Evolution of Plume Core Structures and Turbulence during a Wildland Fire Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Experimental Design
2.1. Site Characterization
2.2. Fuels
2.3. Instrumentation
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Ignition Procedure
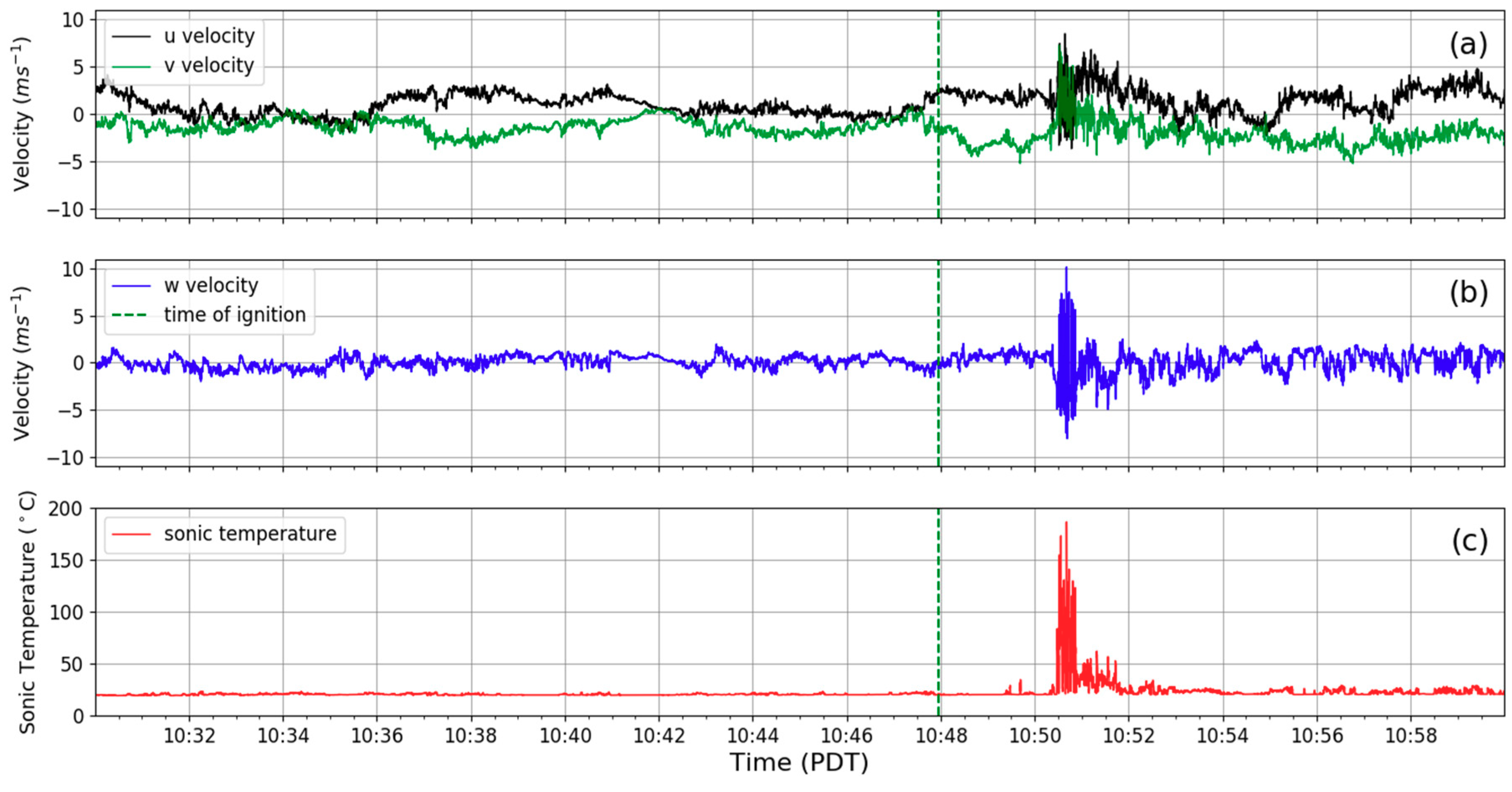
3. Observations and Results
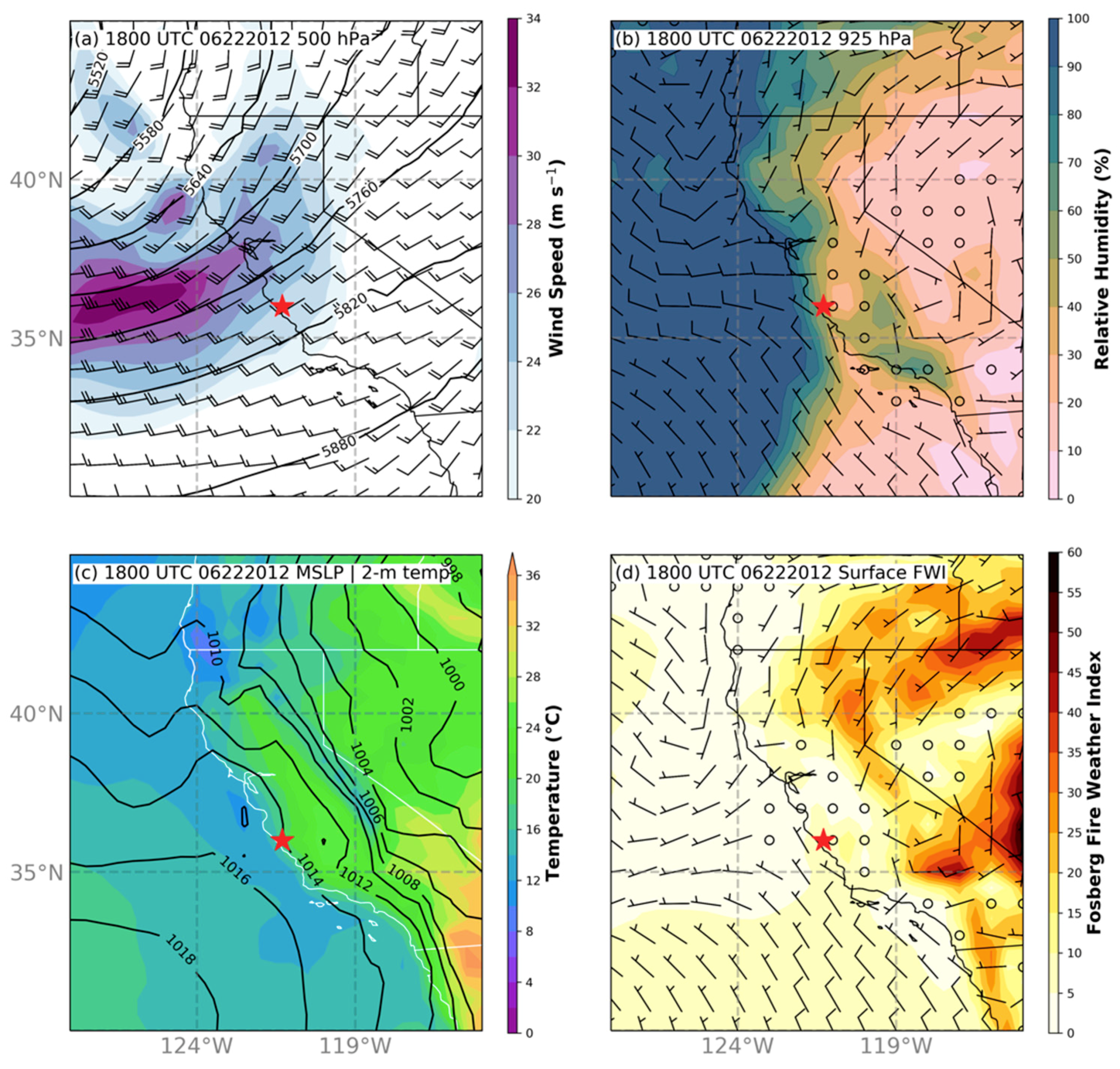
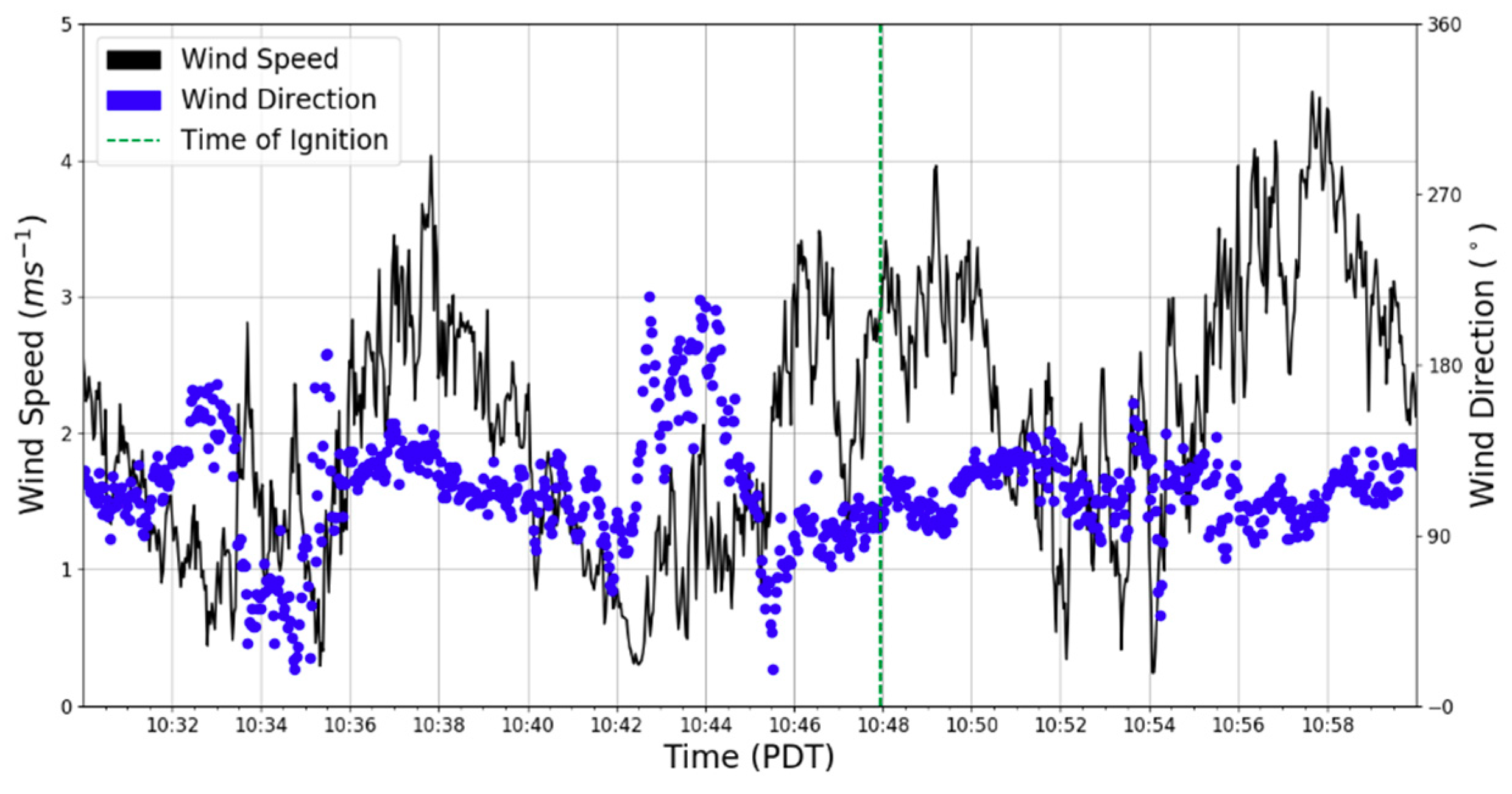
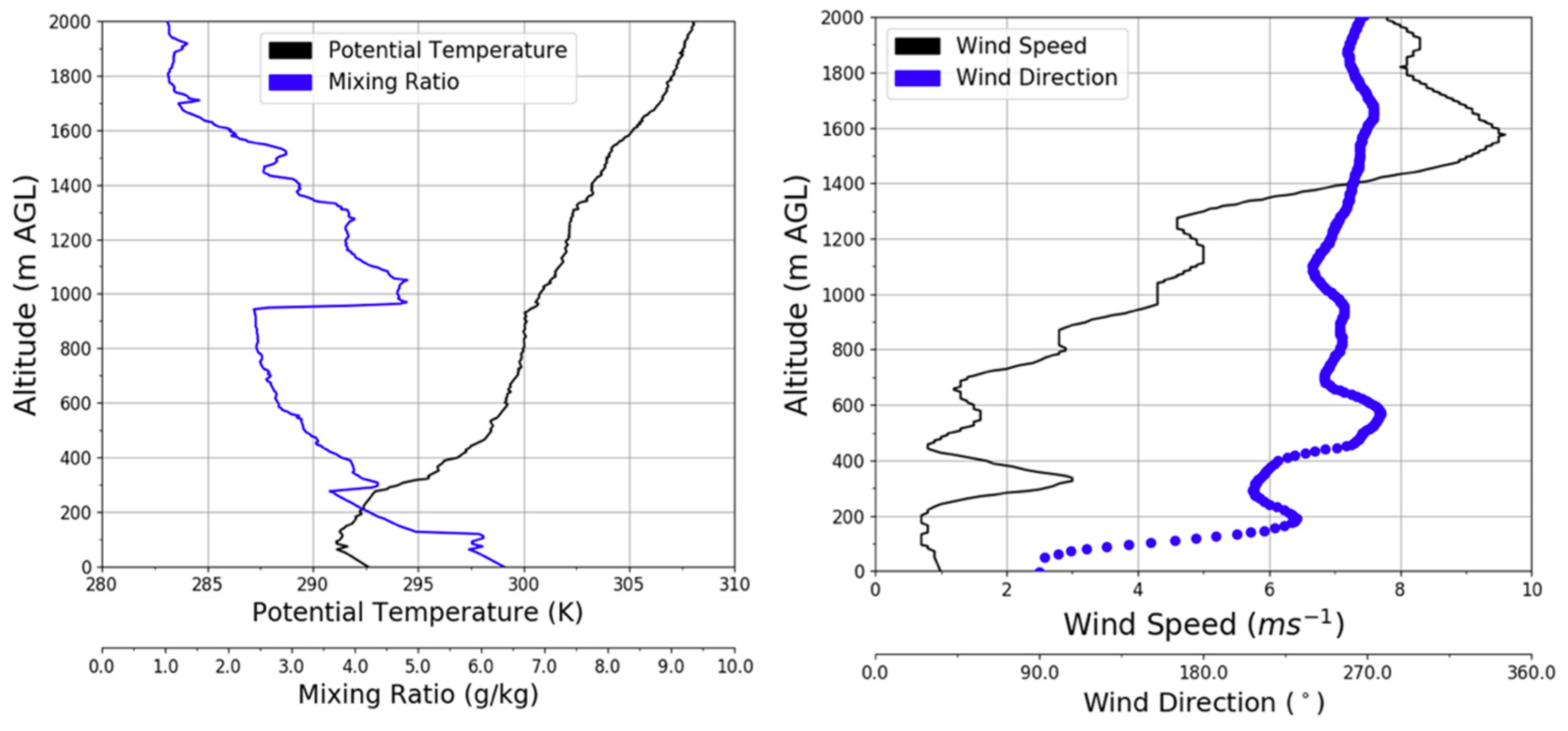
3.1. Background Meteorological Conditions
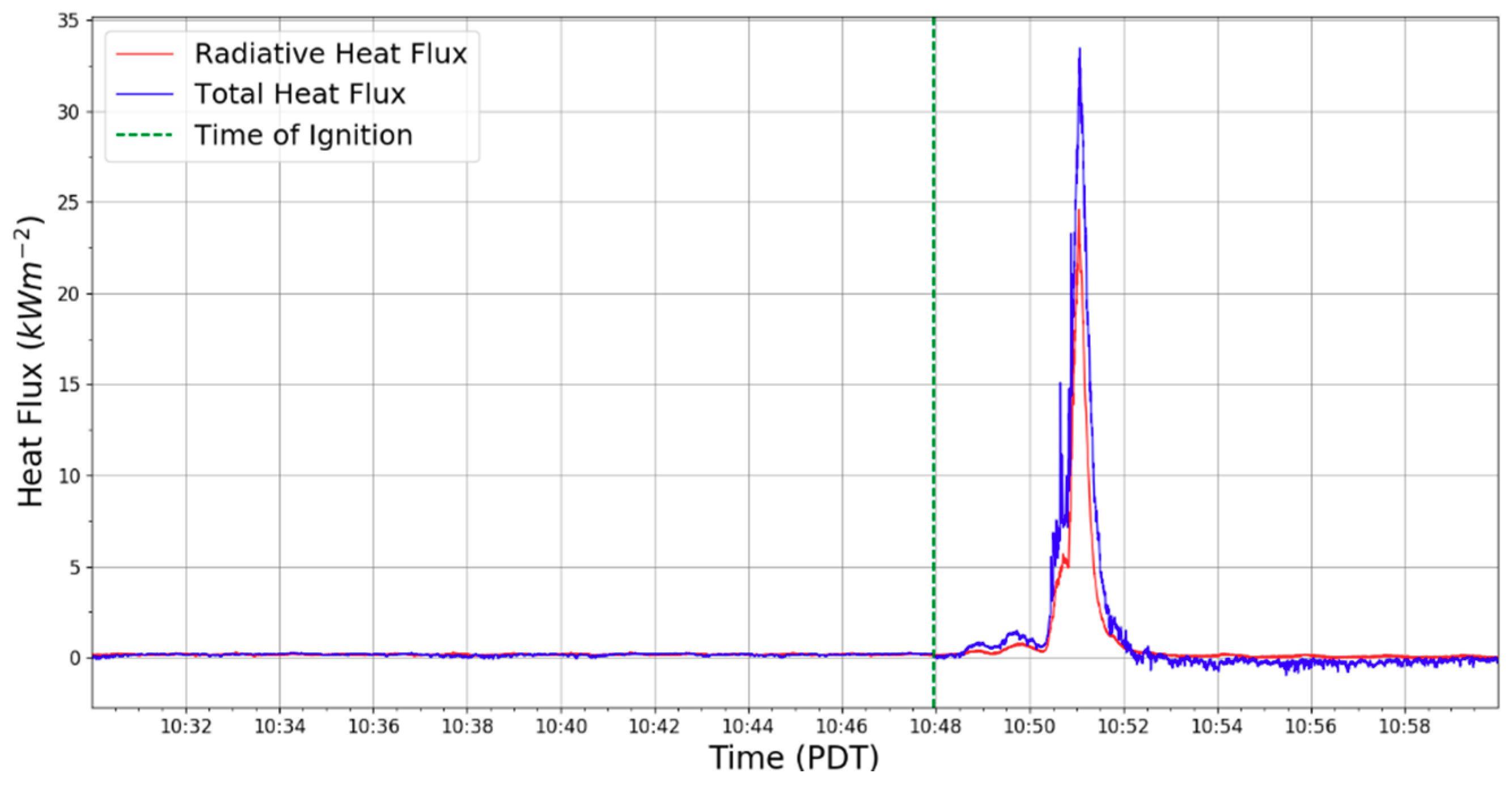
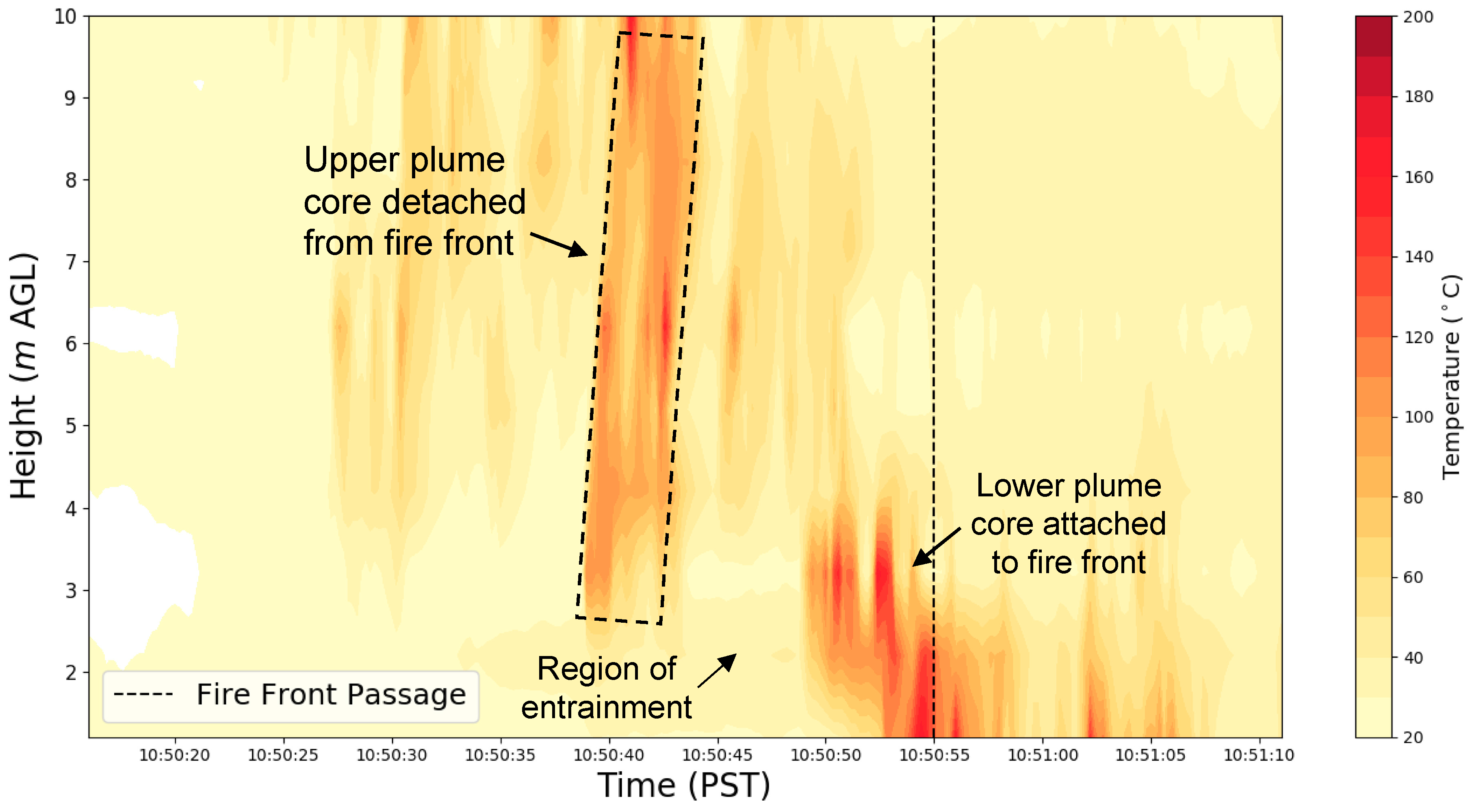
3.2. Fire Behavior
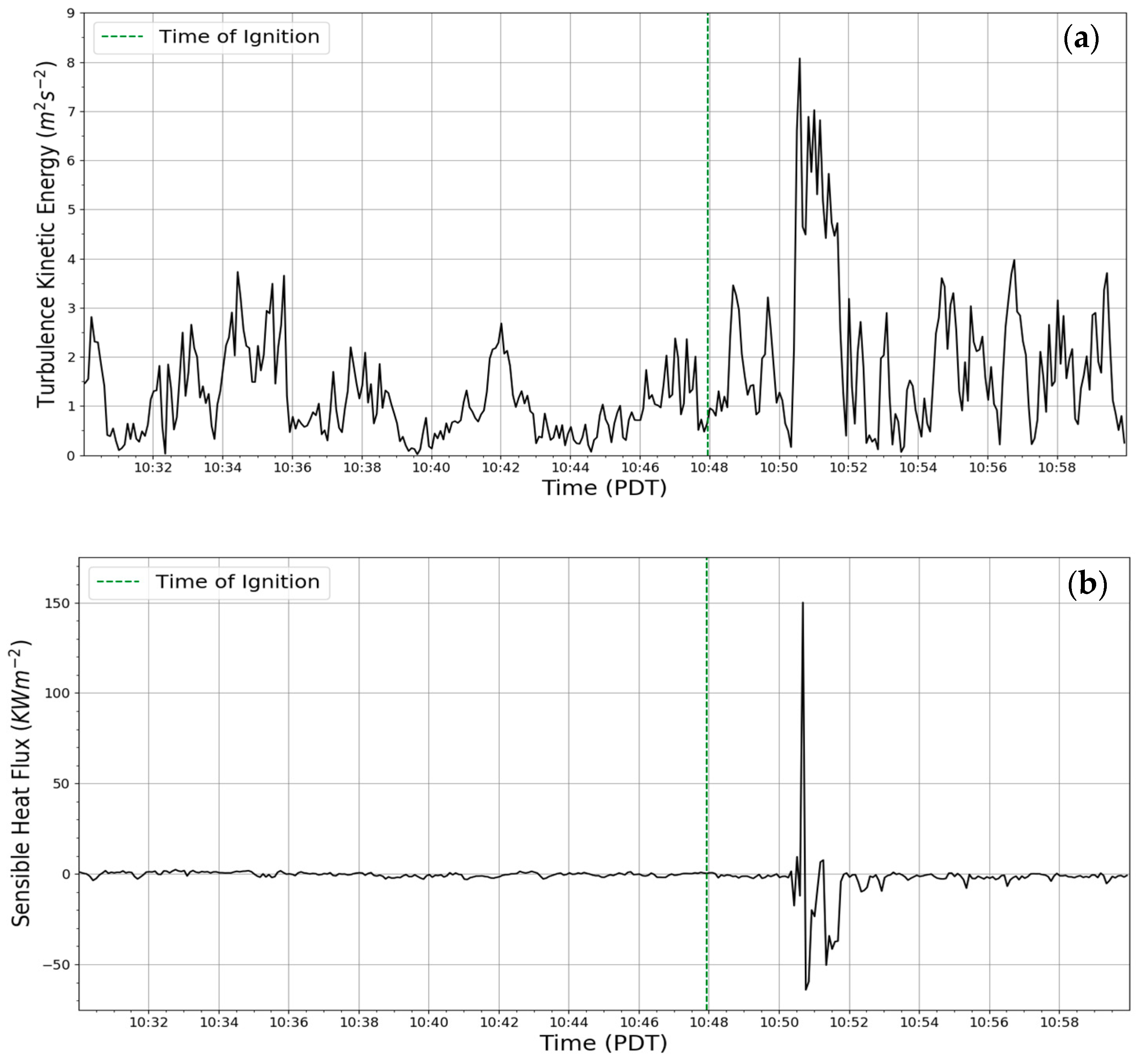
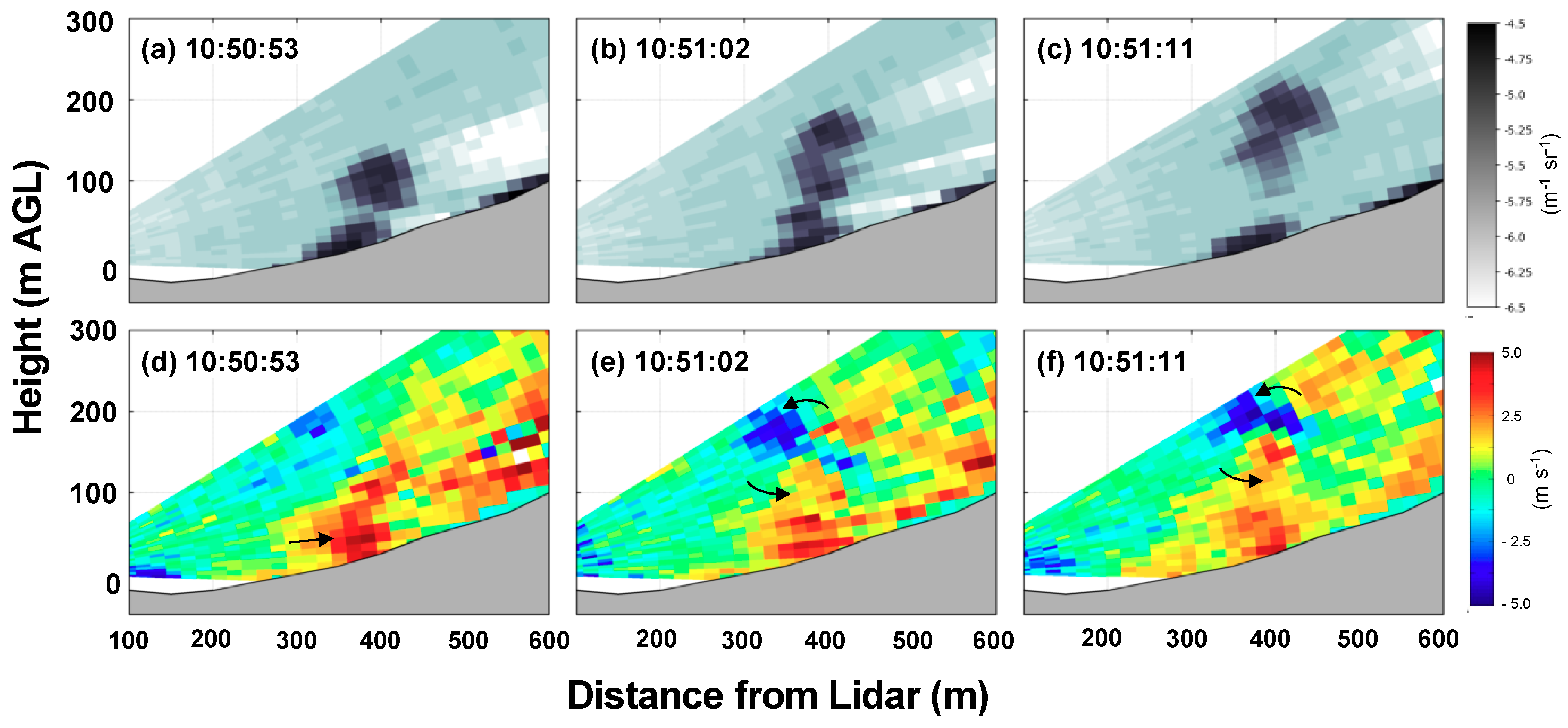
3.3. Plume Micrometeorology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Potter, B.E. Atmospheric interactions with wildland fire behaviour—II. Plume and vortex dynamics. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2012, 21, 802–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lareau, N.P.; Nauslar, N.J.; Abatzoglou, J.T. The Carr Fire Vortex: A Case of Pyrotornadogenesis? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 13,107–13,115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanski, A.K.; Jenkins, M.A.; Yedinak, K.; Mandel, J.; Beezley, J.; Lamb, B. Toward an integrated system for fire, smoke and air quality simulations. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2015, 25, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, R.; Reisner, J.; Coleman, J.J.; Smith, S. Studying wildfire behavior using FIRETEC. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2002, 11, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, C.B.; Kochanski, A.; Seto, D.; Davis, B. The FireFlux II experiment: A model-guided field experiment to improve understanding of fire–atmosphere interactions and fire spread. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2019, 28, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, C.B.; Lareau, N.P.; Kingsmill, D.E.; Bowers, C.L.; Camacho, C.P.; Bagley, R.; Davis, B. The Rapid Deployments to Wildfires Experiment (RaDFIRE): Observations from the Fire Zone. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 2539–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilman, W.E.; Bian, X.; Clark, K.L.; Skowronski, N.S.; Hom, J.L.; Gallagher, M.R. Atmospheric Turbulence Observations in the Vicinity of Surface Fires in Forested Environments. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2017, 56, 3133–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottmar, R.D.; Hiers, J.K.; Butler, B.W.; Clements, C.B.; Dickinson, M.B.; Hudak, A.T.; O’Brien, J.; Potter, B.E.; Rowell, E.M.; Strand, T.M.; et al. Measurements, datasets and preliminary results from the RxCADRE project—2008, 2011 and 2012. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2016, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, E.V.; Skowronski, N.; Thomas, J.; Clark, K.; Gallagher, M.; Hadden, R.; Mell, W.; Simeoni, A. Local measurements of wildland fire dynamics in a field-scale experiment. Combust. Flame 2018, 194, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, D.; Strand, T.M.; Clements, C.B.; Thistle, H.; Mickler, R. Wind and plume thermodynamic structures during low-intensity subcanopy fires. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 198, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, C.; Seto, D. Observations of Fire–Atmosphere Interactions and Near-Surface Heat Transport on a Slope. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2015, 154, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, C.; Zhong, S.; Goodrick, S.; Li, J.; Potter, B.E.; Bian, X.; Heilman, W.E.; Charney, J.J.; Perna, R.; Jang, M.; et al. Observing the Dynamics of Wildland Grass Fires: FireFlux—A Field Validation Experiment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charland, A.M.; Clements, C. Kinematic structure of a wildland fire plume observed by Doppler lidar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 3200–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, C.; Lareau, N.P.; Seto, D.; Contezac, J.; Davis, B.; Teske, C.; Zajkowski, T.J.; Hudak, A.T.; Bright, B.C.; Dickinson, M.B.; et al. Fire weather conditions and fire–atmosphere interactions observed during low-intensity prescribed fires—RxCADRE 2012. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2016, 25, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M.; Olivier, L.D.; Holloway, E.T.; Kropfli, R.A.; Bartram, B.W.; Cupp, R.E.; Post, M.J. Smoke-Column Observations from Two Forest Fires Using Doppler Lidar and Doppler Radar. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1992, 31, 1328–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lareau, N.P.; Clements, C. The Mean and Turbulent Properties of a Wildfire Convective Plume. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2017, 56, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lareau, N.P.; Clements, C. Environmental controls on pyrocumulus and pyrocumulonimbus initiation and development. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 16, 4005–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, N.F.; Guyot, A.; Dowdy, A.; McGowan, H. Wildfire and Weather Radar: A Review. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 124, 266–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, C. Thermodynamic structure of a grass fire plume. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2010, 19, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, C.B.; Oliphant, A.J. The California State University Mobile Atmospheric Profiling System: A Facility for Research and Education in Boundary Layer Meteorology. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1713–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, D.; Clements, C.; Heilman, W.E. Turbulence spectra measured during fire front passage. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 169, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczak, J.M.; Oncley, S.P.; Stage, S.A. Sonic Anemometer Tilt Correction Algorithms. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2001, 99, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosberg, M. Weather in Wildland Fire Management: The Fire Weather Index. In Proceedings of the Conference on Sierra Nevada Meteorology, Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 19–21 June 1978; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Clements, C.; Zhong, S.; Bian, X.; Heilman, W.E.; Byun, D.W. First observations of turbulence generated by grass fires. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Instrument/Sensor | Sampling Frequency | Resolution | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| California State University Mobile Atmospheric Profiling System (CSU-MAPS) | Gill, WindSonic | 1 Hz | 0.01 m s−1 | ±2%, 12 m s−1 |
| Temperature/RH Probe (Vaisala, HMP-45C) | 1 Hz | 0.01 °C | ±0.2 °C | |
| 0.10% | ±2% RH | |||
| Doppler Lidar | Halo Photonics, Streamline 75 | 10 Hz | 0.038 m s−1 | <20 cm s−1 |
| Sodar | ASC Model 4000 | 0.3 Hz | 0.1 m s−1 | <0.5 m s−1 |
| Radiosonde System | Vaisala Radiosonde, RS92-GPS | 1 Hz | 0.1 °C | ±0.5 °C |
| 1% RH | ±5% RH | |||
| 3-D Sonic Anemometer | ATI, model SATI-Sx | 10 Hz | 0.01 °C | ±0.05 °C |
| 0.01 m s−1 | ±0.01 | |||
| Thermocouples | Omega, Type-E, 5SC-TT-E-40 | 5 Hz | 0.01 °C | ±0.5% |
| Automated Weather Stations | Campbell Scientific, CS215, T/RH probe. RM Young 5103 anemometer | 1 Hz | 0.01 °C | ±0.3 °C |
| 0.10% | ±2% RH | |||
| 0.1 m s−1 | Wind Speed: ±0.3 m s−1 Wind Direction: ±3° | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arreola Amaya, M.; Clements, C.B. Evolution of Plume Core Structures and Turbulence during a Wildland Fire Experiment. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11080842
Arreola Amaya M, Clements CB. Evolution of Plume Core Structures and Turbulence during a Wildland Fire Experiment. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(8):842. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11080842
Chicago/Turabian StyleArreola Amaya, Maritza, and Craig B. Clements. 2020. "Evolution of Plume Core Structures and Turbulence during a Wildland Fire Experiment" Atmosphere 11, no. 8: 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11080842
APA StyleArreola Amaya, M., & Clements, C. B. (2020). Evolution of Plume Core Structures and Turbulence during a Wildland Fire Experiment. Atmosphere, 11(8), 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11080842





