Emission Factors and Inventories of Carbonaceous Aerosols from Residential Biomass Burning in Guizhou Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Biomass Fuel Consumption in Guizhou Province
2.2. Stove Testing
2.3. Sample Collection, Pre-Treatment, and Chemical Analysis
2.4. Emission Factors
2.5. Emissions Inventory
2.6. Activity Data (Mn,j)
3. Results and Discussion
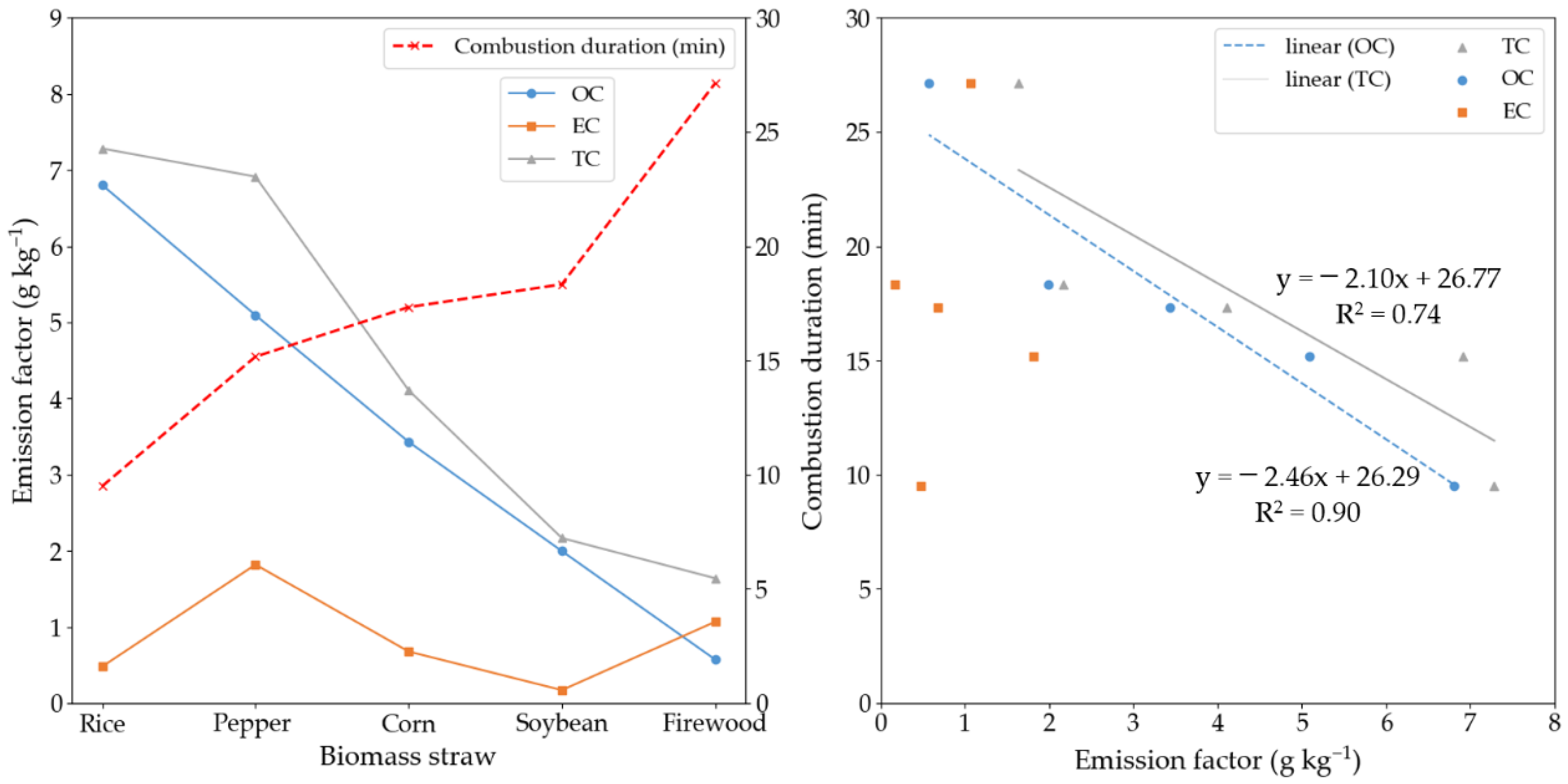
3.1. Emission Factors of Total Carbonaceous Aerosols for Residential Biomass Burning
3.2. OC and EC Emission Factors for Residential Biomass Burning
3.3. OC/EC Ratios and Eight Carbon Fractions from Burning of Different Biomass
3.4. Influence of Fuel Moisture Content and Fuel Pre-Treatment
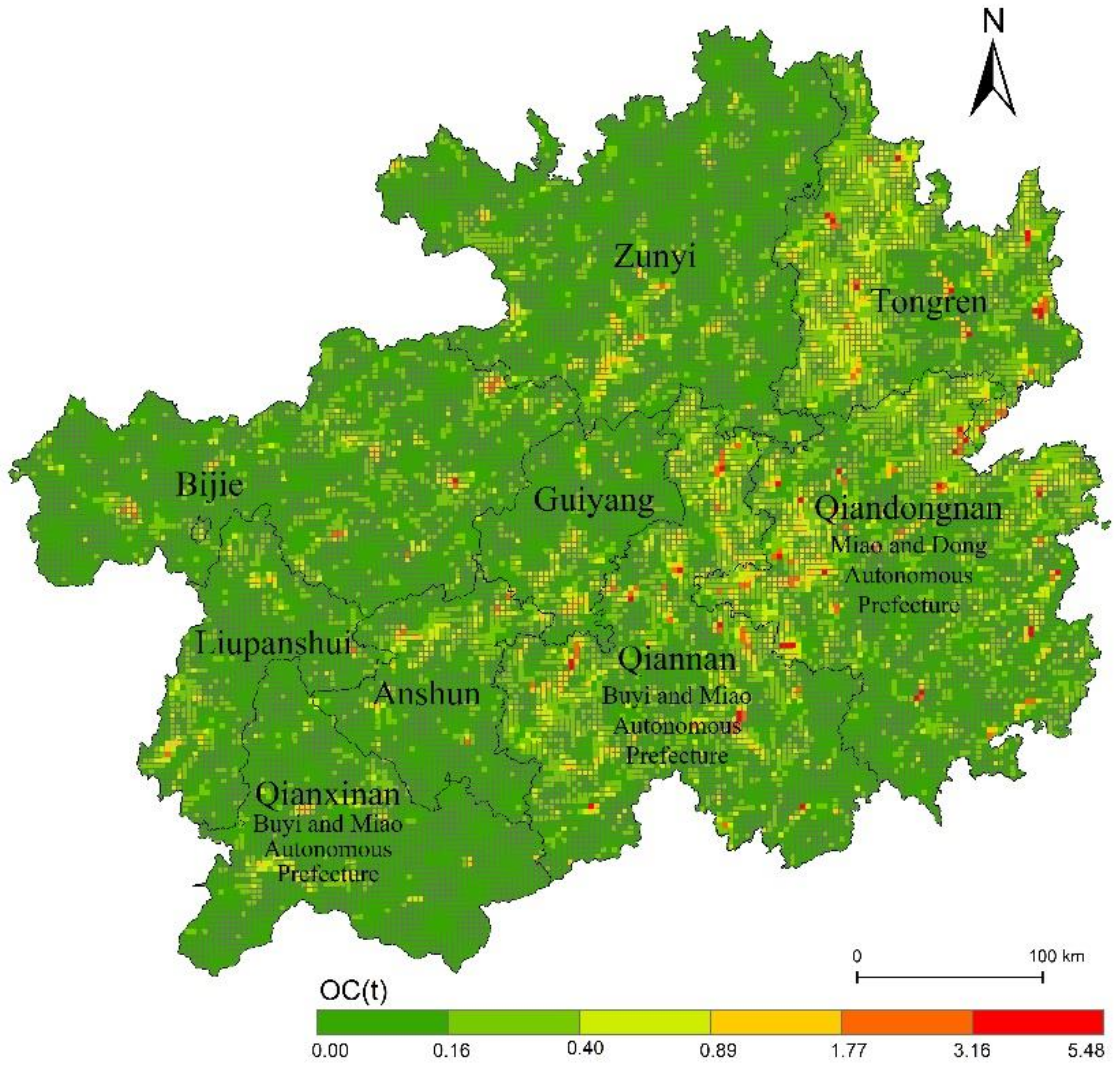
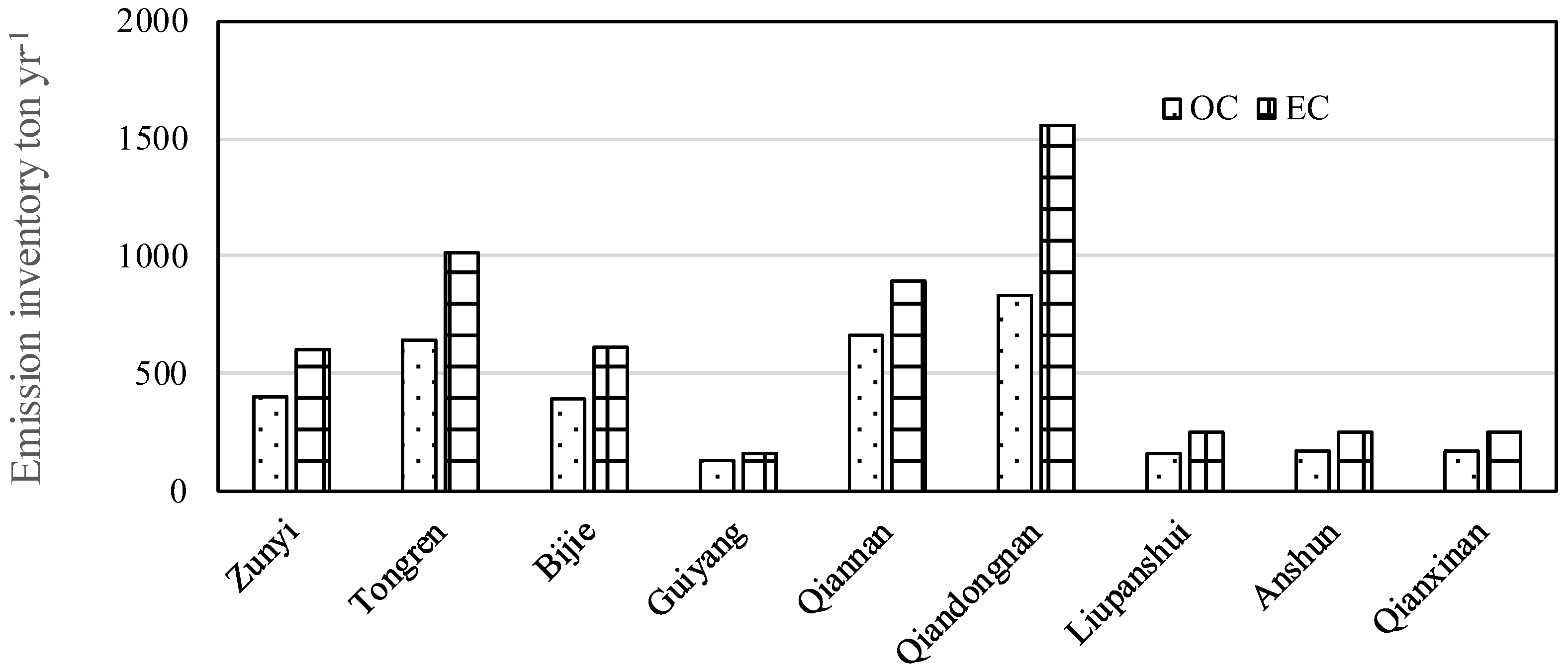
3.5. Emission Inventory of OC and EC from Residential Biomass Burning
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seiler, W.; Crutzen, P.J. Estimates of gross and net fluxes of carbon between the biosphere and the atmosphere from biomass burning. Clim. Change 1980, 2, 207–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Streets, D.G.; Yarber, K.F.; Nelson, S.M.; Woo, J.H.; Klimont, Z. A technology-based global inventory of black and organic carbon emissions from combustion. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D14203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Bond, T. Light absorption by organic carbon from wood combustion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 1773–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature 2001, 409, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streets, D.G.; Gupta, S.; Waldhoff, S.T.; Wang, M.Q.; Bond, T.C.; Yiyun, B. Black carbon emissions in China. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4281–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.-S.; Soden, B.J. Hemispheric climate shifts driven by anthropogenic aerosol—Cloud interactions. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Lohmann, U.; Raga, G.B.; O’Dowd, C.D.; Kulmala, M.; Fuzzi, S.; Reissell, A.; Andreae, M.O. Flood or drought: How do aerosols affect precipitation? Science 2008, 321, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACMR (All China Marketing Research Co. Ltd.). China County Population Census Data with County Maps (Version III); All China Marketing Research Co. Ltd. (2000): Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2004. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zhamg, W. Distribution and comprehensive utilization of straw resources of main crops in Guizhou. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2015, 43, 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wei, W.; Li, D.; Aunan, K.; Hao, J. Air pollutants in rural homes in Guizhou, China—Concentrations, speciation, and size distribution. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4575–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Zhang, H.; He, C. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A.; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, G.; Tao, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, S.; Xue, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, R.; Lu, Y.; Li, W. Emission characteristics for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from solid fuels burned in domestic stoves in rural China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 14485–14494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Xue, M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, W.; Shen, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of carbonaceous particulate matter emission factors among different solid fuels burned in residential stoves. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Tao, S.; Zhu, C.; Min, Y.; Xue, M.; Ding, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, R. Emission factors of particulate matter and elemental carbon for crop residues and coals burned in typical household stoves in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7157–7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xing, X.; Lang, J.; Chen, D.; Cheng, S.; Wei, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, C. A comprehensive biomass burning emission inventory with high spatial and temporal resolution in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2839–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kong, S.; Wu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, S.; Qin, S.; Liu, X.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, M. The moving of high emission for biomass burning in China: View from multi-year emission estimation and human-driven forces. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.; Hao, W. Air toxic emissions from burning of biomass globally-preliminary estimates. In Proceedings of the 85th Annual Meeting and Exhibition, Kansas City, MO, USA, 21–26 June 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, D.; Radke, L. Emissions measurements from vegetation fires: A comparative evaluation of methods and results. In Fire in the Environment: The Ecological, Atmospheric, and Climatic Importance of Vegetation Fires, Proceedings of the Dahlem Workshop Reports: Environmental Sciences Research Report 13; Crutzen, P.J., Goldammer, J.G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons.: Chischester, UK, 1993; pp. 53–76. [Google Scholar]
- Yokelson, R.J.; Griffith, D.W.; Ward, D.E. Open-path Fourier transform infrared studies of large-scale laboratory biomass fires. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 21067–21080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T36055-2018; MAFB Method for Analysis of Forestry Biomass—Determination of Moisture Content. National Committee on Forest Biomass Materials of Standard and Technology: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese)
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Countess, R.J. Sources and chemistry of PM10 aerosol in Santa Barbara County, CA. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhi, G.; Hitzenberger, R.; Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, J. Emission factors and light absorption properties of brown carbon from household coal combustion in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 4769–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhi, G.; Jin, W.; Chen, Y.; Shen, G.; Tian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zong, Z.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, X. Emission factors of organic carbon and elemental carbon for residential coal and biomass fuels in China—A new database for 39 fuel-stove combinations. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 190, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Duan, L.; Hao, J.; Nie, Y. Carbonaceous aerosol emissions from household biofuel combustion in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6076–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirbaş, A. Relationships between lignin contents and heating values of biomass. Energy Convers. Manag. 2001, 42, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKendry, P. Energy production from biomass (part 1): Overview of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiinikka, H.; Gebart, R. The influence of fuel type on particle emissions in combustion of biomass pellets. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2005, 177, 741–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; de Jong, W.; Jansens, P.; Spliethoff, H. Biomass combustion in fluidized bed boilers: Potential problems and remedies. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanatta, E.R.; Reinehr, T.O.; Awadallak, J.A.; Kleinübing, S.J.; dos Santos, J.B.O.; Bariccatti, R.A.; Arroyo, P.A.; da Silva, E.A. Kinetic studies of thermal decomposition of sugarcane bagasse and cassava bagasse. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 125, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y.; Shang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, J. Existence and formation pathways of high-and low-maturity elemental carbon from solid fuel combustion by a time-resolved study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2551–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Ni, H.; Cao, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Wei, C. Characteristics of carbonaceous particles from residential coal combustion and agricultural biomass burning in China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, S.; Verma, M.; Tiwari, S.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Watson, J.G.; Chow, J.C.; Panicker, A.S.; Deb, M.K.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Pervez, Y.F. Household solid fuel burning emission characterization and activity levels in India. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Xu, N.; Qin, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, L.; Huang, X.; He, L. Chemical composition and light absorption of carbonaceous aerosols emitted from crop residue burning: Influence of combustion efficiency. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 13721–13734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guofeng, S.; Siye, W.; Wen, W.; Yanyan, Z.; Yujia, M.; Bin, W.; Rong, W.; Wei, L.; Huizhong, S.; Ye, H.; et al. Emission factors, size distributions, and emission inventories of carbonaceous particulate matter from residential wood combustion in rural China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4207–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McDonald, J.D.; Zielinska, B.; Fujita, E.M.; Sagebiel, J.C.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. Fine particle and gaseous emission rates from residential wood combustion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2080–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Tao, S.; Wei, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yuan, C.; Wang, H. Field measurement of emission factors of PM, EC, OC, parent, nitro-, and oxy-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons for residential briquette, coal cake, and wood in rural Shanxi, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2998–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streets, D.G.; Bond, T.; Carmichael, G.; Fernandes, S.; Fu, Q.; He, D.; Klimont, Z.; Nelson, S.; Tsai, N.; Wang, M.Q. An inventory of gaseous and primary aerosol emissions in Asia in the year 2000. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108(D21), 8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ohara, T.; Akimoto, H. Bottom-up estimate of biomass burning in mainland China. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5262–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Merlet, P. Emission of trace gases and aerosols from biomass burning. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang-Arlt, X.; Fu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, L.; Zellmer, G.F.; Engling, G. Carbonaceous aerosol emitted from biofuel household stove combustion in South China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, H.A.; Cass, G.R.; Huntzicker, J.J.; Heyerdahl, E.K.; Rau, J.A. Characteristics of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon particle concentrations in Los Angeles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1986, 20, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, B.J.; Huntzicker, J.J.; Larson, S.M.; Cass, G.R. Los Angeles summer midday particulate carbon: Primary and secondary aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ren, H.; Amidon, T.E.; Lai, Y. The utilization of soybean straw. I. Fiber morphology and chemical characteristics. BioResources 2015, 10, 2266–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, S.; Gustavsson, L.; Johansson, M.; Persson, H.; Andersen, J.S.; Bjerrum, M.; Andersen, K.S.; Hvidberg, R.B. Measurements of Emissions of EC, OC and Other Pollutants from Residential Wood Combustion in the Nordic Countries; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kindbom, K.; Mawdsley, I. Emission Factors for SLCP Emissions from Residential Wood Combustion in the Nordic Countries; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.B. Technical Manual for Preparation of Urban Air Pollutant Emission Inventory. Available online: http://max.book118.com/html/2018/1116/8107025055001133.shtm (accessed on 16 November 2018). (In Chinese).
- Qin, Y.; Xie, S. Estimation of county-level black carbon emissions and its spatial distribution in China in 2000. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6995–7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tao, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Y. Black carbon emissions in China from 1949 to 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7595–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Song, Y. A high-resolution emission inventory of crop burning in fields in China based on MODIS Thermal Anomalies/Fire products. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Moisture Content (%) | Firewood | Pepper Straw | Rice Straw | Soybean Straw | Corn Straw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard fuel | 15.7 | 20.7 | 15.4 | 16.3 | 17.0 |
| Air-dried fuel | 8.9 | 4.7 | 7.9 | 7.0 | 10.2 |
| Oven-dried fuel | 3.7 | 4.9 | 6.4 | 5.7 | 5.3 |
| Biomass Type | OC Emission Factor (g kg−1) | EC Emission Factor (g kg−1) | OC/EC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average ± Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | n | Average ± Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | n | ||
| Standard samples * | |||||||||
| Firewood | 0.57 ± 0.16 | 0.38 | 0.92 | 24 | 1.1 ± 0.63 | 0.17 | 1.8 | 23 | 0.54 |
| Pepper straw | 5.1± 3.0 | 1.9 | 8.8 | 24 | 1.8 ± 0.77 | 0.81 | 2.9 | 24 | 2.8 |
| Soybean straw | 2.0± 2.4 | 0.43 | 7.4 | 24 | 0.17 ± 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.68 | 24 | 11.7 |
| Rice straw | 6.8± 5.4 | 1.0 | 16.0 | 24 | 0.48 ± 0.40 | 0.13 | 1.2 | 24 | 14.2 |
| Corn straw | 3.4 ± 2.7 | 0.75 | 7.7 | 24 | 0.68 ± 0.29 | 0.40 | 1.4 | 24 | 5.1 |
| Air-dried samples | |||||||||
| Firewood | 0.79 ± 0.12 | 0.59 | 0.94 | 12 | 1.8 ± 0.54 | 1.1 | 2.4 | 8 | 0.44 |
| Pepper straw | 4.5 ± 2.0 | 1.8 | 7.7 | 24 | 1.3 ± 0.57 | 0.63 | 2.6 | 24 | 3.6 |
| Soybean straw | 1.6 ± 0.55 | 0.81 | 2.5 | 23 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 23 | 8.9 |
| Rice straw | 7.0 ± 5.2 | 1.5 | 13.2 | 24 | 0.46 ± 0.38 | 0.14 | 1.1 | 24 | 15.0 |
| Corn straw | 3.6 ± 2.2 | 1.1 | 6.7 | 24 | 0.42 ± 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.67 | 24 | 8.5 |
| Oven-dried samples | |||||||||
| Firewood | 0.59 ± 0.13 | 0.44 | 1.0 | 28 | 1.2 ± 0.52 | 0.63 | 2.4 | 28 | 0.47 |
| Pepper straw | 2.6 ± 1.1 | 1.5 | 4.4 | 24 | 1.2 ± 0.34 | 0.61 | 1.7 | 24 | 2.2 |
| Soybean straw | 3.5 ± 2.0 | 1.3 | 7.7 | 24 | 0.47 ± 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.88 | 24 | 7.5 |
| Rice straw | 13.9 ± 12.1 | 1.2 | 28.1 | 24 | 0.89 ± 0.73 | 0.11 | 2.2 | 24 | 15.7 |
| Corn straw | 4.0 ± 2.7 | 1.1 | 7.9 | 24 | 0.64 ± 0.21 | 0.41 | 1.1 | 24 | 6.2 |
| Emission Inventory | Guiyang | Anshun | Qiandongnan | Qiannan | Tongren | Qianxinan | Bijie | Liupanshui | Zunyi | Guizhou Province |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC in ton year−1 | ||||||||||
| Firewood | 77.3 ± 21.4 | 126.2 ± 34.8 | 825.5 ± 228.0 | 449.7 ± 124.2 | 525.9 ± 145.3 | 128.3 ± 35.4 | 314.5 ± 86.9 | 129.4 ± 35.8 | 308.8 ± 85.3 | 2885.5± 797.0 |
| Pepper straw | 29.8 ± 17.7 | 13.2 ± 7.8 | 2.6 ± 1.6 | 72.2 ± 43.0 | 33.8 ± 20.1 | 14.8 ± 8.8 | 33.5 ± 19.9 | 15.4 ± 9.2 | 37.9 ± 22.6 | 253.4 ± 150.8 |
| Rice straw | 15.4 ± 12.3 | 20.0 ± 16.0 | 7.1 ± 5.7 | 106.9 ± 85.6 | 71.5 ± 57.2 | 12.4 ± 10.0 | 9.1 ± 7.3 | 6.6 ± 5.3 | 35.4 ± 28.3 | 284.4 ± 227.8 |
| Soybean straw | 0.090 ± 0.11 | 0.15 ± 0.18 | 0.027 ± 0.033 | 0.49 ± 0.60 | 0.43 ± 0.51 | 0.06 ± 0.07 | 1.66 ± 2.01 | 0.39 ± 0.47 | 0.62 ± 0.74 | 3.91 ± 4.72 |
| Corn straw | 5.9 ± 4.7 | 3.7 ± 2.9 | 0.18 ± 0.14 | 15.7 ± 12.5 | 5.2 ± 4.2 | 4.7 ± 3.7 | 25.7 ± 20.5 | 8.4 ± 6.7 | 7.4 ± 5.9 | 76.7 ± 61.1 |
| Wheat straw a | 0.28 | 0.34 | 0.014 | 2.9 | 1.1 | 2.9 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 0.91 | 12.4 |
| Sorghum straw a | 0.000 | 0.092 | 0.0080 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 3.2 | 3.8 |
| Rape straw a | 2.83 | 3.9 | 0.40 | 11.6 | 8.3 | 2.0 | 6.4 | 1.3 | 6.4 | 43.2 |
| Sum | 131.5 | 167.6 | 835.9 | 659.6 | 646.6 | 165.1 | 393.0 | 163.4 | 400.6 | 3563.4 |
| EC in ton year−1 | ||||||||||
| Firewood | 146.1 ± 84.8 | 238.4 ± 138.4 | 1559.9 ± 905.4 | 849.7 ± 493.2 | 993.7 ± 576.7 | 242.4 ± 140.7 | 594.2 ± 344.9 | 244.6 ± 142.0 | 583.5 ± 338.6 | 5452.5 ± 3164.7 |
| Pepper straw | 10.6 ± 4.5 | 4.7 ± 2.0 | 0.94 ± 0.40 | 25.8 ± 10.9 | 12.1 ± 5.1 | 5.3 ± 2.2 | 12.0 ± 5.1 | 5.5 ± 2.3 | 13.5 ± 5.7 | 90.4 ± 38.3 |
| Rice straw | 1.1 ± 0.91 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 0.50 ± 0.42 | 7.5 ± 6.3 | 5.0 ± 4.2 | 0.88 ± 0.74 | 0.64 ± 0.54 | 0.47 ± 0.39 | 2.5 ± 2.1 | 20.1 ± 16.9 |
| Soybean straw | 0.0077 ± 0.0096 | 0.013 ± 0.016 | 0.0023 ± 0.0029 | 0.042 ± 0.052 | 0.036 ± 0.045 | 0.0047 ± 0.006 | 0.142 ± 0.176 | 0.033 ± 0.041 | 0.053 ± 0.065 | 0.334 ± 0.414 |
| Corn straw | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 0.73 ± 0.31 | 0.035 ± 0.0149 | 3.1 ± 1.3 | 1.0 ± 0.44 | 0.92 ± 0.40 | 5.1 ± 2.2 | 1.7 ± 0.71 | 1.5 ± 0.63 | 15.2 ± 6.5 |
| Wheat straw a | 0.095 | 0.11 | 0.0048 | 1.0 | 0.38 | 0.96 | 0.72 | 0.62 | 0.31 | 4.174 |
| Sorghum straw a | 0.000 | 0.031 | 0.0027 | 0.065 | 0.094 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.1 | 1.3 |
| Rape straw a | 0.94 | 1.31 | 0.1345 | 3.9 | 2.8 | 0.66 | 2.1 | 0.45 | 2.2 | 14.4 |
| Sum | 160.0 | 246.7 | 1561.6 | 891.1 | 1015.1 | 251.1 | 614.9 | 253.3 | 604.5 | 5598.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-N.; Cheng, Y.; Gu, Z.-L.; Yang, J.-T.; Ren, H.-H. Emission Factors and Inventories of Carbonaceous Aerosols from Residential Biomass Burning in Guizhou Province, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101595
Wang Y-N, Cheng Y, Gu Z-L, Yang J-T, Ren H-H. Emission Factors and Inventories of Carbonaceous Aerosols from Residential Biomass Burning in Guizhou Province, China. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(10):1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101595
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yan-Ni, Yan Cheng, Zhao-Lin Gu, Jing-Ting Yang, and Huan-Huan Ren. 2022. "Emission Factors and Inventories of Carbonaceous Aerosols from Residential Biomass Burning in Guizhou Province, China" Atmosphere 13, no. 10: 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101595
APA StyleWang, Y.-N., Cheng, Y., Gu, Z.-L., Yang, J.-T., & Ren, H.-H. (2022). Emission Factors and Inventories of Carbonaceous Aerosols from Residential Biomass Burning in Guizhou Province, China. Atmosphere, 13(10), 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101595








