Atmospheric Carbonyl Compounds in the Central Taklimakan Desert in Summertime: Ambient Levels, Composition and Sources
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
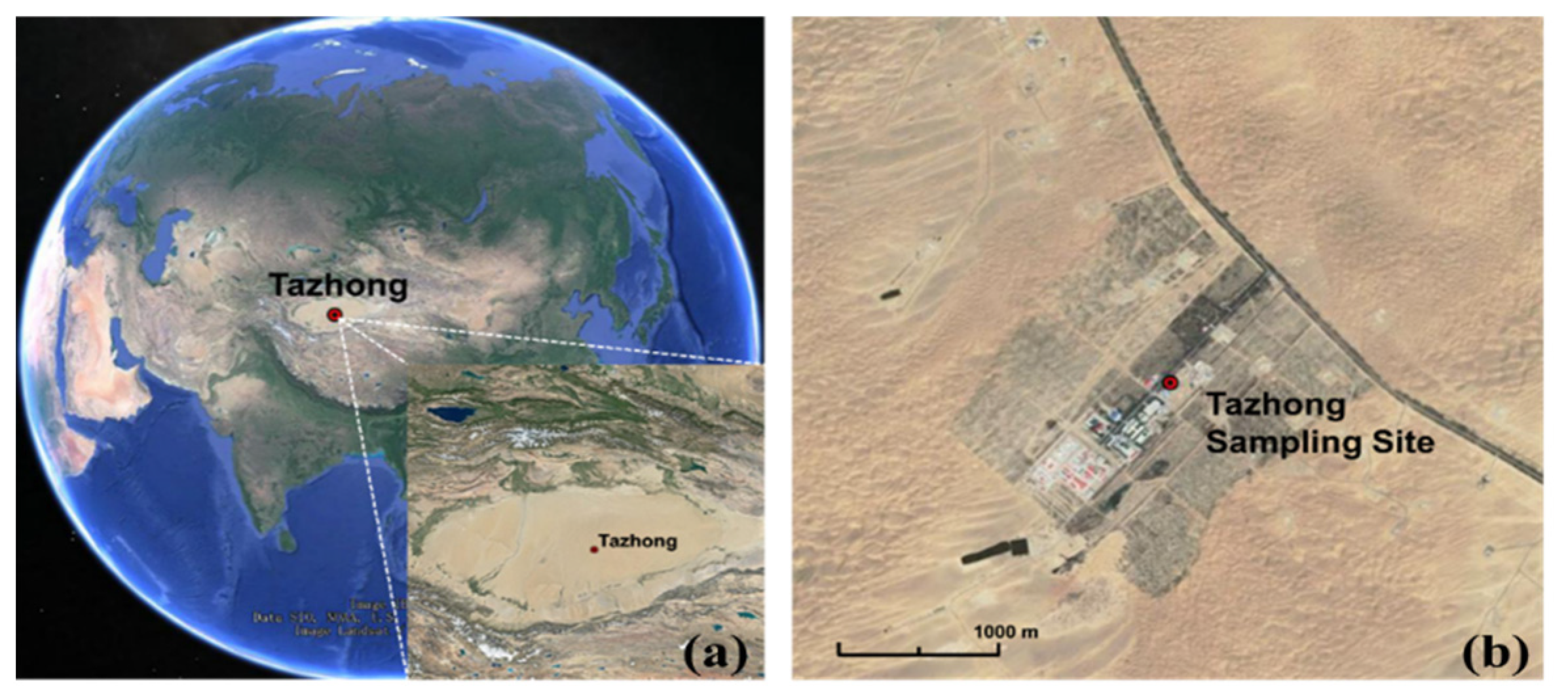
2.1. Sampling Site
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
3. Results and Discussion
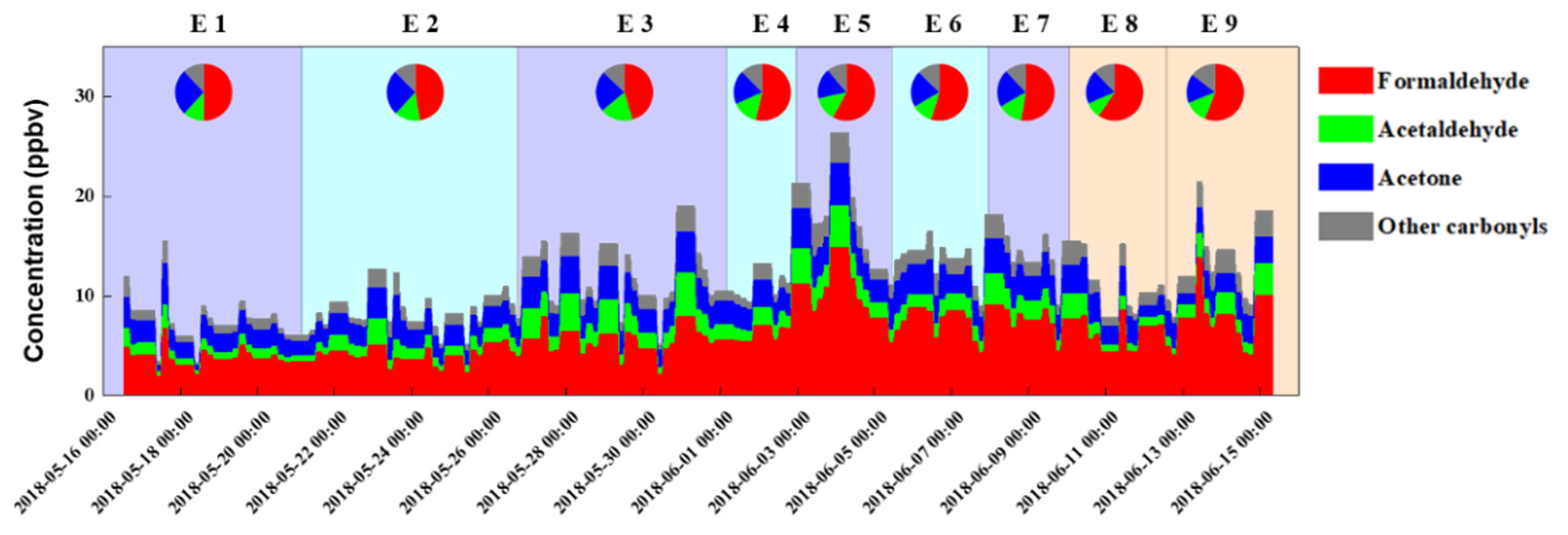
3.1. Carbonyl Concentrations and Compositions
3.2. Sources of Carbonyls
3.2.1. Pearson Correlation
3.2.2. Back Trajectory Analysis
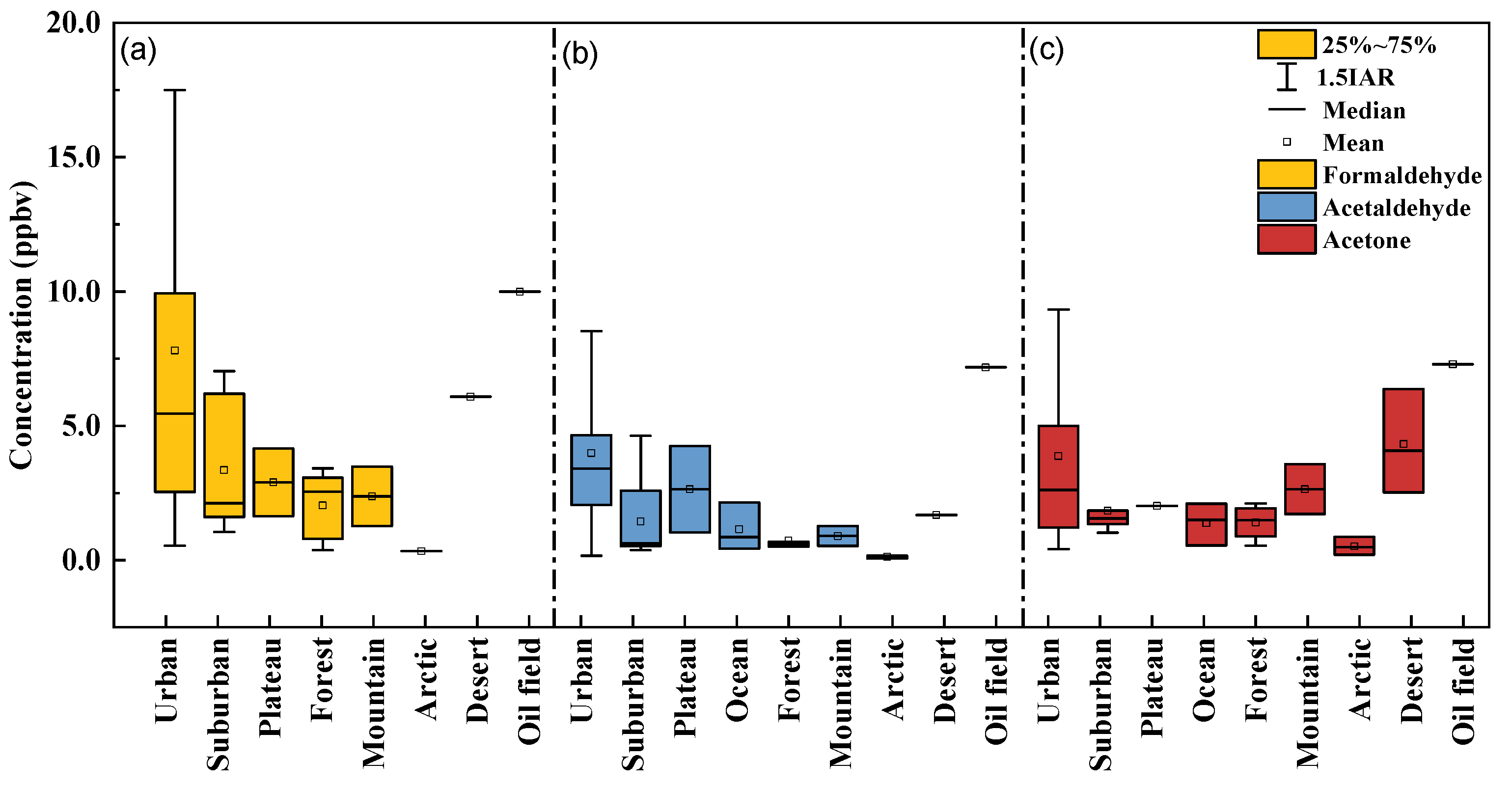
3.3. Comparison with Carbonyls in Various Environments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atkinson, R.; Arey, J. Atmospheric Degradation of Volatile Organic Compounds. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4605–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, T.; Mao, X.; Mo, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Liang, X.; Gao, H.; et al. Oxidative Capacity and Radical Chemistry in a Semi-arid and Petrochemical-industrialized City, Northwest China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1391–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mellouki, A.; Wallington, T.; Chen, J. Atmospheric chemistry of oxygenated volatile organic compounds: Impacts on air qual-ity and climate. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3984–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkamer, R.; Martini, F.S.; Molina, L.T.; Salcedo, D.; Jimenez, J.L.; Molina, M.J. A missing sink for gas-phase glyoxal in Mex-ico City: Formation of secondary organic aerosol. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L19807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Xiong, B.; Feng, J.; Wen, S.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.; Wu, M. Characteristics of carbonyl compounds in ambient air of Shanghai, China. J. Atmos. Chem. 2008, 61, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, L.; Broder, M.W.; Forsyth, C. Toxicological Review of Acetone; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Graus, M.; Schnitzler, J.P.; Hansel, A.; Cojocariu, C.; Rennenberg, H.; Wisthaler, A.; Kreuzwieser, J. Transient release of oxy-genated volatile organic compounds during light-dark transitions in grey poplar leaves. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janson, R.; de Serves, C. Acetone and monoterpene emissions from the boreal forest in northern Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4629–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Hong, Y.-J.; Pal, R.; Jeon, E.-C.; Koo, Y.-S.; Sunwoo, Y. Investigation of carbonyl compounds in air from various industrial emission sources. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possanzini, M.; Di Palo, V.; Cecinato, A. Sources and photodecomposition of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde in Rome am-bient air. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3195–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Shen, H.; Chen, Z. Characterizing summer and winter carbonyl compounds in Beijing atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, T.R.; Brune, W.H.; Ren, X.; Mao, J.; Lesher, R.; Cardenas, B.; Volkamer, R.; Molina, L.T.; Molina, M.J.; Lamb, B.; et al. Atmospheric oxidation in the Mexico City Metropolitan Area (MCMA) during April 2003. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Du, W.; Lv, S.; Ding, Z.; Wang, G. Spatial and Temporal Distributions and Sources of Anthropogenic NMVOCs in the Atmosphere of China: A Review. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.K.; Gu, R.R.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.F.; Saunders, S.; Blake, D.; Louie, P.K.K.; Luk, C.W.Y.; Simpson, I.; Xu, Z.; et al. Oxidative capacity and radical chemistry in the polluted atmosphere of HongKong and Pearl River Delta region: Analysis of a severe photochemical smogepisode. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9891–9903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.-F.; Zhang, B.; Xia, S.-Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, G.-H.; Feng, N. Sources of oxygenated volatile organic compounds (OVOCs) in urban atmospheres in North and South China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Hu, W.W.; Shao, M.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.T.; Lu, S.H.; Zeng, L.M.; Hu, M. VOC emissions, evolutions and contri-butions to SOA formation at a receptor site in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8815–8832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; He, X.; Chen, M.; Tan, J.; Wang, Y. Photochemical Production of Atmospheric Carbonyls in a Rural Area in Southern China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 66, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Grosselin, B.; Daële, V.; Mellouki, A.; Mu, Y. Seasonal, diurnal and nocturnal variations of carbonyl compounds in the semi-urban environment of Orléans, France. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 40, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xue, L.; Yao, L.; Li, Q.; Wen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, T.; et al. Carbonyl compounds at Mount Tai in the North China Plain: Characteristics, sources, and effects on ozone formation. Atmos. Res. 2017, 196, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassaa, N.; Ciccioli, P.; Brancaleoni, E.; Frattoni, M.; Meklati, B.Y. Ambient measurements of selected VOCs in populated and remote sites of the Sahara desert. Atmos. Res. 2011, 100, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Flynn, C.; Welton, E.; Cribb, M. Transport, vertical structure and radiative properties of dust events in southeast China determined from ground and space sensors. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6469–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, D.; Lu, H.; Zhang, G.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Luo, Y.; Ma, X. Influence of Dynamic and Thermal Forcing on the Meridional Transport of Taklimakan Desert Dust in Spring and Summer. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; Wen, H.; Zhong, X.; Fan, Y.; He, Q. Characteristics of precipitation at the Hinterland of the Taklimakan Desert. J. Desert Res. 2017, 3, 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency, United State of America. Compendium Method TO-11A. In Determination of Formaldehyde in Ambient Air Using Adsorbent Cartridge Followed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) [Active Sampling Methodology]; Center for Environmental Research Information Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Gao, R.; Wang, W. Optimization and preliminary application of detection method of carbonyl compounds in the ambient air. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 821–829. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.H.; He, Z.; Zhong, X.F.; Bi, B.; Li, Y.F.; Gao, R.; Li, H.; Wang, W.X. Spatiotemporal patterns and ozone sen-sitivity of gaseous carbonyls at eleven urban sites in southeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Wen, S.; Chi, Y.; Guo, S.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Seasonal and diurnal variations of carbonyl compounds in the urban atmosphere of Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3523–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchaca-Torre, H.L.; Mercado-Hernández, R.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.; Mendoza-Dominguez, A. Diurnal and seasonal variations of carbonyls and their effect on ozone concentrations in the atmosphere of Monterrey, Mexico. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Jiang, F.; Cheng, H.R.; Simpson, I.J.; Wang, X.M.; Ding, A.J.; Wang, T.J.; Saunders, S.M.; Lam, S.H.M.; Blake, D.R.; et al. Concurrent observations of air pollutants at two sites in the Pearl River Delta and the implication of regional transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 7343–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, Y.; Pang, X.; Quan, J.; Zhang, X. Atmospheric carbonyl compounds in Chinese background area: A remote mountain of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D22302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, T.-M.; Jacob, D.J.; Wittrock, F.; Burrows, J.P.; Vrekoussis, M.; Henze, D.K. Global budgets of atmospheric glyoxal and methylglyoxal, and implications for formation of secondary organic aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.-N.; Zhou, X.; Hallock, K. Atmospheric carbonyl compounds at a rural southeastern United States site. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 25933–25944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Helal, W.; Borbon, A.; Sauvage, S.; de Gouw, J.A.; Colomb, A.; Gros, V.; Freutel, F.; Crippa, M.; Afif, C.; Baltensperger, U.; et al. Volatile and intermediate volatility organic compounds in suburban Paris: Variability, origin and importance for SOA formation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10439–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, X.; Mu, Y. Seasonal and diurnal variations of carbonyl compounds in Beijing ambient air. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6313–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Characteristics and Source of Carbonyls and Effects on Photochemistry Pollution in North China Plain. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong University, Shandong, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, A.R.; Volkamer, R.; Molina, L.T.; Molina, M.J.; Samuelson, J.; Mellqvist, J.; Galle, B.; Herndon, S.C.; Kolb, C.E. Separation of emitted and photochemical formaldehyde in Mexico City using a statistical analysis and a new pair of gas-phase tracers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 4545–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atkinson, R. Atmospheric chemistry of VOCs and NOx. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2063–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, A.; Tuazon, E.C.; MAschmann, S.; Arey, J.; Atkinson, R. Products and mechanisms of the gas-phase reactions of OH radicals and O3 with 2-methyl-3-buten-2-ol. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Ho, S.S.H.; Ho, K.; Liu, W.; Cao, J.; Lee, S. Seasonal and diurnal variations of mono- and di-carbonyls in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 113, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, J.J.; Nozière, B.; Tyndall, G.S.; Orzechowska, G.E.; Paulson, S.E.; Rudich, Y. Product studies of the OH- and ozone-initiated oxidation of some monoterpenes. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 11561–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissell, A.; Harry, C.; Aschmann, S.M.; Atkinson, R.; Arey, J. Formation of acetone from the OH radical- and O3-initiated reactions of a series of monoterpenes. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 13869–13879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepson, P.; Hastie, D.; Schiff, H.; Polizzi, M.; Bottenheim, J.; Anlauf, K.; Mackay, G.; Karecki, D. Atmospheric concentra-tions and temporal variations of C1-C3 carbonyl compounds at two rural sites in central Ontario. Atmos. Environ. 1991, 25, 2001–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Xue, L.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Han, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Volatile organic compounds and ozone air pollution in an oil production region in northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7069–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, J.B.; Lerner, B.; Kuster, W.; de Gouw, J. Source Signature of Volatile Organic Compounds from Oil and Natural Gas Operations in Northeastern Colorado. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koss, A.; Gouw Jd Warneke, C.; Gilman, J.; Lerner, B.; Graus, M.; Yuan, B.; Edwards, P.; Brown, S.; Wild, R. Photo-chemical aging of volatile organic compounds associated with oil and natural gas extraction in the Uintah Basin, UT, during a wintertime ozone formation event. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5727–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Kong, S.; Xing, X.; Mao, Y.; Hu, T.; Ding, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, D.; Li, S.; Qi, S. Monitoring of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from an oil and gas station in northwest China for 1 year. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4567–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, B.; Chen, W.; Shao, M.; Wang, M.; Lu, S.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Chang, C.C.; Wang, B. Measurements of ambient hydro-carbons and carbonyls in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 116, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakeas, E.B.; Argyris, D.I.; Siskos, P.A. Carbonyl compounds in the urban environment of Athens, Greece. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellén, H.; Hakola, H.; Reissell, A.; Ruuskanen, T. Carbonyl compounds in boreal coniferous forest air in Hyytiälä, Southern Finland. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liang, H.; Huang, L.; Huang, D. Carbonyl compounds over urban Beijing: Concentrations on haze and non-haze days and effects on radical chemistry. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D. Current pollution status of aldoketones compounds in the ambient air of Shenyang. Environ. Protect. Sci. 2015, 41, 118–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, K.; Ho, S.S.H.; Huang, R.-J.; Dai, W.; Cao, J.; Tian, L.; Deng, W. Spatiotemporal distribution of carbonyl compounds in China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 197, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, B.; Li, X.; Shao, M.; Lu, S.; Chang, C.-C.; Wang, Z.; Hu, W.; Huang, X.; He, L.; et al. Impact of pollution controls in Beijing on atmospheric oxygenated volatile organic compounds (OVOCs) during the 2008 Olympic Games: Observation and modeling implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3045–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, M.; Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; Chang, C.; Huang, S.; Chen, Z. Volatile organic compounds measured in summer in Beijing and their role in ground-level ozone formation. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D00G06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Zhao, D.; Ding, D.; Li, X.; Huang, M.; Gao, Y.; Quan, J.; Zhang, Q. Characterizing the level, photochemical reactivity, emission, and source contribution of the volatile organic compounds based on PTR-TOF-MS during winter haze period in Bei-jing, China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 212, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, P.; Mu, Y. Ambient levels of atmospheric carbonyls in Beijing during the 2008 Olympic Games. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xue, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Lee, S.; Blake, D.R.; Chai, F.; Wang, W. Observations and Explicit Modeling of Summertime Carbonyl Formation in Beijing: Identification of Key Precursor Species and Their Impact on Atmospheric Oxidation Chemistry. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 1426–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Pang, X.; Bai, Z.; Jin, M.; Li, W.; Kong, S. Measurement of carbonyl compounds in ambient air of Tianjin City and Bohai Sea. J. Tianjin Univ. 2011, 44, 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, P.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Z. Analysis and concentration variability of carbonyl compounds in Qingdao atmosphere. China Environ. Sci. 2002, 22, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, M.; Zhu, L.; Yang, K.; Chen, S. Levels and health risks of carbonyl compounds in selected public places in Hangzhou, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Lee, S.-C.; Louie, P.; Ho, K.F. Characterization of hydrocarbons, halocarbons and carbonyls in the atmosphere of Hong Kong. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wen, S.; Lü, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Determination of carbonyl compounds in the atmosphere by DNPH derivatization and LC–ESI-MS/MS detection. Talanta 2007, 72, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Lee, X. Temporal variations of atmospheric carbonyls in urban ambient air and street canyons of a Mountainous city in Southwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2098–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.-J.; Chen, M.; He, X.-L.; Yang, W.-W.; Tan, J.-H. Seasonal and Diurnal Characteristics of Carbonyls in Urban Air in Qinzhou, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Chen, M.; Tan, J. Seasonal and diurnal characteristics of atmospheric carbonyls in Nanning, China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Xu, X. Pollution characteristics and sources of carbonyl compounds in Zhengzhou ambient air of winter and summer. China Environ. Monit. 2014, 30, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Huang, C.; Chen, K.; Peng, Y.; Lai, C. Measurement and source characteristics of carbonyl compounds in the at-mosphere in Kaohsiung city, Taiwan. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 179, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjanasiranont, N.; Prueksasit, T.; Morknoy, D.; Tunsaringkarn, T.; Sematong, S.; Siriwong, W.; Zapaung, K.; Rungsiyothin, A. Determination of ambient air concentrations and personal exposure risk levels of outdoor workers to carbonyl compounds and BTEX in the inner city of Bangkok, Thailand. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, K.; Ohura, T.; Amagai, T.; Fusaya, M. Field monitoring of volatile organic compounds using passive air samplers in an industrial city in Japan. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 153, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.-K.; Jeong, E.-H.; Seo, S.-J.; Hwang, Y.-J.; Han, J.-S.; Bae, S.-O. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Atmospheric Concentrations of Carbonyl Compounds in Seoul Metropolitan Area. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 24, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possanzini, M.; Di Palo, V.; Petricca, M.; Fratarcangeli, R.; Brocco, D. Measurements of lower carbonyls in Rome ambient air. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3757–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosjean, E.; Grosjean, D.; Fraser, M.P.; Cass, G.R. Air Quality Model Evaluation Data for Organics. 2. C1−C14 Carbonyls in Los Angeles Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2687–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murillo, J.H.; Marín, J.F.R.; Román, S.R. Determination of carbonyls and their sources in three sites of the metropolitan area of Costa Rica, Central America. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, A.L.; Siciliano, B.; Dantas, G.; André, M.; da Silva, C.M.; Arbilla, G. Levels of Volatile Carbonyl Compounds in the Atlantic Rainforest, in the City of Rio de Janeiro. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, M.A.; Zamorano, N.; Lissi, E.; Rojas, A.; Gutiérrez, L.; Von Baer, D. Volatile carboxylic compounds in downtown San-tiago, Chile. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardin, E. Long-term monitoring of trace volatile organic compounds in ambient air of Western Australia by proton transfer reaction-mass spectrometry (PTR-MS). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, S.J.; Galbally, I.E.; Cheng, M.; Quigley, S.; Azzi, M. PTR-MS measurement of photochemical smog precursors at an inner city site in Sydney, and comparison with emissions inventories. In Proceedings of the CASANZ 2009 Conference: 19th International Clean Air and Environment Conference, Perth Convention Exhibition Centre, Perth, Australia, 6–9 September 2009; Clean Air Society of Australia and New Zealand: Perth, Australia; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Delikhoon, M.; Fazlzadeh, M.; Sorooshian, A.; Baghani, A.N.; Golaki, M.; Ashournejad, Q.; Barkhordari, A. Characteristics and health effects of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde in an urban area in Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 938–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, S.G.; El-Fadel, M.; Saliba, N.A. Seasonal, diurnal and nocturnal behaviors of lower carbonyl compounds in the urban environment of Beirut, Lebanon. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2459–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Lee, S.-C.; Huang, Y.; Ho, K.F.; Ho, S.S.H.; Yau, P.; Louie, P.; Zhang, R. Diurnal and seasonal trends of carbonyl compounds in roadside, urban, and suburban environment of Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, K.; Ho, S.S.H.; Louie, P.K.; Chan, C.; Lee, S.-C.; Hu, D.; Chan, P.W.; Lee, J.C.W.; Ho, K. Seasonal behavior of carbonyls and source characterization of formaldehyde (HCHO) in ambient air. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legreid, G.; Lööv, J.B.; Staehelin, J.; Hueglin, C.; Hill, M.; Buchmann, B.; Prevot, A.; Reimann, S. Oxygenated volatile organic compounds (OVOCs) at an urban background site in Zürich (Europe): Seasonal variation and source allocation. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8409–8423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.; Fitz, E.; Hagan, T.; Sive, B.; Frinak, E.; Haase, K.; Cottrell, L.; Buckley, S.; Talbot, R. Long-term study of VOCs measured with PTR-MS at a rural site in New Hampshire with urban influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 4677–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlundt, C.; Tegtmeier, S.; Lennartz, S.; Bracher, A.; Cheah, W.; Krüger, K.; Quack, B.; Marandino, C.A. Oxygenated volatile organic carbon in the western Pacific convective centre: Ocean cycling, air-sea gas exchange and atmospheric transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10837–10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Read, K.; Carpenter, L.; Arnold, S.; Beale, R.; Nightingale, P.; Hopkins, J.; Lewis, A.; Lee, J.D.; Mendes, L.; Pickering, S.J. Multiannual Observations of Acetone, Methanol, and Acetaldehyde in Remote Tropical Atlantic Air: Implications for Atmospheric OVOC Budgets and Oxidative Capacity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11028–11039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Wen, S.; Lü, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Characteristics of atmospheric carbonyls and VOCs in Forest Park in South China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 137, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco, R.; Peñuelas, J.; Filella, I.; Llusià, J.; Molowny-Horas, R.; Schallhart, S.; Metzger, A.; Müller, M.; Hansel, A. Contrasting winter and summer VOC mixing ratios at a forest site in the Western Mediterranean Basin: The effect of local biogenic emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 13161–13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khwaja, H.A.; Narang, A. Carbonyls and non-methane hydrocarbons at a rural mountain site in northeastern United States. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 2030–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudries, H.; Bottenheim, J.; Guimbaud, C.; Grannas, A.; Shepson, P.; Houdier, S.; Perrier, S.; Domine, F. Distribution and trends of oxygenated hydrocarbons in the high Arctic derived from measurements in the atmospheric boundary layer and in-terstitial snow air during the ALERT2000 field campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 2573–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabilia, R.; Di Palo, V.; Cassardo, C.; Ciuchini, C.; Pasini, A.; Possanzini, M. Measurements of lower carbonyls and hydro-carbons at Ny-Alesund, Svalbard. Ann. Chim. J. Anal. Environ. Cult. Herit. Chem. 2007, 97, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar]



| Carbonyl | 9:00–13:00 * | 13:00–17:00 * | 17:00–21:00 * | 21:00–9:00 * | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formaldehyde | 5.96 ± 2.96 | 5.55 ± 1.64 | 5.25 ± 1.9 | 6.57 ± 2.67 | 6.08 ± 2.37 |
| Acetaldehyde | 1.42 ± 0.64 | 1.54 ± 0.53 | 1.16 ± 0.45 | 1.98 ± 1.12 | 1.68 ± 0.78 |
| Acetone | 2.51 ± 0.81 | 2.72 ± 0.56 | 2.43 ± 0.43 | 2.50 ± 0.84 | 2.52 ± 0.68 |
| Propionaldehyde | 0.08 ± 0.05 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.09 | 0.10 ± 0.06 |
| Crotonaldehyde | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 0.03 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.02 |
| Butyraldehyde | 0.28 ± 0.13 | 0.28 ± 0.09 | 0.24 ± 0.10 | 0.39 ± 0.21 | 0.33 ± 0.15 |
| Benzaldehyde | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.03 |
| i-Valeraldehyde | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.04 | 0.03 ± 0.03 |
| n-Valeraldehyde | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.02 |
| o-Tolualdehyde | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
| m-Tolualdehyde | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| p-Tolualdehyde | 0.08 ± 0.09 | 0.07 ± 0.07 | 0.05 ± 0.05 | 0.11 ± 0.12 | 0.09 ± 0.09 |
| Hexaldehyde | 0.08 ± 0.05 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.13 ± 0.09 | 0.10 ± 0.06 |
| 2,5-Dimethyl-benzaldehyde | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.03 |
| Methacrolein | 0.06 ± 0.06 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.10 ± 0.08 | 0.08 ± 0.06 |
| Glyoxal | 0.25 ± 0.20 | 0.20 ± 0.16 | 0.14 ± 0.10 | 0.22 ± 0.10 | 0.21 ± 0.15 |
| Methylglyoxal | 0.48 ± 0.31 | 0.49 ± 0.28 | 0.30 ± 0.17 | 0.41 ± 0.14 | 0.42 ± 0.25 |
| Total | 11.39 ± 4.81 | 11.27 ± 2.80 | 9.95 ± 2.96 | 12.7 ± 4.83 | 11.79 ± 4.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, C.; Li, S.; Yin, B.; Gu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Azzi, M.; Li, H.; et al. Atmospheric Carbonyl Compounds in the Central Taklimakan Desert in Summertime: Ambient Levels, Composition and Sources. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050761
Geng C, Li S, Yin B, Gu C, Liu Y, Li L, Li K, Zhang Y, Azzi M, Li H, et al. Atmospheric Carbonyl Compounds in the Central Taklimakan Desert in Summertime: Ambient Levels, Composition and Sources. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(5):761. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050761
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Chunmei, Shijie Li, Baohui Yin, Chao Gu, Yingying Liu, Liming Li, Kangwei Li, Yujie Zhang, Merched Azzi, Hong Li, and et al. 2022. "Atmospheric Carbonyl Compounds in the Central Taklimakan Desert in Summertime: Ambient Levels, Composition and Sources" Atmosphere 13, no. 5: 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050761
APA StyleGeng, C., Li, S., Yin, B., Gu, C., Liu, Y., Li, L., Li, K., Zhang, Y., Azzi, M., Li, H., Wang, X., Yang, W., & Bai, Z. (2022). Atmospheric Carbonyl Compounds in the Central Taklimakan Desert in Summertime: Ambient Levels, Composition and Sources. Atmosphere, 13(5), 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050761








