Dust Criteria Derived from Long-Term Filter and Online Observations at Gosan in South Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
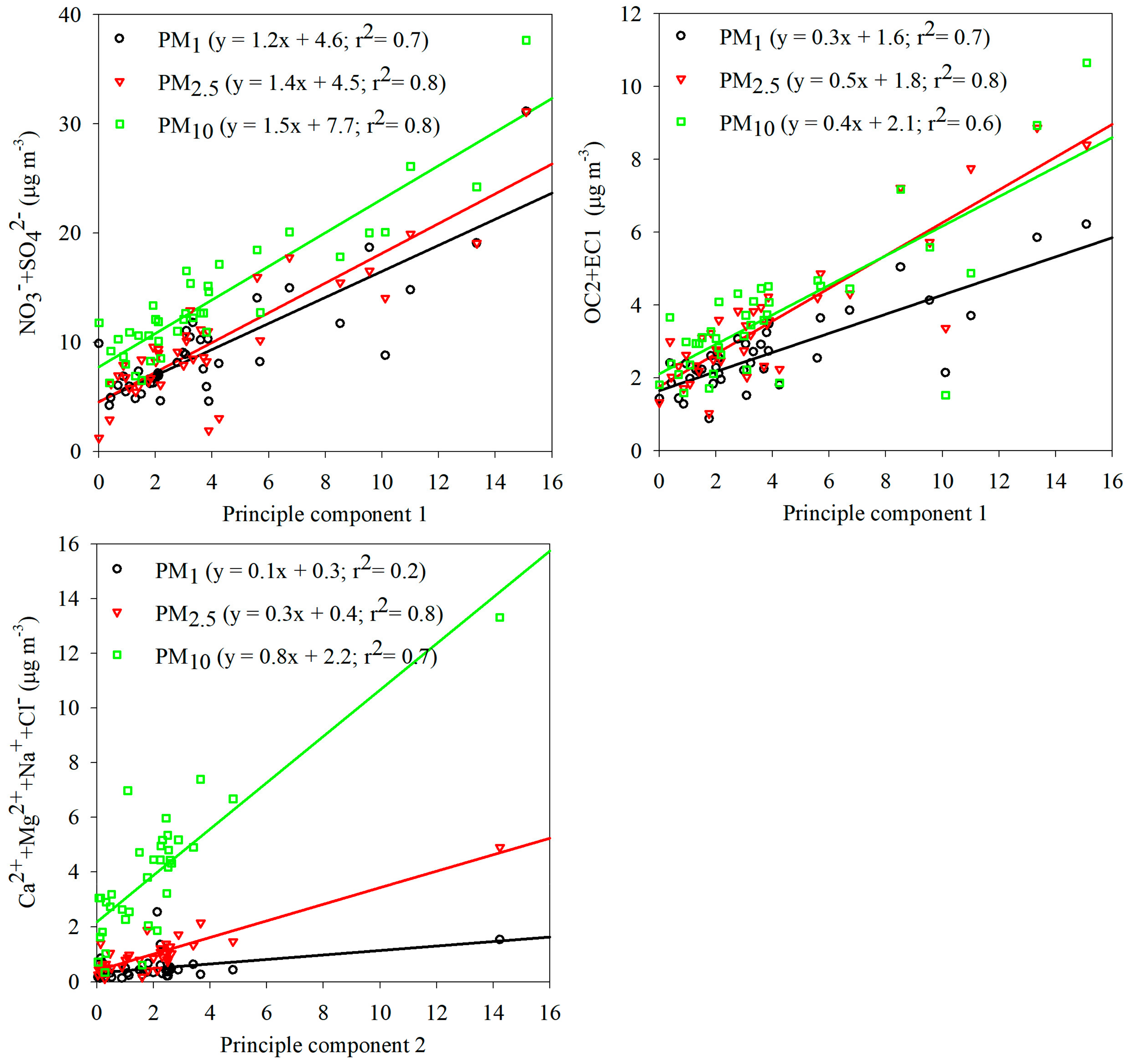
4.1. PCA of PM10, PM2.5, and PM1
4.2. Partitioning the Effect of Dust on Particulate Matters
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Textor, C.; Schulz, M.; Guibert, S.; Kinne, S.; Balkanski, Y.; Bauer, S.; Berntsen, T.; Berglen, T.; Boucher, O.; Chin, M.; et al. Analysis and quantification of the diversities of aerosol life cycles within AeroCom. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 1777–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huneeus, N.; Schulz, M.; Balkanski, Y.; Griesfeller, J.; Prospero, J.; Kinne, S.; Bauer, S.; Boucher, O.; Chin, M.; Dentener, F.; et al. Global dust model intercomparison in AeroCom phase I. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 7781–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Ge, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Lei, S.; Yang, T.; et al. Transport Patterns, Size Distributions, and Depolarization Characteristics of Dust Particles in East Asia in Spring 2018. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson, R.R.; Kondragunta, S.; Stenchikov, G.; Civerolo, K.L.; Doddridge, B.G.; Holben, B.N. The Impact of Aerosols on Solar Ultraviolet Radiation and Photochemical Smog. Science 1997, 278, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, W.; Ding, A.; Wang, T.; Kerminen, V.-M.; George, C.; Xue, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Petäjä, T.; Qi, X.; et al. Polluted dust promotes new particle formation and growth. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Ma, J.; Chu, B.; Ji, D.; Tang, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Hao, J. Mineral dust and NOx promote the conversion of SO2 to sulfate in heavy pollution days. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bègue, N.; Tulet, P.; Pelon, J.; Aouizerats, B.; Berger, A.; Schwarzenboeck, A. Aerosol processing and CCN formation of an intense Saharan dust plume during the EUCAARI 2008 campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3497–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, Q.-L.; Li, R.; Lin, B.; Joseph, E.; Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Morris, V.; Chang, F. Evidence of mineral dust altering cloud microphysics and precipitation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 3223–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prospero, J.M.; Ginoux, P.; Torres, O.; Nicholson, S.E.; Gill, T.E. Environmental Characterization of Global Sources of Atmospheric Soil Dust Identified with the Nimbus 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (Toms) Absorbing Aerosol Product. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 2-1–2-31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choobari, O.A.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Sturman, A. The global distribution of mineral dust and its impacts on the climate system: A review. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhuang, G.; Yuan, H.; Rahn, K.A.; Wang, Z.; An, Z. Aerosol Particles from Dried Salt-Lakes and Saline Soils Carried on Dust Storms over Beijing. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2009, 20, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, M.-C.; You, C.-F.; Cao, J.; Jin, Z. Spatial and seasonal variability of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 aerosols in 14 major cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunwar, B.; Kawamura, K. One-year observations of carbonaceous and nitrogenous components and major ions in the aerosols from subtropical Okinawa Island, an outflow region of Asian dusts. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1819–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Che, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Jing, J.; Cao, J.; Hsu, S.-C. PM2.5 pollution in a megacity of southwest China: Source apportionment and implication. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8679–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attiya, A.A.; Jones, B.G. Assessment of mineralogical and chemical properties of airborne dust in Iraq. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, P.; Schütz, L.; Balkanski, Y.; Desboeufs, K.; Ebert, M.; Kandler, K.; Petzold, A.; Scheuvens, D.; Weinbruch, S.; Zhang, D. Recent progress in understanding physical and chemical properties of African and Asian mineral dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8231–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.L.; Wu, G.J.; Xu, T.L.; Zhou, Q.Q. What is the real role of iron oxides in the optical properties of dust aerosols? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12159–12177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vet, R.; Artz, R.S.; Carou, S. A global assessment of precipitation chemistry and deposition of sulfur, nitrogen, sea salt, base cations, organic acids, acidity and pH, and phosphorus. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 93, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Tian, H.; Pan, S.; Prior, S.; Feng, Y.; Batchelor, W.D.; Chen, J.; Yang, J. Global ammonia emissions from synthetic nitrogen fertilizer applications in agricultural systems: Empirical and process-based estimates and uncertainty. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.C.; Higurashi, A.; Takemura, T.; Song, C.H. Consistency of the aerosol type classification from satellite remote sensing during the Atmospheric Brown Cloud–East Asia Regional Experiment campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-K.; Müller, D.; Lee, C.; Lee, K.H.; Shin, D.; Kim, Y.J.; Noh, Y.M. Vertical variation of optical properties of mixed Asian dust/pollution plumes according to pathway of air mass transport over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6707–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Yan, P.; Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Hu, Z.; Lelieveld, J. Strong air pollution causes widespread haze-clouds over China. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, R.; Praveen, P.S.; Xu, Y.; Ramanathan, V. Solar absorption by elemental and brown carbon determined from spectral observations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17366–17371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, C.E.; Ramanathan, V.; Decremer, D. Observationally constrained estimates of carbonaceous aerosol radiative forcing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11624–11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.C.; Lee, M.; Chun, Y.; Kim, J.; Oh, S. Chemical composition and source signature of spring aerosol in Seoul, Korea. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 18067–18074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klopper, D.; Formenti, P.; Namwoonde, A.; Cazaunau, M.; Chevaillier, S.; Feron, A.; Gaimoz, C.; Hease, P.; Lahmidi, F.; Mirande-Bret, C.; et al. Chemical composition and source apportionment of atmospheric aerosols on the Namibian coast. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 15811–15833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongming, H.; Peixuan, D.; Junji, C.; Posmentier, E.S. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 355, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betsou, C.; Diapouli, E.; Tsakiri, E.; Papadopoulou, L.; Frontasyeva, M.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Ioannidou, A. First-Time Source Apportionment Analysis of Deposited Particulate Matter from a Moss Biomonitoring Study in Northern Greece. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Zhang, K.; Meng, F.; Wang, S.; Lee, M.; Suh, I.; Kim, D.; Jeon, K.; Park, H.; Wang, X.; et al. Characteristics and source apportionment of fine haze aerosol in Beijing during the winter of 2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2573–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Song, M.; Moon, K.J.; Han, J.S.; Lee, G.; Kim, K.-R. Origins and chemical characteristics of fine aerosols during the northeastern Asia regional experiment (Atmospheric Brown Cloud–East Asia Regional Experiment 2005). J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.; Lee, M.; Laj, P.; Kim, S.W.; Ahn, K.H.; Gil, J.; Shang, X.; Zanatta, M.; Kang, K.S. Physical and chemical constraints on transformation and mass-increase of fine aerosols in northeast Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 2021, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Lee, M.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.; Yoon, S.; Kang, K. Ionic and carbonaceous compositions of PM10, PM2.5 and PM1.0 at Gosan ABC Superstation and their ratios as source signature. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2007–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.-W.; Yoon, S.-C.; Lee, G.; Lee, Y.J. Absorption and scattering properties of organic carbon versus sulfate dominant aerosols at Gosan climate observatory in Northeast Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 7781–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Jing, J.; Tao, J.; Hsu, S.-C.; Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Lee, C.S.L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing: Seasonal perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7053–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, J.; Takahashi, K.; Matsumi, Y.; Yabushita, A.; Shimizu, A.; Matsui, I.; Sugimoto, N. Scavenging of pollutant acid substances by Asian mineral dust particles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Howell, S.G.; Zhuang, J.; Huebert, B.J. Attribution of aerosol light absorption to black carbon, brown carbon, and dust in China—Interpretations of atmospheric measurements during EAST-AIRE. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2035–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y. Measurement report: Characterization of severe spring haze episodes and influences of long-range transport in the Seoul metropolitan area in March 2019. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11527–11550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-M.; Bu, J.-O.; Yang, S.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, W.-H.; Kang, C.-H. Influences of Asian Dust, Haze, and Mist Events on Chemical Compositions of Fine Particulate Matters at Gosan Site, Jeju Island in 2014. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 32, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization; Regional Office for Europe. Air Quality Guidelines: Global Update 2005: Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/107823 (accessed on 26 October 2021).
- Escudero, M.; Querol, X.; Cuevas, E.; Ávila, A. Origin of the Exceedances of the European Daily Pm Limit Value in Regional Background Areas of Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 730–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, M.; Querol, X.; Cuevas, E.; Escudero, M.; Querol, X.; Pey, J.; Alastuey, A.; Pérez, N.; Ferreira, F.; Alonso, S.; et al. A Methodology for the Quantification of the Net African Dust Load in Air Quality Monitoring Networks. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 5516–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lijing, Z.; Daniel, Q.T.; Guangjian, W.; Mo, D.; Bo, T. A Systematic Review of Global Desert Dust and Associated Human Health Effects. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

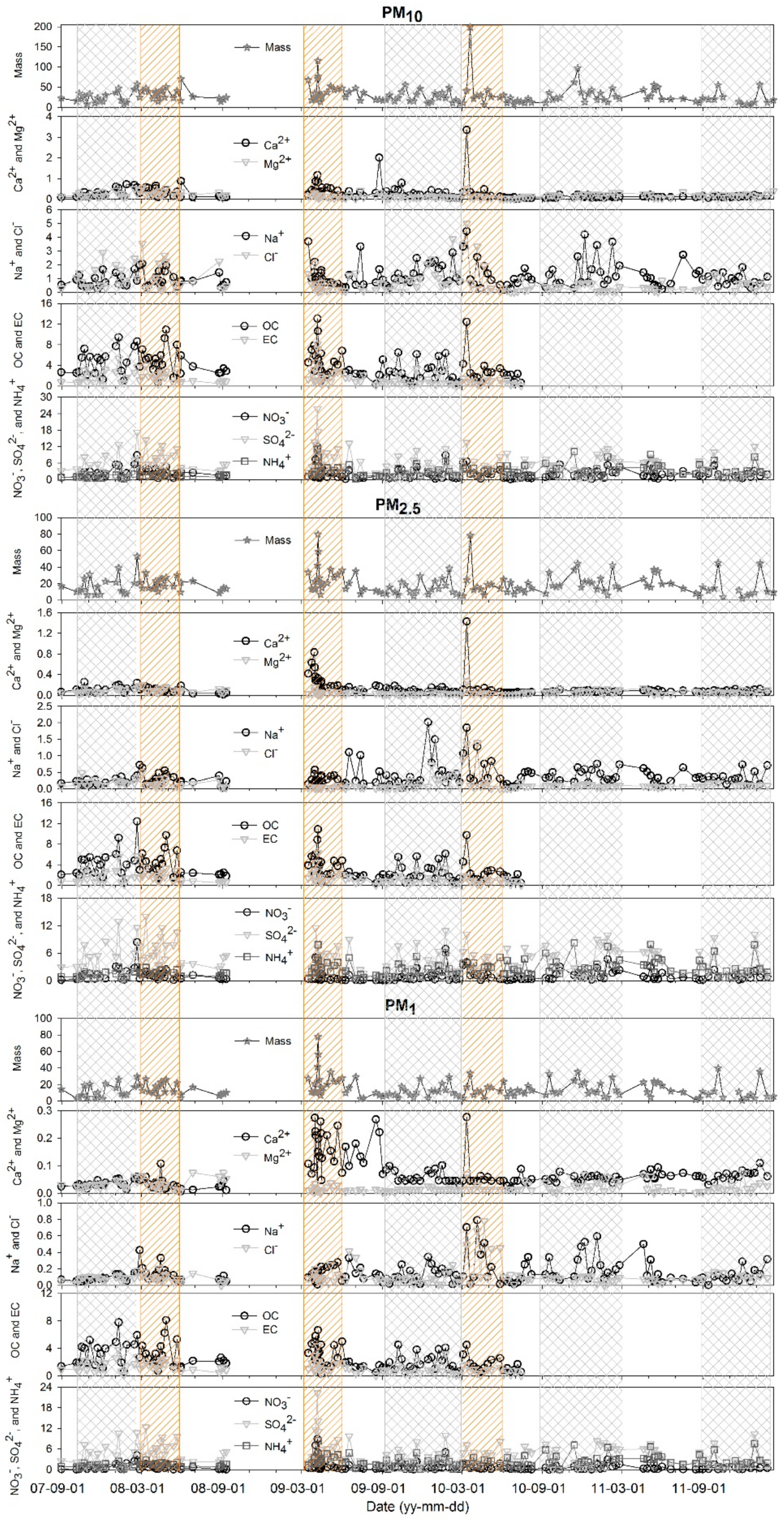

| PM10 | PM2.5 | PM1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10th/50th/90th | 10th/50th/90th | 10th/50th/90th | |||||||
| Total period | |||||||||
| Mass | 30 | 52 | 11/24/49 | 19 | 32 | 7/15/35 | 14 | 25 | 4/11/27 |
| Cl− | 0.8 | 1.7 | 0.09/0.48/2.02 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.03/0.08/0.28 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.03/0.08/0.16 |
| NO3− | 2.1 | 4.1 | 0.55/1.44/4.75 | 1.0 | 2.2 | 0.13/0.55/2.39 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 0.09/0.34/1.64 |
| SO42− | 5.5 | 9.5 | 1.32/4.72/11.14 | 4.4 | 7.5 | 1.04/3.49/8.43 | 4.3 | 7.5 | 0.84/3.6/8.05 |
| Na+ | 1.2 | 1.9 | 0.42/0.92/2.14 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.13/0.28/0.64 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.05/0.11/0.32 |
| NH4+ | 2.8 | 4.6 | 0.98/2.18/5.09 | 2.4 | 4.0 | 0.83/1.9/4.49 | 2.1 | 3.6 | 0.66/1.72/4.06 |
| K+ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.06/0.2/0.5 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.03/0.14/0.41 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.03/0.11/0.37 |
| Mg2+ | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.05/0.15/0.31 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.01/0.05/0.12 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.01/0.01/0.04 |
| Ca2+ | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.07/0.16/0.55 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.04/0.09/0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.02/0.05/0.14 |
| OC | 4.0 | 6.6 | 1.04/2.98/7.48 | 3.4 | 5.7 | 1.22/2.47/6.07 | 2.6 | 4.3 | 0.83/2.09/4.81 |
| OC1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0/0.1/0.27 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0/0.1/0.24 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0/0.08/0.25 |
| OC2 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 0.28/0.71/1.45 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 0.32/0.65/1.44 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.27/0.63/1.22 |
| OC3 | 1.2 | 2.0 | 0.34/0.99/2.19 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 0.32/0.68/1.52 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.28/0.59/1.2 |
| OC4 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 0.12/0.64/1.83 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 0.12/0.45/1.34 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.09/0.34/1.06 |
| OP | 0.9 | 1.7 | 0.17/0.68/2.15 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 0.15/0.69/1.7 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 0.04/0.51/1.51 |
| EC | 1.5 | 2.9 | 0.38/1.01/3.22 | 1.5 | 2.7 | 0.37/1/2.9 | 1.2 | 2.0 | 0.34/0.98/2.2 |
| EC1 | 1.2 | 2.5 | 0.23/0.72/2.72 | 1.1 | 2.3 | 0.22/0.56/2.45 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 0.12/0.54/1.59 |
| EC2+3 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.04/0.28/0.53 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.13/0.37/0.59 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.16/0.38/0.59 |
| Dust period | |||||||||
| Mass | 78 | 146 | 38 | 62 | 21 | 30 | |||
| Cl− | 2.3 | 4.4 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | |||
| NO3− | 4.5 | 6.6 | 2.5 | 3.7 | 0.9 | 1.7 | |||
| SO42− | 6.9 | 11.0 | 5.6 | 8.9 | 4.2 | 7.4 | |||
| Na+ | 2.1 | 3.6 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0.5 | |||
| NH4+ | 3.6 | 6.9 | 3.3 | 6.1 | 2.3 | 4.8 | |||
| K+ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | |||
| Mg2+ | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | |||
| Ca2+ | 0.9 | 2.3 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | |||
| OC | 7.7 | 12.2 | 6.4 | 9.6 | 3.9 | 4.9 | |||
| OC1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |||
| OC2 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 2.2 | 0.8 | 1.0 | |||
| OC3 | 2.4 | 3.7 | 1.9 | 3.2 | 1.0 | 1.3 | |||
| OC4 | 2.3 | 3.7 | 1.3 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 1.1 | |||
| OP | 1.8 | 3.2 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 1.5 | |||
| EC | 1.1 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.9 | 1.3 | 1.8 | |||
| EC1 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |||
| EC2 + 3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | |||
| Haze period | |||||||||
| Mass | 60 | 83 | 45 | 61 | 37 | 54 | |||
| Cl− | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |||
| NO3− | 6.0 | 9.2 | 2.9 | 5.2 | 2.9 | 5.4 | |||
| SO42− | 13.7 | 18.8 | 9.7 | 11.5 | 9.4 | 12.1 | |||
| Na+ | 1.1 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 | |||
| NH4+ | 6.4 | 9.0 | 5.4 | 7.3 | 4.8 | 7.1 | |||
| K+ | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.8 | |||
| Mg2+ | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |||
| Ca2+ | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |||
| OC | 8.4 | 11.3 | 8.0 | 11.1 | 4.9 | 6.7 | |||
| OC1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.3 | |||
| OC2 | 1.9 | 2.6 | 2.0 | 2.7 | 1.3 | 1.7 | |||
| OC3 | 2.0 | 2.6 | 1.7 | 2.3 | 1.0 | 1.3 | |||
| OC4 | 2.2 | 3.3 | 2.1 | 3.1 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |||
| OP | 2.2 | 2.9 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 1.5 | 2.2 | |||
| EC | 4.6 | 7.0 | 4.5 | 6.4 | 2.6 | 3.7 | |||
| EC1 | 4.2 | 6.4 | 4.1 | 6.0 | 2.2 | 3.3 | |||
| EC2 + 3 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | |||
| PM10 | PM2.5 | PM1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 4.7 | 3.1 | 2.5 |
| PC2 | 3.7 | 0.4 | −0.7 |
| Intercept | 31.1 | 19.2 | 14.8 |
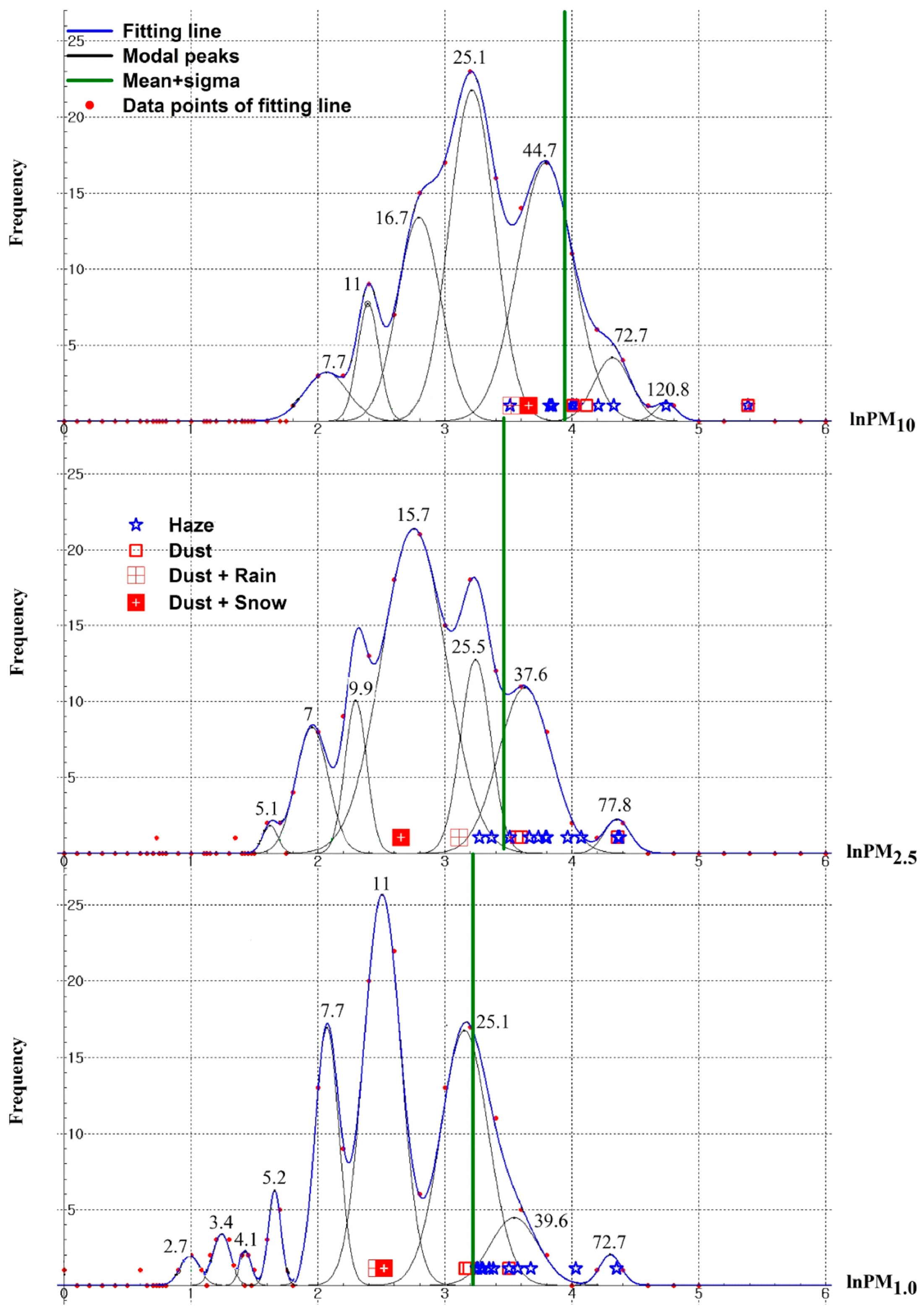
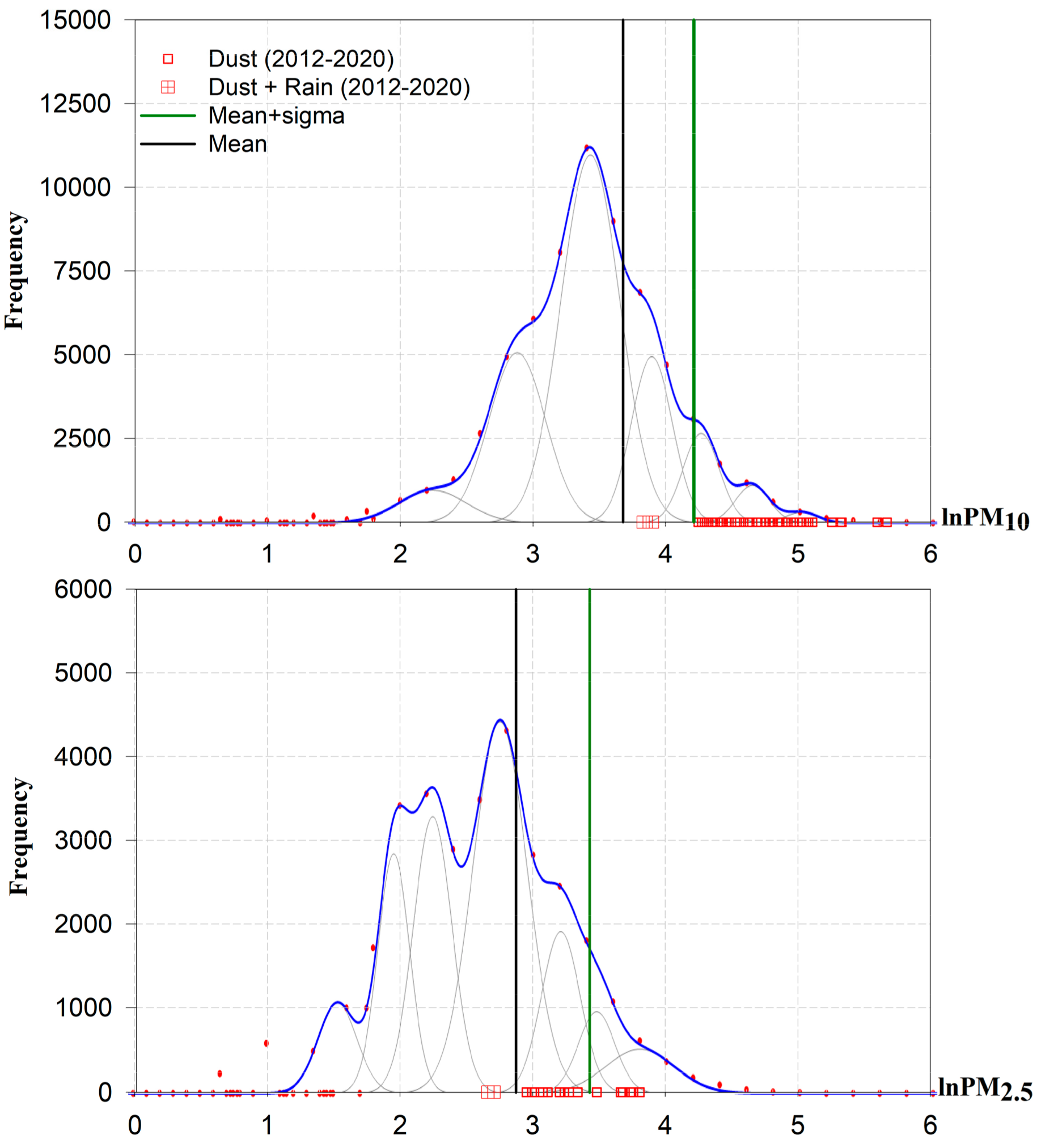
| Median | Mean | * S.D. | Main Mode | Mean + SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 | 24 | 30 | 22 | 25 | 52 |
| PM2.5 | 15 | 19 | 13 | 16 | 32 |
| PM1 | 11 | 14 | 11 | 11 | 25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, X.; Lee, M.; Lim, S.; Gustafsson, Ö.; Lee, G.; Chang, L. Dust Criteria Derived from Long-Term Filter and Online Observations at Gosan in South Korea. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111419
Shang X, Lee M, Lim S, Gustafsson Ö, Lee G, Chang L. Dust Criteria Derived from Long-Term Filter and Online Observations at Gosan in South Korea. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(11):1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111419
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Xiaona, Meehye Lee, Saehee Lim, Örjan Gustafsson, Gangwoong Lee, and Limseok Chang. 2021. "Dust Criteria Derived from Long-Term Filter and Online Observations at Gosan in South Korea" Atmosphere 12, no. 11: 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111419
APA StyleShang, X., Lee, M., Lim, S., Gustafsson, Ö., Lee, G., & Chang, L. (2021). Dust Criteria Derived from Long-Term Filter and Online Observations at Gosan in South Korea. Atmosphere, 12(11), 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111419






