Sources and Variability of Plutonium in Chinese Soils: A Statistical Perspective with Moving Average
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Basic Statistics
2.3. Statistical Analysis
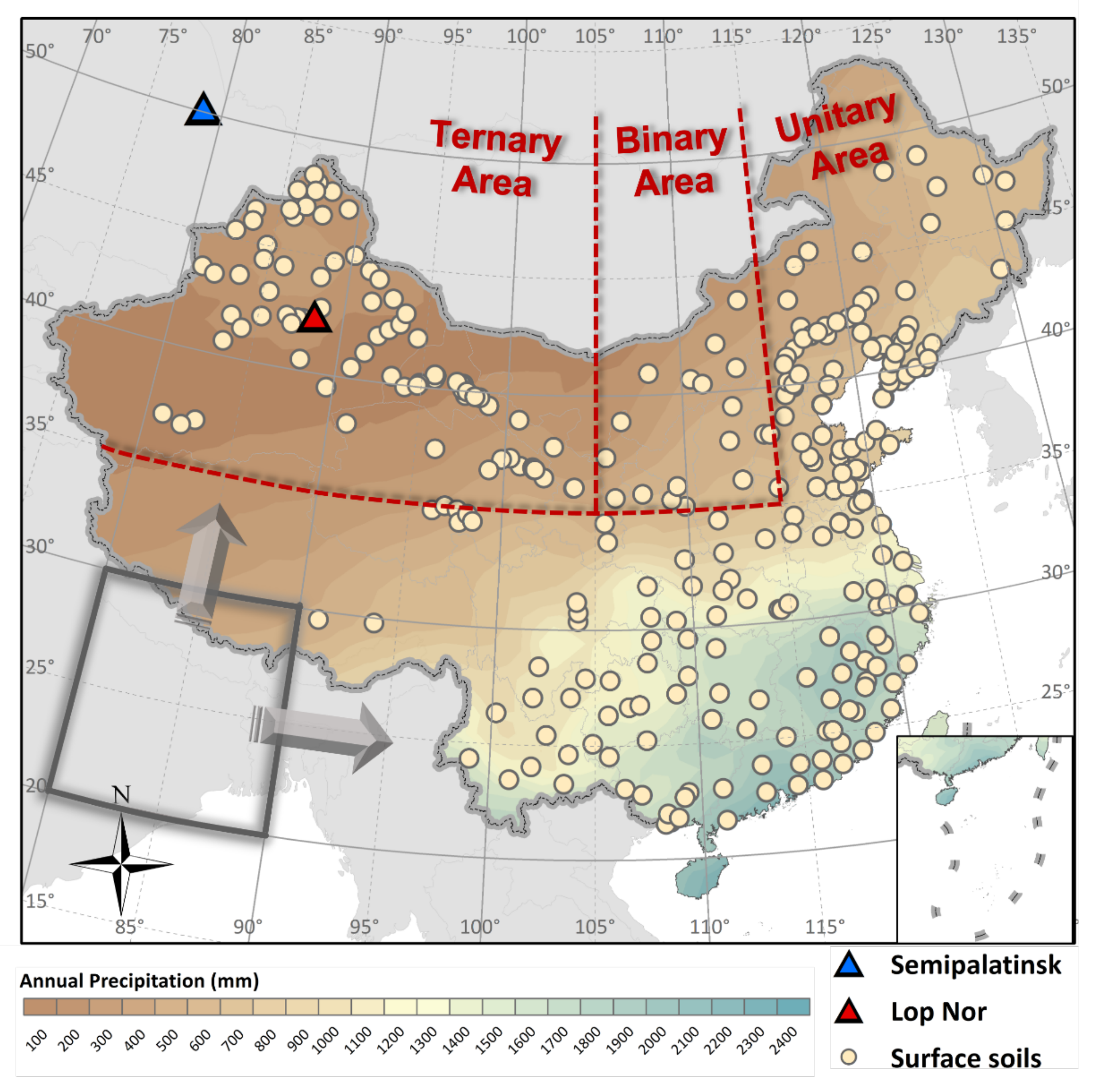
2.4. Geographical Partitioning and Visualization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Sources of Pu in Chinese Soils
3.2. The Ternary Area
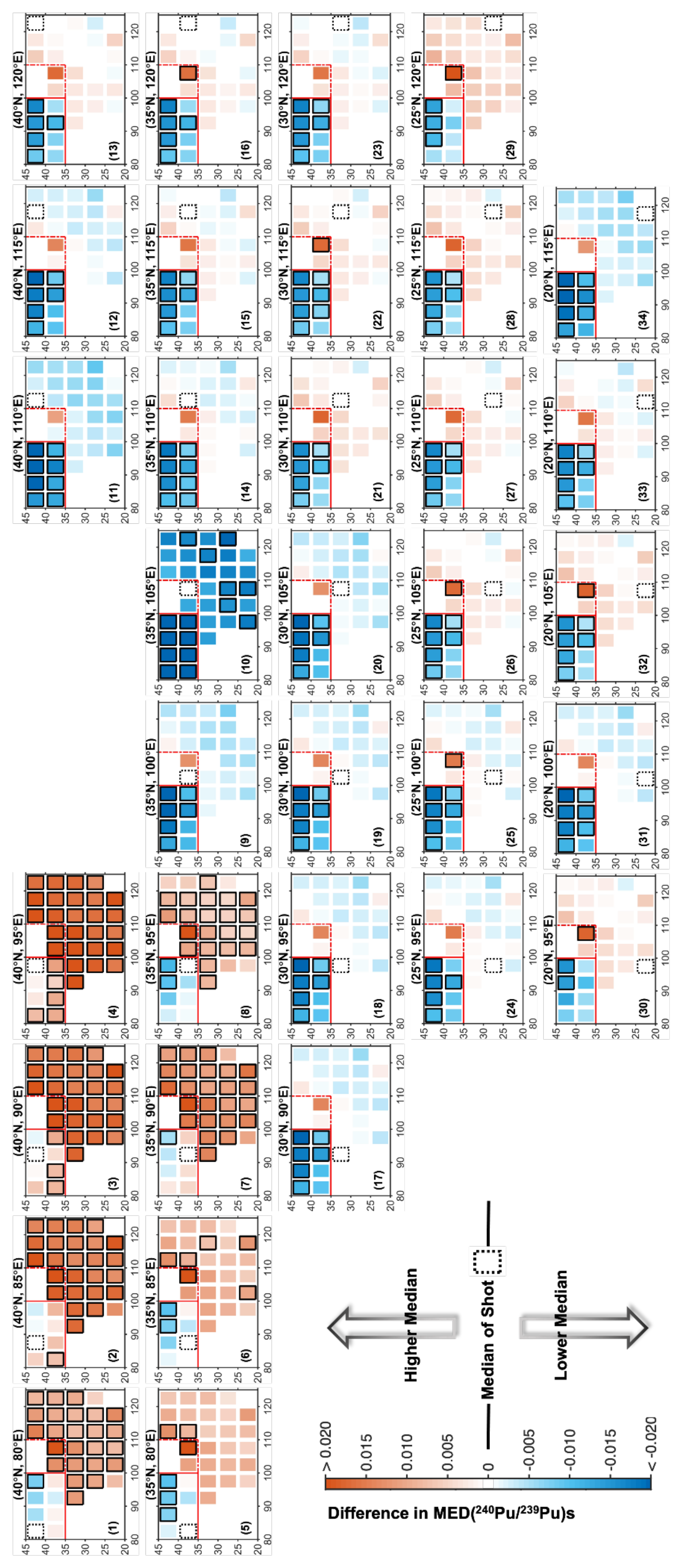
3.2.1. Multiple Influences of the STS, LNTS and the Global Fallout
- As in Figure 2(1)–(8), the MED(Pu/Pu) of the eight target shots (black dashed line) were all lower than the other 26 shots, illustrating the MED(Pu/Pu) in the corresponding area were systematically lower that other areas of China;
- The rank sum tests were conducted between the Pu/Pu datasets in each of the eight target shot with those in the other shots. As in Figure 2(1)–(8), for each of the eight shots, there always exited other shots that have different Pu/Pu data distributions apart from the eight shots. Especially in Figure 2(4), most of the other 26 shots were significantly different from the corresponding target shots.
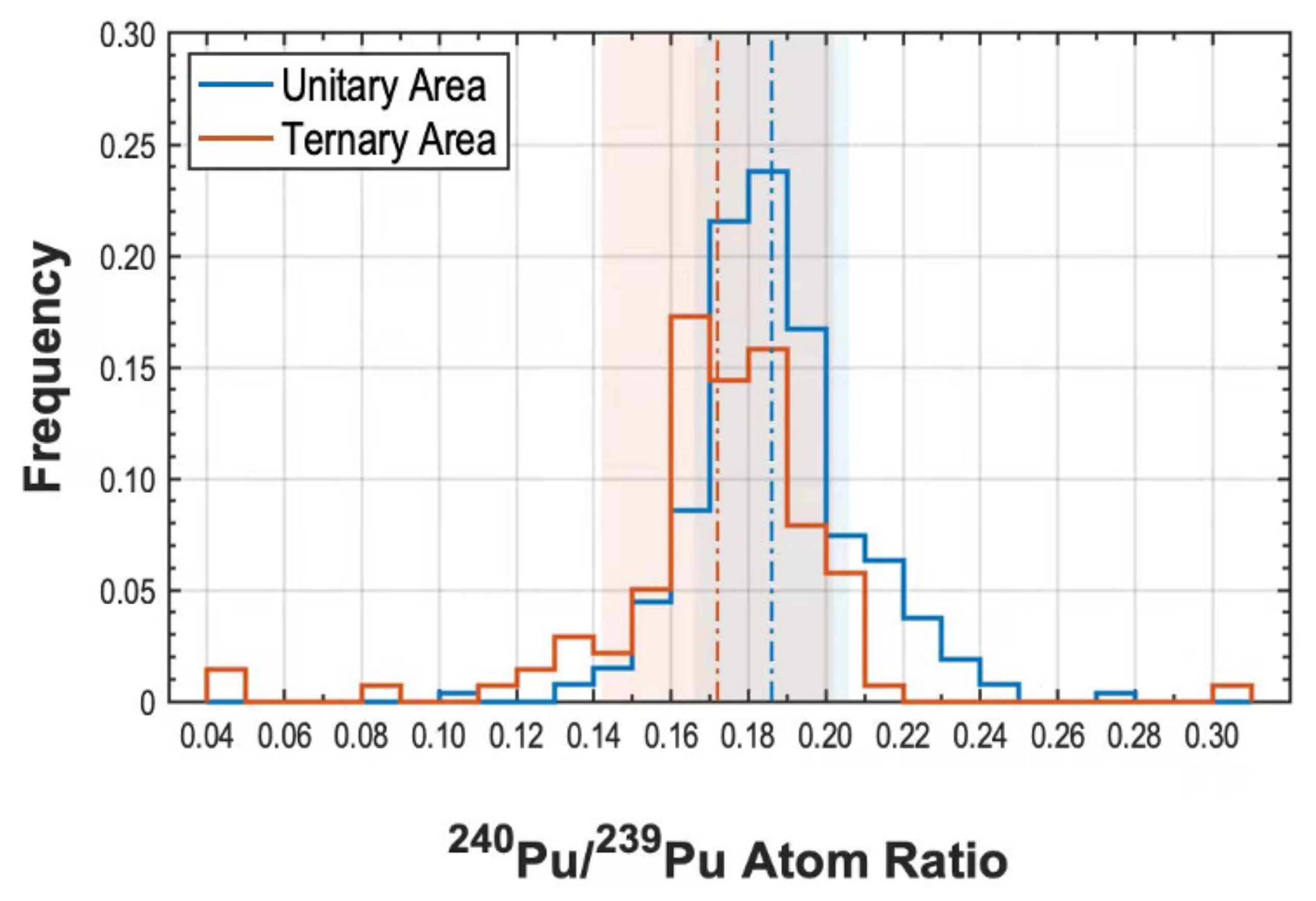
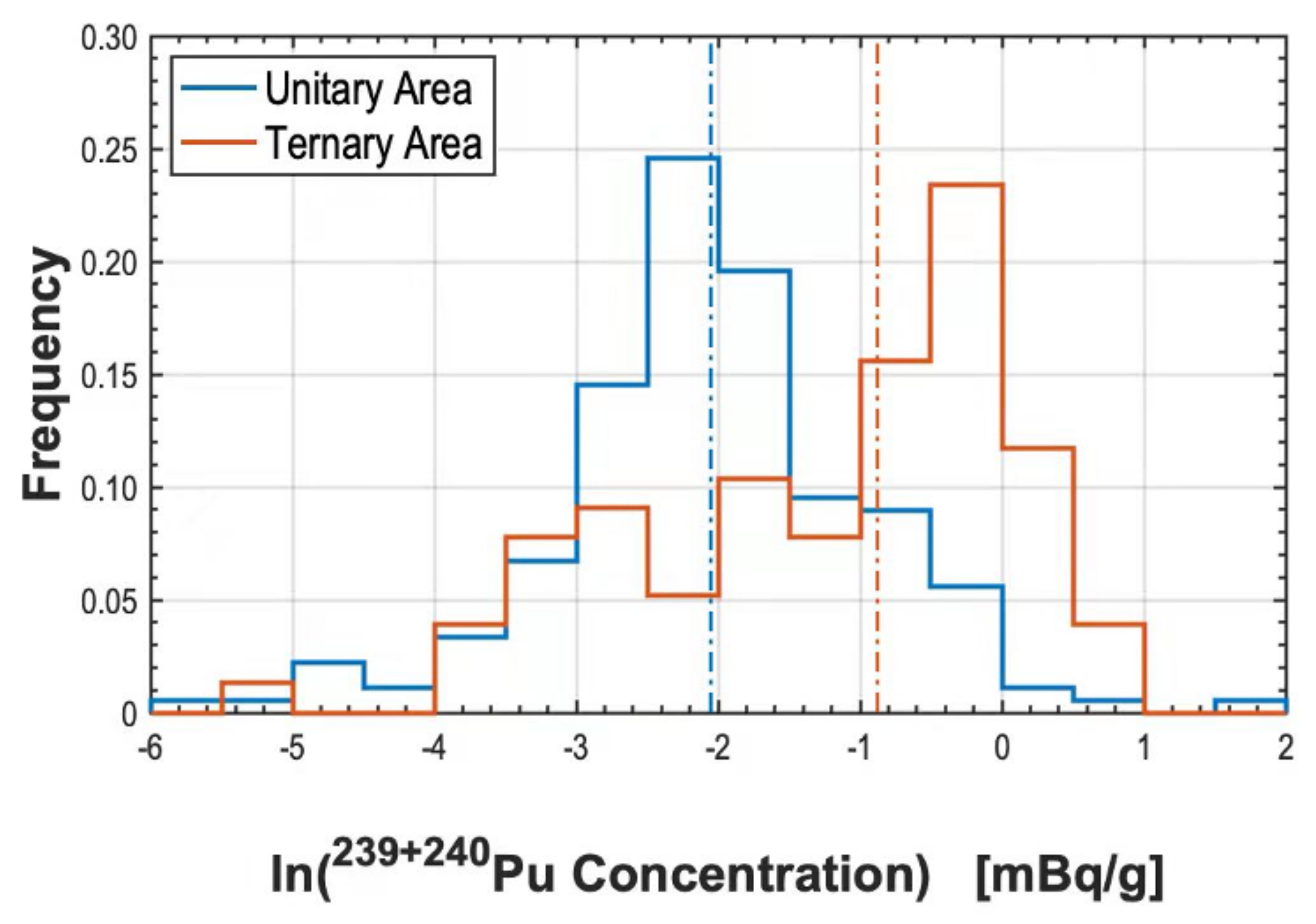
3.2.2. Distribution of Pu in the Ternary Area
Lower Pu/Pu Atom Ratios
Raise of Pu Concentrations
3.3. The Binary Area
3.3.1. Mutual Influences of the LNTS and the Global Fallout
3.3.2. Distribution of Pu in the Binary Area
3.4. The Unitary Area
3.4.1. Exclusive Influence of the Global Fallout
3.4.2. Representative of the Global Fallout in Chinese Soils
Pu/Pu Atom Ratios
Surface Pu Concentrations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| 80–90 E | 85–95 E | 90–100 E | 95–105 E | 100–110 E | 105–115 E | 115–125 E | 120–130 E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40–50 N | 0.1745 | 0.169 | 0.168 | 0.1665 | 0.189 | 0.186 | ||
| 35–45 N | 0.1765 | 0.176 | 0.172 | 0.1775 | 0.1875 | 0.200 | 0.185 | 0.184 |
| 30–40 N | 0.186 | 0.186 | 0.186 | 0.187 | 0.1825 | 0.183 | ||
| 25–35 N | 0.185 | 0.185 | 0.183 | 0.183 | 0.182 | |||
| 20–30 N | 0.182 | 0.186 | 0.182 | 0.184 | 0.188 |
| 80–90 E | 85–95 E | 90–100 E | 95–105 E | 100–110 E | 105–115 E | 115–125 E | 120–130 E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40–50 N | 0.171 ± 0.024 | 0.172 ± 0.031 | 0.162 ± 0.040 | 0.147 ± 0.043 | 0.194 ± 0.022 | 0.188 ± 0.023 | ||
| 35–45 N | 0.181 ± 0.014 | 0.181 ± 0.028 | 0.170 ± 0.037 | 0.170 ± 0.034 | 0.186 ± 0.017 | 0.194 ± 0.018 | 0.191 ± 0.019 | 0.186 ± 0.023 |
| 30–40 N | 0.188 ± 0.016 | 0.184 ± 0.014 | 0.186 ± 0.018 | 0.188 ± 0.021 | 0.186 ± 0.017 | 0.186 ± 0.021 | ||
| 25–35 N | 0.186 ± 0.012 | 0.186 ± 0.015 | 0.184 ± 0.017 | 0.186 ± 0.018 | 0.187 ± 0.021 | |||
| 20–30 N | 0.182 ± 0.017 | 0.189 ± 0.019 | 0.186 ± 0.020 | 0.184 ± 0.020 | 0.189 ± 0.020 |
Appendix B
| Statistical Test | Pu/Pu Atom Ratio | Pu Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| (a) Among 20–30 N, 30–40 N, 40–50 N (of the Unitary area) | ||
| Brown Forsythe | 0.49 | 0.007 |
| Kruskal-Wallis | 0.92 | 0.14 |
| One-way ANOVA | 0.71 | (0.009) * |
| (b) Between the Unitary area and the Ternary area | ||
| Brown Forsythe | 0.10 | <1 × 4−10 |
| Rank sum test | <1 × 5−10 | <1 ×6−10 |
| Students’ t | <1 × 6−10 | (<1 × 5−10) * |
Appendix C

References
- Thakur, P.; Khaing, H.; Salminen-Paatero, S. Plutonium in the atmosphere: A global perspective. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 175, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNSCEAR (Ed.) Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation: United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation: UNSCEAR 2000 Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2000; OCLC: ocm45228885. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Tagami, K.; Guo, Q.; Uchida, S.; Tsukada, H. The transfer of fallout plutonium from paddy soil to rice: A field study in Japan. J. Environ. Radioact. 2019, 196, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Zheng, J.; Guo, Q.; Huang, Z.; Tagami, K.; Uchida, S. Extractability of global fallout Pu from agricultural soils and its potential indication of bioavailability. CATENA 2022, 210, 105884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, A.; Steier, P.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamamoto, M. Isotopic compositions of 236U and Pu isotopes in “black substances” collected from roadsides in Fukushima Prefecture: Fallout from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3691–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sakaguchi, A.; Ochiai, S.; Takada, T.; Hamataka, K.; Murakami, T.; Nagao, S. Isotopic Pu, Am and Cm signatures in environmental samples contaminated by the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 132, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Tagami, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Uchida, S.; Aono, T.; Ishii, N.; Yoshida, S.; Kubota, Y.; Fuma, S.; Ihara, S. Isotopic evidence of plutonium release into the environment from the Fukushima DNPP accident. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bu, W.; Ni, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zheng, J.; Uchida, S. Pu isotopes in soils collected downwind from Lop Nor: Regional fallout vs. global fallout. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, W.; Guo, Q.; Zheng, J.; Uchida, S. Plutonium concentration and 240Pu/239Pu isotopic ratio in the surface soils from the Jiuquan region in northwestern China. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2017, 311, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qiao, J.; Hou, X. Plutonium isotopes in Northern Xinjiang, China: Level, distribution, sources and their contributions. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W. Plutonium Isotopes in the Environment: Distributions and Behaviors. Ph.D. Thesis, Peking University, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Hou, X. Level, distribution and sources of plutonium in the coastal areas of China. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hou, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Dang, H.; Xing, S.; Chen, N. Level, distribution and sources of plutonium in the northeast and north China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krey, P.; Hardy, E.; Pachucki, C.; Rourke, F.; Coluzza, J.; Benson, W. Mass isotopic composition of global fall-out plutonium in soil. In Transuranium Nuclides in the Environment; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, J.; Bond, L.; Beasley, T. Global distribution of Pu isotopes and 237Np. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 237, 483–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tims, S.G.; Froehlich, M.B.; Pan, S.; Fifield, L.K.; Pavetich, S.; Koll, D. The 240Pu/239Pu atom ratio in Chinese soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, Z. Spatial distribution and migration of 239+240Pu in Chinese soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, W.; Zheng, J.; Guo, Q.; Uchida, S. Vertical distribution and migration of global fallout Pu in forest soils in southwestern China. J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 136, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zheng, J.; Guo, Q. Particle-size speciation of Pu isotopes in surface soils from Inner Mongolia (China) and its implications for Asian Dust monitoring. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2017, 120, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Sun, S.; Sun, S.; Wang, H.; Ruan, X.; Liu, Z.; Terrasi, F.; Gialanella, L.; Shen, H. Distribution and sources of plutonium along the coast of Guangxi, China. In Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 437, pp. 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Huang, C.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Han, X.; Liu, Z. Vertical distribution of Pu in forest soil in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Environ. Radioact. 2021, 229, 106548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S. Trace Application of Long-Lived Radionuclides 239+240Pu and 129I in the Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, S.; Zhang, W.; Qiao, J.; Hou, X. Determination of ultra-low level plutonium isotopes (239Pu, 240Pu) in environmental samples with high uranium. Talanta 2018, 187, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Hou, X.; Pan, S. Plutonium in soils from northeast China and its potential application for evaluation of soil erosion. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Pan, S.; Wu, M.; Zhang, K.; Hao, Y. Association of Plutonium isotopes with natural soil particles of different size and comparison with 137Cs. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Lin, J.; Tan, Z.; Huang, W. Distinctive distributions and migrations of 239+240Pu and 241Am in Chinese forest, grassland and desert soils. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Guo, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Huang, W.; Bu, W. First study of 237Np in Chinese soils: Source, distribution and mobility in comparison with plutonium isotopes. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, L.; Yamamoto, M.; Komura, K.; Ueno, K. 239,240Pu, 241Am and 137Cs in soils from several areas in China. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1991, 155, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Tian, M.; Zhou, X.; Wu, W.; Jin, Y. 239+240Pu and 137Cs in soils of three sites from Shanxi and Henan. Radiat. Prot. 2013, 33, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Mai, J.; Guan, Y.; Liu, Z. Radionuclides in the environment around the uranium mines in Guangxi, China. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2020, 159, 109098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Isotopic composition and source of plutonium in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau frozen soils. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yamada, M.; Wu, F.; Liao, H. Characterization of Pu concentration and its isotopic composition in soils of Gansu in northwestern China. J. Environ. Radioact. 2009, 100, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zheng, J.; Liao, H.; Yamada, M. Vertical distributions of plutonium and 137Cs in lacustrine sediments in northwestern China: Quantifying sediment accumulation rates and source identifications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Hoshi, M.; Takada, J.; Oikawa, S.; Yoshikawa, I.; Takatsuji, T.; Sekerbaev, A.K.; Gusev, B. Some aspects of environmental radioactivity around the former Soviet Union""" s Semipalatinsk nuclear test site: Local fallout Pu in Ust"""-Kamenogorsk district. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2002, 252, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Bu, W.; Zheng, J.; Wu, F.; Yamada, M. Vertical Distributions of Radionuclides (239+240Pu, 240Pu/239Pu, and 137Cs) in Sediment Cores of Lake Bosten in Northwestern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3840–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, K.; Povinec, P.P. Sources of plutonium in the atmosphere and stratosphere-troposphere mixing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leifer, R.; Toonkel, L. Plutonium isotopic analysis of stratospheric samples from April 1977. In Report EML-390; Environmental Measurements Laboratory (EML): Manhattan, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 1–407. [Google Scholar]
- Meusburger, K.; Evrard, O.; Alewell, C.; Borrelli, P.; Cinelli, G.; Ketterer, M.; Mabit, L.; Panagos, P.; Van Oost, K.; Ballabio, C. Plutonium aided reconstruction of caesium atmospheric fallout in European topsoils. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zheng, J.; Tagami, K.; Uchida, S. Plutonium concentration and isotopic ratio in soil samples from central-eastern Japan collected around the 1970s. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Komura, K.; Sakanoue, M. 241Am and plutonium in Japanese rice-field surface soils. J. Radiat. Res. 1983, 24, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Lee, M.; Kim, C.; Kim, K. 90Sr, 137Cs, 239+240Pu and 238Pu concentrations in surface soils of Korea. J. Environ. Radioact. 1998, 40, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Lee, C.; Boo, B. Distribution and characteristics of 239,240Pu and 137Cs in the soil of Korea. J. Environ. Radioact. 1997, 37, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Oh, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.; Park, T.; Lujaniene, G.; Valiulis, D.; Šakalys, J. Distribution characteristics of 137Cs, Pu isotopes and 241Am in soil in Korea. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2013, 81, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Areas | Latitude Band | N | Range | AM ± SD | MED | LP | UP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unitary area | 20° N–30° N | 108 | 0.136–0.231 | 0.186 ± 0.020 | 0.185 | 0.173 | 0.196 |
| 30° N–40° N | 101 | 0.103–0.272 | 0.185 ± 0.021 | 0.184 | 0.176 | 0.194 | |
| 40° N–50° N | 55 | 0.144–0.245 | 0.188 ± 0.023 | 0.187 | 0.173 | 0.197 | |
| Total | 264 | 0.103–0.272 | 0.186 ± 0.021 | 0.184 | 0.174 | 0.195 | |
| Binary area | - | 17 | 0.147–0.221 | 0.194 ± 0.018 | 0.200 | 0.182 | 0.203 |
| Ternary area | - | 107 | 0.048–0.216 | 0.172 ± 0.030 | 0.174 | 0.166 | 0.186 |
| Areas | Latitude Band | N | Range | AM ± SD | MED | LP | UP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unitary area | 20° N–30° N | 77 | 0.003–1.3 | 0.16 ± 0.17 | 0.122 | 0.0765 | 0.194 |
| 30° N–40° N | 65 | 0.009–4.783 | 0.36 ± 0.65 | 0.149 | 0.079 | 0.466 | |
| 40° N–50° N | 36 | 0.023–0.67 | 0.16 ± 0.15 | 0.098 | 0.0645 | 0.2045 | |
| Total | 178 | 0.003–4.783 | 0.23 ± 0.41 | 0.1285 | 0.076 | 0.242 | |
| Binary area | - | 7 | 0.040–0.231 | 0.11 ± 0.06 | 0.098 | 0.0765 | 0.1325 |
| Ternary area | - | 77 | 0.005–1.99 | 0.53 ± 0.48 | 0.416 | 0.125 | 0.833 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Ni, Y.; Guo, Q. Sources and Variability of Plutonium in Chinese Soils: A Statistical Perspective with Moving Average. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050769
Li S, Ni Y, Guo Q. Sources and Variability of Plutonium in Chinese Soils: A Statistical Perspective with Moving Average. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(5):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050769
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Sixuan, Youyi Ni, and Qiuju Guo. 2022. "Sources and Variability of Plutonium in Chinese Soils: A Statistical Perspective with Moving Average" Atmosphere 13, no. 5: 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050769
APA StyleLi, S., Ni, Y., & Guo, Q. (2022). Sources and Variability of Plutonium in Chinese Soils: A Statistical Perspective with Moving Average. Atmosphere, 13(5), 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050769






