The Response of Parameterized Orographic Gravity Waves to Rapid Warming over the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
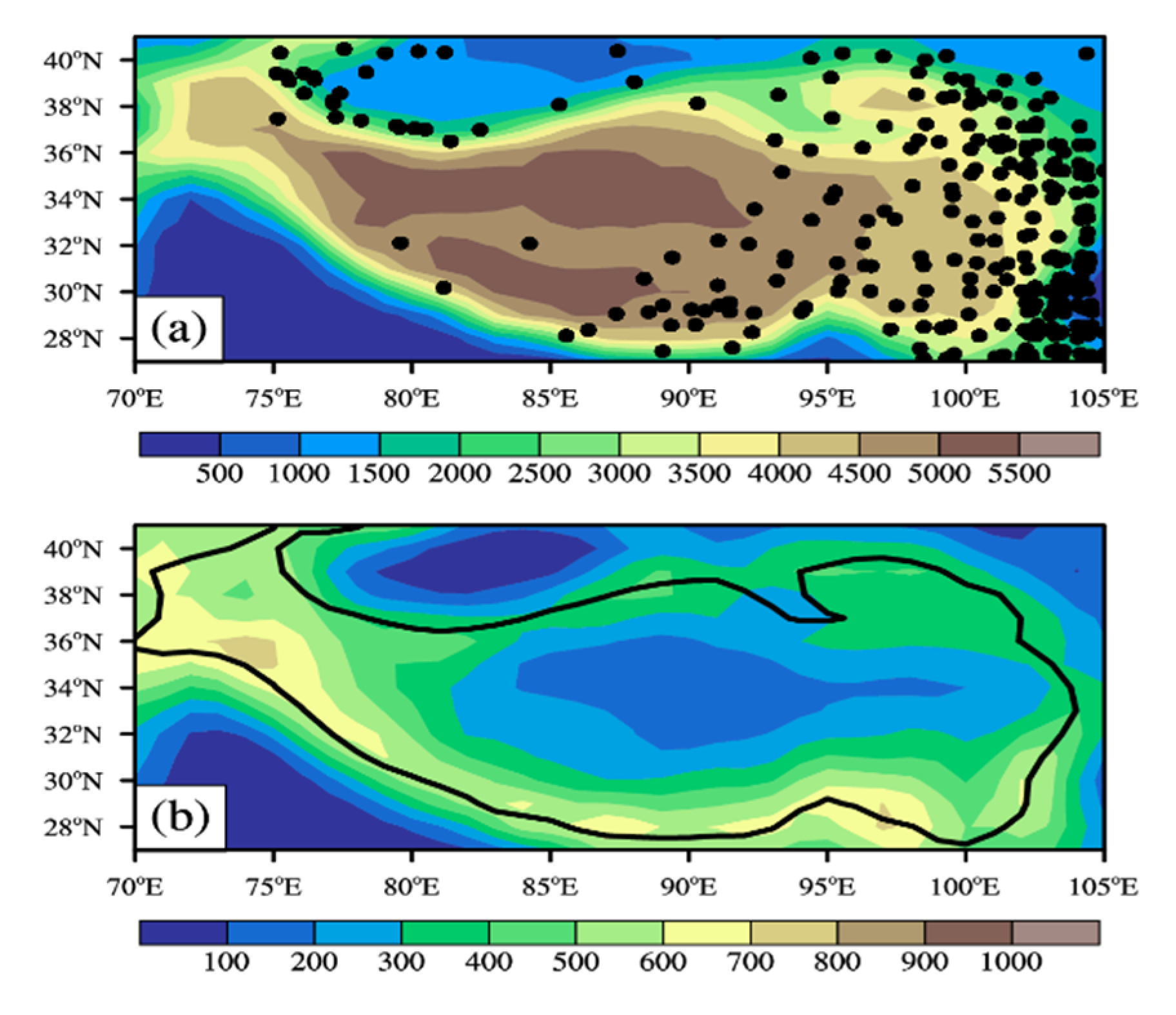
2. Data and Methods
3. Results
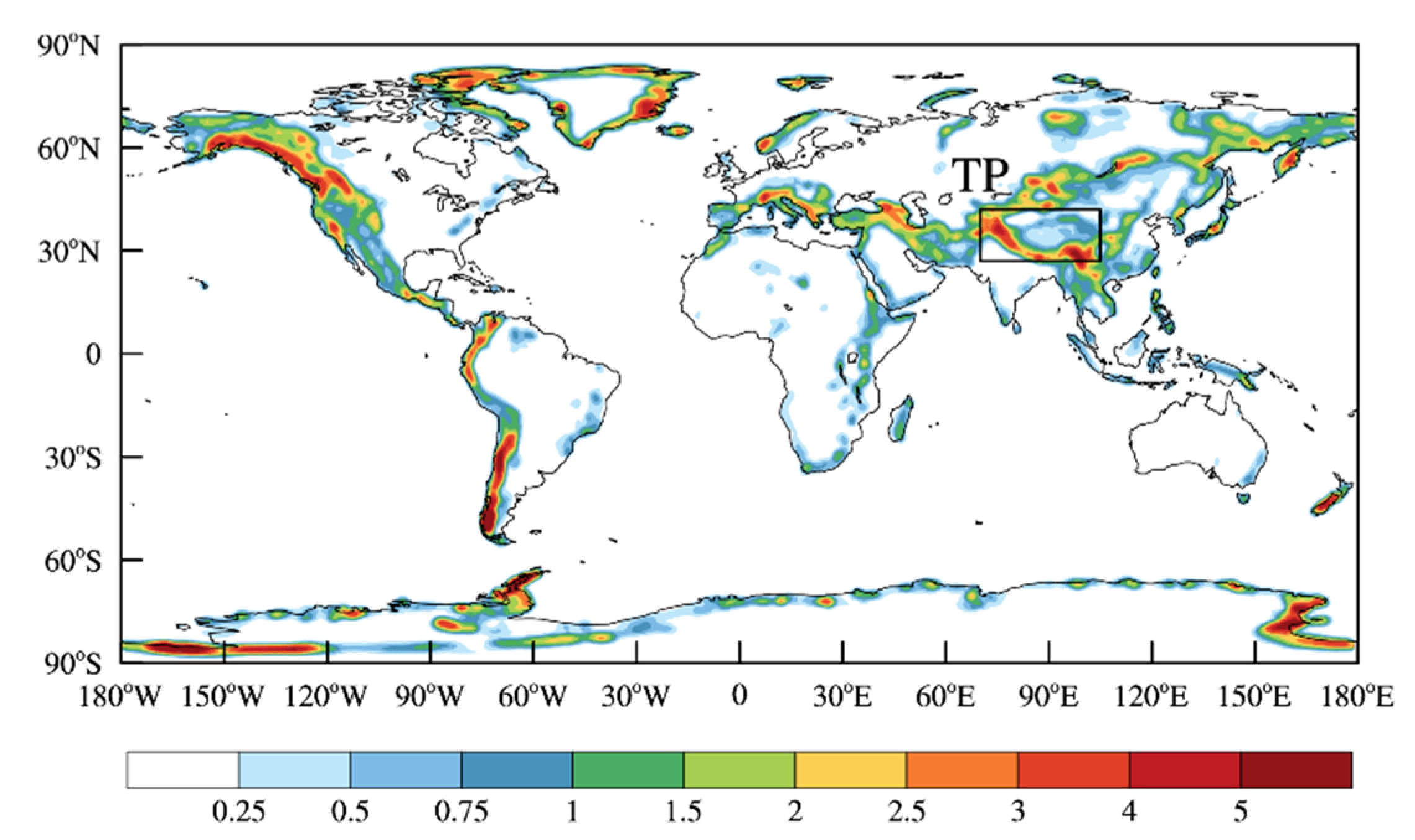
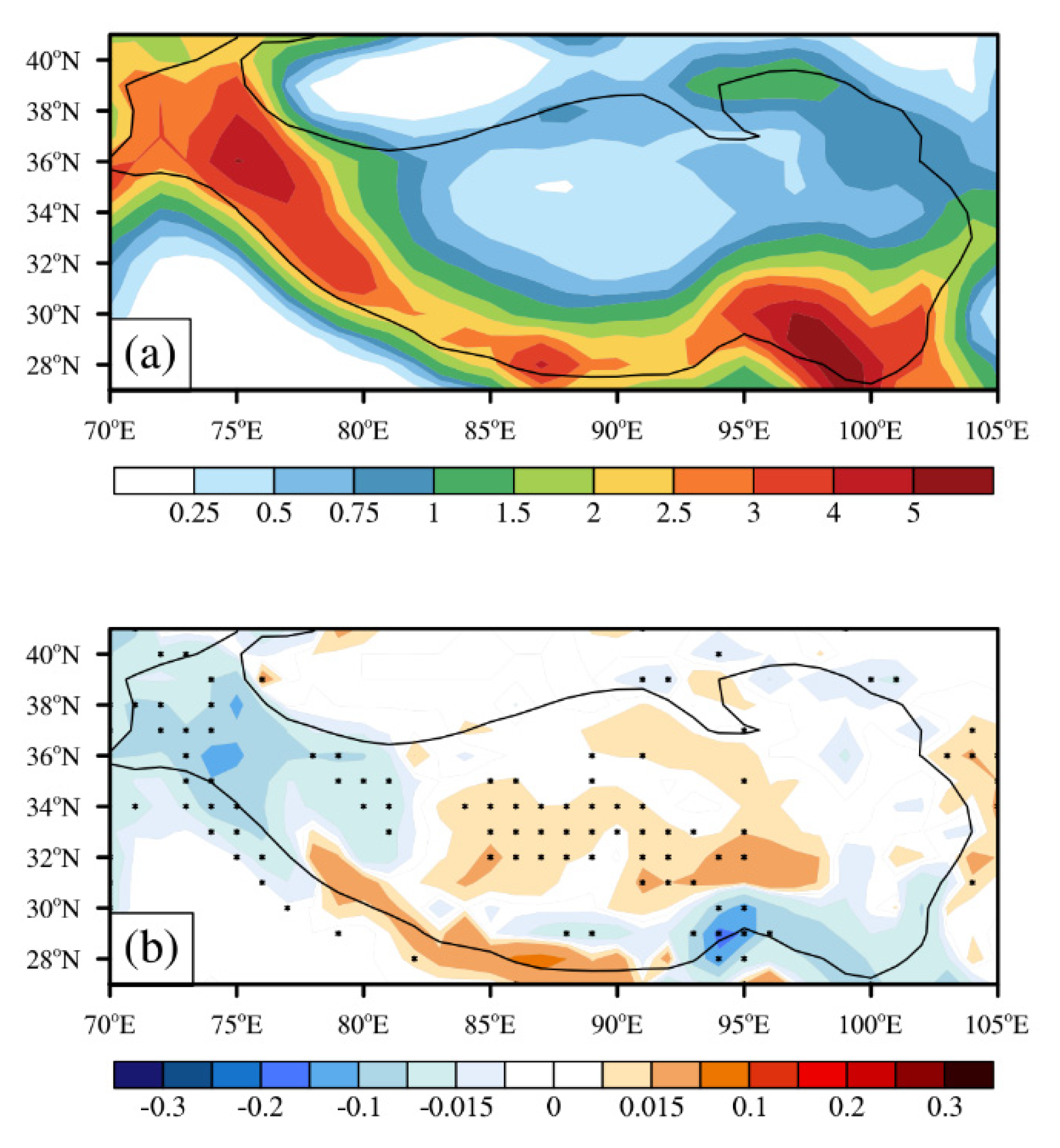
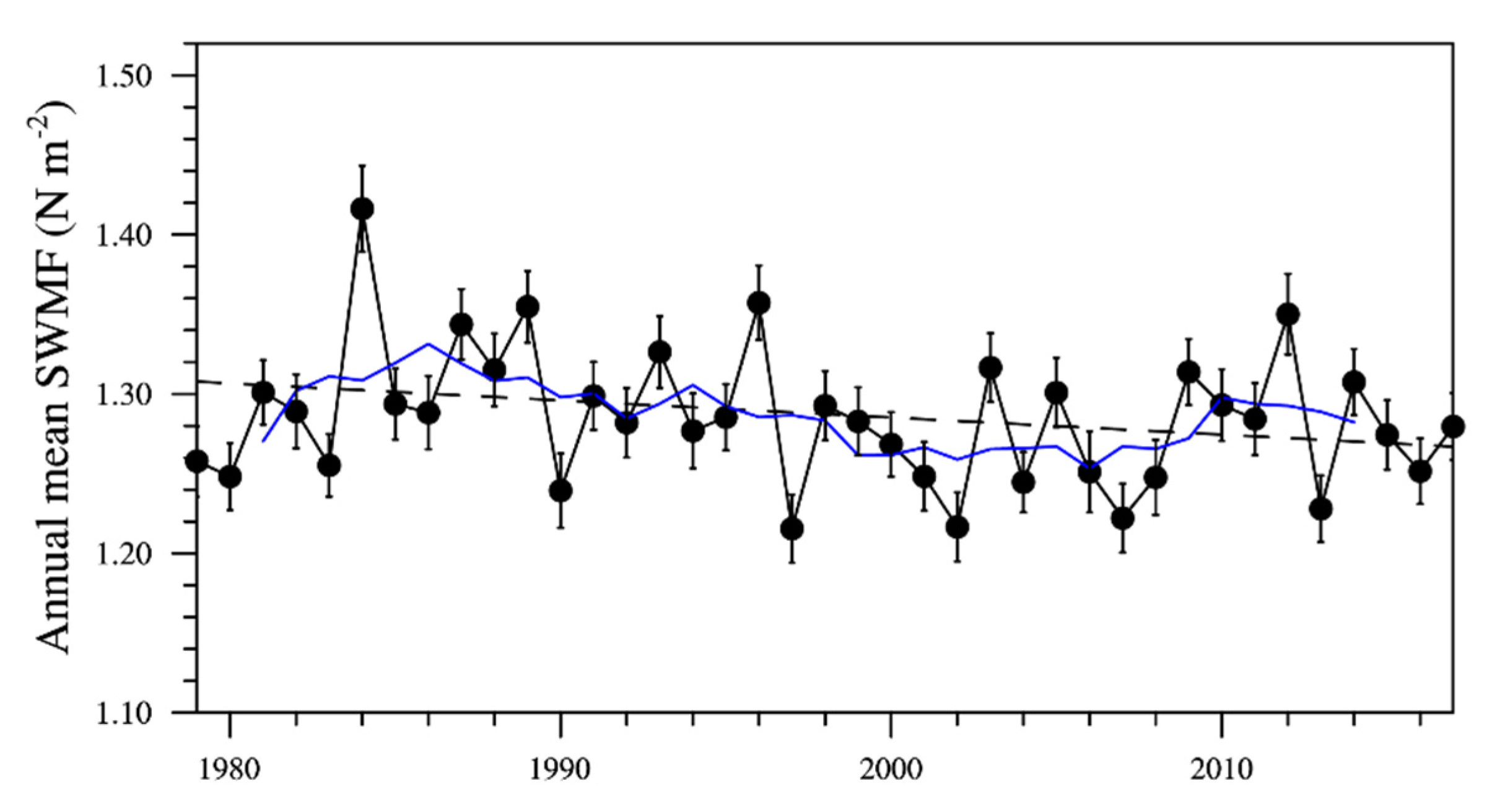
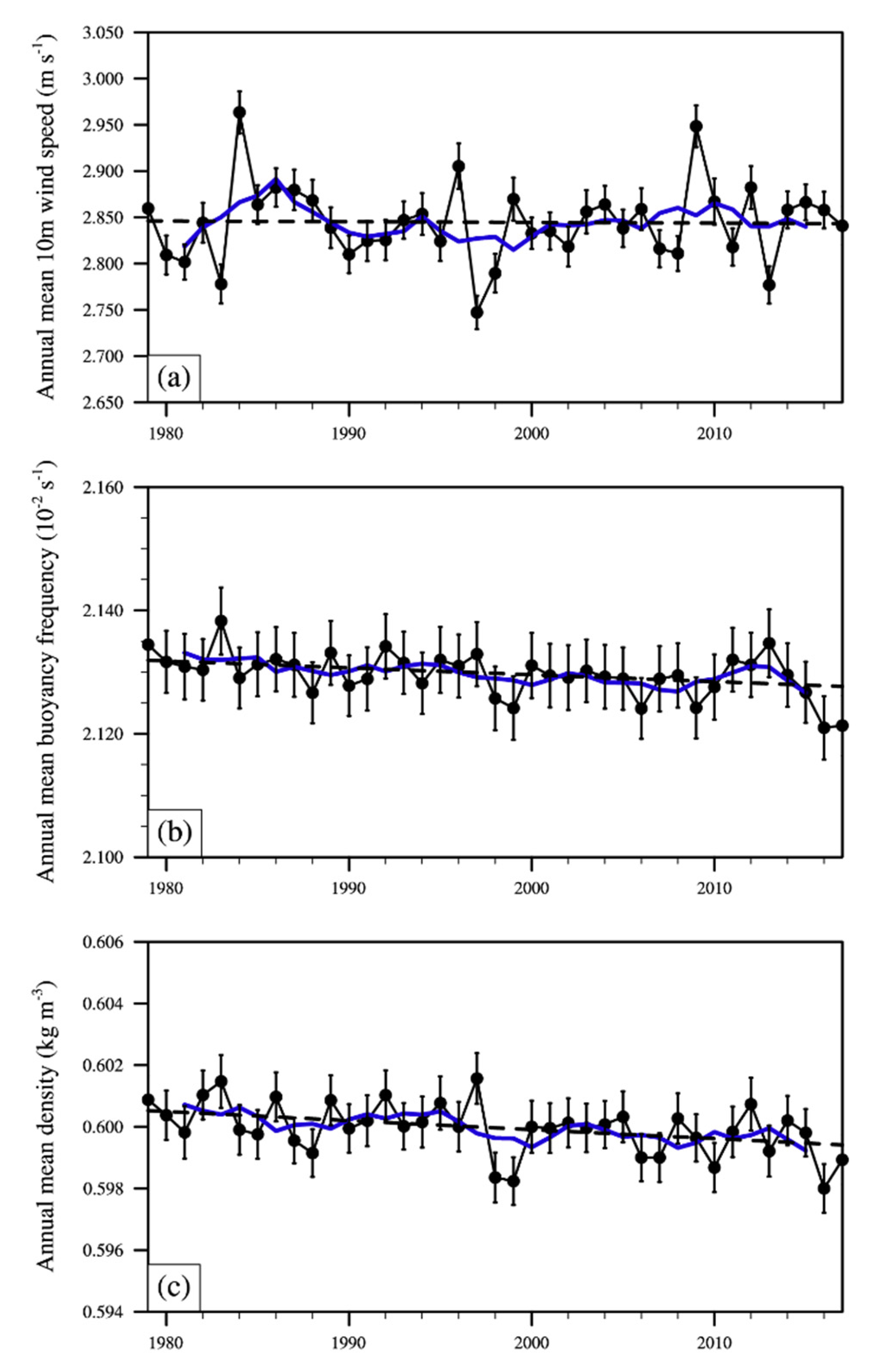
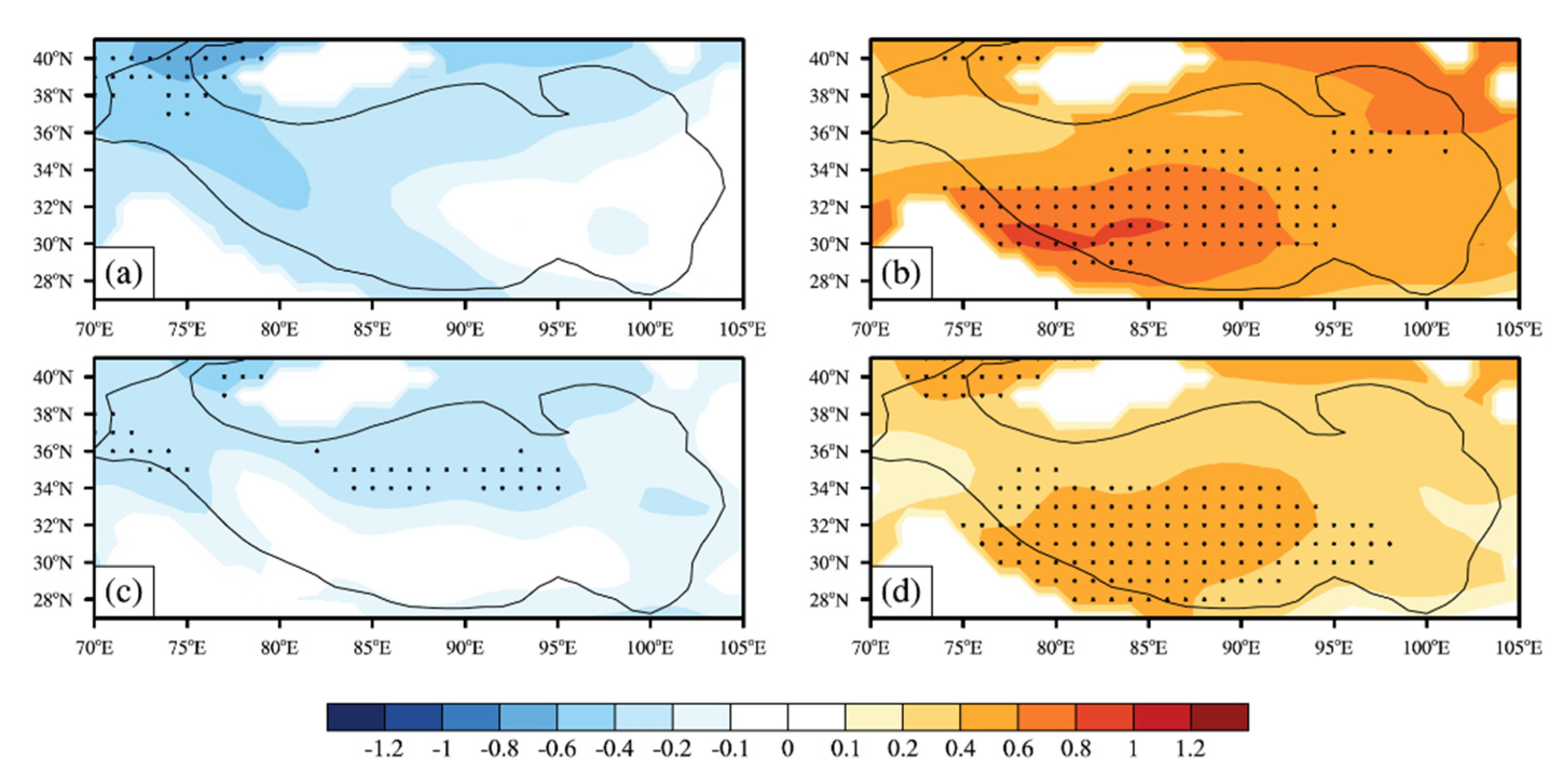
3.1. Climatology and Long-Term Trends of the SWMF
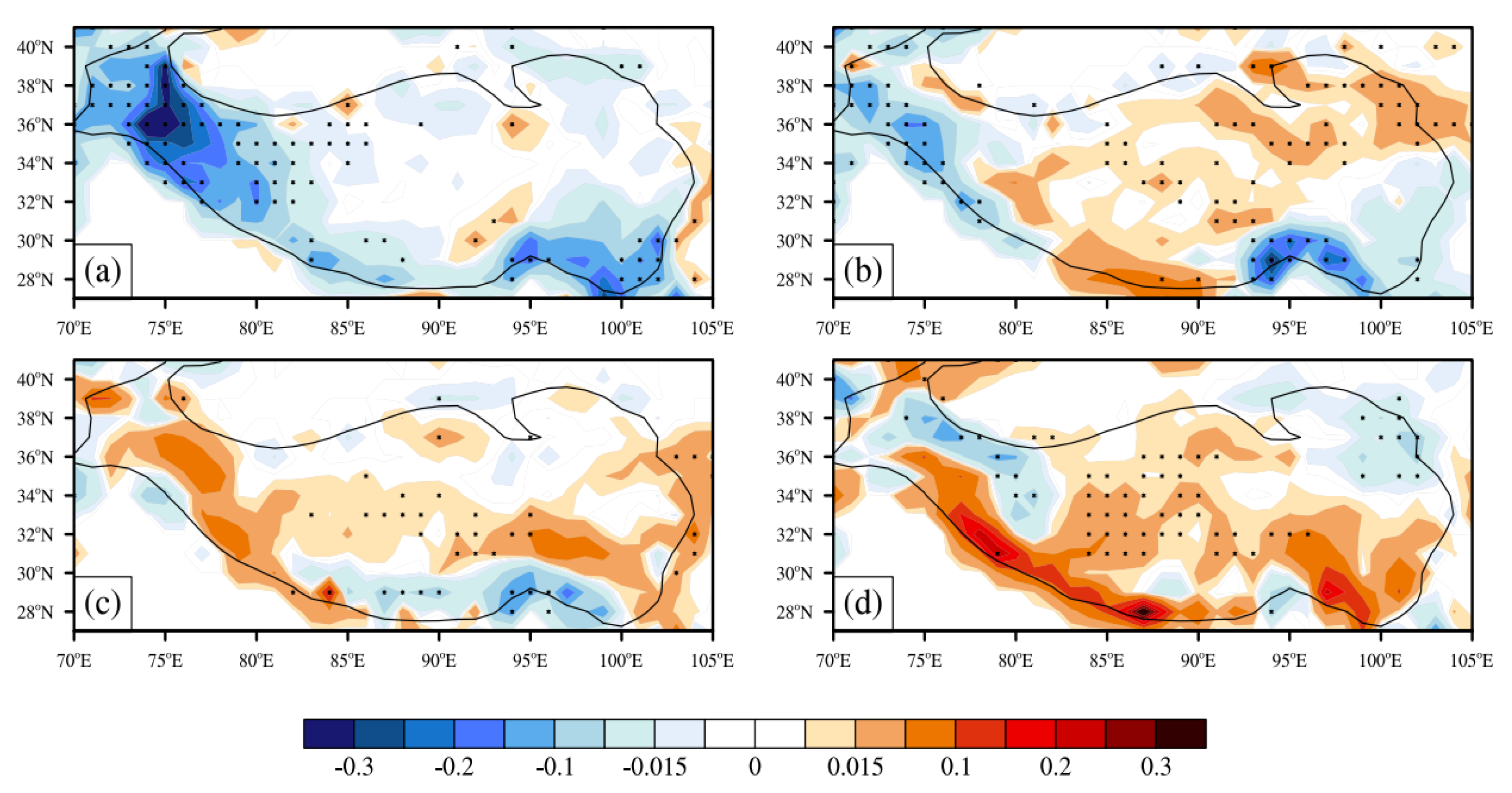
3.2. Cause of the SWMF Trends
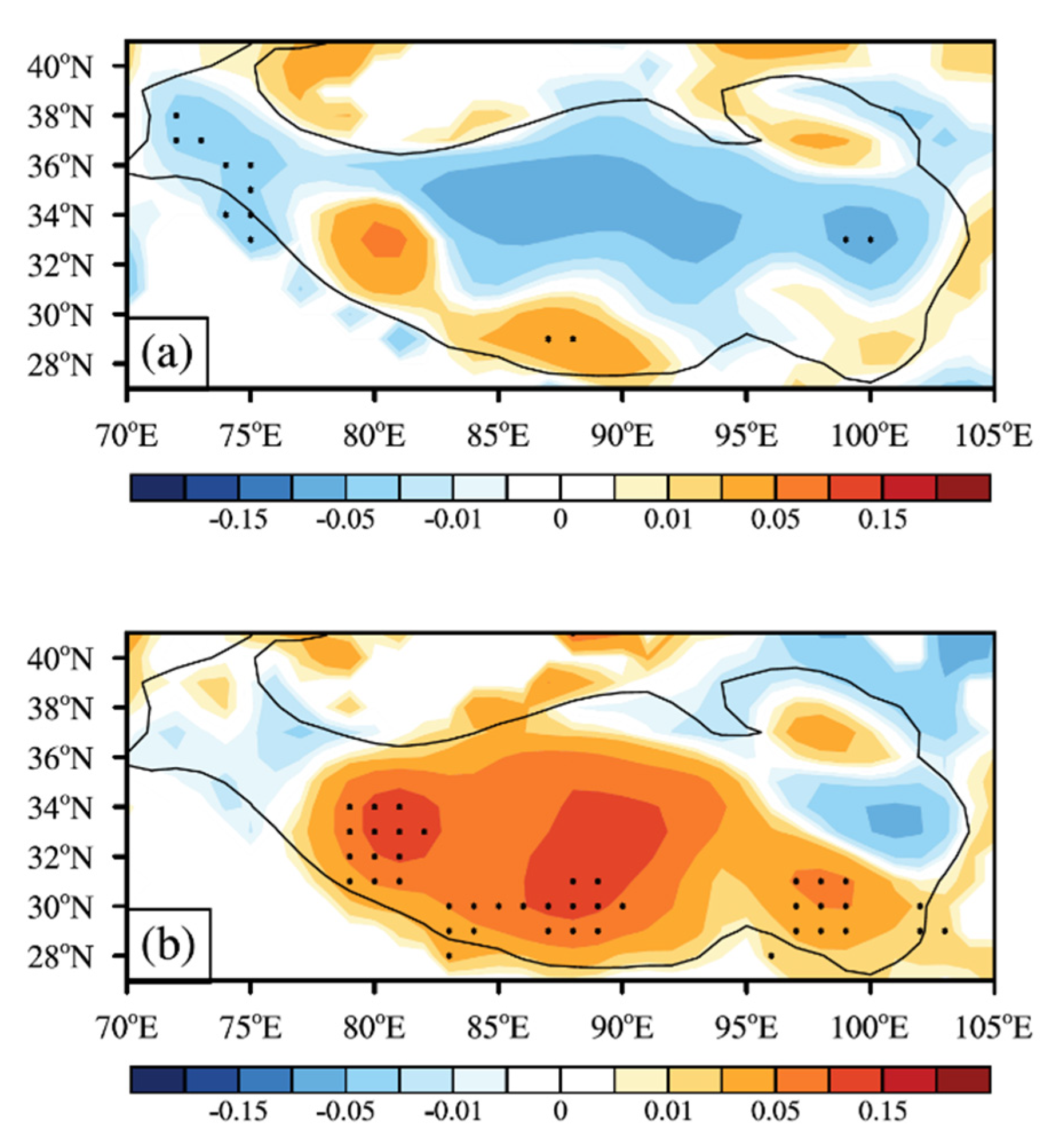
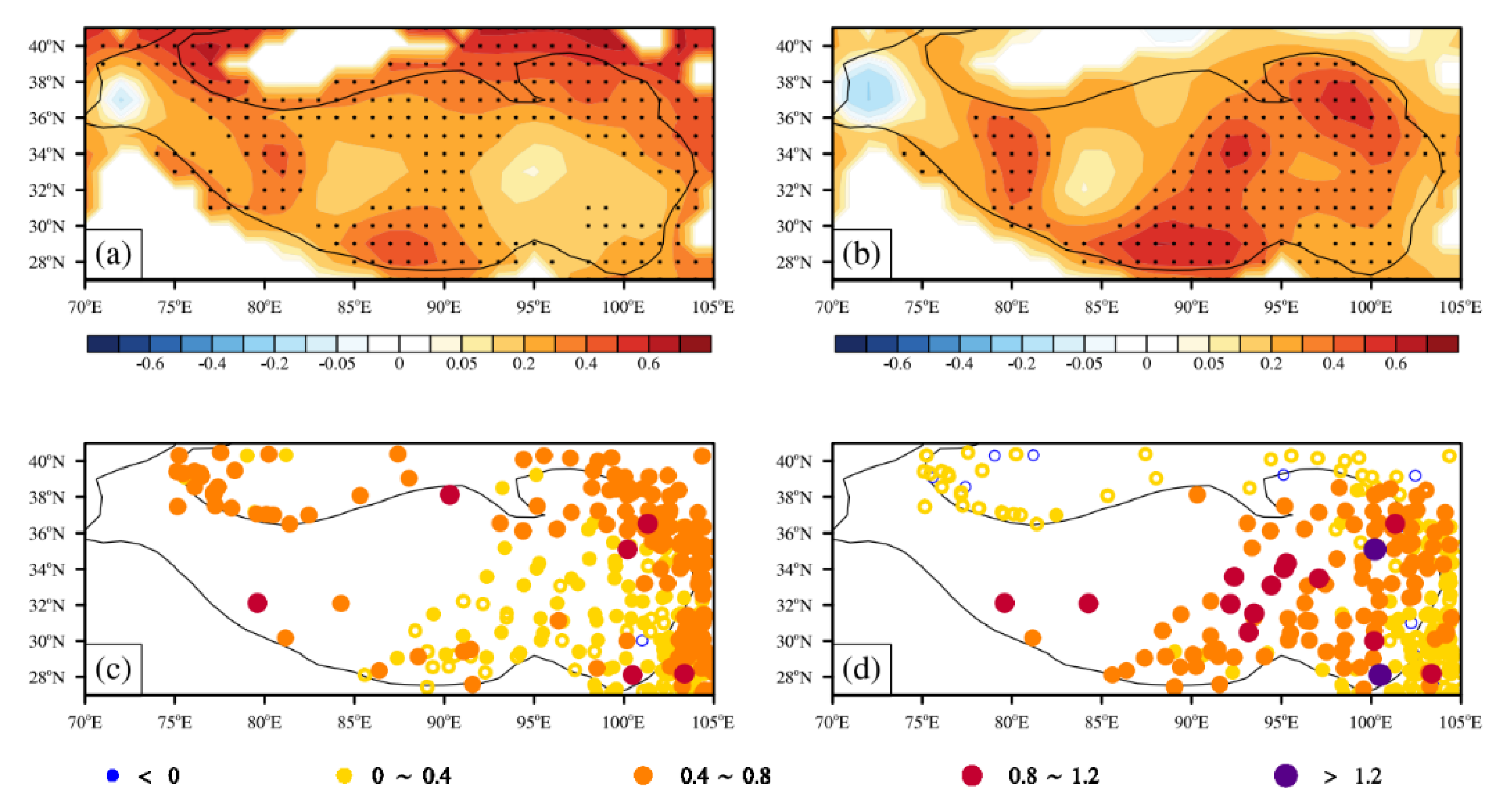
3.3. Linkage to TP Warming
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in tibetan plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Duan, A.; Liu, Y.; Mao, J.; Ren, R.; Bao, Q.; He, B.; Liu, B.; Hu, W. Tibetan plateau climate dynamics: Recent research progress and outlook. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2015, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.B. The influence of mountains on the atmosphere. In Advances in Geophysics; Saltzman, B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 87–230. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, M. The physics of orographic gravity wave drag. Front. Phys. 2014, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Shu, S.; Wang, Y. Another look on the structure of mountain waves: A spectral perspective. Atmos. Res. 2017, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, N.Y.; Boos, W.R. Modulation of subtropical stratospheric gravity waves by equatorial rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckermann, S.; Preusse, P. Global measurements of stratospheric mountain waves from space. Science 1999, 1534–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, K.; Watanabe, S.; Kawatani, Y.; Tomikawa, Y.; Miyazaki, K.; Takahashi, M. On the origins of mesospheric gravity waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, M. Directional absorption of parameterized mountain waves and its influence on the wave momentum transport in the northern hemisphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 2640–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindzen, R. Turbulence and stress owing to gravity-wave and tidal breakdown. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1981, 9707–9714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, M.; Geller, M.; McLandress, C.; Polavarapu, S.; Preusse, P.; Sassi, F.; Sato, K.; Eckermann, S.; Ern, M.; Hertzog, A.; et al. Recent developments in gravity-wave effects in climate models and the global distribution of gravity-wave momentum flux from observations and models. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 1103–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, D.; Alexander, M. Gravity wave dynamics and effects in the middle atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haynes, P.; Marks, C.; Mcintyre, M.; Shepherd, T.; Shine, K. On the downward control of extratropical diabatic circulations by eddy-induced mean zonal forces. J. Atmos. Sci. 1991, 651–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y. Implementation of a turbulent orographic form drag scheme in wrf and its application to the tibetan plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 2443–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.Y.; Boos, W.R. The influence of orographic rossby and gravity waves on rainfall. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandu, I.; Bechtold, P.; Beljaars, A.; Bozzo, A.; Pithan, F.; Shepherd, T.; Zadra, A. Impacts of parameterized orographic drag on the northern hemisphere winter circulation. J. Adv. Modeling Earth Syst. 2016, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Niekerk, A.; Sandu, I.; Vosper, S. The circulation response to resolved versus parametrized orographic drag over complex mountain terrains. J. Adv. Modeling Earth Syst. 2018, 2527–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, N.; Gerber, E.; Buhler, O. Compensation between resolved and unresolved wave driving in the stratosphere: Implications for downward control. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 3780–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Xue, M.; Teixeira, M.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y. Parameterization of directional absorption of orographic gravity waves and its impact on the atmospheric general circulation simulated by the weather research and forecasting model. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 3435–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, B. Climatic warming in the tibetan plateau during recent decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 1729–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Yan, L.; Yin, Z. Elevation dependency of recent and future minimum surface air temperature trends in the tibetan plateau and its surroundings. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Su, Z.; Ma, Y.; Salama, M.; Sobrino, J. Accelerated changes of environmental conditions on the tibetan plateau caused by climate change. J. Clim. 2011, 6540–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.C.; Zhang, Q.G.; Qian, Y.; Ji, Z.M.; Li, C.L.; Cong, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Guo, J.M.; Du, W.T.; Huang, J.; et al. Linking atmospheric pollution to cryospheric change in the third pole region: Current progress and future prospects. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; He, B.; Bao, Q.; Duan, A.; Jin, F. Thermal controls on the asian summer monsoon. Sci. Rep. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, A.; Wu, G. Weakening trend in the atmospheric heat source over the tibetan plateau during recent decades. Part i: Observations. J. Clim. 2008, 3149–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Guo, X.; He, J.; Qin, J.; Koike, T. On the climatology and trend of the atmospheric heat source over the tibetan plateau: An experiments-supported revisit. J. Clim. 2011, 1525–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Duan, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Guo, D.; Wang, H.; Ju, W. Recent recovery of the boreal spring sensible heating over the tibetan plateau will continue in cmip6 future projections. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigmond, M.; Scinocca, J.; Kushner, P. Impact of the stratosphere on tropospheric climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.; Yu, C. The gravity wave momentum flux in hydrostatic flow with directional shear over elliptical mountains. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 2014, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, M. Momentum flux and flux divergence of gravity waves in directional shear flows over three-dimensional mountains. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 3733–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, M.; Gille, J.; Cavanaugh, C.; Coffey, M.; Craig, C.; Eden, T.; Francis, G.; Halvorson, C.; Hannigan, J.; Khosravi, R.; et al. Global estimates of gravity wave momentum flux from high resolution dynamics limb sounder observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ern, M. Absolute values of gravity wave momentum flux derived from satellite data. J. Geophys. Res. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bougeault, P.; Binder, P.; Buzzi, A.; Dirks, R.; Houze, R.; Kuettner, J.; Smith, R.; Steinacker, R.; Volkert, H. The map special observing period. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 433–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dee, D.; Uppala, S.; Simmons, A.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The era-interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Kang, S.; Cong, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, T. Simulation of carbonaceous aerosols over the third pole and adjacent regions: Distribution, transportation, deposition, and climatic effects. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 2831–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maussion, F.; Scherer, D.; Molg, T.; Collier, E.; Curio, J.; Finkelnburg, R. Precipitation seasonality and variability over the tibetan plateau as resolved by the high asia reanalysis. J. Clim. 2014, 1910–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vellore, R.; Kaplan, M.; Krishnan, R.; Lewis, J.; Sabade, S.; Deshpande, N.; Singh, B.; Madhura, R.; Rao, M. Monsoon-extratropical circulation interactions in himalayan extreme rainfall. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 3517–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Guo, X.; Yao, T.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Y. Recent accelerating mass loss of southeast tibetan glaciers and the relationship with changes in macroscale atmospheric circulations. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, F.; Miller, M. A new subgrid-scale orographic drag parametrization: Its formulation and testing. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Li, L.; Fang, Y. Seasonal spatial heterogeneity of warming rates on the tibetan plateau over the past 30 years. Sci. Rep. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.; Wang, S.; Niu, X.; Hui, P.; Zong, P.; Wang, X. Impact of spectral nudging on regional climate simulation over cordex east asia using wrf. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 2339–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tang, J.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Juan, F. Spatiotemporal characteristics of heat waves over china in regional climate simulations within the cordex-ea project. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 799–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chang, C.; Fu, C.; Qi, Y.; Robock, A.; Robinson, D.; Zhang, H. Steady decline of east asian monsoon winds, 1969-2000: Evidence from direct ground measurements of wind speed. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Fu, R. Observed coherent trends of surface and upper-air wind speed over china since 1960. J. Clim. 2013, 2891–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holton, J.R. An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2004; p. 535. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Xu, M.; Hu, Q. Changes in near-surface wind speed in china: 1969–2005. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Fraedrich, K.; Min, J.; Kang, S.; Zhu, X.; Pepin, N.; Zhang, L. Observed surface wind speed in the tibetan plateau since 1980 and its physical causes. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 500 hPa | 400 hPa | 300 hPa | 200 hPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.76 |
| Winter | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.78 | 0.72 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Teixeira, M.A.C.; Tang, J.; Lu, Y. The Response of Parameterized Orographic Gravity Waves to Rapid Warming over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11091016
Li R, Xu X, Wang Y, Teixeira MAC, Tang J, Lu Y. The Response of Parameterized Orographic Gravity Waves to Rapid Warming over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(9):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11091016
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Runqiu, Xin Xu, Yuan Wang, Miguel A. C. Teixeira, Jianping Tang, and Yixiong Lu. 2020. "The Response of Parameterized Orographic Gravity Waves to Rapid Warming over the Tibetan Plateau" Atmosphere 11, no. 9: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11091016
APA StyleLi, R., Xu, X., Wang, Y., Teixeira, M. A. C., Tang, J., & Lu, Y. (2020). The Response of Parameterized Orographic Gravity Waves to Rapid Warming over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere, 11(9), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11091016









