Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Drought and Its Driving Factors in Yangtze River Basin Based on SPEI
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
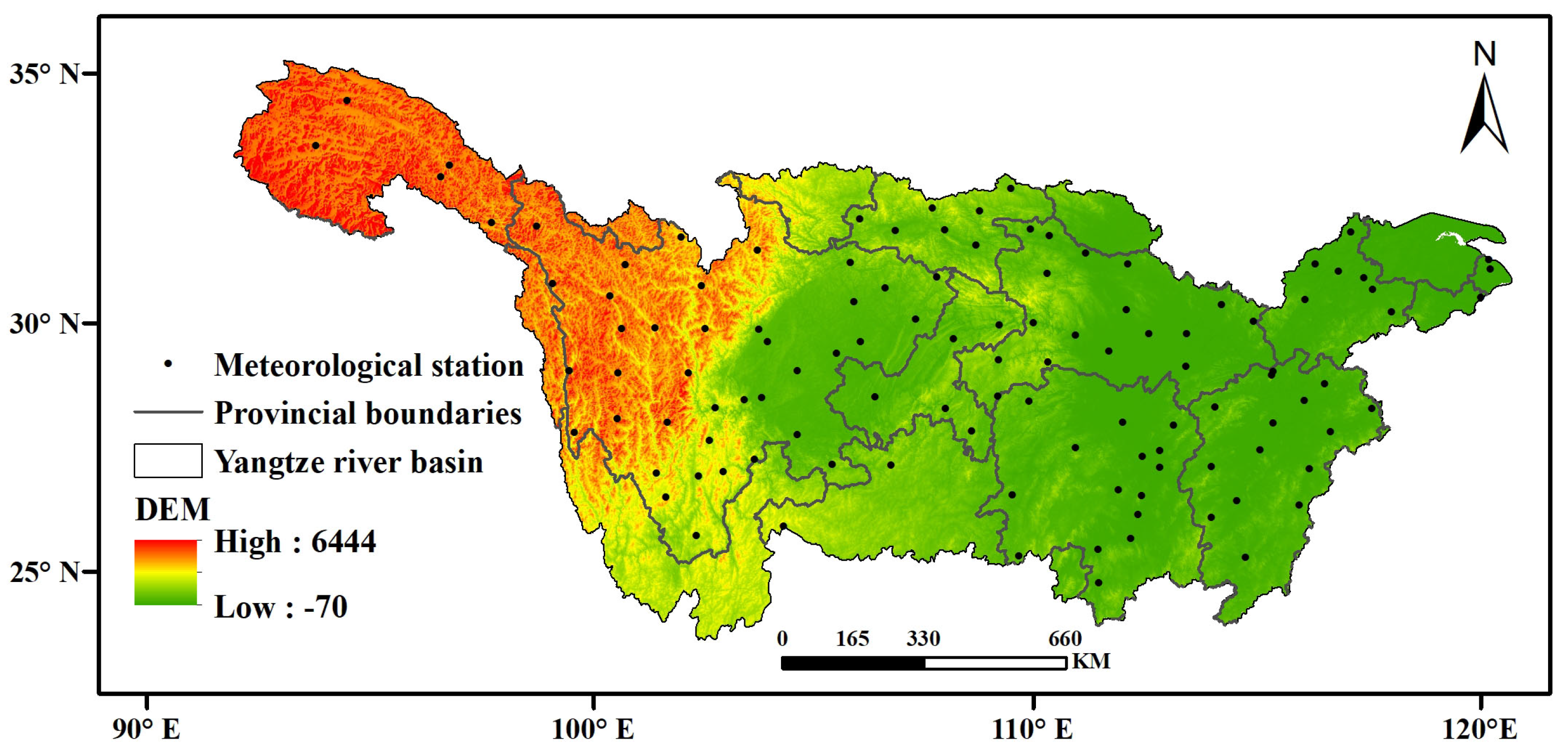
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Standardized Precipitation-Evapotranspiration Index
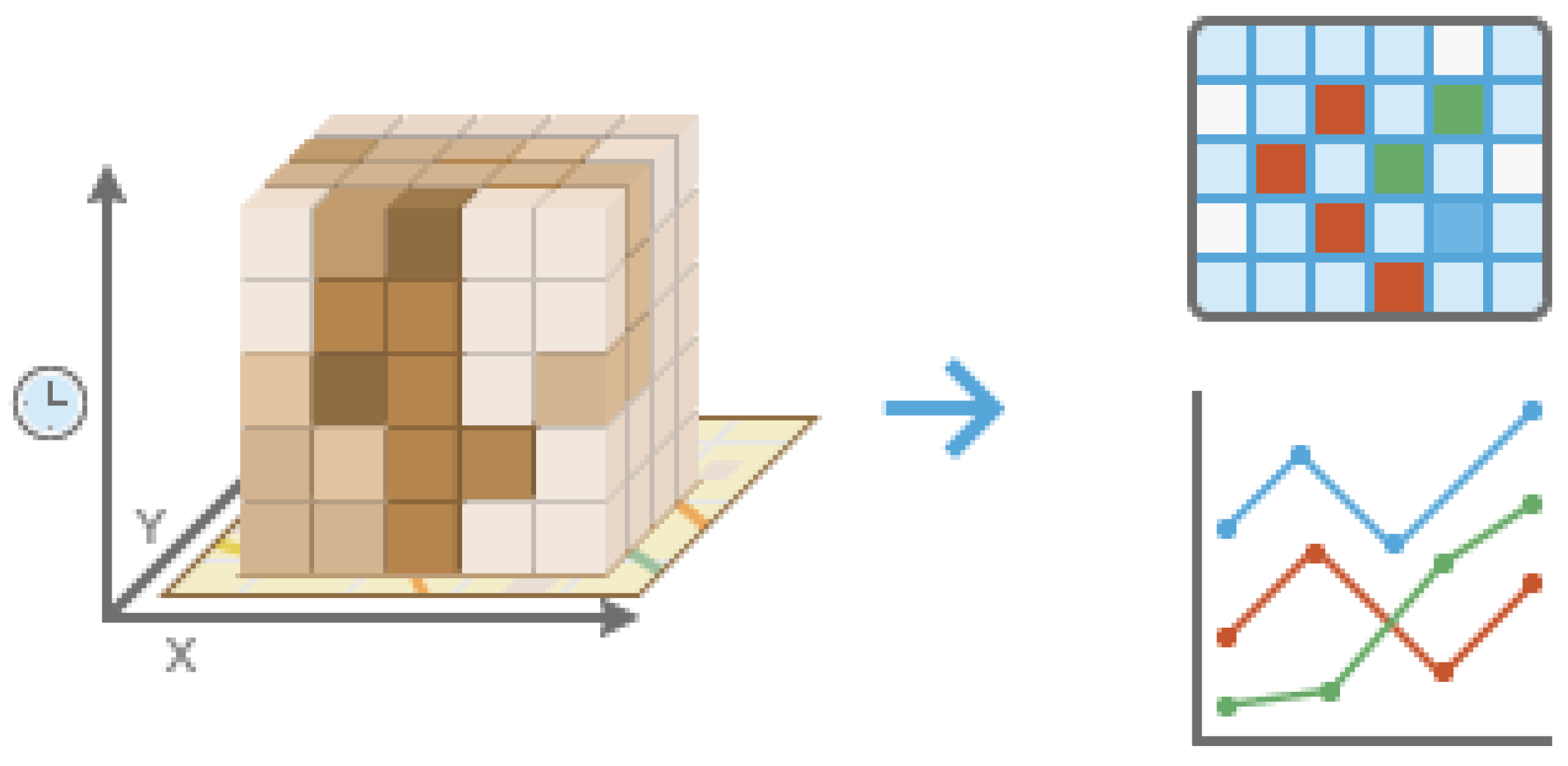
2.3.2. Space-Time Cube
2.3.3. Time Series Clustering Analysis
2.3.4. Emerging Hot Spot Analysis
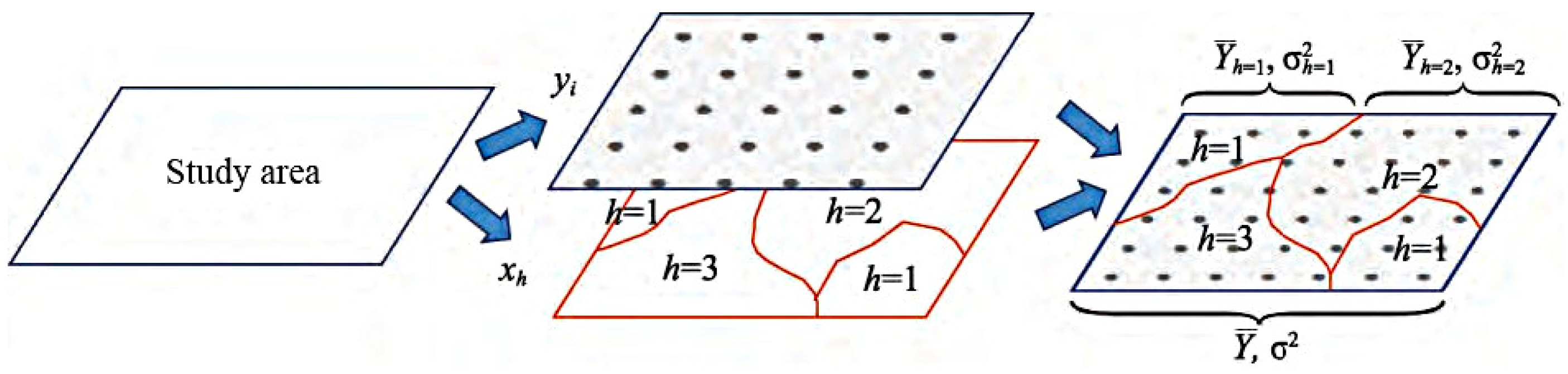
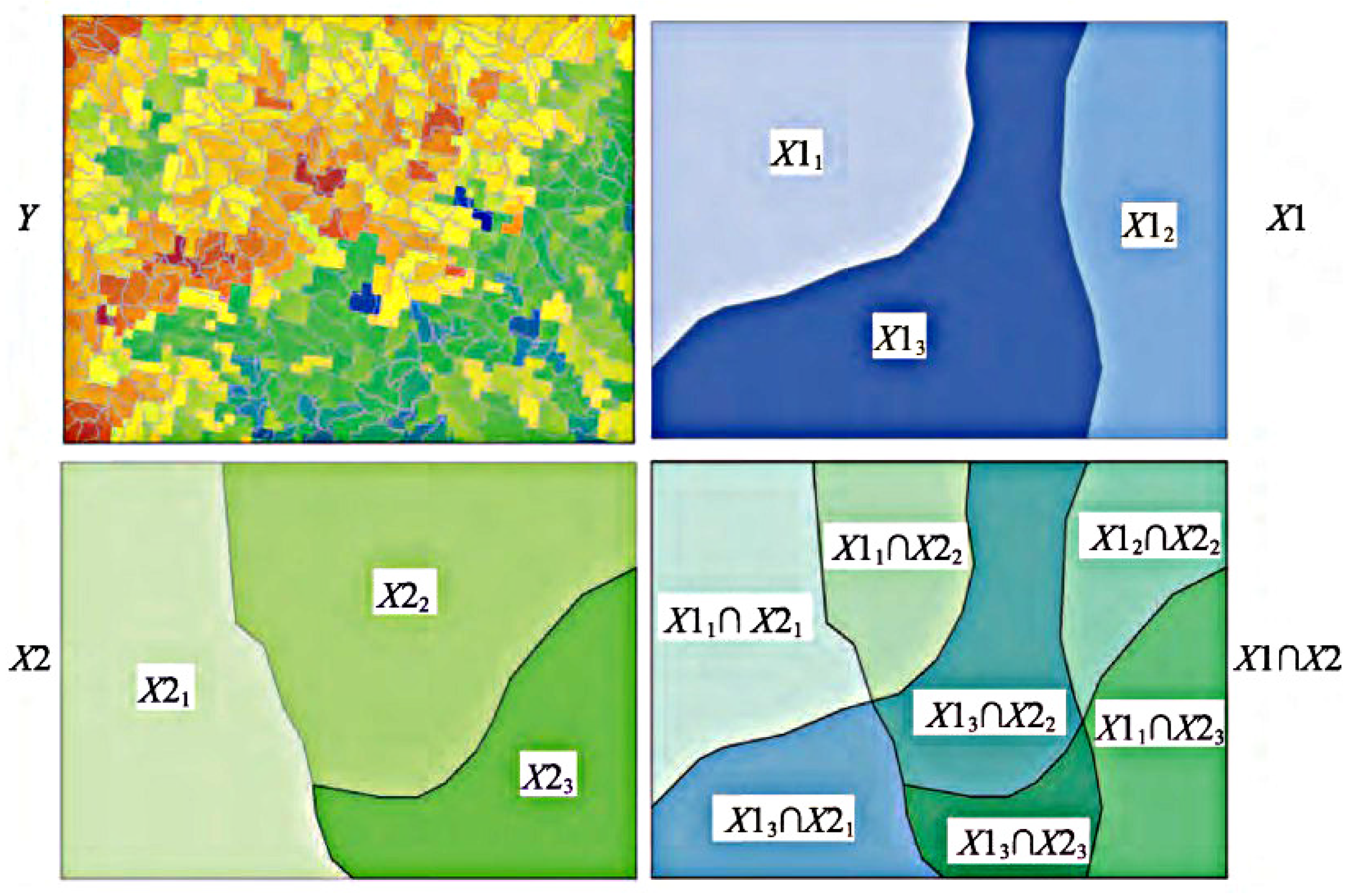
2.3.5. Geodetector
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temporal Variation Characteristics of Drought
3.2. Spatial Variation Characteristics of Drought
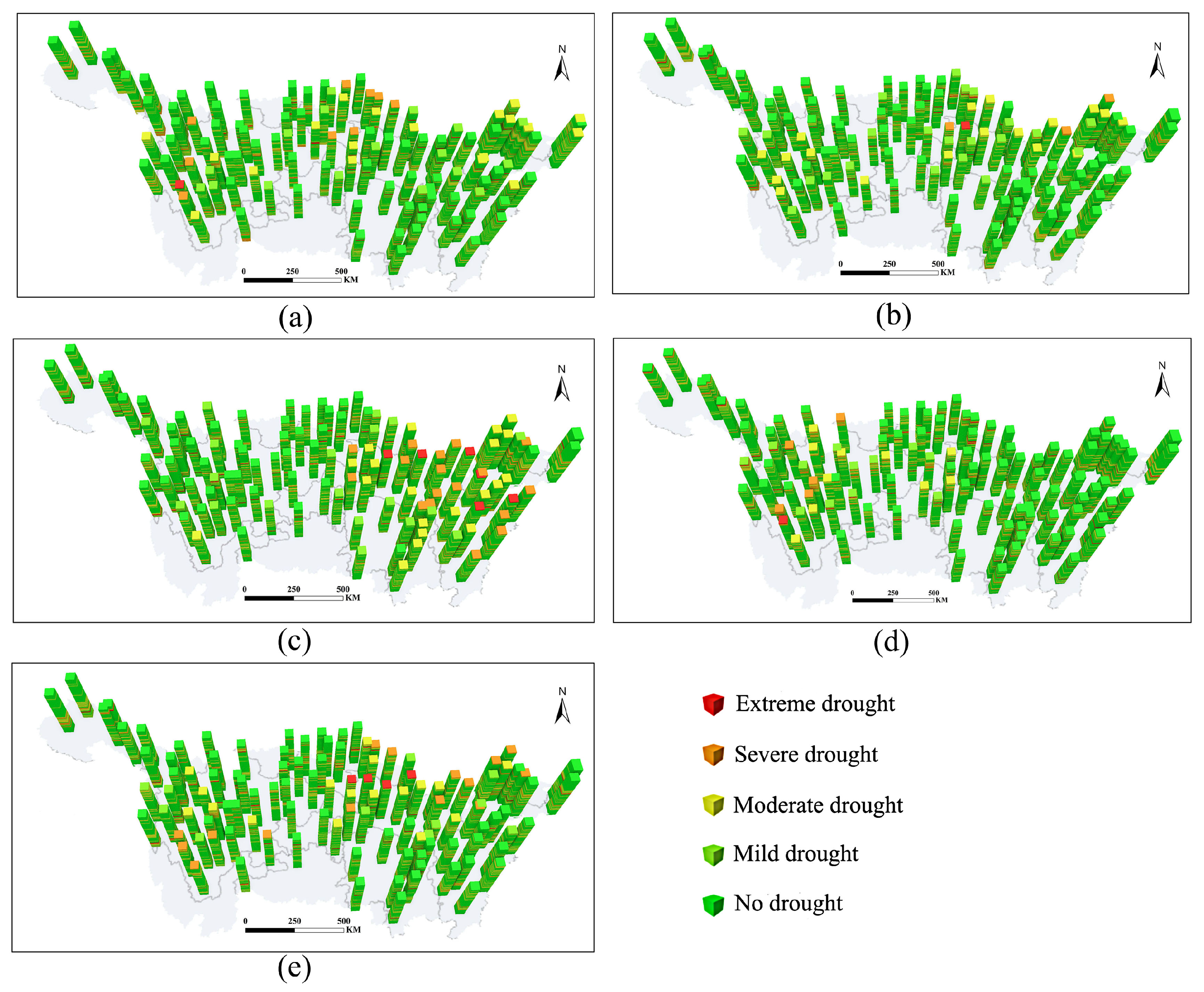
3.2.1. Space-Time Cube for Multi-Scale SPEI
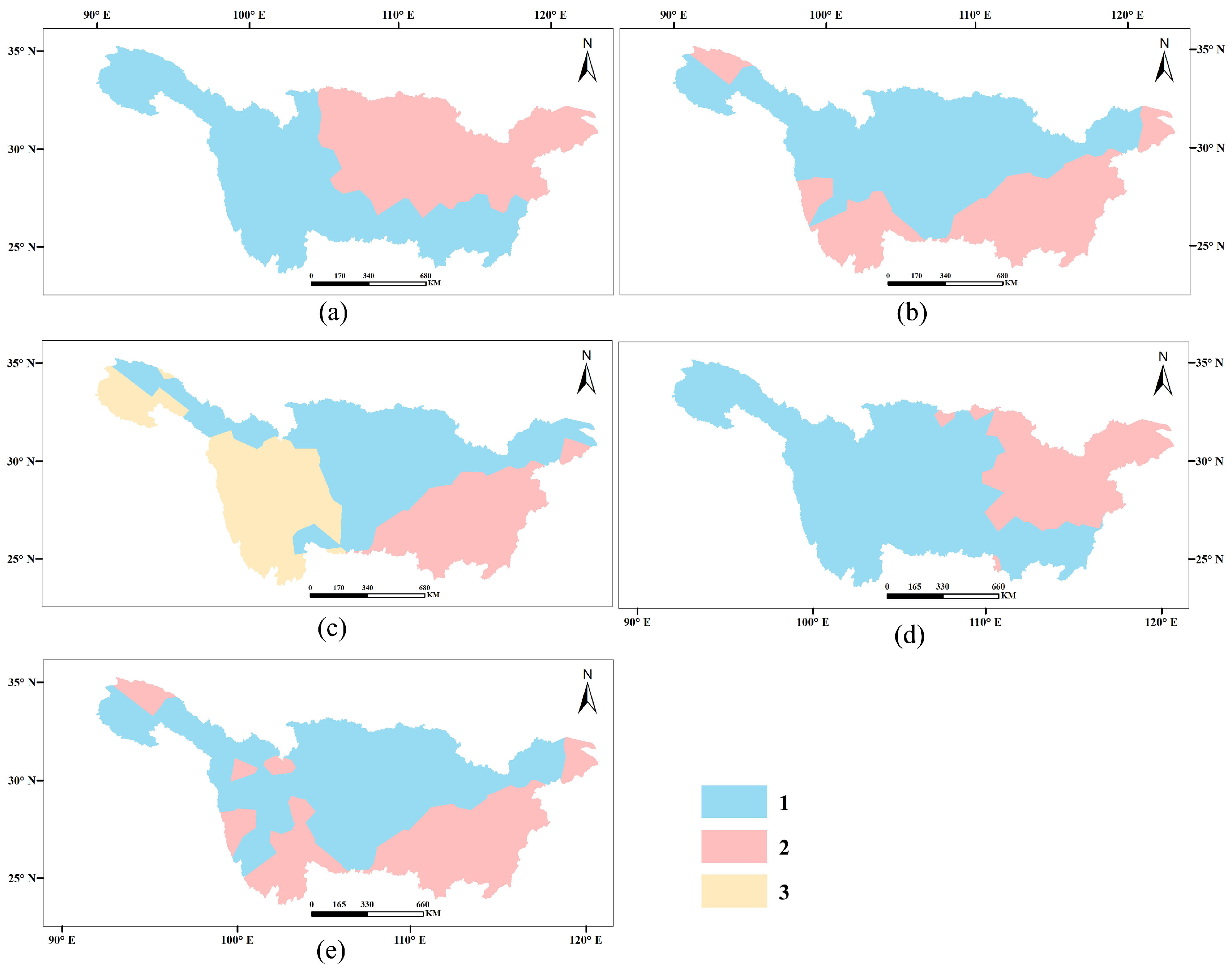
3.2.2. Result of Time Series Clustering Analysis
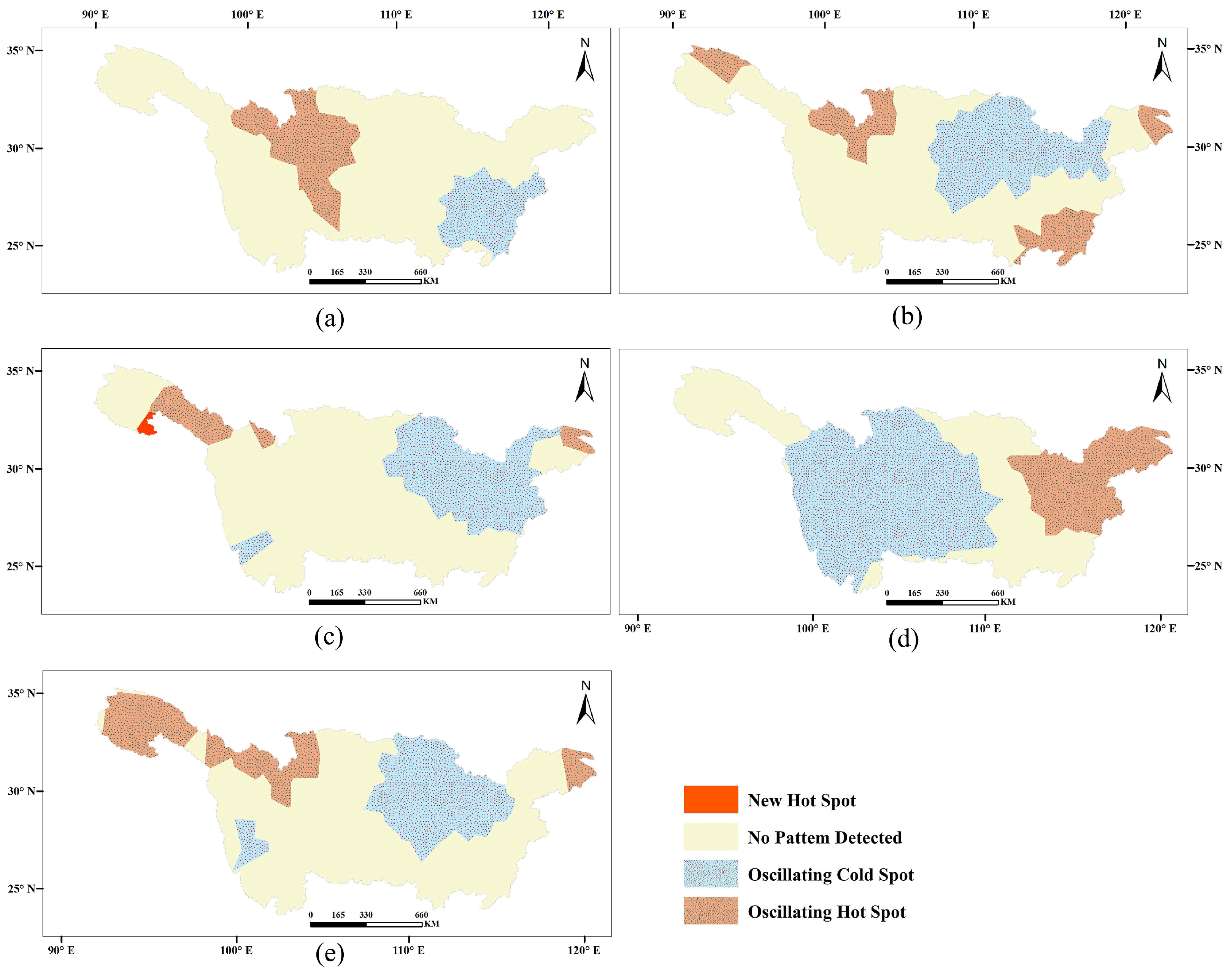
3.2.3. Result of Emerging Hot Spot Analysis
3.3. Analysis of Drought Drivers in the Yangtze River Basin
3.3.1. Factor Detector
3.3.2. Interaction Detector
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haghighi, A.T.; Zaki, N.A.; Rossi, P.M.; Noori, R.; Hekmatzadeh, A.A.; Saremi, H.; Klove, B. Unsustainability Syndrome-From Meteorological to Agricultural Drought in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Water 2020, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tng, D.; Apgaua, D.; Paz, C.P.; Dempsey, R.W.; Cernusak, L.A.; Liddell, M.J.; Laurance, S.G. Drought reduces the growth and health of tropical rainforest understory plants. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 511, 120128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherwood, S. Does a prolonged hardship reduce life span? Examining the longevity of young men who lived through the 1930s Great Plains drought. Popul. Environ. 2022, 43, 530–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yao, H.; Yuan, X.; Lin, B. Dissolved organic carbon response to hydrological drought characteristics: Based on long-term measurements of headwater streams. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhite, D.A. Drought and water crises: Science, technology, and management issues. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1444–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C. Analysis of Drought Change and Its Impact in Central Asia. Adv. Earth Sci. 2022, 37, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, F.; Mazdiyasni, O.; Aghakouchak, A. Evidence of anthropogenic impacts on global drought frequency, duration, and intensity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alahacoon, N.; Edirisinghe, M. A comprehensive assessment of remote sensing and traditional based drought monitoring indices at global and regional scale. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2022, 13, 762–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagge, J.H.; Tallaksen, M.; Xu, C.Y.; Van Lanen, H.A. Standardized Precipitation-evapotranspiration Index (SPEI): Sensitivity to Potential Evapotranspiration Model and Parameters. In Hydrology in a Changing World—Copernicus GmbH (IAHS-AISH Proceedings and Reports); International Association of Hydrological Sciences: Wallingford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.; Mohammadi, G.M.; Saviz, S. Spatial and temporal analysis of drought in various climates across Iran using the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI). Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1279. [Google Scholar]
- Sergio, M.V.; Santiago, B.; Ji, L.-M. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; U.S. Department of Commerce Weather Bureau Research Paper: San Diego, CA, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhan, B.; Srinivasan, R. Development and evaluation of Soil Moisture Deficit Index (SMDI) and Evapotranspiration Deficit Index (ETDI) for agricultural drought monitoring. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 133, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, J. Changes in Drought Characteristics over China Using the Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 5430–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, N.; Shi, Y. Analysis of Drought Characteristics and Driving Forces in the Urban Belt Along the Yellow River in Ningxia Based on SPEI. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Geng, G.; Zhou, H.; Wang, T. Spatial-temporal Evolution of Meteorological Drought in the Wei River Basin Based on SPEI_PM. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2021, 42, 962–974. [Google Scholar]
- Mobilia, M.; Longobardi, A. Prediction of Potential and Actual Evapotranspiration Fluxes Using Six Meteorological Data-Based Approaches for a Range of Climate and Land Cover Types. Isprs Int. J. -Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Jang, D. Analysis of Dryness/Wetness over China Using Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index Based on Two Evapotranspiration Algorithms. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 39, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, M.; Guo, X.; Shi, X.; Han, H. Temporal and spatial evolution of drought in Haihe River Basin from 1960 to 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, B.; Cai, B.; Tian, W. SPEI-based Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Meteorological Drought in the Chaobai River Basin. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 43, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S. Effects of multi-temporal scale drought on vegetation dynamics in Inner Mongolia from 1982 to 2015, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sha, J.; Wang, Z.L. Comparison of drought indices in the analysis of spatial and temporal changes of climatic drought events in a basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 10695–10707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Lu, J.; Chen, X. Spatio-temporal Evolution of Agricultural Drought in the Yangtze River Basin Based on Long-term CCI Soil Moisture Data. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2022, 31, 472–481. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Xu, L.; Fan, H.; Meng, Y. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics and the Evolution Trends of Droughts in the Yangtze River Basin. Res. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Niu, Z.; Wang, L.; Yao, R.; Gui, X.; Xiang, F.; Ji, Y. Impacts of Drought and Climatic Factors on Vegetation Dynamics in the Yellow River Basin and Yangtze River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, B.; Ma, S.; Ma, B.; Cu, Y.Q.; Wang, X.D.; Ma, C.R.; Chen, K.Q.; Zhang, T. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Meteorological Drought and Drought Risk Analysis in Hedong Area of Gansu Province. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2020, 41, 459–469. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago, B.; Sergio, M.V.; Fergus, R.; Borja, L. Standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI) revisited: Parameter fitting, evapotranspiration models, tools, datasets and drought monitoring. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 3001–3023. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, A. The ESRI Guide to GIS Analysis; ESRI Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. An Analysis of Spatial-temporal Distribution Characteristics of Housing Prices in Nanchang Based on Space-time Cube. Jiangxi Sci. 2019, 37, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, D.; Ding, Y. Spatio-temporal pattern mining of the last 40 years of drought in China based on SPEI index and spatio-temporal cube. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2021, 39, 194–201. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, C.B.; Tan, D.C.; Mai, T.Y.; Bei, C.; Qin, J.; Pang, W.; Zhang, Z. An analysis of spatiotemporal pattern for COVID-19 in China based on space-time cube. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mcleod, G. Exploring spatial patterns of Virginia tornadoes using kernel density and space-time cube analysis (1960–2019). ISPRS Int. J. -Geo.-Inf. 2021, 10, 310. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, H.; Argany, M.; Ghanbari, A.; Ahmadi, M. Visualized spatiotemporal data mining in investigation of Urmia Lake drought effects on increasing of PM10 in Tabriz using space-time cube (2004–2019). Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shi, X.; Wong, Y.D. A lane-changing risk profile analysis method based on time-series clustering. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2021, 565, 125567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.Z.; Yu, F.S.; Pedrycz, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. Time-series clustering based on linear fuzzy information granules. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 73, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahreche, A.; Boucheham, B. A fast and accurate similarity measure for long time series classification based on local extrema and dynamic time warping. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 168, 114374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delforge, D.; Watlet, A.; Kaufmann, O.; Van Camp, M. Time-series clustering approaches for subsurface zonation and hydro facies detection using a real time-lapse electrical resistivity dataset. J. Appl. Geophys. 2021, 184, 104203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Qi, B.; Ji, K.; Liu, Z.; Deng, L.; Jiang, L. Emerging hot spot analysis and the spatial–temporal trends of NDVI in the Jing River basin of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The Analysis of Spatial Association by Use of Distance Statistics. Geogr. Anal. 1992, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwanto, P.; Utaya, S.; Handoyo, B. Spatiotemporal analysis of Covid-19 spread with emerging hotspot analysis and space-time cube models in east java, Indonesia. Int. J. -Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y. Analysis Methods of Spatio-temporal Patterns and Its Empirical Applications-A Case Study of Manufacturing Industry of Shandong Province. J. Geomat. Sci. Technol. 2021, 38, 624–630+638. [Google Scholar]
- Betty, E.L.; Bollard, B.; Murphy, S.; Ogle, M.; Hendriks, H.; Orams, M.B.; Stockin, K.A. Using emerging hot spot analysis of stranding records to inform conservation management of a data-poor cetacean species. Biodivers. Conserv. 2019, 29, 643–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, S.N. The spatiotemporal forming of a state of exception: Repurposing hot-spot analysis to map bare-life in southern Arizona’s borderlands. Geo J. 2020, 85, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the heshun region, china. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Hu, Y. Environmental health risk detection with Geogdetector. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 33, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J.F. Optimal discretization for geographical detectors-based risk assessment. Mapp. Sci. Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Gao, B.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, K.; Li, C. Spatial Differentiation and Driving Factors of Rural Settlement in Plateau Lake: A Case Study of the Area Around the Erhai. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 220–229. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Li, J.; Zeng, J.; Ran, D.; Yang, B. Spatial heterogeneity and formation mechanism of eco-environmental effect of land use change in China. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 2173–2187. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, J. Progress of research on the conception, characteristic, and influencing factors of drought propagation from the perspective of geographic sciences. Prog. Geogr. 2022, 548, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Luo, G.; Gao, C. Research Progress of Agricultural Drought from the Perspective of Geography. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 168, 27–34+64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, Q. Investigation about the correlation and propagation among meteorological, agricultural and groundwater droughts over humid and arid/semi-arid basins in China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalm, C.R.; Anderegg, W.R.; Michalak, A.M.; Fisher, J.B.; Biondi, F.; Koch, G.; Litvak, M.; Ogle, K.; Shaw, J.D.; Wolf, A.; et al. Global patterns of drought recovery. Nature 2017, 548, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Li, Z.; Zeng, S.; Zou, L.; She, D.; Cheng, D. Perspectives on eco-water security and sustainable development in the Yangtze River Basin. Geosci. Lett. 2021, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, T.; Shalamzari, M.J. Effects of Climate Change on Vegetation Growth in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, J.; Shalamzari, M.J.; Arshad, A.; Liu, S.; Liu, T.; Tao, H. Monitoring Recent Changes in Drought and Wetness in the Source Region of the Yellow River Basin, China. Water 2022, 14, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ren, Y.; Tao, H.; Shalamzari, M.J. Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics of Heatwaves in Recent Decades over China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Category | Factor |
|---|---|
| Topography | Elevation () |
| Slop () | |
| Soil type () | |
| Meteorology | Average annual temperature () |
| Average annual precipitation () | |
| Socio-economic | population density () |
| GDP () | |
| Night light () | |
| Human footprints () | |
| Traffic location | Distance to water system () |
| Distance to provincial road () | |
| Distance to railroad () |
| Level | Type | SPEI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | No drought | |
| 2 | Mild drought | |
| 3 | Moderate drought | |
| 4 | Severe drought | |
| 5 | Extreme drought |
| Factor | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | q (Average) | q (Sum) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.18 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.41 | 0.27 | 0.56 | |
| 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.05 | ||
| 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.44 | 0.24 | ||
| 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0.42 | 0.25 | 0.59 | |
| 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.43 | 0.70 | 0.34 | ||
| 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.16 | |
| 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | ||
| 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.05 | ||
| 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.07 | ||
| 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.19 | |
| 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.03 | ||
| 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.; Wang, Z.; Han, L.; Shang, J.; Zhao, B. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Drought and Its Driving Factors in Yangtze River Basin Based on SPEI. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121986
Wei J, Wang Z, Han L, Shang J, Zhao B. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Drought and Its Driving Factors in Yangtze River Basin Based on SPEI. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(12):1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121986
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Jieru, Zhixiao Wang, Lin Han, Jiandong Shang, and Bei Zhao. 2022. "Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Drought and Its Driving Factors in Yangtze River Basin Based on SPEI" Atmosphere 13, no. 12: 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121986
APA StyleWei, J., Wang, Z., Han, L., Shang, J., & Zhao, B. (2022). Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Drought and Its Driving Factors in Yangtze River Basin Based on SPEI. Atmosphere, 13(12), 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13121986








