Impact of Soil Moisture Data Assimilation on Analysis and Medium-Range Forecasts in an Operational Global Data Assimilation and Prediction System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. LSM
2.2. ASCAT Soil Moisture Data
2.3. Data Assimilation Method
2.4. Model Configuration
3. Results
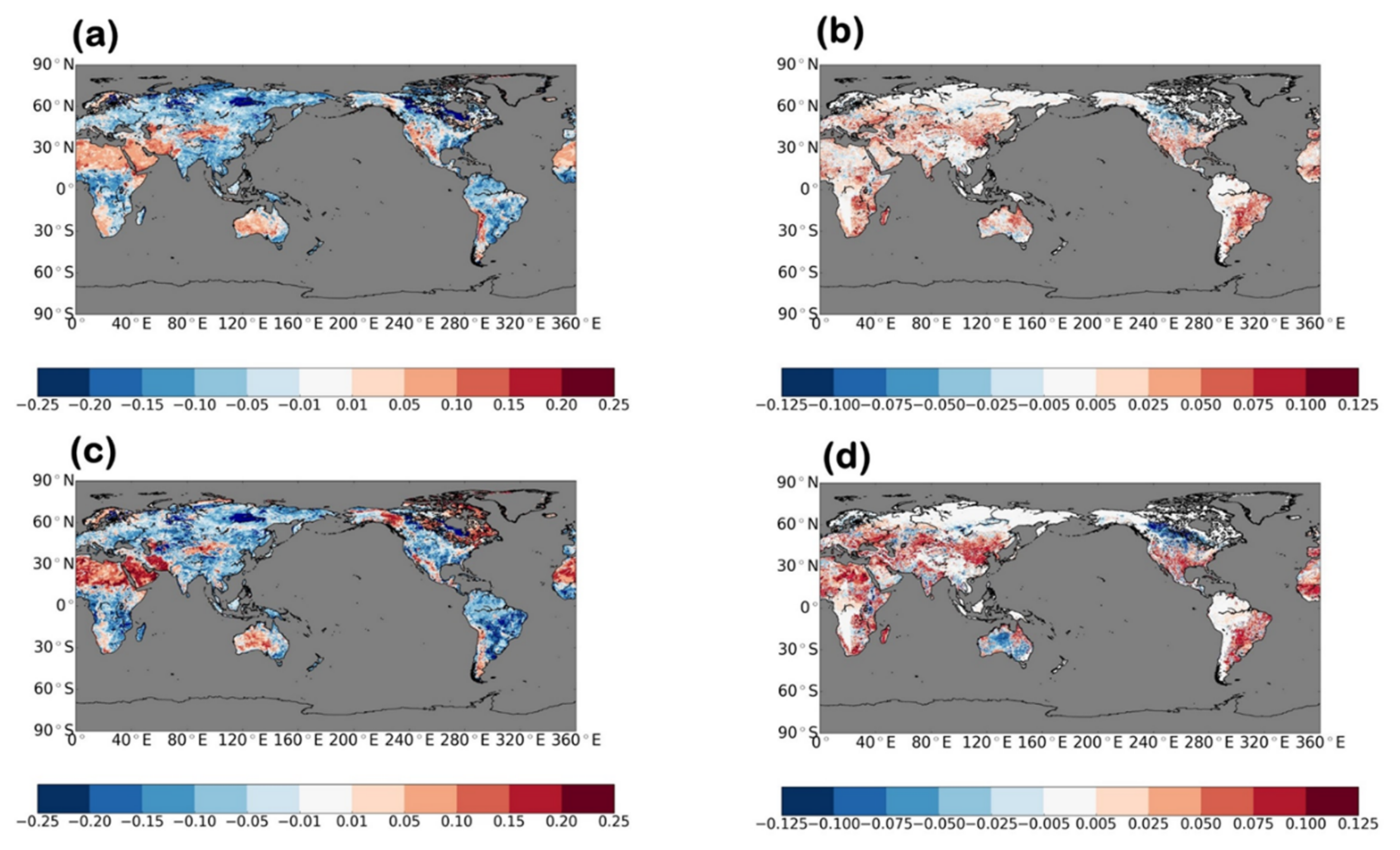
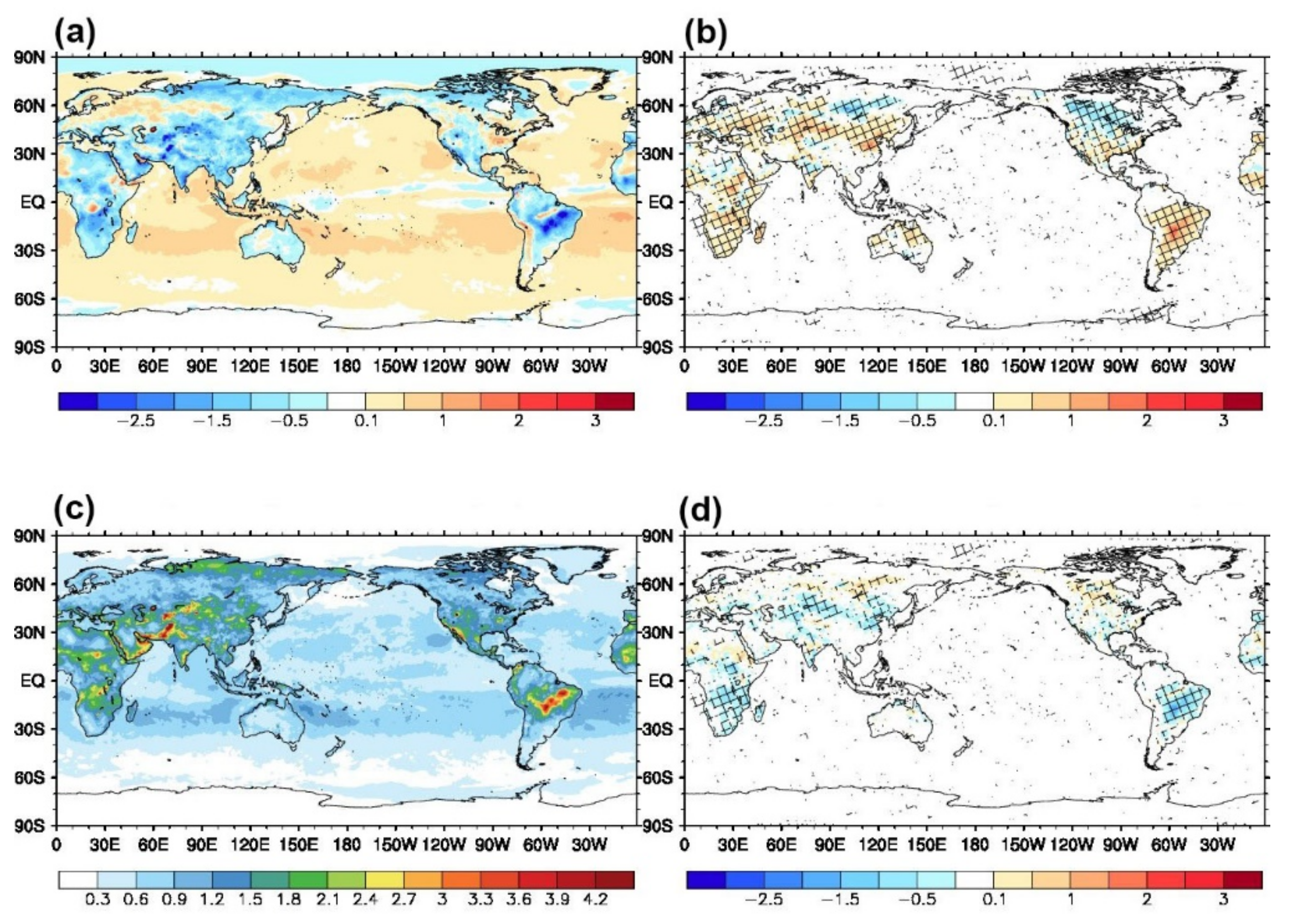
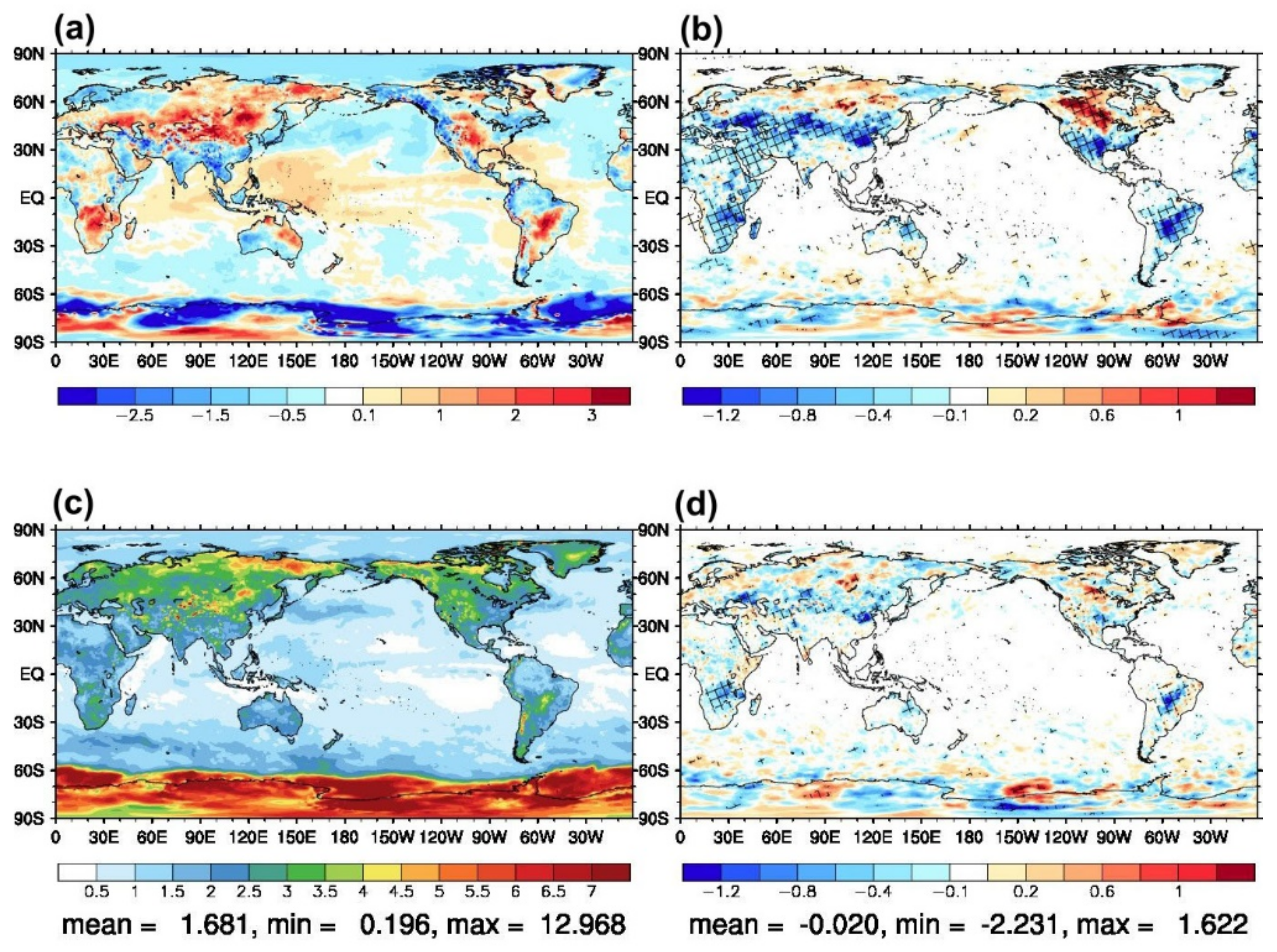
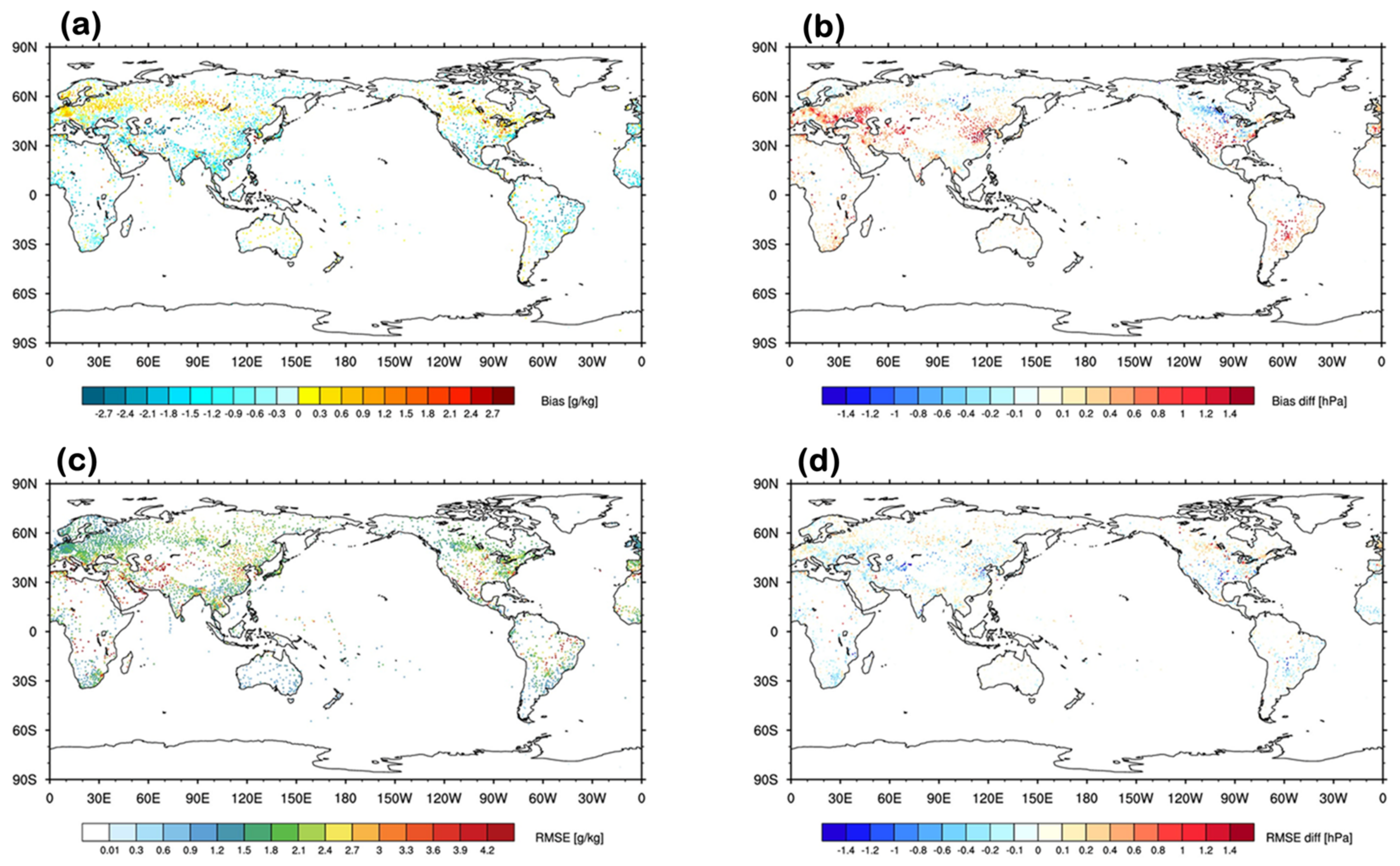
3.1. Effects on Analysis Field
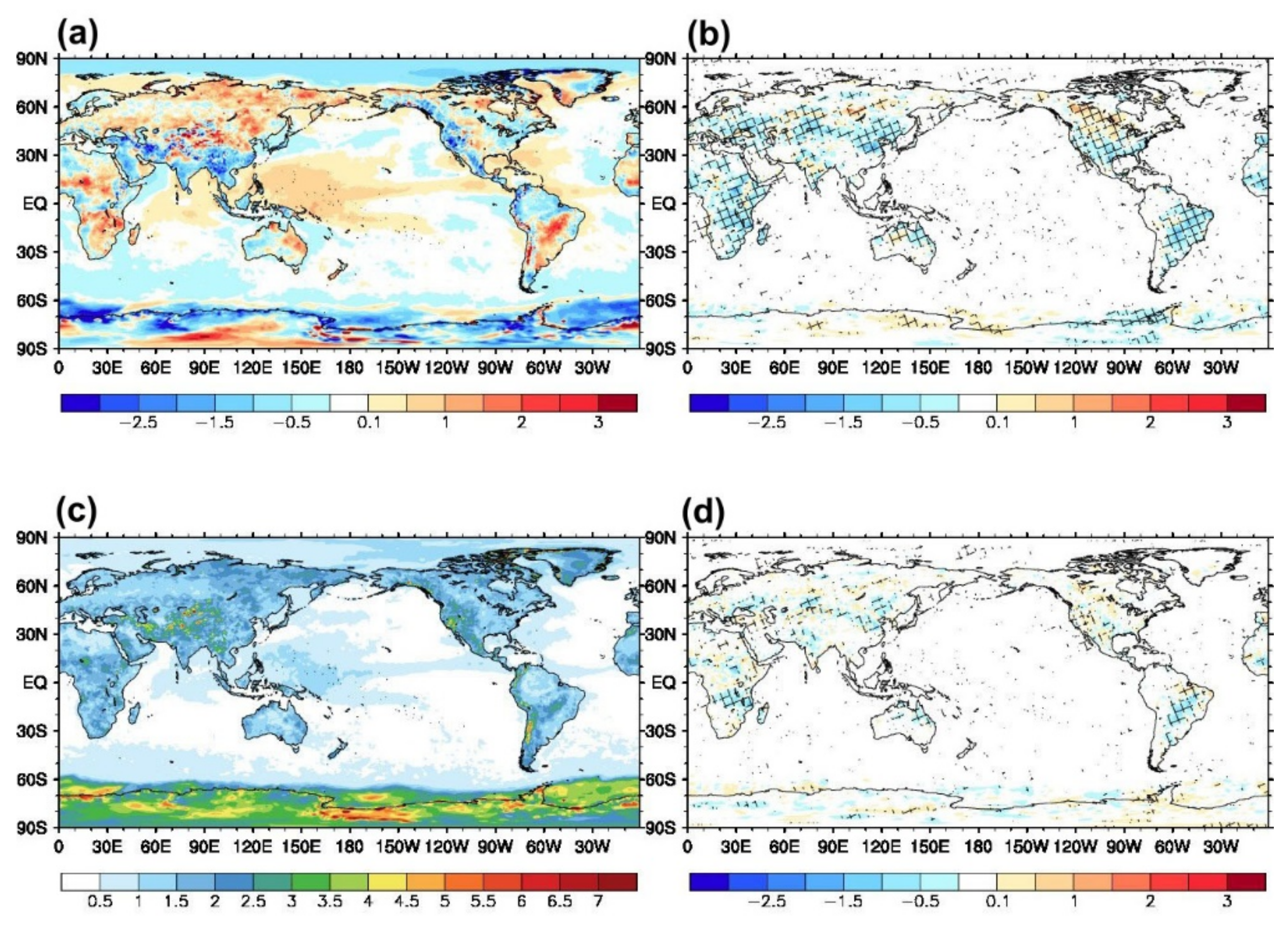
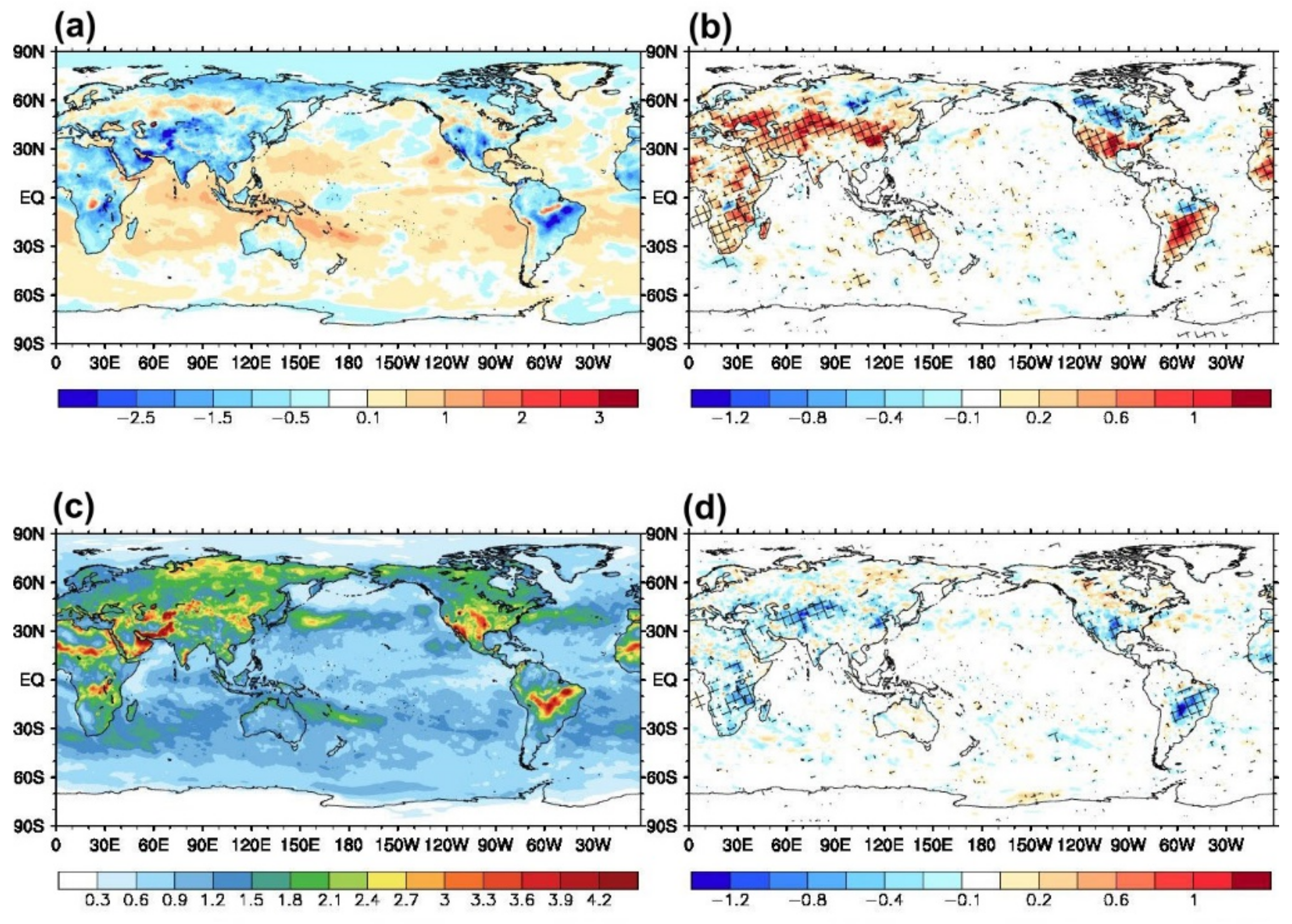
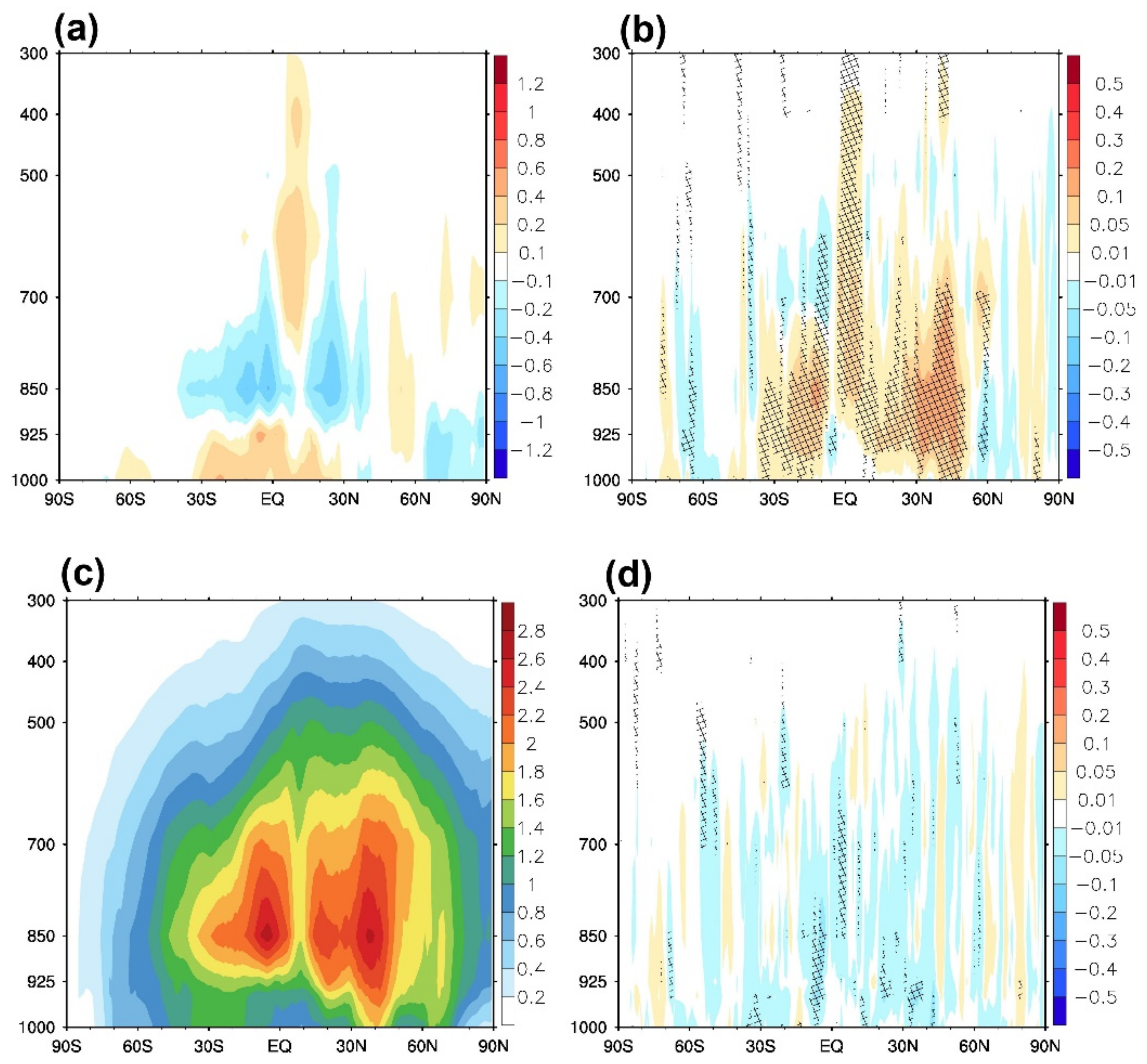
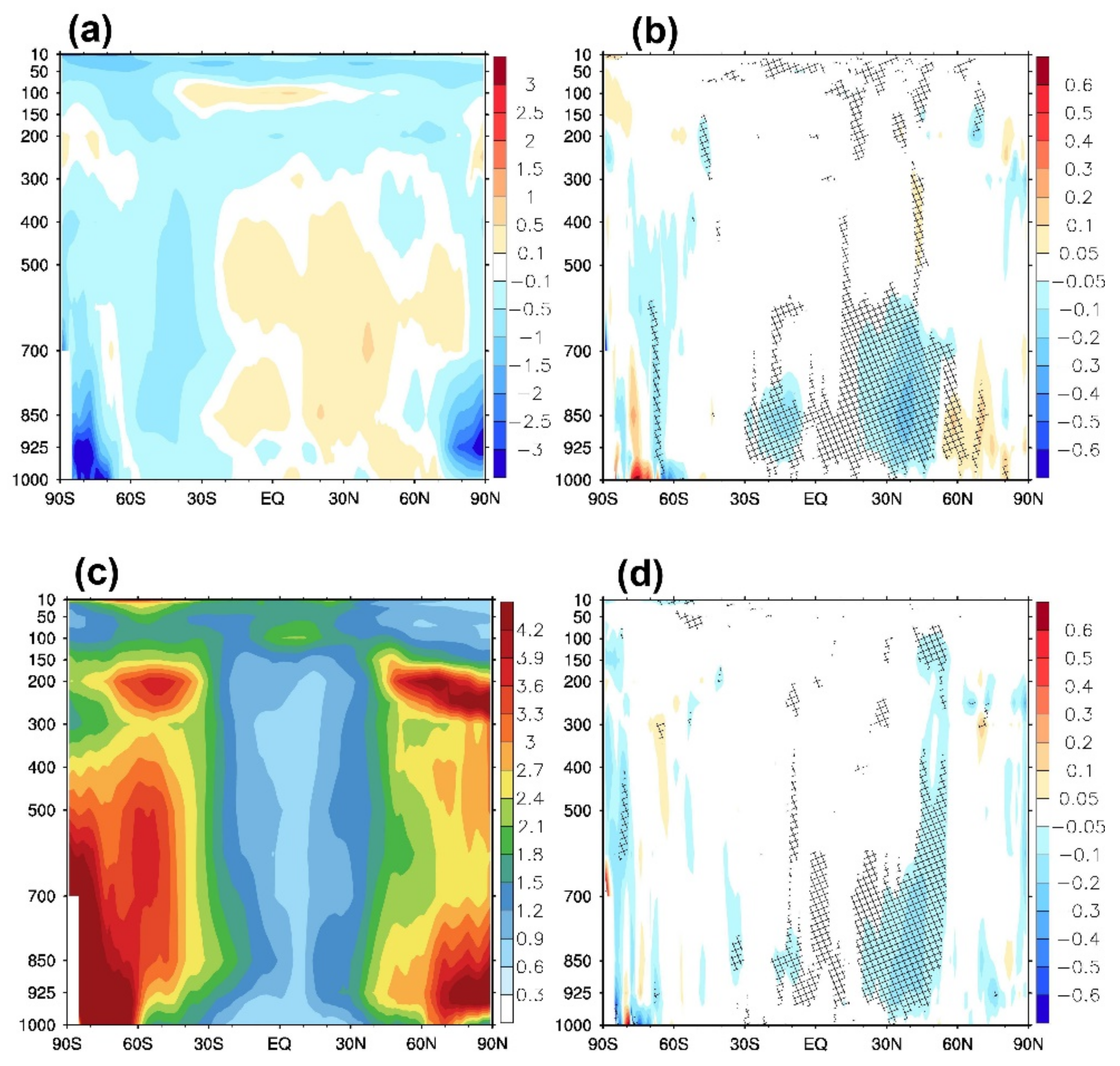
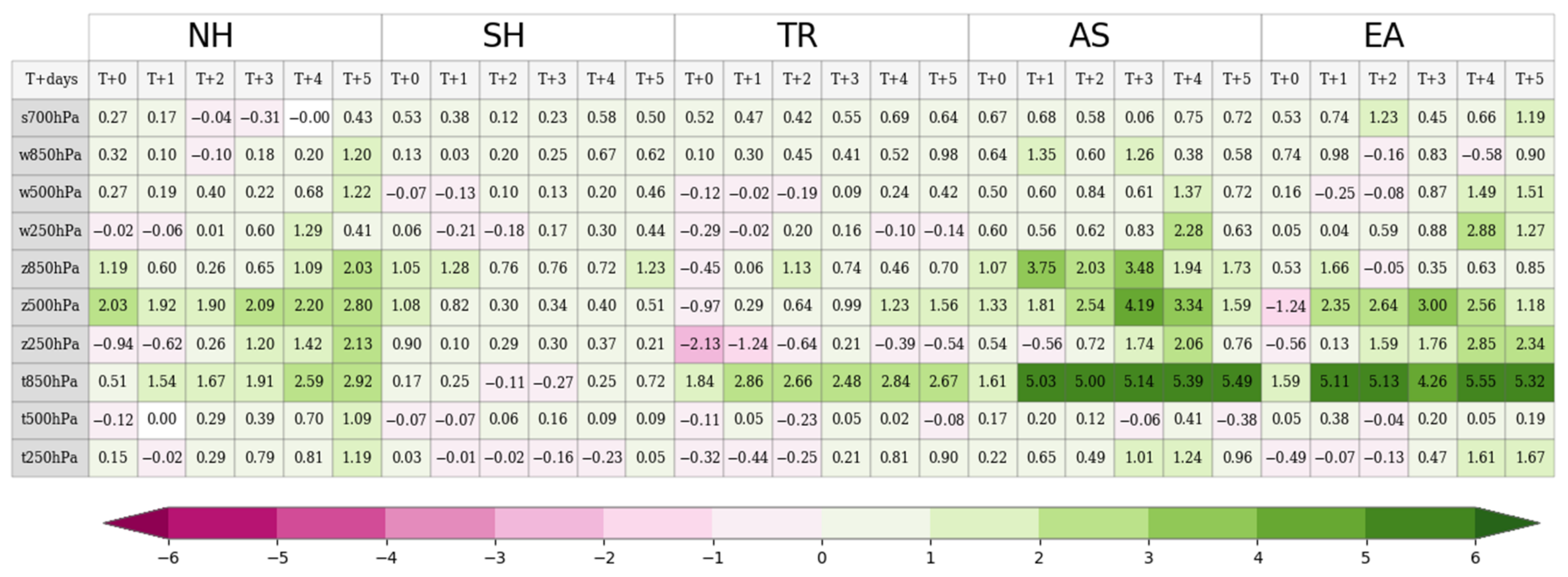
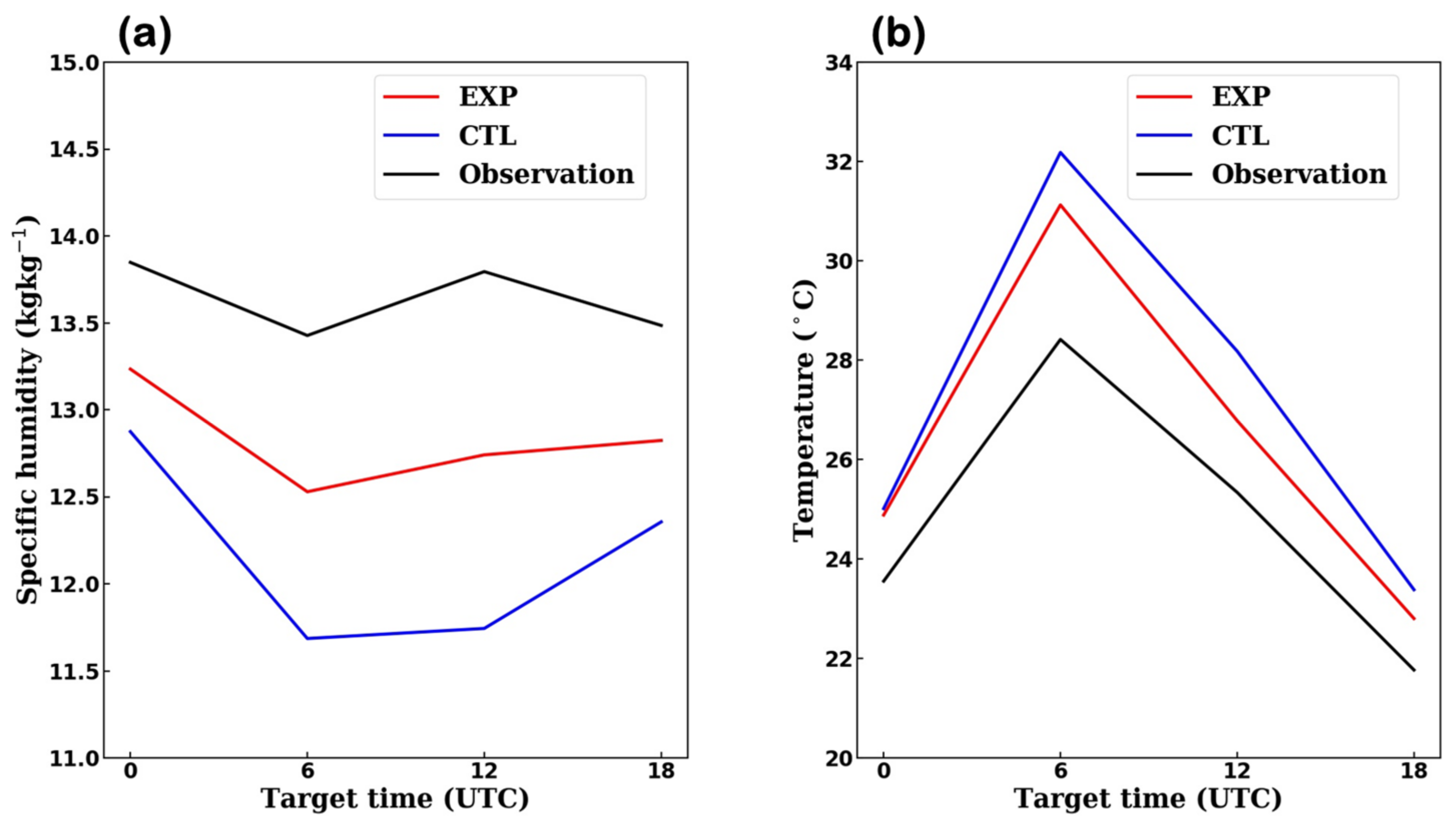
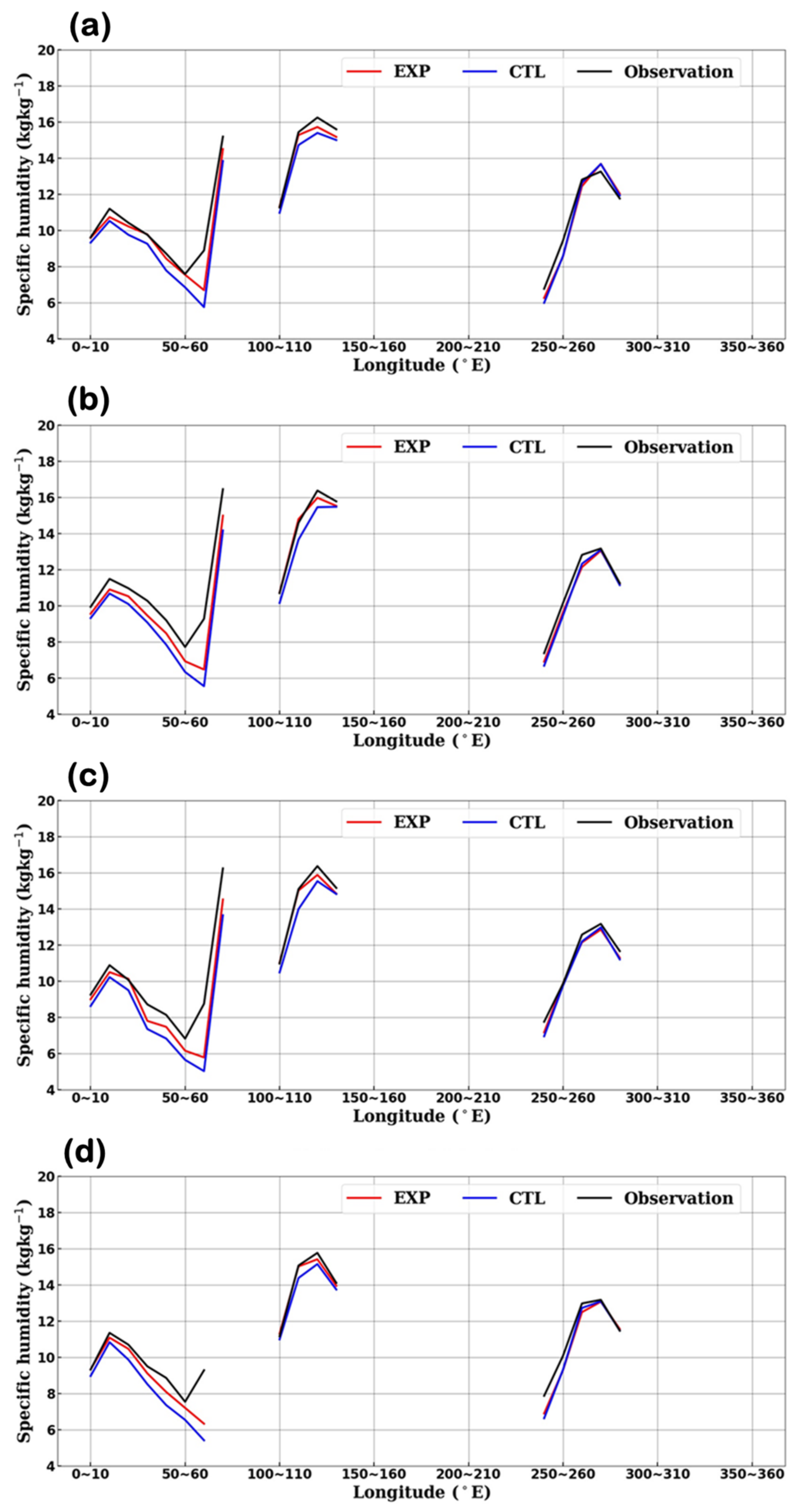
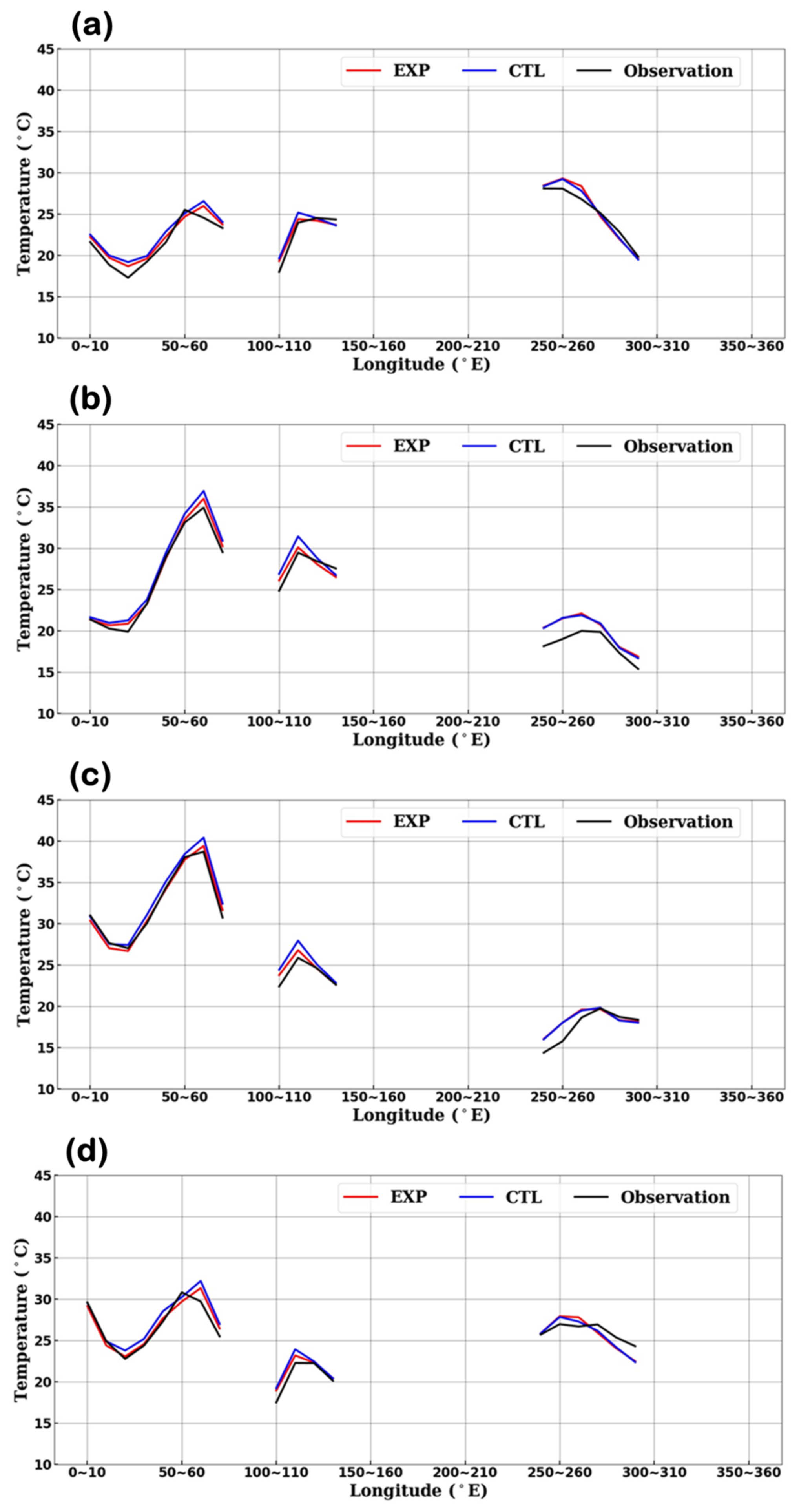
3.2. Effects on Forecast Field
4. Summary and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santanello, J.A., Jr.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Kumar, S.V. Diagnosing the sensitivity of local land-atmosphere coupling via the soil moisture-boundary layer interaction. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 766–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture-climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, E.M.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Vidale, P.L.; Lüthi, D.; Schär, C. Soil moisture-atmosphere interactions during the 2003 European summer heat wave. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 5081–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, R.D.; Mahanama, S.P.P.; Yamada, T.J.; Gianpaolo, B.; Berg, A.A.; Boisserie, M.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J.; Drewitt, G.; Gordon, C.T.; et al. Contribution of land surface initialization to subseasonal forecast skill: First results from a multi-model experiment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L02402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dirmeyer, P.A.; Halder, S. Sensitivity of numerical weather forecasts to initial soil moisture variations in CFSv2. Weather Forecast. 2016, 31, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirmeyer, P.A.; Halder, S.; Bombardi, R. On the barvest of predictability from land states in a global forecast model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 13111–13127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.; Lee, M.I.; Jeong, J.H.; Koster, R.D.; Schubert, S.D.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, D.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, H.K.; MacLachlan, C.; et al. Impact of soil moisture initialization on boreal summer subseasonal forecasts: Mid-latitude surface air temperature and heat wave events. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.; Lee, M.I.; Schubert, S.D.; Koster, R.D.; Kang, H.S. Investiation of the 2016 Eurasia heat wave as event of the recent warming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 114018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delworth, T.L.; Manabe, S. The influence of potential evaporation on the variabilities of simulated soil wetness and climate. J. Clim. 1988, 1, 523–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.; Seneviratne, S.I. Analysis of soil moisture memory from observations in Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D15115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.A.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Akbar, R.; Konings, A.G.; Yueh, S.; Entekabi, D. The global distribution and dynamics of surface soil moisture. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santanello, J.A., Jr.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Ferguson, C.R.; Findell, K.L.; Tawfik, A.B.; Berg, A.; Ek, M.; Gentine, P.; Guillod, B.P.; Heerwaarden, C.; et al. Land-atmosphere interactions: The LoCo perspective. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 1253–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D. Bias reduction in short records of satellite soil moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L19501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dharssi, I.; Bovis, K.J.; Macpherson, B.; Jones, C.P. Operational assimilation of ASCAT surface soil wetness at the Met Office. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2729–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, H.E.; Pan, M.; Miralles, D.G.; Reichle, R.H.; Dorigo, W.A.; Hahn, S.; Sheffield, J.; Karthikeyan, L.; Balsamo, G.; Parlnussa, R.M.; et al. Evaluation of 18 satellite- and model-based soil moisture products using in situ measurments from 826 sensors. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Scipal, K.; de Rosnay, P.; Balsamo, G.; Andersson, E.; Bougeault, P.; Viterbo, P. Towards at Kalman filter based soil moisture analysis system for the operational ECMWF Integrated Forecast System. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rosnay, P.; Drusch, M.; Vasiljevic, D.; Balsamo, G.; Albergel, C.; Isaksen, L. A simplified extended Kalman filter for the global operational soil moisture analysis at ECMWF. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 1199–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Walker, J.P.; Koster, R.D.; Houser, P.R. Extended versus ensemble Kalman filtering for land data assimilation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D.; Liu, P.; Mahanama, S.P.; Jjoku, E.G.; Owe, M. Comparison and assimilation of global soil moisture retrievals from the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for the Earth Observing System (AMSR-E) and the Scanning Multichannel Microwave Radiometer (SMMR). J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2007, 112, D9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, C.S.; Reichle, R.H.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Liu, Q. Assimilation of passive and active microwave soil moisture retrievals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L04401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.V.; Reichle, R.H.; Harrison, K.W.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Yatheendradas, S.; Santanello, J.A. A comparison of methods for a priori bias correction in soil moisture data assimilation. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W03515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lannoy, G.J.M.; Rosnay, P.D.; Reichle, R. Soil moisture data assimilation. In Handbook of Hydrometeorological Ensemble Forecasting; Duan, Q., Pappenberger, F., Wood, A., Wood, A., Cloke, H.L., Schaake, J.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kolassa, J.; Reichle, R.H.; Draper, C.S. Merging active and passive microwave observations in soil moisture data assimilation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhan, X.; Liu, J.; Ek, M. A preliminary assessment of the impact of assimilating satellite soil moisture data products on NCEP Global Forecast System. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.V.; Jasinski, J.; Mocko, D.M.; Rodell, M.; Borak, J.; Li, B.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Peters-Lidard, C.D. NCA-LDAS land analysis: Development and performance of a multisensory, multivariate land data assimilation system for the National Climate Assessment. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 1571–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.; Lee, M.I.; Reichle, R.H. Assimilation of SMAP and ASCAT soil moisture retrievals into the JULES land surface model using the Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Kwon, Y.C.; Kim, T.-H.; Kim, J.-E.E.; Choi, S.-J.; Kwon, I.-H.; Kim, J.; Lee, E.-H.; Park, R.-S.; Kim, D.-I. The Korean Integrated Model (KIM) system for global weather forecasting. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 54, 267–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, I.-H.; Song, H.-J.; Ha, J.-H.; Chun, H.-W.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, S.; Lim, S.; Jo, Y.; Han, H.-J.; Jeong, H.; et al. Development of an operational hybrid data assimilation system at KIAPS. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 54, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K. The Community Noah Land Surface Model (LSM), User’ Guide; National Centers for Environmental Prediction/Environmental Modelling Center: College Park, MD, USA, 2005. Available online: https://ftp.emc.ncep.noaa.gov/mmb/gcp/ldas/noahlsm/ver_2.7.1/ (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Koo, M.-S.; Baek, S.; Seol, K.-H.; Cho, K. Advances in land surface modeling of KIAPS based on the Noah land surface model. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 53, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrt, L.; Pan, H.A. Two-layer model of soil hydrology. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1984, 29, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrt, L.; Ek, M. The influence of atmospheric stability on potential evaporation. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1984, 23, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Mitchell, K.; Shaake, J.; Xue, Y.; Pan, H.; Koren, V.; Duan, Y.; Ek, M.; Betts, A. Modeling of land surface evaporation by four schemes and comparison with FIFE observations. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 7251–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaake, J.C.; Koren, V.I.; Duan, Q.Y.; Mitchell, K.; Chen, F. Simple water balance model for estimating runoff at different spatial and temporal scales. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 7461–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Zion, M.S.; Wood, E.F. A soil vegetation-atmosphere transfer scheme from modeling spatially variable water and energy balance processes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 4303–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.; Park, J.-H.; Boo, K.-O.; Kang, H.-S. Analyzing off-line Noah land surface model spin-up behavior for initialization of global numerical weather prediction model. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2020, 53, 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, E.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Jeong, Y.H.; Kim, K.M.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, K.H.; Bae, J.K. Investigation of Land-Atmosphere Interaction for Global Prediction System; KMA: Seoul, Korea, 2020; pp. 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Boo, K.O.; Kang, H.S. Constructing Land Data Assimilation Process for High Resolution Global Data Assimilation and Prediction System; Numerical Modeling Center/Korea Meteorological Administration (NMC/KMA): Seoul, Korea, 2018; pp. 1–63. (In Korean)
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Ambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Berg, A.A.; Famiglietti, J.S. Evaluation of 10 methods for initializing a Land Surface Model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Hahn, S.; Kidd, R.; Melzer, T.; Bartalis, Z.; Hasenauer, S.; Figa-Saldana, J.; de Rosnay, P.; Jann, A.; Schneider, S.; et al. The ASCAT soil moisture product: A review of its specifications, validation results, and emerging applications. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Yarri, A.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Ducharne, A.; Kerr, Y.H.; Wagner, W.; De Lannoy, G.; Reichle, R.; Al Bitar, A.; Dorigo, W.; Richaume, P.; et al. Global-scale comparison of passive (SMOS) and active (ASCAT) satellite based microwave soil moisture retrievals with soil moisture simulations (MERRA-Land). Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorigo, W.A.; Scipal, K.; Parinussa, R.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wagner, W.; de Jeu, R.A.M.; Naeimi, V. Error characterization of global active and passive microwave soil moisture datasets. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2605–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.V.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Mocko, D.; Reichle, R.; Liu, Y.; Arsenault, K.R.; Xia, Y.; Ek, M.; Riggs, G.; Livneh, B.; et al. Assimilation of remotely sensed soil moisture and snow depth retrievals for drought estimation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 2446–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Crow, W.T.; Keppenne, C.L. An adaptive ensemble Kalman filter for soil moisture data assimilation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W03423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evansen, G. Sequential data assimilation with a non-linear quasi-geostrophic model using Monte Carlo methods to forecast error statistics. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 10143–10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Tian, Y.; Houser, P.R.; Geiger, J.; Olden, S.; Lighty, L.; Eastman, J.L.; Doty, B.; Dirmeyer, P.; et al. Land Information System: An interoperable frame work for high resolution land surface modeling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 21, 1402–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Dong, J.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Mocko, D.; Gómez, B. Role of forcing uncertainty and background model error characterization in snow data assimilation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2637–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryu, D.; Crow, W.T.; Zhan, X.; Jackson, T.J. Correcting unintended perturbation biases in hydrologic data assimilation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 734–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-H.; Chun, H.-W.; Lee, S.; Ha, J.-H.; Song, H.-J.; Kwon, I.-H.; Han, H.-J.; Jeong, H.; Kwon, H.-N.; Kim, T.-H. Development of an observation processing package for data assimilation in KIAPS. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 54, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Reichle, R.H.; Bindlish, R.; Cosh, M.H.; Crow, W.T.; de Jeu, R.; de Lannoy, G.J.M.; Huffman, G.J.; Jackson, T.J. The contributions of precipitation and soil moisture observations to the skill of soil moisture estimates in a land data assimilation system. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 750–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotter, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horanyi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilleland, E. Confidence Intervals for Forecast Verification: Practical Considerations; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, M.; Allen, T.; Bain, C.; Boutle, I.; Edwards, J.; Finnenkoetter, A.; Franklin, C.; Hanley, K.; Lean, H.; Lock, A.; et al. The first Met Office unified model-JULES regional atmosphere and land configuration, RAL1. Geoscientific Model Development. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2020, 13, 1999–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Manual on the Global Data-Processing and Forecasting System; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–148. [Google Scholar]
- Boisvert, L.N.; Wu, D.L.; Vihma, T.; Susskind, J. Verificaiton of air/surface humidity differences from AIRS and ERA-Interim in support of turbulent flux estimation in the Arctic. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boilley, A.; Wald, L. Comparison between meteorological reanalyses from ERA-Interim and MERRA and measurements of daily solar irradiation at surface. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 135143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dong, X.; Xi, B.; Dolinar, E.K.; Stanfield, R.E.; Qiu, S. Quantifying the uncertainties of reanalyzed Arctic cloud and radiation properties using satellite surface observations. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 8007–8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, M.; Schlundt, C.; Stapelberg, S.; Sus, O.; Eliasson, S.; Willén, U.; Meirink, J.F. Comparing ERA-Interim clouds with satellite observations using a simplified satellite simulator. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 17601–17614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Qin, J.; Yang, K.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, X. Does ERA5 outperform satellite products in estimating atmospheric downward longwave radiation at the surface? Atmos. Res. 2021, 252, 105453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-H.; Choi, I.-J.; Kim, K.-B.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Lee, E.; Seol, K.-H. Verification of the global numerical weather prediction using SYNOP surface observation data. Atmosphere 2017, 27, 235–249. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.Y.; Klein, S.A.; Xie, S.; Zhang, C.; Tang, S.; Tang, Q.; Morette, C.J.; Van Weverberg, K.; Petch, J.; Ahlgrimm, M.; et al. Cause: On the role of surface energy budget errors to the warm surface air temperature error over the Central United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 2888–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jun, S.; Park, J.H.; Baek, H.J.; Boo, K.O.; Kang, H.S. Utilization of self-organizing Maps to analyzing systematic bias in numerical model: Surface air temperature forecast of KMA GDAPS. J. Korean Inst. 2018, 28, 601–610. [Google Scholar]
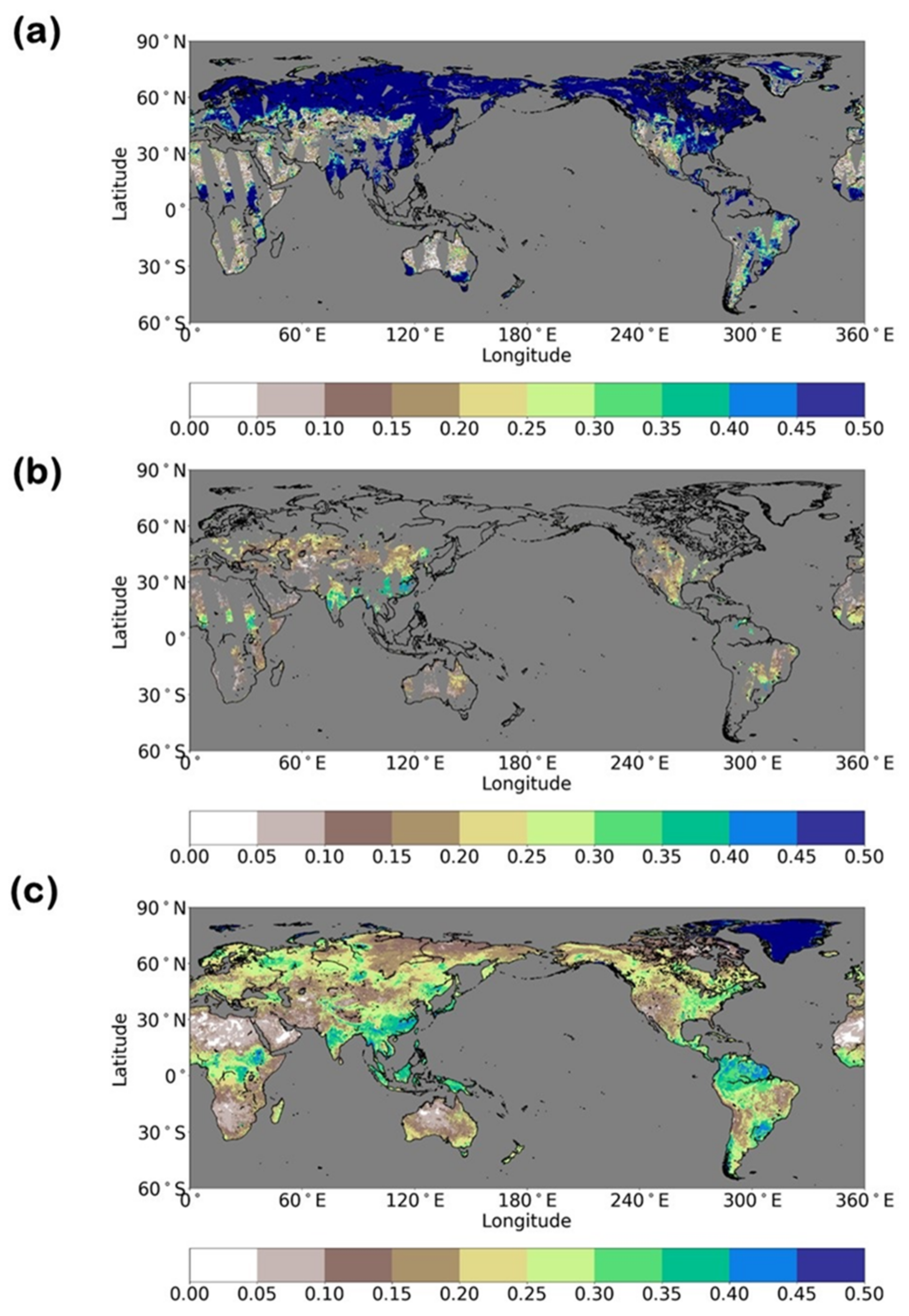
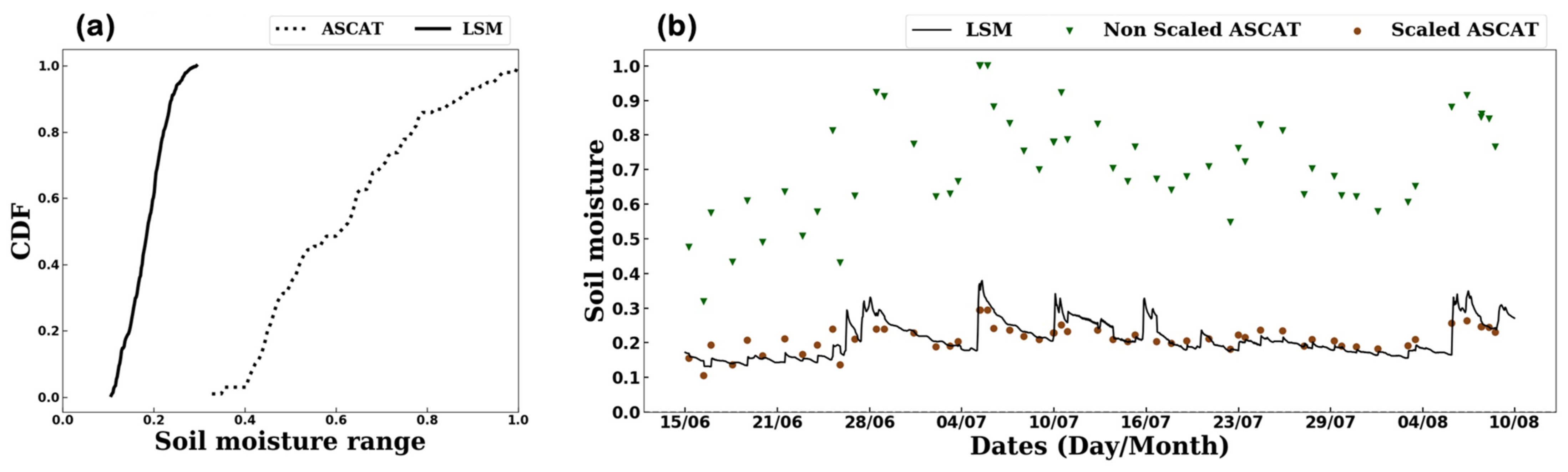
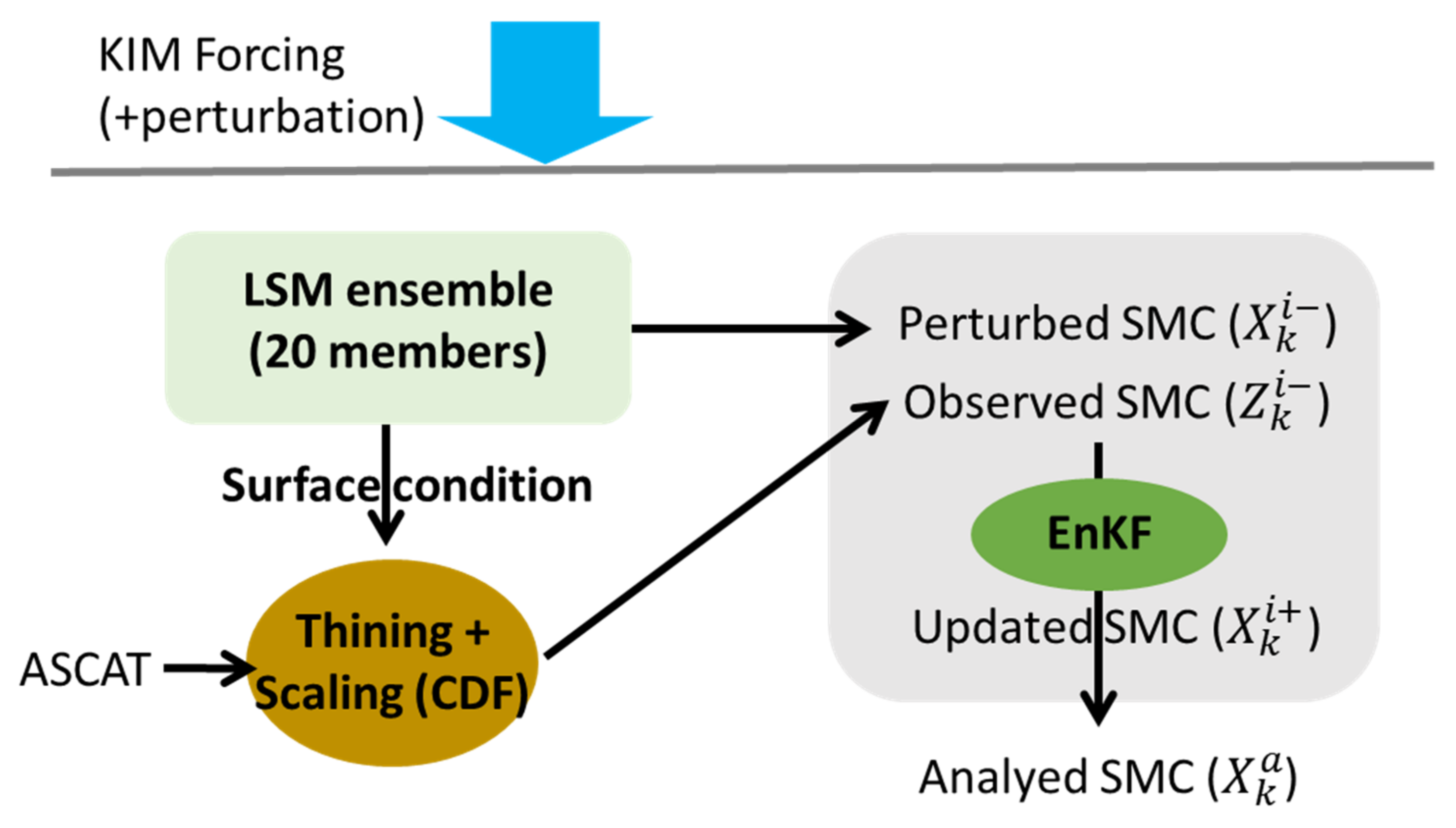
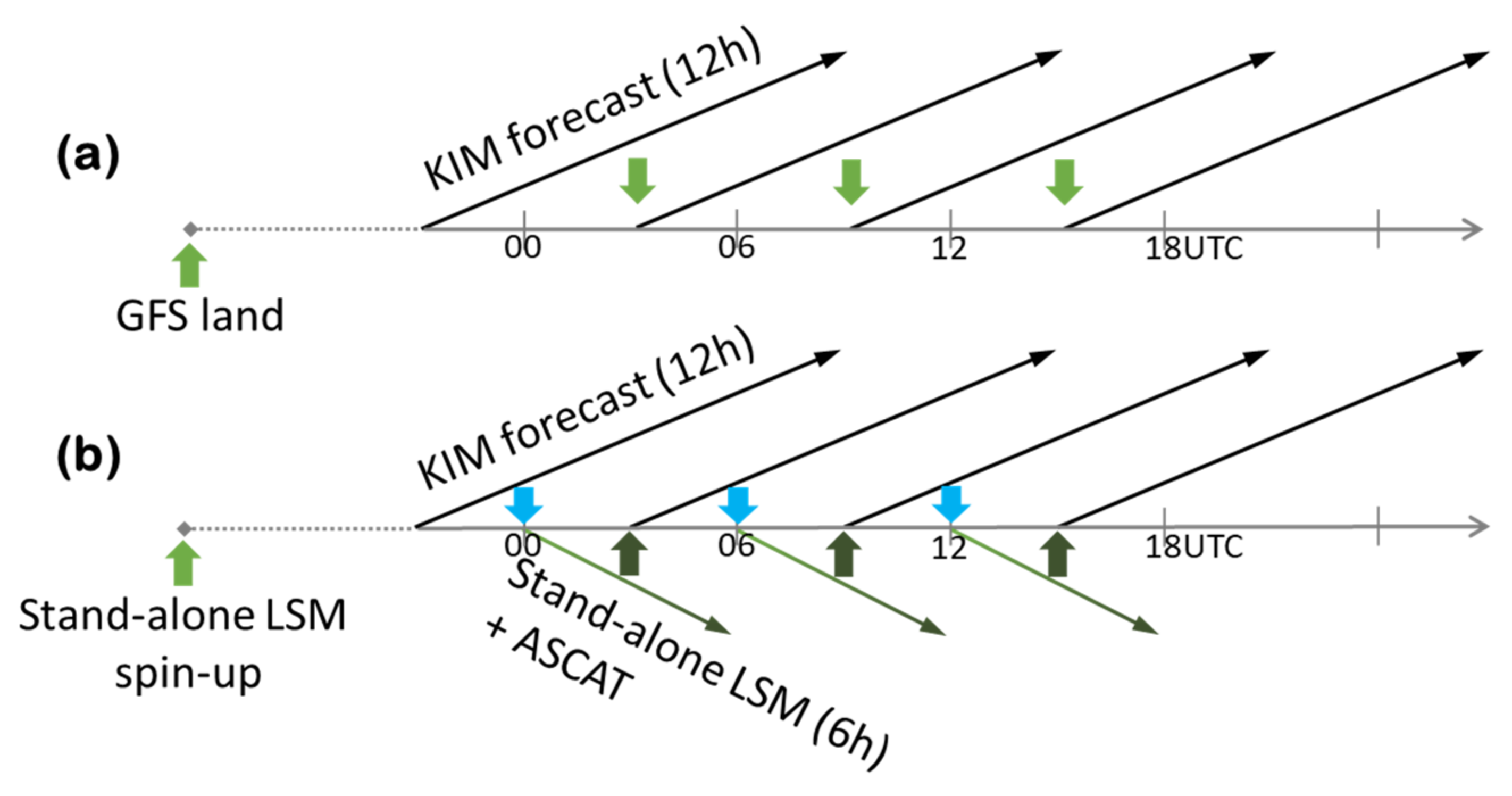

| Variables | Perturbation Types | Standard Deviations | Time Correlations (h) | Cross Correlations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | SW | LW | SM1 | SM2 | SM3 | SM4 | ||||
| P | Multiplicative | 0.5 | 24 | 1.0 | −0.8 | 0.5 | ||||
| SW | Multiplicative | 0.3 | 24 | −0.8 | 1.0 | −0.5 | ||||
| LW | Additive | 50.0 | 24 | −0.5 | 0.5 | 1.0 | ||||
| SM1 | Additive | 0.01 | 12 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |||
| SM2 | Additive | 0.006 | 12 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | |||
| SM3 | Additive | 0.003 | 12 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.6 | |||
| SM4 | Additive | 0.0015 | 12 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.0 | |||
| Experiment | Arid | Tropical | Temperate |
|---|---|---|---|
| EXP | 0.075 | 0.792 * | 0.615 * |
| CTL | 0.006 | 0.351 * | 0.130 * |
| Areas | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Northern Hemisphere (NH) | 90° N–20° N, all longitudes |
| Southern Hemisphere (SH) | 90° S–20° S, all longitudes |
| Tropics (TR) | 20° N–20° S, all longitudes |
| Asia (AS) | 25° N–65° N, 60° E–145° E |
| East Asia (EA) | 20° N–55° N, 100° E–150° E |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jun, S.; Park, J.-H.; Choi, H.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lim, Y.-J.; Boo, K.-O.; Kang, H.-S. Impact of Soil Moisture Data Assimilation on Analysis and Medium-Range Forecasts in an Operational Global Data Assimilation and Prediction System. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091089
Jun S, Park J-H, Choi H-J, Lee Y-H, Lim Y-J, Boo K-O, Kang H-S. Impact of Soil Moisture Data Assimilation on Analysis and Medium-Range Forecasts in an Operational Global Data Assimilation and Prediction System. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(9):1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091089
Chicago/Turabian StyleJun, Sanghee, Jeong-Hyun Park, Hyun-Joo Choi, Yong-Hee Lee, Yoon-Jin Lim, Kyung-On Boo, and Hyun-Suk Kang. 2021. "Impact of Soil Moisture Data Assimilation on Analysis and Medium-Range Forecasts in an Operational Global Data Assimilation and Prediction System" Atmosphere 12, no. 9: 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091089
APA StyleJun, S., Park, J.-H., Choi, H.-J., Lee, Y.-H., Lim, Y.-J., Boo, K.-O., & Kang, H.-S. (2021). Impact of Soil Moisture Data Assimilation on Analysis and Medium-Range Forecasts in an Operational Global Data Assimilation and Prediction System. Atmosphere, 12(9), 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091089






