Seasonal and Day–Night Variations in Carbonaceous Aerosols and Their Light-Absorbing Properties in Guangzhou, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Determination of Carbonaceous Fractions
2.3. Examination of Organic Components, Water-Soluble Ions, and Gaseous Pollutants
2.4. Meteorological Parameters and Boundary Layer Height
2.5. Separation of Light Absorption of BC and BrC
3. Results and Discussion
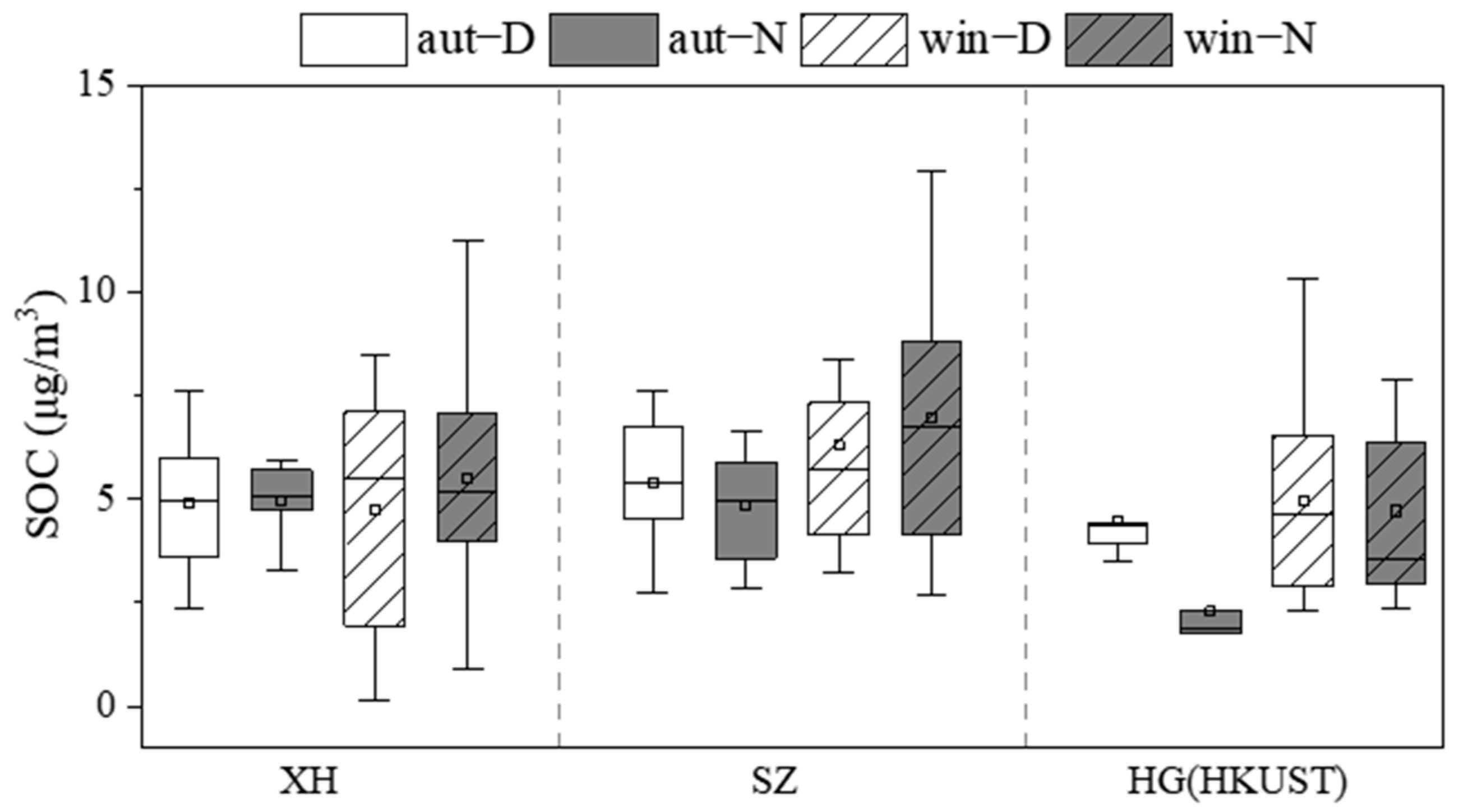
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of OC and EC Mass Concentrations
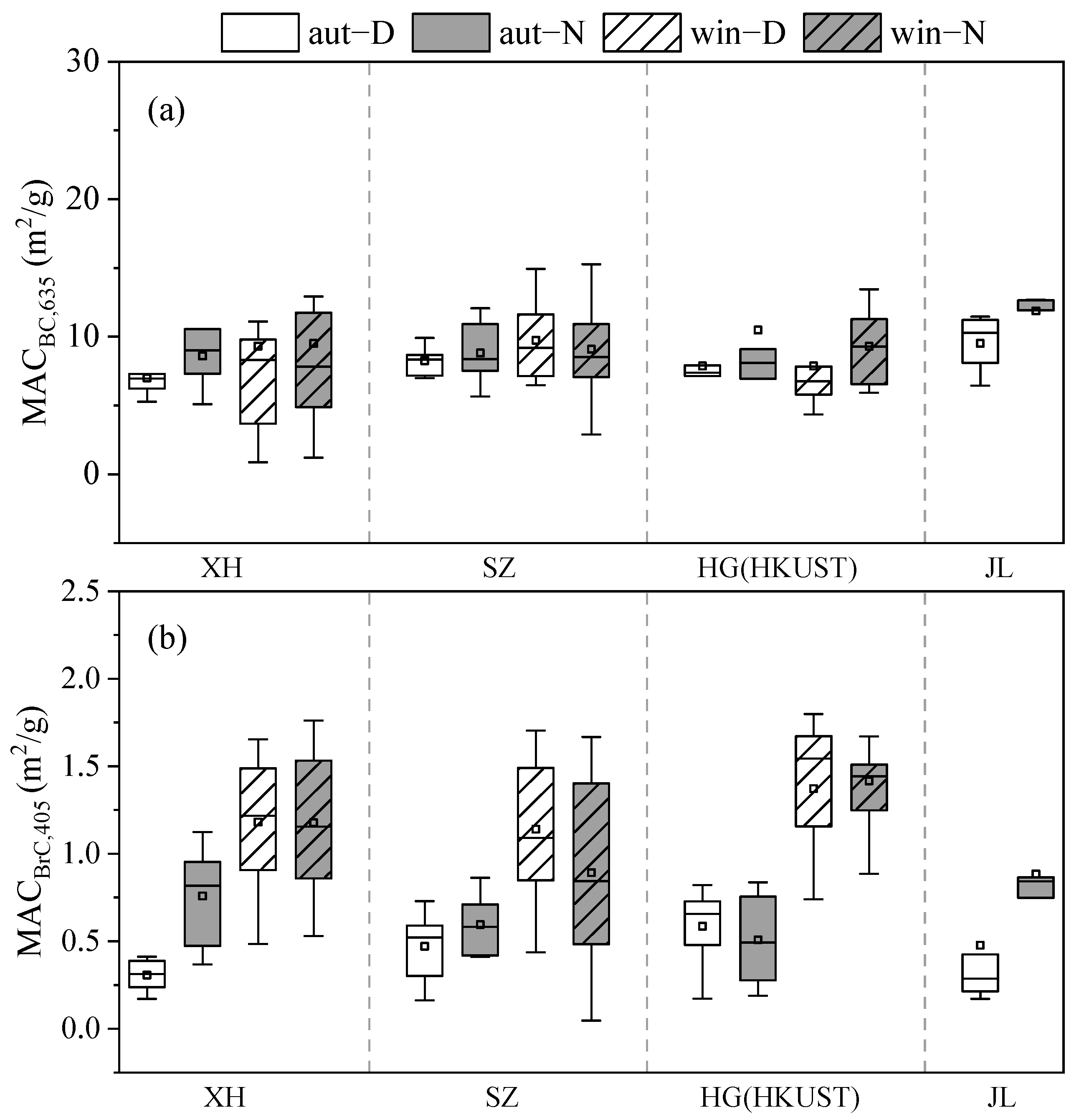
3.2. Light Absorption Properties of OC and EC
3.3. Sources of OC/EC and Light-Absorbing BC/BrC
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-Year Trends of the Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Ambient Air Pollution: An Analysis of Data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.J.; Turpin, B.J. Origins of Primary and Secondary Organic Aerosol in Atlanta: Results’ of Time-Resolved Measurements during the Atlanta Supersite Experiment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4489–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, K.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zou, S.C.; Fung, K.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. Characteristics of Carbonaceous Aerosol in Pearl River Delta Region, China during 2001 Winter Period. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, K.F.; Zou, S.C.; Fung, K.; Li, Y.; Watson, J.G.; Chow, J.C. Spatial and Seasonal Variations of Atmospheric Organic Carbon and Elemental Carbon in Pearl River Delta Region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4447–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, C.; Habib, G.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Miguel, A.H.; Friedlander, S.K. Residential Biofuels in South Asia: Carbonaceous Aerosol Emissions and Climate Impacts. Science 2005, 307, 1454–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Salmon, L.G.; Schauer, J.J.; Zeng, L.M.; Kiang, C.S.; Zhang, Y.H.; Cass, G.R. Seasonal Trends in PM2.5 Source Contributions in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3967–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Ho, K.F.; Zhang, R.J.; Jin, Z.D.; Shen, Z.X.; Chen, G.C.; Kang, Y.M.; et al. Spatial and Seasonal Distributions of Carbonaceous Aerosols over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, X.; Fu, X.; He, Q.; Wang, S.; Bernard, F.; Zhao, X.; Wu, D. Aerosol Scattering Coefficients and Major Chemical Compositions of Fine Particles Observed at a Rural Site in the Central Pearl River Delta, South China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordukhovich, I.; Wilker, E.; Suh, H.; Wright, R.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Schwartz, J. Black Carbon Exposure, Oxidative Stress Genes, and Blood Pressure in a Repeated-Measures Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, G.; Krishnan, R.M.; Beelen, R.; Peters, A.; Ostro, B.; Brunekreef, B.; Kaufman, J.D. Long-Term Air Pollution Exposure and Cardio- Respiratory Mortality: A Review. Environ. Health 2013, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, A.C.; Fevotte, J.; Fletcher, T.; Cassidy, A.; Mannetje, A.; Zaridze, D.; Szeszenia-Dabrowska, N.; Rudnai, P.; Lissowska, J.; Fabianova, E. Occupational Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Lung Cancer Risk: A Multicenter Study in Europe. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 67, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, T. Hydroxyl Radical Generation Mechanism during the Redox Cycling Process of 1, 4-Naphthoquinone. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2935–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Yu, J.Z.; Li, S.X.; Ding, X.; He, Q.F.; Wang, X.M. Roadside and Rooftop Measurements of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM2.5 in Urban Guangzhou: Evaluation of Vehicular and Regional Combustion Source Contributions. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7184–7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.M.; Zhao, X.Y.; Ling, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, T.Y. Tracer-Based Source Apportionment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM2.5 in Guangzhou, Southern China, Using Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2398–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; 2391p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Gelencsér, A. Black Carbon or Brown Carbon? The Nature of Light-Absorbing Carbonaceous Aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3131–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Aiona, P.K.; Li, Y.; Shiraiwa, M.; Laskin, J.; Nizkorodov, S.A.; Laskin, A. Molecular Characterization of Brown Carbon in Biomass Burning Aerosol Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11815–11824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Li, S. Particulate Nitrated Aromatic Compounds from Corn Straw Burning: Compositions, Optical Properties and Potential Health Risks. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ramanathan, V.; Kotamarthi, V.R. Brown Carbon: A Significant Atmospheric Absorber of Solar Radiation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8607–8621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskin, A.; Laskin, J.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Chemistry of Atmospheric Brown Carbon. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4335–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Peng, Y.; Ram, K.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, M.; Wei, J. Investigation of the Uncertainties of Simulated Optical Properties of Brown Carbon at Two Asian Sites Using a Modified Bulk Aerosol Optical Scheme of the Community Atmospheric Model Version 5.3. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Gao, M.; Maenhaut, W.; He, J.; Wu, C.; Cheng, L.; Gao, W.; Sun, Y.; Sun, J.; Xin, J.; et al. The Carbonaceous Aerosol Levels Still Remain a Challenge in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region of China: Insights from Continuous High Temporal Resolution Measurements in Multiple Cities. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Huo, J.; Wang, D.; Fu, Q.; Sun, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, J. Online Measurement of Carbonaceous Aerosols in Suburban Shanghai during Winter over a Three-Year Period: Temporal Variations, Meteorological Effects, and Sources. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 226, 117408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zheng, J.; Huang, Z.; Wu, C.; Zheng, C.; Jia, G.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; et al. Insight into the Characteristics of Carbonaceous Aerosols at Urban and Regional Sites in the Downwind Area of Pearl River Delta Region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, S.; Luo, B.; Zhai, C. Characteristics and Origins of Carbonaceous Aerosol in the Sichuan Basin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.; Yao, R.; Wang, P.; Liu, H.; Xiao, W.; Liu, X.; Cao, J. Characterization of Carbonaceous Fractions in PM2.5 and PM10 over a Typical Industrial City in Central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16855–16867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Naja, M. Characteristics of Carbonaceous Aerosols Derived from Long-Term High-Resolution Measurements at a High-Altitude Site in the Central Himalayas: Radiative Forcing Estimates and Role of Meteorology and Biomass Burning. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14654–14670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, W.; Li, L.; Fai Ho, K.; et al. Optical Properties and Molecular Compositions of Water-Soluble and Water-Insoluble Brown Carbon (BrC) Aerosols in Northwest China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 4889–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Bergstrom, R.W. Light Absorption by Carbonaceous Particles: An Investigative Review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; Deangelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the Role of Black Carbon in the Climate System: A Scientific Assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril-Valle, M.; Coz, E.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Močnik, G.; Pandis, S.N.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Alastuey, A.; Díaz, E.; Pérez, R.M.; Artíñano, B. Characterization of Atmospheric Black Carbon and Co-Pollutants in Urban and Rural Areas of Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.; Hays, M.D.; Geron, C.; Jetter, J. Differences in the OC/EC Ratios That Characterize Ambient and Source Aerosols Due to Thermal-Optical Analysis. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spracklen, D.V.; Jimenez, J.L.; Carslaw, K.S.; Worsnop, D.R.; Evans, M.J.; Mann, G.W.; Zhang, Q.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Allan, J.; Coe, H.; et al. Aerosol Mass Spectrometer Constraint on the Global Secondary Organic Aerosol Budget. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12109–12136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodzic, A.; Kasibhatla, P.S.; Jo, D.S.; Cappa, C.D.; Jimenez, J.L.; Madronich, S.; Park, R.J. Rethinking the Global Secondary Organic Aerosol (SOA) Budget: Stronger Production, Faster Removal, Shorter Lifetime. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7917–7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Cao, C.; Ge, S.; Xie, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Xue, G.; et al. The Characteristics of Atmospheric Brown Carbon in Xi’an, Inland China: Sources, Size Distributions and Optical Properties. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mo, Y.; Ding, P.; Li, J.; Shen, C.; Zhang, G. Dual Carbon Isotopes (14C and 13C) and Optical Properties of WSOC and HULIS-C during Winter in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Huang, R.J.; El Haddad, I.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.; Zotter, P.; Bozzetti, C.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Canonaco, F.; et al. Fossil vs. Non-Fossil Sources of Fine Carbonaceous Aerosols in Four Chinese Cities during the Extreme Winter Haze Episode of 2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Nie, F.; Fei, L. Source Apportionment of Carbonaceous Aerosols Using Hourly Data and Implications for Reducing PM2.5 in the Pearl River Delta Region of South China. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q. Variability of PM2.5 and O3 Concentrations and Their Driving Forces over Chinese Megacities during 2018–2020. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide: Executive Summary; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guangdong Provincial Bureau of Statistics, People’s Republic of China. Guangdong Province Statistical Yearbook 2022; China Statistics Publishing House: Guangdong, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, M.; Tang, M.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; Li, G.; Yu, Y.; et al. Water Soluble Organic Nitrogen (WSON) in Ambient Fine Particles over a Megacity in South China: Spatiotemporal Variations and Source Apportionment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 13045–13060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, M.; Yang, W.; Tang, M.; Huang, X.; Yu, Y.; Fang, H.; Yu, X.; Yu, Q.; Fu, X.; et al. Filter-Based Measurement of Light Absorption by Brown Carbon in PM2.5 in a Megacity in South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Robles, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Trimble, D.L.; Kohl, S.D.; Tropp, R.J.; Fung, K.K. Quality Assurance and Quality Control for Thermal/Optical Analysis of Aerosol Samples for Organic and Elemental Carbon. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 3141–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Chang, M.C.O.; Robinson, N.F.; Trimble, D.; Kohl, S. The IMPROVE_A Temperature Protocol for Thermal/Optical Carbon Analysis: Maintaining Consistency with a Long-Term Database. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turpin, B.J.; Huntzicker, J.J. Identification of Secondary Organic Aerosol Episodes and Quantitation of Primary and Secondary Organic Aerosol Concentrations during SCAQS. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 3527–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Wu, N.; Zhang, Q. Chemical Characteristics and Source Apportionment of Ambient PM1.0 and PM2.5 in a Polluted City in North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 242, 117867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.Z.; Sun, L.; Tian, Y.; Shi, G.; Feng, Y. Chemical Characterization and Source Apportionment of PM1 and PM2.5 in Tianjin, China: Impacts of Biomass Burning and Primary Biogenic Sources. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, D.; Yu, J.Z. Estimation and Uncertainty Analysis of Secondary Organic Carbon Using 1 Year of Hourly Organic and Elemental Carbon Data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2774–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Gao, B.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q.; Deng, W.; Huang, Z.; Ding, X.; Hu, Q.; Huang, Z.; et al. Attributing Risk Burden of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons to Major Emission Sources: Case Study in Guangzhou, South China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Ding, X.; He, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z. PM2.5 Acidity at a Background Site in the Pearl River Delta Region in Fall-Winter of 2007–2012. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros, D.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Identification and Emission Rates of Molecular Tracers in Coal Smoke Particulate Matter. Fuel 2000, 79, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhuang, G.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fu, J.S.; Fu, Q.; Liu, T.; Deng, C. How to Improve the Air Quality over Megacities in China: Pollution Characterization and Source Analysis in Shanghai before, during, and after the 2010 World Expo. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5927–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuanjian, L.; Aihua, W.; Mengxue, T.; Shengji, L.; Ji, L. Review of Screening and Applications of Organic Tracers in Fine Particulate Matter. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Naiema, I.M.; Stone, E.A. Evaluation of Anthropogenic Secondary Organic Aerosol Tracersfrom Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2053–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.E.; Rap, A.; Spracklen, D.V.; Forster, P.M.; Carslaw, K.S.; Mann, G.W.; Pringle, K.J.; Kivekäs, N.; Kulmala, M.; Lihavainen, H.; et al. The Direct and Indirect Radiative Effects of Biogenic Secondary Organic Aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, W.F.; Hildemann, L.M.; Mazurek, M.A.; Cass, G.R. Sources of Fine Organic Aerosol. 1. Charbroilers and Meat Cooking Operations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 1112–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, H.; Saikawa, E.; Wan, X.; Zhu, H.; Ram, K.; Gao, S.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G. Levoglucosan as a Tracer of Biomass Burning: Recent Progress and Perspectives. Atmos. Res. 2019, 220, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneit, B.R.T.; Schauer, J.J.; Nolte, C.G.; Oros, D.R.; Elias, V.O.; Fraser, M.P.; Rogge, W.F.; Cass, G.R. Levoglucosan, a Tracer for Cellulose in Biomass Burning and Atmospheric Particles. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Howell, S.G.; Zhuang, J.; Huebert, B.J. Attribution of Aerosol Light Absorption to Black Carbon, Brown Carbon, and Dust in China—Interpretations of Atmospheric Measurements during EAST-AIRE. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2035–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.-Q.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, Y.-H. Research Progress and Direction of Atmospheric Brown Carbon. Huan Jing ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2014, 35, 4404–4414. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.A.; Chow, J.C.; Wang, X.L.; Robles, J.A.; Sumlin, B.J.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Zimmermann, R. Multi-Wavelength Optical Measurement to Enhance Thermal / Optical Analysis for Carbonaceous Aerosol. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Yun, H.; Gong, Z.H.; Li, X.; He, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Hu, M. Source Apportionment and Secondary Organic Aerosol Estimation of PM2.5 in an Urban Atmosphere in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, M.; Sun, J. Origin, Properties, Measurement and Emission Estimation of Brown Carbon Aerosols. Res. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 1797–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Collaud Coen, M.; Weingartner, E.; Apituley, A.; Ceburnis, D.; Fierz-Schmidhauser, R.; Flentje, H.; Henzing, J.S.; Jennings, S.G.; Moerman, M.; Petzold, A.; et al. Minimizing Light Absorption Measurement Artifacts of the Aethalometer: Evaluation of Five Correction Algorithms. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.A.; Langridge, J.M. On the Attribution of Black and Brown Carbon Light Absorption Using the Ångström Exponent. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10535–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Fu, T.-M.; Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Wang, G.H.; Ho, K.F.; Cheng, M.-C.; You, C.-F.; Wang, T.J. Seasonal and Spatial Variability of the OM/OC Mass Ratios and High Regional Correlation between Oxalic Acid and Zinc in Chinese Urban Organic Aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4307–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Schmid, O.; Yang, H.; Chand, D.; Yu, J.Z.; Zeng, L.-M.; Zhang, Y.-H. Optical Properties and Chemical Composition of the Atmospheric Aerosol in Urban Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6335–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Lu, Z.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Frazier, C.A.; Solomon, P.A.; Thuillier, R.H.; Magliano, K. Descriptive Analysis of PM2.5 and PM10 at Regionally Representative Locations during SJVAQS/AUSPEX. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 2079–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, Q.; Shen, G.; Wu, H. Seasonal Variation of Urban Carbonaceous Aerosols in a Typical City Nanjing in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.Q.; Wei, J.; Ji, Y.Y.; Wu, Z.H.; Bi, F.; Gao, R.; Wang, X.Z.; Li, H. Chemical Composition of Fine Organic Aerosols during a Moderate Pollution Event in Summertime in Beijing: Combined Effect of Primary Emission and Secondary Formation. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhang, X.L.; Xiu, A.J.; Huang, L.; Zhao, H.M.; Wang, K.; Tong, Q.Q. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Biogenic Volatile Organic Compounds Emissions in China. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2019, 39, 4140–4151. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, A.K.; Thapa, A.; Gautam, H. Solar Radiation, Air Temperature, Relative Humidity, and Dew Point Study: Damak, Jhapa, Nepal. Int. J. Photoenergy 2019, 2019, 8369231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, X.; Huang, X.H.H.; Griffith, S.M.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, D.; Yu, J.Z. Impact of Secondary Organic Aerosol Tracers on Tracer-Based Source Apportionment of Organic Carbon and PM2.5: A Case Study in the Pearl River Delta, China. ACS Earth Sp. Chem. 2017, 1, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Lai, S.; Song, J.; Ding, X.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Yue, D.; Zhong, L. Seasonal Cycles of Secondary Organic Aerosol Tracers in Rural Guangzhou, Southern China: The Importance of Atmospheric Oxidants. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gu, F.; Ji, Y.; Ma, S.; Guo, J. Electric Vehicle Adoption and Local PM2.5 Reduction: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 396, 136508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Hao, J. Assessing the Future Vehicle Fleet Electrification: The Impacts on Regional and Urban Air Quality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, C.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W.; Xiao, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Decrease in Ambient Volatile Organic Compounds during the COVID-19 Lockdown Period in the Pearl River Delta Region, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Tao, M.; Chen, N.; Lei, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xin, J.; Li, T.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Exploring the Variation of Black and Brown Carbon during COVID-19 Lockdown in Megacity Wuhan and Its Surrounding Cities, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Fan, Y. Measurement Report: Optical Properties and Sources of Water-Soluble Brown Carbon in Tianjin, North China—Insights from Organic Molecular Compositions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 6449–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Yang, F.; Tian, M.; Shi, G.; Li, L.; Huang, R.J.; Yao, X.; Luo, B.; Zhai, C.; Chen, Y. Brown Carbon Aerosol in Two Megacities in the Sichuan Basin of Southwestern China: Light Absorption Properties and Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Tian, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Shi, G.; Huang, R.J.; Yao, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhai, C.; Zhang, S.; et al. Light Absorption of Brown Carbon in PM2.5 in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, Southwestern China: Implications of Biomass Burning and Secondary Formation. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 229, 117409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, V.; Singh, G.K.; Gupta, T.; Paul, D. Absorption and Radiative Characteristics of Brown Carbon Aerosols during Crop Residue Burning in the Source Region of Indo-Gangetic Plain. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wen, T.; Hu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, G. Composition and Sources of Brown Carbon Aerosols in Megacity Beijing during the Winter of 2016. Atmos. Res. 2021, 262, 105773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Stavroulas, I.; Bougiatioti, A.; Liakakou, E.; Dumka, U.C.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Apportionment of Black and Brown Carbon Spectral Absorption Sources in the Urban Environment of Athens, Greece, during Winter. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Lee, A.K.Y.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; Abbatt, J.P.D. Photochemical Processing of Aqueous Atmospheric Brown Carbon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6087–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Shen, Z.; Takahama, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Ning, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Molecular Absorption and Evolution Mechanisms of PM2.5 Brown Carbon Revealed by Electrospray Ionization Fourier Transform–Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry during a Severe Winter Pollution Episode in Xi’an, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumlin, B.; Fortner, E.; Lambe, A.; Shetty, N.J.; Daube, C.; Liu, P.; Majluf, F.; Herndon, S.; Chakrabarty, R.K. Diel Cycle Impacts on the Chemical and Light Absorption Properties of Organic Carbon Aerosol from Wildfires in the Western United States. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 11843–11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oroumiyeh, F.; Jerrett, M.; Del Rosario, I.; Lipsitt, J.; Liu, J.; Paulson, S.E.; Ritz, B.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Shen, J. Elemental Composition of Fine and Coarse Particles across the Greater Los Angeles Area: Spatial Variation and Contributing Sources. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, P.; Laskin, A.; Laskin, J.; Kathmann, S.M.; Wise, M.; Caylor, R.; Imholt, F.; Selimovic, V.; Shilling, J.E. Optical Properties and Aging of Light-Absorbing Secondary Organic Aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12815–12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Season | TC/PM2.5 (%) | CA/PM2.5 (%) | OC/EC | SOC/OC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| autumn | 15.1 ± 3.7 | 25.8 ± 6.5 | 7.5 ± 2.1 | 73.7 ± 7.3 |
| winter | 17.5 ± 7.2 | 29.6 ± 11.9 | 6.6 ± 2.0 | 68.4 ± 13.1 |
| BLH or Tracers | Season | Autumn (Mean ± 95% C.I.) | Winter (Mean ± 95% C.I.) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Site | XH | JL | SZ | HG | XH | SZ | HKUST | |
| BLH (m) | daytime | 616 ± 20 | 612 ± 25 | 644 ± 24 | 647 ± 32 | 644 ± 98 | 633 ± 104 | 541 ± 77 |
| nighttime | 81 ± 39 | 110 ± 57 | 109 ± 43 | 182 ± 78 | 373 ± 173 | 372 ± 154 | 271 ± 142 | |
| Ratio * | 7.6 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 3.6 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 2.0 | |
| LG (ng/m3) | daytime | 15.2 ± 5.5 | 63.0 ± 94.6 | 17.8 ± 5.5 | 17.0 ± 11.5 | 31.0 ± 11.2 | 37.7 ± 9.9 | 23.0 ± 9.3 |
| nighttime | 43.2 ± 15.3 | 164 ± 174 | 31.4 ± 13.2 | 16.2 ± 11.0 | 43.9 ± 21.5 | 50.0 ± 20.6 | 31.4 ± 12.8 | |
| ΔLG ** | 27.9 | 101 | 13.6 | −0.8 | 12.9 | 12.3 | 8.3 | |
| Ratio *** | 2.8 | 2.6 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.4 | |
| Hopanes (ng/m3) | daytime | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.2 |
| nighttime | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.6 | |
| Δhopanes ** | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | −0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.5 | |
| Ratio * | 1.6 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.8 | |
| HMW-PAHs (ng/m3) | daytime | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.5 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.4 |
| nighttime | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 1.1 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 1.3 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 1.3 ± 0.6 | |
| ΔHMWPAHs ** | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Ratio * | 2.7 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 1.6 | |
| Sterols (ng/m3) | daytime | 4.6 ± 1.9 | 12.0 ± 17.4 | 6.3 ± 6.0 | 2.8 ± 2.4 | 3.1 ± 1.4 | 2.5 ± 0.8 | 1.1 ± 0.4 |
| nighttime | 10.5 ± 16.1 | 15.1 ± 18.0 | 9.8 ± 10.2 | 1.7 ± 1.0 | 6.2 ± 5.9 | 10.1 ± 8.0 | 2.8 ± 2.3 | |
| Δsterols ** | 5.9 | 3.1 | 3.5 | −1.1 | 3.1 | 7.7 | 1.7 | |
| Ratio * | 2.3 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 4.1 | 2.5 | |
| BSOA (ng/m3) | daytime | 122 ± 78 | 245 ± 98 | 149 ± 92 | 101 ± 93 | 12.0 ± 4.7 | 18.3 ± 6.0 | 13.8 ± 6.0 |
| nighttime | 135 ± 80 | 216 ± 145 | 137 ± 85 | 88 ± 84 | 12.8 ± 5.9 | 15.8 ± 5.3 | 13.7 ± 4.4 | |
| ΔBSOA ** | 13.1 | −29.4 | −12.2 | −13.4 | 0.7 | −2.5 | −0.1 | |
| Ratio * | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 1.0 | |
| DHOPA (ng/m3) | daytime | 4.9 ± 3.5 | 10.7 ± 9.2 | 7.0 ± 4.5 | 5.9 ± 4.9 | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 1.0 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| nighttime | 2.0 ± 1.3 | 5.3 ± 3.0 | 3.1 ± 2.4 | 2.2 ± 1.9 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.8 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | |
| ΔDHOPA ** | −2.9 | −5.4 | −3.9 | −3.7 | −0.2 | −0.5 | 0.0 | |
| Ratio * | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 1.0 | |
| Ave ± Std | Decrease in Percentage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 (25–30 September) | 2021 (11–31 November) | ||
| PM2.5 (µg/m3) | 47.9 ± 21.0 | 47.4 ± 14.8 | 1.0 |
| TC (µg/m3) | 12.2 ± 5.5 | 7.4 ± 2.9 | 39.5 |
| OC (µg/m3) | 8.6 ± 4.0 | 6.4 ± 2.6 | 25.4 |
| EC (µg/m3) | 3.6 ± 1.7 | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 73.4 |
| SOC (µg/m3) | 4.3 ± 2.3 | 4.7 ± 2.0 | −8.0 |
| OC/EC | 2.4 ± 0.6 | 6.8 ± 1.6 | −179.7 |
| CA (µg/m3) | 19.1 ± 8.7 | 14.2 ± 5.6 | 25.4 |
| MACBrC,405 (m2/g) | 1.3 | 0.6 | 55.4 |
| MACBC,405 (m2/g) | 13.4 | 14.7 | −9.7 |
| MACTC,405 (m2/g) | 5.0 | 3.4 | 31.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, B.; Tong, M.; Xiao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Song, W.; Talifu, D.; Wang, X. Seasonal and Day–Night Variations in Carbonaceous Aerosols and Their Light-Absorbing Properties in Guangzhou, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101545
Su J, Zhang R, Liu B, Tong M, Xiao S, Wang X, Zhao Q, Song W, Talifu D, Wang X. Seasonal and Day–Night Variations in Carbonaceous Aerosols and Their Light-Absorbing Properties in Guangzhou, China. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(10):1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101545
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Jiannan, Runqi Zhang, Bowen Liu, Mengxue Tong, Shaoxuan Xiao, Xiaoyang Wang, Qilong Zhao, Wei Song, Dilinuer Talifu, and Xinming Wang. 2023. "Seasonal and Day–Night Variations in Carbonaceous Aerosols and Their Light-Absorbing Properties in Guangzhou, China" Atmosphere 14, no. 10: 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101545
APA StyleSu, J., Zhang, R., Liu, B., Tong, M., Xiao, S., Wang, X., Zhao, Q., Song, W., Talifu, D., & Wang, X. (2023). Seasonal and Day–Night Variations in Carbonaceous Aerosols and Their Light-Absorbing Properties in Guangzhou, China. Atmosphere, 14(10), 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101545








