Ionospheric TEC Prediction in China Based on the Multiple-Attention LSTM Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1).
- The LSTM model with multiple attention modules is applied to TEC prediction to make TEC modelling more adaptive and obtain higher prediction accuracy.
- (2).
- An L1 constraint is added to TEC prediction, which can avoid overfitting caused by excessive attention to a historical observation value in TEC modeling.
2. Data and Proposed Model
2.1. Data Description
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.2.1. The TEC Data Stationary Test and Difference Processing
2.2.2. The Pure Randomness Stationarity Test
2.2.3. Normalization of TEC Data
2.2.4. Sample Making
2.3. Experimental Environment
2.4. Evaluation Indexes
2.5. Our Proposed Model
2.5.1. The Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Network
2.5.2. LSTM Based on Multiple-Attention Modules (MA-LSTM) Proposed in This Paper
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Parameter Selection
3.2. Prediction Comparison of Different Stations
3.3. Prediction Comparison of Different Months
3.4. Prediction Comparison of Different Geomagnetic Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaselimi, M.; Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Delikaraoglou, D. A causal long short-term memory sequence to sequence model for TEC prediction using GNSS observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Ding, M. An Approach for Predicting Global Ionospheric TEC Using Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, P.; Zhai, D.; Long, C.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, X. Long short-term memory neural network for ionospheric total electron content forecasting over China. Space Weather 2021, 19, e2020SW002706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Mohanty, S.; Kannaujiya, S. Ionospheric TEC modelling for earthquakes precursors from GNSS data. Quat. Int. 2017, 462, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belehaki, A.; Stanislawska, I.; Lilensten, J. An overview of ionosphere—Thermosphere models available for space weather purposes. Space Sci. Rev. 2009, 147, 271–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samardjiev, T.; Bradley, P.A.; Cander, L.R.; Dick, M.I. Ionospheric mapping computer contouring techniques. Electron. Lett. 1993, 29, 1794–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, S.; Huo, X.; Wu, X. Ionospheric Assimilation of GNSS TEC into IRI Model Using a Local Ensemble Kalman Filter. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Tang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Song, Y.; He, F.; Zhou, C.; Qing, H.; et al. Ionospheric TEC data assimilation based on Gauss–Markov Kalman filter. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 4189–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.A.; Wan, W.X.; Liu, L.B.; Le, H.J.; Chen, Y.D.; Yu, T. Development of a middle and low latitude theoretical ionospheric model and an observation system data assimilation experiment. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M. A MLP neural network as an investigator of TEC time series to detect seismo-ionospheric anomalies. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, K.; Haridas, S.; Choudhary, R.K.; Dinil Bose, P. Neural Network Model for the prediction of TEC variabilities over Indian equatorial sector. Indian J. Sci. Res. 2018, 18, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Watthanasangmechai, K.; Supnithi, P.; Lerkvaranyu, S.; Tsugawa, T.; Nagatsuma, T.; Maruyama, T. TEC prediction with neural network for equatorial latitude station in Thailand. Earth Planets Space 2012, 64, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inyurt, S.; Sekertekin, A. Modeling and predicting seasonal ionospheric variations in Turkey using artificial neural network (ANN). Astrophys. Space Sci. 2019, 364, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yuan, H. Ionospheric single-station TEC short-term forecast using RBF neural network. Radio Sci. 2014, 49, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habarulema, J.B.; McKinnell, L.A.; Cilliers, P.J. Prediction of global positioning system total electron content using neural networks over South Africa. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2007, 69, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwali, A.; Kumar, A.J.S.; Prakash, K.B.; Sivavaraprasad, G.; Ratnam, D.V. Implementation of hybrid deep learning model (LSTM-CNN) for ionospheric TEC forecasting using GPS data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Gong, J. Prediction model for ionospheric total electron content based on deep learning recurrent neural networkormalsize. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2018, 38, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Zeng, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.-S.; Huang, C.-M.; Wu, Z. The comparison of predicting storm-time ionospheric TEC by three methods: ARIMA, LSTM, and Seq2Seq. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chimsuwan, P.; Supnithi, P.; Phakphisut, W.; Myint, L.M.M. Construction of LSTM model for total electron content (TEC) prediction in Thailand. In Proceedings of the 2021 18th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (ECTI-CON), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 19–22 May 2021; pp. 276–279. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Shen, Y. A novel deep learning prediction model for concrete dam displacements using interpretable mixed attention mechanism. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 50, 101407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, A.; Lu, X. Vision-to-language tasks based on attributes and attention mechanism. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 51, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Anomaly detection in quasi-periodic time series based on automatic data segmentation and attentional LSTM-CNN. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 34, 2626–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zou, S.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z. Forecasting global ionospheric TEC using deep learning approach. Space Weather 2020, 18, e2020SW002501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iluore, K.; Lu, J. Long short-term memory and gated recurrent neural networks to predict the ionospheric vertical total electron content. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 70, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Liu, H.; Le, H.; Huang, J.; Yuan, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Ionospheric TEC Prediction Base on Attentional BiGRU. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Liu, A.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, L.; Hernández-Pajares, M.; Krankowski, A.; Yuan, H. Status of CAS global ionospheric maps after the maximum of solar cycle 24. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Hernández-Pajares, M.; Yuan, Y.; Krankowski, A.; Liu, A.; Zha, J.; García-Rigo, A.; Roma-Dollase, D.; Yang, H.; et al. IGS real-time service for global ionospheric total electron content modeling. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A. Supervised sequence labelling. In Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Galassi, A.; Lippi, M.; Torroni, P. Attention in natural language processing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 4291–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
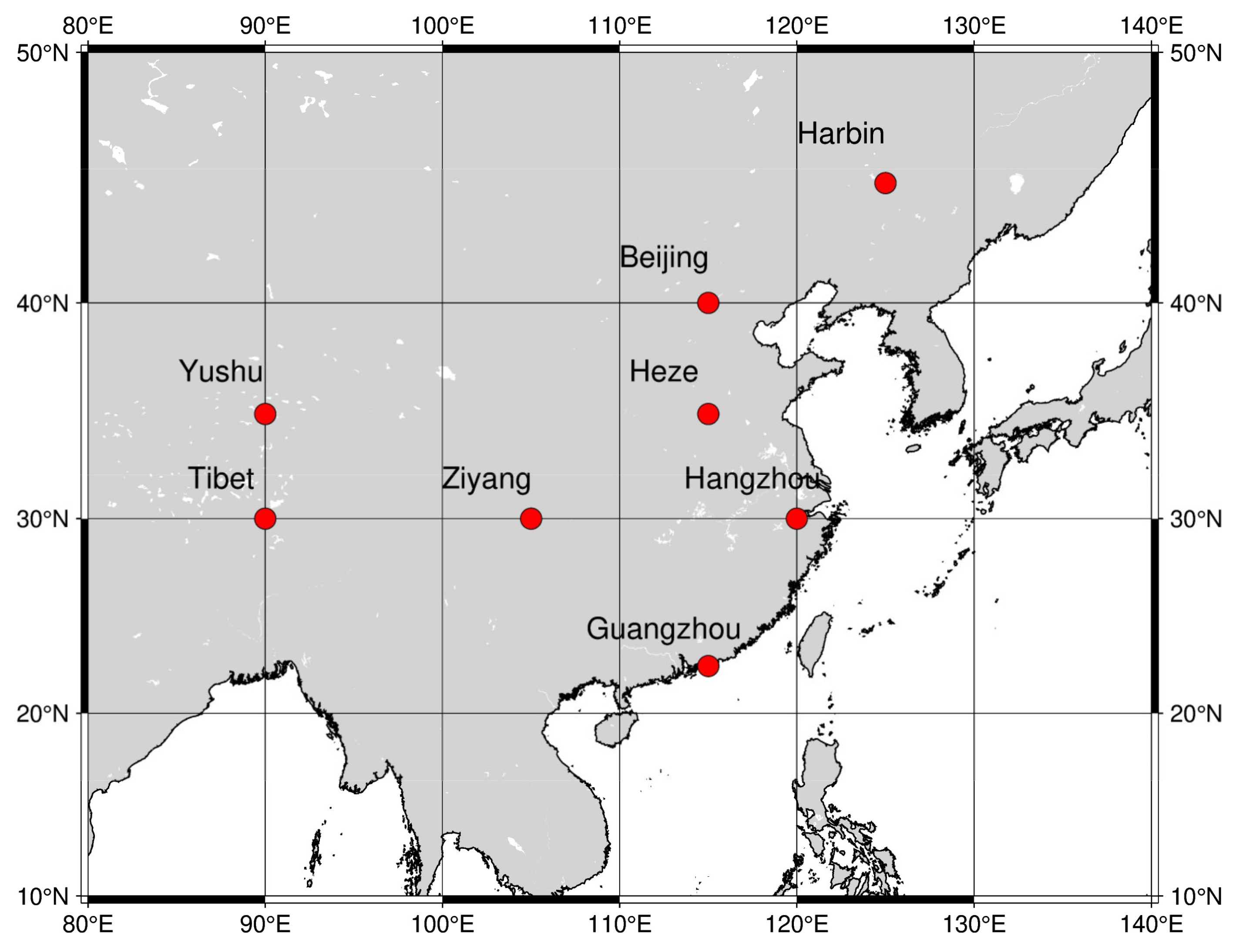










| Region | Lat | Lon |
|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 40° N | 115° E |
| Guangzhou | 22.5° N | 115° E |
| Harbin | 45° N | 125° E |
| Tibet | 30° N | 90° E |
| Yushu | 35° N | 95° E |
| Ziyang | 30° N | 105° E |
| Hangzhou | 30° N | 120° E |
| Heze | 35° N | 115° E |
| Parameter Name | Optimal Value |
|---|---|
| input_dim | 13 |
| optimizer | Adagrad |
| loss | “RMSE” and ”R-Square” |
| activation | “Relu”and “Softmax” |
| activity_regularizer | L1(0.01) |
| learning rate | 0.01 |
| batch_size | 64 |
| num of hidden units | 64 |
| Algorithm | Indicator | Mean | Beijing | Guangzhou | Harbin | Tibet | Yushu | Ziyang | Hangzhou | Heze |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | RMSE (TECU) | 4.137 | 2.962 | 4.683 | 6.834 | 2.745 | 3.880 | 4.561 | 4.225 | 3.208 |
| GRU | 3.846 | 3.221 | 4.613 | 6.676 | 2.683 | 3.031 | 4.392 | 3.487 | 2.664 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 1.581 | 0.801 | 1.867 | 4.244 | 0.650 | 0.957 | 1.354 | 1.445 | 1.331 | |
| MA-LSTM | 1.171 | 0.718 | 1.550 | 3.377 | 0.602 | 0.934 | 1.283 | 0.543 | 0.358 | |
| LSTM | R-square | 0.857 | 0.860 | 0.856 | 0.874 | 0.877 | 0.831 | 0.850 | 0.850 | 0.855 |
| GRU | 0.874 | 0.839 | 0.860 | 0.880 | 0.880 | 0.890 | 0.859 | 0.893 | 0.895 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.979 | 0.988 | 0.974 | 0.953 | 0.992 | 0.987 | 0.985 | 0.980 | 0.972 | |
| MA-LSTM | 0.988 | 0.991 | 0.982 | 0.970 | 0.993 | 0.988 | 0.986 | 0.997 | 0.998 | |
| LSTM | MAPE | 0.188 | 0.153 | 0.217 | 0.268 | 0.149 | 0.183 | 0.205 | 0.184 | 0.150 |
| GRU | 0.179 | 0.166 | 0.214 | 0.267 | 0.153 | 0.143 | 0.200 | 0.154 | 0.135 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.100 | 0.139 | 0.191 | 0.166 | 0.047 | 0.051 | 0.065 | 0.069 | 0.072 | |
| MA-LSTM | 0.054 | 0.037 | 0.075 | 0.136 | 0.034 | 0.047 | 0.061 | 0.024 | 0.018 |
| Algorithm | Indicator | January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | RMSE (TECU) | 4.150 | 4.357 | 3.915 | 3.964 | 3.848 | 4.072 | 4.132 | 4.168 | 4.222 | 3.950 | 4.321 | 4.479 |
| GRU | 3.848 | 4.006 | 3.675 | 3.703 | 3.589 | 3.818 | 3.866 | 3.917 | 3.907 | 3.664 | 3.998 | 4.118 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 1.533 | 1.666 | 1.552 | 1.522 | 1.431 | 1.625 | 1.534 | 1.568 | 1.613 | 1.581 | 1.645 | 1.664 | |
| MA-LSTM | 1.202 | 1.115 | 1.184 | 1.122 | 1.086 | 1.206 | 1.145 | 1.195 | 1.202 | 1.150 | 1.154 | 1.267 | |
| LSTM | R-square | 0.854 | 0.678 | 0.618 | 0.542 | 0.623 | 0.753 | 0.871 | 0.922 | 0.871 | 0.704 | 0.657 | 0.798 |
| GRU | 0.874 | 0.730 | 0.665 | 0.603 | 0.678 | 0.786 | 0.889 | 0.931 | 0.890 | 0.749 | 0.708 | 0.829 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.983 | 0.959 | 0.944 | 0.937 | 0.954 | 0.965 | 0.984 | 0.989 | 0.983 | 0.959 | 0.957 | 0.977 | |
| MA-LSTM | 0.989 | 0.981 | 0.967 | 0.965 | 0.973 | 0.981 | 0.991 | 0.993 | 0.991 | 0.978 | 0.979 | 0.986 | |
| LSTM | MAPE | 0.168 | 0.187 | 0.161 | 0.185 | 0.189 | 0.184 | 0.148 | 0.161 | 0.185 | 0.244 | 0.263 | 0.189 |
| GRU | 0.158 | 0.176 | 0.156 | 0.178 | 0.177 | 0.177 | 0.141 | 0.152 | 0.171 | 0.231 | 0.248 | 0.177 | |
| Att-BiGRU | 0.064 | 0.072 | 0.069 | 0.079 | 0.076 | 0.075 | 0.061 | 0.065 | 0.072 | 0.101 | 0.108 | 0.074 | |
| MA-LSTM | 0.045 | 0.049 | 0.052 | 0.056 | 0.053 | 0.053 | 0.042 | 0.048 | 0.054 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 0.053 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Lei, D.; Yuan, J.; Yuan, G.; Cui, C.; Wang, Y.; Xue, W. Ionospheric TEC Prediction in China Based on the Multiple-Attention LSTM Model. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111939
Liu H, Lei D, Yuan J, Yuan G, Cui C, Wang Y, Xue W. Ionospheric TEC Prediction in China Based on the Multiple-Attention LSTM Model. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(11):1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111939
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Haijun, Dongxing Lei, Jing Yuan, Guoming Yuan, Chunjie Cui, Yali Wang, and Wei Xue. 2022. "Ionospheric TEC Prediction in China Based on the Multiple-Attention LSTM Model" Atmosphere 13, no. 11: 1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111939
APA StyleLiu, H., Lei, D., Yuan, J., Yuan, G., Cui, C., Wang, Y., & Xue, W. (2022). Ionospheric TEC Prediction in China Based on the Multiple-Attention LSTM Model. Atmosphere, 13(11), 1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111939





