Production of Biocoal from Wastewater Sludge and Sugarcane Bagasse: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biomass as an Alternative Energy Resource
2.1. Biomass
- Virgin
- Terrestrial: cultivated crops, forest biomass, energy crops, and grass.
- Aquatic: water plants and algae.
- Waste
- Municipal: MSW, biosolids, sewage, and landfills.
- Agricultural: livestock and manure, agricultural crop residue.
- Forestry residues: bark, leaves, and floor residues.
- Industrial wastes: demolition wood, sawdust, and waste oil or fat.
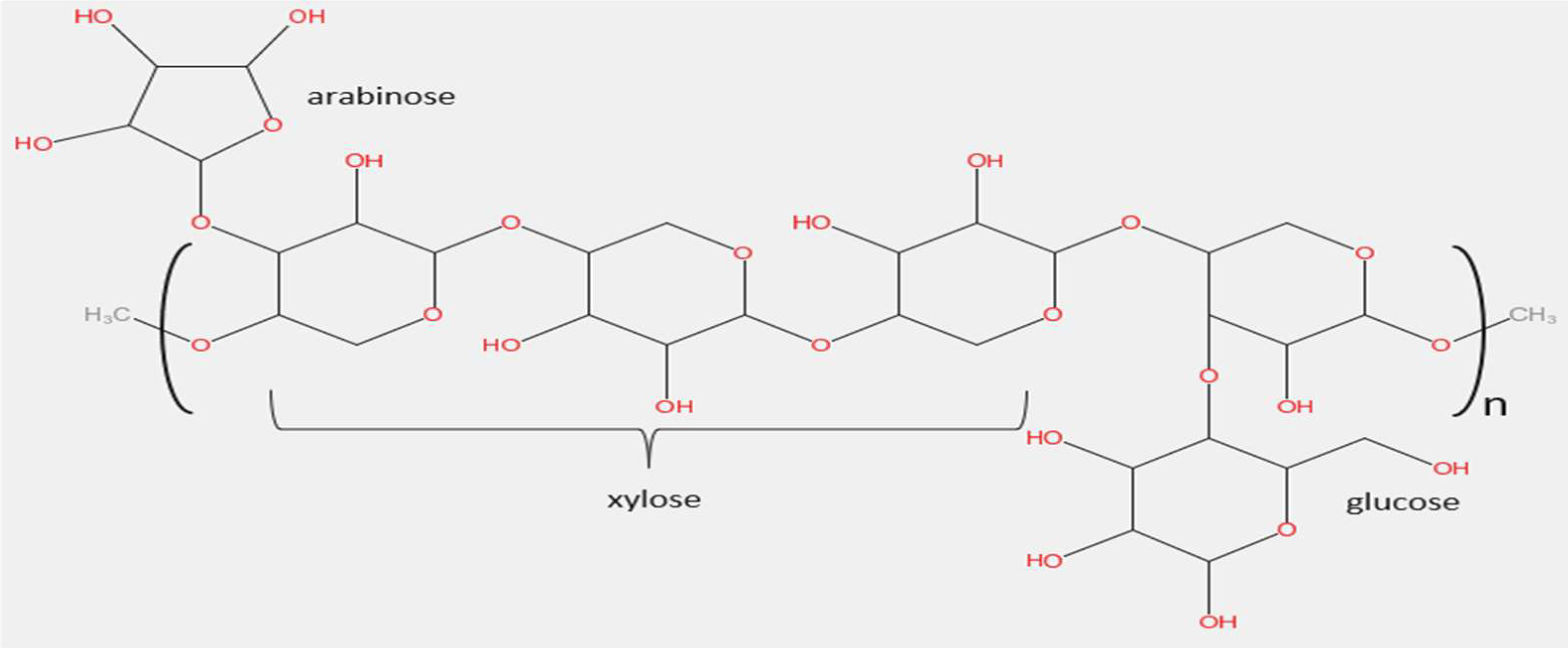
2.2. Sugarcane Bagasse
2.3. Wastewater Sludge
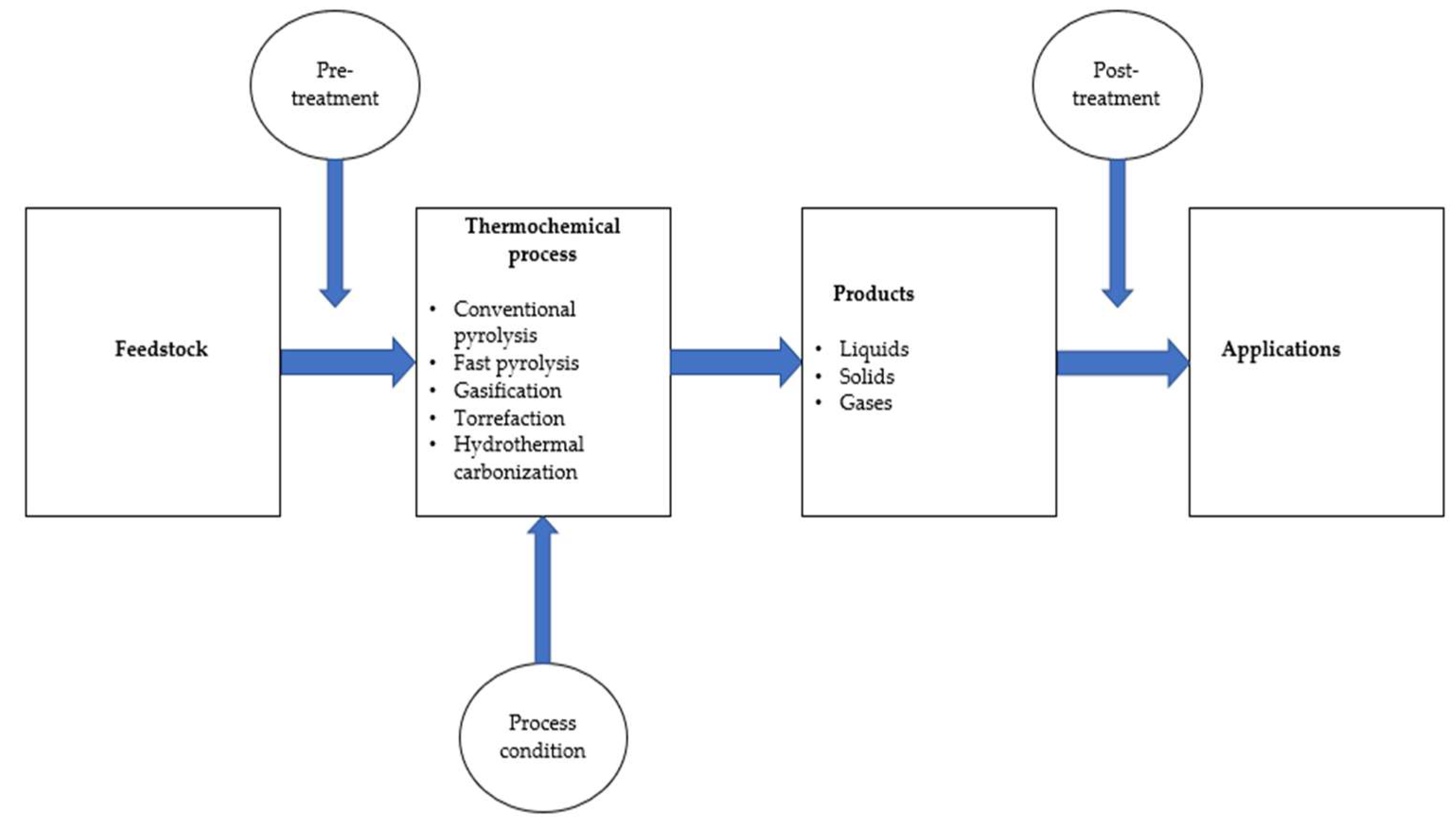
3. Thermochemical Energy Conversion Processes
3.1. Conventional Pyrolysis
3.2. Fast Pyrolysis
3.3. Gasification
3.4. Torrefaction
3.5. Hydrothermal Carbonization
4. Review of the Use of Various Energy Conversion Processes
5. Advantages of Hydrothermal Carbonization
5.1. Reaction Mechanisms
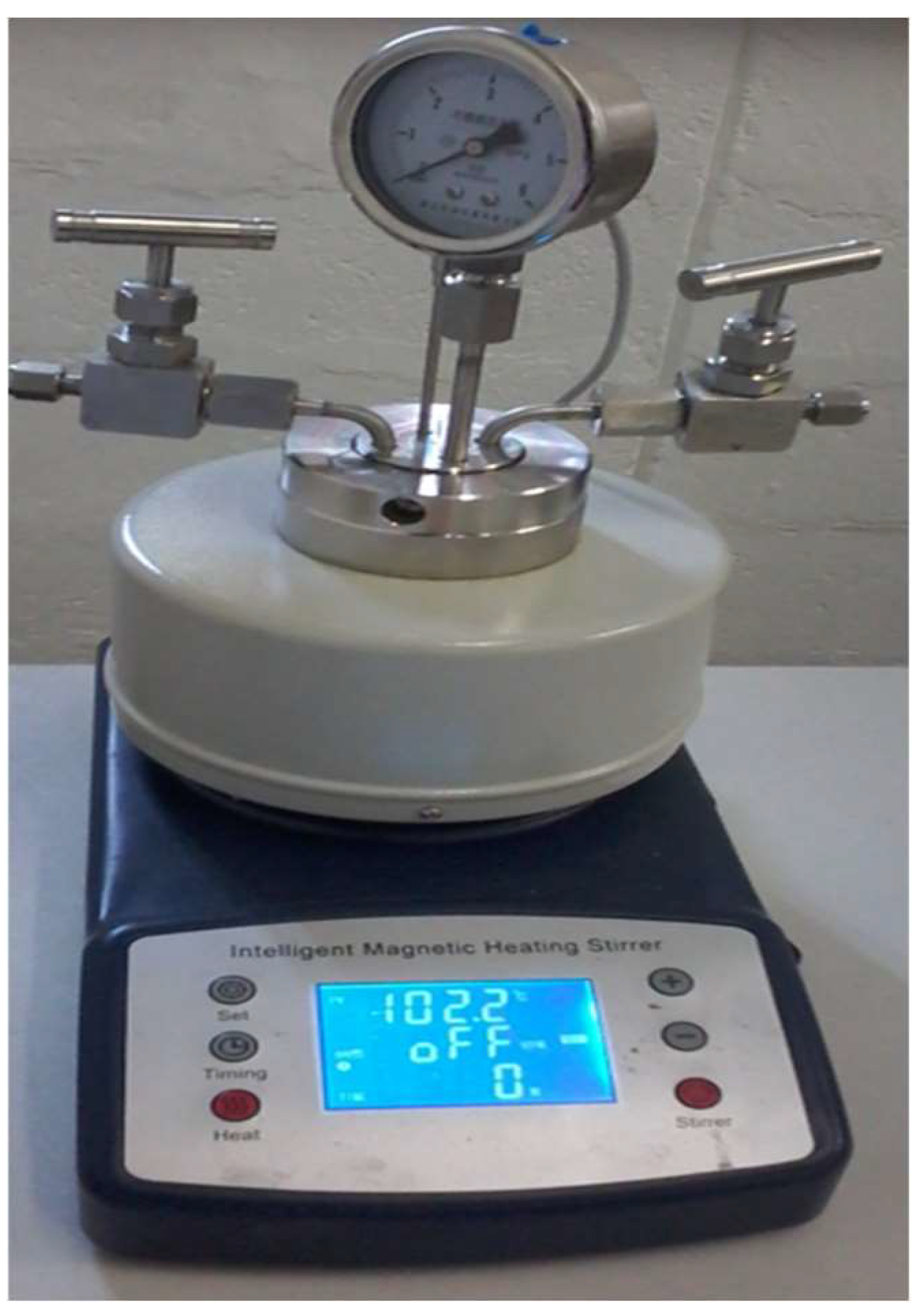
5.2. Production of Biocoal Using the Hydrothermal Carbonization Process
6. Conclusions
- Due to the intricacy of the various biomass sources employed and potential contamination of the biomass feed, there may be considerable variability in the final quality of the hydrochar.
- Since HTC is a novel technology, there are numerous unidentified mechanisms.
- The HTC logistics system can be pricey and time-consuming.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oladejo, J.; Shi, K.; Luo, X.; Yang, G.; Wu, T. A Review of Sludge-to-Energy Recovery Methods. Energies 2018, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maqhuzua, A.B.; Yoshikawaa, K.; Takahashia, F. Potential for thermal conversion of brewer’s spent grain into biocoal via hydrothermal carbonization in Africa. Appl. Energy 2019, 158, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauchhum, L.; Mahanta, P. Carbon dioxide adsorption on zeolites and activated carbon by pressure swing adsorption in a fixed bed. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2014, 5, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kambo, H.S.; Dutta, A. Comparative evaluation of torrefaction and hydrothermal carbonization of lignocellulosic biomass for the production of solid biofuel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskom Power Generation. “Eskom–Coal Power”, Eskom Holdings Ltd., South Africa, 2011. Available online: https://www.eskom.co.za/live/content.php?Item_ID=279 (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- World Bank Development Indicators, 2015. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EG.ELC.COAL.ZS (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Bevan, E.; Fu, J.; Zheng, Y. Challenges and opportunities of hydrothermal carbonisation in the UK; case study in Chirnside. R. Soc. Chem. 2020, 10, 31586–31607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.A.V. Valorization of Secondary Sludge by Hydrothermal Carbonization Coupled with Anaerobic Digestion. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ganeshraj, K.; Karthikeyan, S.; Arasan, S.E.; Muthuganapathy, S. Experimental Investigation of Agriculture and Forest Biomass. Bachelor’s Thesis, Anna University, Chennai, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.M. Carbon Neutrality: Toward a Sustaninable Future 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8454731 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Demirbas, A. Biomass resource facilities and biomass conversion processing for fuels and chemicals. Energy Convers. Manag. 2001, 42, 1357–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.; Adhikari, D.; Goyal, H. Biomass-based energy fuel through biochemical routes: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumuluru, J.S.; Wright, C.T.; Kenny, K.L.; Hess, J.R. A Review on Biomass Densification Technologies for Energy Application. A Technical Report Prepared for the U.S Department of Energy; INL/EXT-10-18420; Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2011; Contract DE-AC07-05ID14517. [Google Scholar]
- Özbay, N.; Pütün, A.E.; Uzun, B.B.; Pütün, E. Biocrude from biomass: Pyrolysis of cottonseed cake. Renew. Energy 2001, 24, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlack, R.D.; Wright, L.L.; Turhollow, A.F.; Graham, R.L.; Stokes, B.J.; Erbach, D.C. Biomass as Feedstock for a Bioenergy and Bioproducts Industry: The Technical Feasibility of a Billion-Ton Annual Supply; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pimchuai, A.; Dutta, A.; Basu, P. Torrefaction of Agriculture Residue to Enhance Combustible Properties. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4638–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazeer, A. Structural analysis of sugarcane bagasse as a feedstock in downdraft gasifier system—A review. Int. J. Res. Eng. Innov. 2017, 1, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Demirbas, A.; Arin, G. An overview of biomass pyrolysis. Energy Sources 2002, 24, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, M. Industrial-Scale Hydrothermal Carbonization of Waste Sludge Materials for Fuel Production 2014. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264197007 (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Libra, J.A.; Ro, K.S.; Kammann, C.; Funke, A.; Berge, N.D.; Neubauer, Y.; Titirici, M.M.; Fuhner, C.; Bens, O.; Kern, J.; et al. Hydrothermal carbonization of biomass residuals: A comparative review of the chemistry, processes, and applications of wet and dry pyrolysis. Biofuels 2011, 2, 89–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barskov, S.; Zappi, M.; Buchireddy, P.; Dufreche, S.; Guillory, J.; Gang, D.; Hernandez, R.; Bajpai, R.; Baudier, J.; Cooper, R.; et al. Torrefaction of biomass: A review of production methods for biocoal from cultured and waste lignocellulosic feedstocks. Renew. Energy 2019, 142, 624–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.T.; Andert, J.; Wirth, B.; Busch, D.; Pielert, J.; Lynam, J.G.; Mumme, J. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Biomass for Energy and Crop Production. Appl. Bioenergy 2014, 1, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, H.; Genel, S. Catalytic hydrothermal liquefaction of lactuca scariola with a heterogeneous catalyst: The investigation of temperature, reaction time and synergistic effect of catalysts. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 309, 123–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Stelt, M.J.C.; Gerhauser, H.; Kiel, J.H.A.; Ptasinski, K.J. Biomass upgrading by torrefaction for the production of biofuels: A review. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3748–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, D.C. Production of Biocoal and Activated Carbon from Biomass. Master’s Thesis, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fialho, L.F.; Carneiro, A.C.O.; Carvalho, A.M.M.L.; Figureueiró, C.G.; Silva, C.M.S.; Magalhães, M.A.; Peres, L.C. Biocoal production with agroforestry biomasses in Brazil. Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.H.; Huang, B.C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.L.; Jiang, S.-F.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.S.; Jiang, H.; Yu, H.-Q. Biocoal: A renewable and massively producible fuel from lignocellulosic biomass. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, eaay0748. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, D.B.; Haryati, S.; Hadiah, F.; Selpiana, S.; Huda, A. Syngas Production Improvement of Sugarcane Bagasse Conversion Using an Electromagnetic Modified Vacuum Pyrolysis Reactor. J. Process. 2020, 8, 252. [Google Scholar]
- Manyuchi, M.M.; Mbohwaa, C.; Muzenda, E. Evaluating the Usability of Bio Coal from Sugar Cane Bagasse as a Solid Fuel. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 33, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.A.W.; Shafee, N.M.; Abdullah, M.O.; Lim, L.L.P. Synthesis and characterization of biocoal from Cymbopogon citrates residue using microwave-induced torrefaction. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2017, 8, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, S.K.; Tabil, L.G.; Meda, V.; Naik, S.N.; Prasad, R. Torrefaction of wheat and barley straw after microwave heating. Fuel 2014, 124, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, P.; Swiechowski, k.; Hnat, M.; Kugler, S.; Stegenta-Dabrowska, S.; Koziel, J.A.; Manczarski, P.; Białowiec, A. Waste to Carbon: Biocoal from Elephant Dung as New Cooking Fuel. Energies 2019, 12, 4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.H.; Ye, S.C.; Sheen, H.K. Hydrothermal carbonization of sugarcane bagasse via wet torrefaction in association with microwave heating. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agar, D.A. A comparative economic analysis of torrefied pellet production based on state-of-the-art pellets. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 97, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couhert, C.; Salvador, S.; Commandre, J.-M. Impact of torrefaction on syngas production from wood. Fuel 2009, 88, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Jordan, B.; Berge, N.D. Thermal conversion of municipal solid waste via hydrothermal carbonization: Comparison of carbonization products to products from current waste management techniques. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, S.; Libra, J.; Berge, N.; Sabio, E.; Ro, K.; Li, L. Hydrothermal Carbonization: Modeling, Final Properties Design and Applications: A Review. Energies 2018, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reza, M.T. Upgrading Biomass by Hydrothermal and Chemical Conditioning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nevada, Reno, NV, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Funke, A.; Ziegler, F. Hydrothermal carbonization of biomass: A summary and discussion of chemical mechanisms for process engineering. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2010, 4, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, R.P.; Ross, A.B. Integration of Hydrothermal Carbonisation with Anaerobic Digestion; Opportunities for Valorisation of Digestate. Energies 2019, 12, 1586. [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä, M.; Forsberg, J.; Söderbergd, C.; Larssonb, S.H.; Dahla, O. Process water properties from hydrothermal carbonization of chemical sludge from a pulp and board mill. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, M.; Hirajima, T.; Sasaki, K. Upgrading of low rank coal and woody biomass mixture by hydrothermal treatment. Fuel 2011, 90, 2578–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Tang, C.; Lia, C.; Yuane, J.; Tran, K.-Q.; Bach, Q.-V.; Qiu, R.; Yang, Y. Wet torrefaction of biomass for high quality solid fuel production: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 91, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, N.D.; Ro, K.S.; Mao, J.; Flora, J.R.V.; Chappell, M.A.; Bae, S. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Municipal Waste Streams: Supporting Information. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5696–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poerschmann, J.; Weiner, B.; Wedwitschka, H.; Baskyr, I.; Koehler, R.; Kopinke, F.D. Characterization of biocoals and dissolved organic matter phases obtained upon hydrothermal carbonization of brewer’s spent grain. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 164, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakkaew, K.; Koottatep, T.; Pussayanavin, T.; Polprasert, C. Hydrochar production by hydrothermal carbonization of faecal sludge. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2015, 5, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Report on the Environment; EPA/600/R-07/045F; National Center for Environmental Assessment: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/roe (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- Khaskhachikh, V.; Krysanova, K.; Krylova, A.; Zaichenko, V.; Lavrenov, V. Influence of the parameters of the hydrothermal carbonization of the biomass on the biocoal obtained from peat. Energy Fuels 2019, 114, 07003. [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä, M.; Fraikin, L.; Léonard, A.; Benavente, V.; Fullana, A. Predicting the drying properties of sludge based on hydrothermal treatment under subcritical conditions. Water Res. 2016, 91, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zvimba, J.; Musvoto, E. From waste to worth–converting wastewater sludge into high-value products. Wastewater Treat. 2018, 17, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.K.; Kim, D.; Han, S.K.; Kim, H.; Park, S. Conversion of organic residue from solid-state anaerobic digestion of livestock waste to produce the solid fuel through hydrothermal carbonization. Environ. Eng. Res. 2018, 23, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Process | Process Conditions | Approximate Product Yield (Weight %) | Recommendations | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | Temperature Range (°C) | Pressure | Residence Time | Liquid | Char | Gas | ||
| Fast pyrolysis | Fast | 450–550 | Depend on the desired distribution of product yield | Seconds | 75 | 12 | 13 | [18] |
| Slow pyrolysis | Slow | 250–450 | Low | Hours to weeks | 30 | 35 | 35 | [18] |
| Torrefaction | Moderate | 200–300 | Atmospheric | Several hours | 0 | 70 | 30 | [24] |
| Gasification | Fast | 900–1500 | Depend on the desired distribution of product yield | 10–20 s | 5 | <10 | >85 | [20] |
| Hydrothermal carbonization | Moderate | 180–250 | High Autogenous | Processing time from minutes to several hours | 5–20 | 50–80 | 2–5 | [20] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mkhwanazi, Z.; Isa, Y.M.; Vallabh, S.T. Production of Biocoal from Wastewater Sludge and Sugarcane Bagasse: A Review. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010184
Mkhwanazi Z, Isa YM, Vallabh ST. Production of Biocoal from Wastewater Sludge and Sugarcane Bagasse: A Review. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(1):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010184
Chicago/Turabian StyleMkhwanazi, Zinhle, Yusuf Makarfi Isa, and Shadana. T. Vallabh. 2023. "Production of Biocoal from Wastewater Sludge and Sugarcane Bagasse: A Review" Atmosphere 14, no. 1: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010184
APA StyleMkhwanazi, Z., Isa, Y. M., & Vallabh, S. T. (2023). Production of Biocoal from Wastewater Sludge and Sugarcane Bagasse: A Review. Atmosphere, 14(1), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010184






