Comparison of the Madden–Julian Oscillation-Related Tropical Cyclone Genesis over the South China Sea and Western North Pacific under Different El Niño-Southern Oscillation Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Identification of the Madden–Julian Oscillation (MJO)-Related Activity
2.2.2. Classification of Different El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Conditions
2.2.3. Definition of Tropical Cyclone (TC) Genesis and Related Index
2.2.4. Statistical Testing
2.2.5. Genesis Potential Index (GPI)
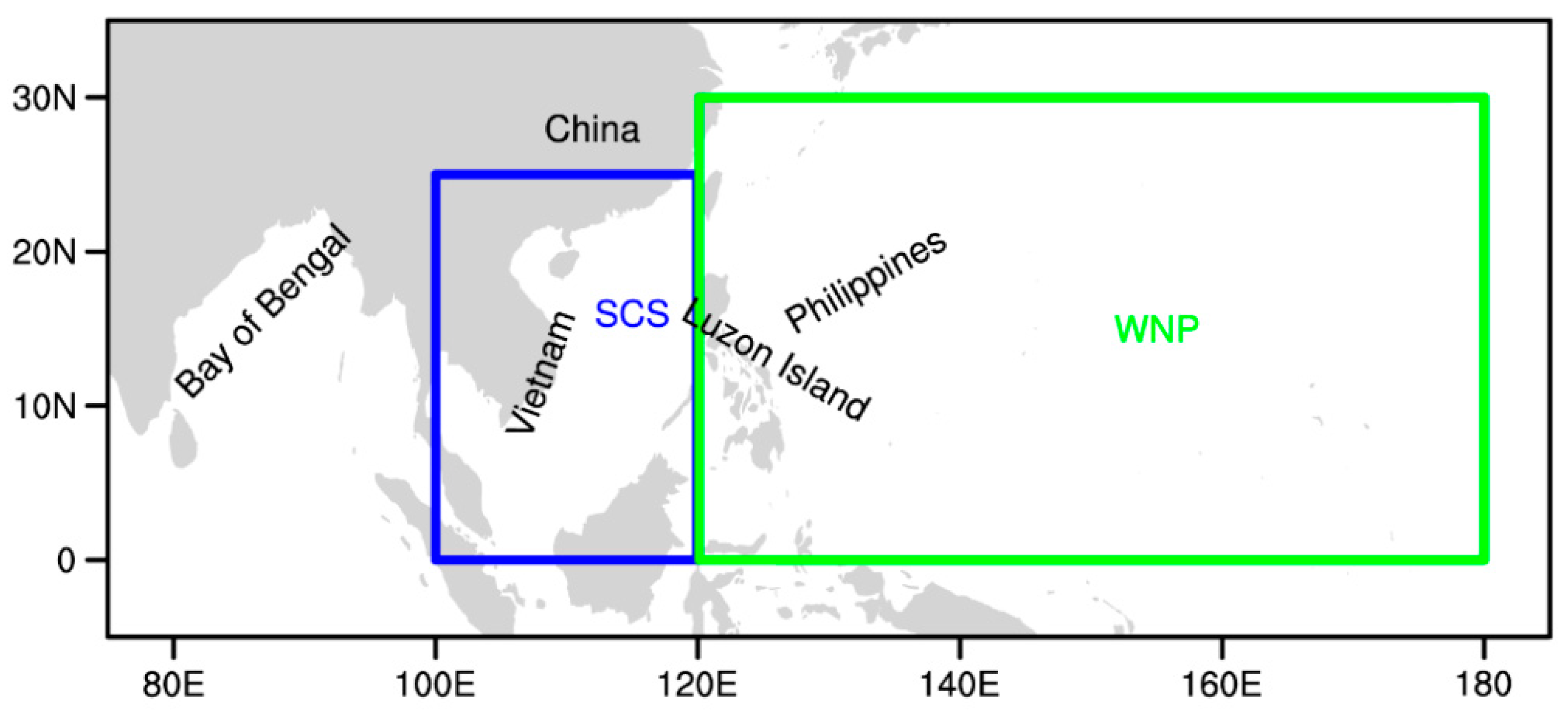
3. South China Sea (SCS) and Western North Pacific (WNP) TC Genesis Characteristics under Different ENSO Conditions
4. MJO-Related TC Genesis over the SCS and WNP under Different ENSO Conditions
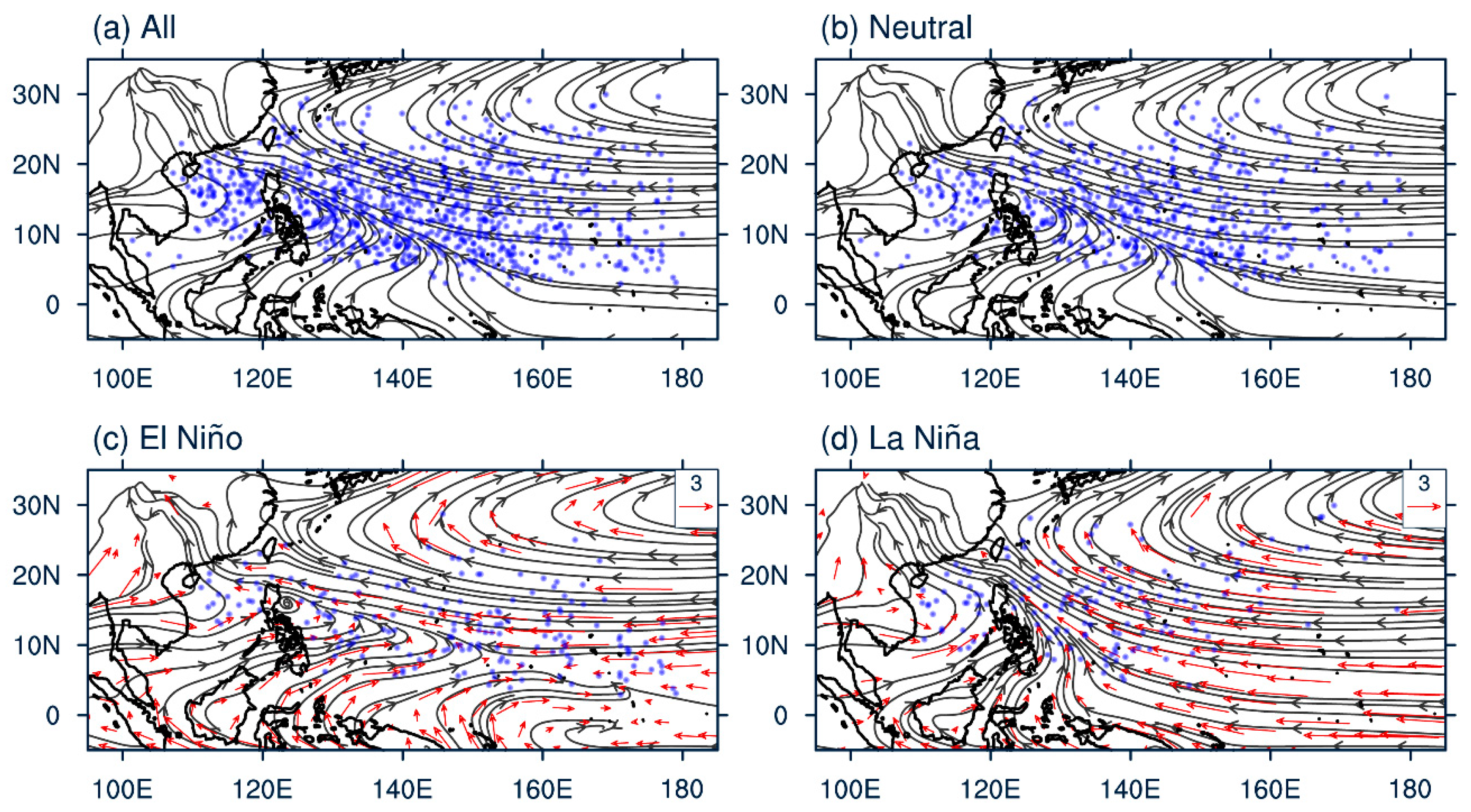
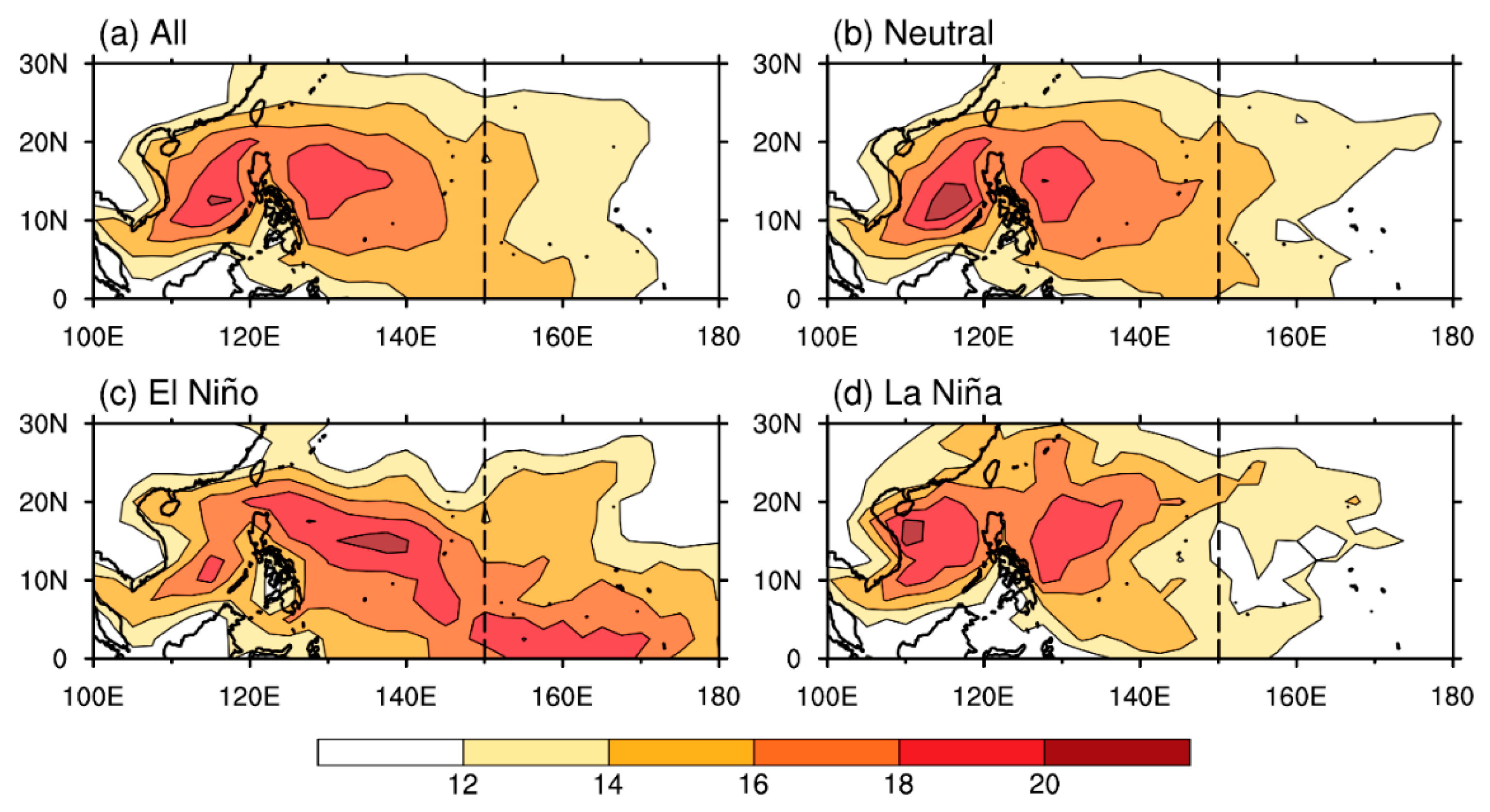
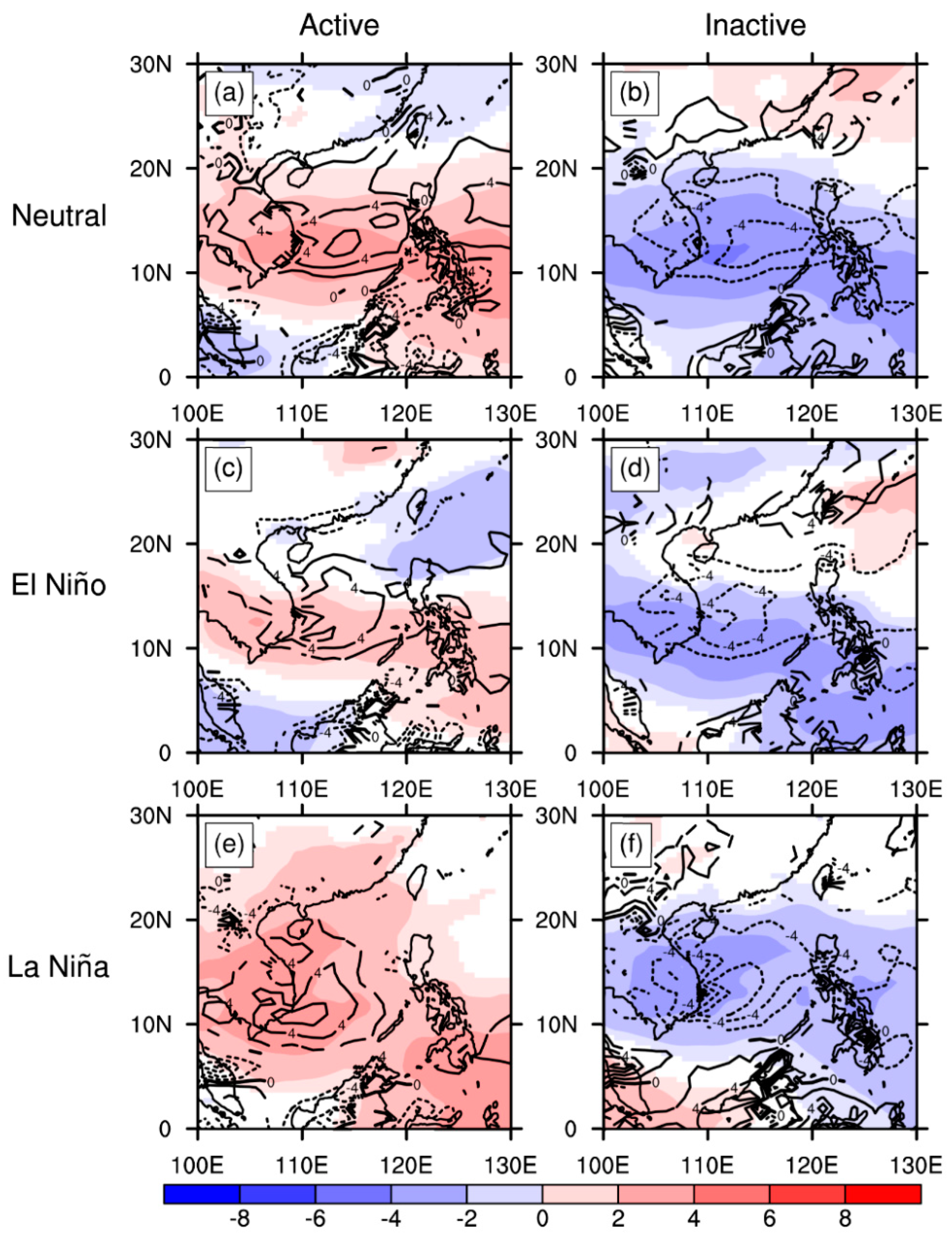
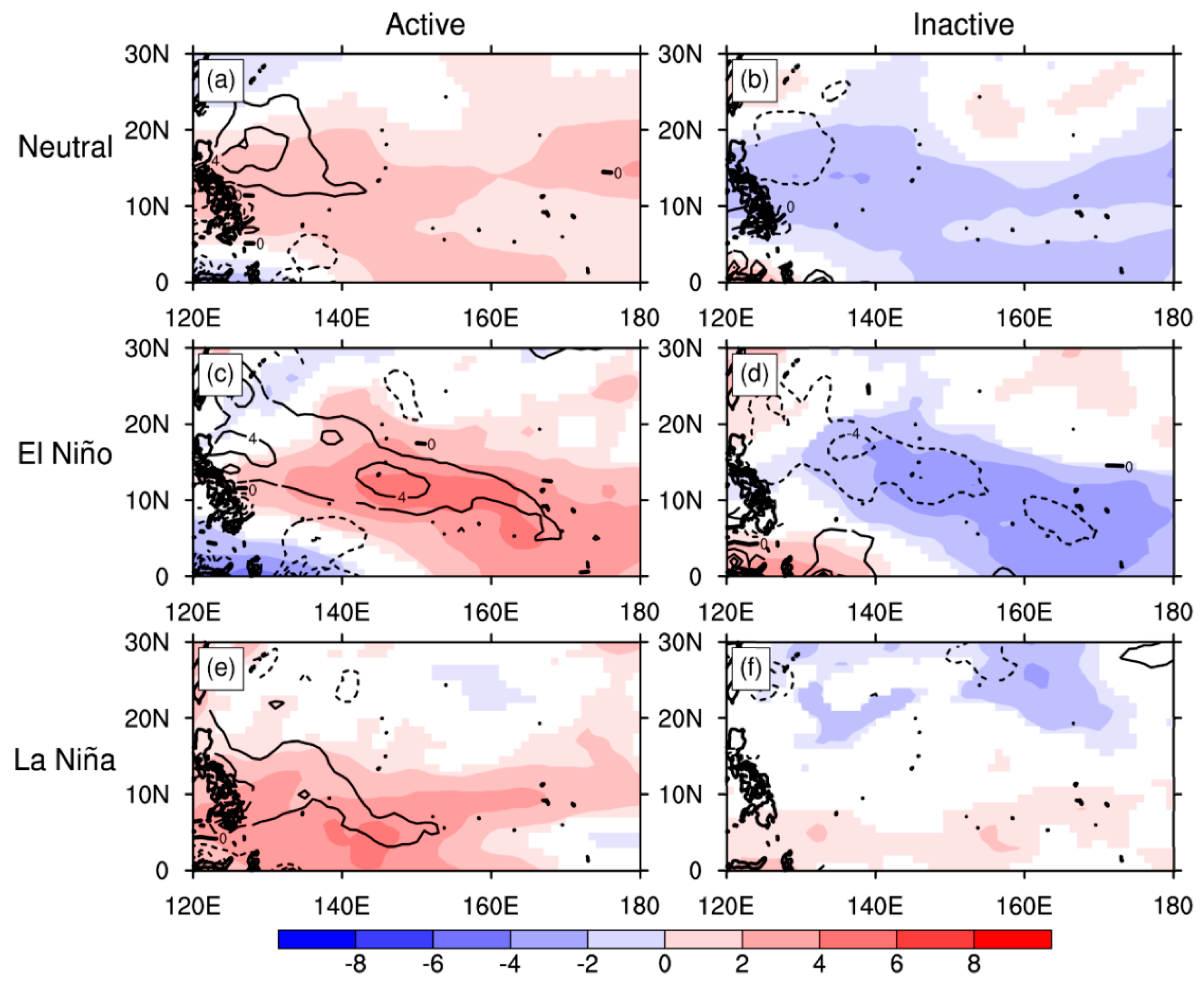
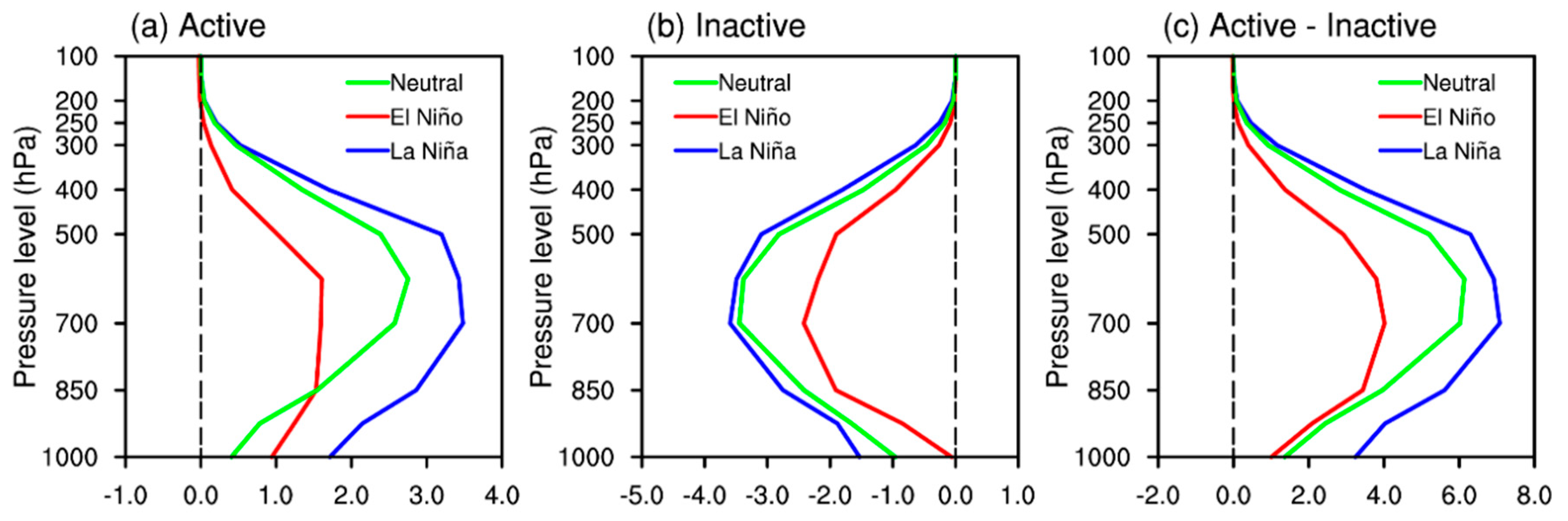
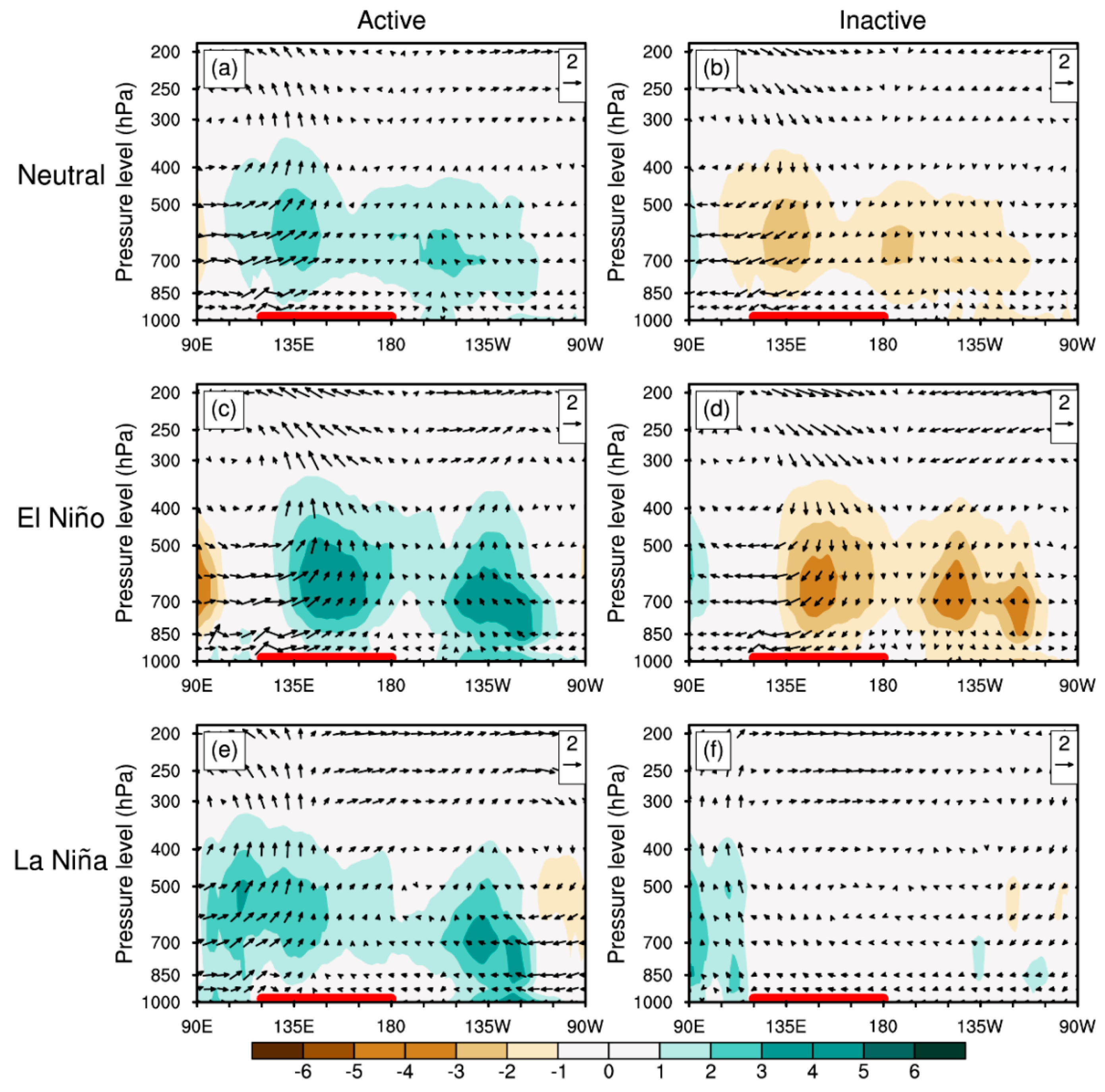
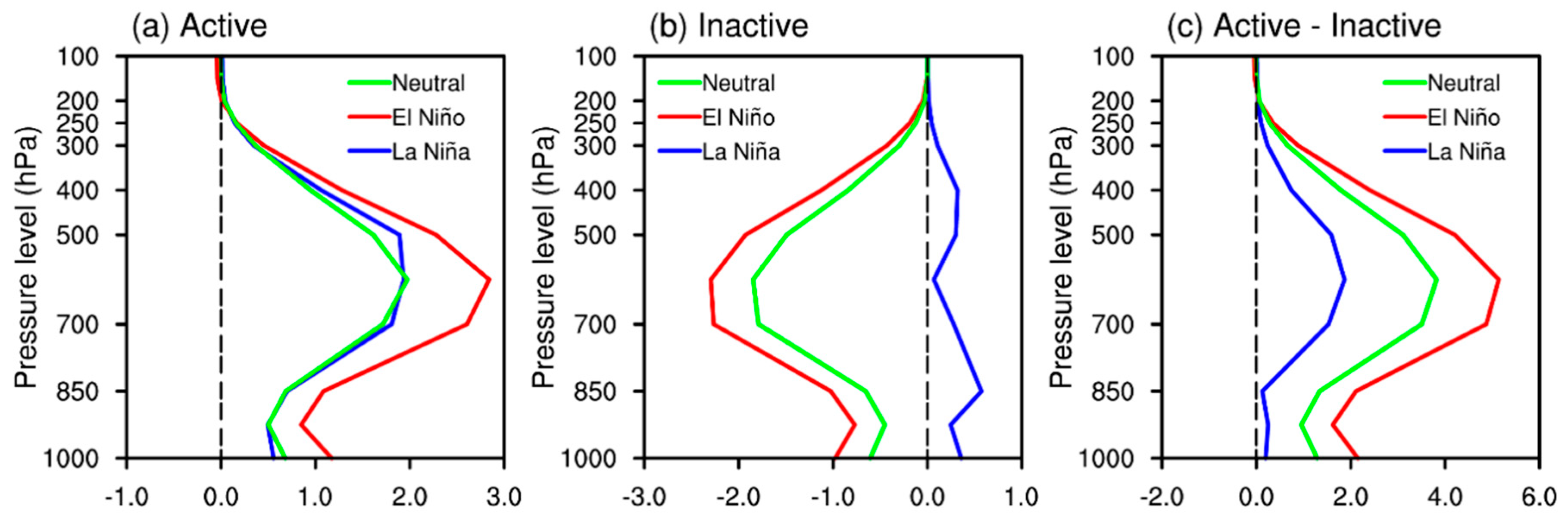
5. Mechanism of MJO-Related TC Genesis over the SCS and WNP under Different ENSO Conditions
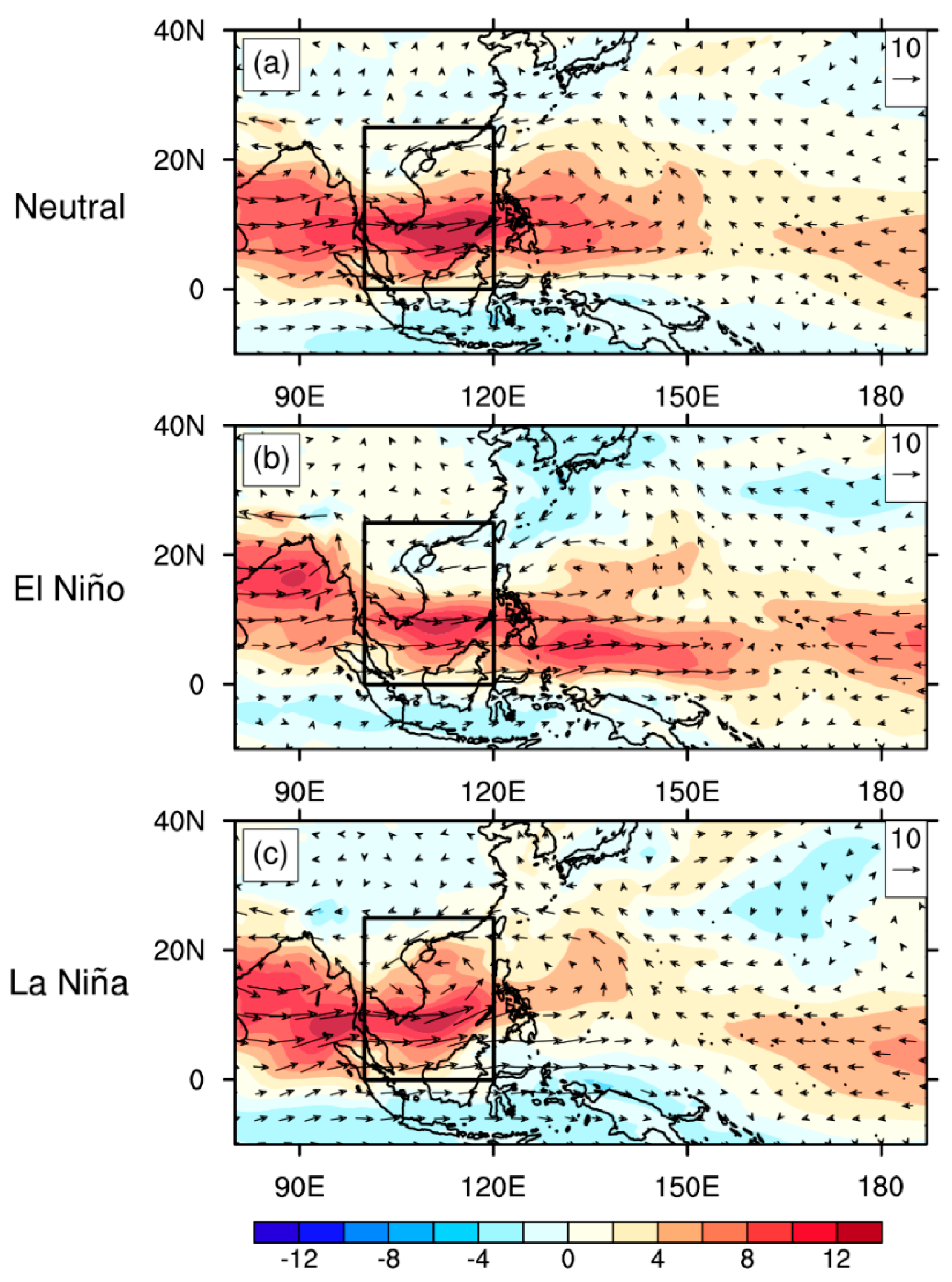
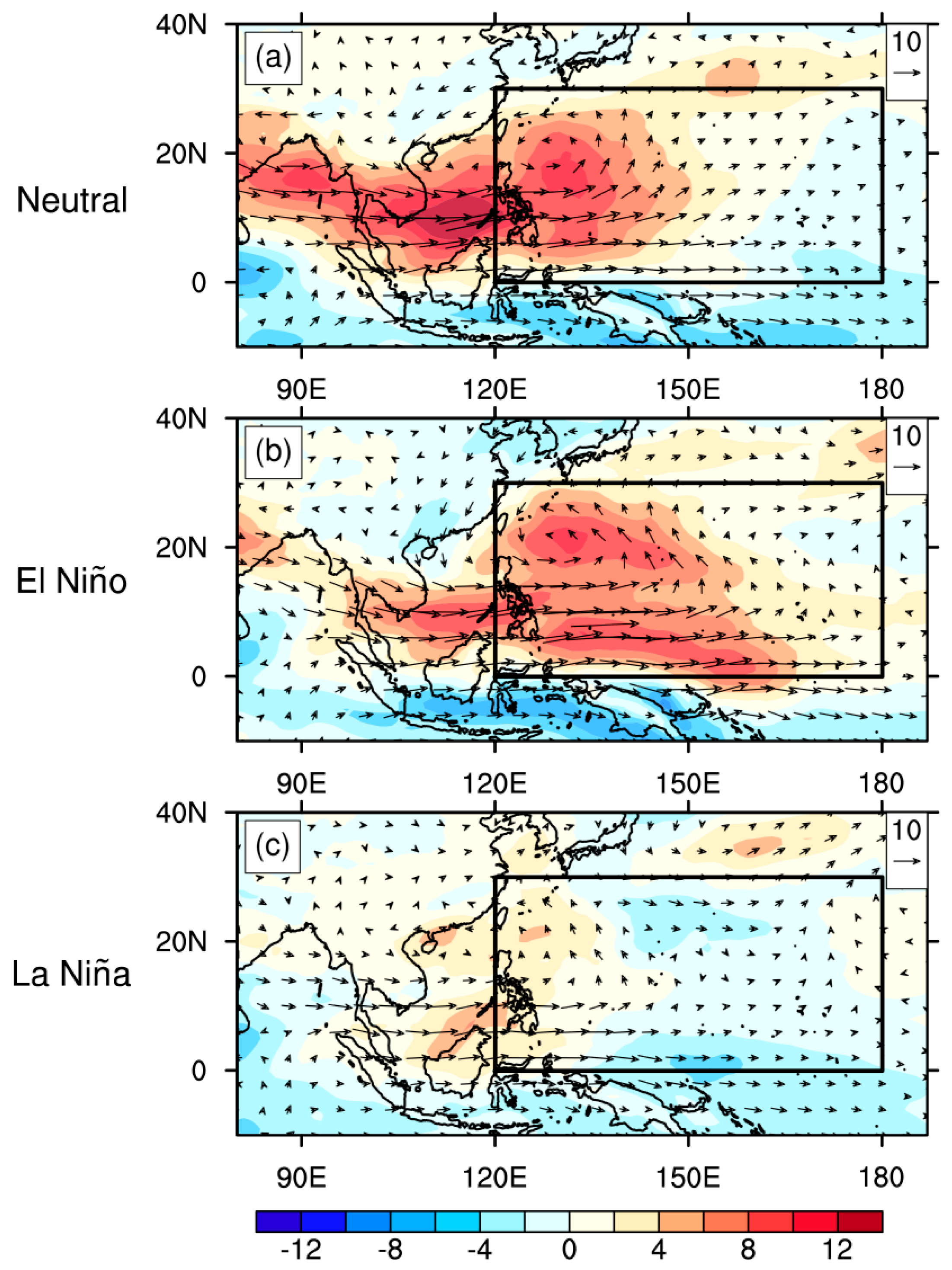
5.1. Environmental Factors for TC Genesis Considering MJO Modulation
5.2. Environmental-Factor-Related Processes
5.3. Primary Environmental Factor over the SCS and the WNP
5.3.1. SCS
5.3.2. WNP
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Q.; Lin, J.; Shou, S. Synoptic Meteorology Principles and Methods, 3rd ed.; China Meteorology Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, J.C. Interannual and interdecadal variations of tropical cyclone activity over the western North Pacific. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 89, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, C.J. Global Overview: Global Guide to Tropical Cyclone Forecasting; World Meteorological Organization Rep: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Liu, Q. Tropical cyclone damages in China: 1983–2006. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.C. Tropical cyclone activity in the northwest Pacific in relation to the El Niño/Southern Oscillation phenomenon. Mon. Weather Rev. 1985, 113, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C. Tropical cyclone activity over the western North Pacific associated with El Niño and La Niña events. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 2960–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chan, J.C. How strong ENSO events affect tropical storm activity over the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Chou, C.; Huang, R. Seasonal modulation of tropical intraseasonal oscillations on tropical cyclone geneses in the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 6339–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, C.; Mu, M.; Duan, W. Seasonal modulations of different impacts of two types of ENSO events on tropical cyclone activity in the western North Pacific. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 2887–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, R.; Bi, M. Contributions of Different Time-Scale Variations to Tropical Cyclogenesis over the Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 3137–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhan, R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H. Contribution of the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation to the Recent Abrupt Decrease in Tropical Cyclone Genesis Frequency over the Western North Pacific since 1998. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 8211–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.C.; Zhou, W. Modulation of Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclone Activity by the ISO. Part I: Genesis and Intensity. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2904–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, E.; Serra, Y. Intraseasonal Modulation of Synoptic-Scale Disturbances and Tropical Cyclone Genesis in the Eastern North Pacific. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 5724–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yoshida, R.; Raga, G.B. Impact of the Madden–Julian Oscillation on Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclogenesis Associated with Large-Scale Patterns. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2015, 54, 1413–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, J. Modulation of Tropical Cyclogenesis Location and Frequency over the Indo-Western North Pacific by the Intraseasonal Indo-Western Pacific Convection Oscillation during the Boreal Extended Summer. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 1435–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, C.; Chung, P.; Sui, C. Influence of Intraseasonal–Interannual Oscillations on Tropical Cyclone Genesis in the Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4949–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Description of Global-Scale Circulation Cells in the Tropics with a 40–50 Day Period. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Wu, X. Physical mechanisms for the maintenance of GCM-simulated Madden–Julian oscillation over the Indian Ocean and Pacific. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 2469–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chang, Y. Impact of boreal summer intra-seasonal oscillations on warm season diurnal convection activity in Taiwan. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2187–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weickmann, K.M.; Lussky, G.R.; Kutzbach, J.E. Intraseasonal (30–60 day) fluctuations of outgoing longwave radiation and 250 mb stream function during northern winter. Mon. Weather Rev. 1985, 113, 941–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knutson, T.R.; Weickmann, K.M.; Kutzbach, J.E. Global-scale intraseasonal oscillations of outgoing longwave radiation and 250 mb zonal wind during Northern Hemisphere summer. Mon. Weather Rev. 1986, 114, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knutson, T.R.; Weickmann, K.M. 30–60 day atmospheric oscillations: Composite life cycles of convection and circulation anomalies. Mon. Weather Rev. 1987, 115, 1407–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Wu, X. Effects of convective processes on GCM simulations of the Madden–Julian oscillation. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 352–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; McFarlane, S.A.; Flaherty, J.E. Characteristics Associated with the Madden–Julian Oscillation at Manus Island. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 3342–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Madden-Julian Oscillation. Rev. Geophys. 2005, 43, RG2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, W.M. Hurricanes: Their formation, structure and likely role in the tropical circulation. In Meteorology over the Tropical Oceans; Shaw, D.B., Ed.; Royal Meteorological Society: Bracknell, UK, 1979; pp. 155–218. [Google Scholar]
- Sobel, A.H.; Maloney, E.D. Effect of ENSO events affect tropical storm activity over the Western North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Li, T. Basin dependence of the MJO modulating tropical cyclone genesis. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 6081–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G. Impact of Intraseasonal Oscillations on the Activity of Tropical Cyclones in Summer over the South China Sea. Part I: Local Tropical Cyclones. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.D.; Matthews, A.J.; Karoly, D.J. The modulation of tropical cyclone activity in the Australian region by the Madden–Julian oscillation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 2970–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotzbach, P.J.; Oliver, E.C. Modulation of Atlantic Basin Tropical Cyclone Activity by the Madden–Julian Oscillation (MJO) from 1905 to 2011. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.C.; Zhou, W.; Chan, J.C.; Huang, P. Asymmetric Modulation of Western North Pacific central by the Madden–Julian Oscillation under ENSO Conditions. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 5374–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Bechtold, P. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, B.; Smith, C.A. Description of a complete (interpolated) outgoing longwave radiation dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheeler, M.; Hendon, H.H. An all-season real-time multivariate MJO index: Development of the index for monitoring and prediction in Australia. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1917–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanczos, C. Applied Analysis; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1956; p. 539. [Google Scholar]
- Arguez, A.; Inamdar, A.; Palecki, M.A.; Schreck, C.J.; Young, A.H. ENSO Normals: A New U.S. Climate Normals Product Conditioned by ENSO Phase and Intensity and Accounting for Secular Trends. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 1381–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Ho, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Sui, C.H.; Park, S.K. Systematic Variation of Summertime Tropical Cyclone Activity in the Western North Pacific in Relation to the Madden–Julian Oscillation. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 1171–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; p. 467. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, S.J.; Robertson, A.W.; Gaffney, S.J.; Smyth, P.; Ghil, M. Cluster Analysis of Typhoon Tracks. Part I: General Properties. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 3654–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.J.; Emanuel, K.A.; Sobel, A.H. Use of a Genesis Potential Index to Diagnose ENSO Effects on Tropical Cyclone Genesis. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4819–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.J.; Wheeler, M.C.; Sobel, A.H. Diagnosis of the MJO Modulation of Tropical Cyclogenesis Using an Empirical Index. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 3061–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K.A.; Norlan, D.S. Tropical cyclone activity and global climate. In Proceedings of the 26th Conference on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, Miami, FL, USA, 2–7 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel, K.A. Sensitivity of tropical cyclones to surface exchange coefficients and a revised steady-state model incorporating eye dynamics. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 3969–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Yu, W.; Li, T.; Murty, V.S.; Tangang, F. Bimodal character of cyclone climatology in the Bay of Bengal modulated by monsoon seasonal cycle. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Tsay, T.; Yen, M.; Cayanan, E.O. Formation of the Philippine Twin Tropical Cyclones during the 2008 Summer Monsoon Onset. Weather Forecast. 2010, 25, 1317–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wen, Z.; Huang, R.; Wu, R. Possible Linkage between the Monsoon Trough Variability and the Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujumdar, M.B.; Preethi, T.P.; Sabin, K.; Ashok, S.; Saeed, D.S.; Pai, K.R. The Asian summer monsoon response to the La Nina event of 2010. Meteorol. Appl. 2012, 19, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
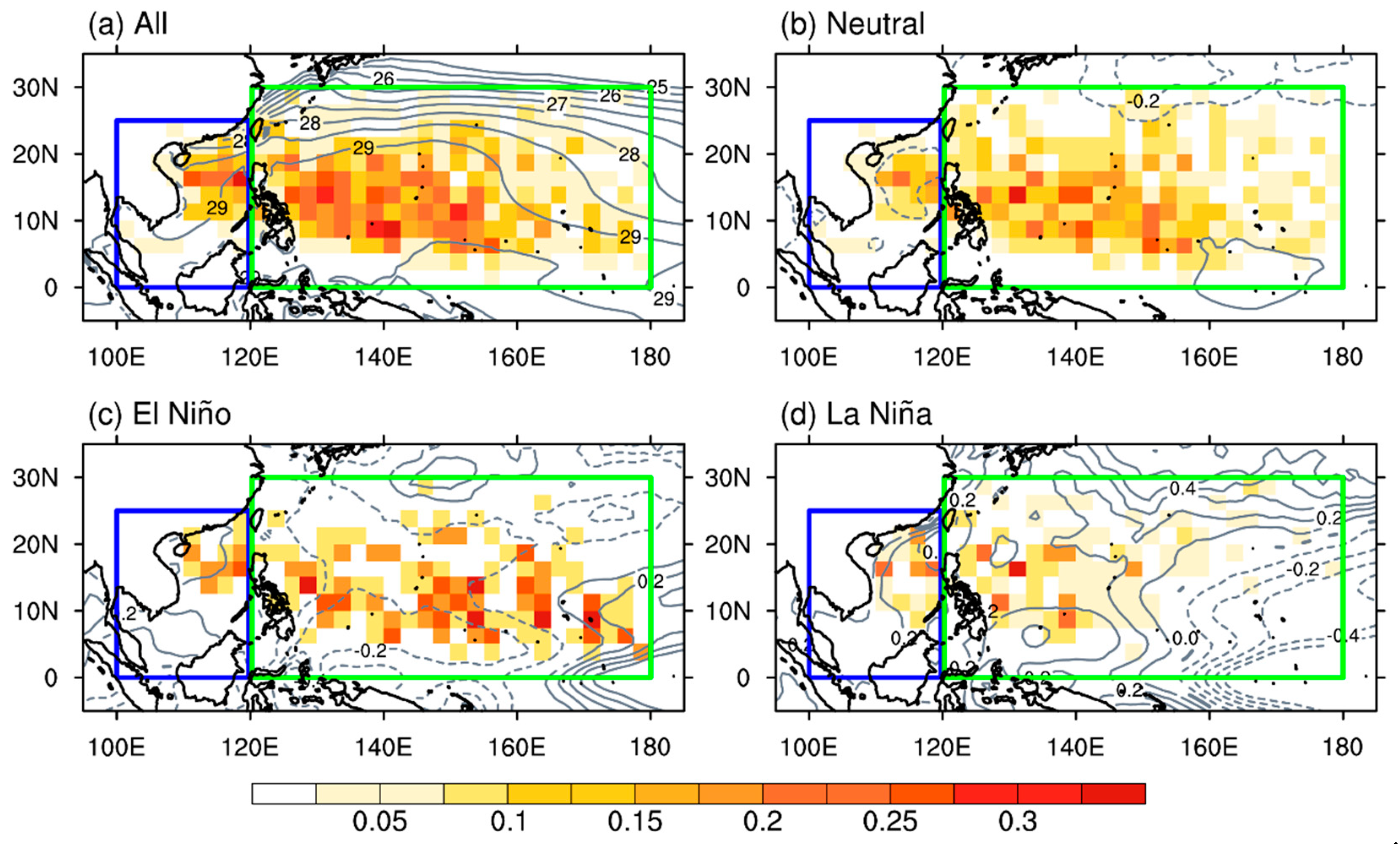
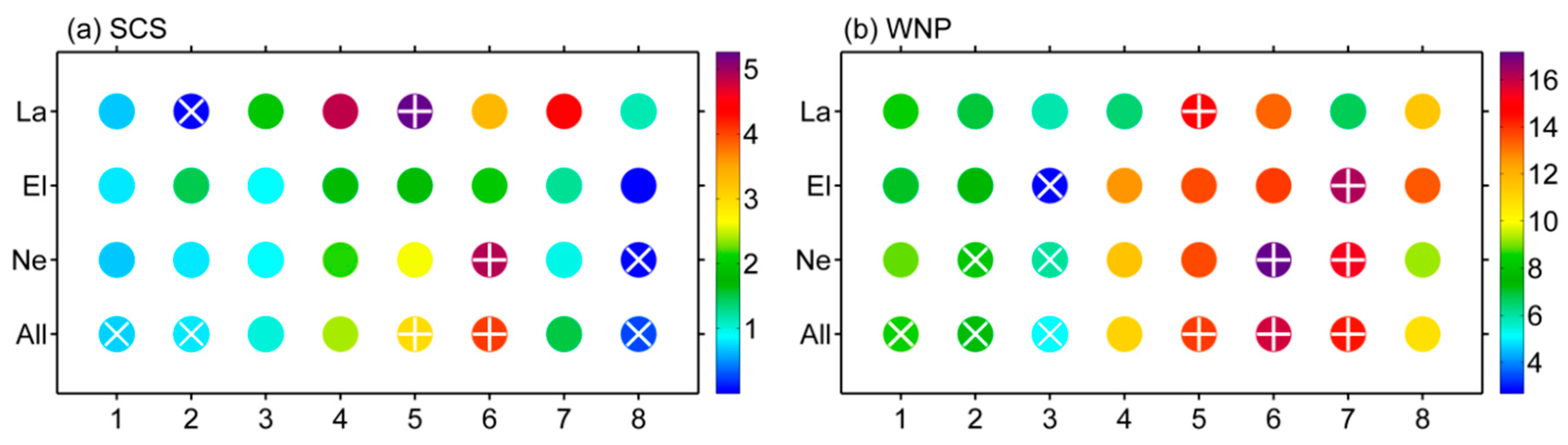

| SCS | Neutral | El Niño | La Niña |
| Active phases | 5 + 6 (3.68% *) | 5 + 6 (1.90%) | 4 + 5 (5.11% *) |
| Inactive phases | 8 + 1 (0.47% *) | 8 + 1 (0.46%) | 8 + 1 + 2 (0.56% *) |
| ESR (active/inactive) | 7.77 | 4.09 | 9.2 |
| WNP | Neutral | El Niño | La Niña |
| Active phases | 6 + 7 (16.45% *) | 6 + 7 (14.92% *) | 5 + 6 (14.22% *) |
| Inactive phases | 2 + 3 (7.35% *) | 2 + 3 (5.28% *) | 3 + 4 (6.19%) |
| ESR (active/inactive) | 2.24 | 2.82 | 2.29 |
| Neutral (Active–Inactive) | El Niño (Active–Inactive) | La Niña (Active–Inactive) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Term1 (Vort) | 2.59 (45%) s | 2.55 (68%) p | 2.73 (48%) s |
| Term2 (Rhum) | 3.42 (60%) p | 1.99 (53%) s | 3.73 (65%) p |
| Term3 (PI) | −0.14 (−2%) | −0.18 (−5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Term4 (Vshear) | −0.16 (−3%) | −0.61 (−16%) | −0.73 (−13%) |
| GPI | 5.71 | 3.75 | 5.73 |
| Neutral (Active–Inactive) | El Niño (Active–Inactive) | La Niña (Active–Inactive) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Term1 (Vort) | 0.54 (54%) | 0.70 (46%) | 0.27 (270%) d |
| Term2 (Rhum) | 1.07 (127%) d | 1.67 (111%) d | −0.11 (−110%) |
| Term3 (PI) | −0.14 (−17%) | −0.3 (−20%) | 0.12 (120%) |
| Term4 (Vshear) | −0.54 (−64%) | −0.56 (−37%) | −0.18 (−180%) |
| GPI | 0.84 | 1.51 | 0.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, C.; Deng, L.; Huang, W.-R.; Chen, J. Comparison of the Madden–Julian Oscillation-Related Tropical Cyclone Genesis over the South China Sea and Western North Pacific under Different El Niño-Southern Oscillation Conditions. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020183
Ye C, Deng L, Huang W-R, Chen J. Comparison of the Madden–Julian Oscillation-Related Tropical Cyclone Genesis over the South China Sea and Western North Pacific under Different El Niño-Southern Oscillation Conditions. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(2):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020183
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Chengyao, Liping Deng, Wan-Ru Huang, and Jinghua Chen. 2020. "Comparison of the Madden–Julian Oscillation-Related Tropical Cyclone Genesis over the South China Sea and Western North Pacific under Different El Niño-Southern Oscillation Conditions" Atmosphere 11, no. 2: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020183
APA StyleYe, C., Deng, L., Huang, W.-R., & Chen, J. (2020). Comparison of the Madden–Julian Oscillation-Related Tropical Cyclone Genesis over the South China Sea and Western North Pacific under Different El Niño-Southern Oscillation Conditions. Atmosphere, 11(2), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020183







