Characteristics and Aging of Traffic-Emitted Particles with Sulfate and Organic Compound Formation in Urban Air
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
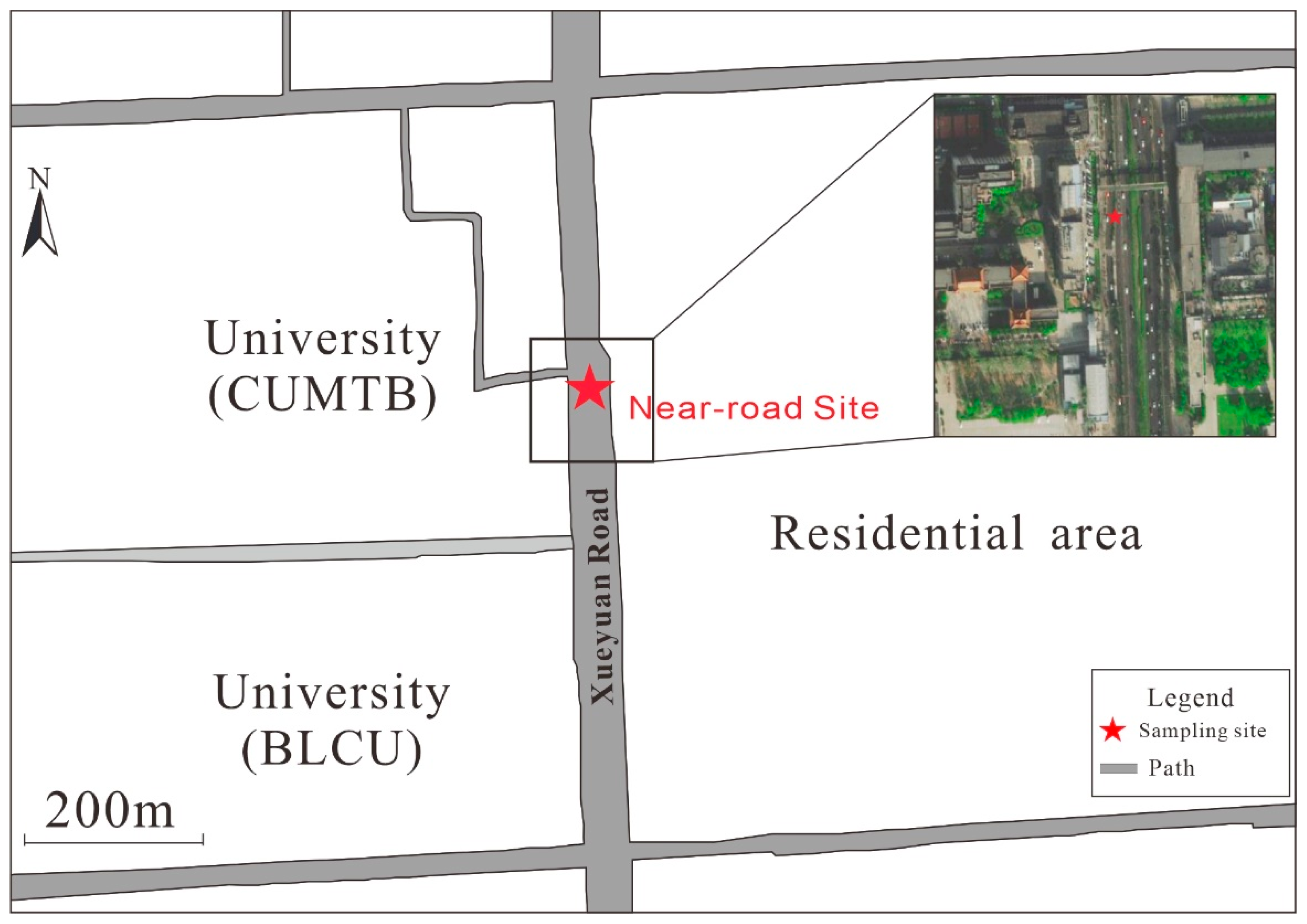
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Microscopic Analysis
3. Results
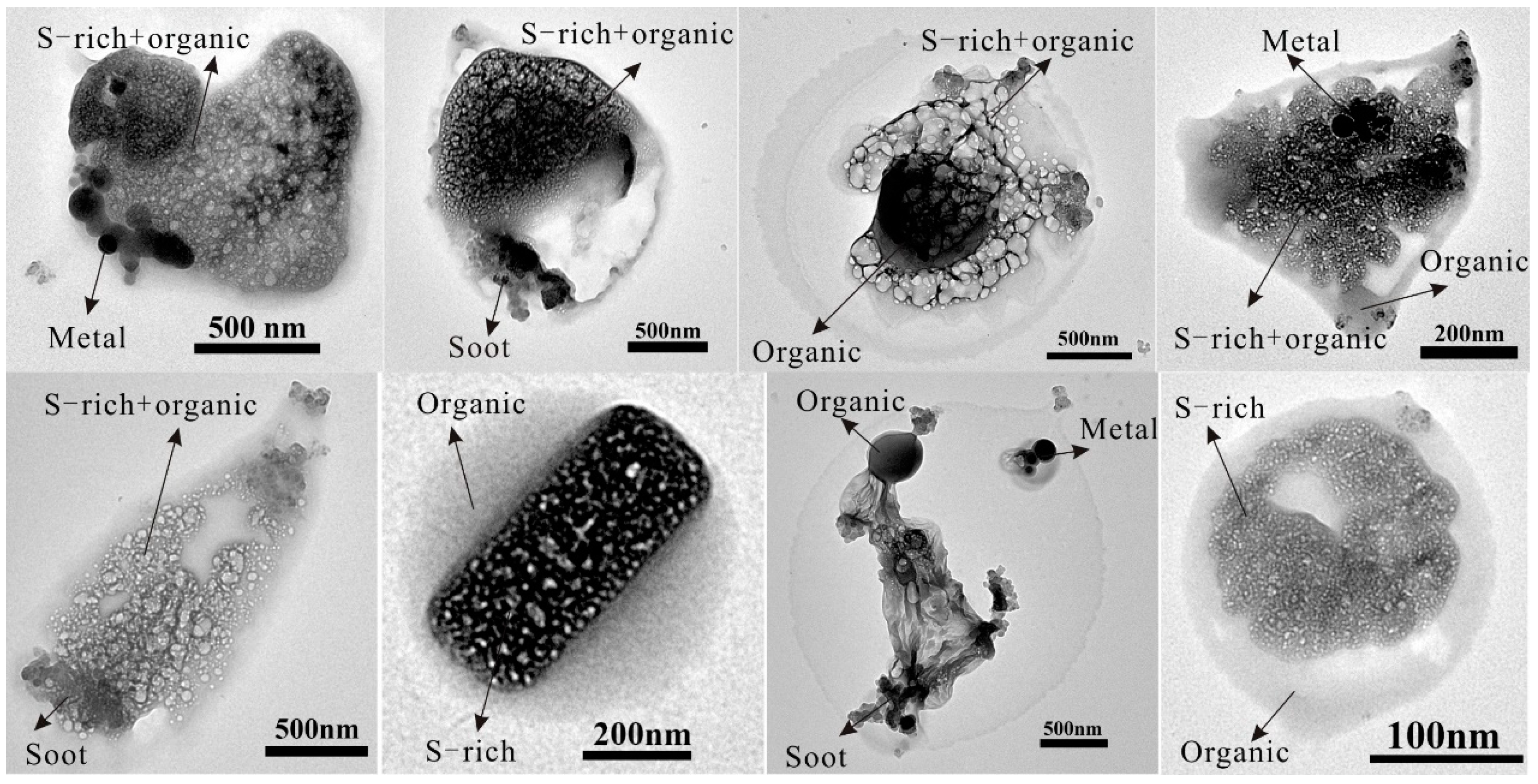
3.1. Major Types of Traffic-Derived Individual Particles
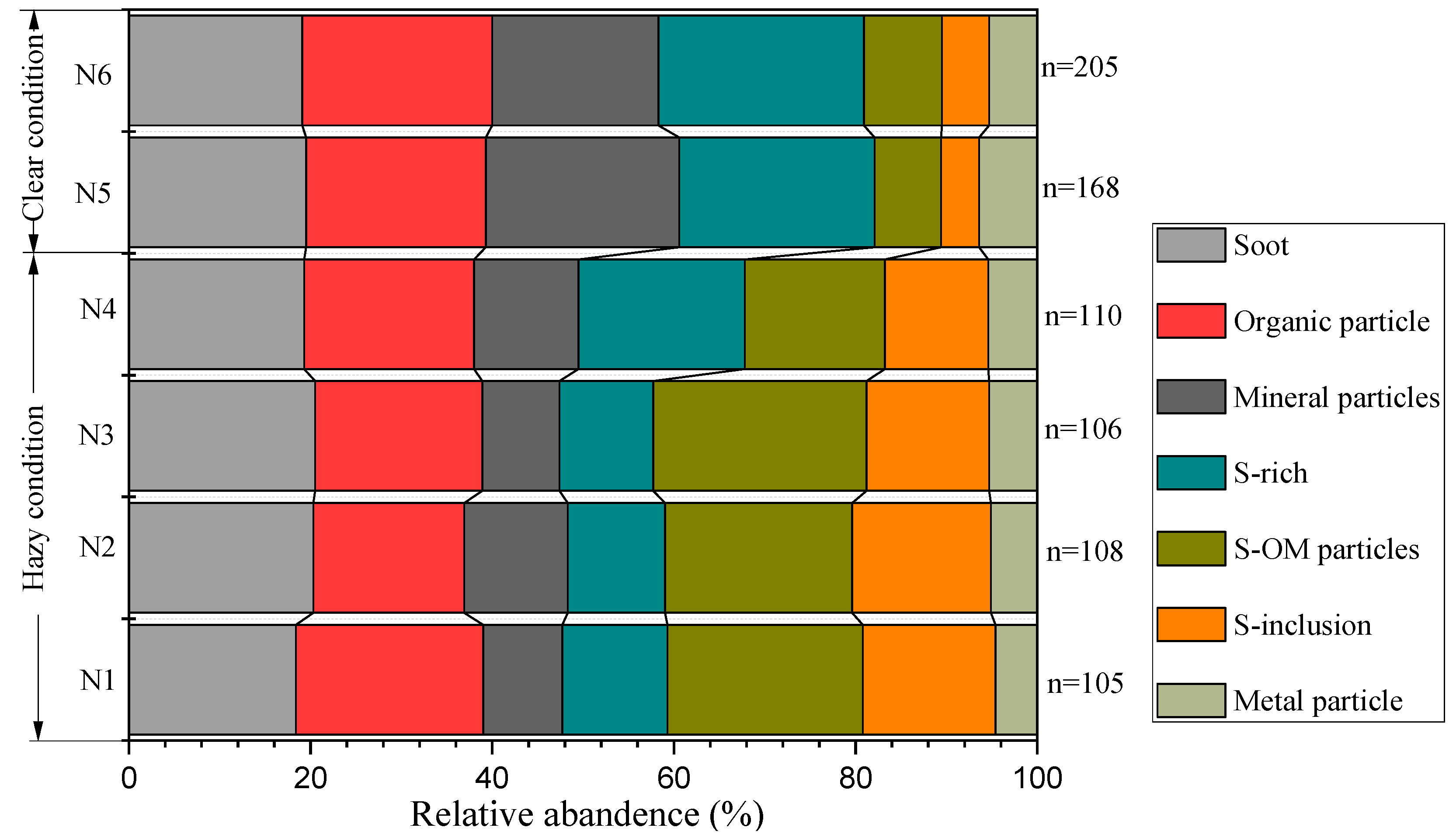
3.2. Relative Abundance
4. Discussion
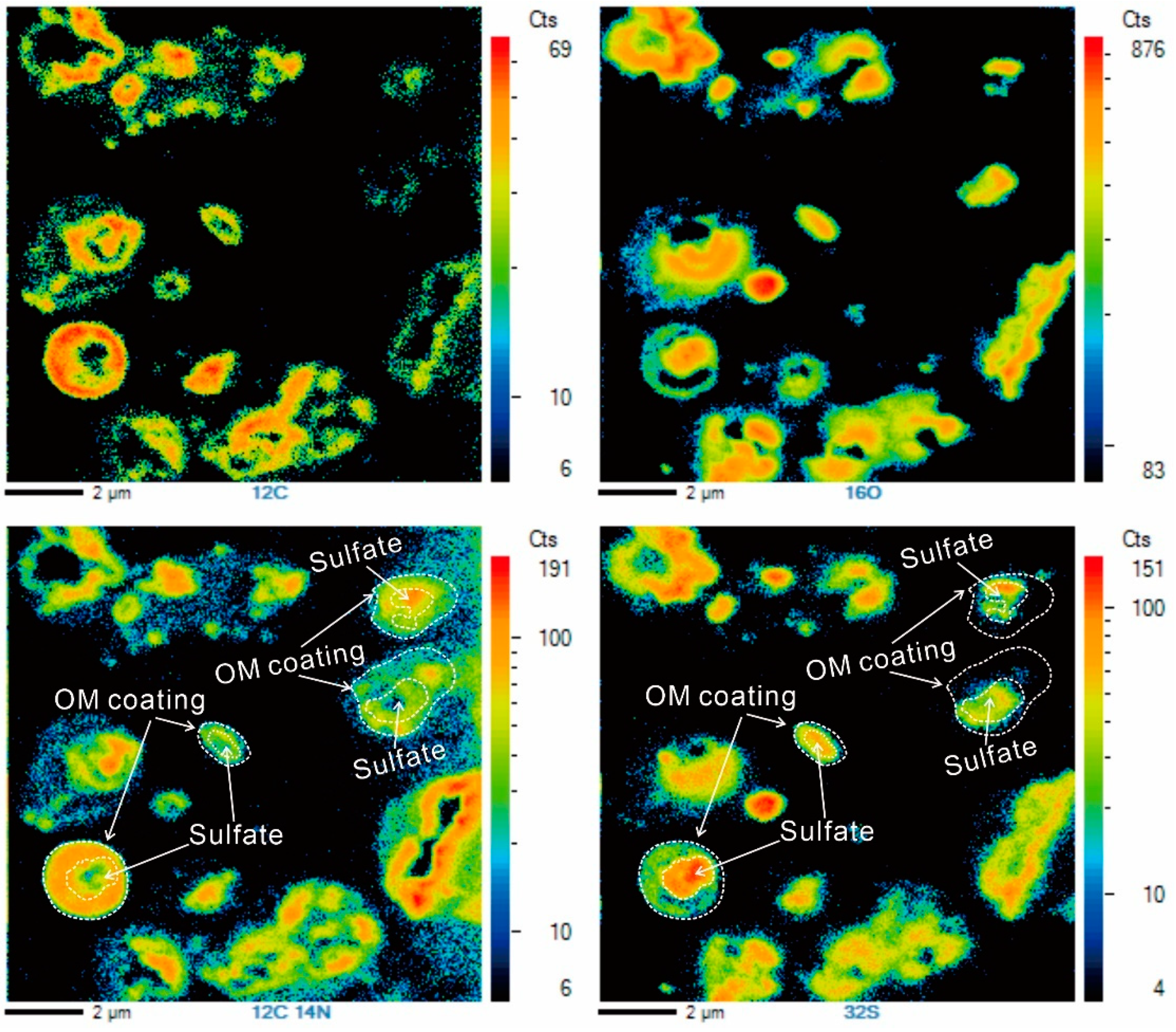
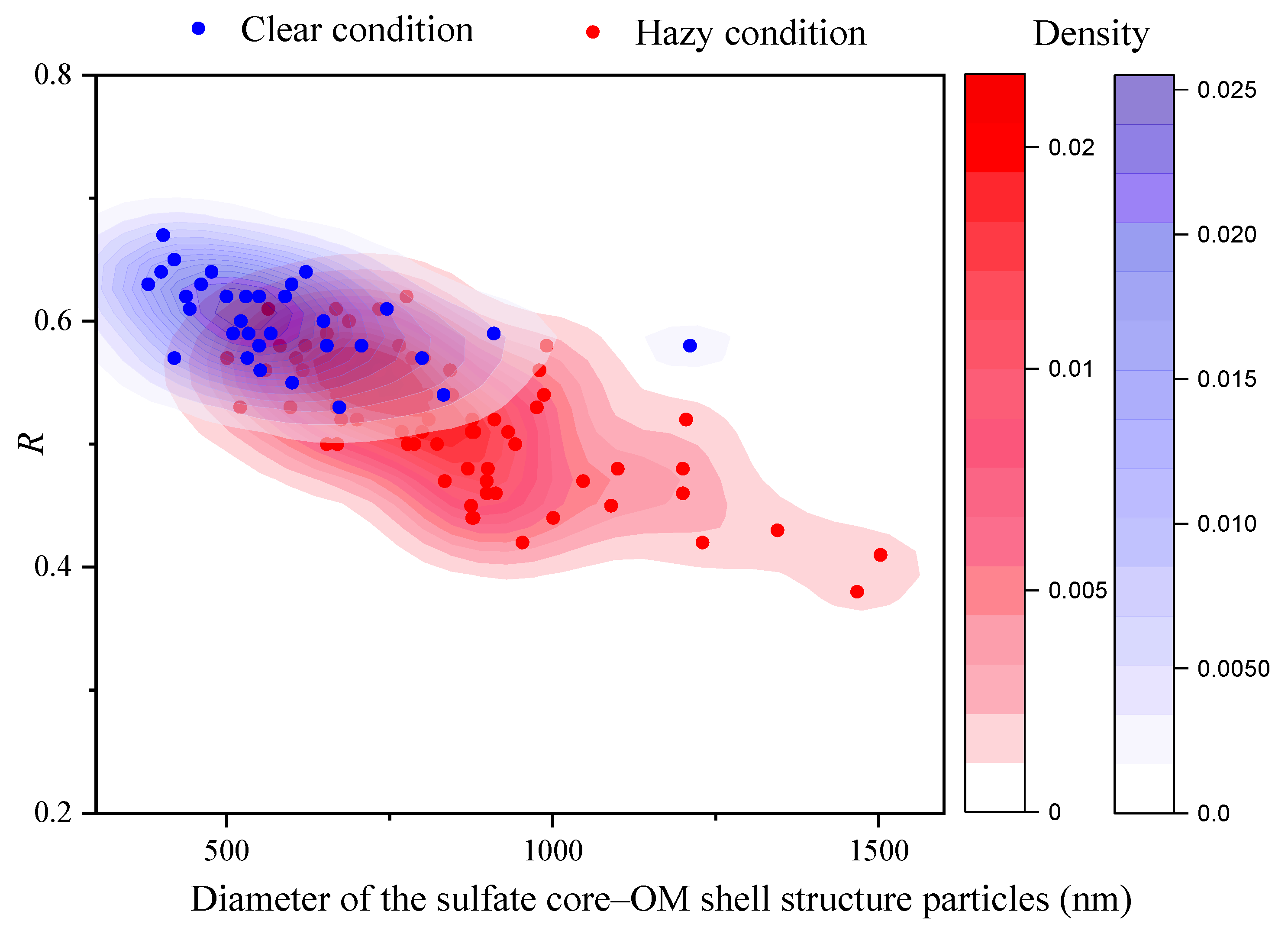
4.1. Mixture of Organic and Sulfate
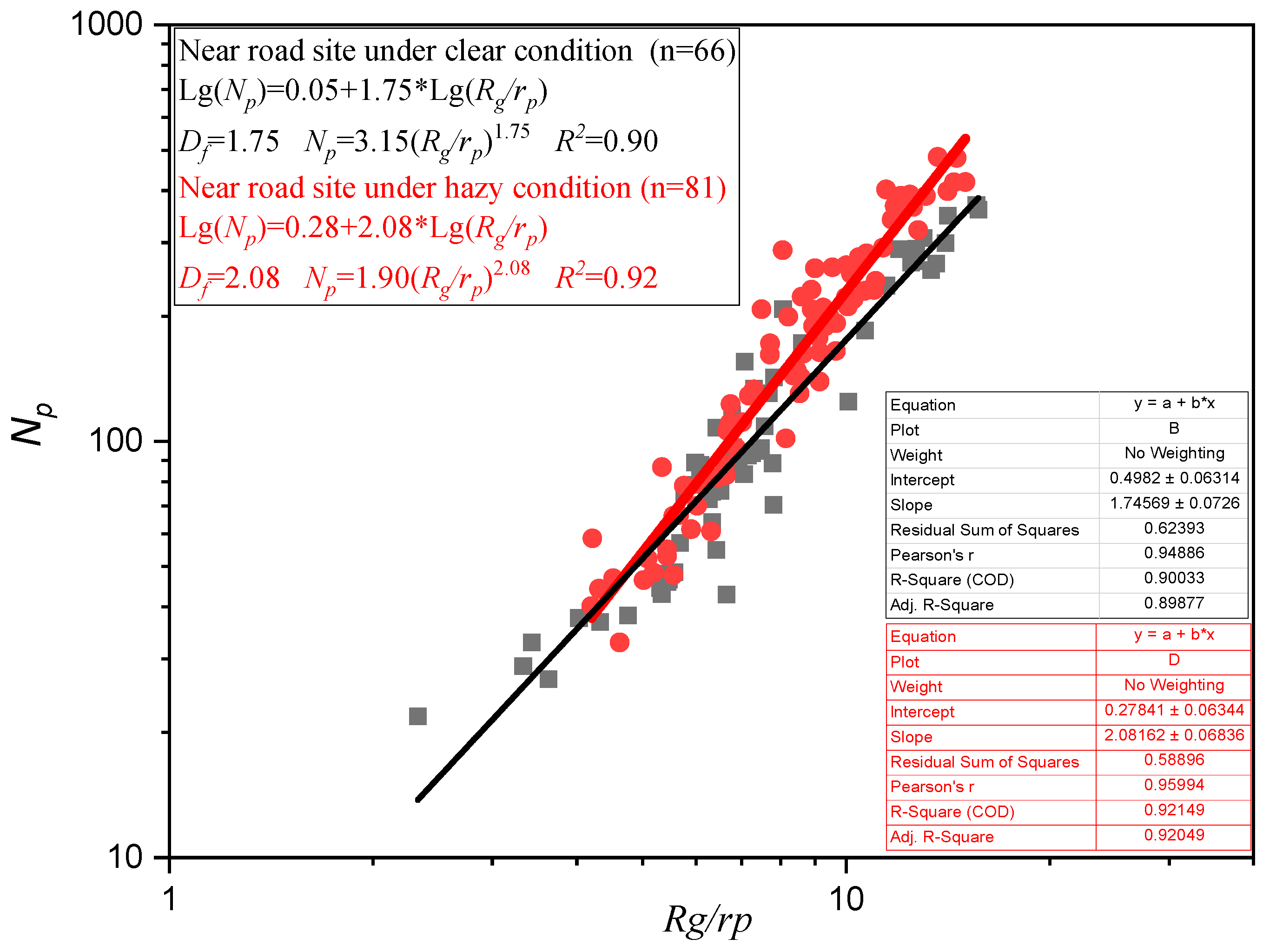
4.2. Aging of Soot Particles
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Hsu, C.; Lin, S.; Chang-Chien, G.; Chen, M.; Fang, G.; Chiang, H. Characteristics of concentrations and metal compositions for PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 in Yunlin County, Taiwan during air quality deterioration. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 2571–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, C.; Afif, C.; Sauvage, S.; Borbon, A.; Salameh, T.; Kfoury, A.; Leonardis, T.; Karam, C.; Formenti, P.; Doussin, J.F.; et al. Determination of gaseous and particulate emission factors from road transport in a Middle Eastern capital. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 83, 102361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, K.A.; Foster, M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; May, A.D.; Ramani, T.; Zietsman, J.; Khreis, H. Urban policy interventions to reduce traffic emissions and traffic-related air pollution: Protocol for a systematic evidence map. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Cai, M.; Xu, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, J.; Yan, J.; Schwab, J.J.; Yuan, C. Chemical nature of PM2.5 and PM10 in the coastal urban Xiamen, China: Insights into the impacts of shipping emissions and health risk. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 227, 117383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, S.; He, K.; Zheng, M. Review of receptor-based source apportionment research of fine particulate matter and its challenges in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.; Martins, M.; Liu, M.; Koutrakis, P. Measurement of the gross alpha activity of the fine fractions of road dust and near-roadway ambient particle matter. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2021, 71, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, P.; Yang, J.; Stamatis, C.; Barsanti, K.C.; Cocker, D.R.; Durbin, T.D.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Karavalakis, G. Evaluating the relationships between aromatic and ethanol levels in gasoline on secondary aerosol formation from a gasoline direct injection vehicle. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Hinds, W.C.; Kim, S.; Shen, S.; Sioutas, C. Study of ultrafine particles near a major highway with heavy-duty diesel traffic. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4323–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Huang, H.; Pan, M.; Huang, R.; Wei, J.; Liu, J. Analysis of morphology, nanostructure, and oxidation reaction of soot particulates from CI engines with dimethoxymethane-diesel blends under different loads and speeds. Fuel 2020, 278, 118263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, X.; Wei, S.; Zhu, R.; Wang, B.; Chen, B.; Kong, M.; Zhang, J.J. Sources, concentrations, and transport models of ultrafine particles near highways: A Literature Review. Build. Environ. 2020, 186, 107325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, A.L.; Jia, Y.; Denbleyker, A.; McDonald-Buller, E.; Fraser, M.P.; Allen, D.T.; Collins, D.R.; Michel, E.; Pudota, J.; Sullivan, D.; et al. Air pollutant concentrations near three Texas roadways, part II: Chemical characterization and transformation of pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4523–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Ketzel, M.; Vardoulakis, S.; Pirjola, L.; Britter, R. Dynamics and dispersion modelling of nanoparticles from road traffic in the urban atmospheric environment-A review. J. Aerosol Sci. 2011, 42, 580–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Ning, Z.; Shen, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Lei, Y.; Xu, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Westerdahl, D.; et al. Variations of aerosol size distribution, chemical composition and optical properties from roadside to ambient environment: A case study in Hong Kong. China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzyk, T.M.; George, B.J.; Vette, A.F.; Williams, R.W.; Croghan, C.W.; Stevens, C.D. Development of a distance-to-roadway proximity metric to compare near-road pollutant levels to a central site monitor. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karner, A.A.; Eisinger, D.S.; Niemeier, D.A. Near-Roadway Air Quality: Synthesizing the Findings from Real-World Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5334–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.K.; Khlystov, A.; Grieshop, A.P. Downwind evolution of the volatility and mixing state of near-road aerosols near a US interstate highway. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2139–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Adams, P.J.; Presto, A.A. Simulations of vehicle-induced mixing and near-road aerosol microphysics using computational fluid dynamics. Aims Environ. Sci. 2018, 5, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbrough, S.; Baldauf, R.W.; Hagler GS, W.; Shores, R.C.; Mitchell, W.; Whitaker, D.A.; Croghan, C.W.; Vallero, D.A. Long-term continuous measurement of near-road air pollution in Las Vegas: Seasonal variability in traffic emissions impact on local air quality. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2013, 6, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Shao, L.; Zhang, D. Aged status of soot particles during the passage of a weak cyclone in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2699–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pang, Y.; Huang, J.; Bi, L.; Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, W. Constructing shapes and mixing structures of black carbon particles with applications to optical calculations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD034620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoli, P.; Fortner, E.C.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Williams, L.R.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Schwab, J.J.; Trimborn, A.; Onasch, T.B.; Demerjian, K.L.; et al. Pollution gradients and chemical characterization of particulate matter from vehicular traffic near major roadways: Results from the 2009 Queens College air quality study in NYC. Aerosol. Sci. Tech. 2012, 46, 1201–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Shao, L.; Zhang, W.; Peng, J.; Wang, W.; Shuai, S.; Hu, M.; Zhang, D. Morphology and size of the particles emitted from a gasoline-direct-injection-engine vehicle and their ageing in an environmental chamber. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 2781–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Hu, M.; Liu, D.; Shi, Z.; et al. Exploring wintertime regional haze in northeast China: Role of coal and biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5355–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Chung, S.H.; Friedrich, H.; Buseck, P.R. Fractal parameters of individual soot particles determined using electron tomography: Implications for optical properties. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D14202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- China, S.; Mazzoleni, C.; Gorkowski, K.; Aiken, A.C.; Dubey, M.K. Morphology and mixing state of individual freshly emitted wildfire carbonaceous particles. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Shao, L. Transmission electron microscopy study of aerosol particles from the brown hazes in northern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 09302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Shao, L.; Zheng, R.; Peng, J.; Wang, W.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Shuai, S.; Hu, M. Individual particles emitted from gasoline engines: Impact of engine types, engine loads and fuel components. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Shao, L.; Zhang, D. Soot particles at an elevated site in eastern China during the passage of a strong cyclone. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 430, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, P.; Pirjola, L.; Heikkilä, J.; Lähde, T.; Tzamkiozis, T.; Ntziachristos, L.; Keskinen, J.; Rönkkö, T. Exhaust particles of modern gasoline vehicles: A laboratory and an on-road study. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giere, R.; Blackford, M.; Smith, K. TEM study of PM2.5 emitted from coal and tire combustion in a thermal power station. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6235–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Lee, S.; Gu, Z.; Ho, K.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R. PM2.5 and PM10-2.5 chemical composition and source apportionment near a Hong Kong roadway. Particuology 2015, 18, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tunved, P.; Dall’Osto, M.; Shen, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Z. Organic coating on sulfate and soot particles during late summer in the Svalbard Archipelago. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10433–10446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Z. Microscopic evidence for phase separation of organic species and inorganic salts in fine ambient aerosol particles, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2234–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lian, X.; Peng, L.; Jiang, F.; Bi, X.; Li, L.; et al. Impact of in-cloud aqueous processes on the chemical compositions and morphology of individual atmospheric aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 14063–14075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Shao, L.; Hu, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, C.; Xing, J.; Huang, X.; Hu, M. Characteristics and aging of traffic-derived particles in a highway tunnel at a coastal city in southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, A.K.; Martin, S.T.; Hanna, S.J.; Smith, M.L.; Bodsworth, A.; Chen, Q.; Kuwata, M.; Liu, A.; You, Y.; Zorn, S.R. Predicting the relative humidities of liquid-liquid phase separation, efflorescence, and deliquescence of mixed particles of ammonium sulfate, organic material, and water using the organic-to-sulfate mass ratio of the particle and the oxygen-to-carbon elemental ratio of the organic component. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 10995–11006. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty, R.K.; Moosmueller, H.; Arnott, W.P.; Garro, M.A.; Walker, J. Structural and fractal properties of particles emitted from spark ignition engines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6647–6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarieiro, A.L.N.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Da Rocha, G.O.; de Andrade, J.B. An investigation on morphology and fractal dimension of diesel and Diesel-Biodiesel soot agglomerates. J. Brazil. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.K.; Schnitzler, E.G.; Jaeger, W.; Olfert, J.S. Relative humidity dependence of soot aggregate restructuring induced by secondary organic aerosol: Effects of water on coating viscosity and surface tension. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; He, C.; Bi, L.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Z.; Li, W. Fractal dimensions and mixing structures of soot particles during atmospheric processing. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China, S.; Salvadori, N.; Mazzoleni, C. Effect of traffic and driving characteristics on morphology of atmospheric soot particles at freeway On-Ramps. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3128–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, Y.; Liu, L.; Bi, L.; Kang, S.; Li, W. Mixing state and fractal dimension of soot particles at a remote site in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8227–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ID | Sampling Time | T (°C) | RH (%) | P (hPa) | Wind (m s−1) | PM2.5 (µg·m−3) | Weather Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 6 January 2017 9:00 | 3.3 | 64.0 | 102.0 | 1.6 | 173 | hazy |
| N2 | 6 January 2017 18:00 | 3.7 | 61.9 | 101.6 | 1.8 | 237 | hazy |
| N3 | 7 January 2017 9:00 | 3.7 | 60.0 | 101.6 | 1.6 | 182 | hazy |
| N4 | 7 January 2017 18:00 | 3.2 | 83.0 | 101.4 | 1.2 | 103 | hazy |
| N5 | 8 January 2017 9:00 | 2.9 | 39.9 | 101.5 | 5.8 | 25 | sunny |
| N6 | 8 January 2017 18:00 | 4.2 | 34.2 | 101.3 | 5.4 | 19 | sunny |
| Fractal Dimension | Probable Dominant Source | Literatures |
|---|---|---|
| 1.75–2.08 | roadside environment | This study |
| 1.70–1.78 | light-duty passenger vehicle | Chakrabarty et al. (2006) [37] |
| 1.74 | biomass burning | Chakrabarty et al. (2006) [37] |
| 1.85 | biomass burning | China et al. (2013) [25] |
| 2.4 | Asian dust soot | Adachi et al. (2007) [24] |
| 1.8–2.0 | diesel vehicle | China et al. (2014) [41] |
| 2.00 | ambient environment | Wang et al. (2017) [40] |
| 1.80 | Tunnel environment | Wang et al. (2017) [40] |
| 1.88 | ambient environment (Background) | Yuan et al. (2019) [42] |
| 1.89–1.99 | diesel vehicle | Guarieiro et al. (2017) [38] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, J.; Shao, L.; Chen, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D. Characteristics and Aging of Traffic-Emitted Particles with Sulfate and Organic Compound Formation in Urban Air. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040608
Xing J, Shao L, Chen F, Wang W, Zhang D. Characteristics and Aging of Traffic-Emitted Particles with Sulfate and Organic Compound Formation in Urban Air. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(4):608. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040608
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Jiaoping, Longyi Shao, Feifeng Chen, Wenhua Wang, and Daizhou Zhang. 2022. "Characteristics and Aging of Traffic-Emitted Particles with Sulfate and Organic Compound Formation in Urban Air" Atmosphere 13, no. 4: 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040608
APA StyleXing, J., Shao, L., Chen, F., Wang, W., & Zhang, D. (2022). Characteristics and Aging of Traffic-Emitted Particles with Sulfate and Organic Compound Formation in Urban Air. Atmosphere, 13(4), 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040608







