Seasonal Variation Characteristics of VOCs and Their Influences on Secondary Pollutants in Yibin, Southwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
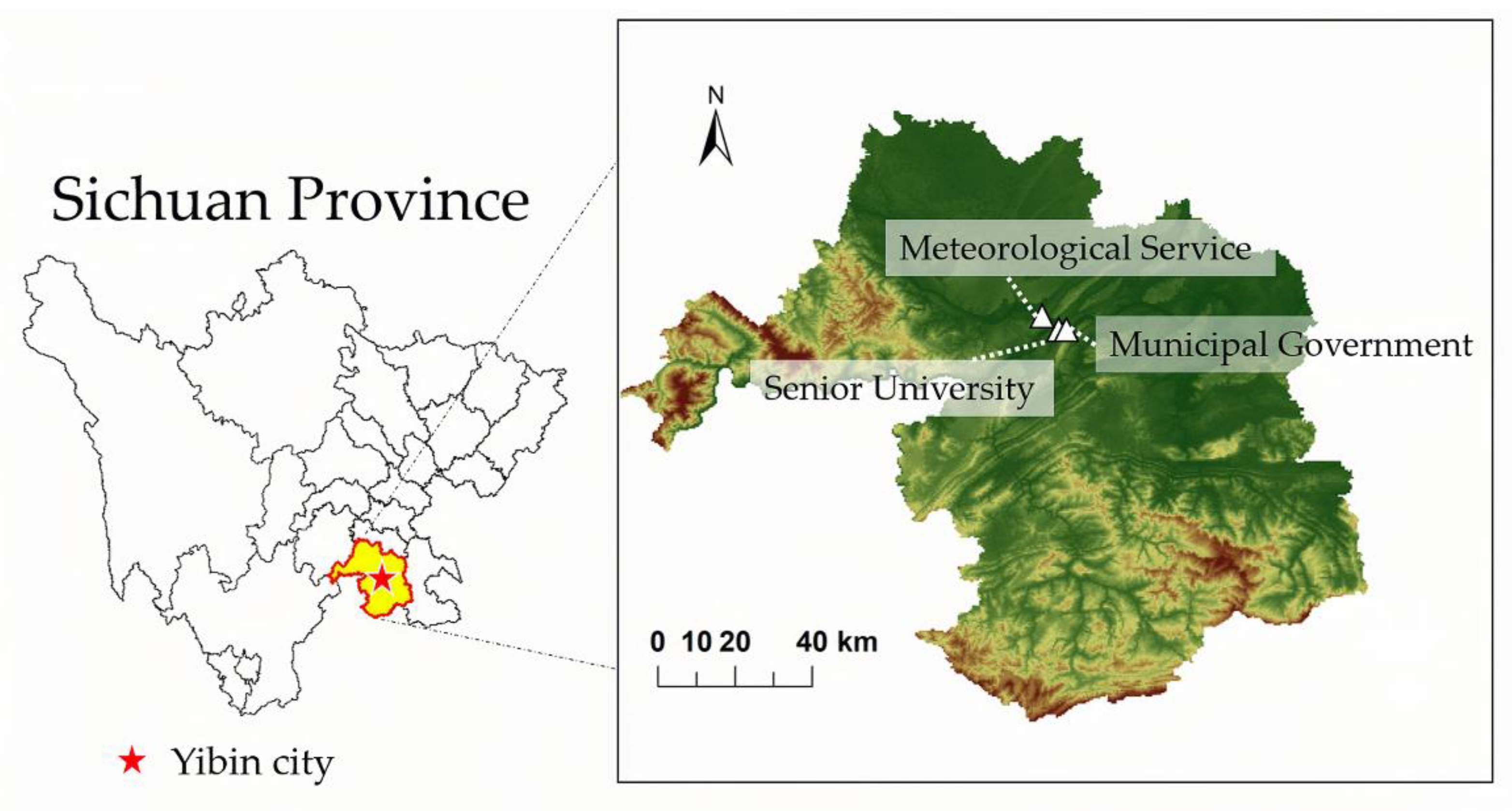
2.1. On-Line Sampling and Analysis
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. The OH Loss Rate of VOCs (LOH)
2.2.2. Ozone Formation Potential (OFP)
2.2.3. Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation Potential (SOAP)
2.2.4. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF)
3. Results and Discussions
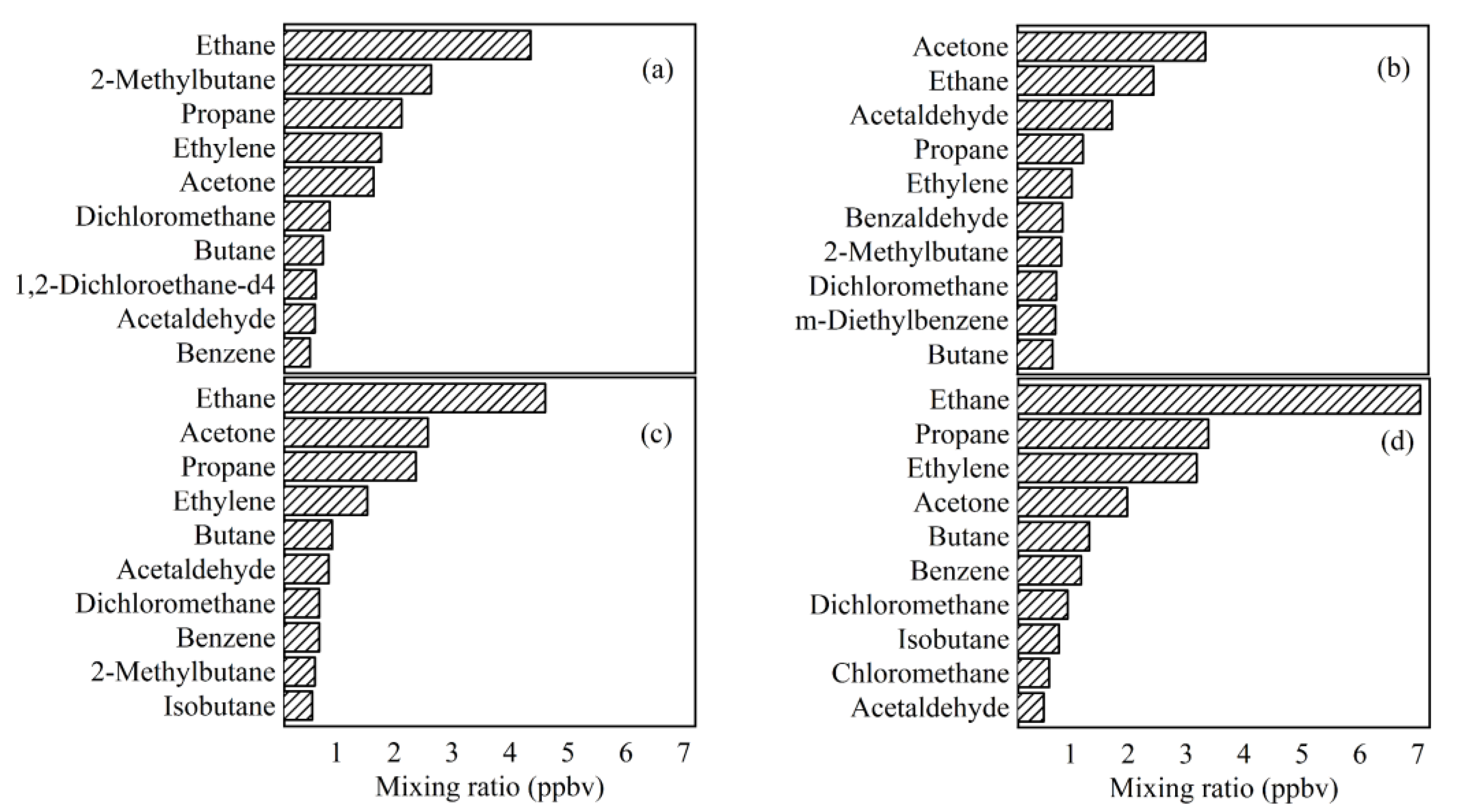
3.1. Basic Data Analysis
3.2. Diurnal Variation Characteristics
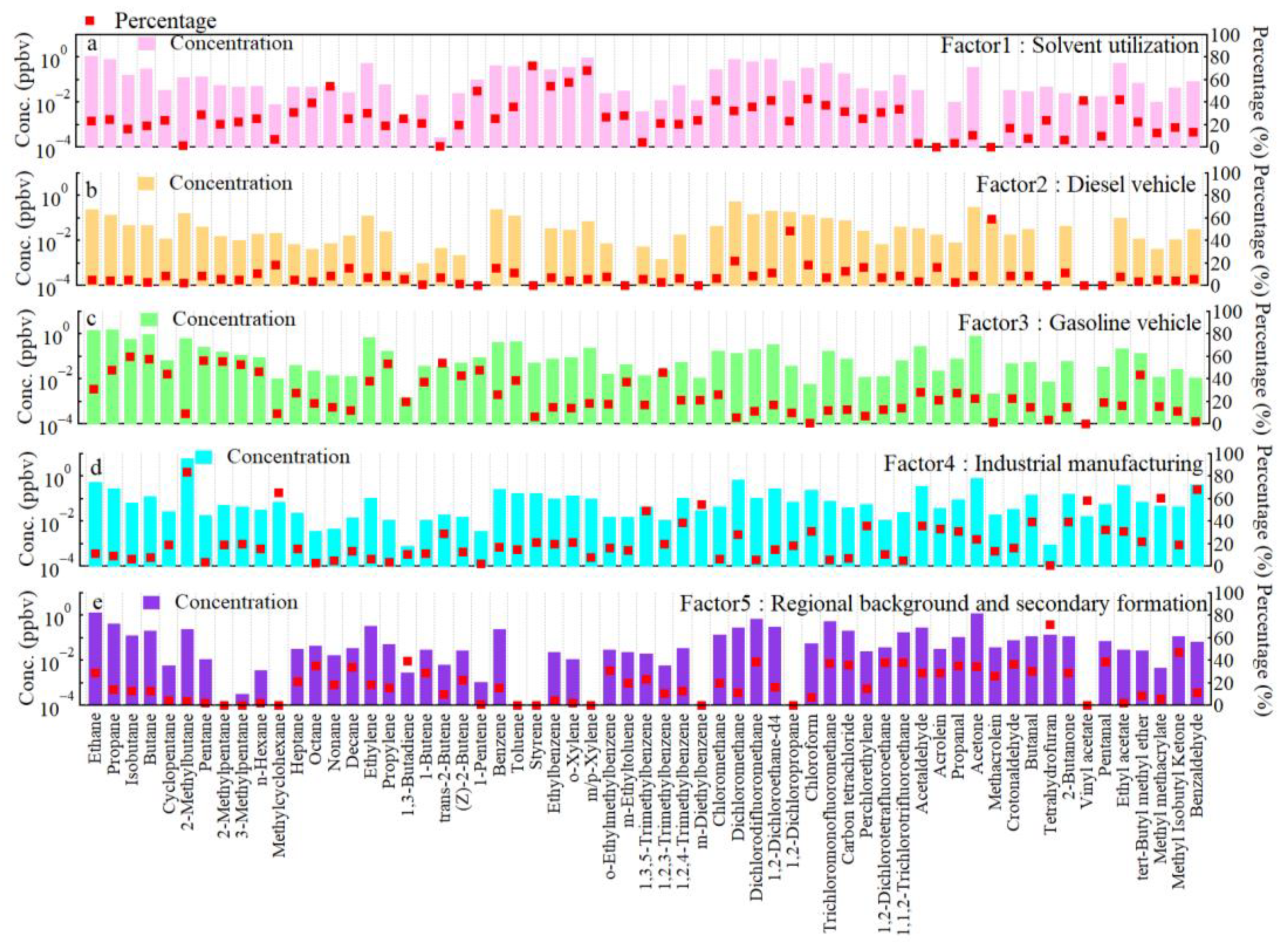
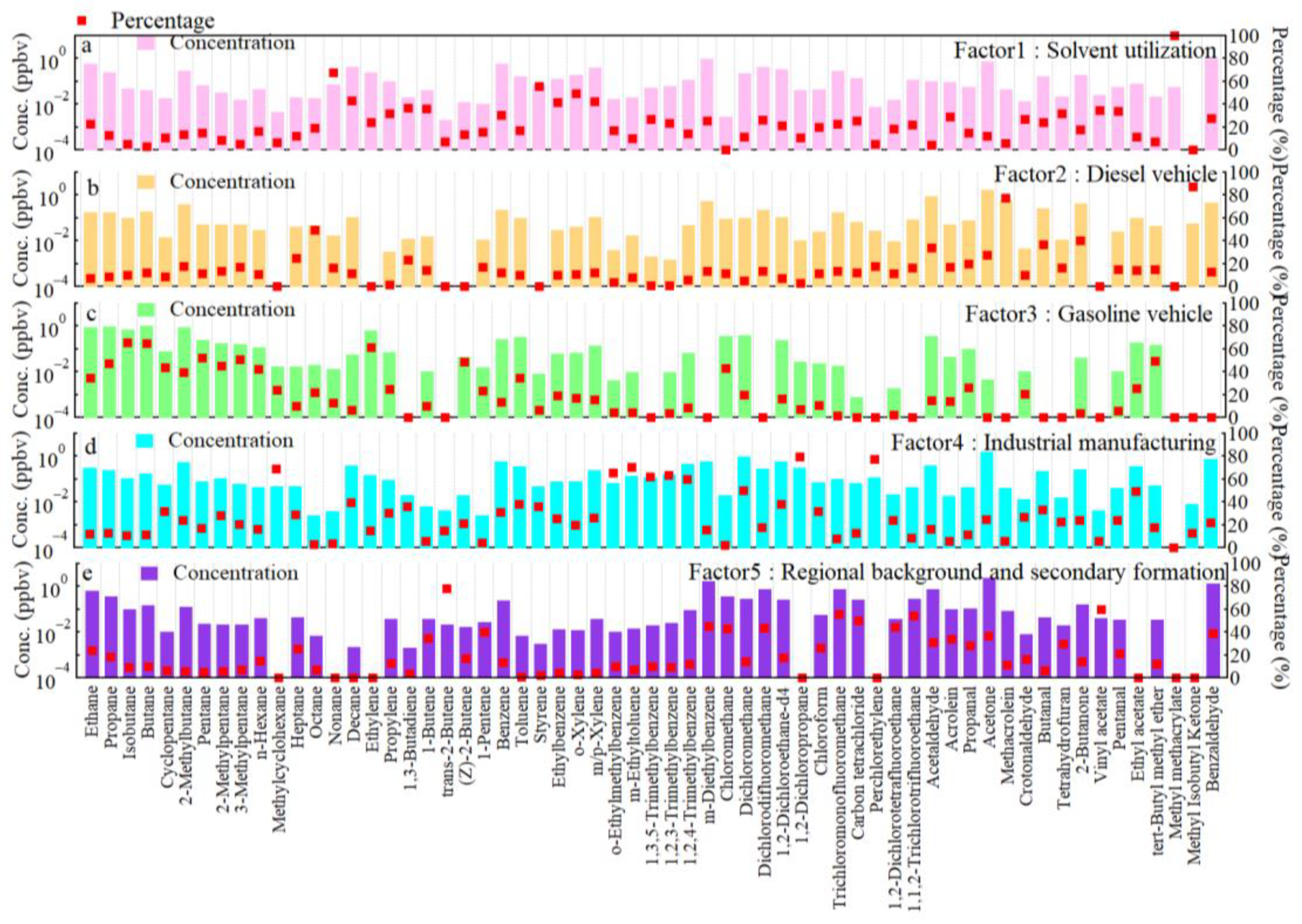
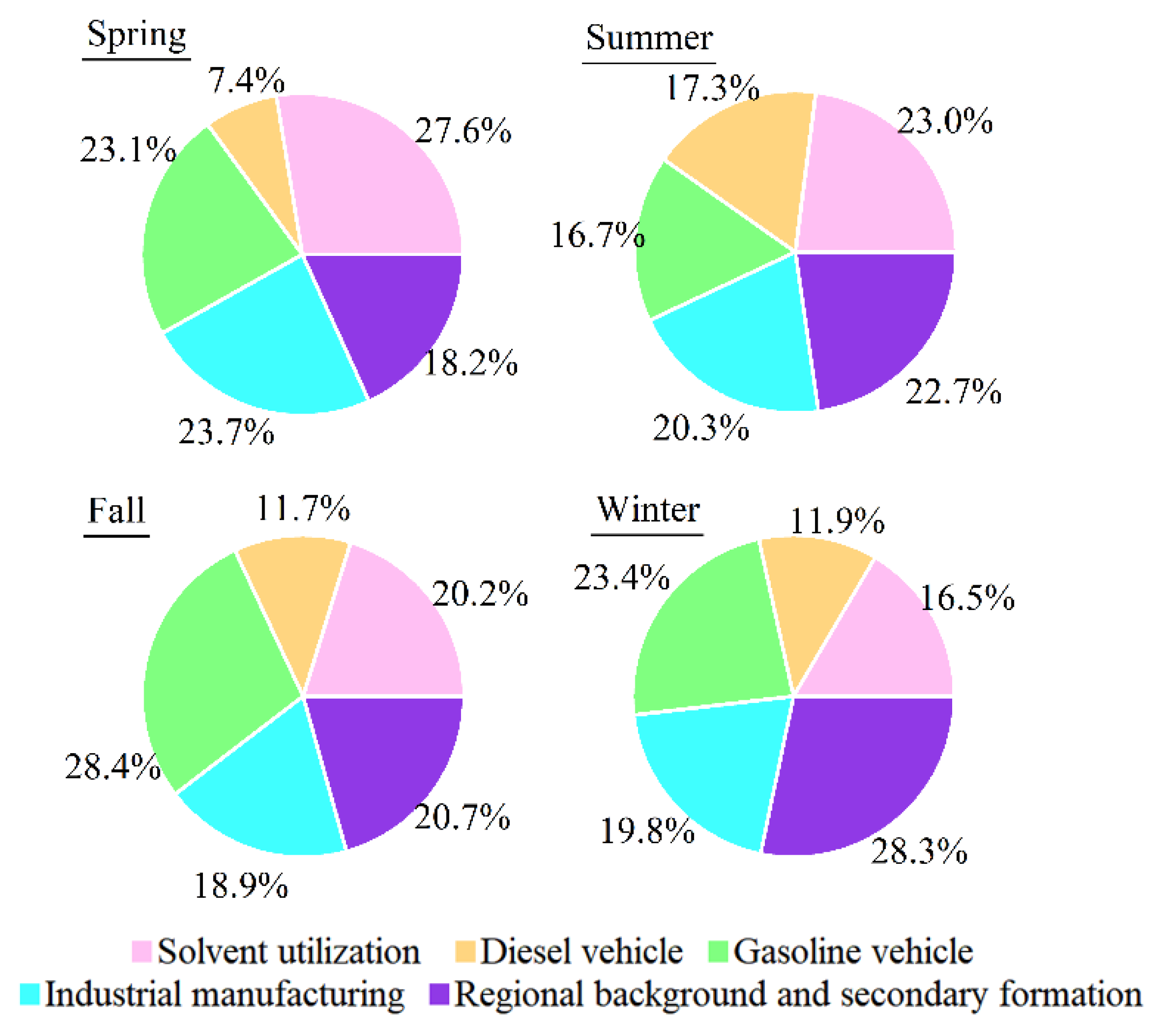
3.3. Source Apportionment of VOCs in Yibin
3.4. VOC Reactivities and Potentials to Secondary Pollutants
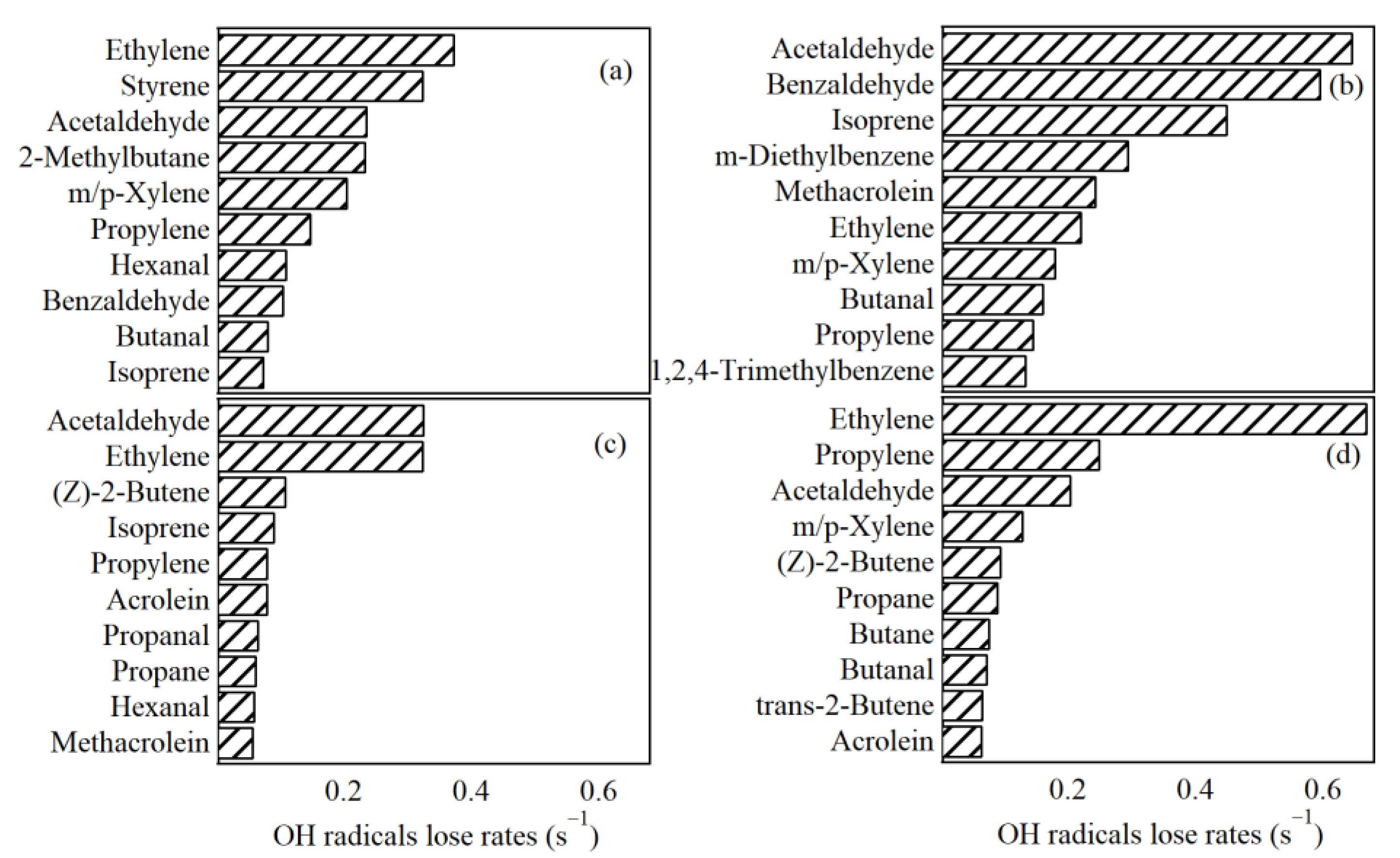
3.4.1. LOH of VOC Species
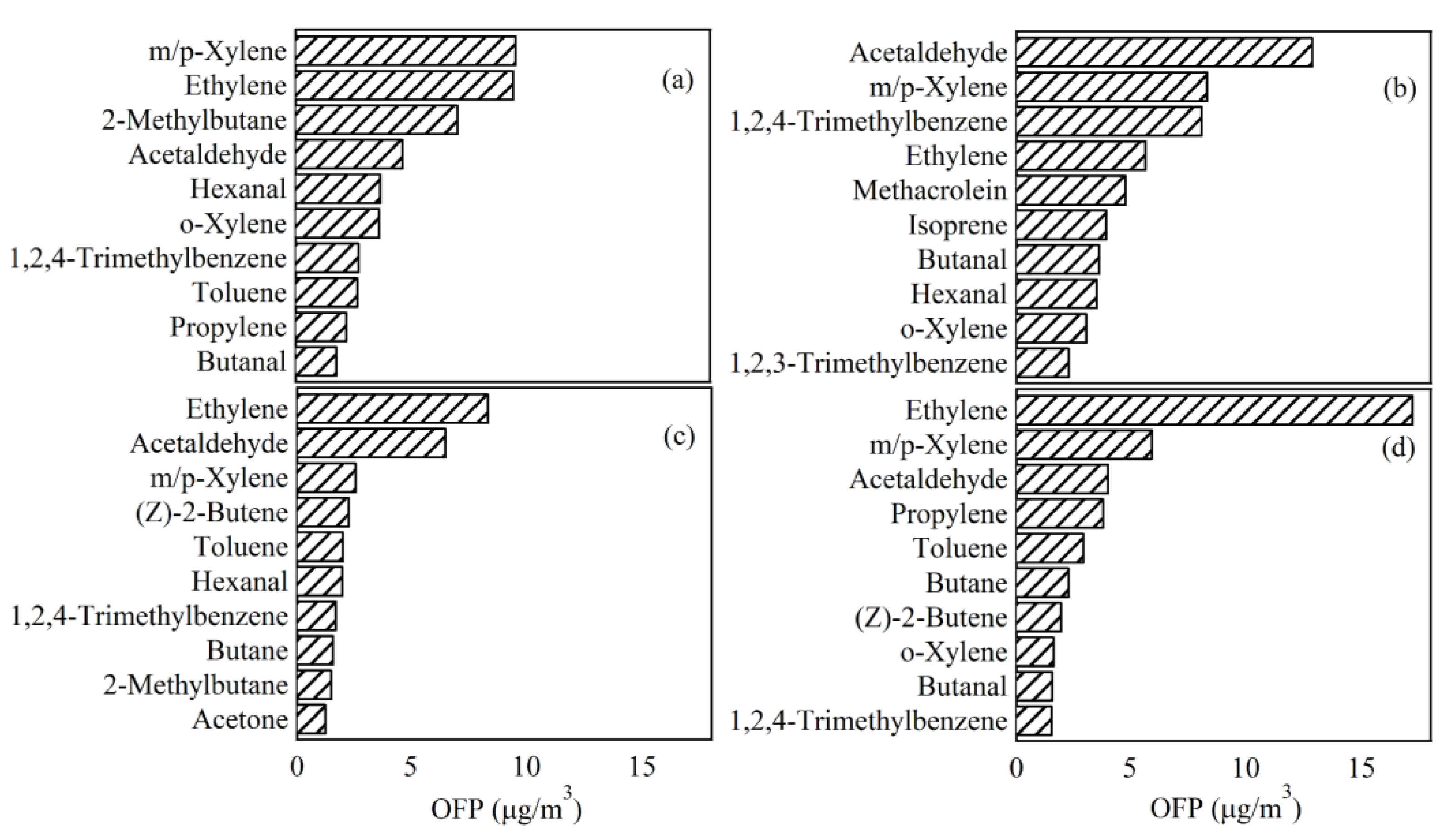
3.4.2. OFP of Ambient VOCs
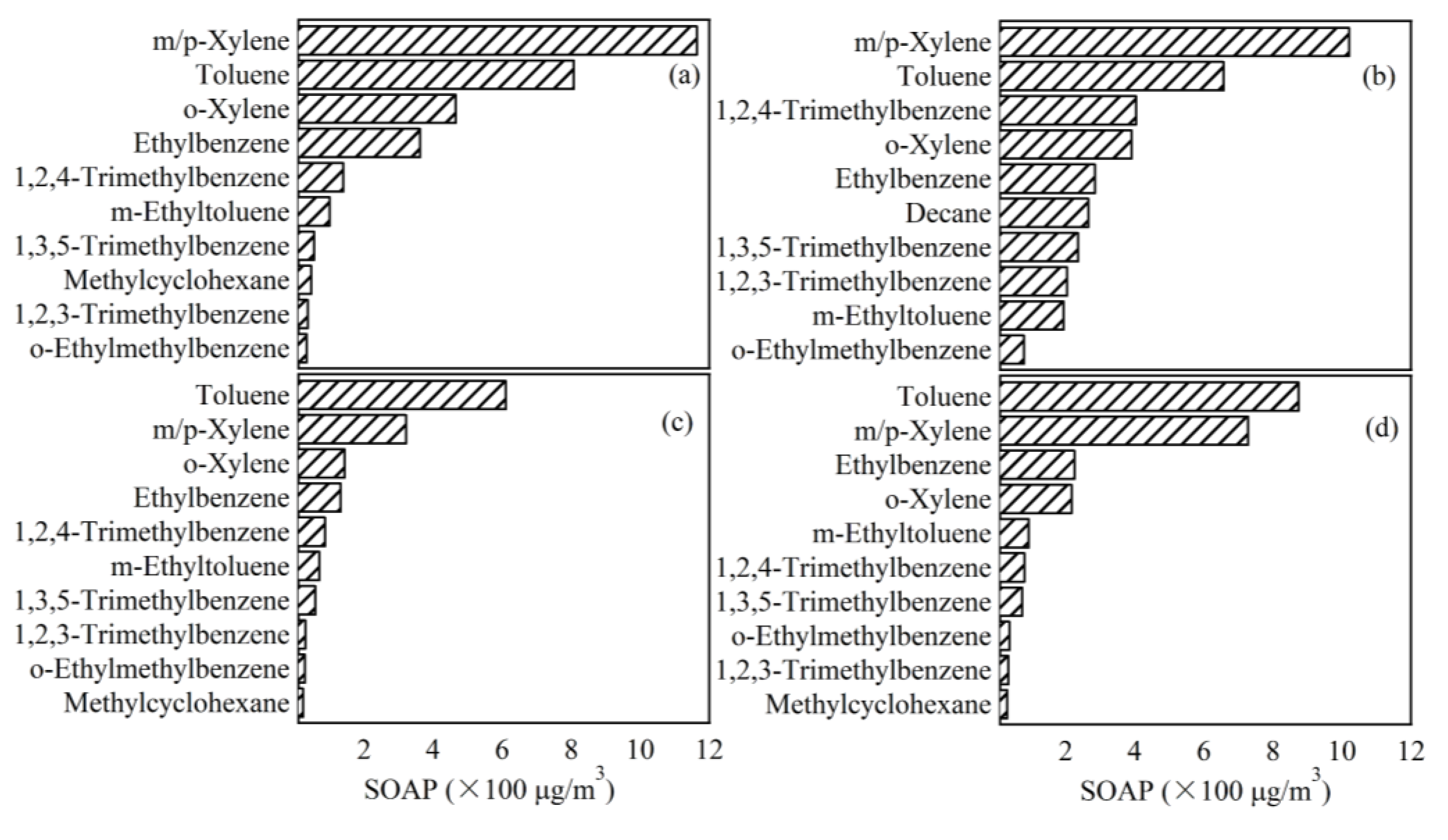
3.4.3. SOAP of VOCs
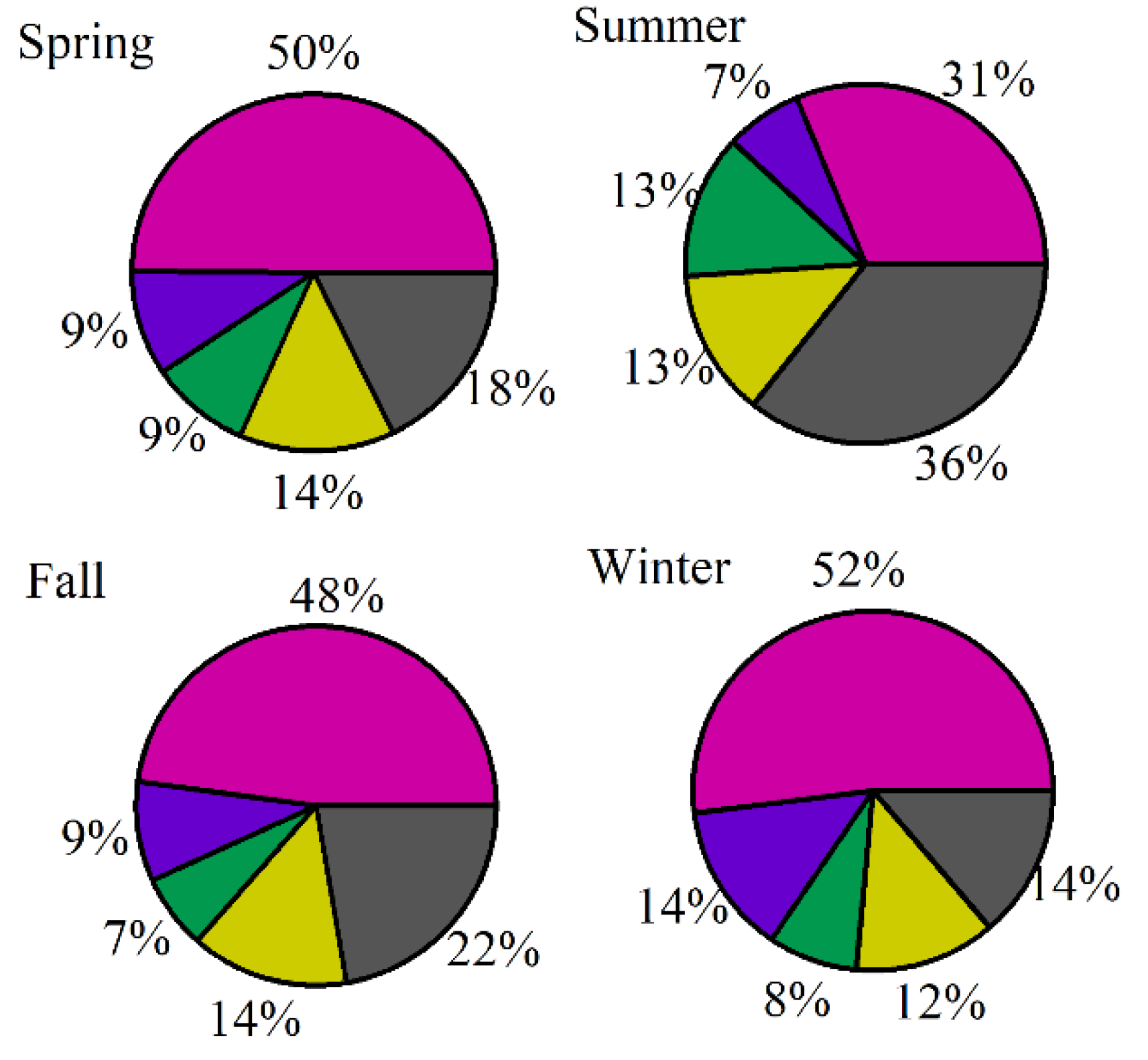
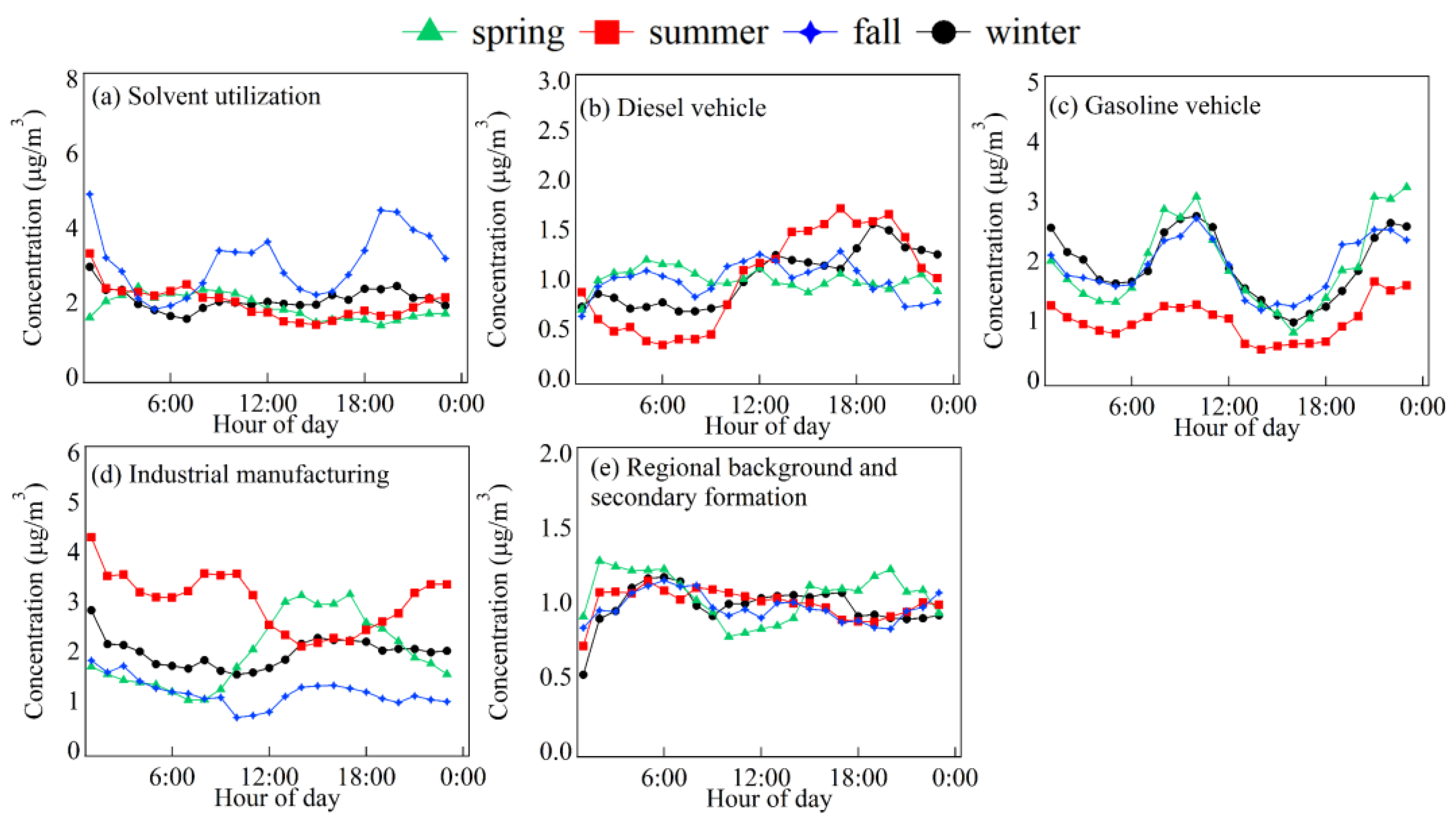
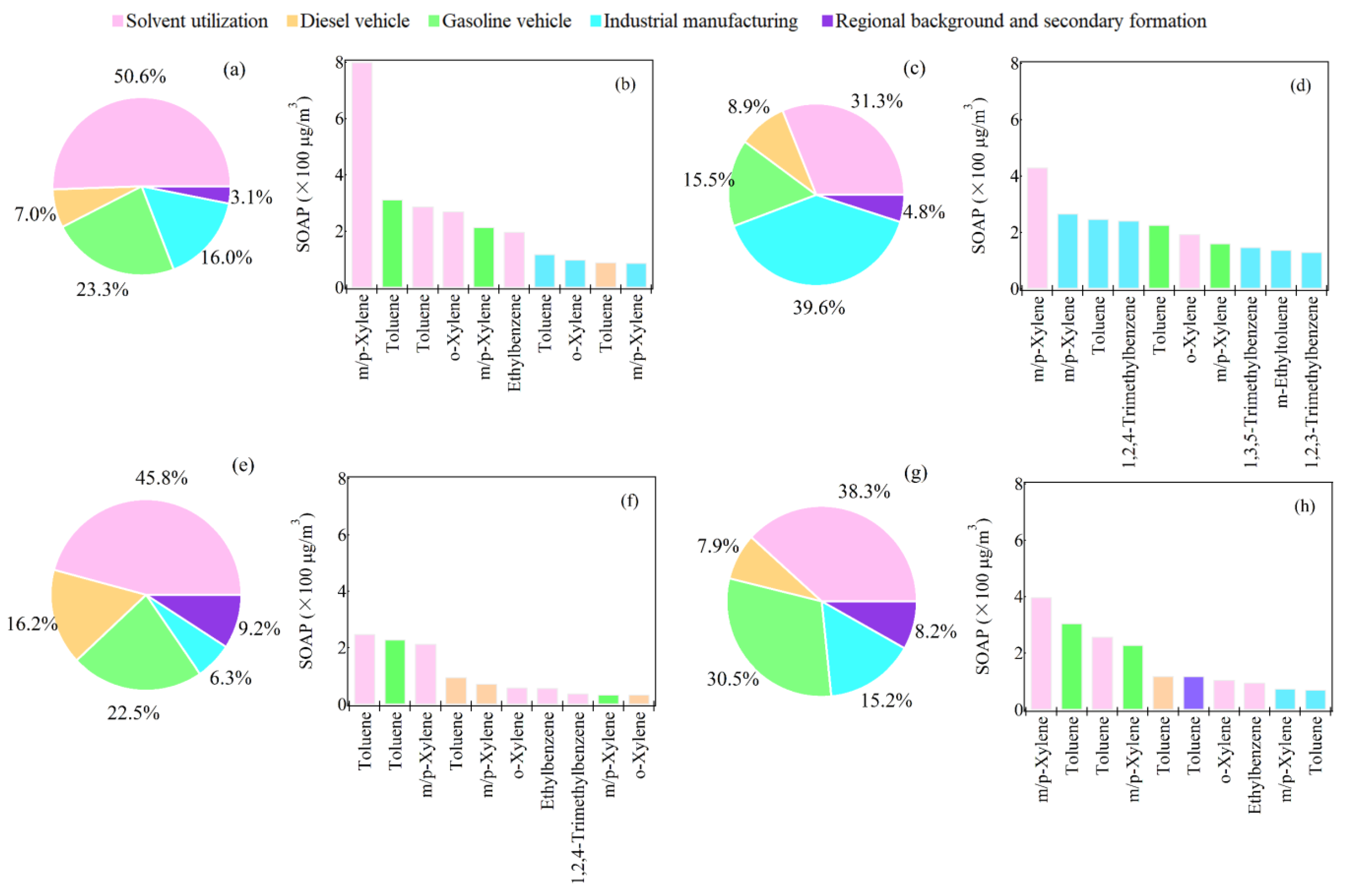
3.5. Contributions of VOC Sources to the Secondary Pollutant Formation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forstner, H.J.L.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Secondary organic aerosol from the photooxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons: Molecular composition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dowd, C.D.; Aalto, P.; Hameri, K.; Kulmala, M.; Hoffmann, T. Aerosol formation—Atmospheric particles from organic vapours. Nature 2002, 416, 497–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odum, J.R.; Jungkamp, T.P.W.; Griffifin, R.J.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. The atmospheric aerosol-forming potential of whole gasoline vapor. Science 1997, 276, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, R. Atmospheric chemistry of VOCs and NOx. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2063–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Takami, A.; Isozaki, T.; Hikida, T.; Shimono, A.; Imamura, T. Mass spectrometric study of secondary organic aerosol formed from the photo-oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R. Gas-phase tropospheric chemistry of organic compounds. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 2, 11–216. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, R.; Tuazon, E.C.; Carter, W.P.L. Extent of H-atom abstraction from the reaction of the OH radical with 1-butene under atmospheric conditions. J. Chem. Kinet. 1995, 17, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Chiu, M.Y.; Ho, K.F.; Zou, S.C.; Wang, X. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in urban atmosphere of Hong Kong. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechapanya, W.; Eusebi, A.; Kimura, Y.; Allen, D.T. Secondary oganic aerosol formation from aromatic precursors. 1. Mechanisms for individual hydrocarbons. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3662–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, M.; Mari, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Multi-compartmental environmental surveillance of a petrochemical area: Levels of micropollutants. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopian, N.A.; Jalaludin, J.; Tamrin, S.B.M. Risk of respiratory health impairment among susceptible population living near petrochemical industry—A review article. Iran. J. Public Health 2016, 45, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Chiang, H.C.; Shie, R.H.; Ku, C.H.; Lin, T.Y.; Chen, M.J.; Chen, N.T.; Chen, Y.C. Ambient VOCs in residential areas near a large-scale petrochemical complex: Spatiotemporal variation, source apportionment and health risk. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smedt, I.; Stavrakou, T.; Müller, J.F.; van der A, R.J.; Van Roozendael, M. Trend detection in satellite observations of formaldehyde tropospheric columns. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L18808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G. Sulfur dioxide and primary carbonaceous aerosol emissions in China and India, 1996–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9839–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Bei, N.; Huang, R.J.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Tie, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T.; Su, X.; et al. Summertime ozone formation in Xi’an and surrounding areas, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4323–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, N.; Wang, N. Characterization and source identification of ambient VOCs in Jinan, China. Air Qual. Atmos Health 2016, 9, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.L.; Gao, T.Y.; Zhang, J.B. Wintertime characteristic of peroxyacetyl nitrate in the Chengyu district of southwestern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Control Ser. 2018, 25, 23143–23156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Niu, X.Y.; Huang, Y.; Cui, L.; Xu, H.M.; et al. Urban VOC profiles, possible sources, and its role in ozone formation for a summer campaign over Xi’an, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Control Ser. 2019, 26, 27769–27782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Feng, M.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, F.; Jiang, W.; Wei, F. Observation-Based Summer O3 Control Effect Evaluation: A Case Study in Chengdu, a Megacity in Sichuan Basin, China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Cheng, S.; Li, G.; Wang, G.; Wang, H. Characteristics of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from a petroleum refinery in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Liao, X.; Xu, L.; Chen, J. Pollution characteristics of volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere of Haicang District in Xiamen City, Southeast China. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, M.; Lu, S.; Chang, C.-C.; Wang, J.-L.; Chen, G. Volatile organic compound (VOC) measurements in the pearl river delta (PRD) region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 1531–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.H.; Bai, Y.H.; Chen, Y.K.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.H. The characteristics of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from motor vehicle in Beijing. China Environ. Sci. 2003, 23, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Chameides, W.L.; Fehsenfeld, F.; Rodgers, M.O.; Cardelino, C.; Martines, J.; Parrish, D.; Lonneman, W.; Lawson, D.R.; Rasmussen, R.A.; Zimmerman, P.; et al. Ozone precursor relationships in the ambient atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 6037–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Zhao, C.S.; Geng, F.H.; Tie, X.; Tang, X.; Peng, L.; Zhou, G.Q.; Yu, Q.; Xu, J.M.; Guenther, A. Ozone photochemical production in urban Shanghai, China: Analysis based on ground level observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D15301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, X.; Madronich, S.; Li, G.H.; Ying, Z.M.; Weinheimer, A.; Apel, E.; Campos, T. Simulation of Mexico City plumes during the MIRAGE-Mex Field campaign using the WRF-Chem model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 4621–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, F.H.; Cai, C.; Tie, X.; Yu, Q.; An, J.; Peng, L.; Zhou, G.; Xu, J. Analysis of VOC emissions using PCA/APCS receptor model at city of Shanghai, China. J. Atmos. Chem. 2010, 62, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheff, P.A.; Wadden, R.A. Receptor modeling of volatile organic compounds. 1. Emission inventory and validation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Xia, J.; Li, Y. Elevated 3D structures of PM2.5 and impact of complex terrain-forcing circulations on heavy haze pollution over Sichuan Basin, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9253–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.; Arey, J. Atmospheric degradation of volatile organic compounds. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4605–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, L.; Carter, W.P.L.; Pei, C.; Chen, T.; Mu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Development of ozone reactivity scales for volatile organic compounds in a Chinese megacity. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 11053–11068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosjean, D. Insitu organic aerosol formation during a smog episode: Estimated production and chemical functionality. Atmos. Environ. 1992, 26, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B. Source apportionment of volatile organic compounds in an urban environment at the Yangtze River Delta, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. 2017, 72, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Kong, S.; Xing, X.; Mao, Y.; Hu, T.; Ding, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, D.; Li, S.; Qi, S. Monitoring of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from an oil and gas station in Northwest China for 1 year. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4567–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Kong, S.; Yan, Y.; Chen, N.; Yao, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Niu, Z.; Zheng, S.; et al. Compositions, sources and health risks of ambient volatile organic compounds (VOCs) at a petrochemical industrial park along the Yangtze River. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, X.; Chen, N.; Guo, H.; Zhang, W.H.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M. Ambient volatile organic compounds and their effect on ozone production in Wuhan, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, J.; Hao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, L.; Xie, S. Evolution process and sources of ambient volatile organic compounds during a severe haze event in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 560–561, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhuang, G.; Huang, K.; Liu, T.; Deng, C.; Xu, J. Probing the severe haze pollution in three typical regions of China: Characteristics, sources and regional impacts. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, N.; Varea, M.; Gil-Moltó, J.; Yubero, E. BTX in urban areas of eastern Spain: A focus on time variations and sources. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 18267–18276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, D.B. Atmospheric volatile organic compound measurements during the Pittsburgh Air Quality Study: Results, interpretation, and quantification of primary and secondary contributions. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D07S07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Xue, H.; Wang, X. Levels, characteristics and health risk assessment of VOCs in different functional zones of Hefei. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 160, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.; Liu, H.; Xie, S.; Zhou, L.; Song, T.; Shi, G.; Jiang, W.; Yang, F.; Wei, F. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and source origins of volatile organic compounds in a megacity of Sichuan Basin, China. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Yu, Y.; Mo, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yin, S.; Peng, K.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Cai, H. Industrial sector-based volatile organic compound (VOC) source profiles measured in manufacturing facilities in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456–457, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, M.A.; Kindzierski, W.B. Ambient volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in communities of the Athabasca oil sands region: Sources and screening health risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Shao, M.; Lu, S. Compilation of a source profile database for hydrocarbon and OVOC emissions in China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.J.; Geng, F.H.; Tie, X.X.; Yu, Q.O.; An, J.L. Characteristics and source apportionment of VOCs measured in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5005–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Shao, M.; Lu, S.; Qu, H.; Zhou, M.; Sun, J.; Gou, B. Process-specific emission characteristics of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from petrochemical facilities in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, B.; Dai, Q.; Li, H.; Mao, H. Temperature dependence and source apportionment of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) at an urban site on the north China plain. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 207, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.B.; O’Hara, D.; Herlth, D.; Sachse, W.; Blake, D.R.; Bradshaw, J.D.; Kanakidou, M.; Crutzen, P.J. Acetone in the atmosphere: Distribution, sources, and sinks. J. Geophys Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 1805–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Wang, N.; Zhou, L.; Yang, F.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, J.; Han, L.; Li, J. Component characteristics and source apportionment of volatile organic compounds during summer and winter in downtown Chengdu, southwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 258, 118485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, J.P.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.J.; Wang, H.L. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during non-haze and haze days in Shanghai: Characterization and secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Control Ser. 2017, 24, 18619–18629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, L.R.; Liu, X.G.; Tan, Q.W.; Feng, M.; An, J.L.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Cheng, N.L. VOC characteristics, sources and contributions to SOA formation during haze events in Wuhan, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2624–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Bi, J.; Liu, Q.; Ling, Z.H.; Shen, G.F.; Chen, F.; Qiao, Y.Z.; Li, C.Y.; Ma, Z.W. Sources of volatile organic compounds and policy implications for regional ozone pollution control in an urban location of Nanjing, East China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3905–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, L.; Luo, T.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, S.; Huang, G.; Chen, D.; Lan, Y.; Yang, F. Seasonal Variation Characteristics of VOCs and Their Influences on Secondary Pollutants in Yibin, Southwest China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091389
Kong L, Luo T, Jiang X, Zhou S, Huang G, Chen D, Lan Y, Yang F. Seasonal Variation Characteristics of VOCs and Their Influences on Secondary Pollutants in Yibin, Southwest China. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(9):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091389
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Lan, Tianzhi Luo, Xia Jiang, Shuhua Zhou, Gang Huang, Dongyang Chen, Yuting Lan, and Fumo Yang. 2022. "Seasonal Variation Characteristics of VOCs and Their Influences on Secondary Pollutants in Yibin, Southwest China" Atmosphere 13, no. 9: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091389
APA StyleKong, L., Luo, T., Jiang, X., Zhou, S., Huang, G., Chen, D., Lan, Y., & Yang, F. (2022). Seasonal Variation Characteristics of VOCs and Their Influences on Secondary Pollutants in Yibin, Southwest China. Atmosphere, 13(9), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091389



