-Q. Nitrate sources and formation of rainwater constrained by nitrate isotopes in Southeast Asia: Example from Singapore. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathee, L.; Kang, S.; Rupakheti, D.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Sillanpää, M. Water-Soluble Ionic Composition of Aerosols at Urban Location in the Foothills of Himalaya, Pokhara Valley, Nepal. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khare, P.; Goel, A.; Patel, D.; Behari, J. Chemical characterization of rainwater at a developing urban habitat of Northern India. Atmos. Res. 2004, 69, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W.; Moon, S.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, L. Hydro-Geochemical and Sr Isotope Characteristics of the Yalong River Basin, Eastern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for Chemical Weathering and Controlling Factors. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2019, 20, 1221–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, G. Chemical composition of rainwater and anthropogenic influences in Chengdu, Southwest China. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.P.; Tiwari, S.; Matwale, J.L.; Pervez, S.; Tunved, P.; Safai, P.D.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bisht, D.S.; Singh, S.; Hopke, P.K. Sources of chemical species in rainwater during monsoon and non-monsoonal periods over two mega cities in India and dominant source region of secondary aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 146, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Han, G. Sulfur isotope and chemical composition of the rainwater at the Three Gorges Reservoir. Atmos. Res. 2015, 155, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.-W.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Shen, C.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Long, A.-M. Chemical Composition and Sources of Marine Aerosol over the Western North Pacific Ocean in Winter. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Ye, B.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Cadle, S.H.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P.A. Characterization of Atmospheric Mineral Components of PM2.5 in Beijing and Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 343, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, D.S.; Dentener, F.; Smith, P.; Grace, J.; Feely, R.A. Global nitrogen deposition and carbon sinks. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Li, Q.; Ye, R.; Tian, K.; Tian, X. The Impact of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Particulate Matter (PM2.5) on Litter Decomposition in Chinese Subtropical Forests. Forests 2020, 11, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.-L.; Calmels, D.; Han, G.; Gaillardet, J.; Liu, C.-Q. Sulfuric acid as an agent of carbonate weathering constrained by δ13CDIC: Examples from Southwest China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 270, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, G. Major ions and δ34SSO4 in Jiulongjiang River water: Investigating the relationships between natural chemical weathering and human perturbations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.A.; Hartmann, J.; Lauerwald, R.; Sobek, S.; McDonald, C.; Hoover, M.; Butman, D.; Striegl, R.; Mayorga, E.; Humborg, C.; et al. Global carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters. Nature 2013, 503, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.-F.; Li, S.-L.; Zhong, J.; Maberly, S.C.; Li, C.; Wang, F.-S.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Liu, C.-Q. Climatic and anthropogenic regulation of carbon transport and transformation in a karst river-reservoir system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, T.; Huang, X.; Han, X.; Yang, H.; Cai, Z.; Yao, L.; Han, X.; Zhang, M.; Huang, C. Characteristics, sources and environmental implications of atmospheric wet nitrogen and sulfur deposition in Yangtze River Delta. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 219, 116904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, N.; Luo, L.; Xiao, H.; Xiao, H. Chemical characterization and source analysis of water-soluble inorganic ions in PM2.5 from a plateau city of Kunming at different seasons. Atmos. Res. 2020, 234, 104687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hien, P.D.; Bac, V.T.; Thinh, N.T.H. PMF receptor modelling of fine and coarse PM10 in air masses governing monsoon conditions in Hanoi, northern Vietnam. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Mendoza, J.A.; Lee, C.H.; Kang, J.-H. Characterization and source identification of pollutants in runoff from a mixed land use watershed using ordination analyses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 9774–9790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Site | F− | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | NH4+ | Rainwater Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNKFP (this study) | 5.0 | 25.7 | 18.1 | 79.9 | 6.6 | 7.2 | 12.3 | 52.9 | 56.3 | Karst forest |
| Guiyang 2007–2008 | 14.3 | 9.8 | 39.6 | 237.8 | 1.8 | 11.1 | 18.6 | 217.6 | 77.0 | Karst city |
| Guiyang 2009–2010 | 19.9 | 5.7 | 26.1 | 274.6 | 10.9 | 10.2 | 62.2 | 349.4 | 35.4 | Karst city |
| Puding 2008 | 2.8 | 54.5 | 17.0 | 152.4 | 10.8 | 9.1 | 3.9 | 155.8 | 33.1 | Karst agriculture |
| Puding 2012–2013 | — | 17.0 | 12.3 | 168.7 | 7.4 | 4.3 | 18.5 | 112.9 | 32.1 | Karst agriculture |
| Prague | 2.7 | 18.3 | 72.9 | 129.0 | 8.0 | 23.4 | 10.3 | 319.9 | — | Bohemian karst |
| Beijing 2011–2012 | 12.0 | 50.9 | 42.6 | 357.0 | 21.5 | 9.2 | 53.3 | 273.0 | 346.0 | Inland megacity |
| Shenzhen 2008–2009 | — | 45.9 | 23.7 | 59.3 | 36.4 | 2.0 | 11.8 | 18.1 | 14.7 | Coastal megacity |
| Alxa 2013–2015 | — | 202.8 | 69.7 | 471.4 | 232.5 | 34.1 | 72.1 | 663.0 | 167.2 | Desert |
| Eastern Tien Shan 2003–2004 | — | 16.5 | 9.6 | 53.0 | 19.0 | 4.0 | 18.1 | 174.2 | 25.2 | Mountain area |
| Yongxing Island 2013 | — | 214.4 | 8.9 | 38.0 | 209.7 | 5.8 | 45.6 | 128.8 | 8.7 | Oceanic island |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, J.; Han, G. Rainwater Chemistry Reveals Air Pollution in a Karst Forest: Temporal Variations, Source Apportionment, and Implications for the Forest. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121315
Zeng J, Han G. Rainwater Chemistry Reveals Air Pollution in a Karst Forest: Temporal Variations, Source Apportionment, and Implications for the Forest. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(12):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121315
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Jie, and Guilin Han. 2020. "Rainwater Chemistry Reveals Air Pollution in a Karst Forest: Temporal Variations, Source Apportionment, and Implications for the Forest" Atmosphere 11, no. 12: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121315
APA StyleZeng, J., & Han, G. (2020). Rainwater Chemistry Reveals Air Pollution in a Karst Forest: Temporal Variations, Source Apportionment, and Implications for the Forest. Atmosphere, 11(12), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121315






