Deep Neural Networks for Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Computational Background
2. Materials and Methods
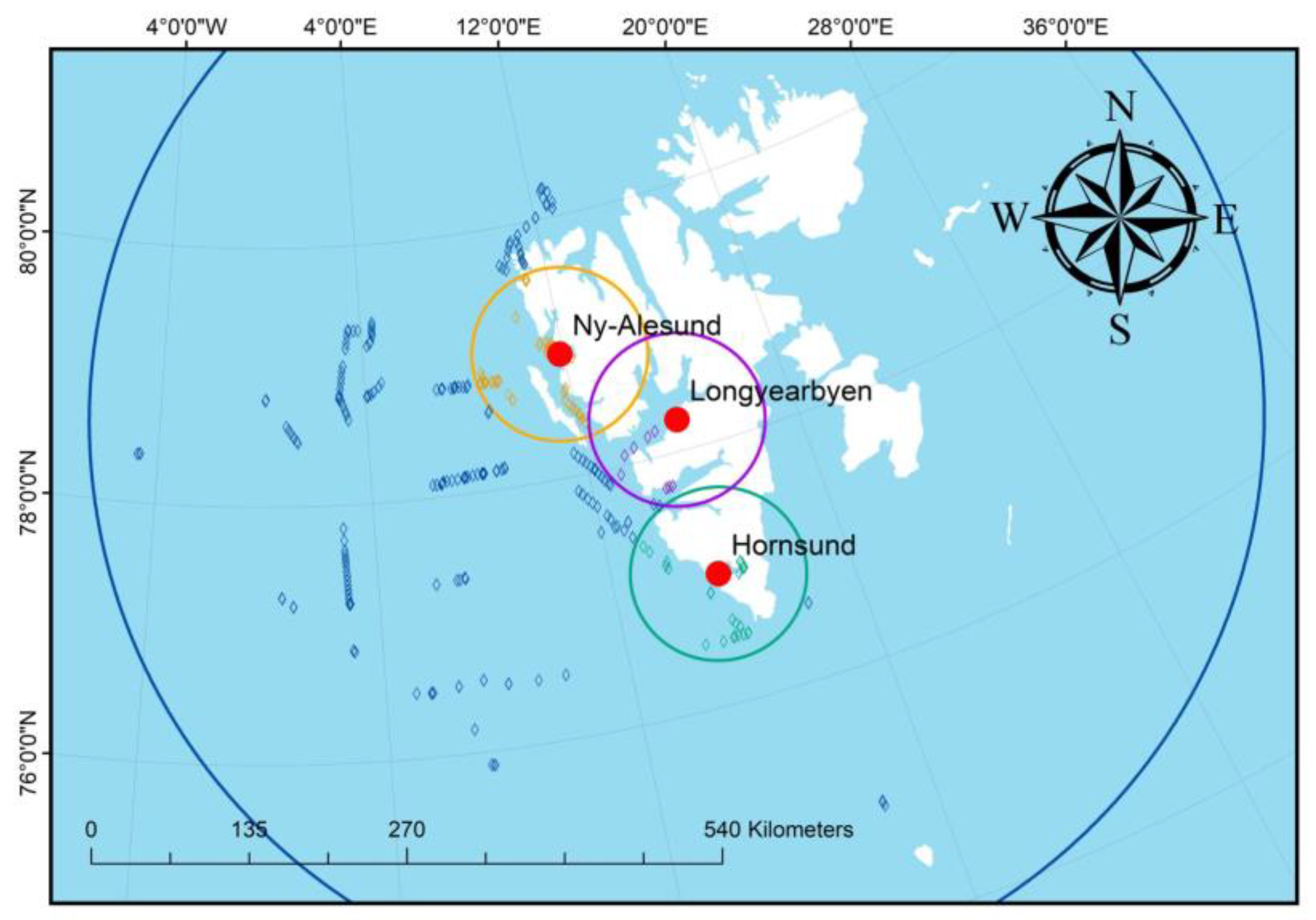
2.1. Defining the Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. AERONET (MAN): AOD Data
2.2.2. Norwegian Climate Centre (NCC): Meteorological Data
2.2.3. MODIS Global Fires: Biomass Burning Event Data
2.2.4. Making the BBE Data: Evaluating BBE Intensity
2.3. Machine/Experiment Settings
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Linear Model vs. DNN
3.2. DNN without BBE (−BBE) vs. DNN with BBE (+BBE)
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AMAP. Arctic Climate Change Update 2021: Key Trends and Impacts. Summary for Policy-Makers; Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP): Tromsø, Norway, 2021; 16p. [Google Scholar]
- Serreze, M.C.; Barry, R.G. Processes and Impacts of Arctic Amplification: A Research Synthesis. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011, 77, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, T.-F.; Xiao, C.-D. An Overview of Black Carbon Deposition and Its Radiative Forcing over the Arctic. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2016, 7, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Xing, T.; Guang, J.; Xue, Y.; Che, Y. Aerosol Optical Depth over the Arctic Snow-Covered Regions Derived from Dual-Viewing Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schutgens, N.; Sayer, A.M.; Heckel, A.; Hsu, C.; Jethva, H.; de Leeuw, G.; Leonard, P.J.T.; Levy, R.C.; Lipponen, A.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. An AeroCom/AeroSat Study: Intercomparison of Satellite AOD Datasets for Aerosol Model Evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12431–12457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Zhang, H.K.; Li, Z.; de Leeuw, G.; Huang, B. Himawari-8 Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrieval Using a Deep Neural Network Trained Using AERONET Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonchyk, M.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Li, Y. Author Correction: Combined Use of Satellite and Surface Observations to Study Aerosol Optical Depth in Different Regions of China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Lee, H.; Park, J. A First Approach to Aerosol Classification Using Space-Borne Measurement Data: Machine Learning-Based Algorithm and Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Sayer, A.M.; Holben, B.N.; Hsu, N.C.; Sakerin, S.M.; Macke, A.; Nelson, N.B.; Courcoux, Y.; Smyth, T.J.; Croot, P.; et al. Effect of Wind Speed on Aerosol Optical Depth over Remote Oceans, Based on Data from the Maritime Aerosol Network. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D.M.; McClain, C.R.; Eck, T.F.; Sakerin, S.M.; Macke, A.; Croot, P.; Zibordi, G.; et al. Maritime Aerosol Network as a Component of Aerosol Robotic Network. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakszys, P. Horizontal Variability of Aerosol Optical Properties over the European Arctic. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Oceanology Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot, Poland, 2018; p. 577. [Google Scholar]
- Voiland, A. Aerosols: Tiny Particles, Big Impact. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/features/Aerosols (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Keras: Deep Learning for Humans. 2015. Available online: https://keras.io (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Stone, R.S.; Sharma, S.; Herber, A.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Nelson, D.W. A Characterization of Arctic Aerosols on the Basis of Aerosol Optical Depth and Black Carbon Measurements. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2014, 2, 000027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mei, L.; Xue, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; Hou, T.; Guang, J.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; He, X. Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval in the Arctic Region Using MODIS Based on Prior Knowledge. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2011, 4, 7597–7622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istomina, L.; Marks, H.; Huntemann, M.; Heygster, G.; Spreen, G. Improved Cloud Detection over Sea Ice and Snow during Arctic Summer Using MERIS Data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6459–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwarkar, P.; Sunder Raman, R. Population Exposure across Central India to PM2.5 Derived Using Remotely Sensed Products in a Three-Stage Statistical Model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, E.; Giamarelou, M.; Bossioli, E.; Zarmpas, P.; Theodosi, C.; Matsoukas, C.; Tombrou, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Biskos, G. Particulate Pollution Transport Episodes from Eurasia to a Remote Region of Northeast Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 128, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Source Dataset | Input Parameters |
|---|---|
| AERONET (MAN) | Time |
| Air Mass | |
| Latitude | |
| Longitude | |
| Water Vapor | |
| Site | |
| Day | |
| Month | |
| Year | |
| Norwegian Climate Centre | Average daily Temperature |
| Average daily Wind Speed | |
| MODIS Global Fires | BBE Intensity (calculated using Brightness, Latitude, Longitude, Day, Month, Year) |
| FRP |
| Layer | Nodes |
|---|---|
| Input layer | 13 |
| Hidden Layer 1 | 12 |
| Hidden Layer 2 | 12 |
| Hidden Layer 3 | 11 |
| Hidden Layer 4 | 9 |
| Hidden Layer 5 | 6 |
| Output Layer | 1 |
| Layer | Nodes |
|---|---|
| Input layer | 55 |
| Hidden Layer 1 | 54 |
| Hidden Layer 2 | 46 |
| Hidden Layer 3 | 42 |
| Hidden Layer 4 | 39 |
| Hidden Layer 5 | 21 |
| Hidden Layer 6 | 3 |
| Output layer | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zbizika, R.; Pakszys, P.; Zielinski, T. Deep Neural Networks for Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010101
Zbizika R, Pakszys P, Zielinski T. Deep Neural Networks for Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(1):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleZbizika, Renee, Paulina Pakszys, and Tymon Zielinski. 2022. "Deep Neural Networks for Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval" Atmosphere 13, no. 1: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010101
APA StyleZbizika, R., Pakszys, P., & Zielinski, T. (2022). Deep Neural Networks for Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval. Atmosphere, 13(1), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010101








