Frequency and Characteristics of Inland Advecting Sea Breezes in the Southeast United States
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
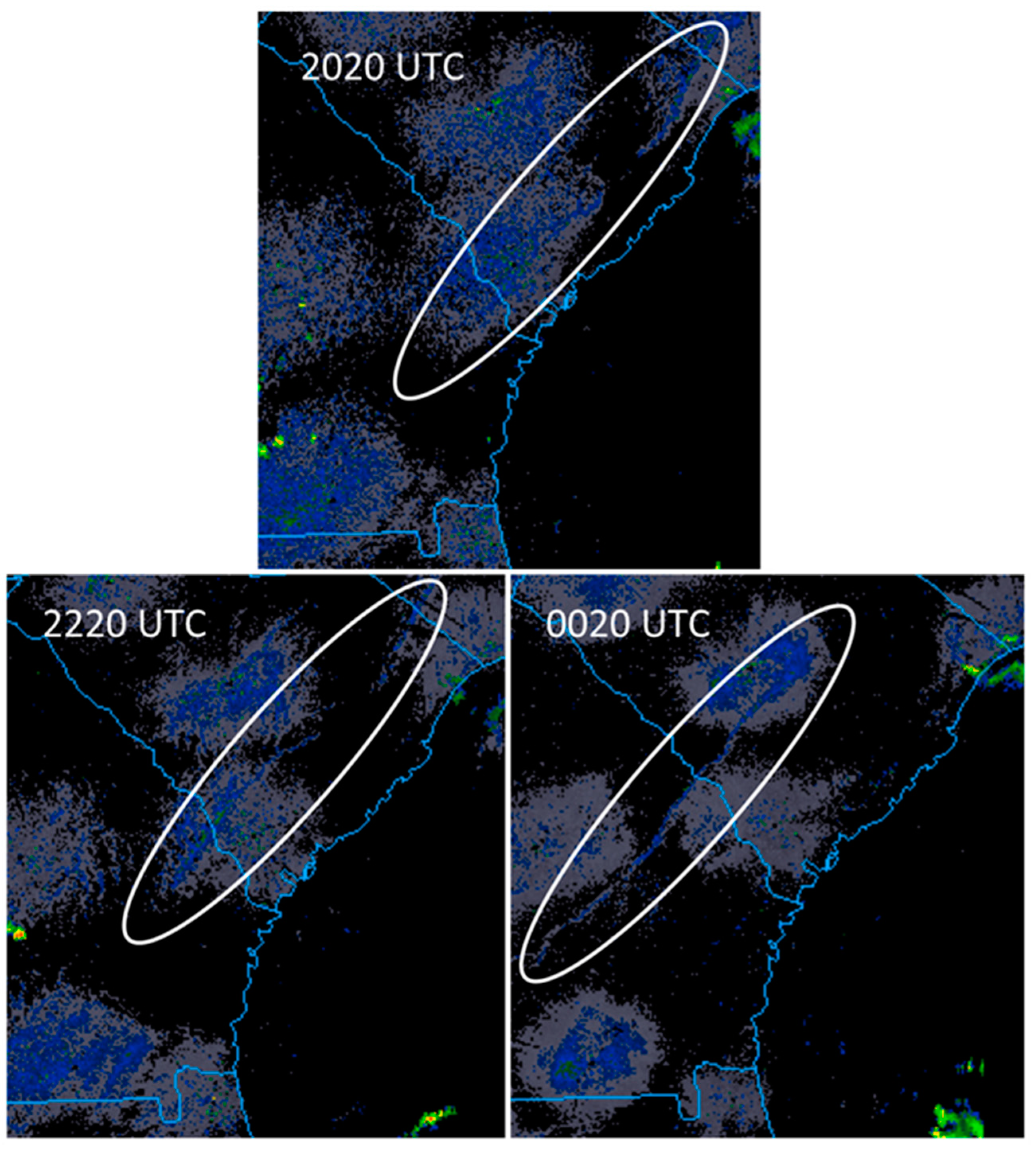
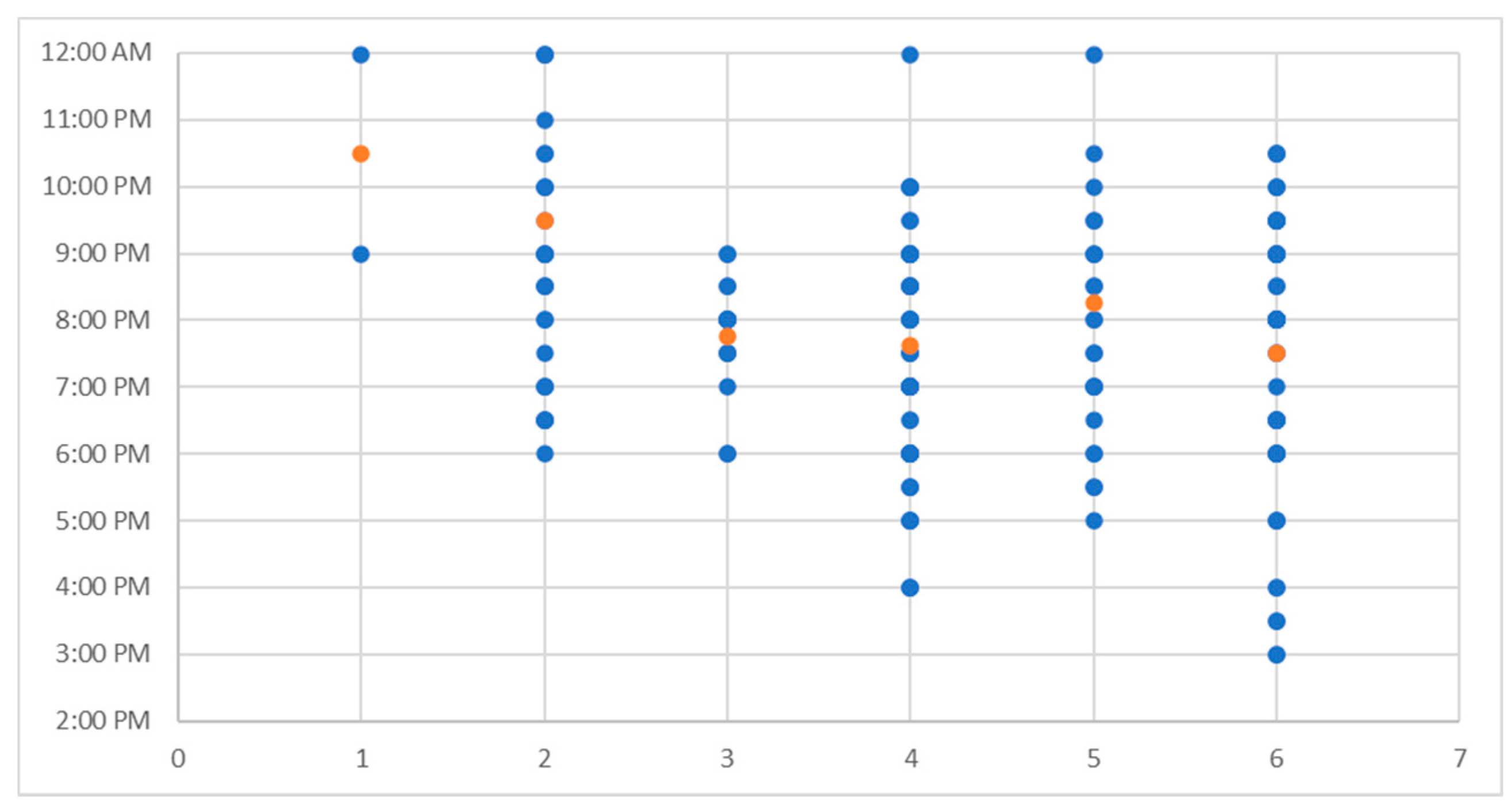
2.1. Identifying Sea Breezes
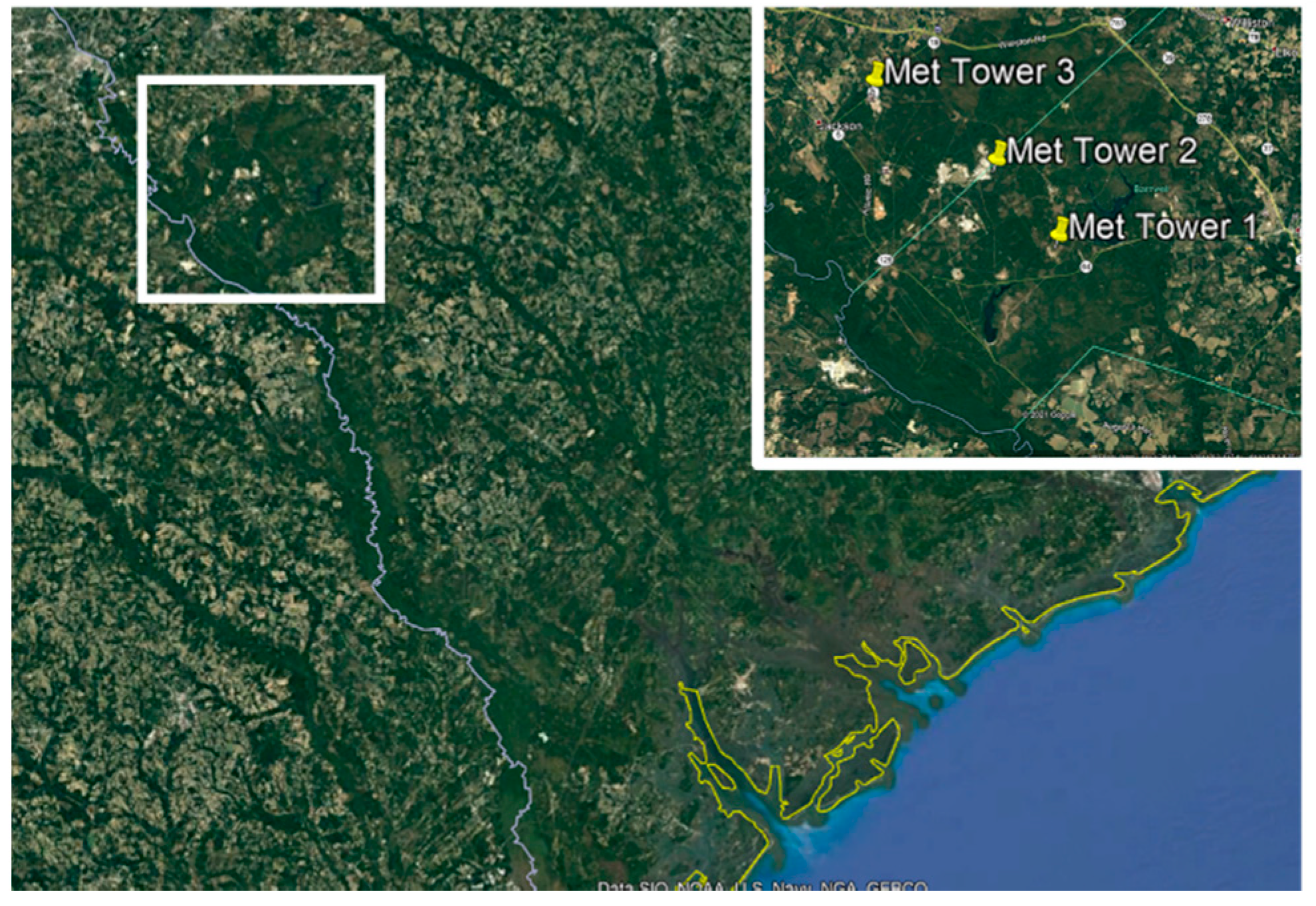
2.2. Meteorological Measurements
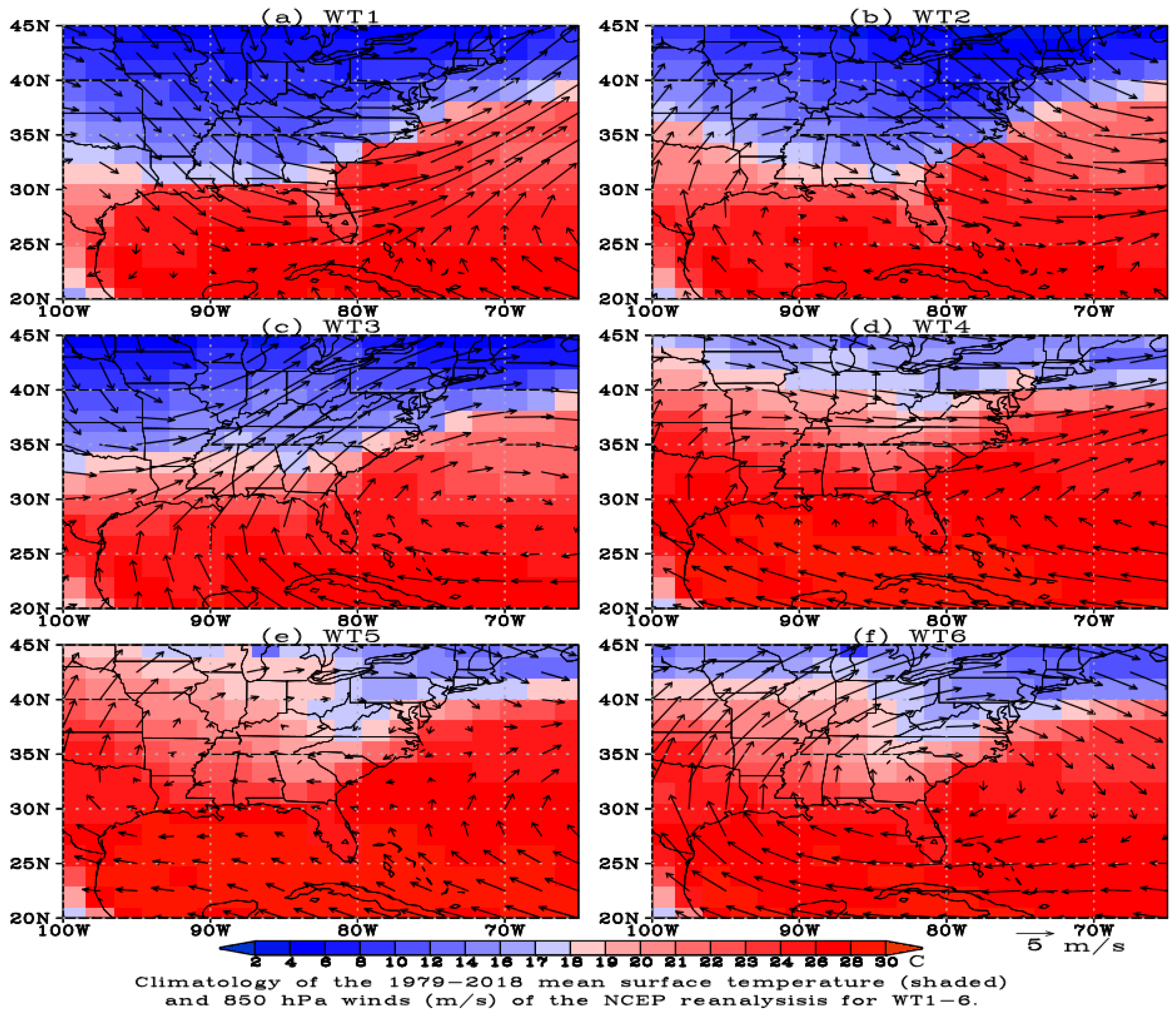
2.3. Synoptic Pattern Classification
3. Results and Discussion
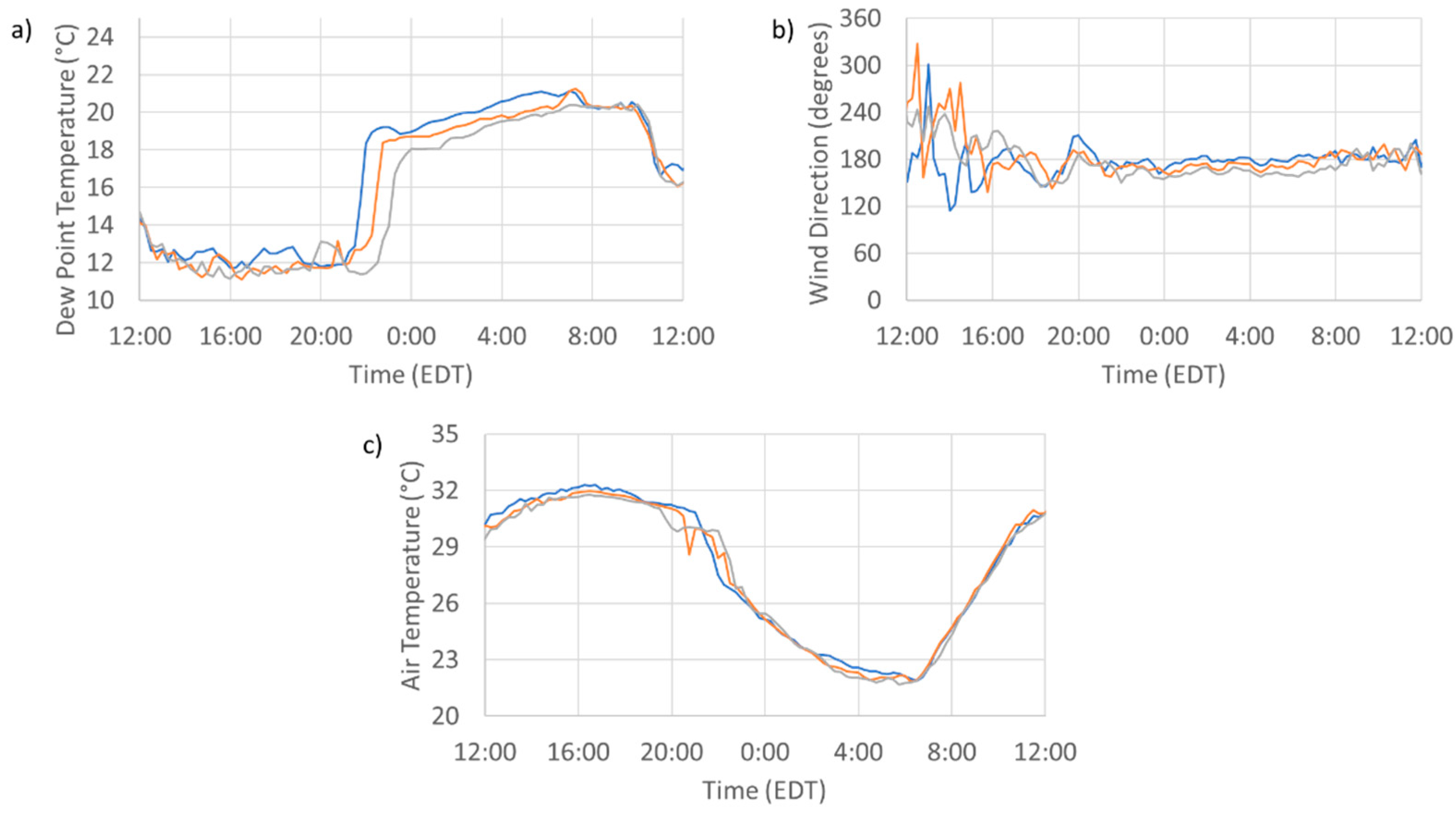
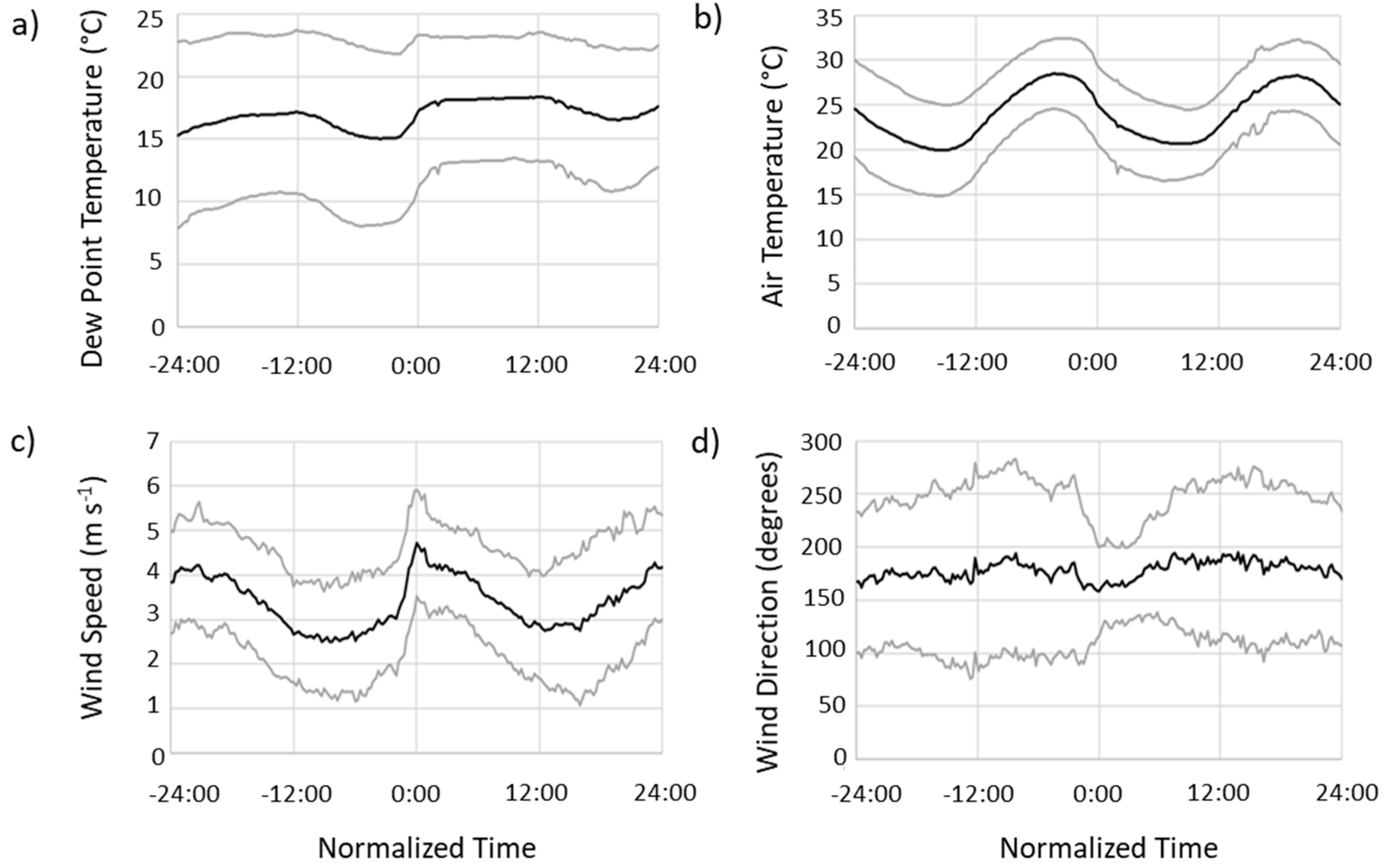
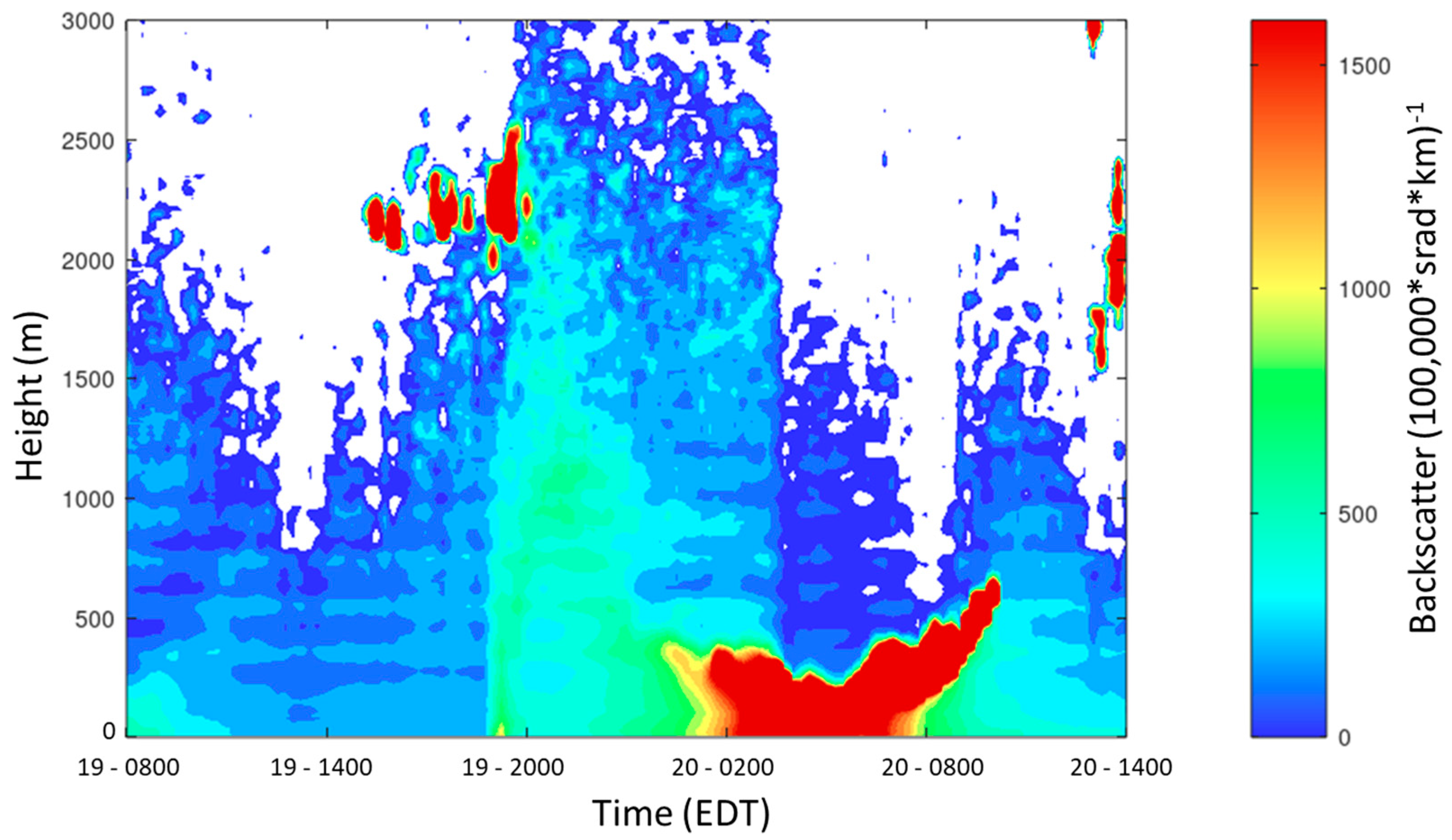
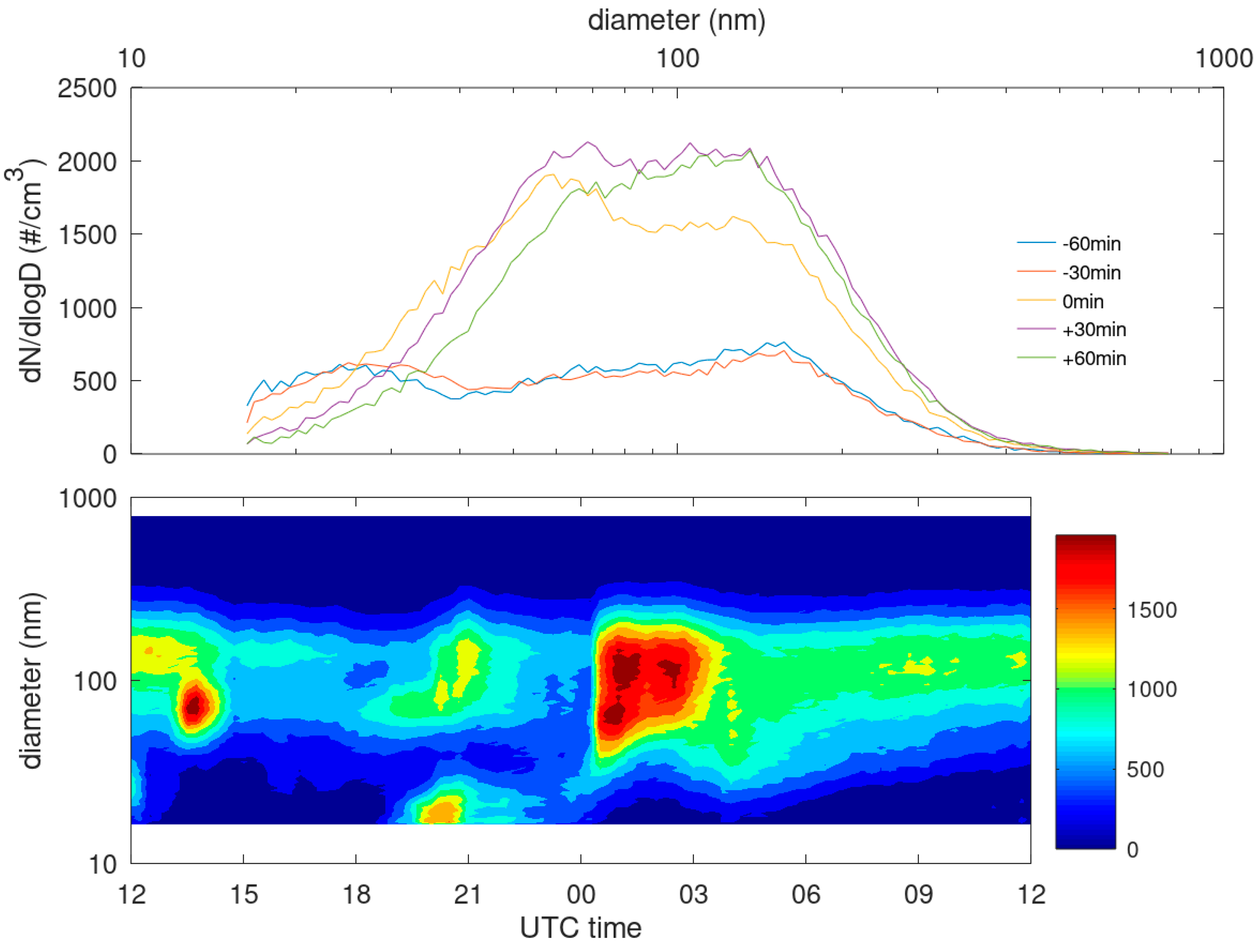
3.1. Measured Effects of the Sea Breeze
3.2. Influence of Synoptic Case on Sea Breeze Frequency
3.3. Identification of Additional Sea Breezes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buckley, R.L.; Kurzeja, R.J. An observational and numerical study of the nocturnal sea breeze. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 531–546. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.T.K.; Keim, B.D.; Talbot, R.W.; Mao, H. Sea breeze: Structure, forecasting and impacts. Rev. Geophys. 2003, 41, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, J.E.; Mansfield, D.A.; Milford, J.R. Inland penetration of sea breeze fronts. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1977, 103, 47–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Guan, H.; Gharib, S.; Batelaan, O.; Simmons, C.T. Cooling power of sea breezes and its inland penetration in dry-summer Adelaide, Australia. Atmos. Res. 2021, 250, 105409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muppa, S.K.; Anandan, V.K.; Kesarkar, K.A.; Rao, S.V.B.; Reddy, P.N. Study on deep inland penetration of sea breeze over complex terrain in the tropics. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104–105, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yum, S.S.; Hudson, J.G. Maritime/continental microphysical contrasts in stratus. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2002, 54, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Xi, B.; Kennedy, A.; Minnis, P.; Wood, R. A 19-month record of marine aerosol-cloud-radiation properties derived from DOE ARM mobile facility deployment at the Azores. Part I: Cloud fraction and single-layered MBL cloud properties. J. Clim. 2013, 27, 3665–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Logan, T.; Dong, X.; Xi, B. Aerosol properties and their impacts on surface CCN at the ARM Southern Great Plains Site during the 2011 Midlatitude Continental Convective Clouds Experiment. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Donner, L.J.; Phillips, T.J.; Ming, Y. Examination of aerosol effects on precipitation in deep convective clouds during the 1997 ARM summer experiment. Q. J. R. Meteorol. 2008, 134, 1201–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Halloran, T.L.; Fuentes, J.K.; Tao, W.K.; Li, X. Sensitivity of convection to observed variation in aerosol size distributions and composition at a rural site in the southeastern United States. J. Atmos. Chem. 2015, 72, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Iwai, H.; Ishii, S.; Saito, K.; Seko, H.; Sha, W.; Iwasaki, T. Structures of the sea breeze front in dual-doppler lidar observation and coupled mesoscale-to-LES modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2397–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbeck, S.; Viner, B.; Rivera-Giboyeaux, A. Meteorological monitoring program at the Savannah River Site. In SRNL-TR-2020-00197 Rev. 0; Savannah River National Laboratory: Aiken, SC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Moron, V.; Robertson, A.W.; Ward, M.N.; Ndiaye, O. Weather types and rainfall over Senegal. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 266–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, J.-H.; Robertson, A.W.; Moron, V. Interaction among ENSO, the monsoon and diurnal cycle in rainfall variability over Java, Indonesia. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 3509–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.-H.; Robertson, A.W.; Moron, V. Diurnal cycle in different weather regimes and rainfall variability over Borneo associated with ENSO. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 1772–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.-H. Multi-scale climate processes and rainfall variability in Sumatra, Peninsula Malaysia and Singapore associated with ENSO in boreal fall and winter. Int. J. Clim. 2020, 40, 4171–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, C.D.; Qian, J.-H.; Agel, L.; Barlow, M.; Moron, V. Winter weather regimes in the Northeast United States. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 2963–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werth, D.; Buckley, R.; Zhang, G.; Kurzeja, R.; Leclerc, M.; Duarte, H.; Parker, M.; Watson, T. Quantifying the local influence at a tall tower site in nocturnal conditions. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2017, 127, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.-H.; Viner, B.; Noble, S.; Werth, D. Precipitation characteristics of warm season weather types in the southeastern United States of America. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2021. In Review. [Google Scholar]
- Arritt, R.W. Effects of the large-scale flow on characteristic features of the sea breeze. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1993, 32, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Miao, S.; Tewari, M.; Bao, J.-W.; Kusaka, H. A numerical study of interactions between surface forcing and sea breeze circulations and their effects on stagnation in the greater Houston area. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D12105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azorin-Molina, C.; Tijm, S.; Chen, D. Development of selection algorithms and databases for sea breeze studies. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2011, 106, 531–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Month | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | |
| 2015 | 2 | 3 | 9 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 2016 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 9 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 2017 | 6 | 14 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| 2018 | 2 | 8 | 11 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 2 |
| 2019 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 4 | 0 |
| Year | Class | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | Total | |
| 2015 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 5 | 9 | 28 |
| 2016 | 0 | 7 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 9 | 30 |
| 2017 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 17 | 3 | 12 | 43 |
| 2018 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 16 | 8 | 14 | 47 |
| 2019 | 0 | 8 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 9 | 29 |
| 2015–2019 | 2 | 27 | 17 | 59 | 19 | 53 | |
| Year | Class | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | Total | |
| 2015 | 15 | 25 | 18 | 73 | 61 | 53 | 245 |
| 2016 | 24 | 24 | 30 | 61 | 47 | 59 | 245 |
| 2017 | 24 | 21 | 33 | 84 | 41 | 42 | 245 |
| 2018 | 29 | 31 | 19 | 75 | 43 | 48 | 245 |
| 2019 | 20 | 28 | 30 | 64 | 47 | 56 | 245 |
| 2015–2019 | 112 | 129 | 130 | 357 | 239 | 258 | |
| Year | Class | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| 2015 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.17 | |
| 2016 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.15 | |
| 2017 | 0.04 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.07 | 0.29 | |
| 2018 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.29 | |
| 2019 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.16 | |
| 2015–2019 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.21 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viner, B.; Noble, S.; Qian, J.-H.; Werth, D.; Gayes, P.; Pietrafesa, L.; Bao, S. Frequency and Characteristics of Inland Advecting Sea Breezes in the Southeast United States. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12080950
Viner B, Noble S, Qian J-H, Werth D, Gayes P, Pietrafesa L, Bao S. Frequency and Characteristics of Inland Advecting Sea Breezes in the Southeast United States. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(8):950. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12080950
Chicago/Turabian StyleViner, Brian, Stephen Noble, Jian-Hua Qian, David Werth, Paul Gayes, Len Pietrafesa, and Shaowu Bao. 2021. "Frequency and Characteristics of Inland Advecting Sea Breezes in the Southeast United States" Atmosphere 12, no. 8: 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12080950
APA StyleViner, B., Noble, S., Qian, J.-H., Werth, D., Gayes, P., Pietrafesa, L., & Bao, S. (2021). Frequency and Characteristics of Inland Advecting Sea Breezes in the Southeast United States. Atmosphere, 12(8), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12080950








