The Intraseasonal Variations of the Leading Mode of Summer Precipitation Anomalies in Meiyu Area of East Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
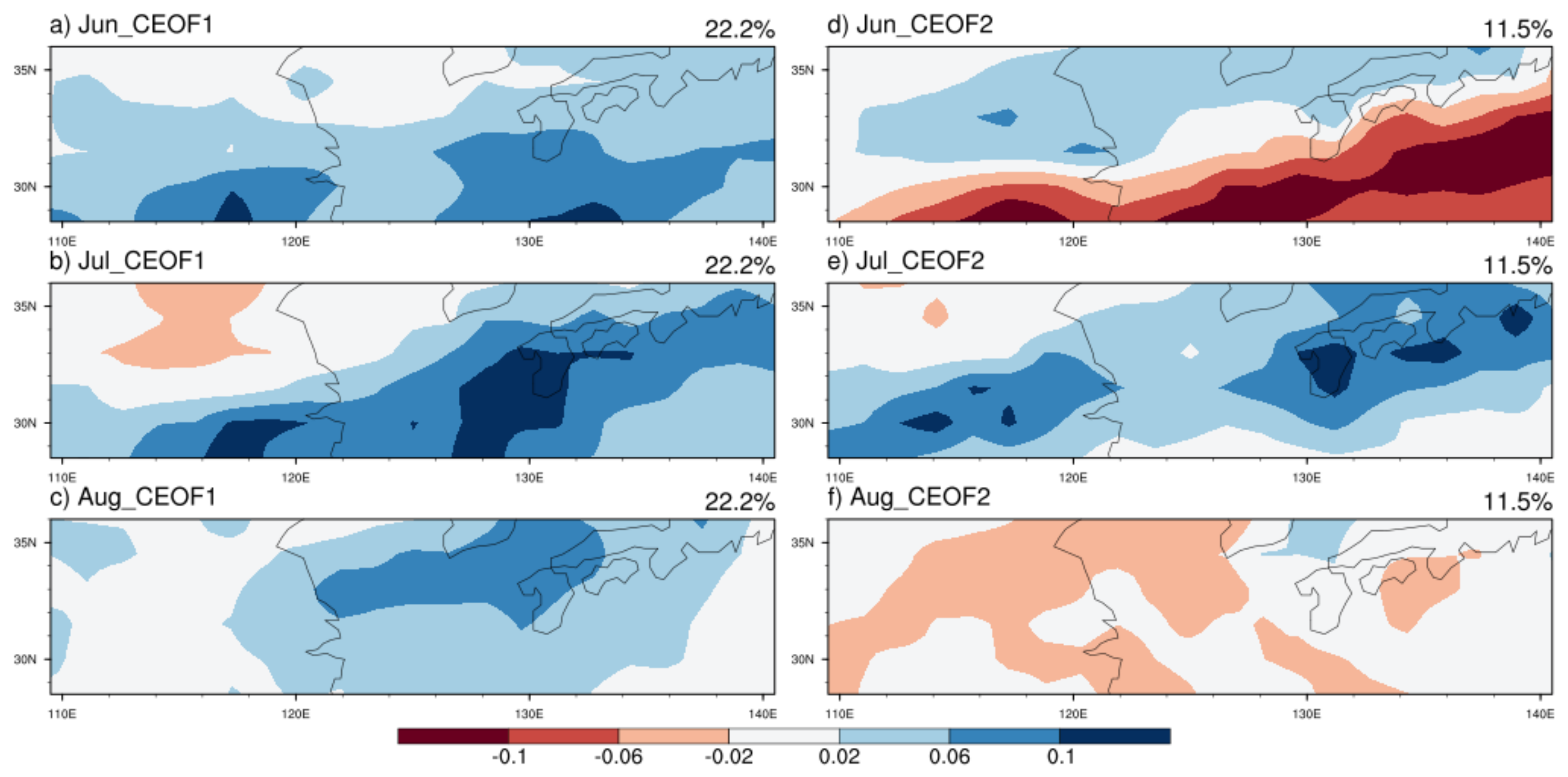
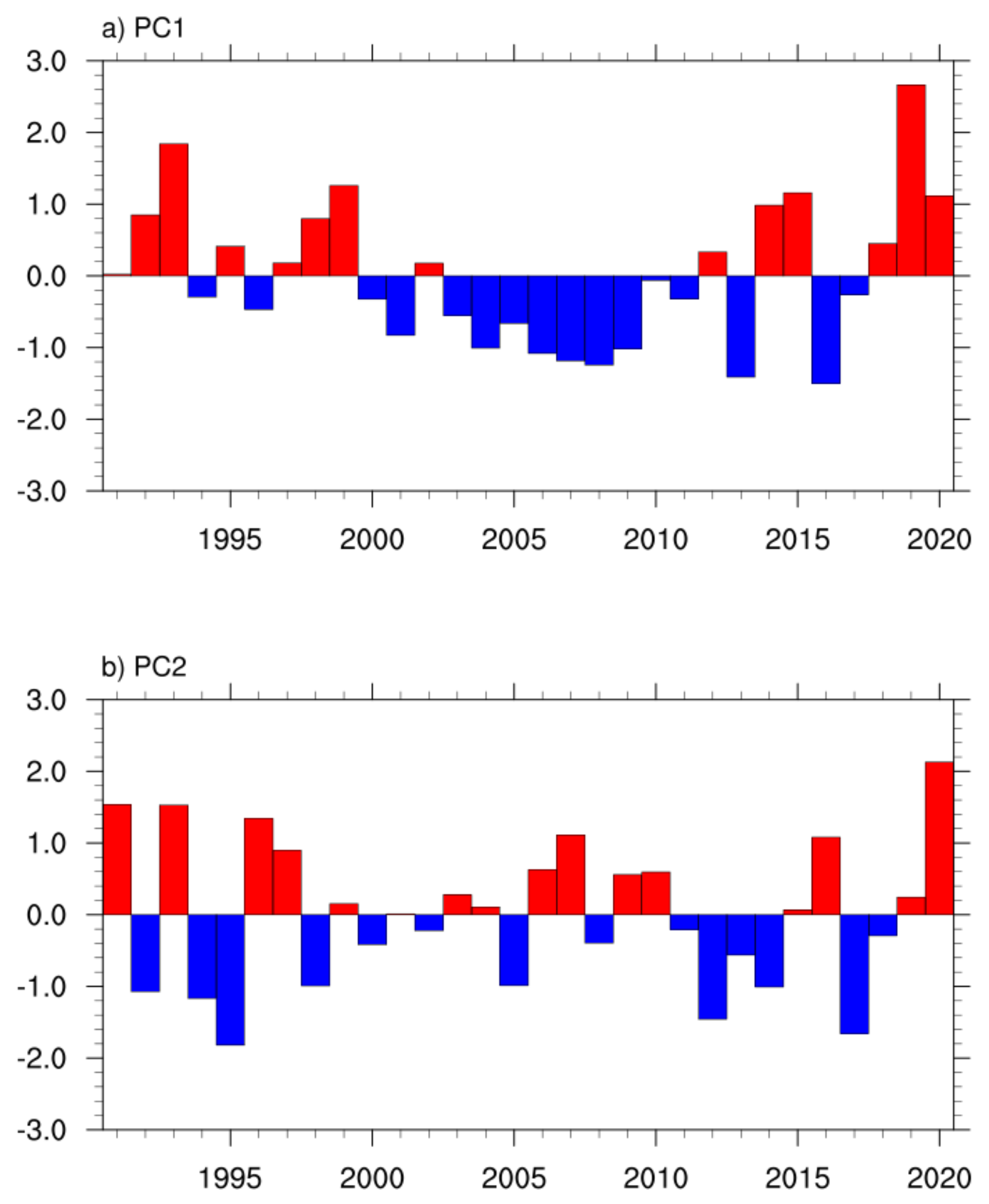
2.2.1. Combined Empirical Orthogonal Function
2.2.2. Regression Analysis
2.2.3. Synthetic Difference Analysis
3. Characteristics of Precipitation in Summer
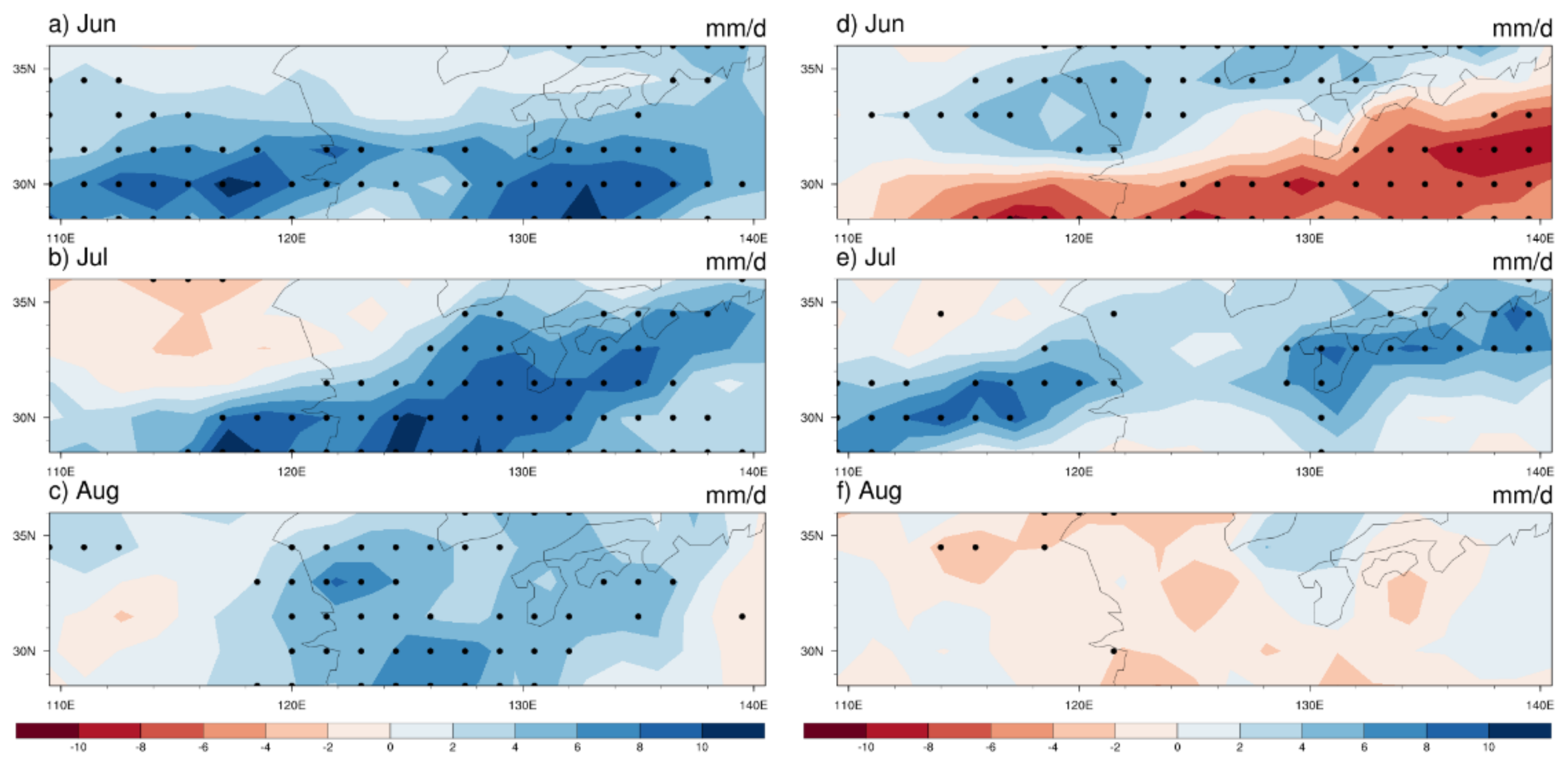
3.1. Mean and Standard Deviation of Precipitation
3.2. The Intraseasonal Variations of Summer Precipitation Anomalies
4. Characteristics of Circulation and SST
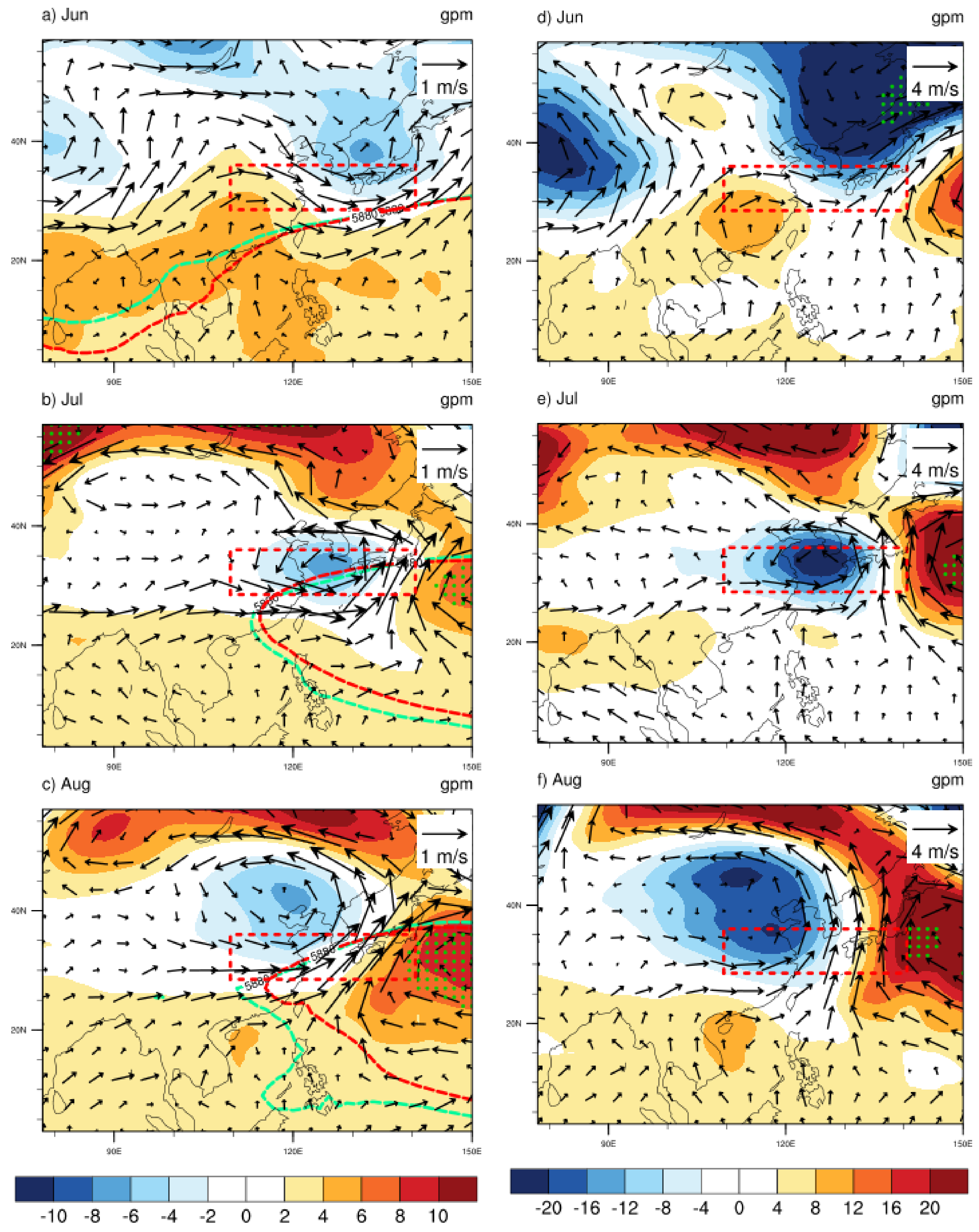
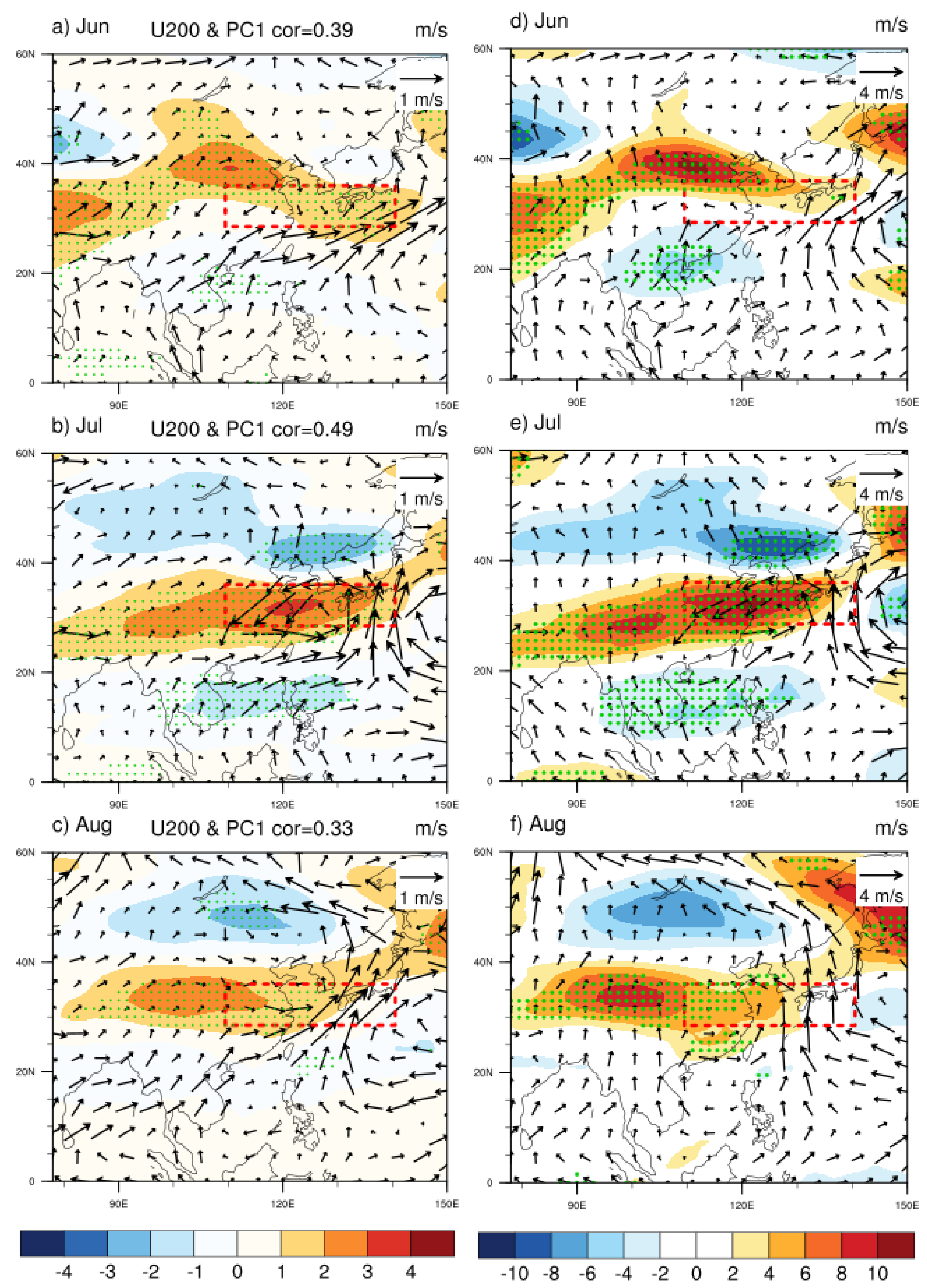
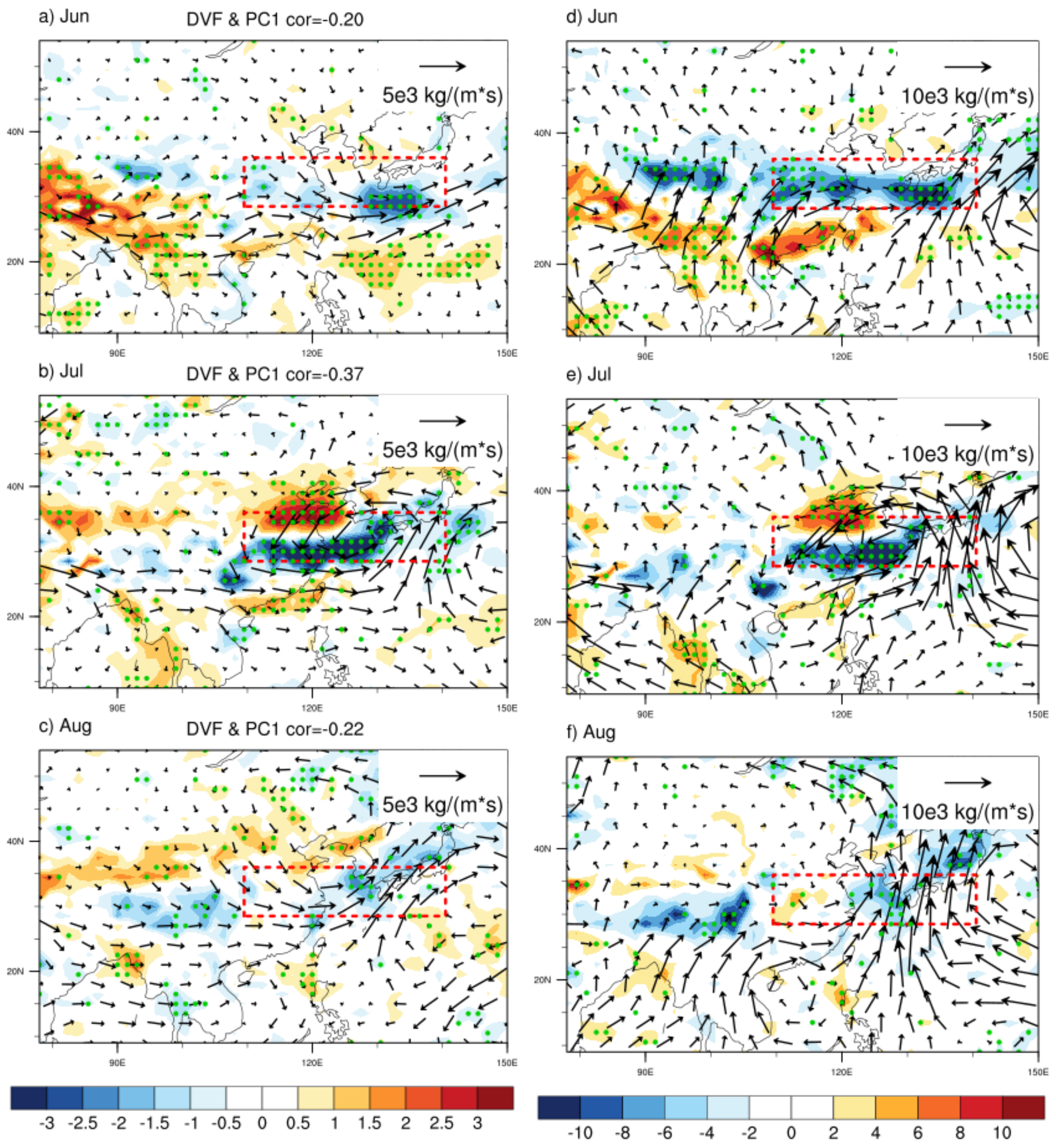
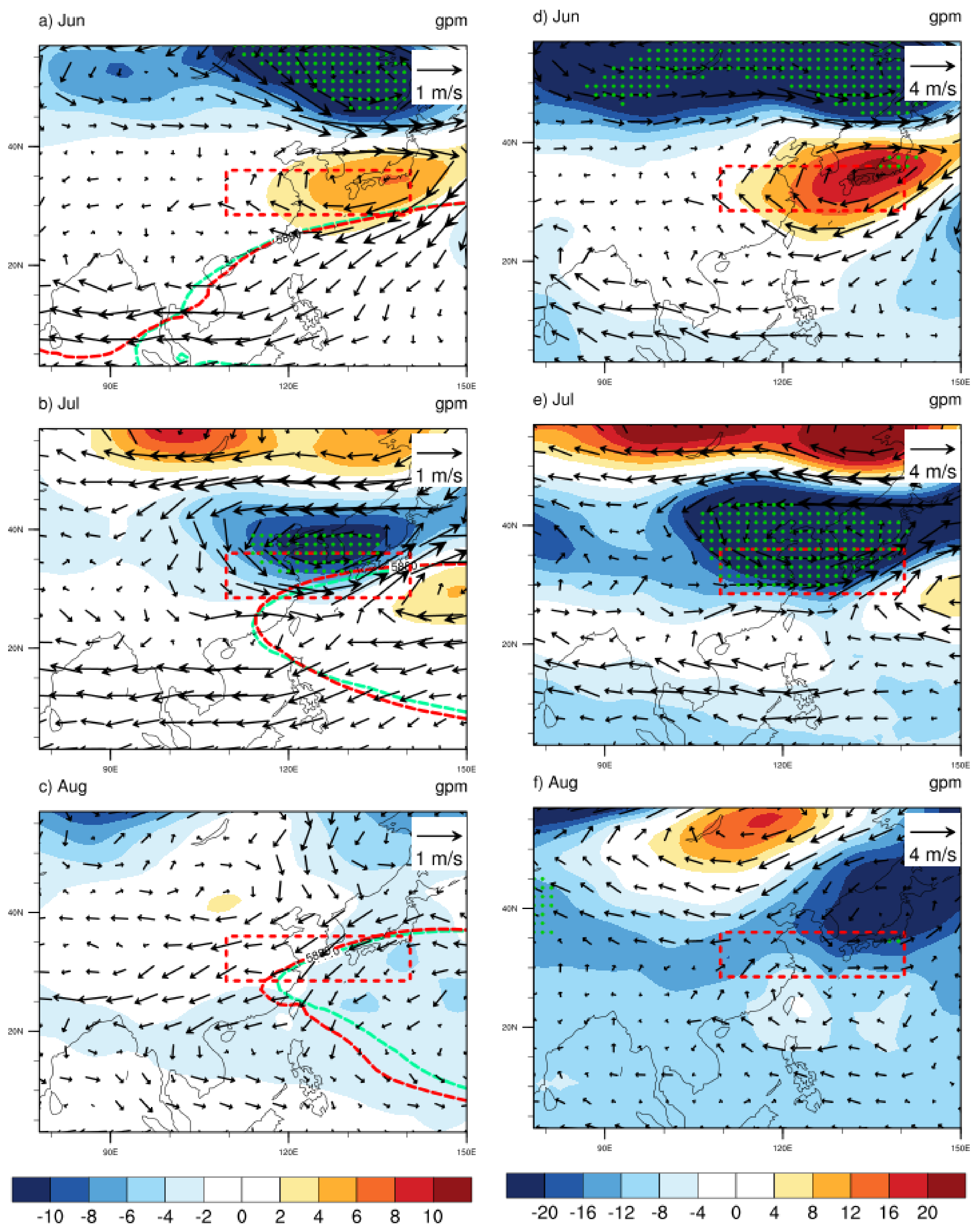
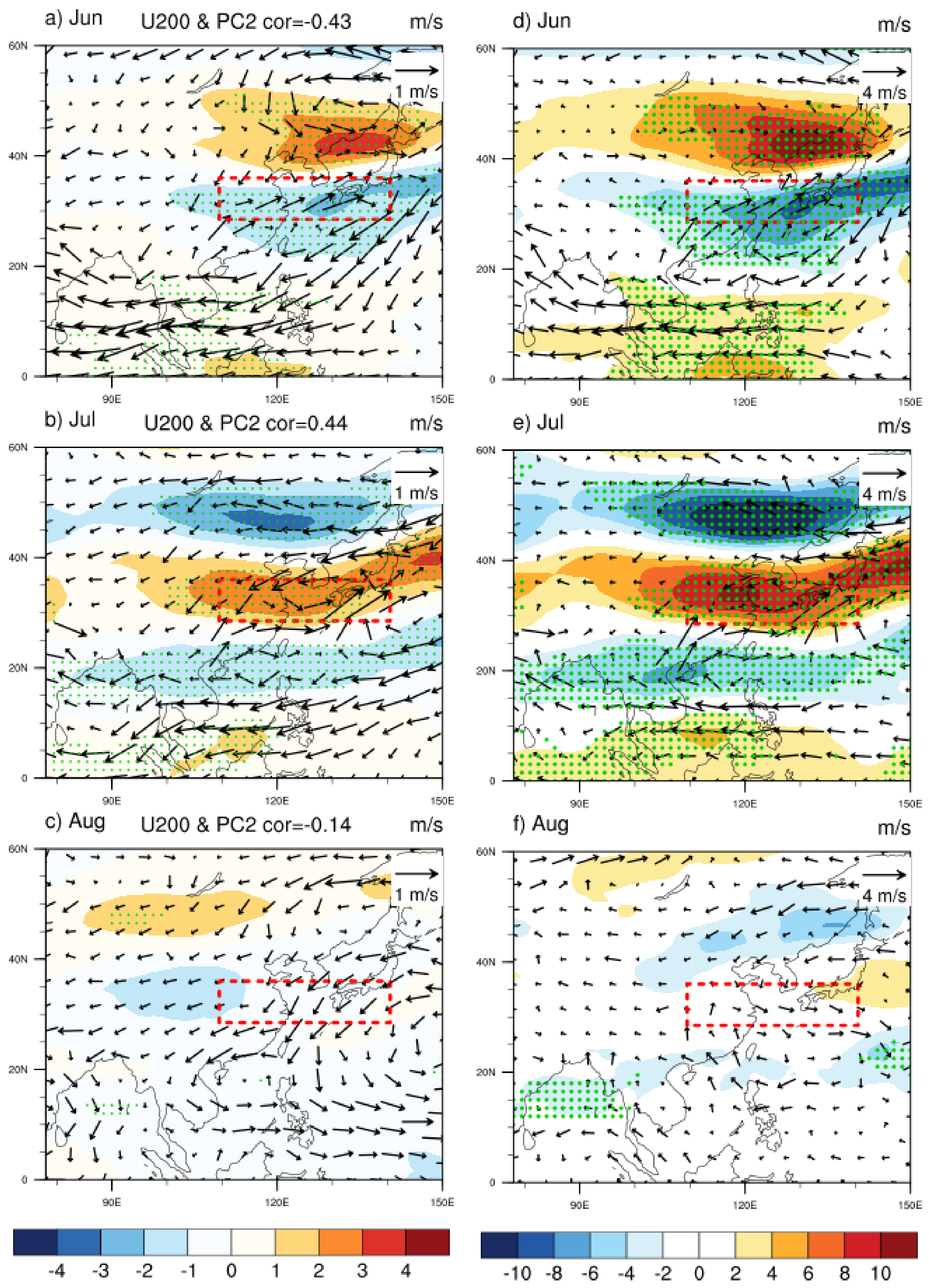
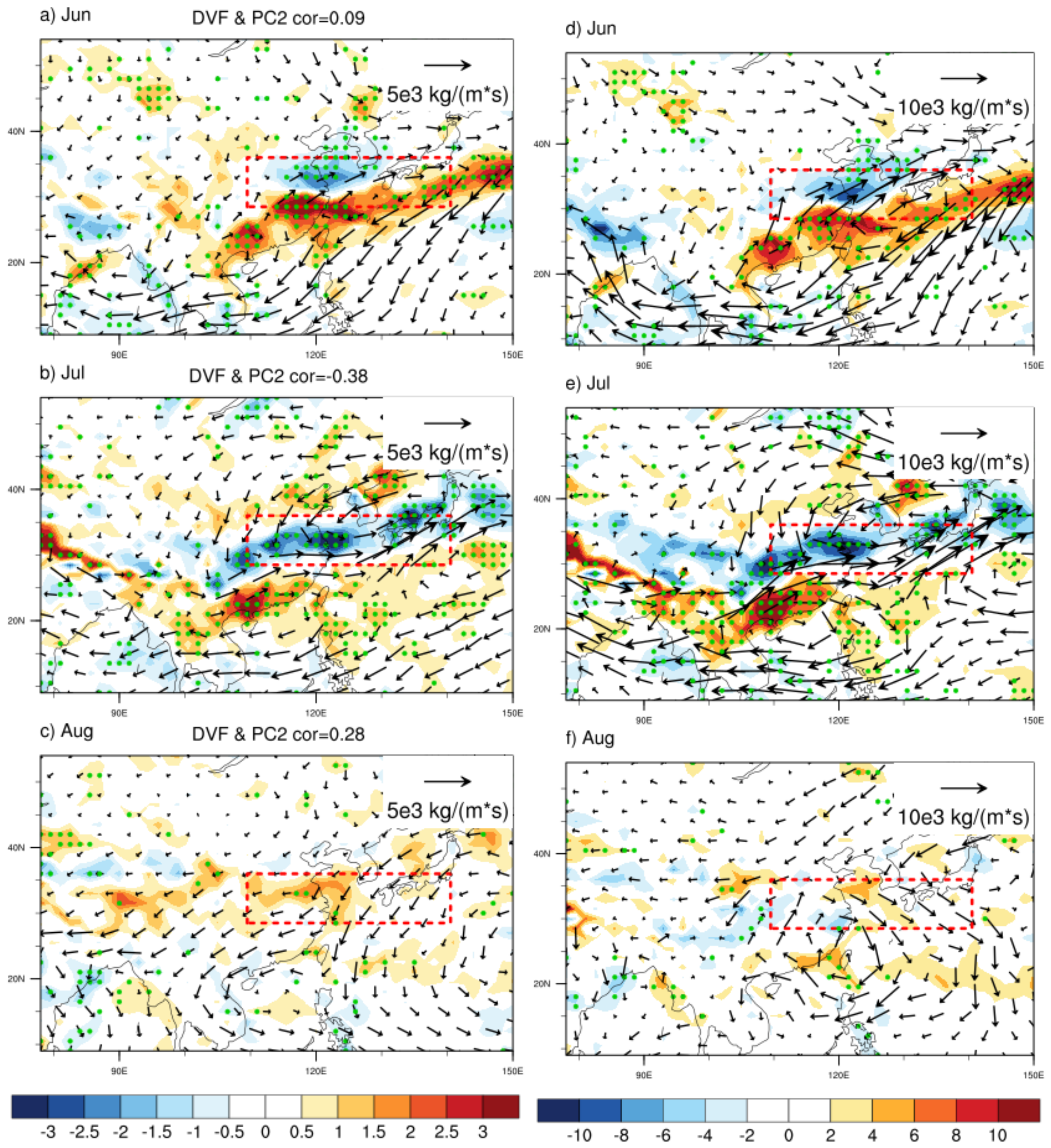
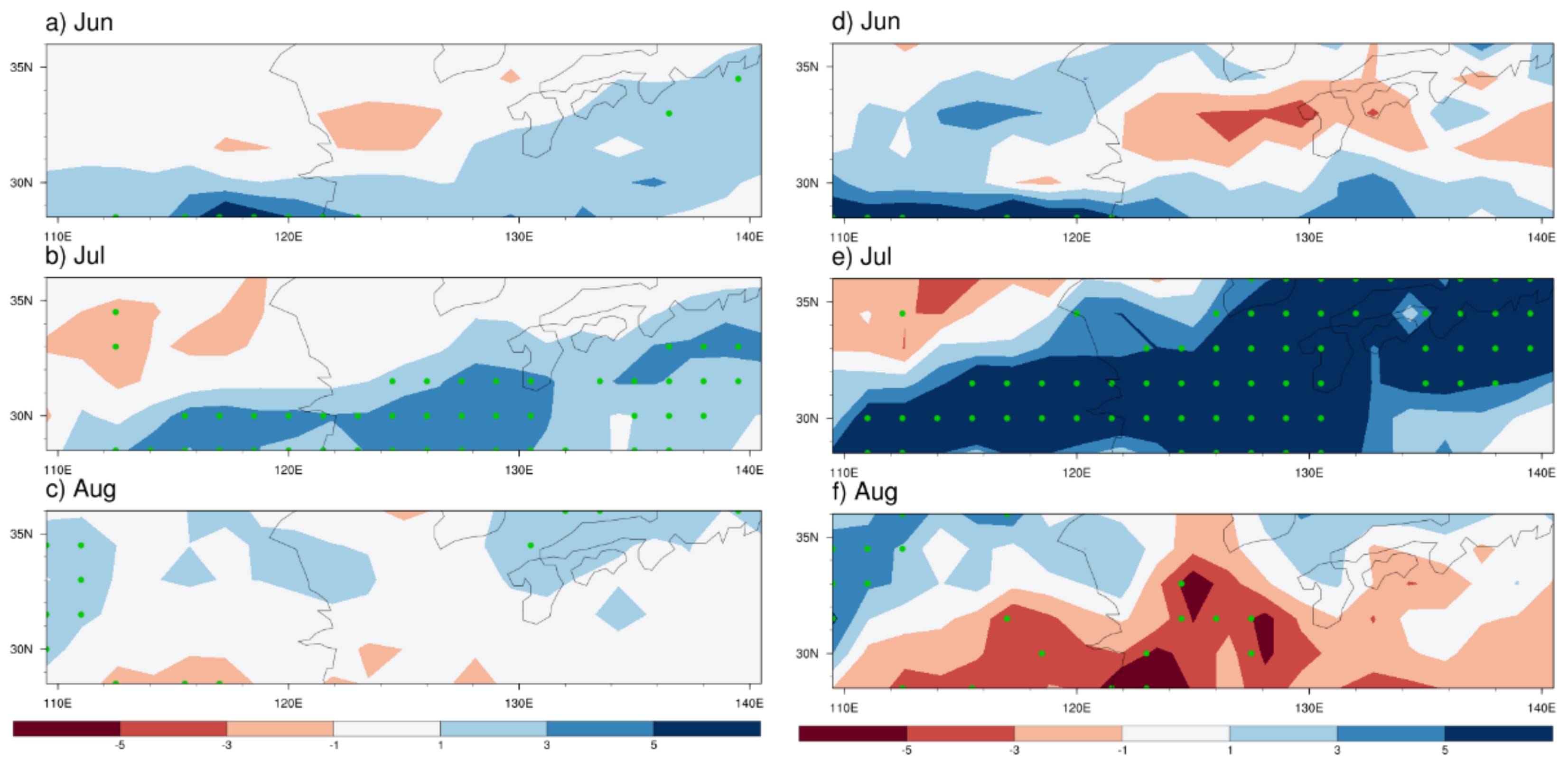
4.1. Circulation Anomaly
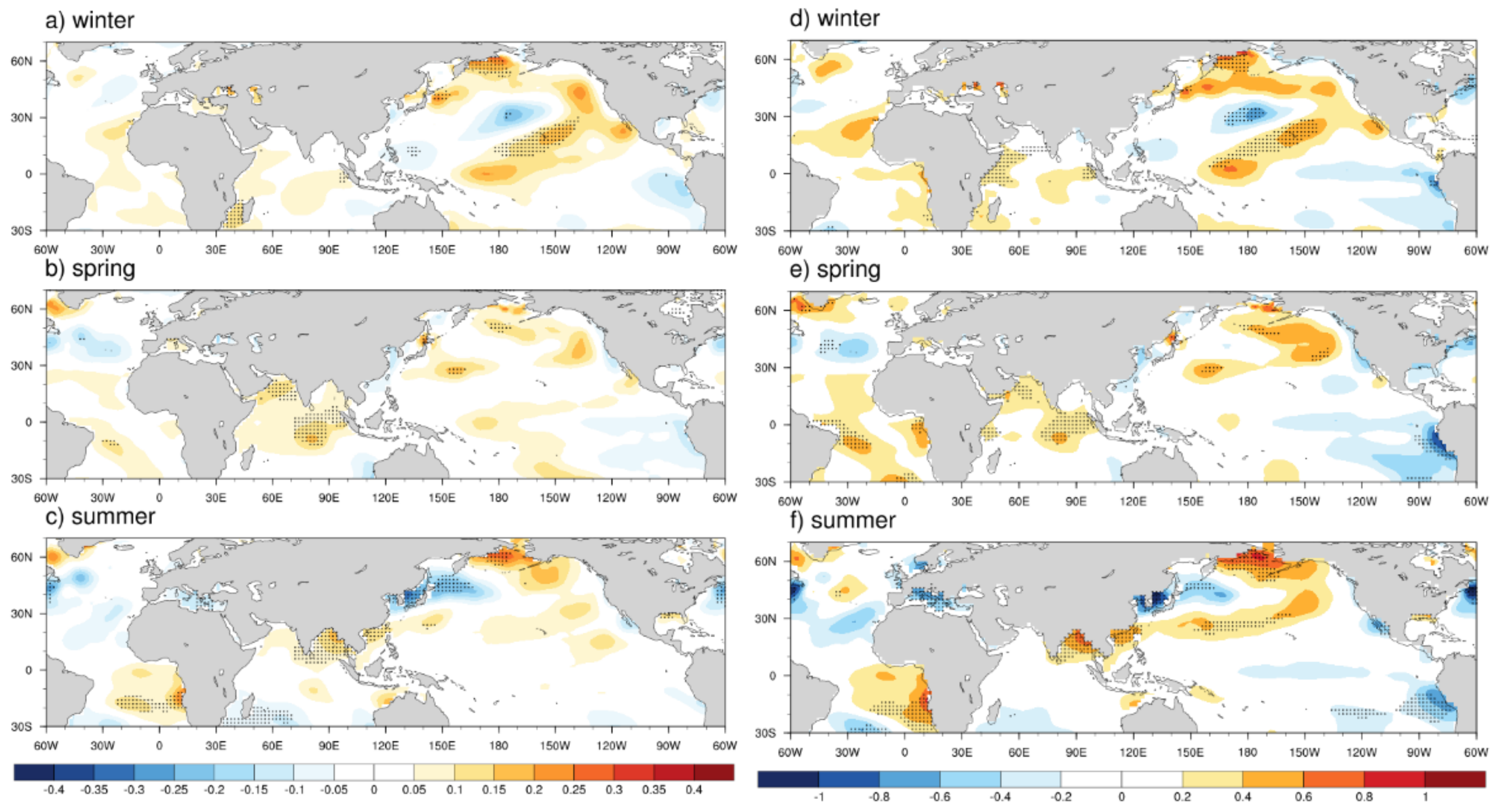
4.2. SSTAs
5. Summary and Discussion
5.1. Summary
5.2. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yihui, D.; Johnny, C.L.C. The East Asian summer monsoon: An overview. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 89, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Chen, L. A review of recent research on the East Asian summer monsoon in China. In Review in Monsoon Meteorology; Chang, C.P., Krishnamurti, T.N., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 60–92. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, M.; Zheng, Z.; Fu, Q. Characteristics of Meiyu seen from multiple observational analyses and reanalyses. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2021EA001647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.H.; Kwon, W.T.; Ryoo, S.B. Review of the researches on Changma and future observational study (KORMEX). Adv. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 14, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, K. The early summer rainy season (BAIU) over Japan. In Monsoon Meteorology; Chang, C.P., Krishnamurti, T.N., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 93–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.H.; Liang, P.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.C. Multiscale variability of Meiyu and its prediction: A new review. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Q.; Yan, Y.H.; Zhu, C.W.; Ma, S.M.; Li, J.Y. Record-breaking Mei-yu rainfall around the Yangtze River in 2020 regulated by the subseasonal phase transition of the North Atlantic Oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL090342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.B.; Chen, D.; Wang, B.; Cheung, H.N.; Liu, F.; Cheng, J.B.; Tang, S.K.; Zhang, Z.P.; Feng, G.L.; Dong, W.J. The Longest 2020 Meiyu Season Over the Past 60 Years: Subseasonal Perspective and Its Predictions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, N. China has just Contained the Coronavirus. Now it’s Battling Some of the Worst Floods in Decades. CNN, 14 July 2020. Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/2020/07/14/asia/china-flood-coronavirus-intl-hnk/index.html(accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Liang, P.; Ding, Y.H. Climatology of intraseasonal Oscillation of East Asia Meiyu. Acta. Meteorol. Sinica. 2012, 3, 418–435. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, P.; Chen, L.J.; Ding, Y.H.; He, J.; Zhou, B. Relationship between long-term variability of Meiyu over the Yangtze River and ocean and Meiyu’s predictability study. Acta Meteorol. Sinica. 2018, 76, 379–393. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wu, R.; Fu, X. Pacific-East Asian Teleconnection: How Does ENSO Affect East Asian Climate? J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1517–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, C.C.; Klingaman, N.P.; Vidale, P.L.; Turner, A.G.; Demory, M.E.; Liang, G. A comprehensive analysis of coherent rainfall patterns in China and potential drivers. Part I: Interannual variability. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.P.; Hu, K.M.; Jan, H.; Du, Y. Indian Ocean Capacitor Effect on Indo–Western Pacific Climate during the Summer following El Niño. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 730–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, D.; Ding, Y.H. Oceanic forcings of the interdecadal variability in East Asian summer rainfall. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 7633–7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Si, D.; Liu, Y.J.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Song, Y. On the characteristics, driving forces and inter-decadal variability of the East Asian summer monsoon. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 42, 90–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto, M. Simulated change of the East Asian circulation under global warming scenario. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L16701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, P.W. Effects of black carbon aerosol in South Asia on Asian summer monsoon. Plateau Meteorol. 2009, 28, 419–424. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jung, W.S.; Panicker, A.S.; Lee, D.I.; Park, S.H. Estimates of aerosol indirect effect from Terra MODIS over Republic of Korea. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 976813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.C. Numerical study of the impacts of urban expansion on Meiyu precipitation over Eastern China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2015, 29, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Zhao, J.J. Intraseasonal variation of the East Asian summer monsoon in La Niña years. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2017, 10, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Fan, K. Pacific decadal oscillation and the decadal change in the intensity of the interannual variability of the South China Sea summer monsoon. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2017, 10, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.; Yeh, S.W. Influence of the Pacific decadal oscillation on the relationship between El Niño and the Northeast Asian summer monsoon. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 4525–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Zhang, W.; Jin, F.F.; Stuecker, M.F.; Levine, A.F.Z. Modulation of the Relationship between ENSO and Its Combination Mode by the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 4679–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, P.; Dwivedi, S.; Goswami, B.N.; Kucharski, F. A new perspective on ENSO-Indian summer monsoon rainfall relationship in a warming environment. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.Z. The Record-breaking Meiyu in 2020 and Associated Atmospheric Circulation and Tropical SST Anomalies. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1980–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Z. Towards influence of Arabian Sea SST anomalies on the withdrawal date of Meiyu over the Yangtze-Huaihe River basin. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, L. A comparative study of the interannual variation of summer rainfall anomolies between the Huaihe Meiyu season and the Jiangnan Meiyu season and their climate background. Acta Meteor. Sin. 2011, 69, 334–343. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, W.; Fong, S.K.; Leong, K.C.; Leong, W.K. Interannual and interdecadal variations of precipitation over eastern China during Meiyu season and their relationships with the atmospheric circulation and SST. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 36, 397–410. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Wang, H.; Zhou, B.; Li, H. Interdecadal variation in the synoptic features of Meiyu in the Yangtze River valley region and relationship with the Pacific decadal oscillation. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 6251–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wang, P.X.; Bai, H.Z. Intra-seasonal inhomogeneity of summer extreme precipitation in the east part of Northwest China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2008, 19, 111–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian Summer Monsoon and tropical pacific SSTs. Part II: Meridional structure of the monsoon. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 4326–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.J.; Singh, V.P.; Luo, M.; Xie, Z.H. Summer extreme precipitation in eastern China: Mechanisms and impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2766–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, G.R.; Bell, T.L.; Cahalan, R.F.; Moeng, F.J. Sampling Errors in the Estimation of Empirical Orthogonal Functions. Mon. Weather Review 1982, 110, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.X.; Xiao, T.G.; Jin, R.H. Analysis of Time and Space and Circulation Characteristics of EAP Teleconnection Patterns in the Northern Hemisphere in Summer. J. Chengdu Univ. Inf. Technol. 2018, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhai, P.; Liao, Z.; Li, L. Persistent precipitation extremes in the Yangtze River Valley prolonged by opportune configuration among atmospheric teleconnections. Quart. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 2603–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, X. Reintensification of the Anomalous Western North Pacific Anticyclone during the El Nio Modoki Decaying Summer: Relative Importance of Tropical Atlantic and Pacific SST Anomalies. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 3271–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Su, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wen, Q.; Feng, G. Thermodynamic and dynamic effects of increased moisture sources over the tropical indian ocean in recent decades. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 7081–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, K.C.; Barnes, E.A.; Maloney, E.D. Prediction of the midlatitude response to strong Madden-Julian Oscillation events on S2S time scales. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitart, F.; Robertson, A.W. The sub-seasonal to seasonal prediction project (S2S) and the prediction of extreme events. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, G.; Tong, M. The Intraseasonal Variations of the Leading Mode of Summer Precipitation Anomalies in Meiyu Area of East Asia. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020217
Jia Z, Zheng Z, Feng G, Tong M. The Intraseasonal Variations of the Leading Mode of Summer Precipitation Anomalies in Meiyu Area of East Asia. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(2):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020217
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Zikang, Zhihai Zheng, Guolin Feng, and Mingjun Tong. 2022. "The Intraseasonal Variations of the Leading Mode of Summer Precipitation Anomalies in Meiyu Area of East Asia" Atmosphere 13, no. 2: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020217
APA StyleJia, Z., Zheng, Z., Feng, G., & Tong, M. (2022). The Intraseasonal Variations of the Leading Mode of Summer Precipitation Anomalies in Meiyu Area of East Asia. Atmosphere, 13(2), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020217





