Edge Detection Method for Determining Boundary Layer Height Based on Doppler Lidar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
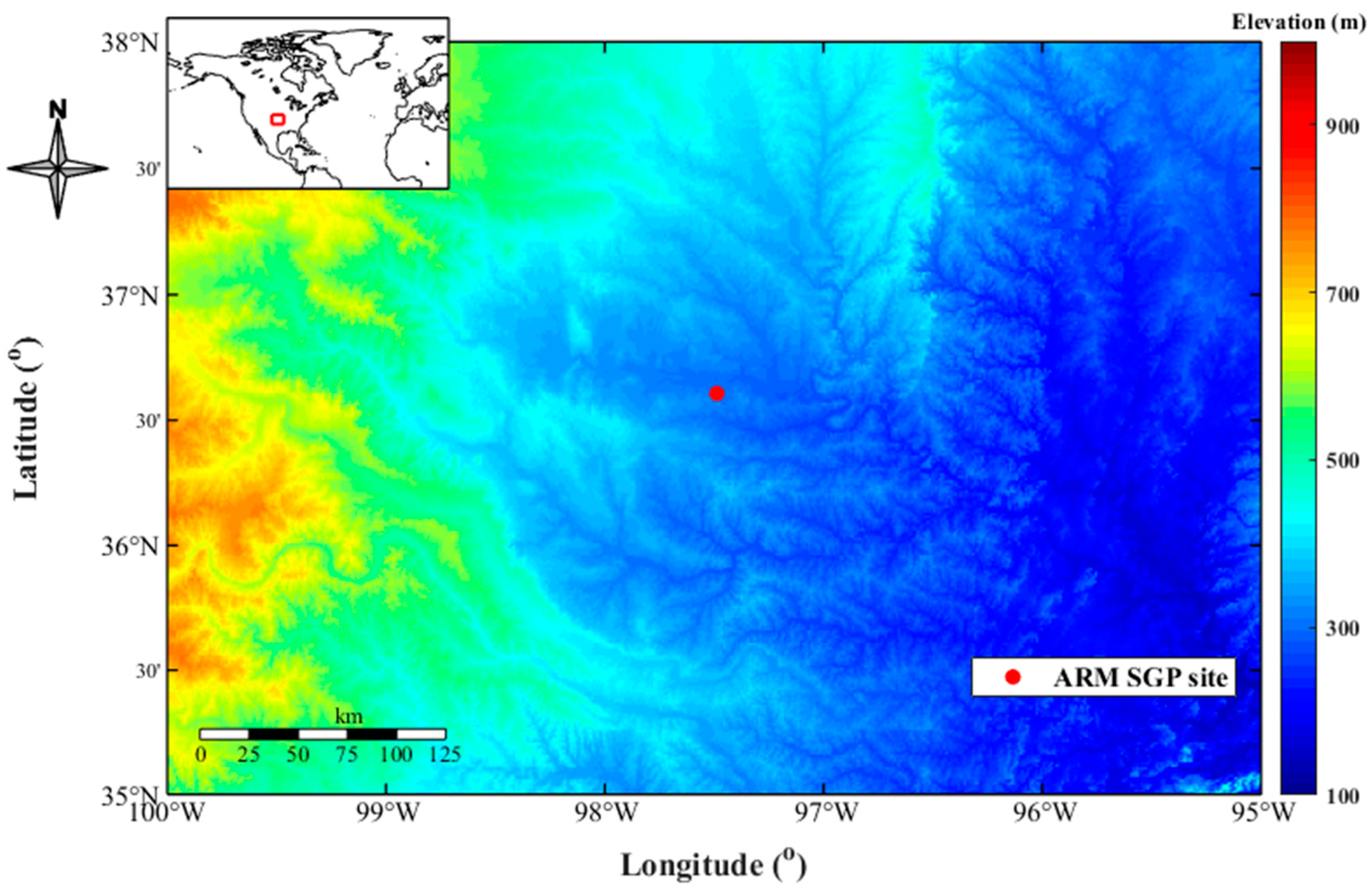
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Vertical Velocity Variance of Doppler Lidar Wind ()
2.1.2. BLH Retrieval Using RS
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. The Variance Method
2.2.2. The Peak Method
2.2.3. The WCT Method
2.2.4. The ED Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Diurnal Cases
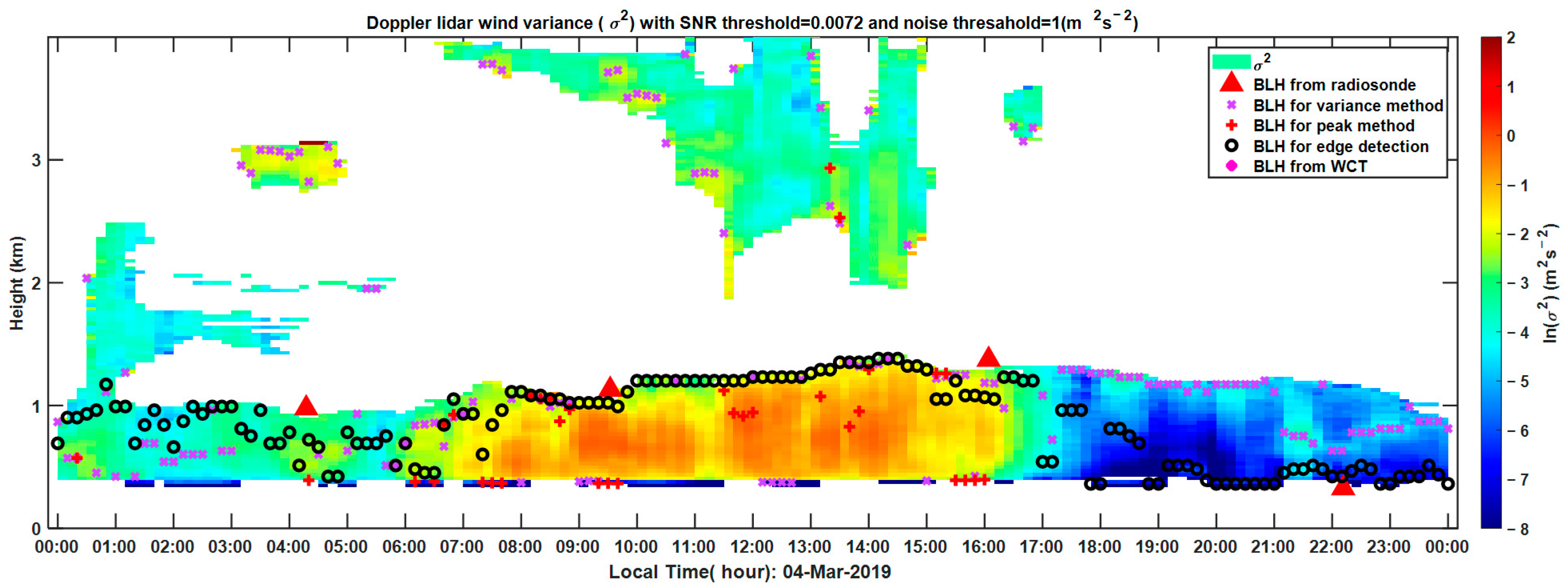
3.1.1. Extreme Atmospheric Condition
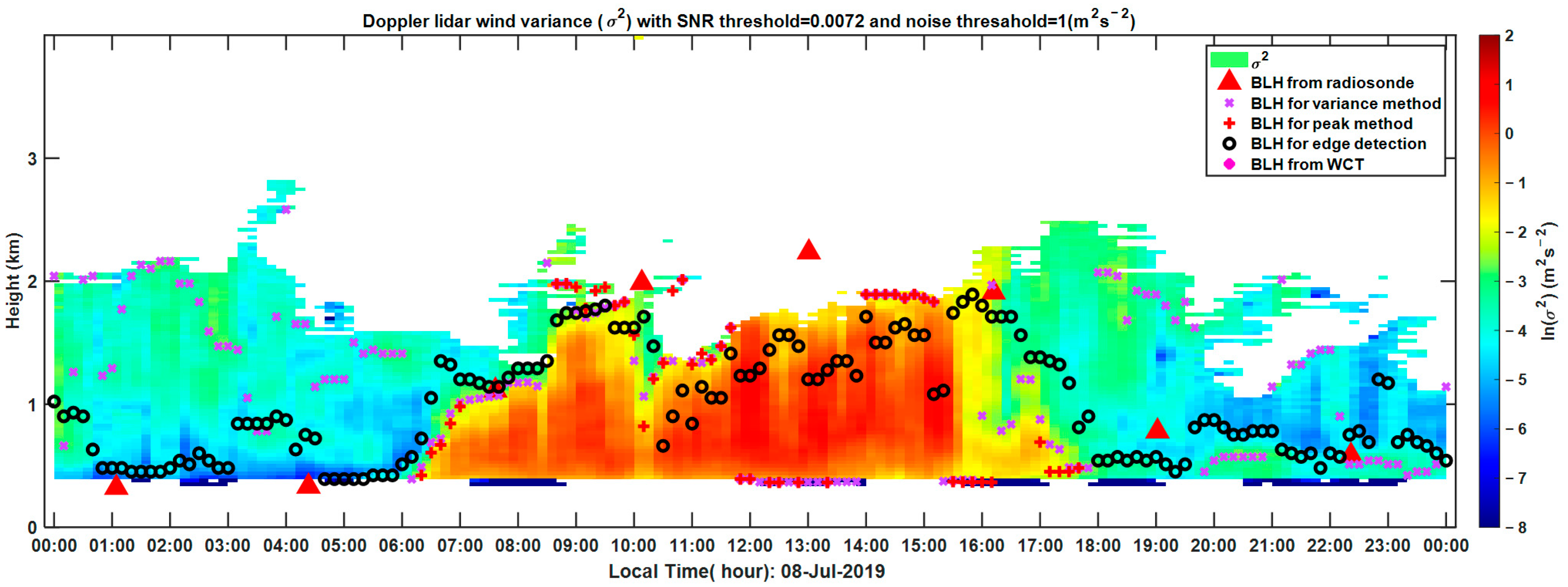
3.1.2. Routine Atmospheric Condition
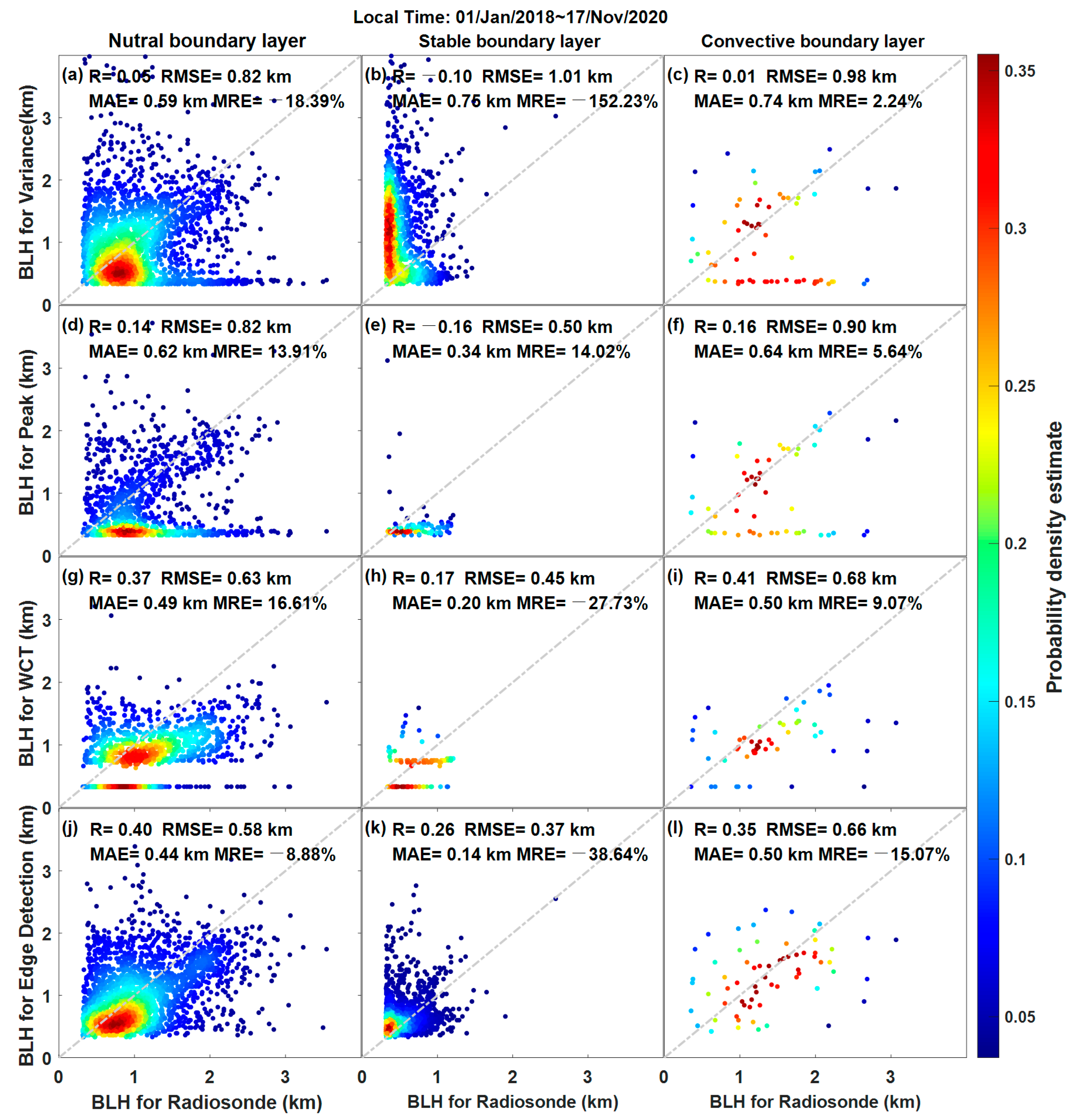
3.2. Statistical Comparison
3.3. Long-Term Analysis
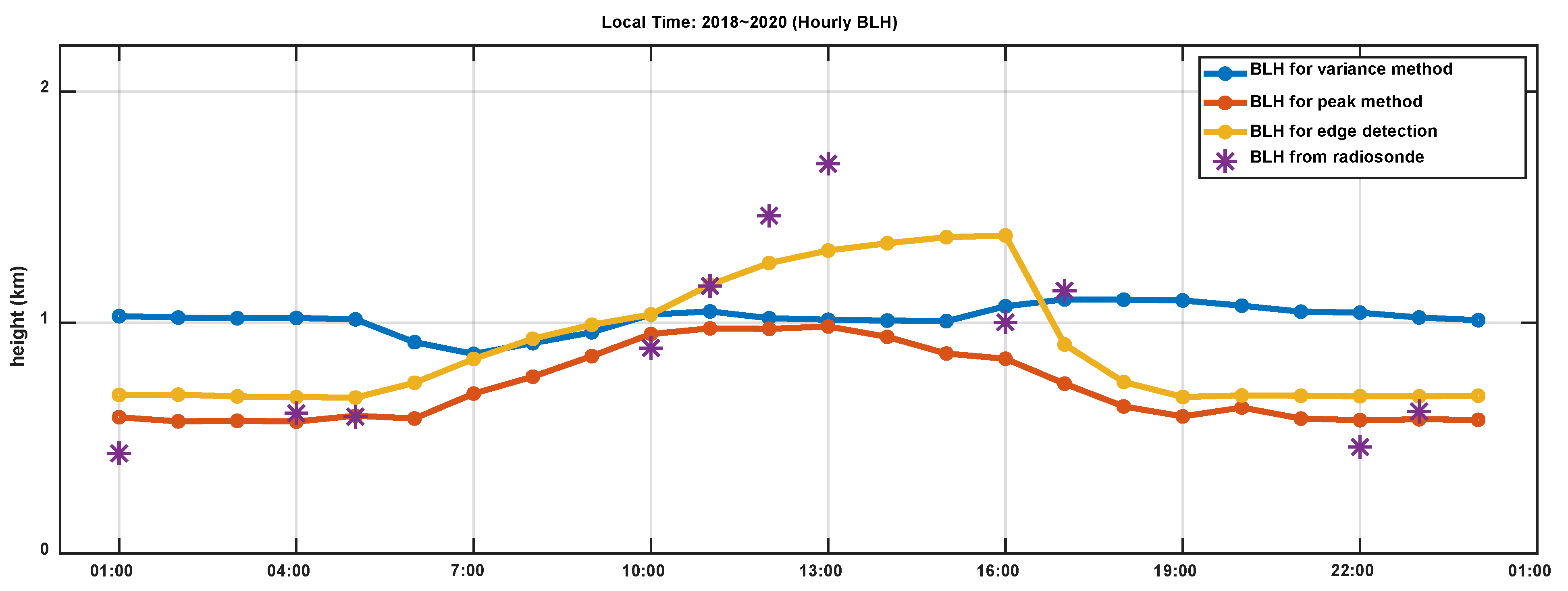
3.3.1. Diurnal Cycle
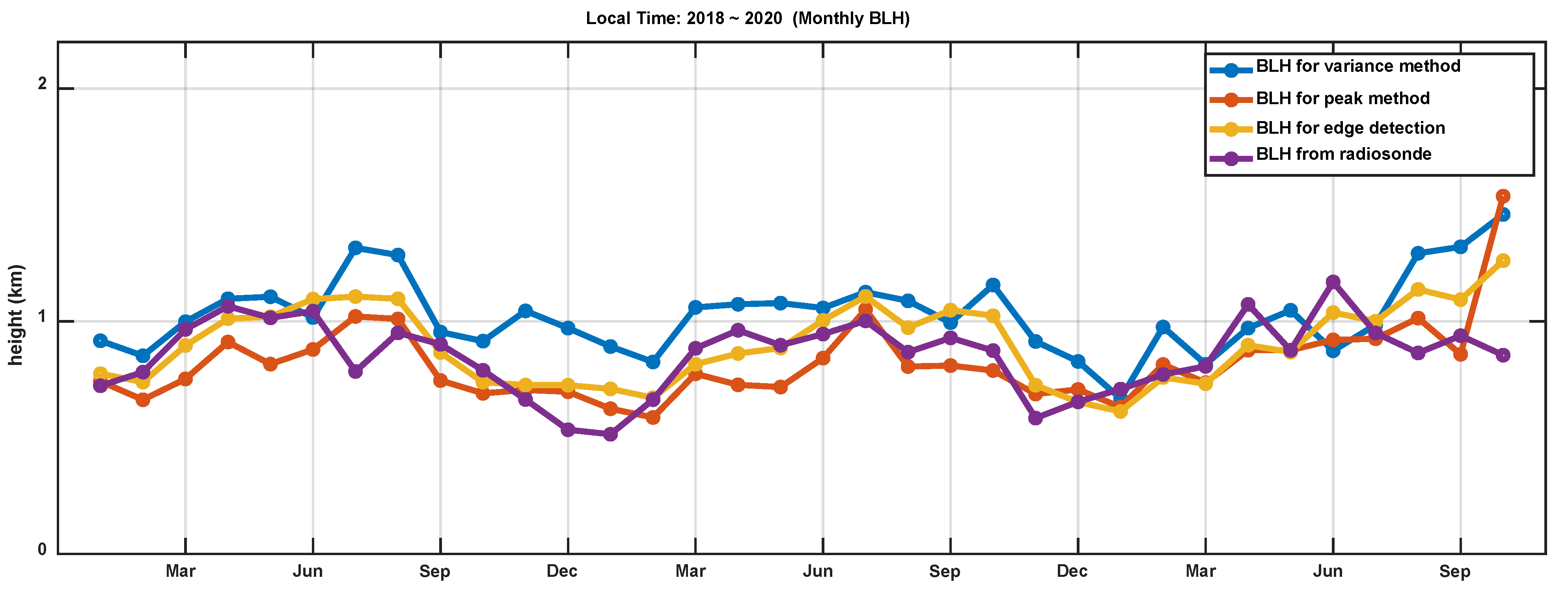
3.3.2. Annual Cycle
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Garratt, J. Review: The atmospheric boundary layer. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 89–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manninen, A.J.; Marke, T.; Tuononen, M.; O’Connor, E.J. Atmospheric Boundary Layer Classification with Doppler Lidar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8172–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liang, X.Z. Observed Diurnal Cycle Climatology of Planetary Boundary Layer Height. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 5790–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. A Review of Techniques for Diagnosing the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height (ABLH) Using Aerosol Lidar Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steyn, D.G.; Baldi, M.; Hoff, R.M. The Detection of Mixed Layer Depth and Entrainment Zone Thickness from Lidar Backscatter Profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, I.M. Finding Boundary Layer Top: Application of a Wavelet Covariance Transform to Lidar Backscatter Profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucker, S.C.; Senff, C.J.; Weickmann, A.M.; Brewer, W.A.; Banta, R.; Sandberg, S.P.; Law, D.C.; Hardesty, R.M. Doppler Lidar Estimation of Mixing Height Using Turbulence, Shear, and Aerosol Profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, P. Review and intercomparison of operational methods for the determination of the mixing height. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1001–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, J. A comprehensive evaluation of planetary boundary layer height retrieval techniques using lidar data under different pollution scenarios. Atmos. Res. 2021, 253, 105483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Huang, S.; Yan, Y.; Lou, M. Unraveling the relationships between boundary layer height and PM2.5 pollution in China based on four-year radiosonde measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, M.R. Doppler LiDAR Measurements of Boundary Layer Heights over San Jose, California. Ph.D. Thesis, San Jose State University, San Jose, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Frehlich, R.; Meillier, Y.; Jensen, M.L.; Balsley, B.; Sharman, R. Measurements of Boundary Layer Profiles in an Urban Environment. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2006, 45, 821–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, R.K.; Krishnamurthy, R. Doppler Lidar (DL) Instrument Handbook; DOE Office of Science Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) User Facility: Lemont, IL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Strawbridge, K.; Snyder, B. Planetary boundary layer height determination during Pacific 2001 using the advantage of a scanning lidar instrument. Atmospheric Environ. 2004, 38, 5861–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menut, L.; Flamant, C.; Pelon, J.; Flamant, P.H. Urban boundary-layer height determination from lidar measurements over the Paris area. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Gao, Z.; Kalogiros, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, X. Estimate of boundary-layer depth in Nanjing city using aerosol lidar data during 2016–2017 winter. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 205, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, J.C.; Delgado, R.; Berkoff, T.A.; Hoff, R.M. Determination of Planetary Boundary Layer Height on Short Spatial and Temporal Scales: A Demonstration of the Covariance Wavelet Transform in Ground-Based Wind Profiler and Lidar Measurements*. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1566–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, R.K.; Sivaraman, C.; Shippert, T.R.; Riihimaki, L.D. Doppler Lidar Vertical Velocity Statistics Value-Added Product; DOE ARM Climate Research Facility: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Gao, Z.; Miao, S.; Chen, F.; LeMone, M.A.; Li, J.; Hu, F.; Wang, L. Estimate of Boundary-Layer Depth over Beijing, China, Using Doppler Lidar Data During SURF-2015. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2017, 162, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berg, L.K.; Newsom, R.K.; Turner, D. Year-Long Vertical Velocity Statistics Derived from Doppler Lidar Data for the Continental Convective Boundary Layer. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2017, 56, 2441–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, J.; Beveridge, S.L.; Da Silva, M.P.A.; Tanamachi, R.L.; Rocadenbosch, F.; Turner, D.D.; Frasier, S.J. Convective boundary-layer height estimation from combined radar and Doppler lidar observations in VORTEX-SE. Remote Sens. Clouds Atmos. 2020, 11531, 115310X. [Google Scholar]
- Drew, D.R.; Barlow, J.F.; Lane, S.E. Observations of wind speed profiles over Greater London, UK, using a Doppler lidar. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2013, 121, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Automatic Detection of Boundary Layer Height Using Doppler Lidar Measurements. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/meteo-01379589/ (accessed on 26 August 2021).
- Xiang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Fan, G.; Zhou, P.; Lü, L.; Liu, Y. Retrieve of planetary boundary layer height based on image edge detection. Chin. J. Lasers 2016, 43, 0704003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Huang, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T. Evaluation of retrieval methods of daytime convective boundary layer height based on lidar data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4578–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, C.; McFarlane, S.; Chapman, E.; Jensen, M.; Toto, T.; Liu, S.; Fischer, M. Planetary Boundary Layer (PBL) Height Value Added Product (VAP): Radiosonde Retrievals; US Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, J.H.; Rasmussen, A.; Ellermann, T.; Lyck, E. Mesoscale influence on long-range transport—evidence from ETEX modelling and observations. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 4207–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, J.F.; Dunbar, T.M.; Nemitz, E.G.; Wood, C.R.; Gallagher, M.W.; Davies, F.; O’Connor, E.; Harrison, R.M. Boundary layer dynamics over London, UK, as observed using Doppler lidar during REPARTEE-II. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 2111–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Versaci, M.; Morabito, F.C. Image Edge Detection: A New Approach Based on Fuzzy Entropy and Fuzzy Divergence. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, X.-M.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, T. Atmosphere Boundary Layer Height (ABLH) Determination under Multiple-Layer Conditions Using Micro-Pulse Lidar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Chang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Dai, T.; Chen, S. An improved method for automatic determination of the planetary boundary layer height based on lidar data. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2020, 257, 107382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleeman, J.; Halem, M.; Yang, Z.; Caicedo, V.; Demoz, B.; Delgado, R. A deep machine learning approach for lidar based boundary layer height detection. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020–2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Online, 26 September–2 October 2020. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Jin, Z.; Tong, P.; Xu, W.; Wang, W. Edge Detection Method for Determining Boundary Layer Height Based on Doppler Lidar. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091103
Pan Y, Jin Z, Tong P, Xu W, Wang W. Edge Detection Method for Determining Boundary Layer Height Based on Doppler Lidar. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(9):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091103
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Ya’ni, Zhili Jin, Pengfei Tong, Weiwei Xu, and Wei Wang. 2021. "Edge Detection Method for Determining Boundary Layer Height Based on Doppler Lidar" Atmosphere 12, no. 9: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091103
APA StylePan, Y., Jin, Z., Tong, P., Xu, W., & Wang, W. (2021). Edge Detection Method for Determining Boundary Layer Height Based on Doppler Lidar. Atmosphere, 12(9), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091103






