Suppressing Grid-Point Storms in a Numerical Forecasting Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Experiments
2.1. KIM and a Case Description
2.2. New Tiedtke Scheme (NTDK) and MOD Experiments
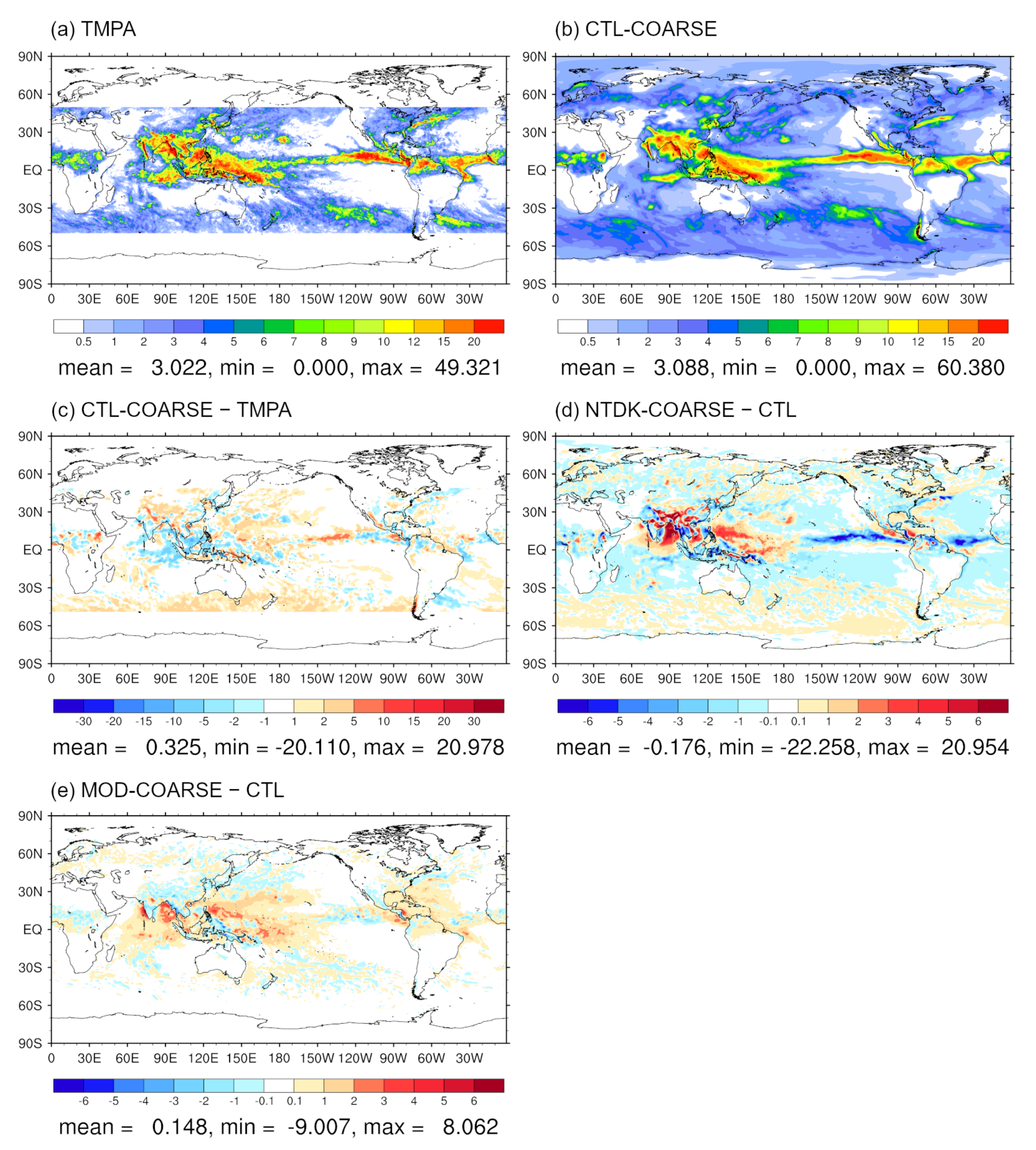
2.3. CTL-COARSE, NTDK-COARSE, and MOD-COARSE Experiments
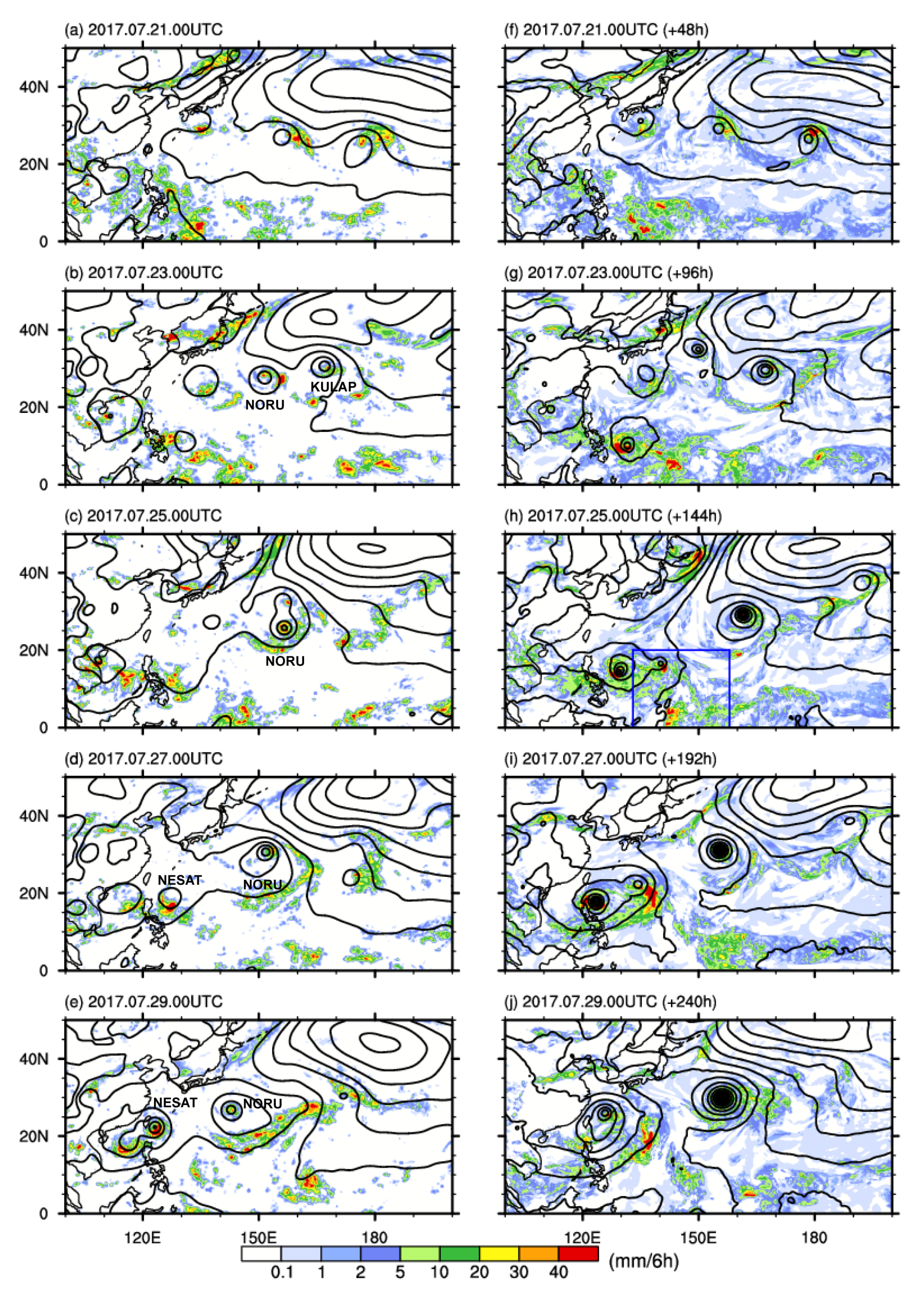
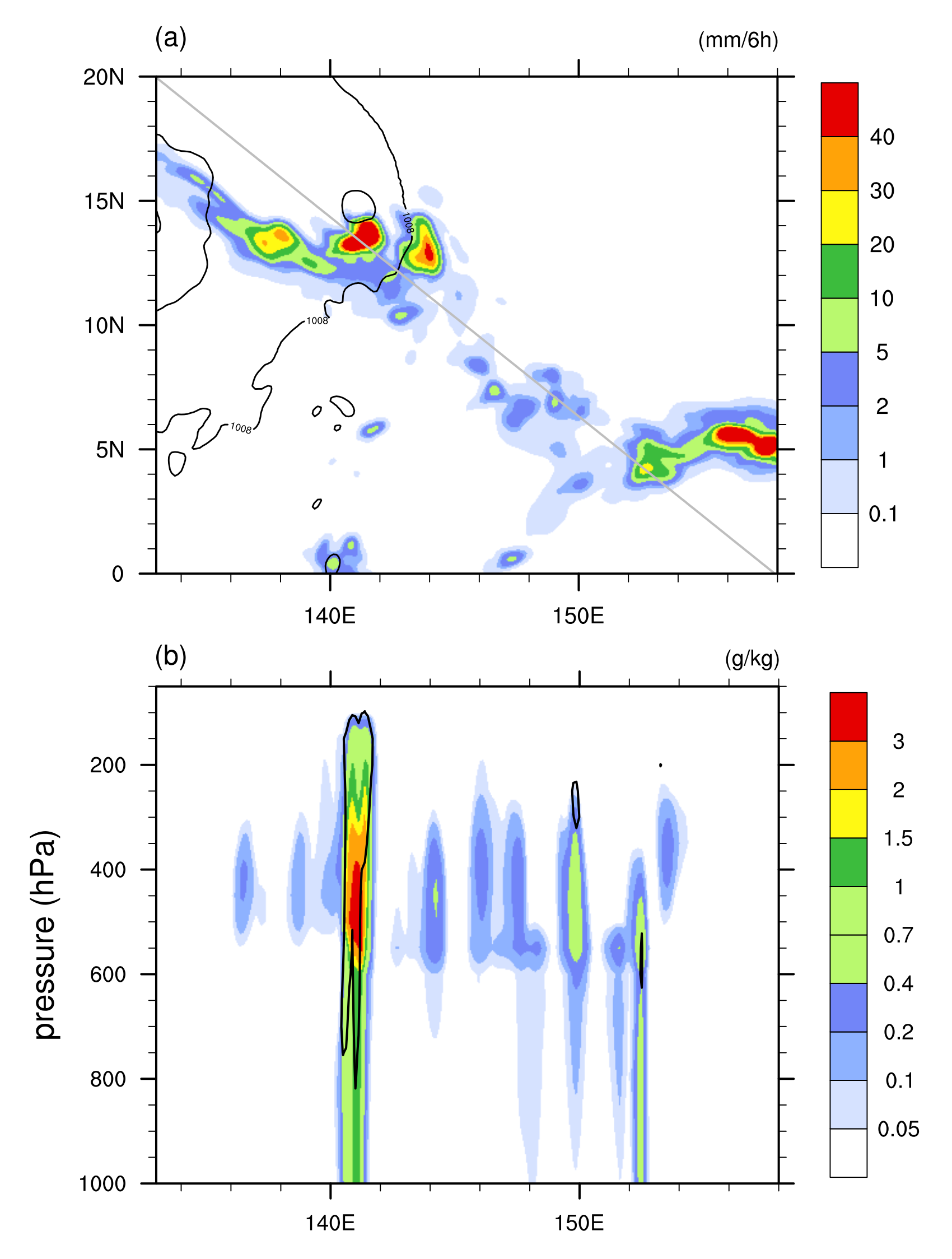
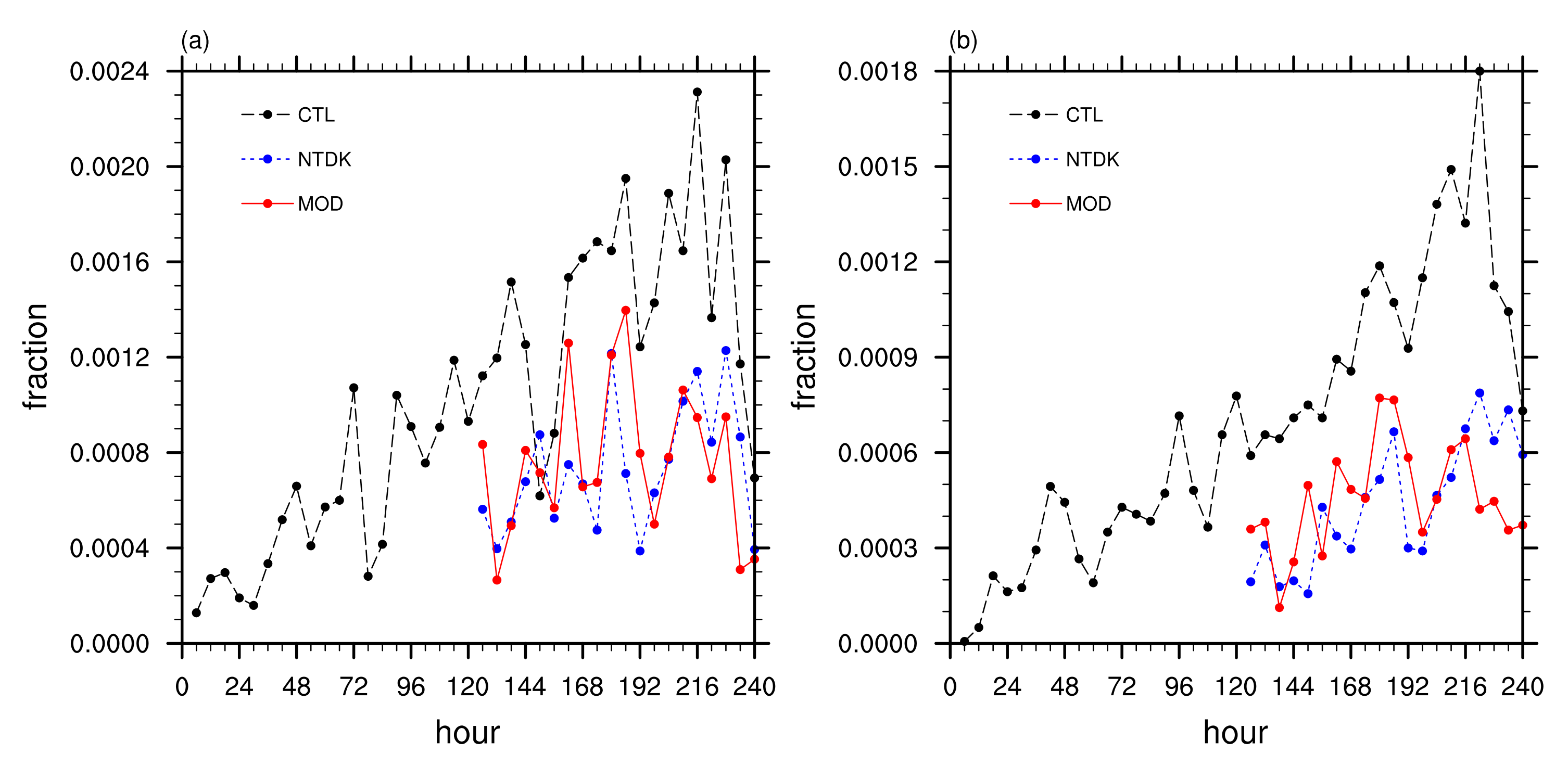
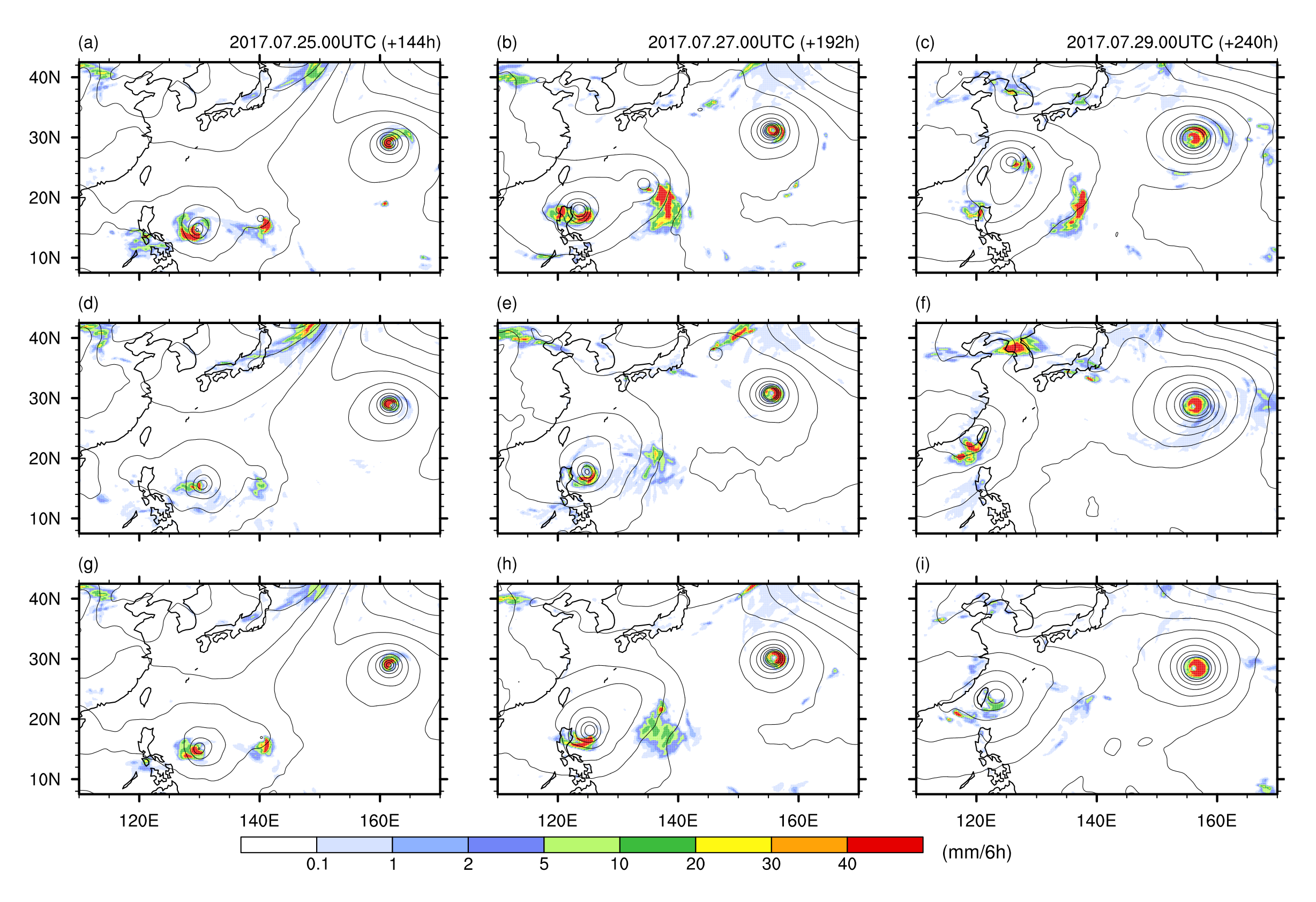
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Grid-Point Storms and Heating and Drying Tendencies
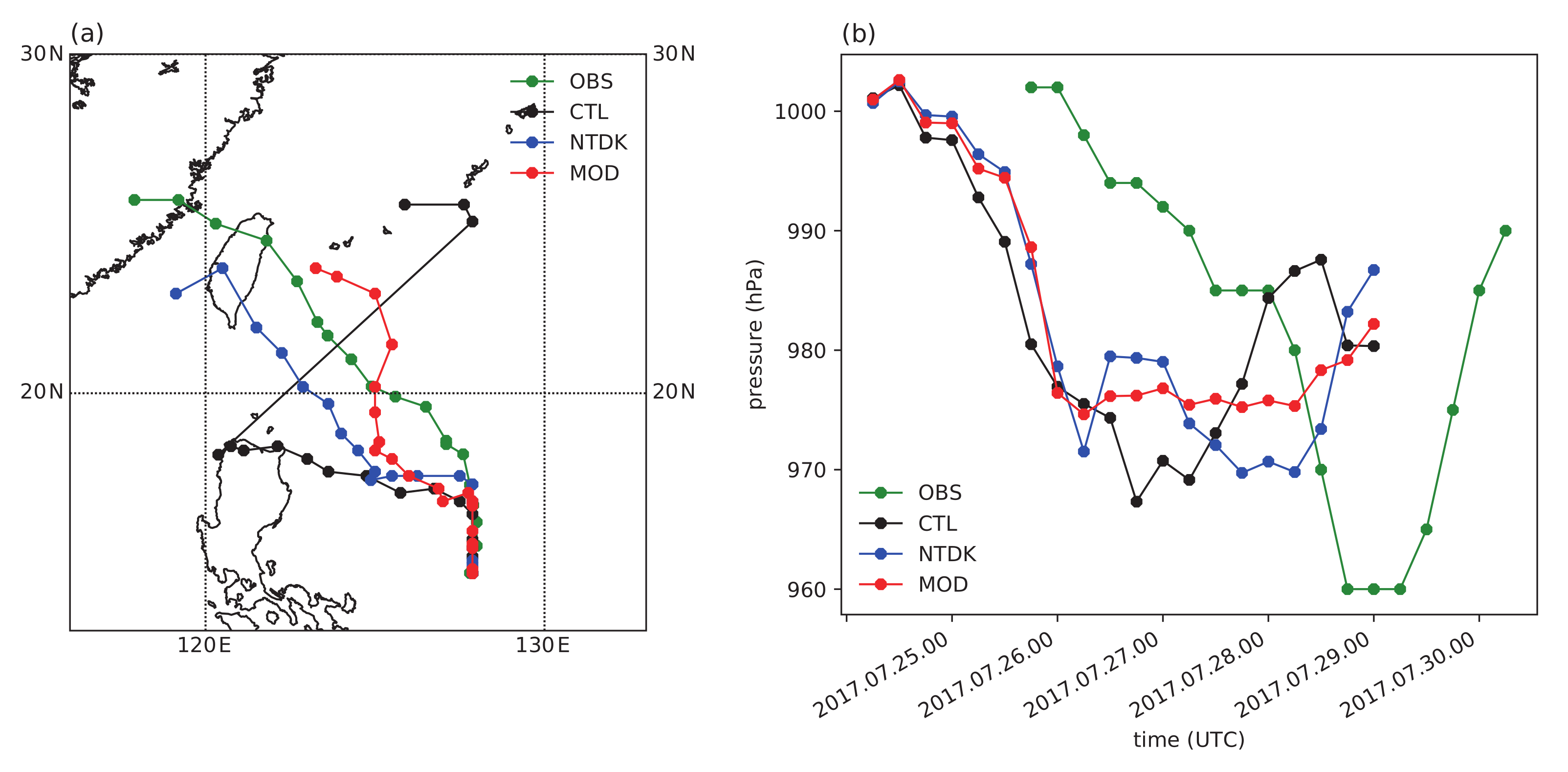
3.2. Impact of Convection Scheme Modification: Case Experiment
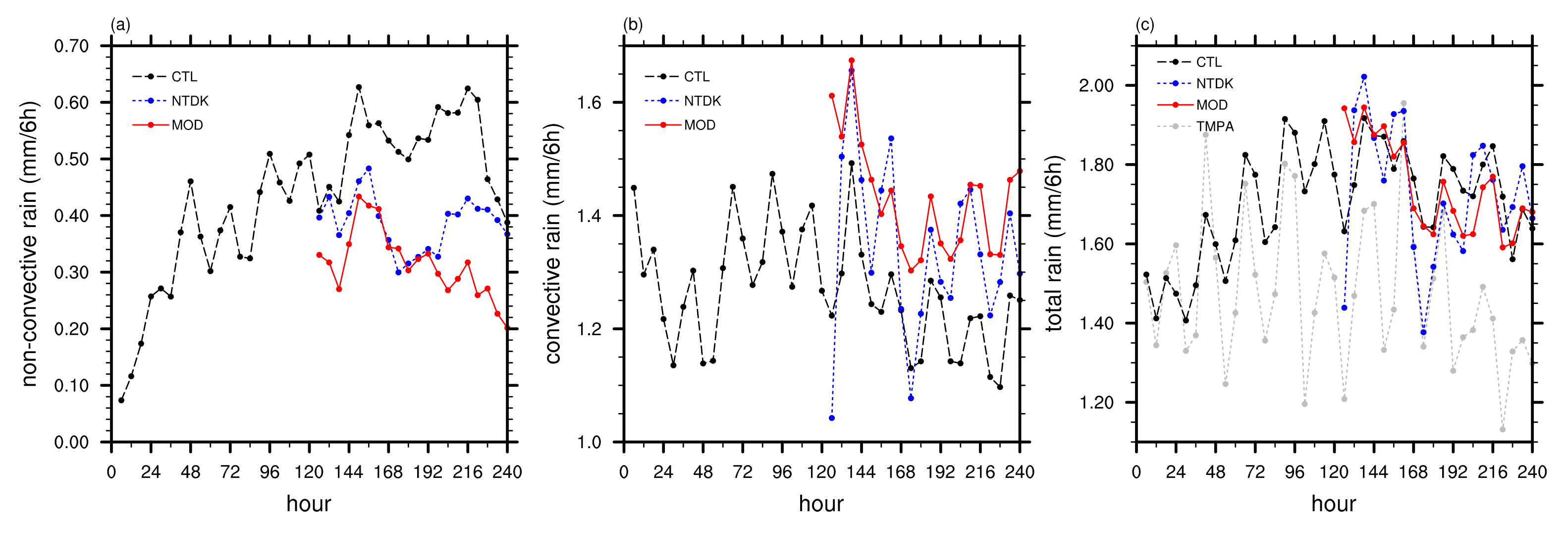
3.3. Impact of Convection Scheme Modification: Medium-Range Forecast Experiments
4. Summary and Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bechtold, P.; Köhler, M.; Jung, T.; Doblas-Reyes, F.; Leutbecher, M.; Rodwell, M.J.; Vitart, F.; Balsamo, G. Advances in simulating atmospheric variability with the ECMWF model: From synoptic to decadal time-scales. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 1337–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pan, H.L. Revision of convection and vertical diffusion schemes in the NCEP Global Forecast System. Weather Forecast. 2011, 26, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; Hsie, E.Y.; Moncrieff, M.W. A comparison of explicit and implicit predictions of convective and stratiform precipitating weather systems with a meso-β-scale numerical model. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1988, 114, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, J.; Dudek, M. Parameterization of convective precipitation in mesoscale numerical models: A critical review. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 326–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.Y.; Kwon, Y.C.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, J.E.E.; Choi, S.J.; Kwon, I.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, E.H.; Park, R.S.; Kim, D.I. The Korean Integrated Model (KIM) system for global weather forecasting. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 54, 267–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Giraldo, F.X.; Kim, J.; Shin, S. Verification of a non-hydrostatic dynamical core using the horizontal spectral element method and vertical finite difference method: 2-D aspects. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 2717–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.J.; Hong, S.Y. A global non-hydrostatic dynamical core using the spectral element method on a cubed-sphere grid. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 52, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Kwon, I.H. Spectral transformation using a cubed-sphere grid for a three-dimensional variational data assimilation system. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 2581–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Chun, H.W.; Lee, S.; Ha, J.H.; Song, H.J.; Kwon, I.H.; Han, H.J.; Jeong, H.; Kwon, H.N.; Kim, T.H. Development of an observation processing package for data assimilation in KIAPS. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 54, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S. A revised radiation package of G-packed McICA and two-stream approximation: Performance evaluation in a global weather forecasting model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2017, 9, 1628–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.S.; Chae, J.H.; Hong, S.Y. A revised prognostic cloud fraction scheme in a global forecasting system. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, M.S.; Baek, S.; Seol, K.H.; Cho, K. Advances in land modeling of KIAPS based on the Noah Land Surface Model. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 53, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, M.S.; Choi, H.J.; Han, J.Y. A parameterization of turbulent-scale and mesoscale orographic drag in a global atmospheric model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8400–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Hong, S.Y. Impact of air-sea interaction on East Asian summer monsoon climate in WRF. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Hong, S.Y. Impact of the sea surface salinity on simulated precipitation in a global numerical weather prediction model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.H.; Hong, S.Y. Representation of the subgrid-scale turbulent transport in convective boundary layers at gray-zone resolutions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 250–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Lee, E.; Park, R.; Kwon, Y.C.; Hong, S.Y. Impact of turbulent mixing in the stratocumulus-topped boundary layer on numerical weather prediction. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 54, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Hong, S.Y. An updated subgrid orographic parameterization for global atmospheric forecast models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 12445–12457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Han, J.Y.; Koo, M.S.; Chun, H.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Hong, S.Y. Effects of non-orographic gravity wave drag on seasonal and medium-range predictions in a global forecast model. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 54, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Dudhia, J.; Chen, S.H. A revised approach to ice microphysical processes for the bulk parameterization of clouds and precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.Y.; Hong, S.Y.; Lim, K.S.S. Coupling WRF double-moment 6-class microphysics schemes to RRTMG radiation scheme in weather research forecasting model. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 5070154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Hong, S.Y. The use of partial cloudiness in a bulk cloud microphysics scheme: Concept and 2D results. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 2711–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Hong, S.Y.; Lim, K.S.S.; Han, J. Sensitivity of a cumulus parameterization scheme to precipitation production representation and its impact on a heavy rain event over Korea. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.C.; Hong, S.Y. A mass-flux cumulus parameterization scheme across gray-zone resolutions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Hong, S.Y. Precipitation forecast experiments using the weather research and forecasting (WRF) model at gray-zone resolutions. Weather Forecast. 2018, 33, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Hong, S.Y.; Kwon, Y.C. The performance of a revised simplified Arakawa–Schubert (SAS) convection scheme in the medium-range forecasts of the Korean Integrated Model (KIM). Weather Forecast. 2020, 35, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S). ERA5: Fifth Generation of ECMWF Atmospheric Reanalyses of the Global Climate. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/home (accessed on 2 January 2019).
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedtke, M. A comprehensive mass flux scheme for cumulus parameterization in large-scale models. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 1779–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bechtold, P.; Semane, N.; Lopez, P.; Chaboureau, J.P.; Beljaars, A.; Bormann, N. Representing equilibrium and nonequilibrium convection in large-scale models. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 734–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Hamilton, K. Improved representation of boundary layer clouds over the Southeast Pacific in ARW-WRF using a modified Tiedtke cumulus parameterization scheme. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 3489–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.-B.; Han, J.-Y. Suppressing Grid-Point Storms in a Numerical Forecasting Model. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091194
Park S-B, Han J-Y. Suppressing Grid-Point Storms in a Numerical Forecasting Model. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(9):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091194
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seung-Bu, and Ji-Young Han. 2021. "Suppressing Grid-Point Storms in a Numerical Forecasting Model" Atmosphere 12, no. 9: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091194
APA StylePark, S.-B., & Han, J.-Y. (2021). Suppressing Grid-Point Storms in a Numerical Forecasting Model. Atmosphere, 12(9), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091194





