Cloud Nowcasting with Structure-Preserving Convolutional Gated Recurrent Units
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Data Source
3. Methodology
3.1. Eulerian and Lagrangian Persistence
3.2. Computing Displacement with Optical Flow
3.2.1. Farneback
3.2.2. DeepFlow
3.2.3. Dense Inverse Search (DIS)
3.2.4. Ensemble Model
3.3. Convolutional Gated Recurrent Unit Network
3.4. Sequential Loss Functions
3.5. Model Training and Evaluation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Optical Flow vs. ConvGRU Nowcasts
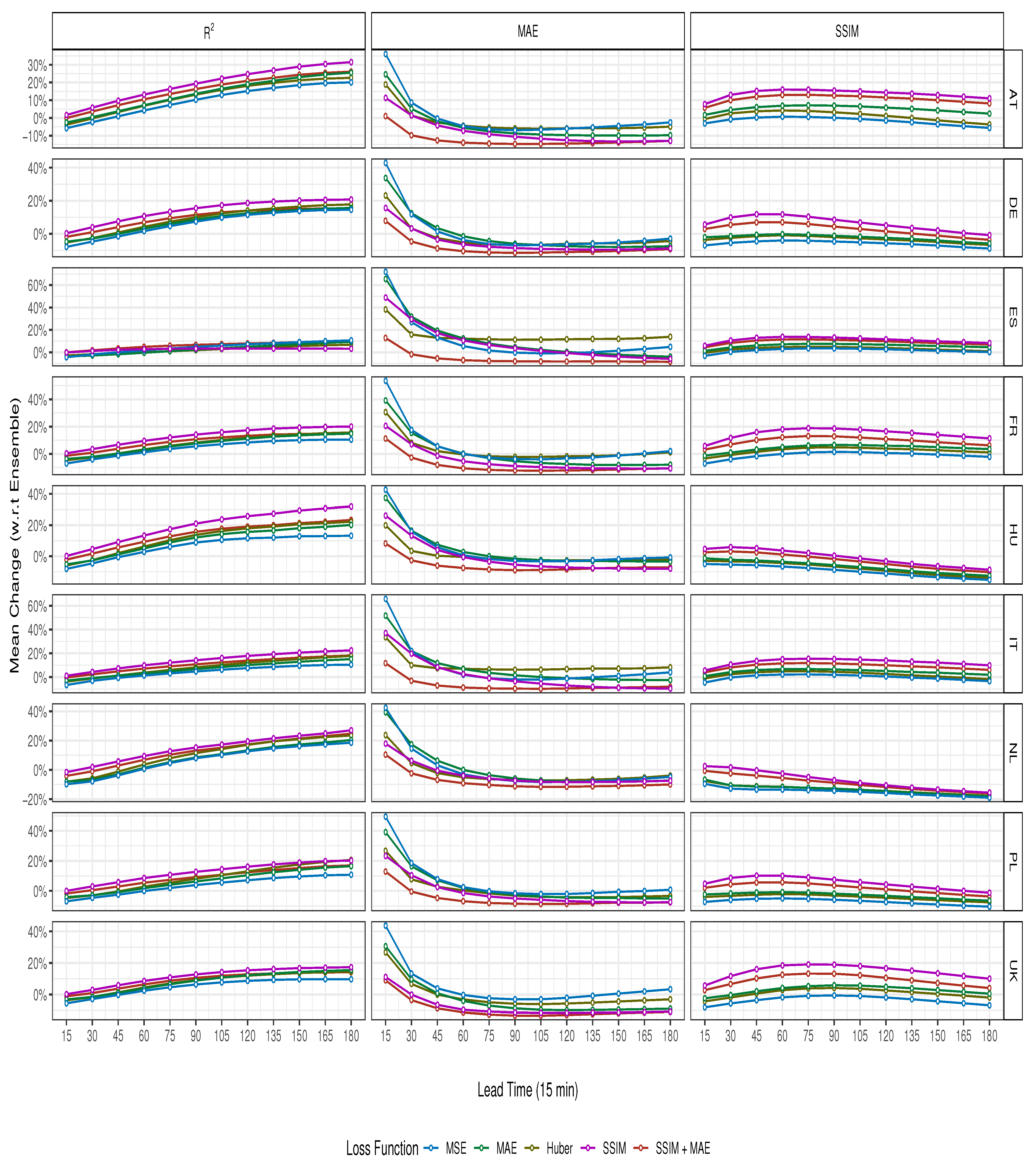
4.2. Regional Effects on ConvGRU Performance
Key Findings
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Example Training Data

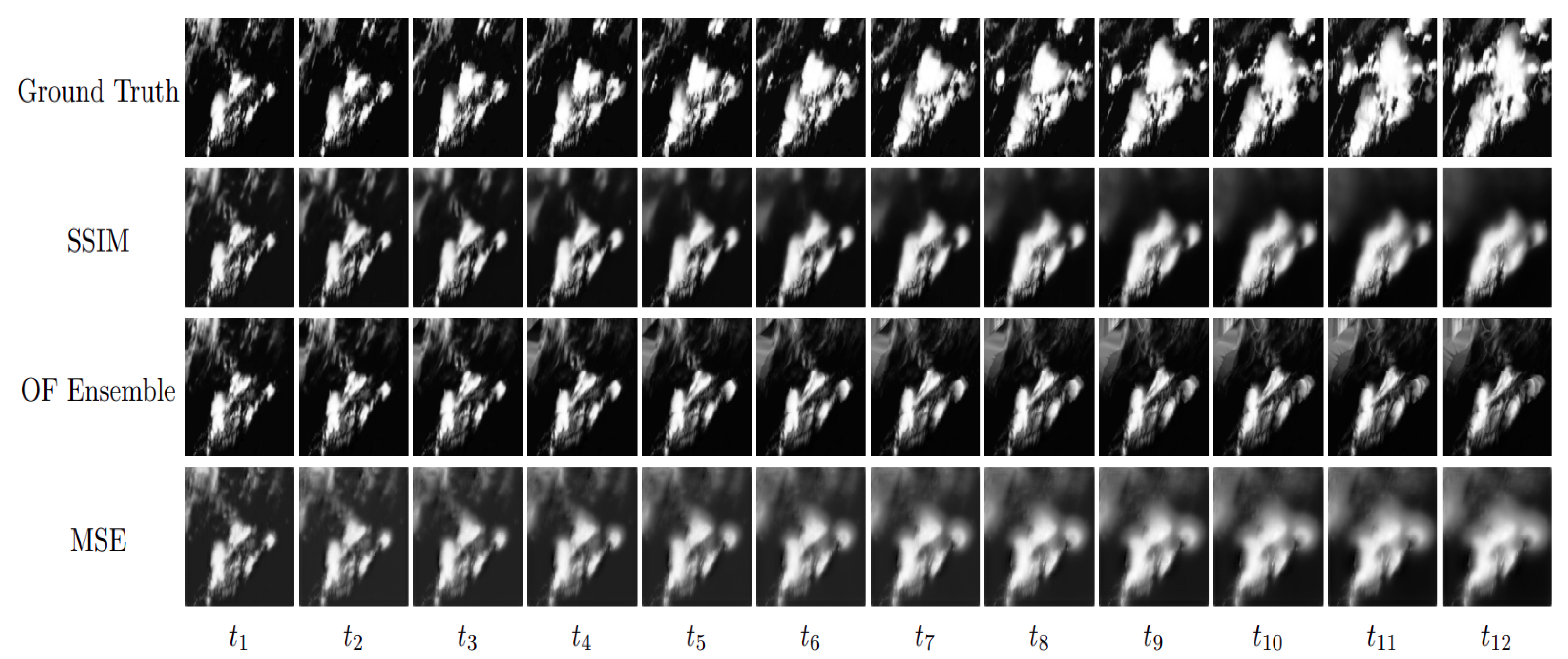
Appendix B. Example Nowcasts






References
- Schneider, T.; Teixeira, J.; Bretherton, C.S.; Brient, F.; Pressel, K.G.; Schär, C.; Siebesma, A.P. Climate goals and computing the future of clouds. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quante, M. The role of clouds in the climate system. EDP Sci. 2004, 121, 61–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.C.; Jacobs, J.; Nikitina, R.; Wang, W. Guidelines for Nowcasting Techniques; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Purdom, J.F.W. Some Uses of High-Resolution GOES Imagery in the Mesoscale Forecasting of Convection and Its Behavior. Mon. Weather Rev. 1976, 104, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewert, C.W.; Koenig, M.; Mecikalski, J.R. Application of Meteosat second generation data towards improving the nowcasting of convective initiation. Meteorol. Appl. 2010, 17, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benas, N.; Finkensieper, S.; Stengel, M.; van Zadelhoff, G.J.; Hanschmann, T.; Hollmann, R.; Meirink, J.F. The MSG-SEVIRI-based cloud property data record CLAAS-2. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Xi, D.G.; Li, Z.L.; Hong, Y. A new methodology for pixel-quantitative precipitation nowcasting using a pyramid Lucas Kanade optical flow approach. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, D.; Romano, F.; Cersosimo, A.; Cimini, D.; Di Paola, F.; Gentile, S.; Geraldi, E.; Larosa, S.; Nilo, S.T.; Ricciardelli, E.; et al. Nowcasting Surface Solar Irradiance with AMESIS via Motion Vector Fields of MSG-SEVIRI Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, W.c.; Wong, W.k. Operational Application of Optical Flow Techniques to Radar-Based Rainfall Nowcasting. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowler, N.E.; Pierce, C.E.; Seed, A.W. STEPS: A probabilistic precipitation forecasting scheme which merges an extrapolation nowcast with downscaled NWP. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 132, 2127–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirch, T.; Bugliaro Goggia, L.; Zinner, T.; Möhrlein, M.; Vazquez-Navarro, M. Cloud and DNI nowcasting with MSG/SEVIRI for the optimized operation of concentrating solar power plants. Atmos. Meas. Tech. (AMT) 2017, 10, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, B.; Kuhn, P.; Wilbert, S.; Prahl, C.; Pitz-Paal, R.; Blanc, P.; Schmidt, T.; Yasser, Z.; Santigosa, L.R.; Heineman, D. Nowcasting of DNI maps for the solar field based on voxel carving and individual 3D cloud objects from all sky images. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2033, 190011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulescu, M.; Paulescu, E.; Badescu, V. Chapter 9—Nowcasting solar irradiance for effective solar power plants operation and smart grid management. In Predictive Modelling for Energy Management and Power Systems Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yang, Z.; Goh, H.; Huang, Q.; Li, G. A novel sky image-based solar irradiance nowcasting model with convolutional block attention mechanism. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.Y.; Wong, W.k.; Woo, W.c. Convolutional LSTM Network: A Machine Learning Approach for Precipitation Nowcasting. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.04214. [Google Scholar]
- Ayzel, G.; Scheffer, T.; Heistermann, M. RainNet v1.0: A convolutional neural network for radar-based precipitation nowcasting. In Geoscientific Model Development Discussions; 2020; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, A.; Li, H.; Cui, L.; Chen, Y. A Convection Nowcasting Method Based on Machine Learning. Advances in Meteorology 2020, 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sønderby, C.K.; Espeholt, L.; Heek, J.; Dehghani, M.; Oliver, A.; Salimans, T.; Agrawal, S.; Hickey, J.; Kalchbrenner, N. MetNet: A Neural Weather Model for Precipitation Forecasting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12140. [Google Scholar]
- Espeholt, L.; Agrawal, S.; Sønderby, C.; Kumar, M.; Heek, J.; Bromberg, C.; Gazen, C.; Hickey, J.; Bell, A.; Kalchbrenner, N. Skillful Twelve Hour Precipitation Forecasts using Large Context Neural Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.07470. [Google Scholar]
- Berthomier, L.; Pradel, B.; Perez, L. Cloud Cover Nowcasting with Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 Tenth International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA), Paris, France, 9–12 November 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knol, D.; de Leeuw, F.; Meirink, J.F.; Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V. Deep Learning for Solar Irradiance Nowcasting: A Comparison of a Recurrent Neural Network and Two Traditional Methods. In Proceedings of the Computational Science—ICCS 2021, Krakow, Poland, 16–18 June 2021; Paszynski, M., Kranzlmüller, D., Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V., Dongarra, J.J., Sloot, P.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 309–322. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, V.S.; Czibula, G.; Mihuleţ, E. DeePS at: A deep learning model for prediction of satellite images for nowcasting purposes. In Knowledge-Based and Intelligent Information & Engineering Systems: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference KES2021, Szczecin, Poland, 8–10 September 2021; Volume 192, pp. 622–631. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mehrkanoon, S. AA-TransUNet: Attention Augmented TransUNet For Nowcasting Tasks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.04996. [Google Scholar]
- Greuell, W.; Meirink, J.F.; Wang, P. Retrieval and validation of global, direct, and diffuse irradiance derived from SEVIRI satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2340–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, U.; Zawadzki, I. Scale-Dependence of the Predictability of Precipitation from Continental Radar Images. Part I: Description of the Methodology. Mon. Weather Rev. 2002, 130, 2859–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, B.D.; Kanade, T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 August 1981; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: Burlington, MA, USA, 1981; Volume 2, pp. 674–679. [Google Scholar]
- Ayzel, G.; Heistermann, M.; Winterrath, T. Optical flow models as an open benchmark for radar-based precipitation nowcasting (rainymotion v0.1). Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 1387–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnebäck, G. Two-Frame Motion Estimation Based on Polynomial Expansion. In Image Analysis. SCIA 2003. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Bigun, J., Gustavsson, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 2749, pp. 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinzaepfel, P.; Revaud, J.; Harchaoui, Z.; Schmid, C. DeepFlow: Large Displacement Optical Flow with Deep Matching. In Proceedings of the ICCV—IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kroeger, T.; Timofte, R.; Dai, D.; Van Gool, L. Fast Optical Flow using Dense Inverse Search. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.03590 [cs]. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Gao, Z.; Lausen, L.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.Y.; Wong, W.k.; Woo, W.c. Deep Learning for Precipitation Nowcasting: A Benchmark and A New Model. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03458 [cs]. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555 [cs]. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, J.G.; Mehrkanoon, S. Broad-UNet: Multi-scale feature learning for nowcasting tasks. Neural Netw. 2021, 144, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C. Mean squared error: Love it or leave it? A new look at Signal Fidelity Measures. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2009, 26, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.; Sheikh, H.; Simoncelli, E. Image Quality Assessment: From Error Visibility to Structural Similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phuong, T.T.; Phong, L.T. On the Convergence Proof of AMSGrad and a New Version. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 61706–61716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovik, A. Handbook of Image and Video Processing, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, Q.K.; Song, S.K. Computer Vision in Precipitation Nowcasting: Applying Image Quality Assessment Metrics for Training Deep Neural Networks. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Islam, T.; Sekimoto, Y.; Mattmann, C.; Wilson, B. Convcast: An embedded convolutional LSTM based architecture for precipitation nowcasting using satellite data. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | DeepFlow | 14.36 | −12.79 | 6.93 |
| DIS | 11.86 | −10.69 | 2.90 | |
| Farneback | 14.12 | −12.50 | 7.68 | |
| Ensemble | 18.28 | −16.89 | 11.2 | |
| 8 | DeepFlow | 11.24 | −6.83 | −0.2 |
| DIS | 9.20 | −5.89 | −2.7 | |
| Farneback | 10.66 | −6.43 | 0.85 | |
| Ensemble | 19.28 | −12.21 | 6.56 | |
| 12 | DeepFlow | 8.56 | −4.95 | −1.9 |
| DIS | 6.86 | −4.32 | −3.7 | |
| Farneback | 8.01 | −4.54 | −0.5 | |
| Ensemble | 19.73 | −10.67 | 5.89 |
| Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | MSE | 4.27 | −1.78 | 1.42 |
| MAE | 5.95 | 0.12 | 3.69 | |
| Huber | 6.33 | −2.46 | 3.12 | |
| SSIM | 8.11 | −0.06 | 8.63 | |
| SSIM + MAE | 7.63 | −9.27 | 7.28 | |
| 8 | MSE | 13.43 | −7.42 | 8.86 |
| MAE | 15.17 | −6.50 | 10.53 | |
| Huber | 16.05 | −2.17 | 9.92 | |
| SSIM | 15.95 | −7.65 | 13.61 | |
| SSIM + MAE | 16.43 | −11.95 | 13.03 | |
| 12 | MSE | 19.23 | −6.38 | 11.59 |
| MAE | 20.96 | −7.23 | 12.85 | |
| Huber | 22.29 | −0.72 | 12.31 | |
| SSIM | 21.10 | −9.48 | 15.53 | |
| SSIM + MAE | 22.21 | −11.18 | 15.07 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kellerhals, S.A.; De Leeuw, F.; Rodriguez Rivero, C. Cloud Nowcasting with Structure-Preserving Convolutional Gated Recurrent Units. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101632
Kellerhals SA, De Leeuw F, Rodriguez Rivero C. Cloud Nowcasting with Structure-Preserving Convolutional Gated Recurrent Units. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(10):1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101632
Chicago/Turabian StyleKellerhals, Samuel A., Fons De Leeuw, and Cristian Rodriguez Rivero. 2022. "Cloud Nowcasting with Structure-Preserving Convolutional Gated Recurrent Units" Atmosphere 13, no. 10: 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101632
APA StyleKellerhals, S. A., De Leeuw, F., & Rodriguez Rivero, C. (2022). Cloud Nowcasting with Structure-Preserving Convolutional Gated Recurrent Units. Atmosphere, 13(10), 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101632








