Behavior of Selenium during Chemical-Looping Gasification of Coal Using Copper-Based Oxygen Carrier
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Coal Samples and Oxygen Carriers
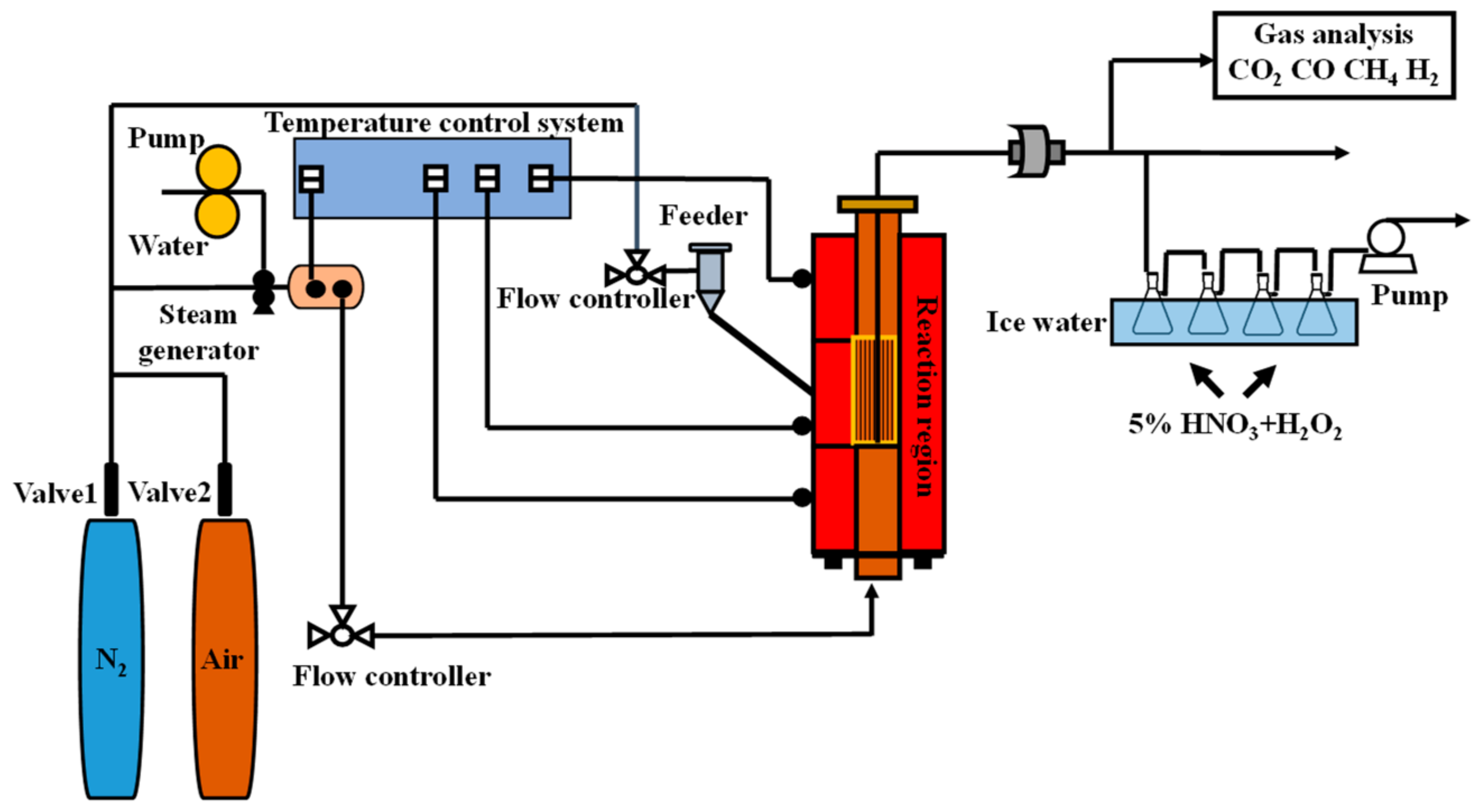
2.2. Experimental Conditions and Methods
2.3. Analysis of Selenium
2.4. Thermodynamic Simulation
2.5. Data Calculation
2.5.1. Selenium Mass Balance
2.5.2. The Indexes of CLG Performance
3. Results and Discussion
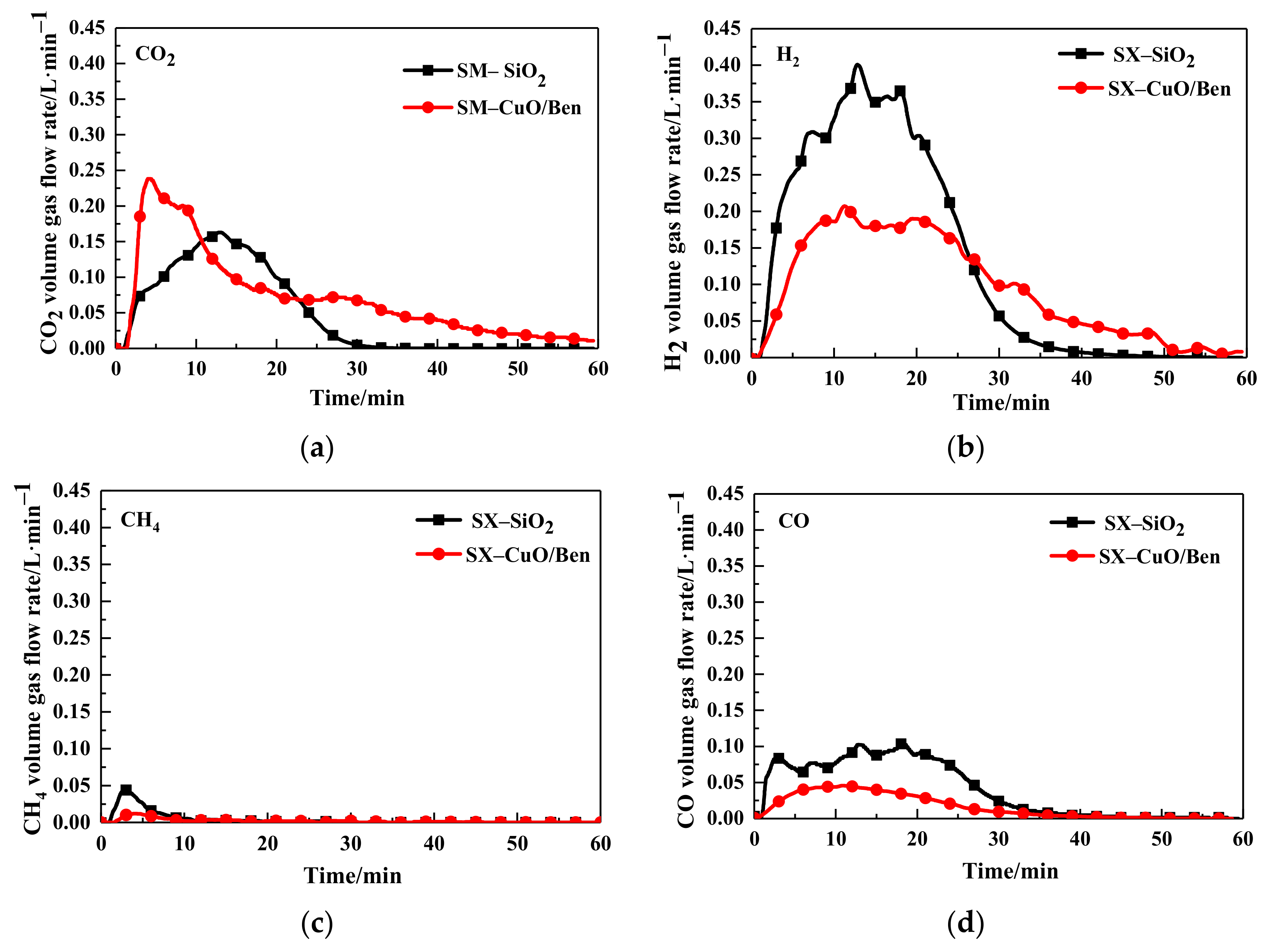
3.1. Gasification Characteristics
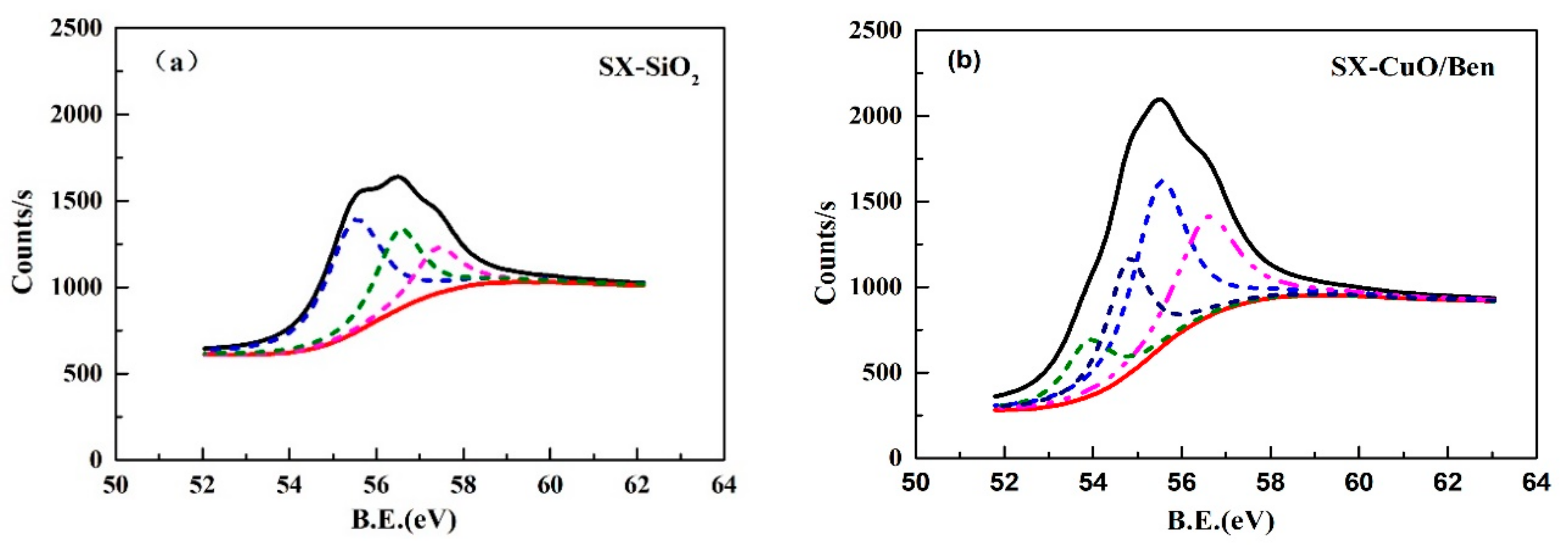
3.2. Morphology of Selenium in CLG
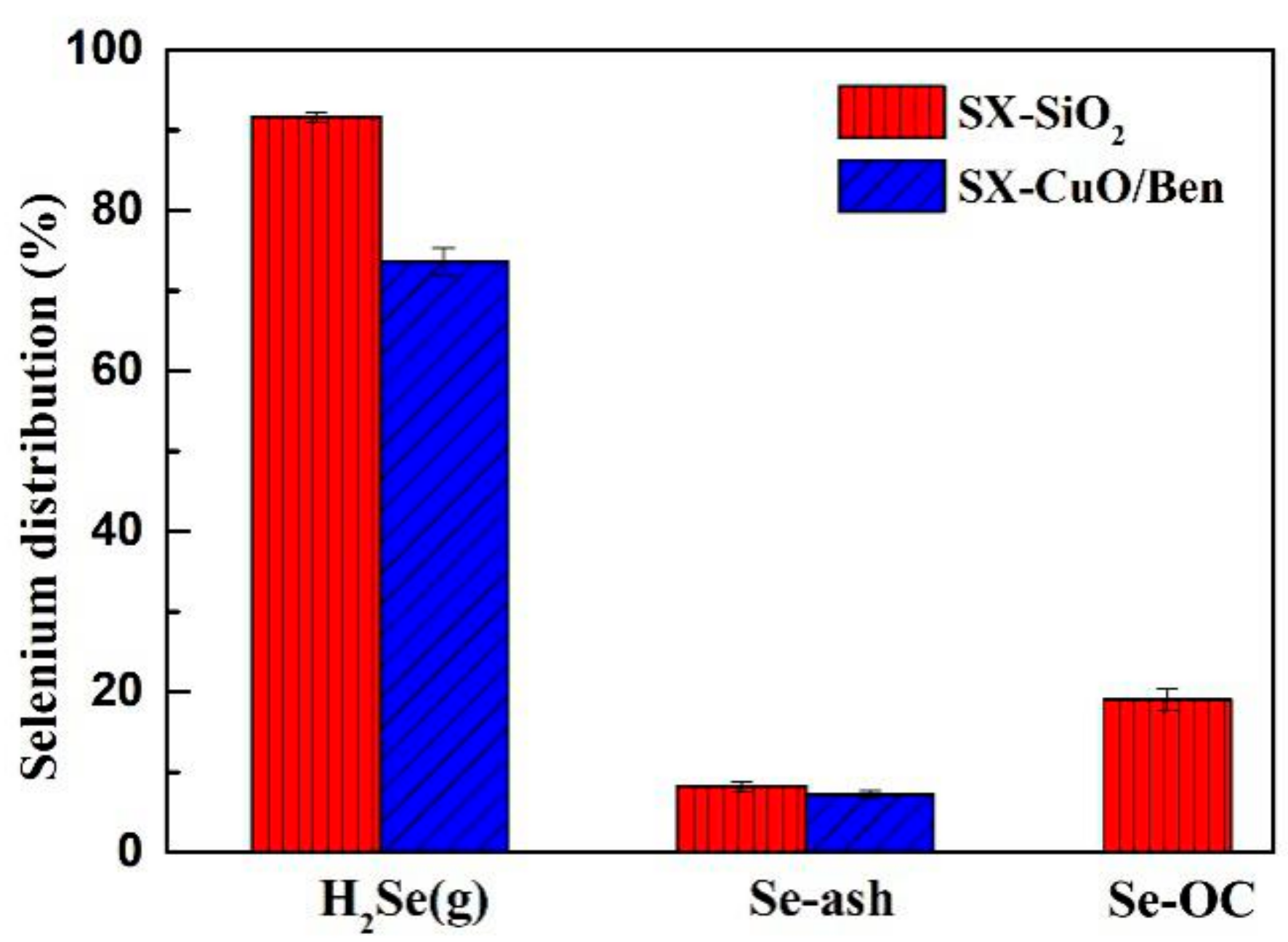
3.2.1. Selenium Distribution
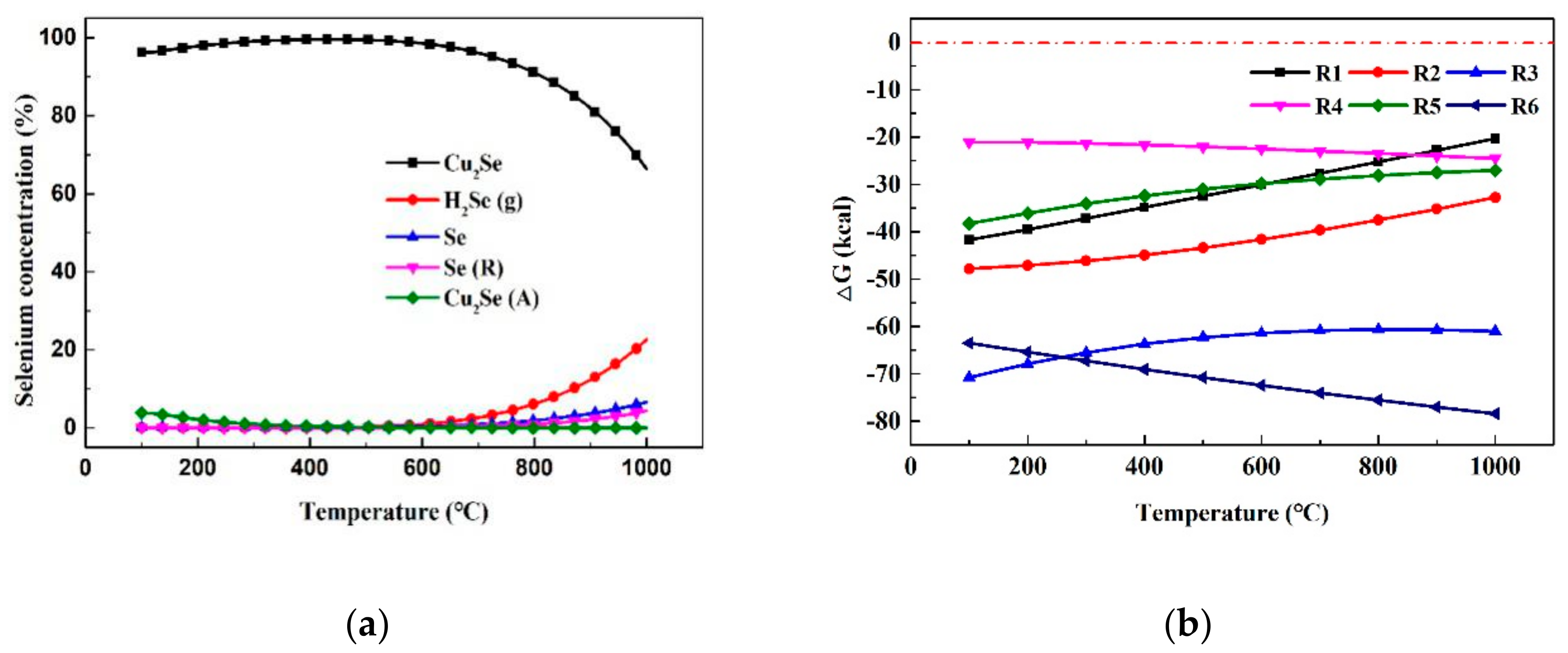
3.2.2. Thermodynamic Calculations
3.3. Effects of Experimental Conditions on the Behavior of Selenium
3.3.1. The Effects of Oxygen Carriers
3.3.2. The Influence of Coal Types
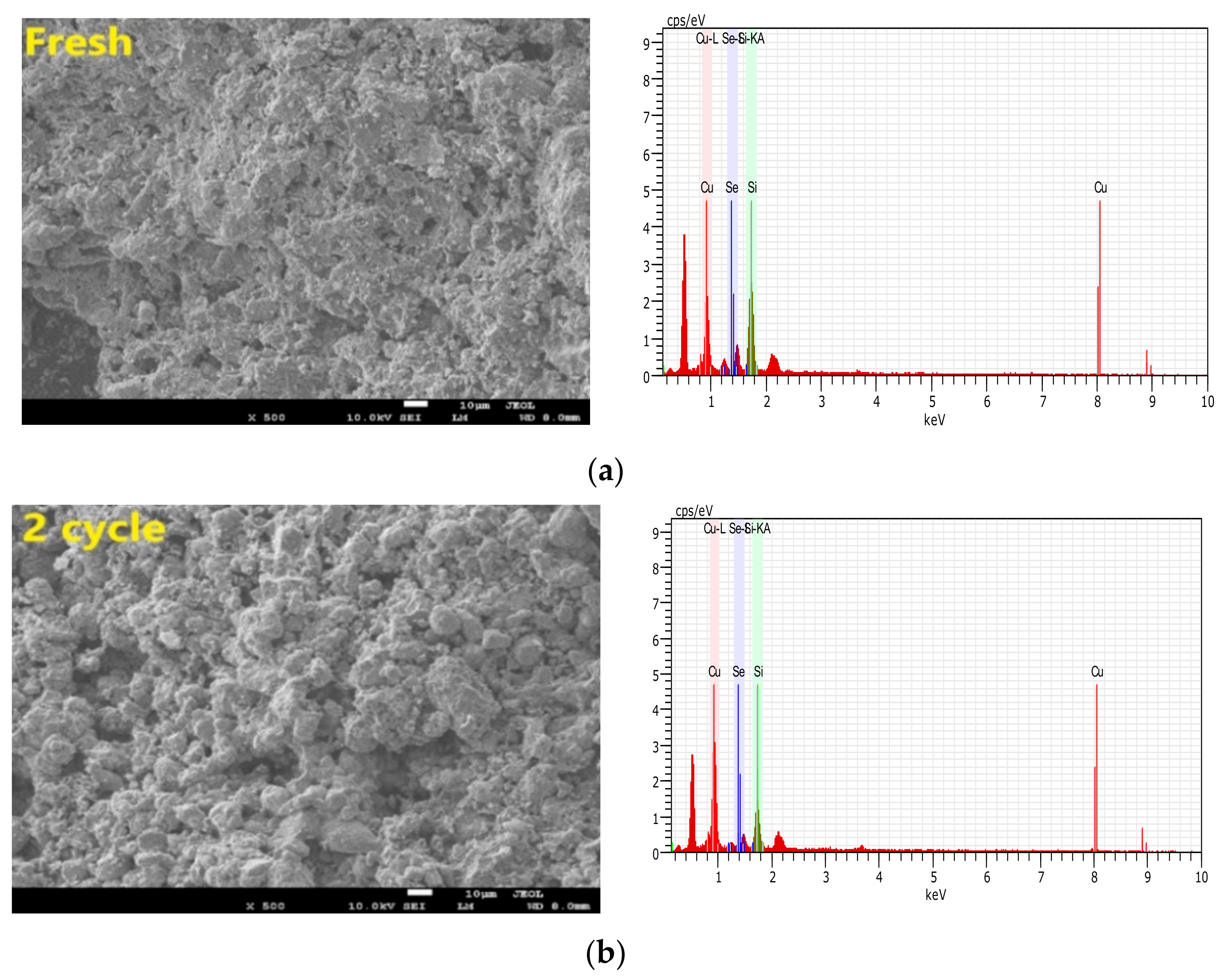
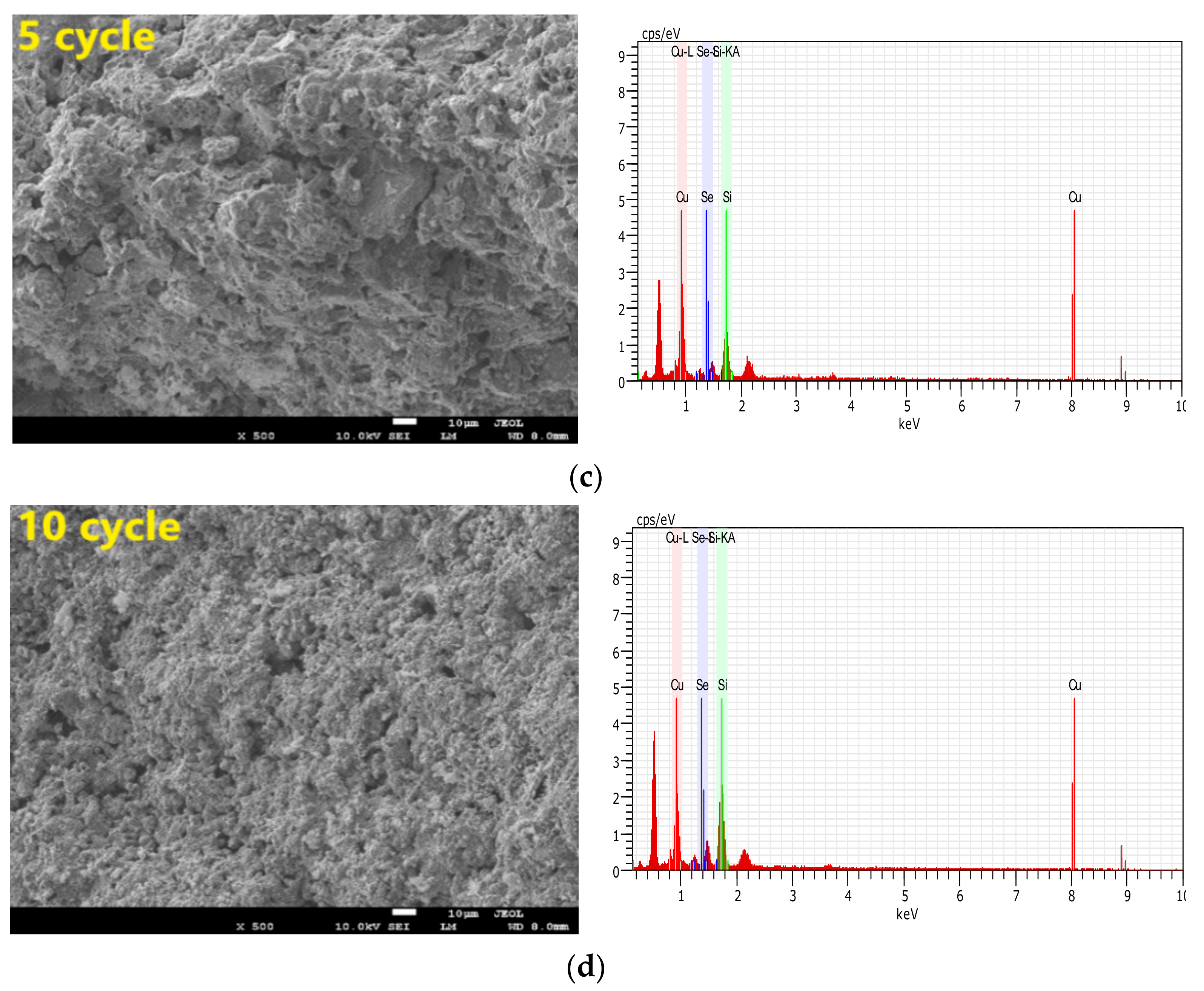
3.3.3. Recycle and Regeneration Performance
4. Conclusions
- During the CLG process, the distribution of selenium in the flue gas, coal ash and OCs is 73.65%, 7.28% and 19.07%, respectively. The CuO/Ben oxygen carrier promoted the transformation of the gaseous selenium to particulate selenium.
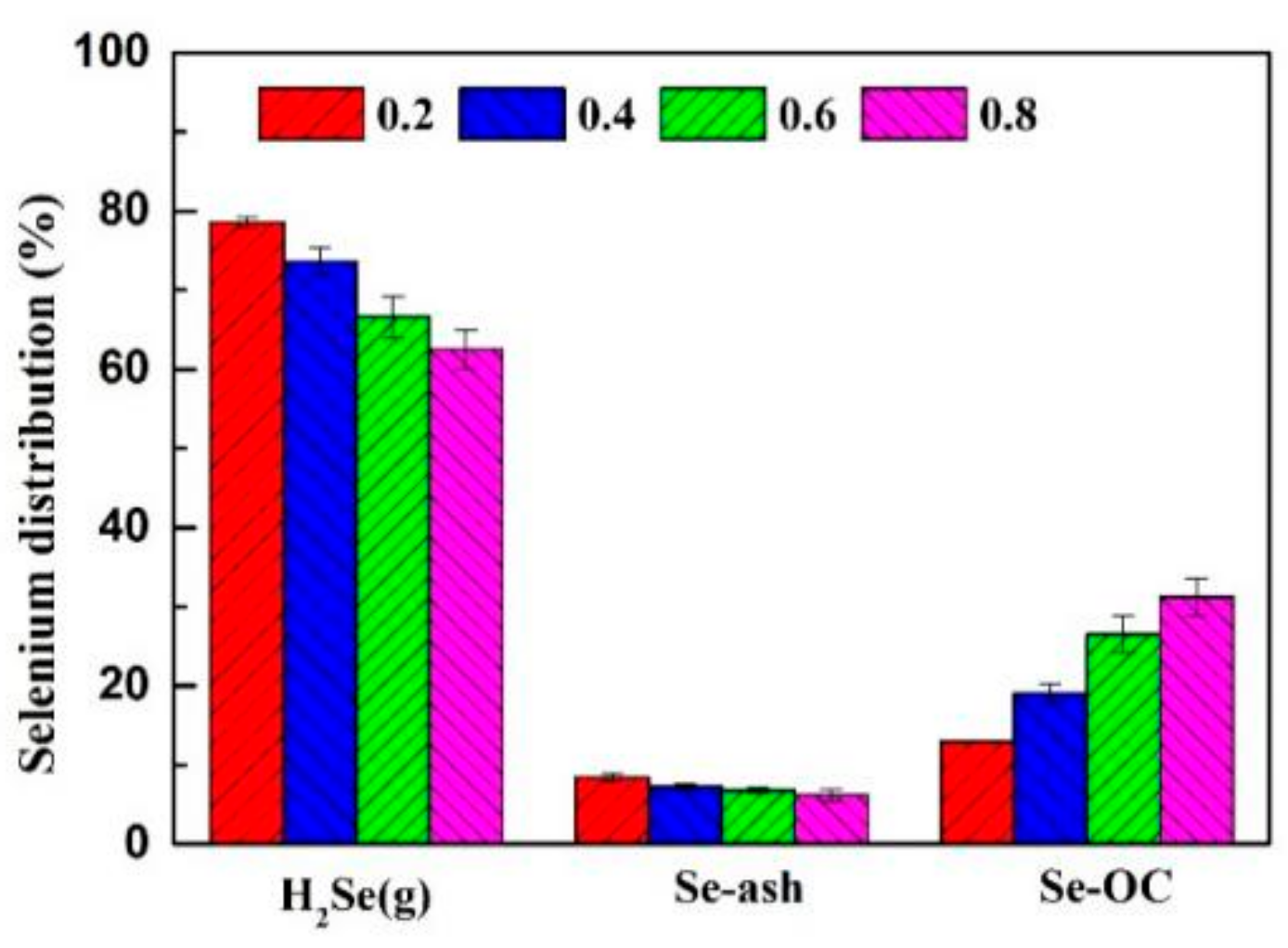
- As the oxygen–carbon ratio increased from 0.2 to 0.8, the content of H2Se (g) decreased from 78.62% to 62.53%, and the content of selenium in the oxygen carrier increased from 12.96% to 31.26%, indicating that the oxygen–carbon ratio increase improved the conversion ability of H2Se (g) to Cu2Se. The behavior of selenium during CLG is generally suitable to SX, NX, NM coals.
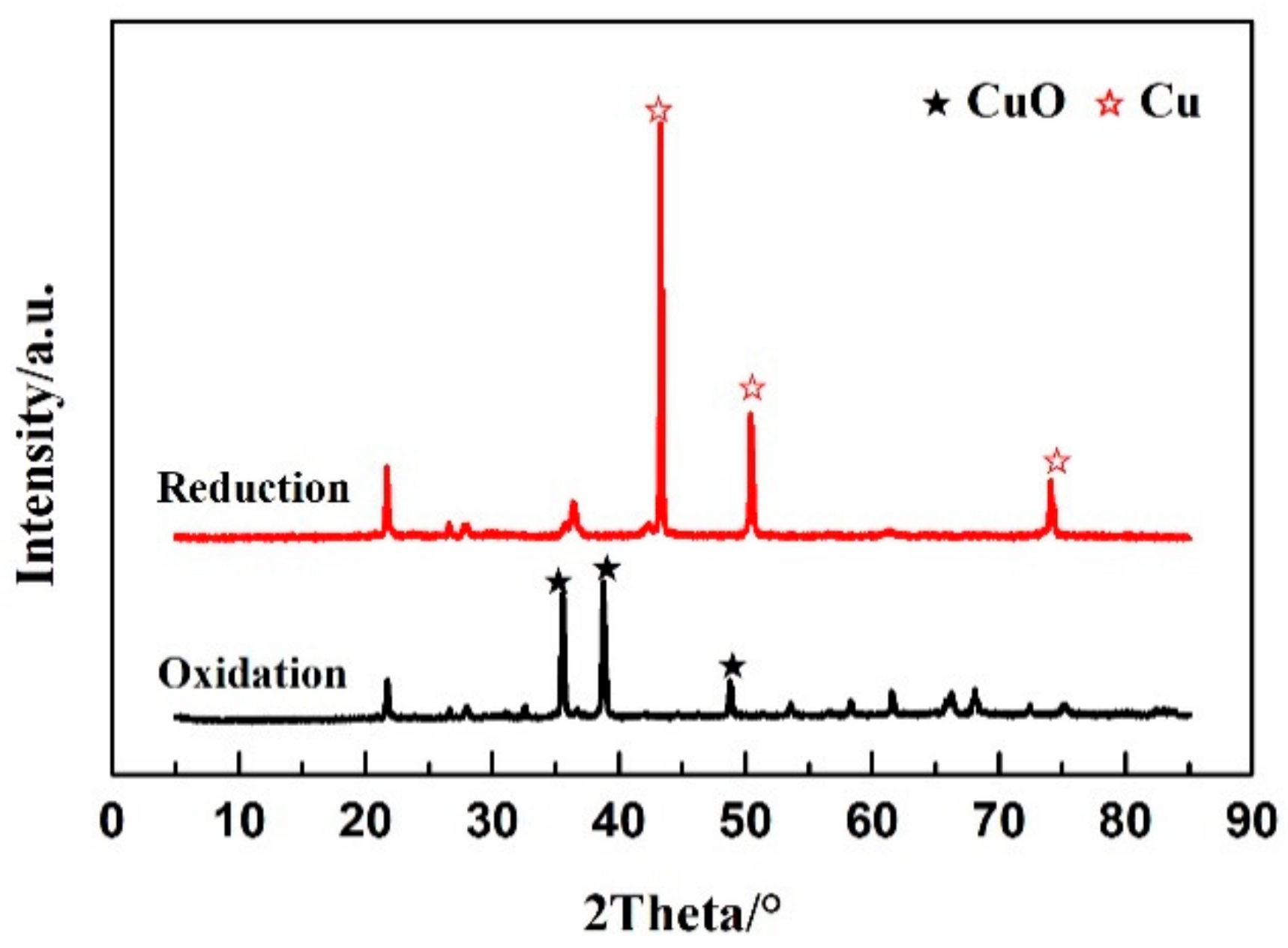
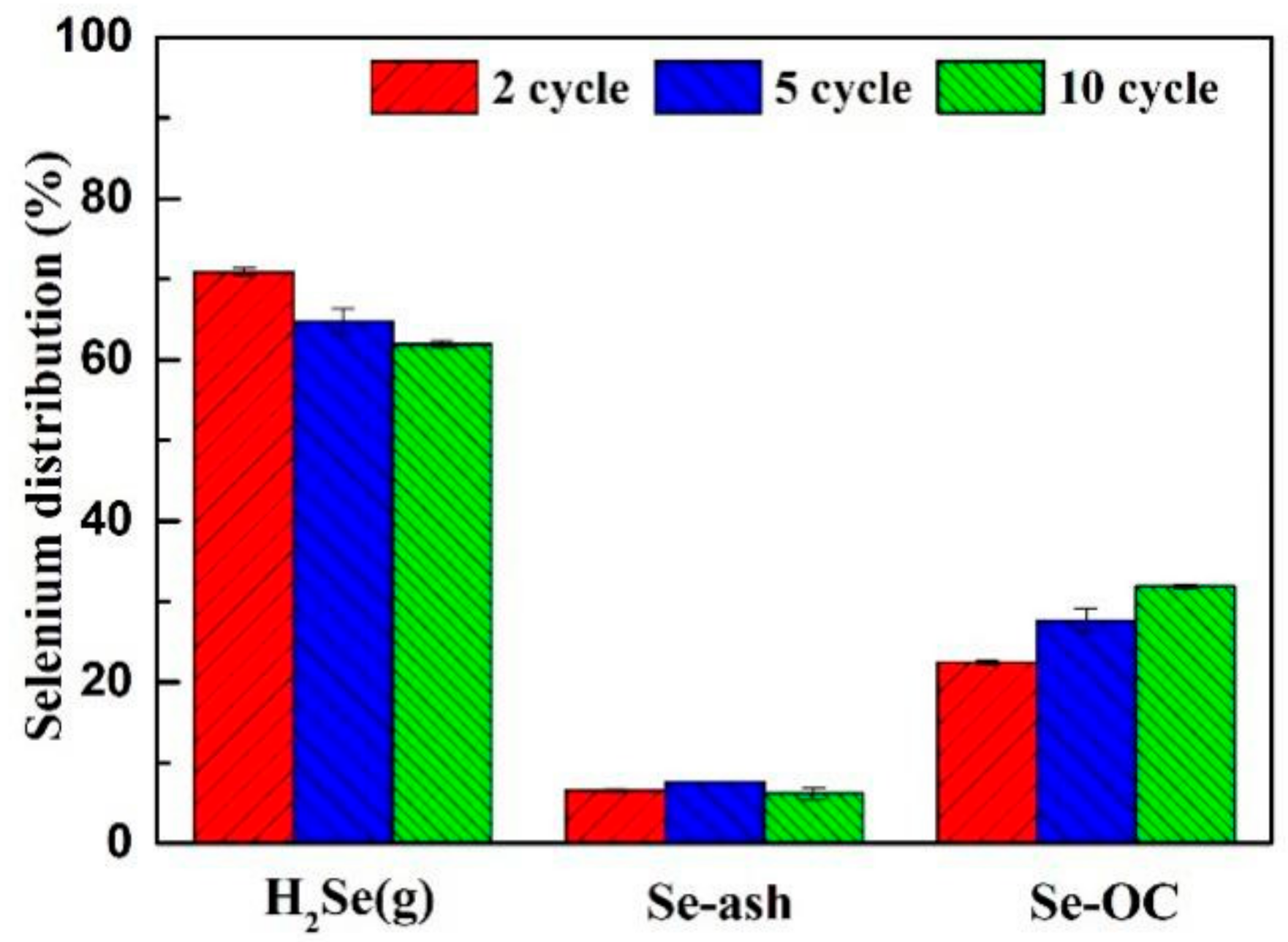
- By acquisition of lattice oxygen and the thermal decomposition of selenium, the reduced CuO/Ben OCs were regenerated in an air reactor. With the regeneration cycles increased to 10 times, the capacity of the CuO/Ben OCs to capture selenium was strengthened slightly.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Q.J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Jia, W.H.; Ryu, H.J. Coal chemical looping gasification for syngas generation using an iron-based oxygen carrier. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 53, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.J.; Hu, X.D.; Liu, Y.Z.; Jia, W.H.; Yang, M.M.; Wu, M.; Tian, H.J.; Ryu, H.J. Coal chemical-looping gasification of Ca-based oxygen carriers decorated by CaO. Powder Technol. 2015, 275, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Yu, Q.B. Thermodynamic analysis of hydrogen-enriched syngas generation coupled with in situ CO2 capture using chemical looping gasification method. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 131, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Jia, W.H.; Guo, Q.J.; Ryu, H.J. Effect of gasifying medium on the coal chemical looping gasification with CaSO4 as oxygen carrier. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 22, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Means, N.; Shekhawat, D.; Berry, D.; Massoudi, M. Chemical-looping combustion and gasification of coals and oxygen carrier development: A brief review. Energies 2015, 8, 10605–10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pishahang, M.; Larring, Y.; Adánez, J.; Gayán, P.; Sunding, M. Fe2O3-Al2O3 oxygen carrier materials for chemical looping combustion, a redox thermodynamic and thermogravimetric evaluation in the presence of H2S. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 134, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Wang, X.Y.; Hua, X.N.; Zhao, C.C.; Wang, W. The reduction mechanism and kinetics of Fe2O3 by hydrogen for chemical-looping hydrogen generation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 129, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.C.; Xu, W.T.; Liu, K.; Song, Q. Transformation of selenium during coal thermal conversion: Effects of atmosphere and inorganic content. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 205, 106446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G. Relevance, essentiality and toxicity of trace elements in human health. Mol. Asp. Med. 2005, 26, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkel, L.H.E.; Johnson, C.A.; Lenz, M.; Grundl, T.; Leupin, O.X.; Amini, M.; Charlet, L. Environmental selenium research: From microscopic processes to global understanding. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Sun, Y.N.; Yan, B.B.; Yang, R.L.; Liu, B.; Cheng, Z.J.; Ma, W.C. Distribution of trace elements during coal gasification: The effect of upgrading method. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Luo, K.L. Geochemical valuation and intake of F, As, and Se in coal wastes contaminated areas and their potential impacts on local inhabitants, Shaanxi China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2667–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Antón, M.A.; Díaz-Somoano, M.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Martínez-Tarazona, M.R. Retention of arsenic and selenium compounds present in coal combustion and gasification flue gases using activated carbons. Fuel. Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, C.L.; Zhang, C.; Yu, S.H.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Fang, Q.; Chen, G. Experimental and density functional theory study of the adsorption characteristics of CaO for SeO2 in simulated flue gas and the effect of CO2. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 10872–10881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Somoano, M.; Martinez-Tarazona, M.R. Retention of arsenic and selenium compounds using limestone in a coal gasification flue gas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuzono, T.; Nakajima, T.; Fujishima, H.; Takanashi, H.; Akira, O. Behavior of selenium in the flue gas of pulverized coal combustion system: Influence of kind of coal and combustion conditions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 167, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Gauthier, D.; Flamant, G.; Peraudeau, G.; Lu, J.D.; Zheng, C.G. Fate of selenium in coal combustion: Volatilization and speciation in the flue gas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1406–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.J. Temporal measurements and kinetics of selenium release during coal combustion and gasification in a fluidized bed. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Hower, J.C.; Dai, S.F.; Mardon, S.M.; Liu, G.J. Determination of chemical speciation of arsenic and selenium in high-As coal combustion ash by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: Examples from a Kentucky stoker ash. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 17637–17645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiara, T.; Izquier, M.T.; Abad, A.; Gayan, P.; Garcia-Labiano, F.; de Diego, L.F.; Adanez, J. Mercury release and speciation in chemical looping combustion of coal. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 2786–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, M.; Ma, J.J.; Guo, Q.J. Transformation and migration of mercury during chemical-Looping gasification of coal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 20481–20490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Song, N.; Zhang, Y.S.; Cao, Y.; Orndorff, W.; Pan, W.P. Mercury sorption properties of HBr-modified fly ash in a fixed bed reactor. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 124, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Gauthier, D.; Flamant, G.; Wang, Y.M. Behavior of selenium in the combustion of coal or coke spiked with Se. Combust. Flame 2004, 138, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, T.; Xu, H.; Pan, W.P. Effect of modified fly ash injection on As, Se, and Pb emissions in coal-fired power plant. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Sun, X.Q.; Gao, M.G.; Ma, J.J.; Guo, Q.J. Transformation and migration of cadmium during chemical-looping combustion/gasification of municipal solid waste. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 365, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.C.; Mei, D.F.; Tian, X.; Zhang, S.B.; Yang, J.P.; Wang, C.Q.; Chen, G.P.; Zhao, Y.C.; Zheng, C.G.; Zhao, H.B. Fate of mercury in volatiles and char during in situ gasification chemical-looping combustion of coal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7887–7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.C.; Wang, C.Q.; Zhao, H.B.; Tian, X. Sulfur fate during the lignite pyrolysis process in a chemical looping combustion environment. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 4493–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.S.; Li, W.H.; Orndorff, W.; Cao, Y.; Pan, W.P. Partitioning effect of mercury content and speciation in gypsum slurry as a function of time. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 119, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Shen, L.H. Release and transformation of phosphorus in chemical looping combustion of sewage sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasah, J.; Jensen, B.; Dyrstad-Cincotta, N.; Gerber, J.; Laudal, D.; Mann, M.; Srinivasachar, S. Method for separation of coal conversion products from oxygen carriers. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2019, 88, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monazam, E.R.; Breault, Q.W.; Siriwardane, R.; Tian, H.J.; Simonyi, T.; Carpenter, S. Effect of carbon deposition on the oxidation rate of copper/bentonite in the chemical looping process. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6576–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, E.; Yılmaz, D.; Leion, H. Experimental and thermodynamic study on the interaction of copper oxygen carriers and oxide compounds commonly present in ashes. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 2502–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, Y.D.; Liu, W.Q. Evaluating redox reactivity of CuO-based oxygen carriers synthesized with organometallic precursors. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, T.T.; Jin, X.Y.; Hu, Z.Q.; Liu, S.M.; Xiao, B.; Chen, Z.H.; Hu, M. CuO supported on olivine as an oxygen carrier in chemical looping processes with pine sawdust used as fuel. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.J.; Liu, Y.Z.; Jia, W.H.; Yang, M.M.; Hu, X.D.; Ryu, H.J. Performance of Ca-Based oxygen carriers decorated by K2CO3 or Fe2O3 for coal chemical looping combustion. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7053–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 17211:2015; Stationary Source Emissions—Sampling and Determination of Selenium Compounds in Flue Gas. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Alexander, V.N.; Anna, K.V.; Stephen, W.G.; Cedric, J. Distributed by the Measurement Services Division of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Material Measurement Laboratory (MML); Material Measurement Laboratory: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.T.; Chen, H.; Zhang, K.Y.; Qin, A.M.; Chen, S.P. Room-temperature rapid synthesis of Cu2Sex and its phase transformation to CuO by electrochemical method. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 797, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Proximate Analysis wt/% | Ultimate Analysis wt/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Aad | Vad | FCad | Cad | Had | Nad | Sad | Oad | Se(μg/g) | |
| SX | 7.14 | 5.84 | 29.71 | 57.31 | 69.08 | 7.17 | 0.76 | 0.3 | 14.03 | 0.36 |
| NX | 5.18 | 4.56 | 26.95 | 63.31 | 77.6 | 5.16 | 1.46 | 0.46 | 10.77 | 0.19 |
| NM | 11.52 | 5.07 | 27.26 | 56.15 | 74.08 | 4.91 | 0.7 | 0.02 | 14.29 | 0.17 |
| Sample | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SX ash | 51.43 | 11.73 | 22.09 | 8.91 | 5.03 | 2.35 | 0.44 |
| NX ash | 47.87 | 13.62 | 18.86 | 7.19 | 7.73 | 2.84 | 0.55 |
| NM ash | 62.86 | 8.16 | 20.96 | 9.00 | 7.12 | 0.97 | 0.15 |
| Sample | Yi (%) | Gsyn (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CO | H2 | CH4 | ||
| SX/SiO2 | 20.85 | 18.02 | 59.44 | 1.69 | 0.82 |
| SX/(CuO/Ben) | 39.39 | 8.62 | 51.01 | 0.98 | 0.61 |
| Sample | Cu2Se (%) | Se (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 53.90 eV | 55.5 eV | 56.5 eV | 57.4 eV | 54.7 eV | |
| SX-SiO2 | - | 52.68 | 29.89 | 17.43 | - |
| SX-CuO/Ben | 12.03 | 33.57 | 27.30 | - | 27.1 |
| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh | 0.578 | 0.121 |
| 2 Cycles | 0.668 | 0.130 |
| 5 Cycles | 1.233 | 0.143 |
| 10 Cycles | 1.809 | 0.168 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Hu, J.; Kang, H.; Han, Z.; Guo, Q. Behavior of Selenium during Chemical-Looping Gasification of Coal Using Copper-Based Oxygen Carrier. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040547
Ma J, Hu J, Kang H, Han Z, Guo Q. Behavior of Selenium during Chemical-Looping Gasification of Coal Using Copper-Based Oxygen Carrier. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(4):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040547
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jingjing, Jiameng Hu, Huifen Kang, Ziheng Han, and Qingjie Guo. 2022. "Behavior of Selenium during Chemical-Looping Gasification of Coal Using Copper-Based Oxygen Carrier" Atmosphere 13, no. 4: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040547
APA StyleMa, J., Hu, J., Kang, H., Han, Z., & Guo, Q. (2022). Behavior of Selenium during Chemical-Looping Gasification of Coal Using Copper-Based Oxygen Carrier. Atmosphere, 13(4), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040547





