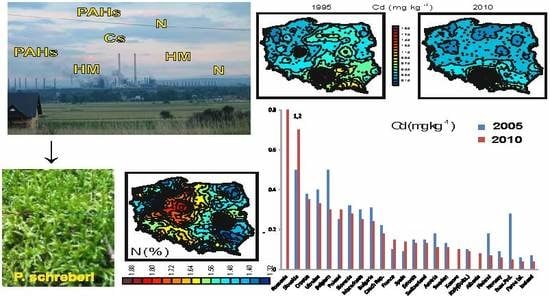
Use of Bioindication Methods in National, Regional and Local Monitoring in Poland—Changes in the Air Pollution Level over Several Decades
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials and Sample Collection
2.3. Laboratory Work
3. Results and Discussion
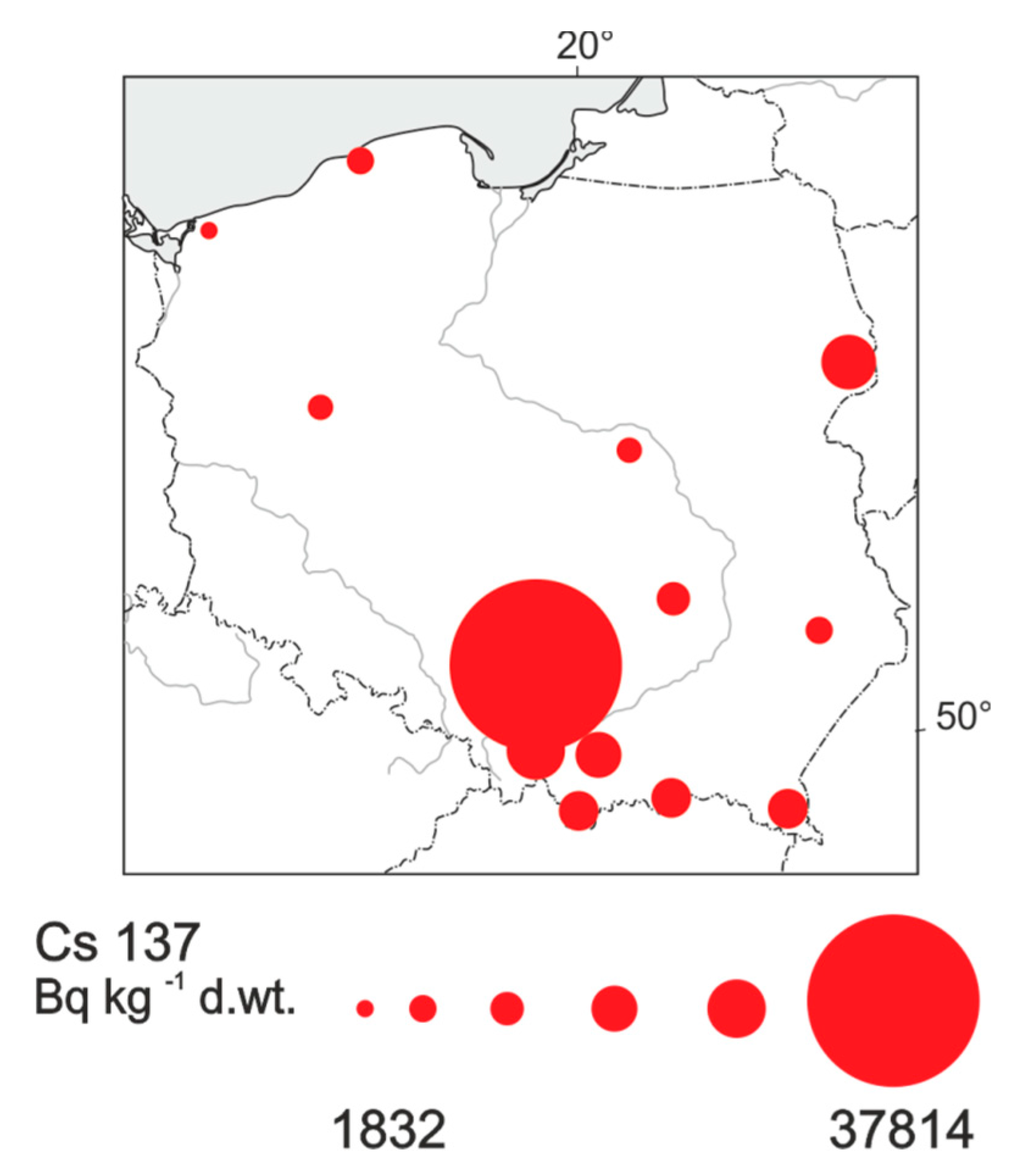
3.1. A Large Spatial Scale—The Whole Area of Poland
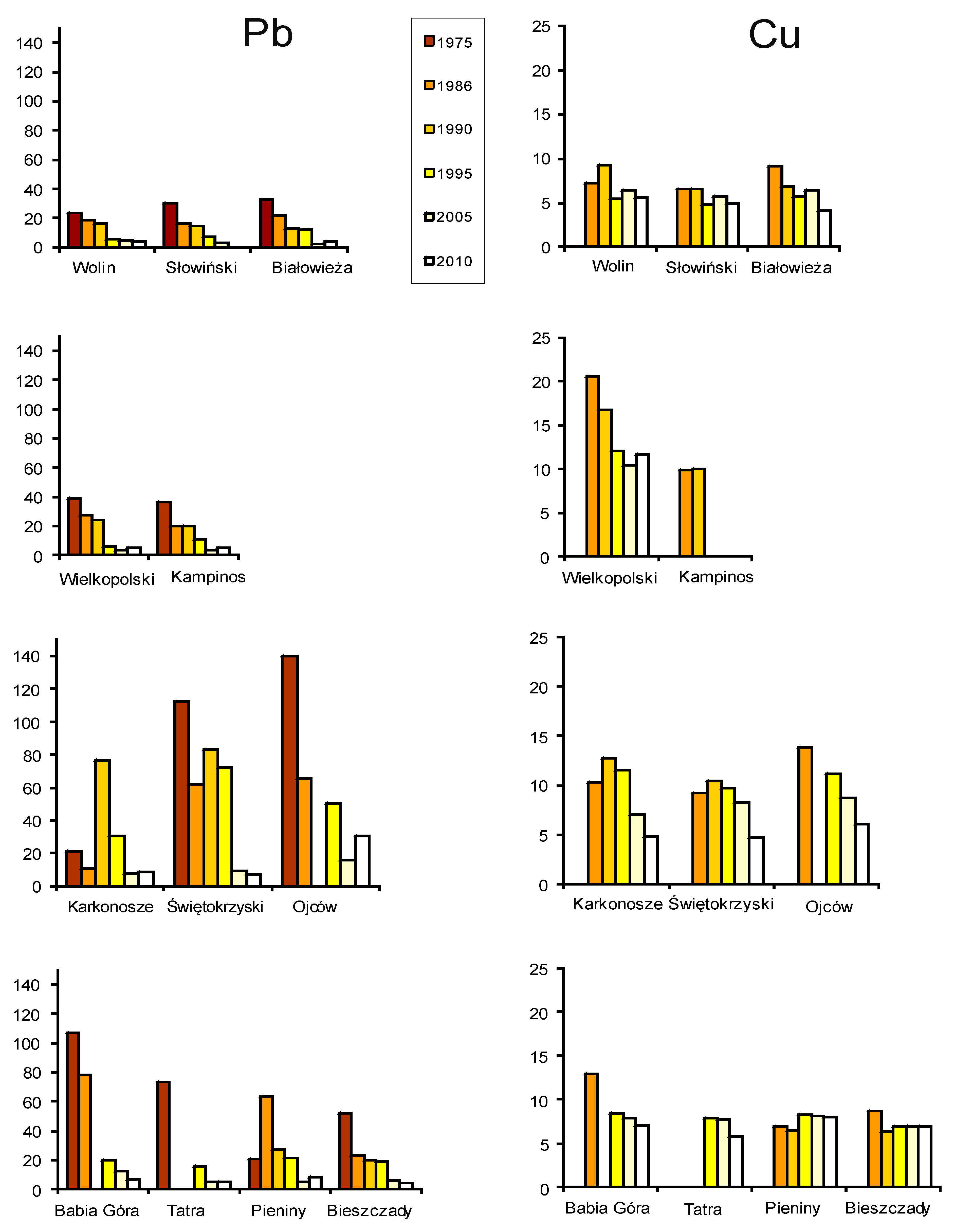
3.2. Air Pollution in the Area of Polish National Parks
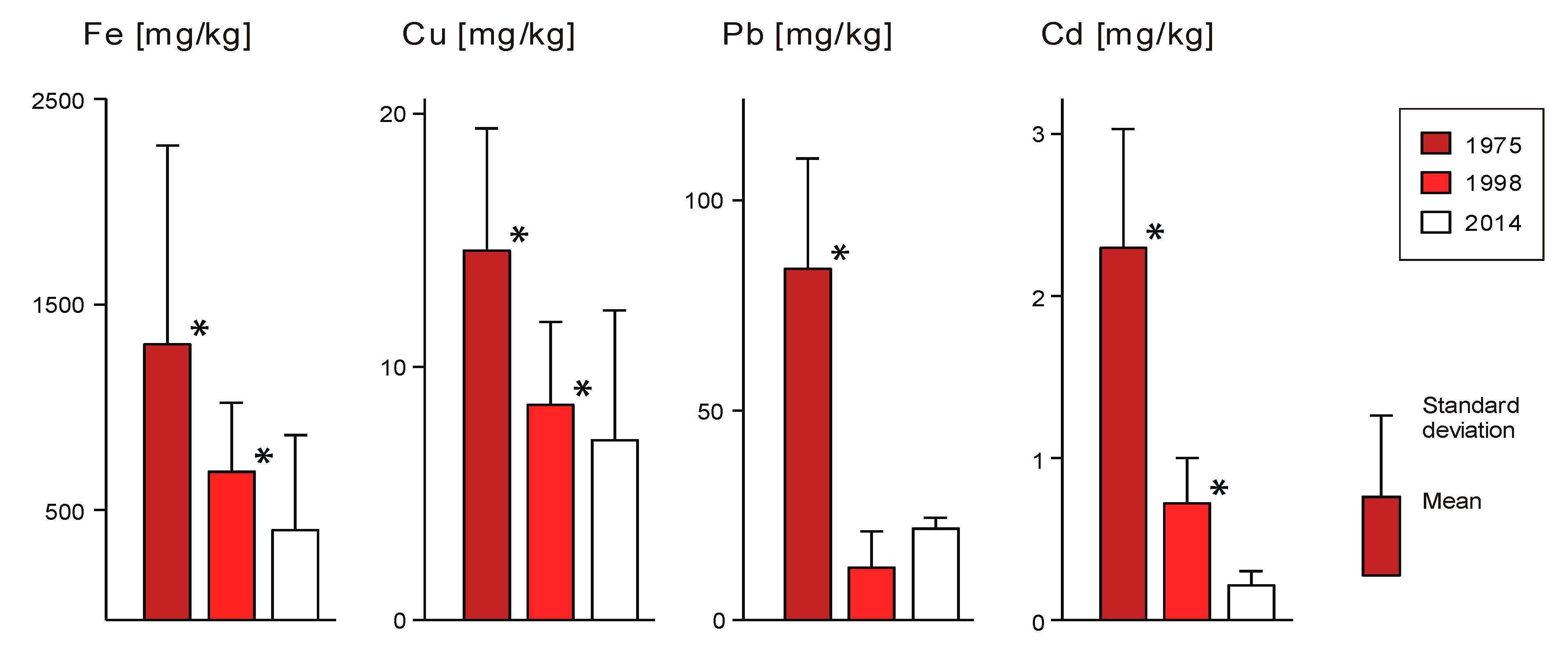
3.3. The Niepołomice Forest—A Model Research Area on a Small Spatial Scale
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rűhling, Å.; Tyler, G. Ecological approach to the lead problem. Bot. Notiser 1968, 121, 321. [Google Scholar]
- Rűhling, Å.; Tyler, G. Heavy metal deposition in Scandinavia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1973, 2, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G. Moss analysis–a method for surveying heavy metal deposition. In The Second International Clean Air Congress; Englund, H.M., Berry, W.T., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970; pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Kovács, K. Biological Indicators in Environmental Protection; Akademiai Kiado: Budapest, Hungary, 1992; pp. 1–207. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, G. Bryophytes and heavy metals: A literature review. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1990, 104, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markert, B. Plants as Biomonitors: Indicators for Heavy Metals in the Terrestrial Environment, 1st ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 1–645. [Google Scholar]
- Markert, B.; Breure, A.M.; Zehmeister, H.G. Bioindicators/Biomonitors–Principles, Assessment, Concepts; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Maschke, J. Moose als Bioindikatoren von Schwermetall-Imissionen. Eine Übersicht der bereits untersuchten lokalen und regionalen Gebiete. Bryophytorum Bibliotheca 1981, 22, 1–492. [Google Scholar]
- Harmens, H.; Norris, D.A.; Sharps, K.; Mills, G.; Alber, R.; Aleksiayenak, Y.; Blum, O.; Cucu-Man, S.-M.; Dam, M.; De Tammerman, L.; et al. Heavy metal and nitrogen concentrations in mosses are declining across Europe whilst some “hotspots” remain in 2010. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harmens, H.; Norris, D.A.; Cooper, D.M.; Mills, G.; Steinnes, E.; Kubin, E.; Thöni, L.; Aboal, J.R.; Alber, R.; Carballeira, A.; et al. Nitrogen concentrations in mosses indicate the spatial distribution of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in Europe. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2852–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmens, H.; Schnyder, E.; Thöni, L.; Cooper, D.M.; Mills, G.; Leblond, S.; Mohr, K.; Poikolainen, J.; Santamaria, J.; Skudnik, M.; et al. Relationship between site-specific nitrogen concentrations in mosses and measured wet bulk atmospheric nitrogen deposition across Europe. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapusta, P.; Szarek-Łukaszewska, G.; Godzik, B.; Łopata, B. Recent nitrogen deposition in Poland monitored with moss Pleurozium schreberi. Pol. Bot. J. 2014, 59, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ares, A.; Aboal, J.R.; Fernandez, J.A.; Real, C.; Carballeira, A. Use of the terrestrial moss Pseudoscleropodium purum to detect sources of small scale contamination by PAHs. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5501–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dołęgowska, S.; Migaszewski, Z.M. PAH concentrations in the moss species Hylocomium splendens (Hedw.) B.S.G. and Pleurozium schreberi (Brid.) Mitt. from the Kielce area (south-central Poland). Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2011, 74, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foan, L.; Domercq, M.; Bermejo, R.; Santamaría, J.M.; Simon, V. Mosses as an integrating tool for monitoring PAH atmospheric deposition: comparison with total deposition and evaluation of bioconcentration factors. A year-long case-study. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gałuszka, A. Distribution patterns of PAHs and trace elements in mosses Hylocomium splendens (Hedw.) B.S.G. and Pleurozium schreberi (Brid.) Mitt. from different forest communities: A case study, south-central Poland. Chemosphere 2006, 67, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdol, R.; Bragazza, L.; Marchesini, R.; Medici, A.; Pedrini, P.; Benedetti, S.; Bovolenta, A.; Coppi, S. Use of moss (Tortula muralis Hedw.) for monitoring organic and inorganic air pollution in urban and rural sites in Northern Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4069–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godzik, B.; Szarek-Łukaszewska, G.; Kapusta, P.; Stępień, K. PAHs concentrations in Poland using moss Pleurozium schreberi as bioindicator. Pol. Bot. J. 2014, 59, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harmens, H.; Foan, L.; Simon, V.; Mills, G. Terrestrial mosses as biomonitors of atmospheric POPs pollution: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carballeiraa, A.; Fernandeza, J.A.; Aboala, J.R.; Realb, C.; Couto, J.A. Moss: A powerful tool for dioxin monitoring. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5776–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugur, A.; Ozden, B.; Sa, M.M.; Yener, G. Biomonitoring of 210Po and 210Pb using lichens and mosses around a uraniferous coal-fired power plant in western Turkey. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krmar, M.; Wattanavatee, K.; Radnovic, D.; Slivka, J.; Bhongsuwan, T.; Frontasyeva, M.V.; Pavlov, S.S. Airborne radionuclides in mosses collected at different latitudes. J. Environ. Radioactiv. 2013, 117, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosior, G.; Dołhańczuk-Śródka, A.; Ziembik, Z. The use of moss Pleurozium schreberi (Brid.) Mitt. as bioindicator of radionuclide contamination in industrial areas Upper Silesia. Ecol. Chem. Eng. 2017, 24, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castello, M. A comparison between two moss species used as transplants for airborne trace element biomonitoring in NE Italy. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 133, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, P.; Adamo, P.; Capozzi, F.; Di Palma, A.; Senatore, A.; Spagnuolo, V.; Giordano, S. Air pollution monitoring using emission inventories combined with the moss bag approach. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2016, 541, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosior, G.; Samecka-Cymerman, A.; Kolon, K.; Kempers, A.J. Bioindication capacity of metal pollution of native and transplanted Pleurozium schreberi under various levels of pollution. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samecka-Cymerman, A.; Kempers, A.J. Differences in concentrations of heavy metals between native and transplanted Pohlia nutans (Hedw.) Lindb.–a case study from a dump exposed to industrial emissions in Poland. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2007, 16, 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.-Q.; Wang, D.-Y.; He, M.; Zhang, C. Monitoring of atmospheric heavy metal deposition in Chongqing, China–based on moss bag technique. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 148, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ares, A.; Aboal, J.R.; Carballeira, A.; Giordano, S.; Adamo, P.; Fernández, J.Á. Moss bag biomonitoring: A methodological review. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2012, 432, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, Z.; Carballeira, A.; Fernandez, J.A.; Aboal, J.R. On the use of epigeic mosses to biomonitor atmospheric deposition of nitrogen. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdol, R.; Marchesini, R.; Iacumin, P.; Brancaleoni, L. Monitoring temporal trends of air pollution in an urban area using mosses and lichens as biomonitors. Chemosphere 2014, 108, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpin, U.; Berlekamp, J.; Markert, B.; Wolterbeek, B.; Grodzińska, K.; Siewers, U.; Lieth, H.; Weckert, V. The distribution of heavy metals in a transect of the three states the Netherlands, Germany and Poland, determined with the aid of moss monitoring. Sci. Tot. Environ. 1996, 187, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłos, A.; Rajfur, M.; Sramek, I.; Wacaławek, M. Use of lichen and moss in assesment of forest contamination with heavy metals in Paraded and Glacensis Euroregions (Poland and Czech Republic). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 222, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rűhling, Å.; Tyler, G. Recent changes in the deposition of heavy metals in Northern Europe. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1984, 22, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rűhling, Å.; Rasmussen, L.; Pilegaard, K.; Makinen, A.; Steinnes, E. Atmospheric heavy metal deposition in northern Europe 1995. Nord 1997, 37, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Suchara, I.; Florek, M.; Godzik, B.; Mankovska, B.; Rabnecz, G.; Sucharova, J.; Tuba, Z.; Kapusta, P. Part I: Eight toxic metals. In Mapping of Main Sources of Pollutants and Their Transport in the Visegrad Space; KLEMO Zvolen: Průhonice, Czech Republic, 2007; pp. 1–127. [Google Scholar]
- Grodzińska, K.; Szarek-Łukaszewska, G.; Godzik, B. Survey of heavy metal deposition in Poland using mosses as indicators. Sci. Tot. Environ. 1999, 229, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta, P.; Szarek-Łukaszewska, G.; Godzik, B. Present and past deposition of heavy metals in Poland as determined by moss monitoring. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 2047–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rűhling, Å. Atmospheric heavy metal deposition in Europe–estimations based on moss analysis. Nord 1994, 9, 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Rűhling, Å.; Steiness, E. Atmospheric heavy metal deposition in Europe 1995–1996. Nord 1998, 15, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Buse, A.; Norris, D.; Harmens, H.; Buker, P.; Ashenden, T.; Mills, G. Heavy Metals in European Mosses 2000/2001 Survey; Centre for Ecology and Hydrology: Bangor, UK, 2003; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Harmens, H.; Norris, D. Spatial and Temporal Trends in Heavy Metal Accumulation in Mosses in Europe (1990–2005); Centre for Ecology & Hydrology: Bangor, UK, 2008; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Harmens, H.; Norris, D.; Mills, G. Heavy Metals and Nitrogen in Mosses: Spatial Patterns in 2010/2011 and Long-Term Temporal Trends in Europe; Centre for Ecology & Hydrology: Bangor, UK, 2013; pp. 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, W.; Nickel, S.; Schönrock, S.; Meyer, M.; Wosniok, W.; Harmens, H.; Frontasyeva, M.V.; Alber, R.; Aleksiayenak, J.; Barandovski, L.; et al. Spatially valid data of atmospheric deposition of heavy metals and nitrogen derived by moss surveys for pollution risk assessments of ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, T.; An, L.; Wang, M.; Lou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Quing, Y.; Glime, J. Spatial and temporal changes of heavy metal concentrations in mosses and its indication to the environments in the past 40 years in the city of Shanghai, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5390–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, P.; Fang, Y. Monitoring airborne heavy metal using mosses in the city of Xuzhou, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J. Trace element accumulation in the moss Hypnum cupressiforme Hedw. and the trees Quercus ilex L. and Pinus halepensis Mill. in Catalonia. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumelis, G.; Brown, D.H.; Nikodemus, O.G.; Tjarve, D. The monitoring and risk assessment of Zn deposition around a metal smelter in Latvia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1999, 58, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, F.; Sanei, H.; Garrett, R.G.; Labonté, M.; Duncan, W.F. A review of the moss-monitoring survey around the Trail smelter, British Columbia. Geochem. Explora. Environ. Anal. 2006, 6, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bačeva, K.; Stafilov, T.; Šajn, R.; Tănăselia, C. Moss biomonitoring of air pollution with heavy metals in the vicinity of a ferronickel smelter plant. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2012, 47, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grodzińska, K. Mosses as bioindicators of heavy metal pollution in Polish National Parks. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1978, 9, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makomaska, M. Heavy metal contamination of pinewoods in the Niepołomice Forest (Southern Poland). Bull. Pol. Sci. Sér. Sci. Biol. Cl. II 1978, 26, 679–685. [Google Scholar]
- Grodzińska, K.; Szarek, G.; Godzik, B. Heavy metal deposition in Polish national parks–changes during ten years. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1990, 49, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godzik, B.; Szarek, G. Heavy metals in mosses from the Niepołomice Forest, southern Poland–changes in 1975–1992. Fragm. Flor. Geobot. 1993, 38, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Grodzińska, K.; Szarek, G.; Godzik, B.; Braniewski, S.; Chrzanowska, E. Mapping air pollution in Poland by measuring heavy metal concentration in mosses. In Climate and Atmospheric Deposition Studies in Forests; Solon, J., Roo-Zielińska, E., Bytnerowicz, A., Eds.; IGSO PAS: Warszawa, Poland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Grodzińska, K.; Szarek-Łukaszewska, G.; Godzik, B.; Braniewski, S.; Budziakowska, E.; Chrzanowska, E.; Pawłowska, B.; Zielonka, T. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Poland Using the Moss Monitoring Method; Państwowa Inspekcja Ochrony Środowiska: Warszawa, Poland, 1997; pp. 1–83. [Google Scholar]
- Szarek-Łukaszewska, G.; Grodzińska, K.; Braniewski, S. Heavy metal concentration in moss Pleurozium schreberi in the Niepołomice Forest, Poland: Changes during 20 years. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2002, 79, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta, P.; Stanek, M.; Szarek-Łukaszewska, G.; Godzik, B. Long-term moss monitoring of atmospheric deposition near a large steelworks reveals the growing importance of local non-industrial sources of pollution. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinnes, E.; Rühling, A.; Lippo, H.; Makinen, A. Reference materials for large –scale metal deposition surveys. Accredit. Qual. Assur 1997, 2, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Środowisko. Rocznik statystyczny; Główny Urząd Statystyczny: Warszawa, Poland, 1998. (In Polish)
- Środowisko. Rocznik statystyczny; Główny Urząd Statystyczny: Warszawa, Poland, 2012. (In Polish)
- Kosonen, Z.; Thimonier, A.; Schnyder, E.; Thoni, L. Nitrogen concentration in moss compared with N load in precipitation and with total N deposition in Switzerland. Environm. Pollut. 2018, 239, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gydersen, H.; Pilegaard, K.; Rasmussen, L.; Rűhling, Å. Mosses analyses used as a mean of surveying the atmospheric heavy metal deposition in Sweden, Denmark, and Greenland in 1980. National Swedish Environment Protection Board. Bulletin 1983, 1670, 1–144. [Google Scholar]
- Godzik, B.; Kapusta, P. Long-term studies on the level of environmental pollution using bioindicative properties of forest species of mosses. In Proceedings of the Trees and Forests in a Changing Environment, Kórnik, Poland, 17–19 October 2016. (In Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Grodzińska, K.; Godzik, B.; Szarek, G. Skażenie polskich parków narodowych metalami ciężkimi, siarka i radionuklidami [Heavy metals, sulphur and radioactive Cs137 pollution of Polish national parks]. Prądnik. Prace i materiały Muzeum im. Prof. Władysława Szafera 1993, 7–8, 153–158. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, J.; Fredro-Braniecki, S.; Reed, D.; Maclean, A.; Strong, M. Niepołomice Forest–a GIS analysis of ecosystems response to industrial pollution. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 98, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
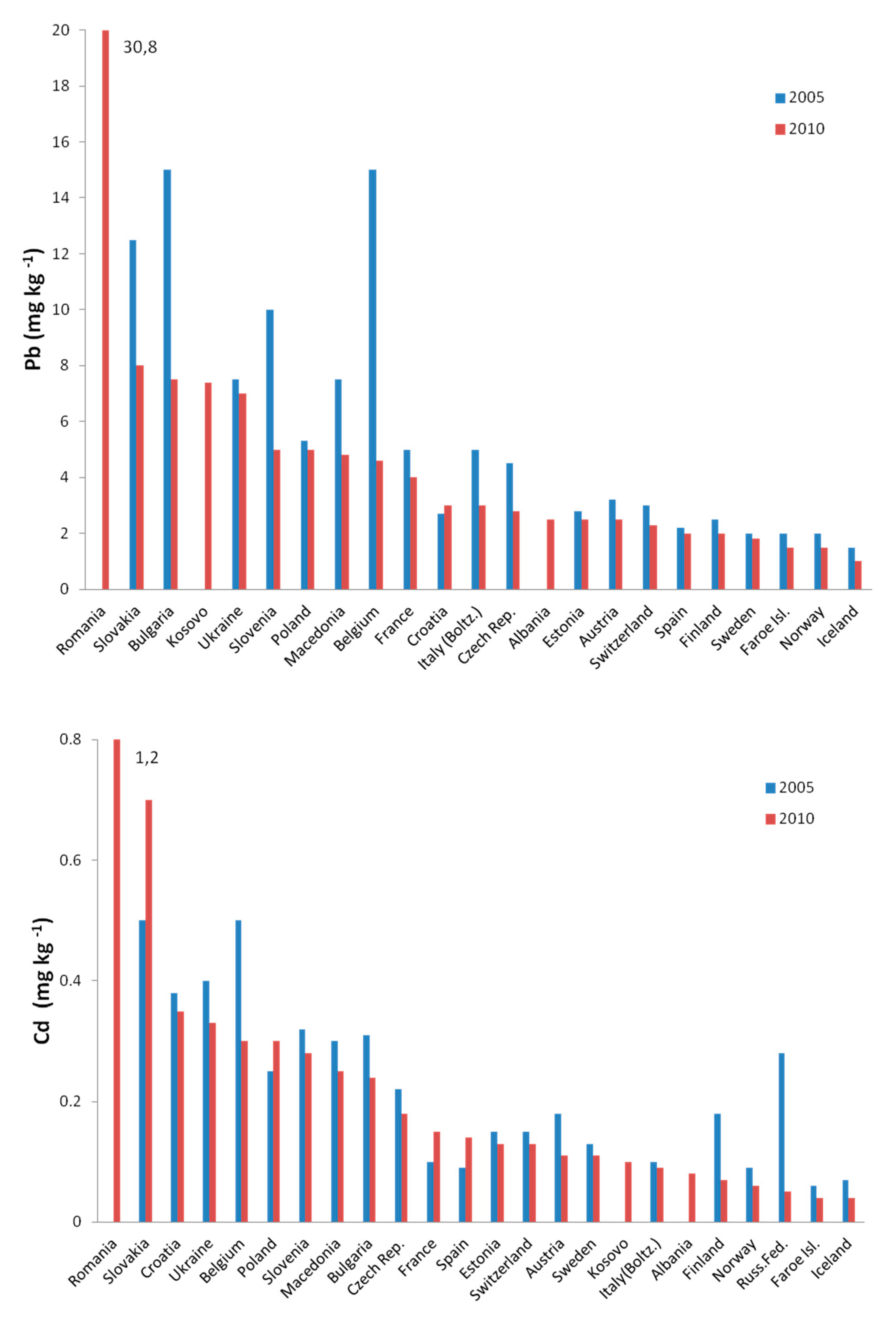
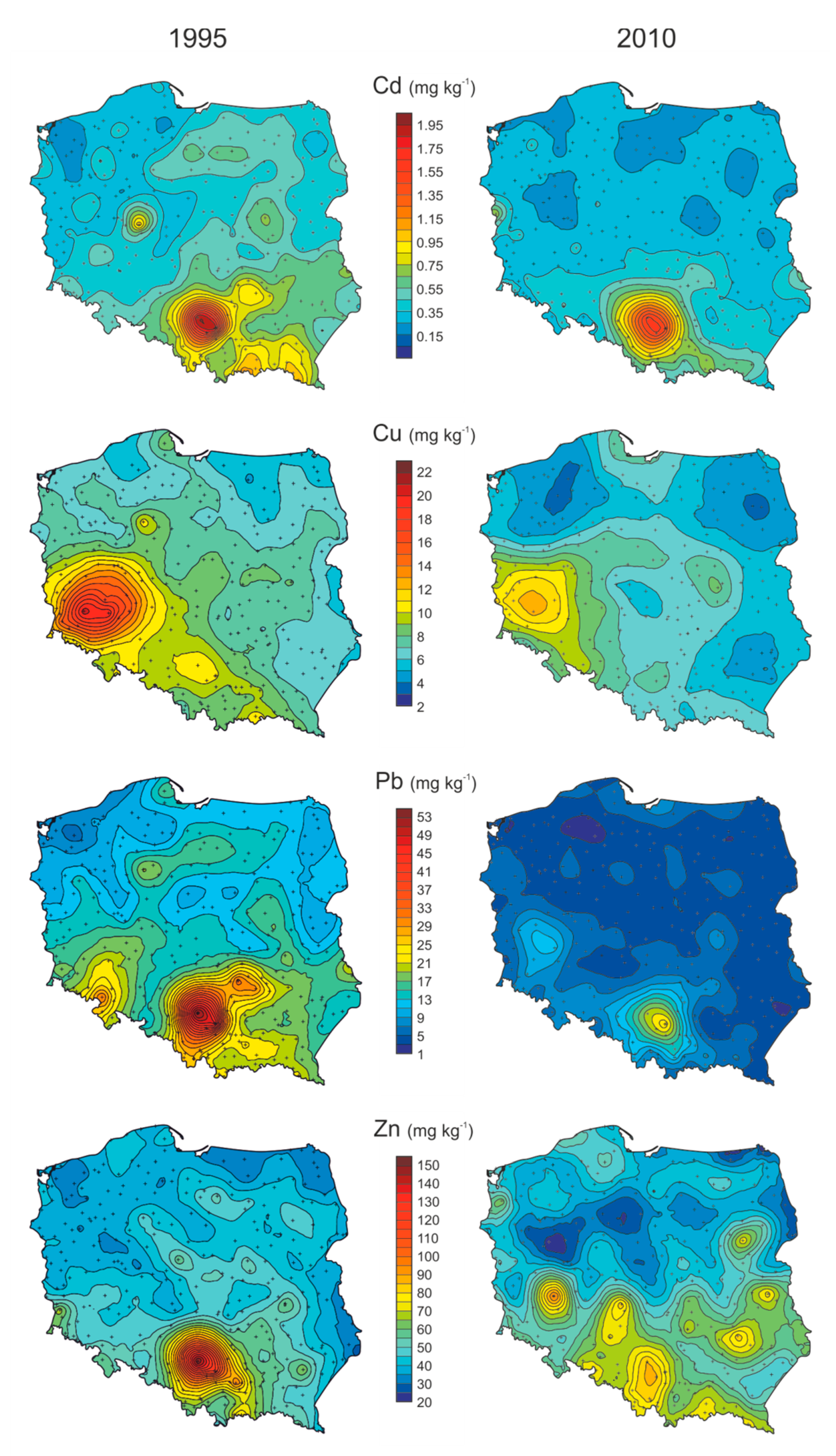
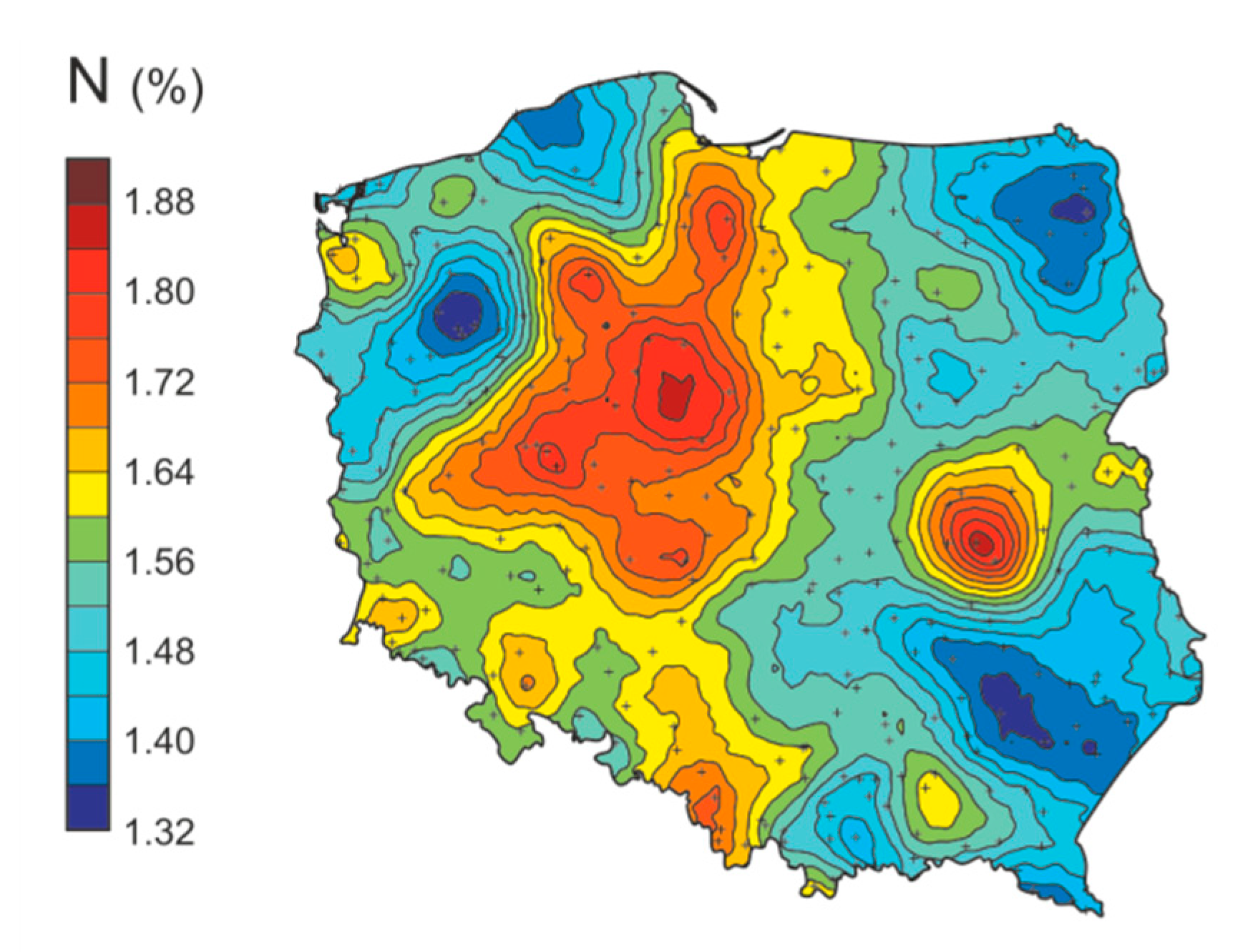

| Area | Year | Sampling Sites | Element |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poland | 1990 | 150 | Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, Fe, Hg, V |
| 1995 | 297 | Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, Fe, V, Hg | |
| 2001 | 116 | Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, Fe, V | |
| 2010 | 320 (PAHs–30) | Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, V, Hg, N, 16 PAHs | |
| 2015 | 117 | Cd, Cr, Cu, Co, Ni, Pb, Zn, Fe, Mo, Hg, V, As, N, P, Ca, K, Mg | |
| National parks (NP) | 1975 | 12 NP–24 | Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, Mn, Fe, K, Ca, Mg, Na |
| 1986 | 14 NP–28 | Cd, Co, Cr, Ni, Cu, Pb, Zn, Mn, Fe, K, Ca, Mg, Na, 137Cs | |
| 2005 | 23 NP–272 | Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, Fe, Zn | |
| 2010 | 23NP–46 | Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, V, Hg, N | |
| The Niepołomice Forest | 1975 | 15 | Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn, Fe, Mn |
| 1992 | 15 | Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn, Fe, Mn | |
| 1998 | 77 | Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn, Fe | |
| 2014 | 95 | Cd, Cr, Cu, Co, Ni, Pb, Zn, Fe, Mn, Mo, V, As, Ca, K, Mg, Na, N, P |
| Region | N | Sum of PAHs | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silesia–Kraków | 10 | 7.350 | 4.075 |
| Mazovia | 10 | 2.127 | 1.686 |
| Podlasie | 10 | 0.838 | 0.943 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godzik, B. Use of Bioindication Methods in National, Regional and Local Monitoring in Poland—Changes in the Air Pollution Level over Several Decades. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020143
Godzik B. Use of Bioindication Methods in National, Regional and Local Monitoring in Poland—Changes in the Air Pollution Level over Several Decades. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(2):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020143
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodzik, Barbara. 2020. "Use of Bioindication Methods in National, Regional and Local Monitoring in Poland—Changes in the Air Pollution Level over Several Decades" Atmosphere 11, no. 2: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020143
APA StyleGodzik, B. (2020). Use of Bioindication Methods in National, Regional and Local Monitoring in Poland—Changes in the Air Pollution Level over Several Decades. Atmosphere, 11(2), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020143