Error Characteristics of GNSS Derived TEC
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. GNSS Observation
2.2. Algorithm
2.2.1. STEC Measurement and Arc Bias
2.2.2. The Ionosphere Model
2.2.3. Matrix Equations Construction
2.2.4. Solution of the Matrix Equations
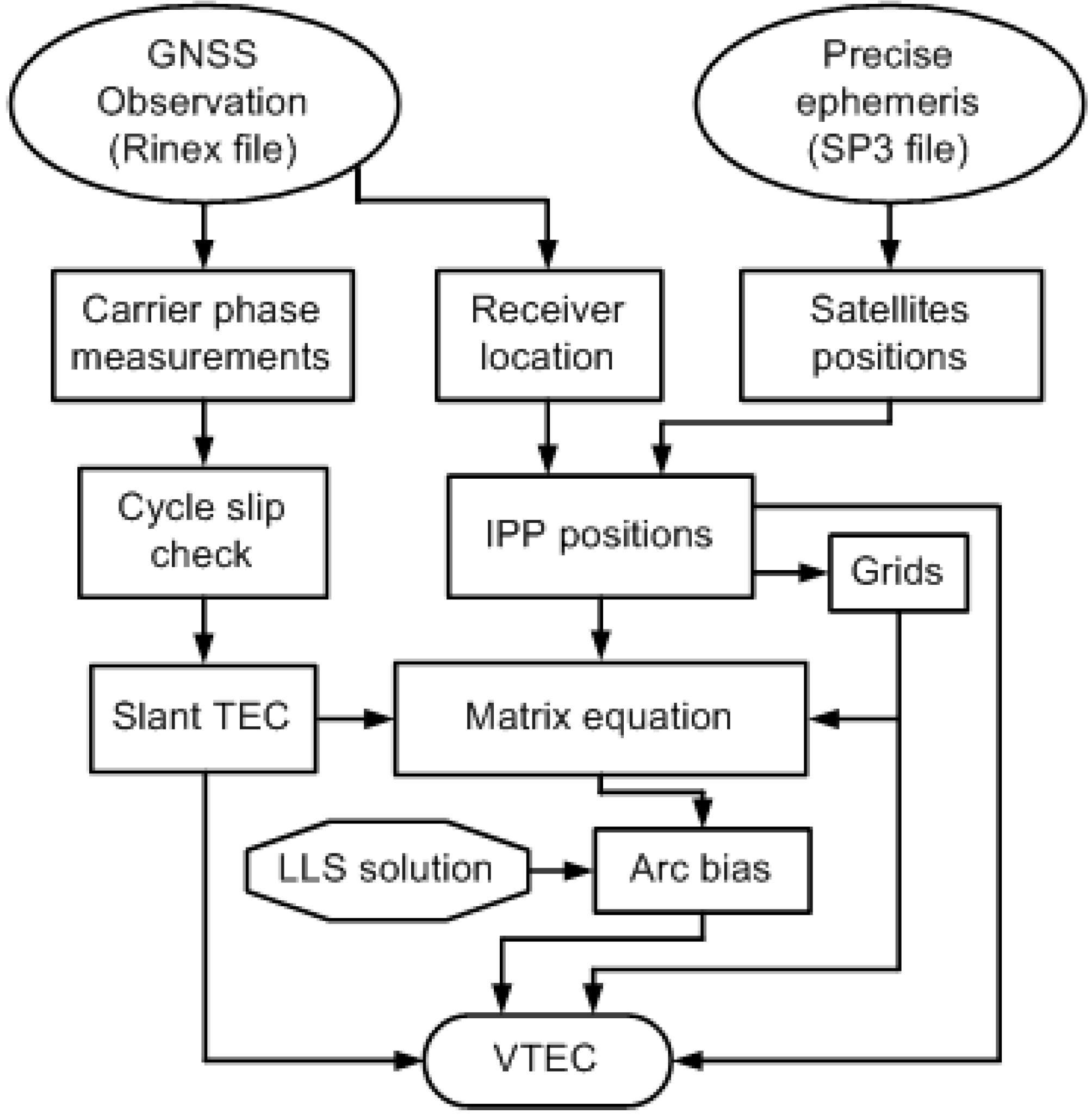
2.2.5. Program Flowchart
2.3. Error Analysis Method
2.3.1. Error Estimation
2.3.2. Statistical Characteristics
3. Results
3.1. Derived VTEC
3.2. Error Analysis
3.2.1. Measurement Error
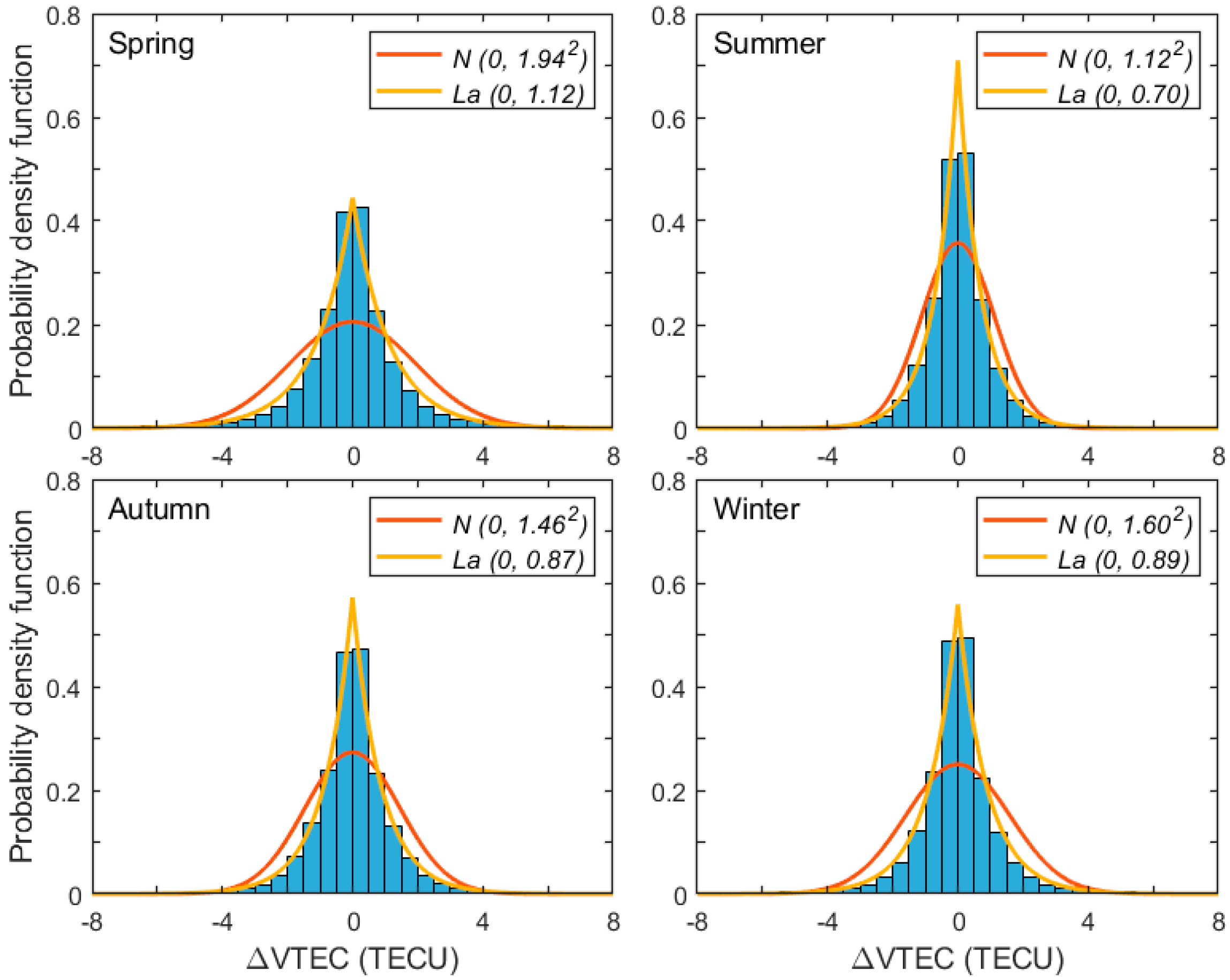
3.2.2. Error of the Derived TEC
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lanyi, G.E.; Roth, T. A comparison of mapped and measured total ionospheric electron content using Global Positioning System and beacon satellites observations. Radio Sci. 1988, 23, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, A.J.; Wilson, B.D.; Yuan, D.J.; Ho, C.H.; Lindqwister, U.J.; Runge, T.F. A global mapping technique for GPSderived ionospheric electron content measurements. Radio Sci. 1998, 33, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J. New approaches in global ionospheric determination using ground GPS data. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 1999, 61, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Saito, A.; Tsugawa, T.; Fukao, S.; Miyazaki, S. A new technique for mapping of total electron content using GPS network in Japan. Earth Planets Space 2002, 54, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunini, C.; Meza, A.; Azpilicueta, F.; Van Zele, M.A.; Gende, M.; Diaz, A. A New Ionosphere Monitoring Technology Based on GPS. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2004, 290, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, F.; Nayir, H.; Sezen, U.; Arikan, O. Estimation of single station interfrequency receiver bias using GPS-TEC. Radio Sci. 2008, 43, RS4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Shi, L.Q.; Hao, Y.Q.; Xiao, Z. Accuracy analysis of the GPS instrumental bias estimated from observations in middle and low latitudes. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, B.K.; Park, J.U.; Roh, K.M.; Lee, S.J. Comparison of GPS receiver DCB estimation methods using a GPS network. Earth Planets Space 2013, 65, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, R.S.; Kumar, S.; Jayachandran, P.T. Receiver DCB estimation and GPS vTEC study at a low latitude station in the South Pacific. J. Atmos. Sol. -Terr. Phys. 2016, 149, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Maruyama, T. Derivation of TEC and estimation of instrumental biases from GEONET in Japan. Ann. Geophys. 2003, 21, 2083–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J.; Orus, R.; Garcia-Rigo, A.; Feltens, J.; Komjathy, A.; Schaer, S.C.; Krankowski, A. The IGS VTEC maps: A reliable source of ionospheric information since 1998. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.M.; Schuh, H.; Todorova, S.; Schmidt, M. Global ionosphere maps of VTEC from GNSS, satellite altimetry, and Formosat-3/COSMIC data. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma-Dollase, D.; Hernández-Pajares, M.; Krankowski, A.; Kotulak, K.; Ghoddousi-Fard, R.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Shi, C.; Wang, C.; et al. Consistency of seven different gnss global ionospheric mapping techniques during one solar cycle. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A.; Wielgosz, P. Carrier phase bias estimation of geometry-free linear combination of GNSS signals for ionospheric TEC modeling. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Ma, G.; Maruyama, T.; Li, J.; Wan, Q.; Wang, X.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J. High-precision VTEC derivation with GEONET. Earth Planets Space 2000, 72, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtarov, P.; Pancheva, D.; Andonov, B.; Pashova, L. Global TEC maps based on GNNS data: 2. Model evaluation. J. Geophys. Res.-Space phys. 2013, 118, 4609–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, D.A. Long-tailed distributions for position errors in navigation. Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraci, M.; Borja, M.C. Notebook: The Laplace distribution. Significance 2018, 15, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewitt, G. An automatic editing algorithm for GPS data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes in Fortran 77; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992; pp. 670–673. [Google Scholar]
- Lay, D.C.; Lay, S.R.; McDonald, J.J. Linear Algebra and Its Applications; Pearson: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.R. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?—Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2014, 7, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Q.; Ma, G.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Maruyama, T.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J. Performance evaluation of IRI-2016 with GPS-derived TEC at the meridian of 110° E in China of 2014. J. Atmos. Sol. -Terr. Phys. 2020, 201, 105206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

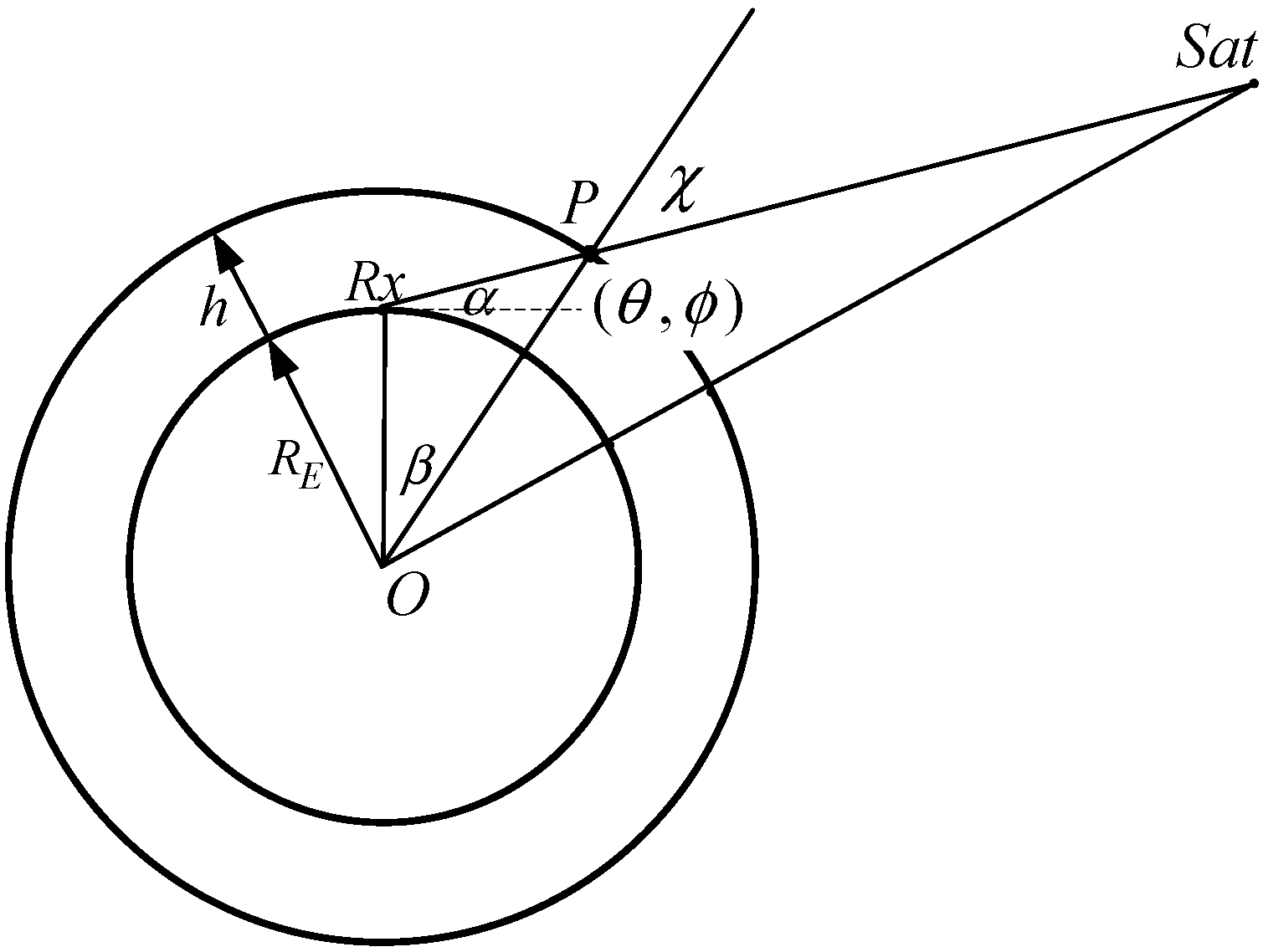

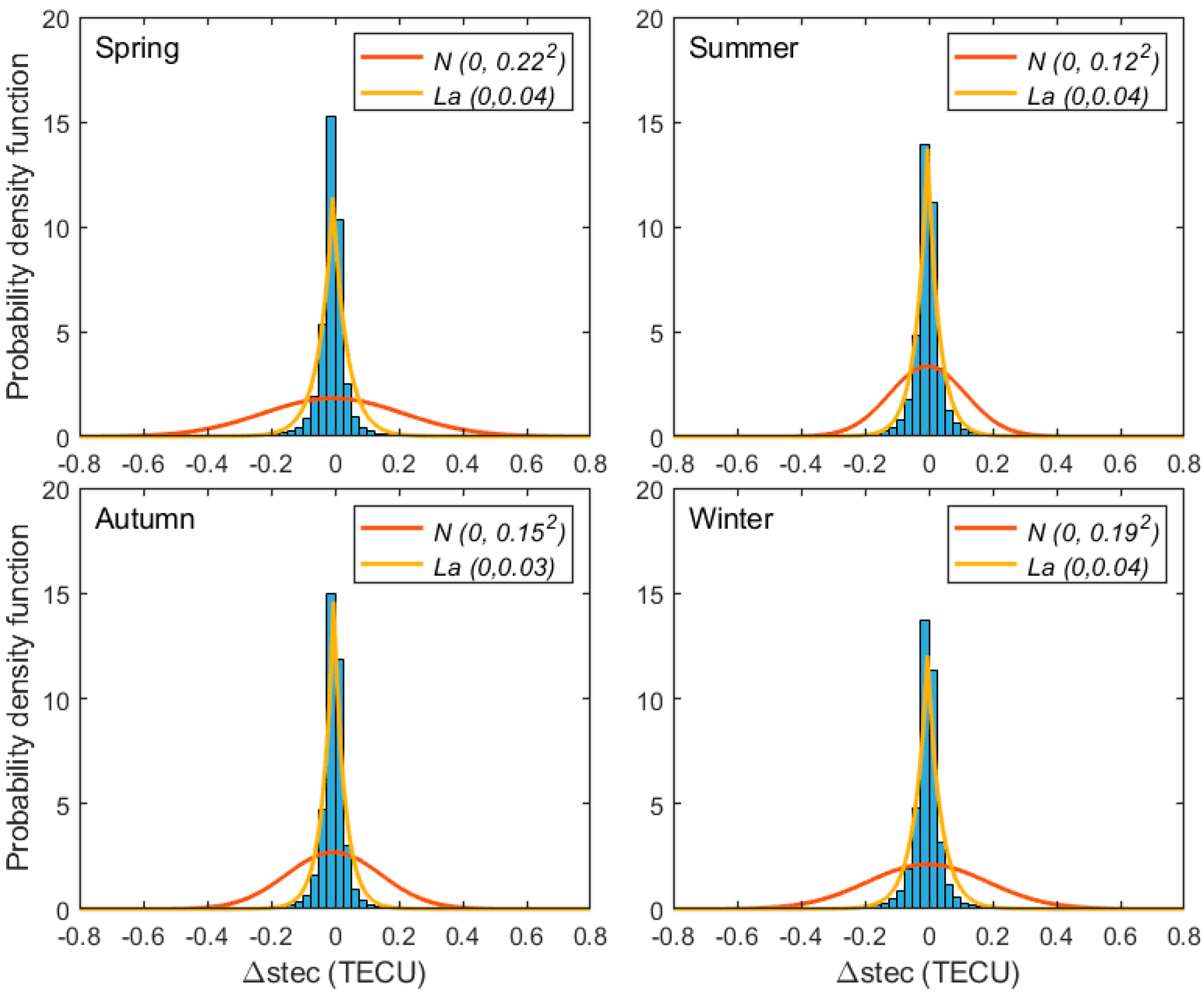
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (TECU) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| (TECU) | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| (TECU) | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.19 |
| 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.20 | 0.21 |
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80.7 | 74.8 | 77.1 | 77.9 | |
| 92.4 | 90.0 | 91.6 | 91.6 | |
| 95.7 | 94.8 | 95.6 | 95.6 | |
| 97.8 | 95.6 | 97.5 | 97.7 | |
| 99.1 | 98.6 | 99.0 | 99.1 | |
| 99.3 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 99.4 |
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (TECU) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| (TECU) | 1.12 | 0.70 | 0.87 | 0.89 |
| (TECU) | 1.94 | 1.12 | 1.46 | 1.60 |
| 0.58 | 0.63 | 0.60 | 0.56 |
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68.93 | 64.72 | 65.63 | 66.74 | |
| 87.85 | 87.62 | 87.92 | 87.82 | |
| 93.70 | 95.15 | 95.08 | 94.49 | |
| 84.8 | 80.9 | 83.0 | 85.7 | |
| 95.1 | 95.8 | 96.1 | 95.7 | |
| 97.8 | 98.5 | 98.4 | 98.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, G.; Fan, J.; Wan, Q.; Li, J. Error Characteristics of GNSS Derived TEC. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020237
Ma G, Fan J, Wan Q, Li J. Error Characteristics of GNSS Derived TEC. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(2):237. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020237
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Guanyi, Jiangtao Fan, Qingtao Wan, and Jinghua Li. 2022. "Error Characteristics of GNSS Derived TEC" Atmosphere 13, no. 2: 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020237
APA StyleMa, G., Fan, J., Wan, Q., & Li, J. (2022). Error Characteristics of GNSS Derived TEC. Atmosphere, 13(2), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020237






