Functional Kriging for Spatiotemporal Modeling of Nitrogen Dioxide in a Middle Eastern Megacity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
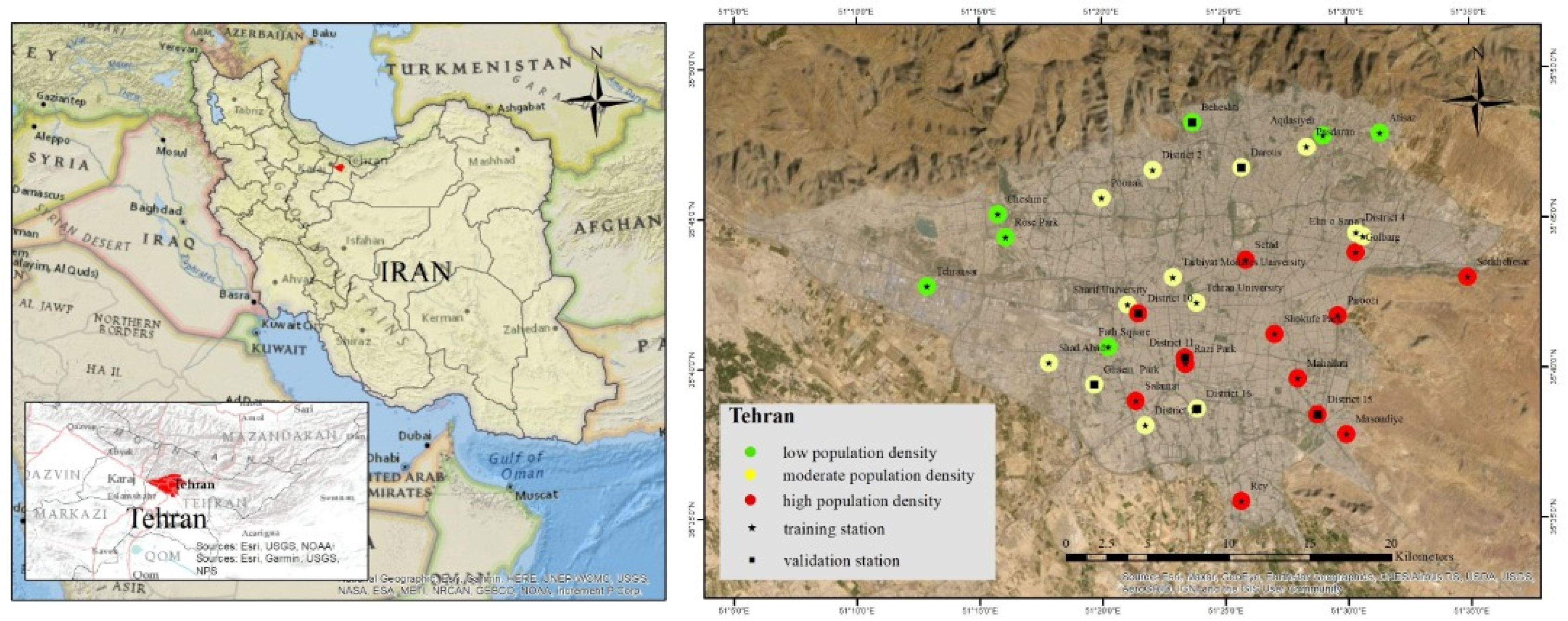
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Kriging for Functional Data
2.3.1. Expressing Functional Data Using Basis Functions Set
2.3.2. Estimating the Trace-Variogram
2.3.3. Choosing the Optimum Number of Basis Functions
2.3.4. Goodness-of-Fit Criteria
2.4. Functional Analysis of Variance
2.5. Software and Packages
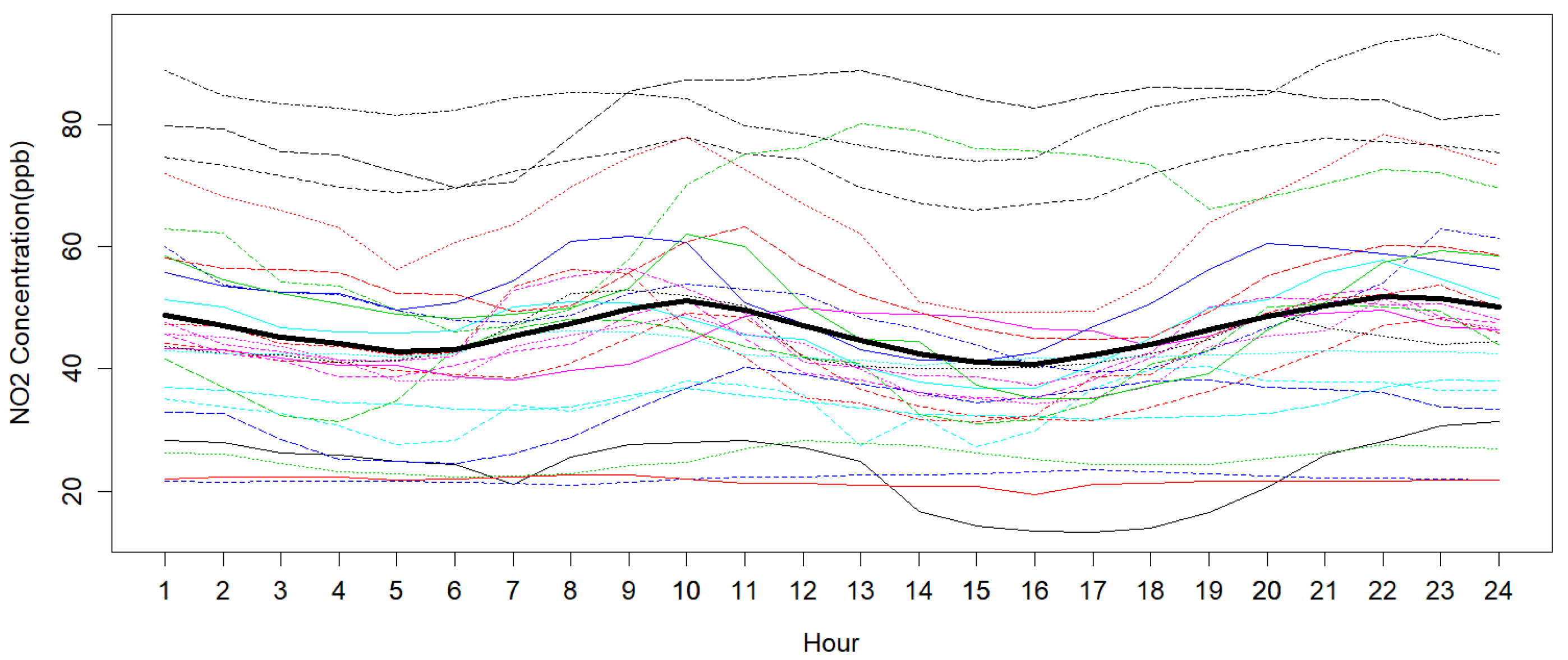
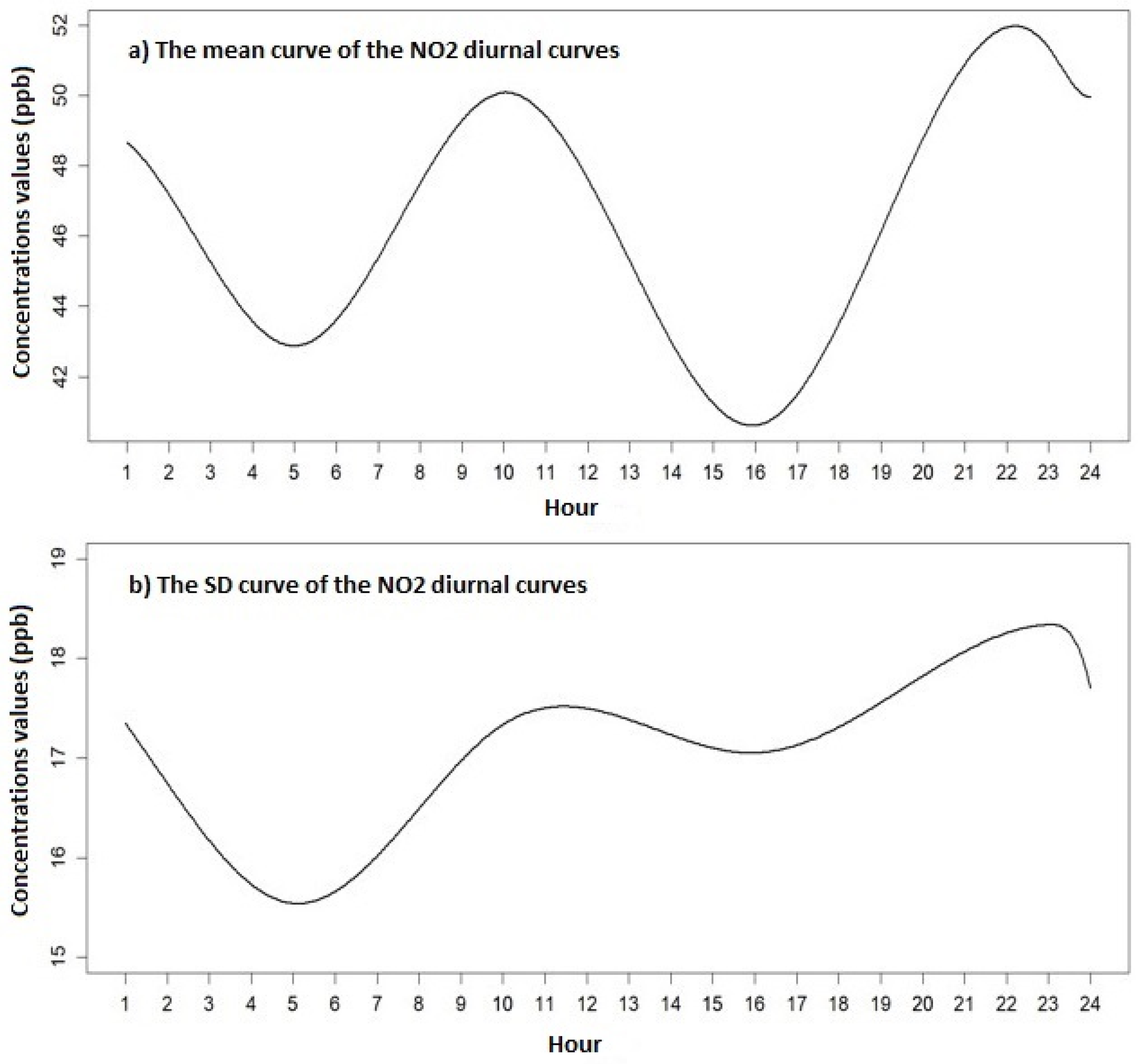
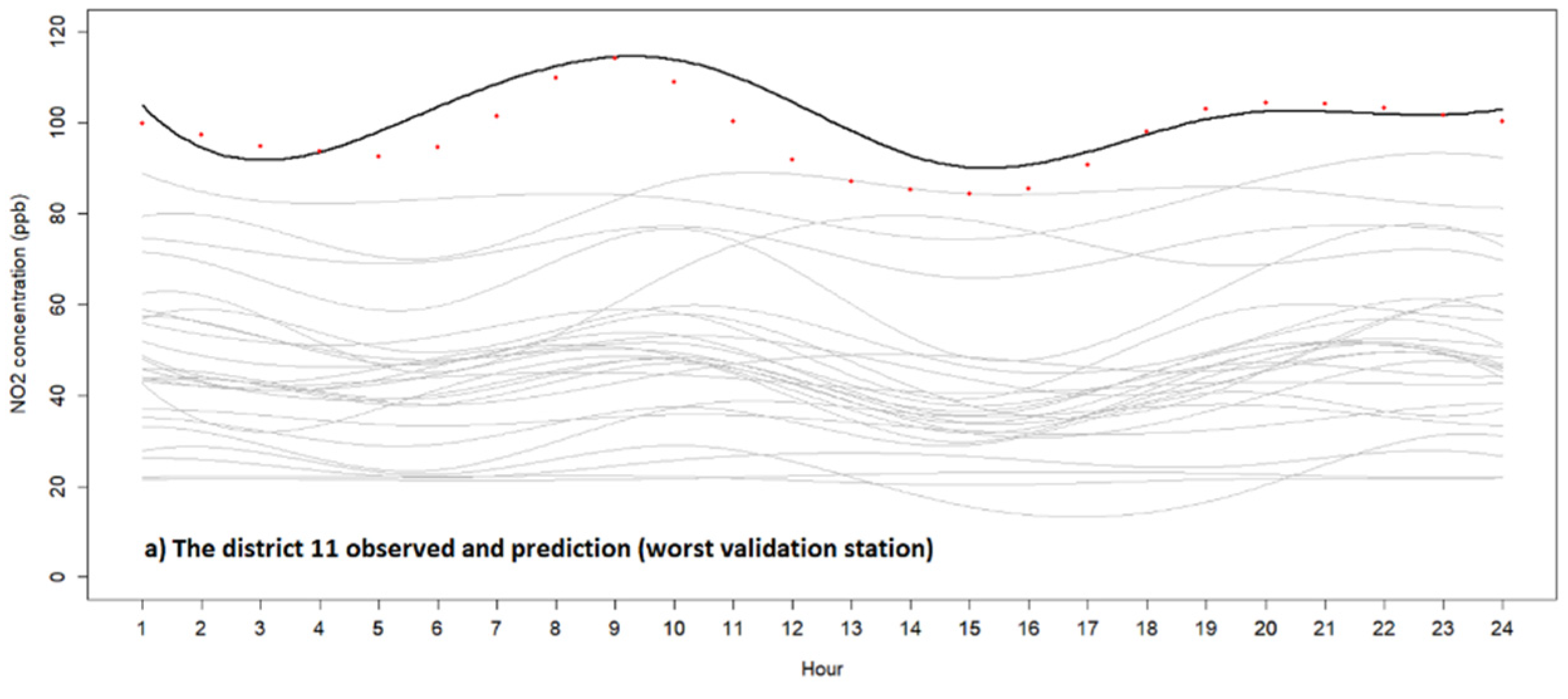
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kavousi, A.; Sefidkar, R.; Alavimajd, H.; Rashidi, Y. Spatial analysis of CO and PM10 pollutants in Tehran city. Arch. Adv. Biosci. J. Paramed. Sci. 2013, 4, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, R.; Andersen, Z.; Chen, J.; Stafoggia, M.; de Hoogh, K.; Katsouyanni, K.; Vienneau, D.; Rodopoulou, S.; Samoli, E.; Lim, Y.; et al. Long-term exposure to air pollution and mortality in a Danish nationwide administrative cohort study: Beyond mortality from cardiopulmonary disease and lung cancer. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominski, F.; Lorenzetti Branco, J.; Buonanno, G.; Stabile, L.; Gameiro da Silva, M.; Andrade, A. Effects of air pollution on health: A mapping review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habre, R.; Coull, B.; Moshier, E.; Godbold, J.; Grunin, A.; Nath, A.; Castro, W.; Schachter, N.; Rohr, A.; Kattan, M.; et al. Sources of indoor air pollution in New York City residences of asthmatic children. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movassaghi, K.; Campanella, L.; Avino, P. The first investigation on PM10 and SO2 levels in an Iranian megacity, Isfahan, and a relative comparison with Rome. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2008, 17, 786–792. [Google Scholar]
- Kamińska, J.; Jiménez, F.; Lucena-Sánchez, E.; Sciavicco, G.; Turek, T. Lag Variables in Nitrogen Oxide Concentration Modelling: A Case Study in Wrocław, Poland. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedrahmat, Z.; Vosoughi, M.; Tahmasebi Birgani, Y.; Neisi, A.; Goudarzi, G.; Takdastan, A. Prediction of O3 in the respiratory system of children using the artificial neural network model and with selection of input based on gamma test, Ahvaz, Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 10941–10950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafoggia, M.; Bellander, T.; Bucci, S.; Davoli, M.; de Hoogh, K.; de’ Donato, F.; Gariazzo, C.; Lyapustin, A.; Michelozzi, P.; Renzi, M.; et al. Estimation of daily PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations in Italy, 2013–2015, using a spatiotemporal land-use random-forest model. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Q.; Amini, H.; Shi, L.; Kloog, I.; Silvern, R.; Kelly, J.; Sabath, M.; Choirat, C.; Koutrakis, P.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. Assessing NO2 concentration and model uncertainty with high spatiotemporal resolution across the contiguous united states using ensemble model averaging. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bai, Z.; Kong, S.; Han, B.; You, Y.; Ding, X.; Du, S.; Liu, A. A land use regression for predicting NO2 and PM10 concentrations in different seasons in Tianjin region, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S. Emission Load Distribution and Prediction of NO2 and PM10 using ISCST3 and CALINE4 Line Source Modeling. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 6, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Koutrakis, P. Daily ambient NO2 concentration predictions using satellite ozone monitoring instrument NO2 data and land use regression. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2305–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiusolo, M.; Cadum, E.; Stafoggia, M.; Galassi, C.; Berti, G.; Faustini, A.; Bisanti, L.; Vigotti, M.A.; Dessì, M.P.; Cernigliaro, A.; et al. Short-term effects of nitrogen dioxide on mortality and susceptibility factors in 10 Italian cities: The EpiAir study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whitworth, K.W.; Symanski, E.; Lai, D.; Coker, A.L. Kriged and modeled ambient air levels of benzene in an urban environment: An exposure assessment study. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Araki, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Kondo, A. Application of regression kriging to air pollutant concentrations in Japan with high spatial resolution. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halimi, M.; Farajzadeh, M.; Zarei, Z. Modeling spatial distribution of Tehran air pollutants using geostatistical methods incorporate uncertainty maps. Pollution 2016, 2, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi-Shahri, S.M.; Fassò, A.; Mahaki, B.; Amini, H. Concurrent spatiotemporal daily land use regression modeling and missing data imputation of fine particulate matter using distributed space-time expectation maximization. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyaztas, U.; Salih, S.Q.; Chau, K.W.; Al-Ansari, N.; Yaseen, Z.M. Construction of functional data analysis modeling strategy for global solar radiation prediction: Application of cross-station paradigm. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2019, 13, 1165–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Finch, C.F. Applications of functional data analysis: A systematic review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2013, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giraldo, R.; Mateu, J. Kriging for Functional Data. Encycl. Environ. 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, W.; Giraldo, R.; Mateu, J. A universal kriging approach for spatial functional data. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, S. The Functional Spatio-Temporal Statistical Model with Application to O3 Pollution in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, H.; Taghavi-Shahri, S.M.; Henderson, S.; Hosseini, V.; Hassankhany, H.; Naderi, M.; Ahadi, S.; Schindler, C.; Künzli, N.; Yunesian, M. Annual and seasonal spatial models for nitrogen oxides in Tehran, Iran. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amini, H.; Schindler, C.; Hosseini, V.; Yunesian, M.; Künzli, N. Land Use Regression Models for Alkylbenzenes in a Middle Eastern Megacity: Tehran Study of Exposure Prediction for Environmental Health Research (Tehran SEPEHR). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8481–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shamsoddini, A.; Aboodi, M.R.; Karami, J. Tehran air pollutants prediction based on Random Forest feature selection method. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.—ISPRS Arch. 2017, 42, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.; Wan, L.; Lin, H.; Lin, C.; Wei, C. Long-Term Ambient Air Pollutant Exposure and Risk of Recurrent Headache in Children: A 12-Year Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, H.; Dehlendorff, C.; Lim, Y.; Mehta, A.; Jørgensen, J.; Mortensen, L.; Westendorp, R.; Hoffmann, B.; Loft, S.; Cole-Hunter, T.; et al. Long-term exposure to air pollution and stroke incidence: A Danish Nurse cohort study. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehbi, H.-M.; Blangiardo, M.; Gulliver, J.; Fecht, D.; de Hoogh, K.; Al-Kanaani, Z.; Tillin, T.; Hardy, R.; Chaturvedi, N.; Hansell, A.L. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Mortality with over 25 Years Follow-up: A Combined Analysis of Two British Cohorts. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toro, R.; Downward, G.S.; van der Mark, M.; Brouwer, M.; Huss, A.; Peters, S.; Hoek, G.; Nijssen, P.; Mulleners, W.M.; Sas, A. Parkinson’s Disease and Long-Term Exposure to Outdoor Air Pollution: A Matched Case-Control Study in the Netherlands. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Beelen, R.; Stafoggia, M.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, Z.J.; Hoffmann, B.; Fischer, P.; Houthuijs, D.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Weinmayr, G. Long-Term Exposure to Elemental Constituents of Particulate Matter and Cardiovascular Mortality in 19 European Cohorts: Results from the ESCAPE and TRANSPHORM Projects. Environ. Int. 2014, 66, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, R.; Qiu, H.; Lai, P.-C.; Wong, P.; Thach, T.-Q.; Allen, R.; Brauer, M.; Tian, L.; Barratt, B. Long Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Mortality in an Elderly Cohort in Hong Kong. Environ. Int. 2018, 117, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yorifuji, T.; Kashima, S.; Tsuda, T.; Ishikawa-Takata, K.; Ohta, T.; Tsuruta, K.; Doi, H. Long-Term Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution and the Risk of Death from Hemorrhagic Stroke and Lung Cancer in Shizuoka, Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefian, F.; Mahvi, A.H.; Yunesian, M.; Hassanvand, M.S.; Kashani, H.; Amini, H. Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children: A Case-Control Study in Tehran, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, D.; Kwon, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, W. Air Pollution and Incidence of Lung Cancer by Histological Type in Korean Adults: A Korean National Health Insurance Service Health Examinee Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Zoest, V.; Osei, F.B.; Hoek, G.; Stein, A. Spatio-temporal regression kriging for modelling urban NO2 concentrations. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masoudi, M.; Behzadi, F.; Sakhaei, M. Concentration of NO2 in the air over Tehran, Iran. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2017, 42, 728–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, H.; Taghavi-Shahri, S.M.; Henderson, S.B.; Naddafi, K.; Nabizadeh, R.; Yunesian, M. Land use regression models to estimate the annual and seasonal spatial variability of sulfur dioxide and particulate matter in Tehran, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, R.; Delicado, P.; Mateu, J. Ordinary kriging for function-valued spatial data. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2011, 18, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ignaccolo, R.; Mateu, J.; Giraldo, R. Kriging with external drift for functional data for air quality monitoring. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 1171–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramsay, J.; Hooker, G.; Graves, S. Linear models for functional responses. In Functional Data Analysis with R and MATLAB; Use R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 147–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Giraldo, R.; Delicado, P.; Mateu, J. Geofd: Spatial Prediction for Function Value Data. R Package, Version 2.0. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=geofd (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Ramsay, J.; Graves, S.; Hooker, G. FDA: Functional Data Analysis. R Package, Version 5.5.1. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=fda (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- World Health Organization; European Centre for Environment. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2. 5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Amini, H. WHO air quality guidelines need to be adopted. Int. J. Public Health 2021, 66, 1604483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, A.; Aliasghari, P.; Hosseini, V. Black carbon and PM2.5 monitoring campaign on the roadside and residential urban background sites in the city of Tehran. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 218, 116928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichowicz, R.; Stelęgowski, A. Average Hourly Concentrations of Air Contaminants in Selected Urban, Town, and Rural Sites. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 77, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno, T.; Karanasiou, A.; Amato, F.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Calzolai, G.; Chiari, M.; Coz, E.; Artíñano, B.; Lumbreras, J.; et al. Daily and hourly sourcing of metallic and mineral dust in urban air contaminated by traffic and coal-burning emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Yigit Avdan, Z. Space-borne air pollution observation from Sentinel-5p Tropomi: Relationship between pollutants, geographical and demographic data. Int. J. Eng. Geosci. 2020, 5, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorrami, Z.; Pourkhosravani, M.; Rezapour, M.; Etemad, K.; Taghavi-Shahri, S.; Künzli, N.; Amini, H.; Khanjani, N. Multiple air pollutant exposure and lung cancer in Tehran, Iran. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhjirgan, P.; Kashani, H.; Naddafi, K.; Nabizadeh, R.; Amini, H.; Yunesian, M. Maternal exposure to air pollutants and birth weight in Tehran, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorrami, Z.; Pourkhosravani, M.; Eslahi, M.; Rezapour, M.; Akbari, M.; Amini, H.; Taghavi-Shahri, S.; Künzli, N.; Etemad, K.; Khanjani, N. Multiple air pollutants exposure and leukaemia incidence in Tehran, Iran from 2010 to 2016: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e060562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
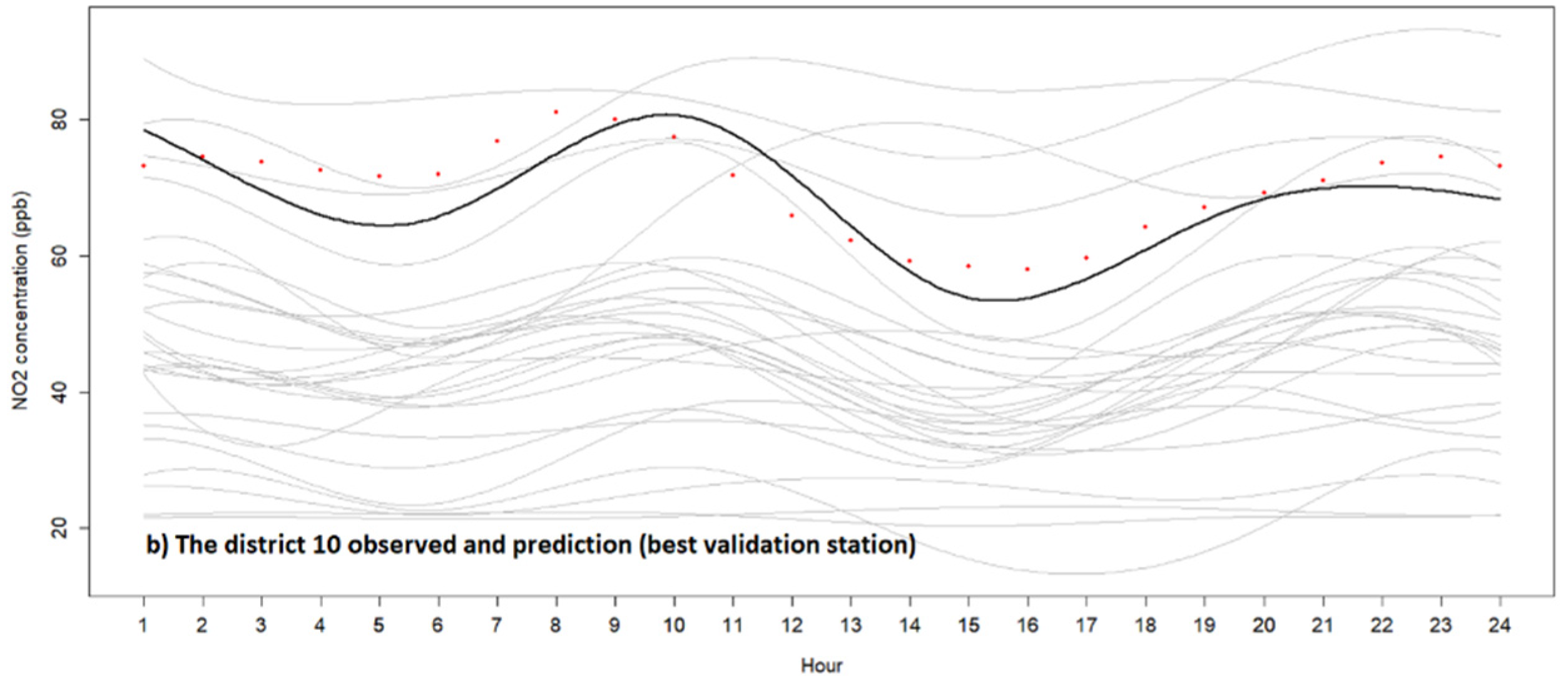
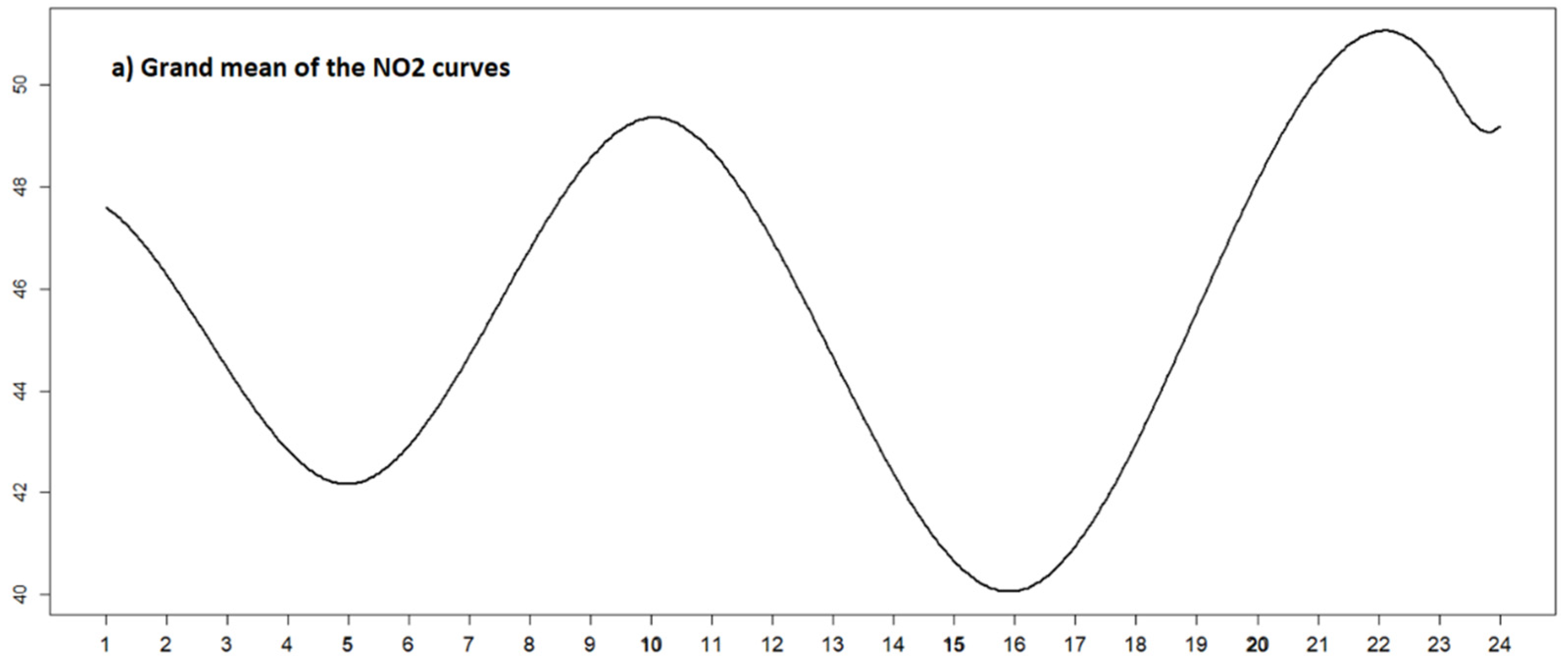

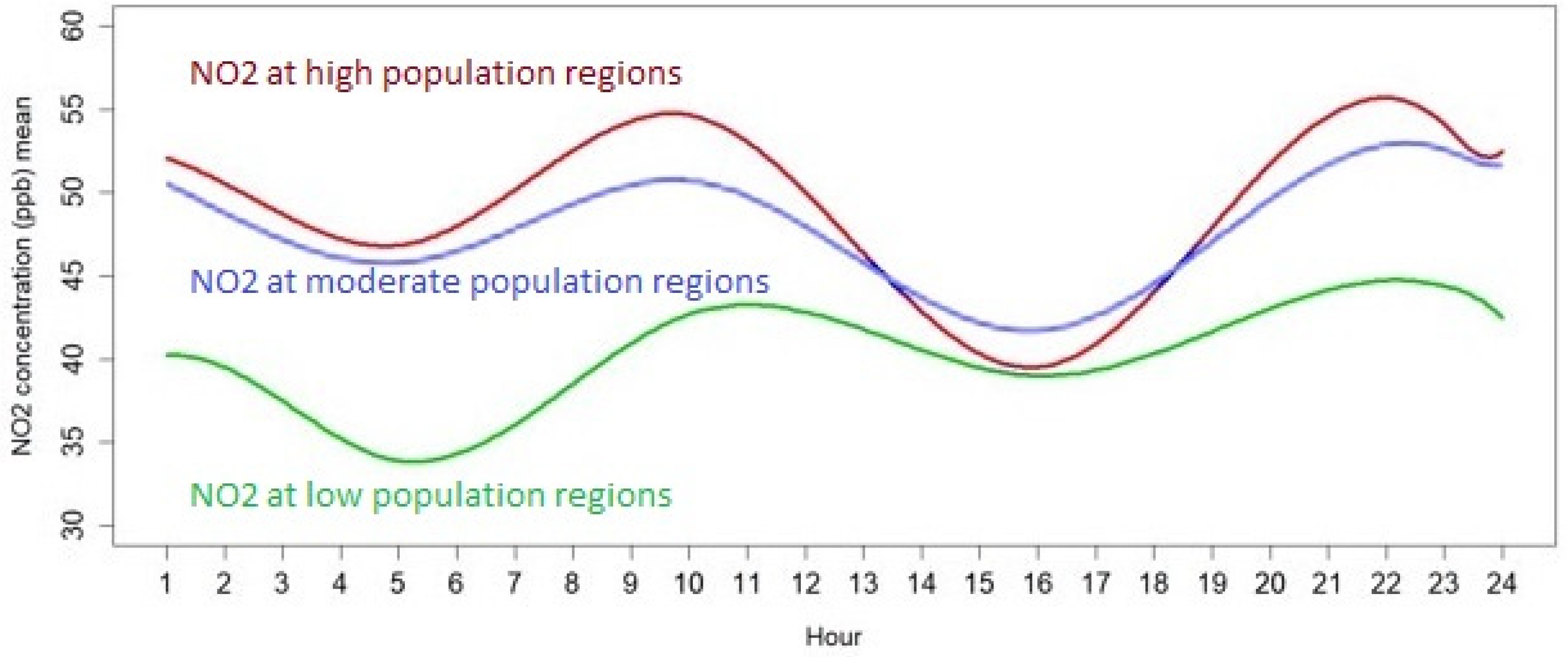
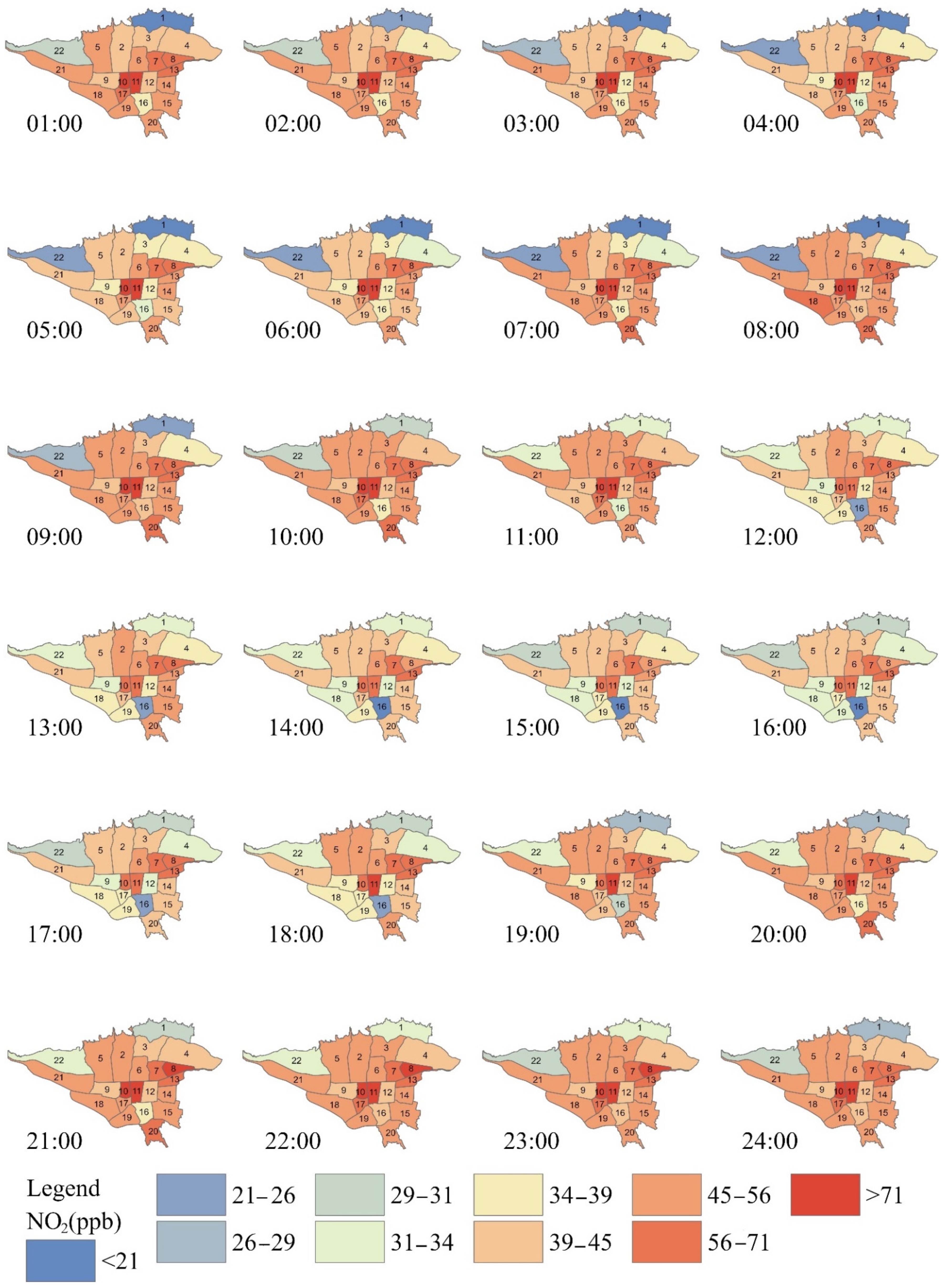
| Model | Range | Nug | Sill | SSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | 0.0864 | 8314.3153 | 5083.0897 | 10,041 × 103 |
| Exponential | 0.0248 | 7231.8342 | 6038.3758 | 10,081 × 103 |
| Gaussian | 0.0444 | 6973.2334 | 6452.3365 | 10,049 × 103 |
| Matérn with fixed kappa = 1 | 1554.782 | 8184.138 | 12943.076 | 10,131 × 103 |
| Station Name | NMBF | RMSE | WNNR | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beheshti | 0.134 | 7.24 | 0.0276 | 0.649 |
| Darous | −0.030 | 4.65 | 0.0004 | 0.846 |
| Ghaem | 0.033 | 5.51 | 0.0029 | 0.839 |
| District 10 | 0.001 | 2.49 | 0.0096 | 0.903 |
| District 11 | 0.142 | 6.52 | 0.0517 | 0.614 |
| District 15 | 0.130 | 6.17 | 0.0165 | 0.739 |
| District 16 | −0.066 | 3.45 | 0.0080 | 0.877 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmadi Basiri, E.; Taghavi-Shahri, S.M.; Mahaki, B.; Amini, H. Functional Kriging for Spatiotemporal Modeling of Nitrogen Dioxide in a Middle Eastern Megacity. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071095
Ahmadi Basiri E, Taghavi-Shahri SM, Mahaki B, Amini H. Functional Kriging for Spatiotemporal Modeling of Nitrogen Dioxide in a Middle Eastern Megacity. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(7):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071095
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmadi Basiri, Elham, Seyed Mahmood Taghavi-Shahri, Behzad Mahaki, and Heresh Amini. 2022. "Functional Kriging for Spatiotemporal Modeling of Nitrogen Dioxide in a Middle Eastern Megacity" Atmosphere 13, no. 7: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071095
APA StyleAhmadi Basiri, E., Taghavi-Shahri, S. M., Mahaki, B., & Amini, H. (2022). Functional Kriging for Spatiotemporal Modeling of Nitrogen Dioxide in a Middle Eastern Megacity. Atmosphere, 13(7), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071095







