Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Mercury Exposure via Indoor and Outdoor Household Dust in Three Iranian Cities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
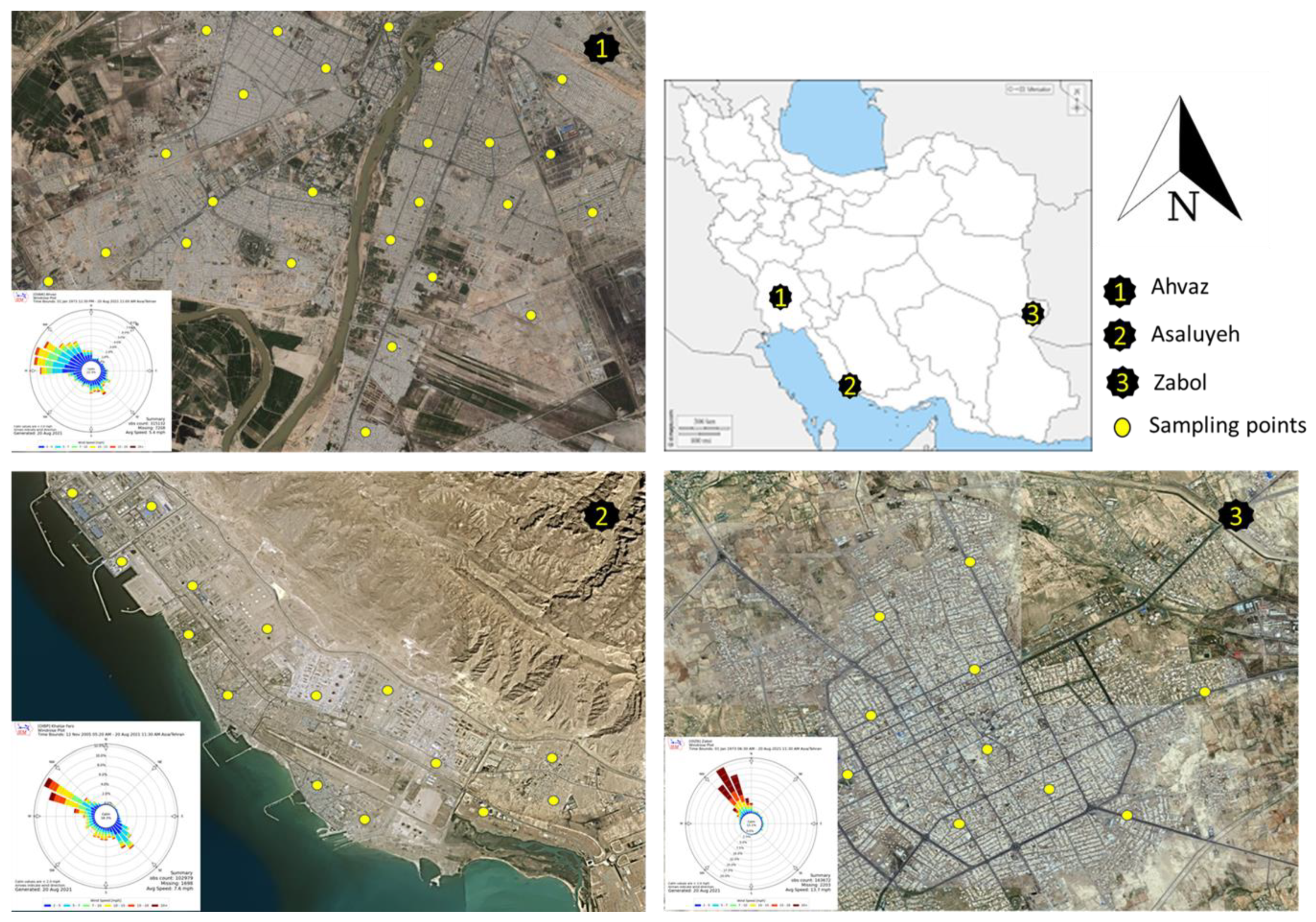
2. Study Areas
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
3.2. Analytical Procedures
3.3. Statistical Analysis
- CF < 1 low contamination;
- 1 ≤ CF < 3 moderate contamination;
- 3 ≤ CF < 6 considerable contamination;
- CF ≥ 6 very high contamination.
3.4. Human Health Risk Assessment
3.4.1. Exposure Assessment
3.4.2. Non-Carcinogenic Risk Assessment
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Total Concentration of PBM in Urban Dust
4.2. Degree of Contamination by PBM
4.3. Non-Carcinogenic Health Risk Assessment
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manalis, N.; Grivas, G.; Protonotarios, V.; Moutsatsou, A.; Samara, C.; Chaloulakou, A. Toxic metal content of particulate matter (PM10), within the Greater Area of Athens. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihankhah, T.; Saeedi, M.; Karbassi, A. A comparative study of elemental pollution and health risk assessment in urban dust of different land-uses in Tehran’s urban area. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 124984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, A.; Bautista, F.; Gutiérrez-Ruiz, M.; Ceniceros-Gómez, A.E.; Cejudo, R.; Goguitchaichvili, A. Heavy metal pollution of street dust in the largest city of Mexico, sources and health risk assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, T.; Lian, H.; Ding, Z. Bioaccessibility and health risk of arsenic, mercury and other metals in urban street dusts from a mega-city, Nanjing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, S.K.; Kamber, B.S.; McGowan, H.A. Scavenging of atmospheric trace metal pollutants by mineral dusts: Inter-regional transport of Australian trace metal pollution to New Zealand. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2460–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, S.; Moore, F.; Vasiluk, L.; Hale, B.A. The geochemical fingerprinting of geogenic particles in road deposited dust from Tehran metropolis, Iran: Implications for provenance tracking. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 190, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.U.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Ullah, H.; Abbas, Q.; Munir, M.A.M. A systematic review on global pollution status of particulate matter-associated potential toxic elements and health perspectives in urban environment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1131–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, N.; Yubero, E.; Nicolás, J.; Varea, M.; Crespo, J. Characterization of metals in PM1 and PM10 and health risk evaluation at an urban site in the western Mediterranean. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavani, A.; Tobías, A.; Querol, X.; Stafoggia, M.; Abdolshahnejad, M.; Mayvaneh, F.; Guo, Y.; Hadei, M.; Hashemi, S.S.; Khosravi, A. Short-term effects of particulate matter during desert and non-desert dust days on mortality in Iran. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakor, M.; Modabberi, S.; Argyraki, A. Assessing the contamination level, sources and risk of potentially toxic elements in urban soil and dust of Iranian cities using secondary data of published literature. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 645–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N. Heavy metals pollution assessment and its associated human health risk evaluation of urban soils from Indian cities: A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morera-Gómez, Y.; Alonso-Hernández, C.M.; Santamaría, J.M.; Elustondo, D.; Lasheras, E.; Widory, D. Levels, spatial distribution, risk assessment, and sources of environmental contamination vectored by road dust in Cienfuegos (Cuba) revealed by chemical and C and N stable isotope compositions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 2184–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golia, E.; Tsiropoulos, G.; Füleky, G.; Floras, S.; Vleioras, S. Pollution assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils of different taxonomy orders in central Greece. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlak, M.; Tunçay, T.; Botsou, F. Heavy Metals in Soil and Sand from Playgrounds of Çanakkale City (Turkey), and Related Health Risks for Children. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wang, T.; Lian, H.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J. Bioaccessibility and health risk of arsenic and heavy metals (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn and Mn) in TSP and PM2.5 in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 57, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Duan, X.; Zhao, X.; Ma, J.; Dong, T.; Huang, N.; Sun, C.; He, B.; Wei, F. Health risks from the exposure of children to As, Se, Pb and other heavy metals near the largest coking plant in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarpour, A.; Watts, M.J.; Madhani, A.; Elahi, S. Source, spatial distribution and pollution assessment of Pb, Zn, Cu, and Pb, isotopes in urban soils of Ahvaz City, a semi-arid metropolis in southwest Iran. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.P.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, I.; Aherne, J.; Wentworth, G.R. Impacts and effects indicators of atmospheric deposition of major pollutants to various ecosystems-A review. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1953–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Ram, K.; Tripathee, L.; Kang, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, P.; Ghimire, P.S. Study on Mercury in PM10 at an Urban Site in the Central Indo-Gangetic Plain: Seasonal Variability and Influencing Factors. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 2729–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xia, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, F.; Guo, X. Mercury in urban soils with various types of land use in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, J. Urban environmental mercury in Changchun, a metropolitan city in Northeastern China: Source, cycle, and fate. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 330, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.D.; Yalala, B.; Cukrowska, E.; Godoi, R.H.; Potgieter-Vermaak, S. A scoping study of component-specific toxicity of mercury in urban road dusts from three international locations. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Q.; Lu, X.; Fang, F.; Wang, Y. Distribution and speciation of mercury in the peat bog of Xiaoxing’an Mountain, northeastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 124, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacyna, E.G.; Pacyna, J.; Sundseth, K.; Munthe, J.; Kindbom, K.; Wilson, S.; Steenhuisen, F.; Maxson, P. Global emission of mercury to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources in 2005 and projections to 2020. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2487–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindler, R. Estimating the natural background atmospheric deposition rate of mercury utilizing ombrotrophic bogs in southern Sweden. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP); United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Technical Background Report to the Global Atmospheric Mercury Assessment; Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme: Oslo, Norway; UNEP Chemicals Branch: Nairobi, Kenya, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kelepertzis, E.; Argyraki, A. Mercury in the urban topsoil of Athens, Greece. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4049–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, S.; Chon, H.-T. Assessment of the level of mercury contamination from some anthropogenic sources in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 147, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Mason, R.P.; Chan, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Pirrone, N. Mercury as a global pollutant: Sources, pathways, and effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4967–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.; Pereira, M.; Duarte, A.; Ajmone-Marsan, F.; Davidson, C.; Grčman, H.; Hossack, I.; Hursthouse, A.; Ljung, K.; Martini, C. Mercury in urban soils: A comparison of local spatial variability in six European cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Qin, X.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, B.; Huang, K.; Deng, C. Characteristics of particulate-bound mercury at typical sites situated on dust transport paths in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, S.a.; Stratton, W. Atmospheric mercury speciation: Concentrations and behavior of reactive gaseous mercury in ambient air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, N.; Schäfer, J.; Blanc, G.; Chen, Y.; Chai, F.; Cen, K.; Norra, S. Atmospheric particulate mercury in the megacity Beijing: Spatio-temporal variations and source apportionment. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 109, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Kang, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Rupakheti, M.; Sun, S.; Tripathee, L.; Rupakheti, D.; Panday, A.K.; Sillanpää, M. Characterizations of atmospheric particulate-bound mercury in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal, South Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, F.M.; Kraepiel, A.M.; Amyot, M. The chemical cycle and bioaccumulation of mercury. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1998, 29, 543–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, J.D.; Voldner, E.C. Modeling atmospheric concentrations of mercury and deposition to the Great Lakes. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lei, Y.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Cui, S.; Wang, Q. Chemical source profiles of urban fugitive dust PM2. 5 samples from 21 cities across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.W.; Ali, W.; Meng, B.; Abrar, M.M.; Lu, B.; Qin, C.; Zhao, L.; Feng, X. Mercury contamination status of rice cropping system in Pakistan and associated health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Mao, H.; Li, P.; Li, T.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhen, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Total gaseous mercury in a coastal city (Qingdao, China): Influence of sea-land breeze and regional transport. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 235, 117633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coufalík, P.; Zvěřina, O.; Mikuška, P.; Komárek, J. Seasonal variability of mercury contents in street dust in Brno, Czech Republic. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 93, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, T.W.; Magos, L.; Myers, G.J. The toxicology of mercury—Current exposures and clinical manifestations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ordóñez, A.; Álvarez, R.; De Miguel, E.; Charlesworth, S. Spatial and temporal variations of trace element distribution in soils and street dust of an industrial town in NW Spain: 15 years of study. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sondreal, E.A.; Benson, S.A.; Pavlish, J.H.; Ralston, N.V. An overview of air quality III: Mercury, trace elements, and particulate matter. Fuel Processing Technol. 2004, 85, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, L.Y.; Wang, L.; Lei, K.; Huang, J.; Zhai, Y. Contamination assessment of mercury and arsenic in roadway dust from Baoji, China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2489–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, S.; De Miguel, E.; Ordóñez, A. A review of the distribution of particulate trace elements in urban terrestrial environments and its application to considerations of risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2011, 33, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massey, D.D.; Kulshrestha, A.; Taneja, A. Particulate matter concentrations and their related metal toxicity in rural residential environment of semi-arid region of India. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, A.; Chen, Y.-f. Gaseous elemental mercury as an indoor air pollutant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4170–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, K.; Good, N.; Wilson, A.; Mölter, A.; Moore, B.F.; Carpenter, T.; Peel, J.L.; Volckens, J. The Fort Collins commuter study: Variability in personal exposure to air pollutants by microenvironment. Indoor Air 2019, 29, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Wang, W.; Chan, C.Y.; Cheung, K.C.; Man, Y.B.; Wang, X.; Wong, M.H. Contamination and risk assessment (based on bioaccessibility via ingestion and inhalation) of metal (loid) s in outdoor and indoor particles from urban centers of Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.U.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Abbas, Q.; Ullah, H.; Munir, M.A.M.; Zhang, H. Compositional characteristics of black-carbon and nanoparticles in air-conditioner dust from an inhabitable industrial metropolis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdenelli, M.; Cecchini, C.; Orpianesi, C.; Dadea, G.; Cresci, A. Efficacy of antimicrobial filter treatments on microbial colonization of air panel filters. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nourmoradi, H.; Khaniabadi, Y.O.; Goudarzi, G.; Daryanoosh, S.M.; Khoshgoftar, M.; Omidi, F.; Armin, H. Air quality and health risks associated with exposure to particulate matter: A cross-sectional study in Khorramabad, Iran. Health Scope 2016, 5, e31766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, S.; Khademi, H.; Ayoubi, S.; Cano, A.F.; Acosta, J.A. Seasonal and spatial variations in dust deposition rate and concentrations of dust-borne heavy metals, a case study from Isfahan, central Iran. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghtaderi, T.; Aminiyan, M.M.; Alamdar, R.; Moghtaderi, M. Index-based evaluation of pollution characteristics and health risk of potentially toxic metals in schools dust of Shiraz megacity, SW Iran. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 410–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmardeh Behrooz, R.; Kaskaoutis, D.; Grivas, G.; Mihalopoulos, N. Human health risk assessment for toxic elements in the extreme ambient dust conditions observed in Sistan, Iran. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modabberi, S.; Tashakor, M.; Soltani, N.S.; Hursthouse, A.S. Potentially toxic elements in urban soils: Source apportionment and contamination assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbasi, S.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Mahmoudi, M.R. Fractionation, source identification and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in street dust of the most important center for petrochemical products, Asaluyeh County, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarpour, A.; Ghanavati, N.; Watts, M.J. Spatial distribution and human health risk assessment of mercury in street dust resulting from various land-use in Ahvaz, Iran. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadian, M.; Behrangi, A.; Sorooshian, A. Impact of drought on dust storms: Case study over Southwest Iran. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 124029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmabadi, H.; Khalidy, R.; Saeedi, M. Transport routes and potential source regions of the Middle Eastern dust over Ahvaz during 2005–2017. Atmos. Res. 2020, 241, 104947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, N.H.; Karami, S.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Tegen, I.; Moradi, M.; Opp, C. Atmospheric dynamics and numerical simulations of six frontal dust storms in the Middle East region. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Sorooshian, A.; Goudarzi, G.; Nikfal, A.; Baneshi, M.M. Temporal profile of PM10 and associated health effects in one of the most polluted cities of the world (Ahvaz, Iran) between 2009 and 2014. Aeolian Res. 2016, 22, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goudarzi, G.; Alavi, N.; Geravandi, S.; Idani, E.; Behrooz, H.R.A.; Babaei, A.A.; Alamdari, F.A.; Dobaradaran, S.; Farhadi, M.; Mohammadi, M.J. Health risk assessment on human exposed to heavy metals in the ambient air PM10 in Ahvaz, southwest Iran. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MalAmiri, N.; Rashki, A.; Hosseinzadeh, S.R.; Kaskaoutis, D. Mineralogical, geochemical, and textural characteristics of soil and airborne samples during dust storms in Khuzestan, southwest Iran. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, N.H.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Rashki, A.; Mohammadpour, K. Long-Term Variability of Dust Events in Southwestern Iran and Its Relationship with the Drought. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Moghaddamnia, A.; Pahlavanravi, A.; Panjehkeh, N. Dust storm frequency after the 1999 drought in the Sistan region, Iran. Clim. Res. 2010, 41, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.; Goudie, A.S.; Kahn, R. Dryness of ephemeral lakes and consequences for dust activity: The case of the Hamoun drainage basin, southeastern Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 552–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidianpour, M.; Jahanshahi, S.M.A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Rashki, A.; Nastos, P.G. Climatology of the Sistan Levar wind: Atmospheric dynamics driving its onset, duration and withdrawal. Atmos. Res. 2021, 260, 105711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javan, S.; Rahdar, S.; Miri, M.; Djahed, B.; Kazemian, H.; Fakhri, Y.; Eslami, H.; Fallahzadeh, R.A.; Gholizadeh, A.; Taghavi, M. Modeling of the PM10 pollutant health effects in a semi-arid area: A case study in Zabol, Iran. Modeling Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Middleton, N.J.; Goudie, A.S. Dust storms in Iran–Distribution, causes, frequencies and impacts. Aeolian Res. 2021, 48, 100655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio-Salas, R.; Ruiz, J.; De la O-Villanueva, M.; Valencia-Moreno, M.; Moreno-Rodríguez, V.; Gómez-Alvarez, A.; Grijalva, T.; Mendivil, H.; Paz-Moreno, F.; Meza-Figueroa, D. Tracing geogenic and anthropogenic sources in urban dusts: Insights from lead isotopes. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loska, K.; Wiechula, D.; Korus, I. Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRS Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahim, G.; Parker, R. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, The United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.; Yan, T.; Birch, G.; Zhu, Y. Pollution and health risk of potentially toxic metals in urban road dust in Nanjing, a mega-city of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-H.; Chen, L.-J.; Yu, L.; Guo, Z.-B.; Shan, C.-Q.; Lin, J.-Q.; Gu, Y.-G.; Yang, Z.-B.; Yang, Y.-X.; Shao, J.-R. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of human exposure to oral bioaccessibility of heavy metals via urban street dusts from different functional areas in Chengdu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt-Karakus, P.B. Determination of heavy metals in indoor dust from Istanbul, Turkey: Estimation of the health risk. Environ. Int. 2012, 50, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, X.; Ku, T.; Li, G.; Sang, N. Heavy metals bound to fine particulate matter from northern China induce season-dependent health risks: A study based on myocardial toxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xinmin, Z.; Kunli, L.; Xinzhang, S.; Jian’an, T.; Yilun, L. Mercury in the topsoil and dust of Beijing City. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Baptista, L.; De Miguel, E. Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: A tropical urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4501–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christoforidis, A.; Stamatis, N. Heavy metal contamination in street dust and roadside soil along the major national road in Kavala’s region, Greece. Geoderma 2009, 151, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahakyan, L.; Tepanosyan, G.; Maghakyan, N.; Kafyan, M.; Melkonyan, G.; Saghatelyan, A. Contamination levels and human health risk assessment of mercury in dust and soils of the urban environment, Vanadzor, Armenia. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedić, A.B.; Pucarević, M.; Ninkov, J.; Stojić, N.S.; Milić, D. Mercury content and distribution in household dust and soil in the town of Šid. Zb. Matice Srp. Za Prir. Nauk. 2019, 137, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, P.; Subramanian, K.; Jessiman, B. A multi-element profile of house dust in relation to exterior dust and soils in the city of Ottawa, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 267, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Wang, S.; Sun, H.; Huang, W.; Wang, G.; Nan, Z. Assessment of source and health risk of metal (loid) s in indoor/outdoor dust of university dormitory in Lanzhou City, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 32333–32344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmeddin, A.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Lahijanzadeh, A. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in road dust from urban industrial areas of Ahvaz megacity, Iran. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 1187–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; De Caritat, P. Chemical Elements in the Environment: Factsheets for the Geochemist and Environmental Scientist; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Anderson, C.W.; Xing, Y.; Shang, L. Remediation of mercury contaminated sites—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jia, Z. Heavy metals in soils from a representative rapidly developing megacity (SW China): Levels, source identification and apportionment. Catena 2018, 163, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gworek, B.; Dmuchowski, W.; Baczewska-Dąbrowska, A.H. Mercury in the terrestrial environment: A review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Feng, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Yin, R.; Li, Z.; Bi, X.; Wu, Y. Levels, sources, isotope signatures, and health risks of mercury in street dust across China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, G.; Cheristanidis, S.; Chaloulakou, A.; Koutrakis, P.; Mihalopoulos, N. Elemental composition and source apportionment of fine and coarse particles at traffic and urban background locations in Athens, Greece. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1642–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, P.M.; Humphrey, J.L.; Carlton, E.J.; Adgate, J.L.; Barton, K.E.; Root, E.D.; Miller, S.L. Impact of outdoor air pollution on indoor air quality in low-income homes during wildfire seasons. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, G.; Lin, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q. Mathematical model of particle penetration through smooth/rough building envelop leakages. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Lewis, M. Lead and other heavy metals in soils impacted by exterior legacy paint in residential areas of south west England. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, C.; Rasmussen, P.E. Determination of Total Mercury and Carbon in a National Baseline Study of Urban House Dust. Geosciences 2022, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Xing, X.; Wen, D.; Wang, B.; Qin, N.; Wei, F.; Duan, X. Quantificational exposure, sources, and health risks posed by heavy metals in indoor and outdoor household dust in a typical smelting area in China. Indoor Air 2020, 30, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosar, M.; Šajn, R.; Biester, H. Binding of mercury in soils and attic dust in the Idrija mercury mine area (Slovenia). Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 369, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grangeon, S.; Guédron, S.; Asta, J.; Sarret, G.; Charlet, L. Lichen and soil as indicators of an atmospheric mercury contamination in the vicinity of a chlor-alkali plant (Grenoble, France). Ecol. Indic. 2012, 13, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Bloom, N. Mercury in petroleum. Fuel Processing Technol. 2000, 63, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahmardeh Behrooz, R.; Esmaili-Sari, A.; Bahramifar, N.; Kaskaoutis, D.; Saeb, K.; Rajaei, F. Trace-element concentrations and water-soluble ions in size-segregated dust-borne and soil samples in Sistan, southeast Iran. Aeolian Res. 2017, 25, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrizi, E.; Biglari, H.; Amiri, R.; Baneshi, M.; Mobini, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, G.; Zarei, A.; Narooie, M.R. Determine the important heavy metals in air dust of zahedan, Iran. Pollut. Res. 2017, 36, 474–480. [Google Scholar]
- Naraki, H.; Keshavarzi, B.; Zarei, M.; Moore, F.; Abbasi, S.; Kelly, F.J.; Dominguez, A.O.; Jaafarzadeh, N. Urban street dust in the Middle East oldest oil refinery zone: Oxidative potential, source apportionment، and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarzadeh, Z.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Marsan, F.A.; Padoan, E. Potentially toxic elements in the Middle East oldest oil refinery zone soils: Source apportionment, speciation, bioaccessibility and human health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 40573–40591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y. Spatial distribution, bioavailability, and health risk assessment of soil Hg in Wuhu urban area, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 179, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhu, X.; Feng, Q.; Guo, J.; Sun, X.; Liang, Y. Pollution, sources, and bonding mechanism of mercury in street dust of a subtropical city, southern China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Li, Z.; Bi, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, S.; Yuan, X. Distribution, sources and health risk assessment of mercury in kindergarten dust. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 73, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, G.; Shen, M.; Hu, R.; Sun, M.; Liu, Y. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in indoor dust from different functional areas in Hefei, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakor, M.; Modabberi, S. Human Health Risks Associated with Potentially Harmful Elements from Urban Soils of Hamedan City, Iran. Pollution 2021, 7, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zheng, N.; Tang, L.; Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Hua, X. Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of human exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb pollution in urban street dust across China between 2009 and 2018. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Azevedo, B.; Barros Furieri, L.; Peçanha, F.M.; Wiggers, G.A.; Frizera Vassallo, P.; Ronacher Simões, M.; Fiorim, J.; de Batista, P.R.; Fioresi, M.; Rossoni, L. Toxic effects of mercury on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 949048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanavati, N.; Nazarpour, A.; De Vivo, B. Ecological and human health risk assessment of toxic metals in street dusts and surface soils in Ahvaz, Iran. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morman, S.A.; Plumlee, G.S. The role of airborne mineral dusts in human disease. Aeolian Res. 2013, 9, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, V.; Shaheen, S.M.; Levizou, E.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Vithanageh, M.; Oki, Y.S.; Bolanj, N.; Rinklebe, J. A critical prospective analysis of the potential toxicity of trace element regulation limits in soils worldwide: Are they protective concerning health risk assessment?—A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 819–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittis, G.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Lelieveld, J. Role of soil moisture in the amplification of climate warming in the eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East. Clim. Res. 2014, 59, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Certified Value | Our Results | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NIST-1633 | 0.141 | 0.153 | +8.5% |
| NIST-2709 | 1.400 | 1.455 | +3.9% |
| NIST-2711 | 6.250 | 6.011 | −3.9% |
| Particulate-Bound Mercury (PBM) | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indoor dust | ||||||||
| Ahvaz (n = 36) | 0.04 | 3.95 | 0.67 | 0.37 | 0.86 | 2.48 | 6.04 | |
| Asaluyeh (n = 30) | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.09 | 0.13 | |
| Zabol (n = 20) | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.60 | 1.82 | |
| Outdoor dust | ||||||||
| Ahvaz (n = 36) | 0.02 | 1.06 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 5.75 | 33.5 | |
| Asaluyeh (n = 30) | 0.02 | 0.26 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 4.61 | 23.6 | |
| Zabol (n = 20) | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.93 | |
| Uncontaminated soil 1 | 0.07 | |||||||
| Exterior dusts (street/road/roadway dusts) | Beijing (China) 2 | 0.34 | ||||||
| Hamedan (Iran) 3 | 0.01 | 1.34 | 0.15 | |||||
| Luanda (Angola) 4 | 0.13 | |||||||
| Nanjing (China) 5 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 0.12 | |||||
| Kavala (Greece) 6 | 0.10 | |||||||
| Aviles (Spain) 7 | 1.20 | 10.80 | 0.002 | |||||
| Vanadzor (Armenia) 8 | 0.04 | 0.54 | 0.26 | |||||
| Household dust | Šid (Serbia) 9 | 0.005 | 1.56 | 0.13 | ||||
| Ottawa (Canada) 10 | 0.01 | 37.00 | 1.72 | |||||
| Adults | Children | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Household | HQ(ing) | HQ(inh) | HQ(drm) | HI | HQ(ing) | HQ(inh) | HQ(drm) | HI | |
| Ahvaz | Min | 3.76 × 10−7 | 3.10 × 10−6 | 7.51 × 10−9 | 3.48 × 10−6 | 3.51 × 10−6 | 1.11 × 10−1 | 1.76 × 10−5 | 1.11 × 10−1 |
| Max | 3.38 × 10−5 | 2.79 × 10−4 | 6.75 × 10−7 | 3.13 × 10−4 | 3.16 × 10−4 | 9.98 | 1.58 × 10−3 | 9.98 | |
| Med | 3.16 × 10−6 | 2.61 × 10−5 | 6.31 × 10−8 | 2.93 × 10−5 | 2.95 × 10−5 | 9.33 × 10−1 | 1.48 × 10−4 | 9.33 × 10−1 | |
| Asaluyeh | Min | 1.19 × 10−7 | 9.80 × 10−7 | 2.37 × 10−9 | 1.10 × 10−6 | 1.11 × 10−6 | 3.51 × 10−1 | 5.55 × 10−6 | 3.51 × 10−2 |
| Max | 1.01 × 10−6 | 8.33 × 10−6 | 2.02 × 10−8 | 9.36 × 10−6 | 9.44 × 10−6 | 2.98 × 10−1 | 4.72 × 10−5 | 2.98 × 10−1 | |
| Med | 2.65 × 10−7 | 2.18 × 10−6 | 5.28 × 10−9 | 2.45 × 10−6 | 2.47 × 10−6 | 7.80 × 10−2 | 1.23 × 10−5 | 7.80 × 10−2 | |
| Zabol | Min | 7.47 × 10−8 | 6.15 × 10−7 | 1.49 × 10−9 | 6.91 × 10−7 | 6.97 × 10−7 | 2.20 × 10−2 | 3.49 × 10−6 | 2.20 × 10−2 |
| Max | 7.23 × 10−7 | 5.95 × 10−6 | 1.44 × 10−8 | 6.69 × 10−6 | 6.74 × 10−6 | 2.13 × 10−1 | 3.37 × 10−5 | 2.13 × 10−1 | |
| Med | 3.37 × 10−7 | 2.77 × 10−6 | 6.72 × 10−9 | 3.11 × 10−6 | 3.14 × 10−6 | 9.92 × 10−2 | 1.57 × 10−5 | 9.92 × 10−2 | |
| Outdoor | |||||||||
| Ahvaz | Min | 1.55 × 10−7 | 1.28 × 10−6 | 3.10 × 10−9 | 1.44 × 10−6 | 1.45 × 10−6 | 4.58 × 10−2 | 7.25 × 10−6 | 4.58 × 10−2 |
| Max | 9.06 × 10−6 | 7.46 × 10−5 | 1.81 × 10−7 | 8.38 × 10−5 | 8.46 × 10−5 | 2.67 | 4.23 × 10−4 | 2.67 | |
| Med | 3.67 × 10−7 | 3.02 × 10−6 | 7.32 × 10−9 | 3.39 × 10−6 | 3.42 × 10−6 | 1.08 × 10−1 | 1.71E × 10−5 | 1.08 × 10−1 | |
| Asaluyeh | Min | 1.59 × 10−7 | 1.31 × 10−6 | 3.18 × 10−9 | 1.47 × 10−6 | 1.49 × 10−6 | 4.70 × 10−2 | 7.44 × 10−6 | 4.70 × 10−2 |
| Max | 4.90 × 10−7 | 4.04 × 10−6 | 9.78 × 10−9 | 4.54 × 10−6 | 4.57 × 10−6 | 1.44 × 10−1 | 2.29 × 10−5 | 1.44 × 10−1 | |
| Med | 1.94 × 10−7 | 1.6 × 10−6 | 3.86 × 10−9 | 1.80 × 10−6 | 1.81 × 10−6 | 5.71 × 10−2 | 9.04 × 10−6 | 5.71 × 10−2 | |
| Zabol | Min | 6.95 × 10−9 | 5.72 × 10−8 | 1.39 × 10−10 | 6.43 × 10−8 | 6.49 × 10−8 | 2.05 × 10−3 | 3.24 × 10−7 | 2.05 × 10−3 |
| Max | 8.04 × 10−7 | 6.62 × 10−6 | 1.60 × 10−8 | 7.44 × 10−6 | 7.50 × 10−6 | 2.37 × 10−1 | 3.75 × 10−5 | 2.37 × 10−1 | |
| Med | 4.17 × 10−7 | 3.44 × 10−6 | 8.32 × 10−9 | 3.87 × 10−6 | 3.89 × 10−6 | 1.23 × 10−1 | 1.95 × 10−5 | 1.23 × 10−1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dahmardeh Behrooz, R.; Tashakor, M.; Asvad, R.; Esmaili-Sari, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Mercury Exposure via Indoor and Outdoor Household Dust in Three Iranian Cities. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040583
Dahmardeh Behrooz R, Tashakor M, Asvad R, Esmaili-Sari A, Kaskaoutis DG. Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Mercury Exposure via Indoor and Outdoor Household Dust in Three Iranian Cities. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(4):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040583
Chicago/Turabian StyleDahmardeh Behrooz, Reza, Mahsa Tashakor, Reza Asvad, Abbas Esmaili-Sari, and Dimitris G. Kaskaoutis. 2022. "Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Mercury Exposure via Indoor and Outdoor Household Dust in Three Iranian Cities" Atmosphere 13, no. 4: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040583
APA StyleDahmardeh Behrooz, R., Tashakor, M., Asvad, R., Esmaili-Sari, A., & Kaskaoutis, D. G. (2022). Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Mercury Exposure via Indoor and Outdoor Household Dust in Three Iranian Cities. Atmosphere, 13(4), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040583







