Simulation Analyses on a Downburst Event That Caused a Severe Tower Toppling down Accident in Zhejiang (China)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data, Model Configuration, and Methods
2.1. Data
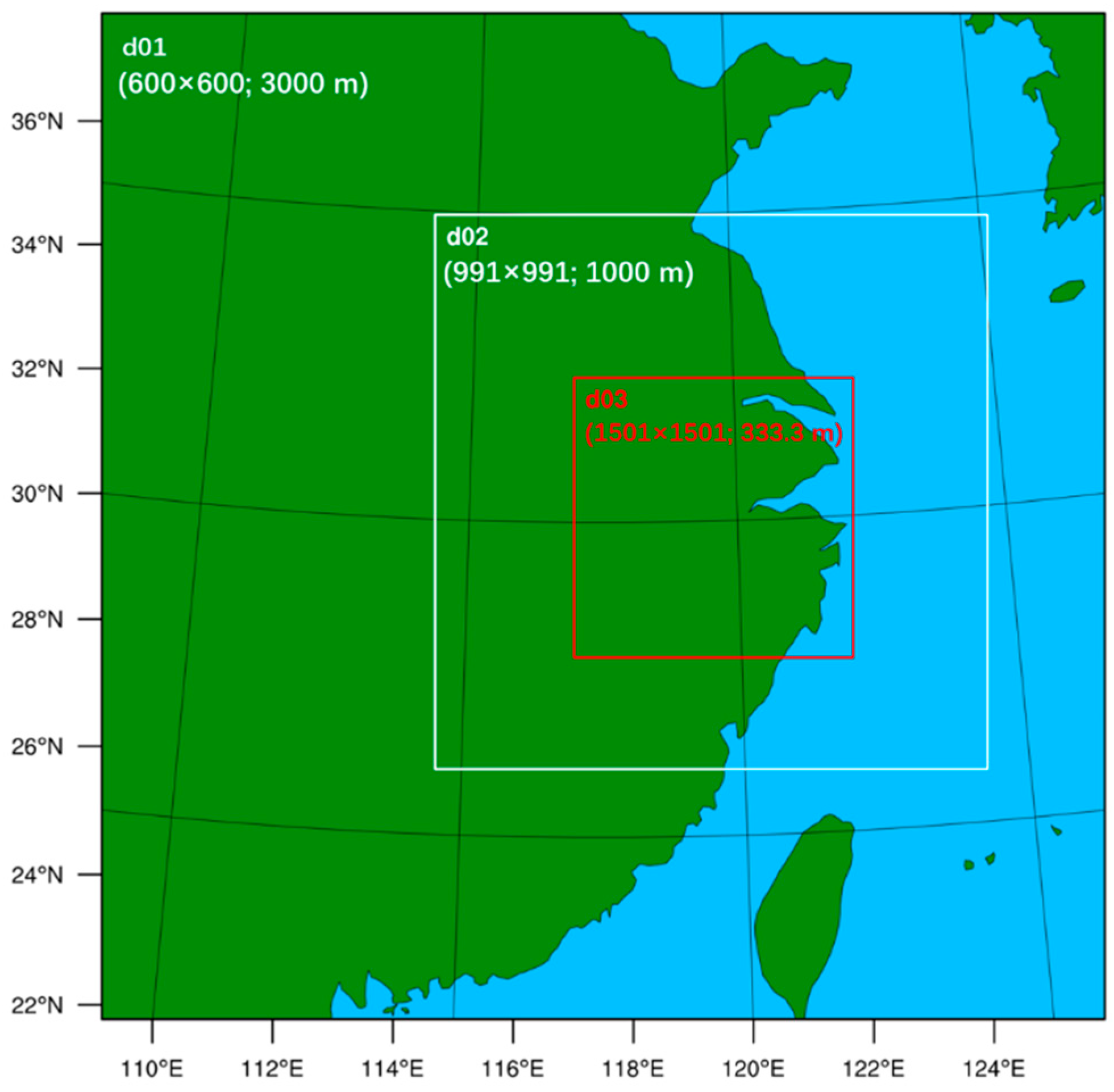
2.2. Model Configuration
2.3. Kinetic Energy Budget
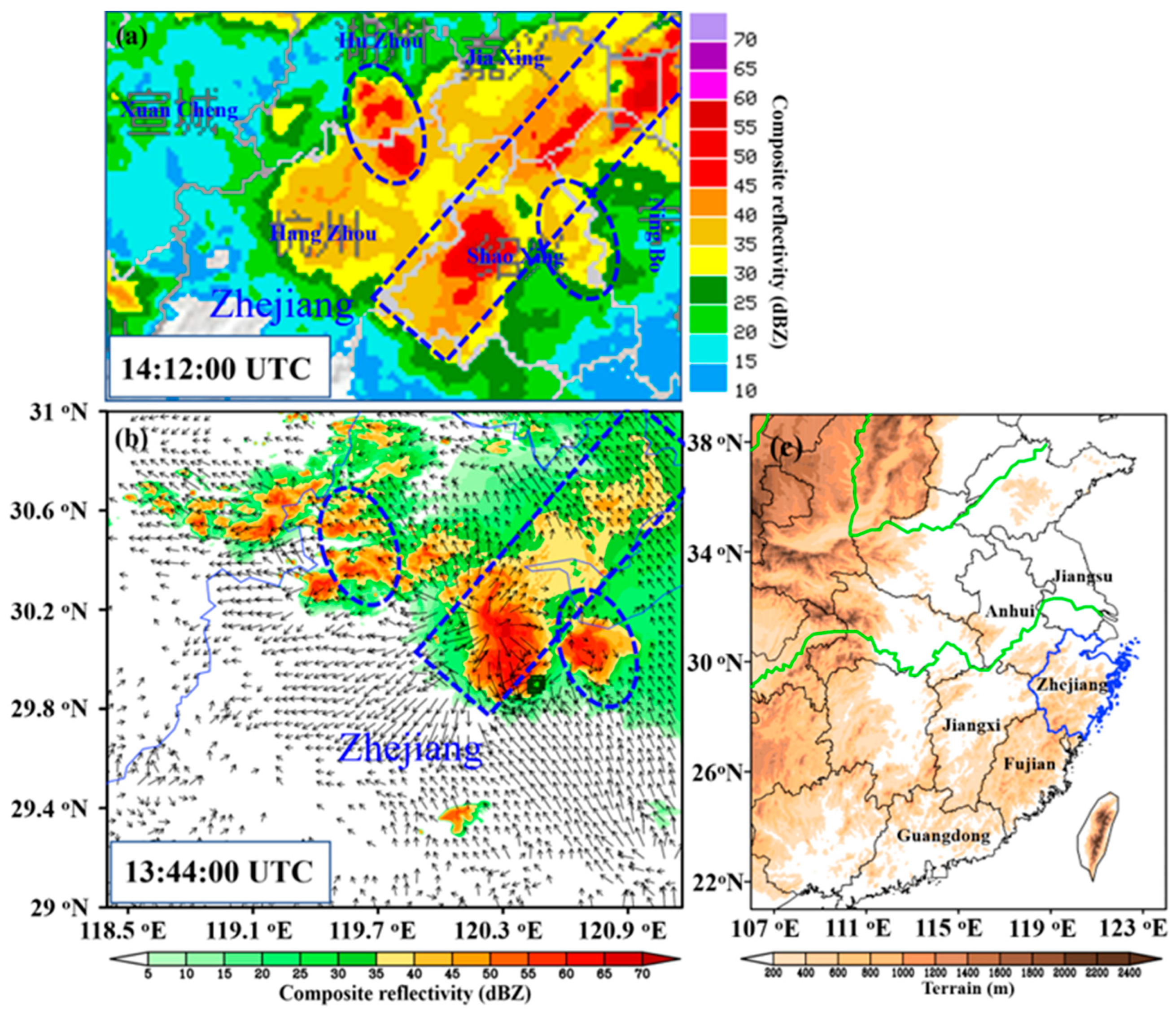
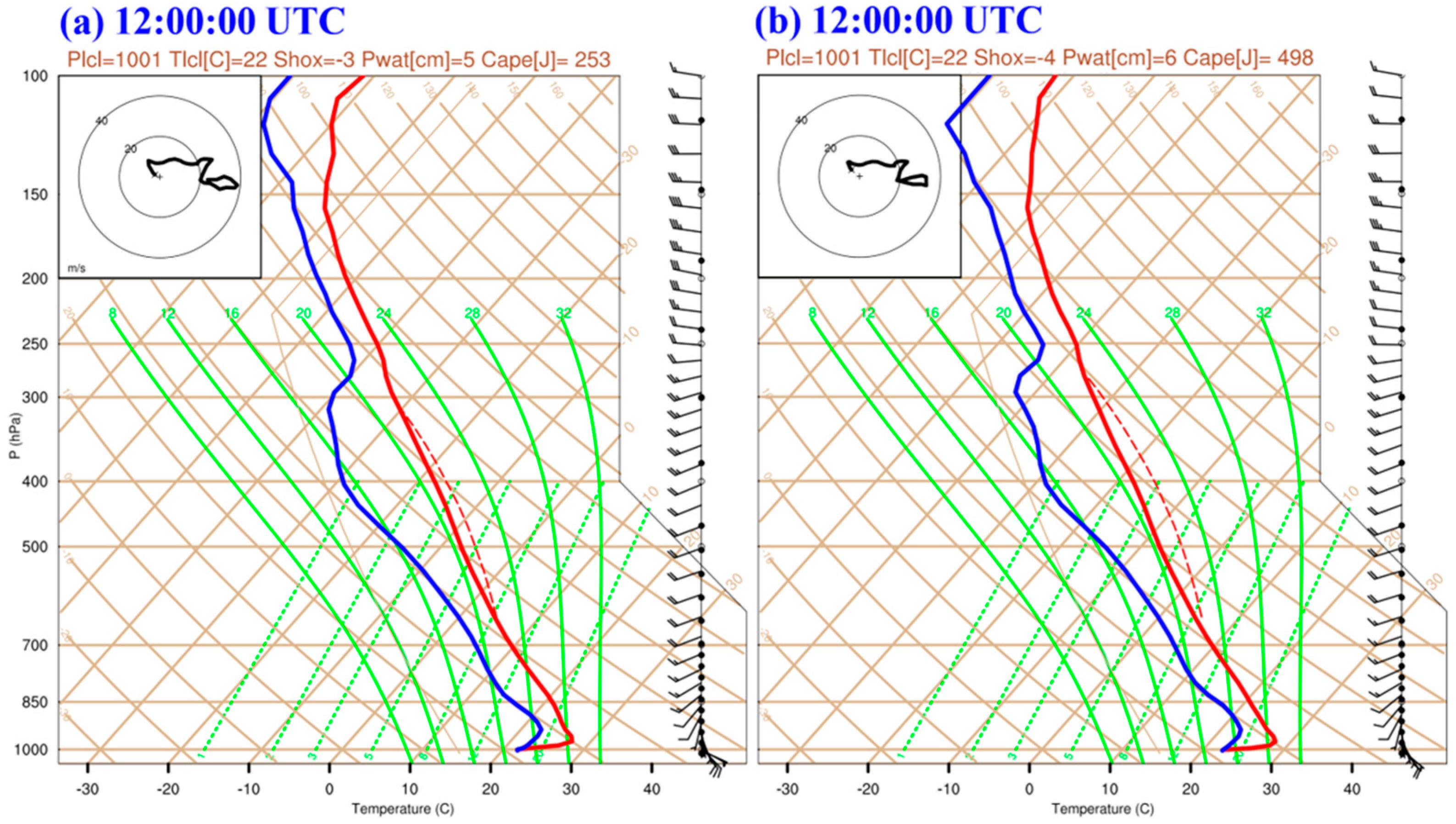
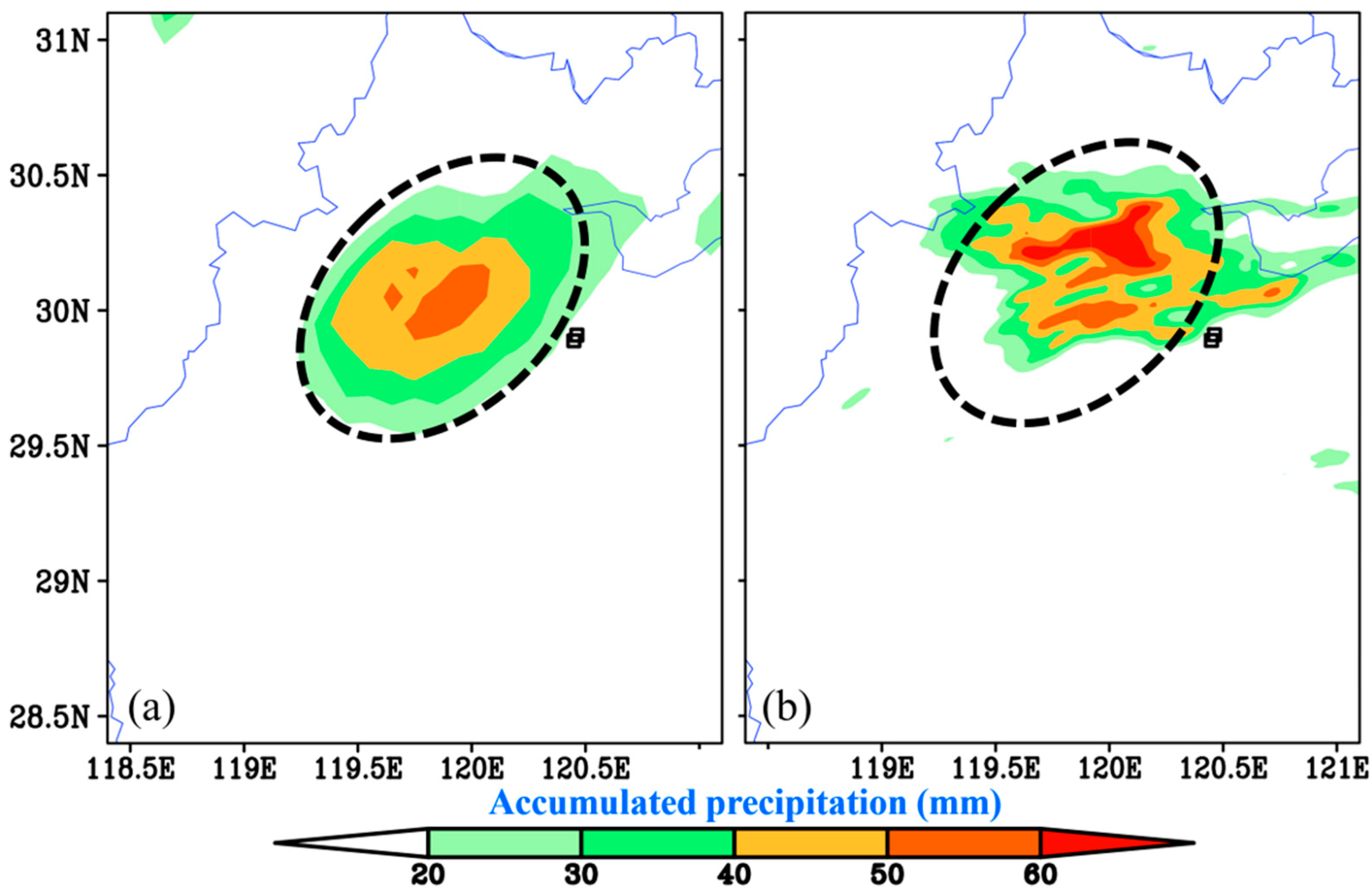
3. Simulation Validation
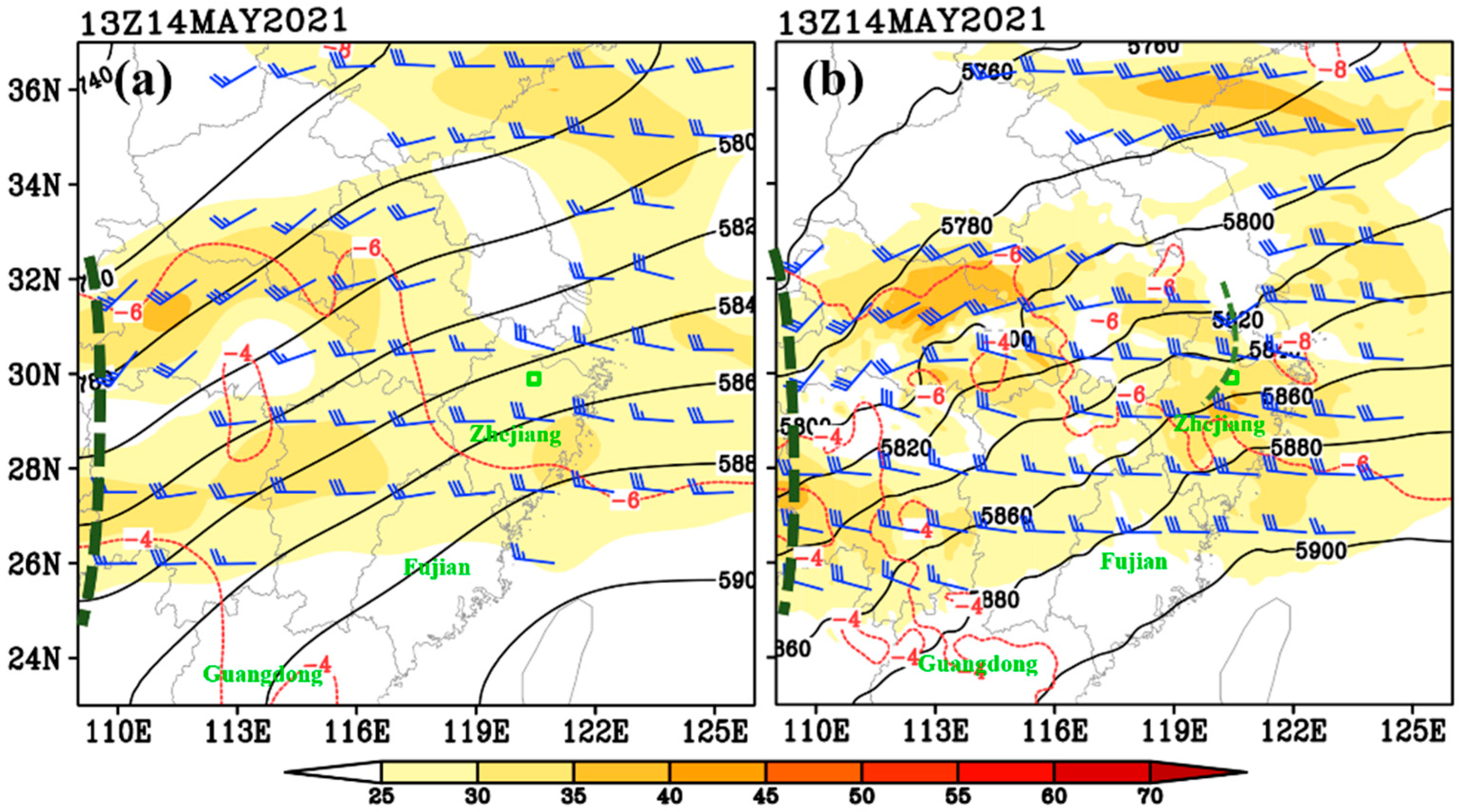
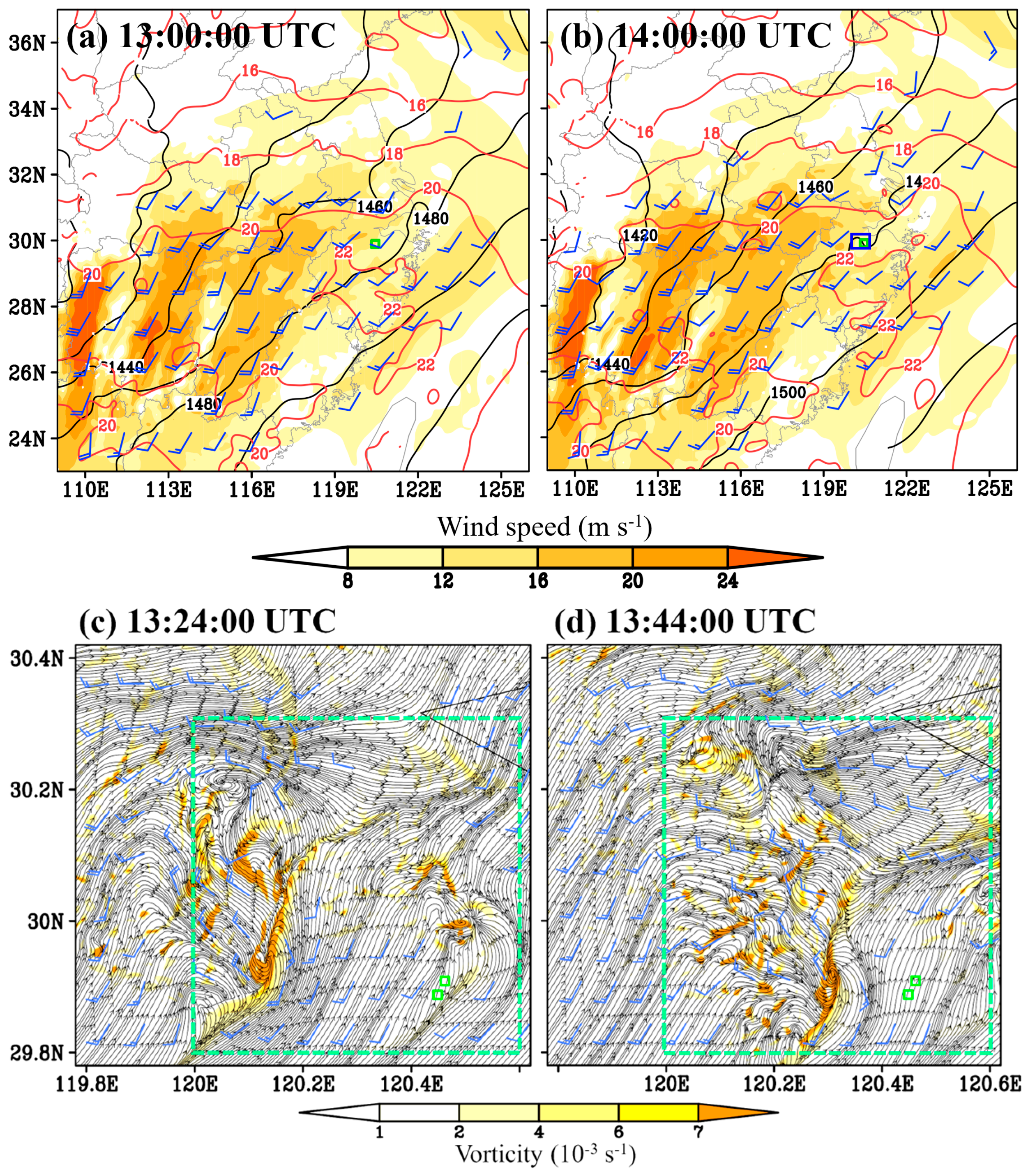
4. Synoptic Analyses
5. Downburst Event That Caused the Accident
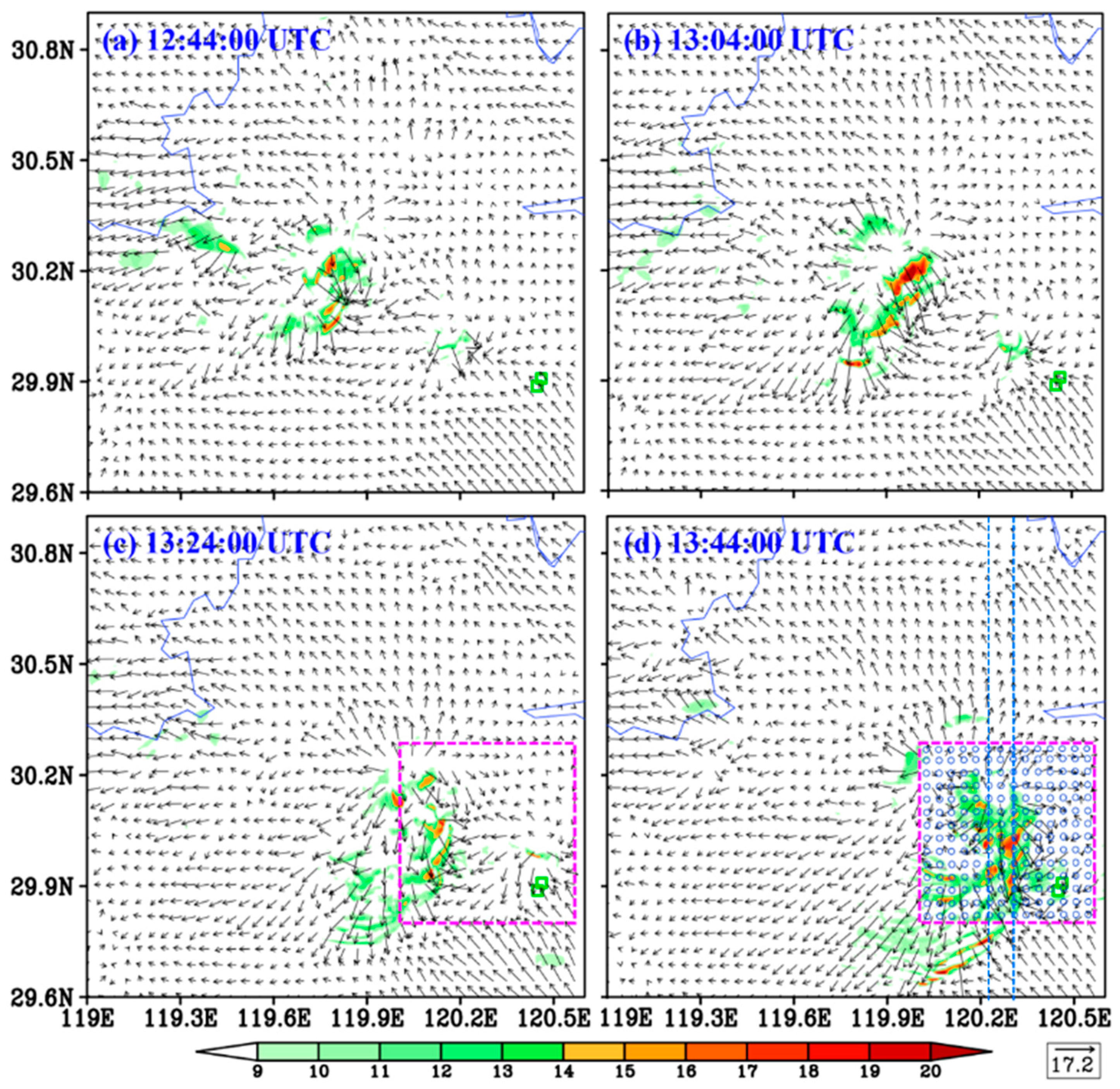
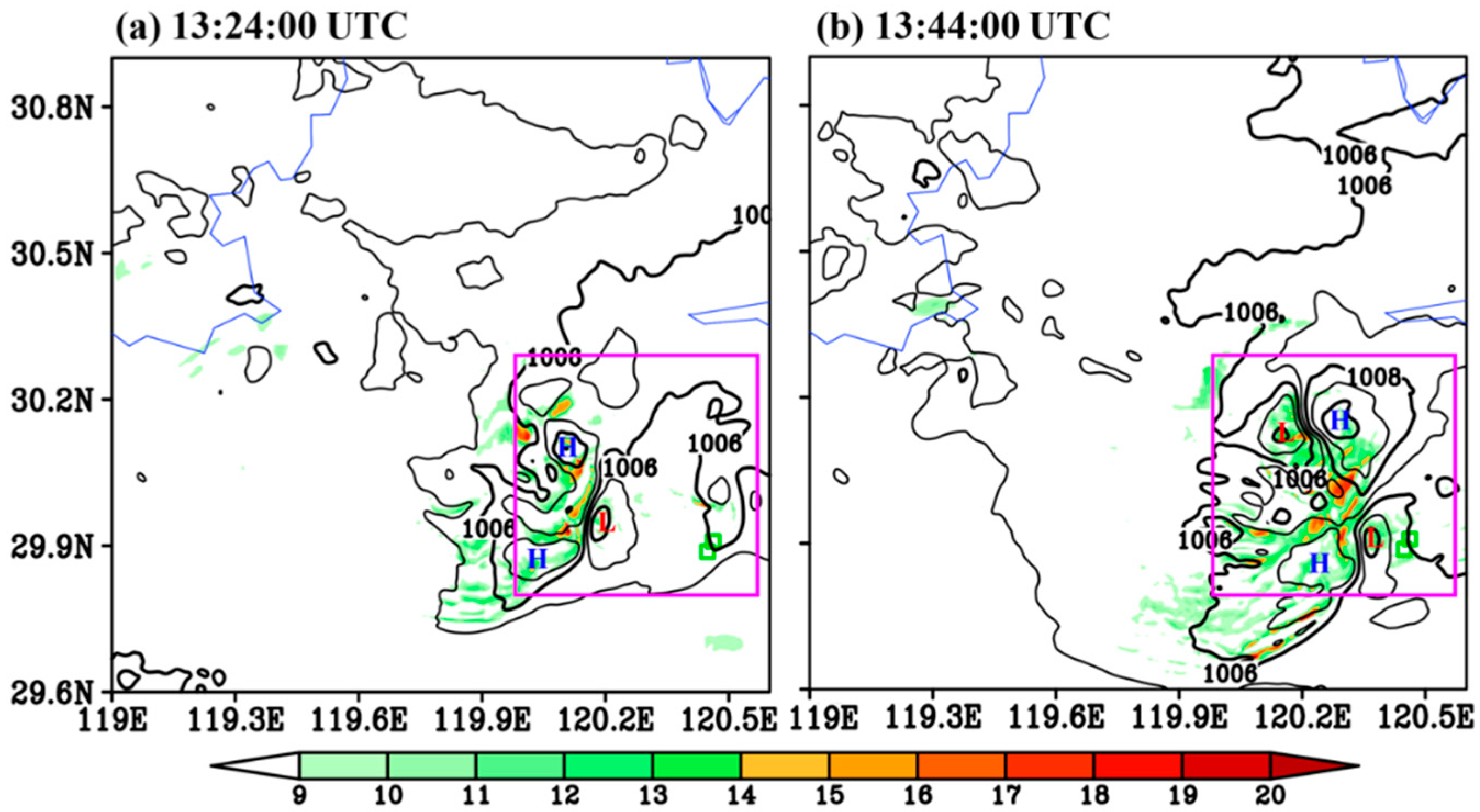
5.1. Horizontal Structure
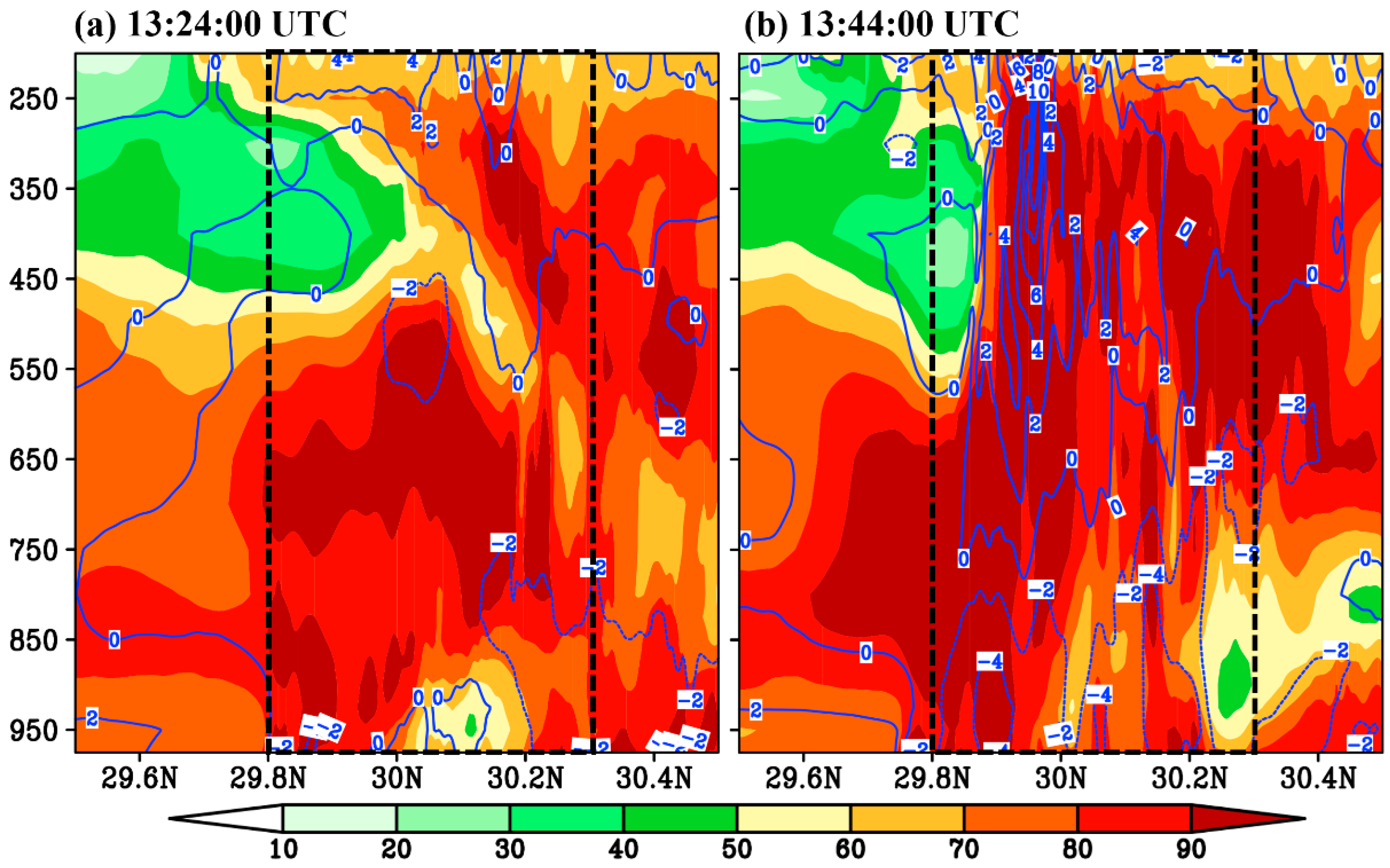
5.2. Vertical Structure
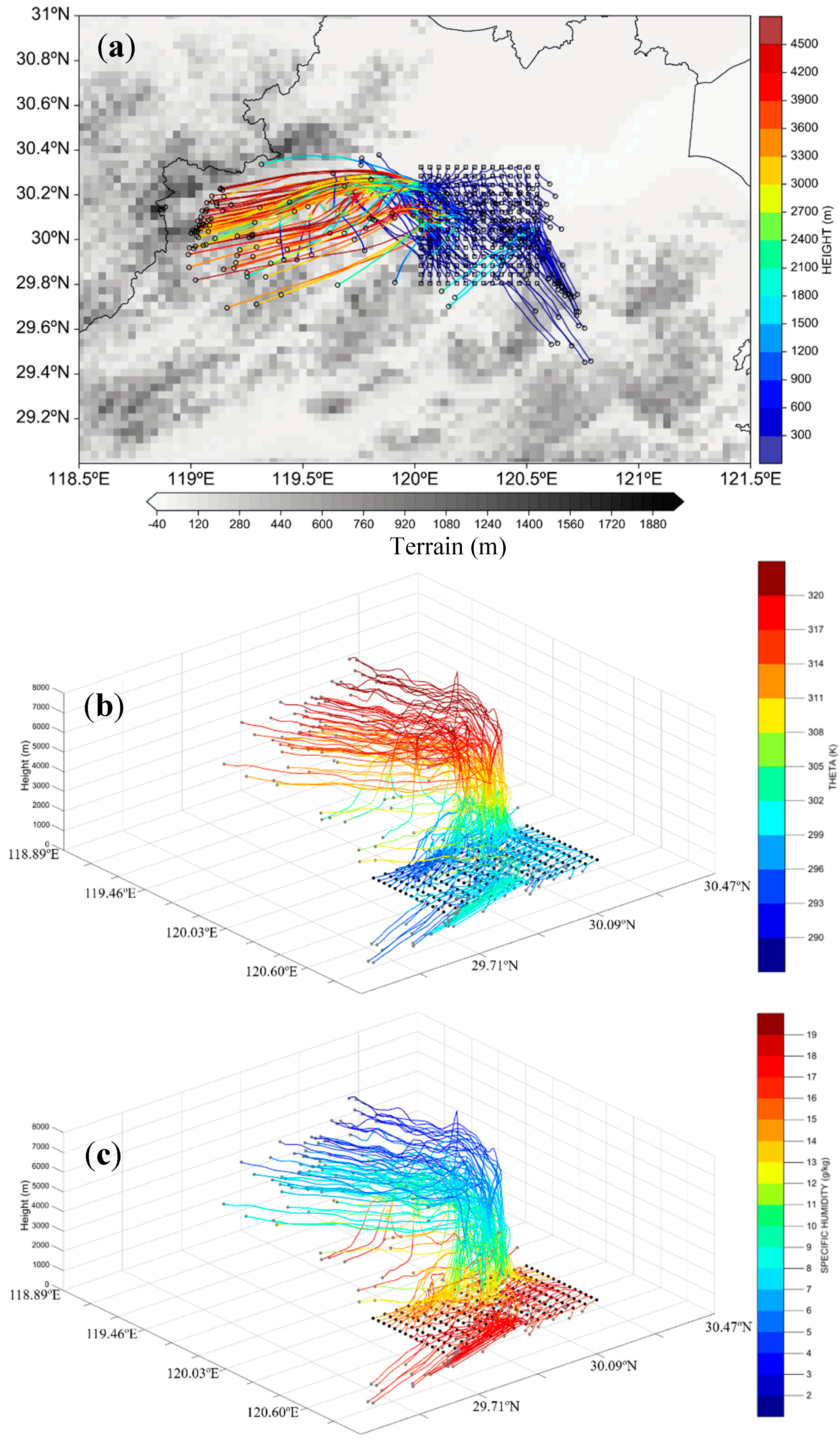
5.3. Backward Trajectory Analysis
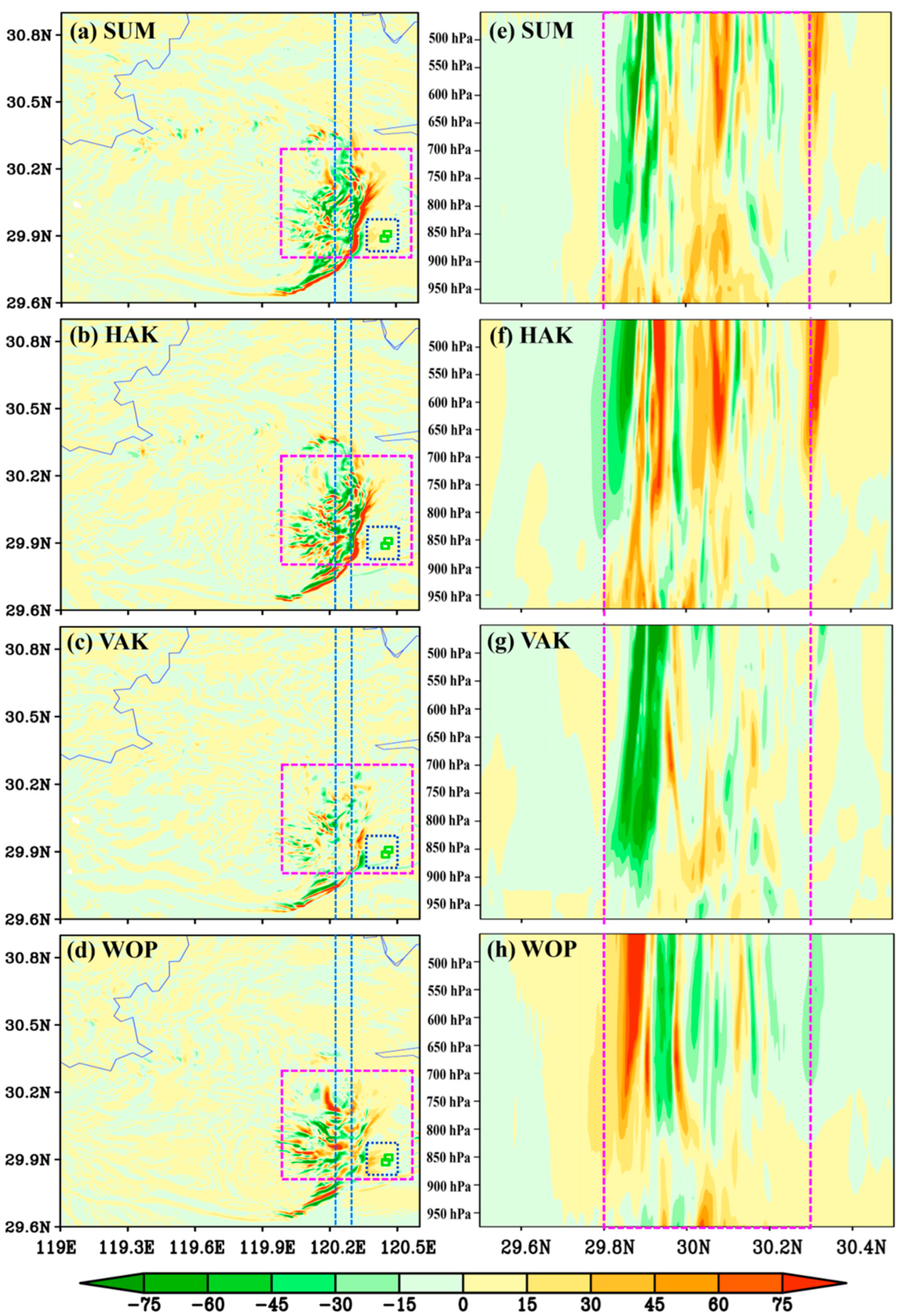
5.4. Kinetic Energy Budget Analyses
6. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, Y.-G.; Tian, F.-Y.; Meng, Z.-Y.; Xue, M.; Yao, D.; Bai, L.; Zhou, X.; Mao, X.; Wang, M. Survey and Multi-Scale Characteristics of Wind Damage Caused by Convective Storms in the Surrounding Area of the Capsizing Accident of Cruise Ship “Dongfangzhixing”. Meteorol. Mon. 2016, 42, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- American Meteorological Society. 2023. Available online: https://glossary.ametsoc.org/wiki/Downburst (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Fujita, T.T. The Downburst: Microburst and Macroburst, Report of Projects NIMROD and JAWS; Satellite and Mesometeorology Research Project, Department of the Geophysical Sciences, The University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- PennState. 2023. Available online: https://www.e-education.psu.edu/meteo3/node/2232 (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Meng, Z.; Yao, D.; Bai, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, K.; Tian, F.; Wang, M. Wind estimation around the shipwreck of Oriental Star based on field damage surveys and radar observations. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujita, T.T. Tornadoes and Downbursts in the Context of Generalized Planetary Scales. J. Atmos. Sci. 1981, 38, 1511–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.M.; Elmore, K.L.; Dulin, S.A. A Damaging Downburst Prediction and Detection Algorithm for the WSR-88D. Weather Forecast. 2004, 19, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotzek, N. Derivation of physically motivated wind speed scales. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuster, C.M.; Heinselman, P.L.; Schuur, T.J. Rapid-Update Radar Observations of Downbursts Occurring within an Intense Multicell Thunderstorm on 14 June 2011. Weather Forecast. 2016, 31, 827–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolgiani, P.; Fernández-González, S.; Valero, F.; Merino, A.; García-Ortega, E.; Sánchez, J.L.; Martín, M.L. Simulation of Atmospheric Microbursts Using a Numerical Mesoscale Model at High Spatiotemporal Resolution. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.-L.; Yu, X.-D.; Li, C.-L.; Huang, X.-X.; Yan, L.-J.; He, Q.-R.; Mai, W.; Chen, Z. Comparative Analysis of Damage Survey of Microburst in Lingui of Guangxi and Tornado in Zhanjiang of Guangdong in 2019. Meteorol. Mon. 2021, 47, 230–241. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.-J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.-B.; Leng, L.; Fu, Z.-K. A Downburst Nowcasting Method Based on Observations of S-Band New Generation Weather Radar. Meteorol. Mon. 2021, 47, 919–931. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.-Y.; Zhuang, X.-R.; Zhang, J.; Mu, R.; Sun, K.-Y. Statistical analysis of the structural characteris-tics of typical downbursts in Jiangsu province, China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2022, 80, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savory, E.; Parke, G.A.; Zeinoddini, M.; Toy, N.; Disney, P. Modelling of tornado and microburst-induced wind loading and failure of a lattice transmission tower. Eng. Struct. 2001, 23, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, A.; El Damatty, A.; Savory, E. Finite element modeling of transmission line under downburst wind loading. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2005, 42, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-G.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Ni, H.-Y.; Li, T.; Pan, F.; Li, D. Cause Analysis of a 500 kV Transmission Line Tower Collapse Incurred by Downburst. Zhejiang Electr. Power 2021, 40, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Orf, L.; Savory, E.; Novacco, C. Proposed large-scale modelling of the transient features of a downburst outflow. Wind. Struct. 2007, 10, 315–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech, J.; Gayà, M.; Aran, M.; Figuerola, F.; Amaro, J.; Arús, J. Tornado damage analysis of a forest area using site survey observations, radar data and a simple analytical vortex model. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, B.C.; Orf, L.; Savory, E. A parametric study of downburst line near-surface outflows. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2011, 99, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ren, Y.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, B.; Wei, J. Simulation of Phase-to-ground Spacer for Anti-galloping of 500 kV Horizontal Arranged Transmission Lines. Gaodianya Jishu/High Volt. Eng. 2017, 43, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colquhoun, J.R. A Decision Tree Method of Forecasting Thunderstorms, Severe Thunderstorms and Tornadoes. Weather Forecast. 1987, 2, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, Q.; Chou, Y.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M. A Numerical Study of Downbursts Using the BLASIUS Model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2022, 61, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horanyi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-C.; Fu, S.-M.; Sun, J.-H.; Fu, R.; Jin, S.-L.; Ji, D.-S. A 14-year statistics-based semi-idealized modeling study on the formation of a type of heavy rain–producing southwest vortex. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2019, 20, e894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, N.; Zhang, K.; Qing, C.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Luo, T. Analysis of wind-speed profiles and optical turbulence above Gaomeigu and the Tibetan Plateau using ERA5 data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 501, 4692–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Mo, Z.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, J.; Xiong, S.; He, H. Evaluation of Hourly PWV Products Derived From ERA5 and MERRA-2 Over the Tibetan Plateau Using Ground-Based GNSS Observations by Two Enhanced Models. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, G.; Cheng, X.; Chen, Y. Reduction of uncertainties in surface heat flux over the Tibetan Plateau from ERA-Interim to ERA5. Int. J. Clim. 2022, 42, 6277–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Stocker, E.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Tan, J. GPM IMERG Final Precipitation L3 1 Day 0.1 Degree × 0.1 Degree V06; Savtchenko, A., Ed.; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2019.
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Duda, M.G.; Huang, X.-Y.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3; NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bernardino, A.; Mazzarella, V.; Pecci, M.; Casasanta, G.; Cacciani, M.; Ferretti, R. Interaction of the Sea Breeze with the Urban Area of Rome: WRF Mesoscale and WRF Large-Eddy Simulations Compared to Ground-Based Observations. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2022, 185, 333–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling an Advanced Land Surface–Hydrology Model with the Penn State–NCAR MM5 Modeling System. Part I: Model Implementation and Sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A New Vertical Diffusion Package with an Explicit Treatment of Entrainment Processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Lim, J. The WRF Single-Moment 6-Class Microphysics Scheme (WSM6). Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 42, 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical Study of Convection Observed during the Winter Monsoon Experiment Using a Mesoscale Two-Dimensional Model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Cao, X.; Ma, X.; Su, H.; Jing, Y.; Zhu, K. Improving the Wind Power Density Forecast in the Middle- and High-Latitude Regions of China by Selecting the Relatively Optimal Planetary Boundary Layer Schemes. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, A.Y.; Kovadlo, P.G.; Lezhenin, A.A.; Korobov, O.A.; Kiselev, A.V.; Russkikh, I.V.; Kolobov, D.Y.; Shikhovtsev, M.Y. Influence of Atmospheric Flow Structure on Optical Turbulence Characteristics. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Yu, F.; Wang, D.; Xia, R. A comparison of two kinds of eastward-moving mesoscale vortices during the mei-yu period of 2010. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-M.; Liu, R.-X.; Sun, J.-H. On the Scale Interactions that Dominate the Maintenance of a Persistent Heavy Rainfall Event: A Piecewise Energy Analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xia, R.; Sun, J.; Fu, S.; Jiang, L.; Chen, B.; Tian, F. Layer-Wise Formation Mechanisms of an Entire-Troposphere-Thick Extratropical Cyclone That Induces a Record-Breaking Catastrophic Rainstorm in Beijing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 10567–10591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Jin, S.; Shen, W.; Li, D.; Liu, B.; Sun, J. A kinetic energy budget on the severe wind production that causes a serious state grid failure in Southern Xinjiang China. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2020, 21, e977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, J.R. An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, 4th ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.-M.; Mai, Z.; Sun, J.-H.; Li, W.-L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.-Q. Impacts of Convective Activity over the Tibetan Plateau on Plateau Vortex, Southwest Vortex, and Downstream Precipitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 76, 3803–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Tang, H.; Li, W.; Sun, J. On the Evolution of a Long-Lived Mesoscale Convective Vortex that Acted as a Crucial Condition for the Extremely Strong Hourly Precipitation in Zhengzhou. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD036233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Mai, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, W.; Zhong, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. A semi-idealized modeling study on the long-lived eastward propagating mesoscale convective system over the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1996–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-M.; Sun, J.-H.; Luo, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.-C. Formation of Long-Lived Summertime Mesoscale Vortices over Central East China:Semi-Idealized Simulations Based on a 14-Year Vortex Statistic. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 74, 3955–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etherton, B.; Santos, P. Sensitivity of WRF Forecasts for South Florida to Initial Conditions. Weather Forecast. 2008, 23, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hach, Y.; Jabiri, A.; Ziad, A.; Bounhir, A.; Sabil, M.; Abahamid, A.; Benkhaldoun, Z. Meteorological profiles and op-tical turbulence in the free atmosphere with NCEP/NCAR data at Oukaïmeden—I. Meteorological parameters analysis and tropospheric wind regimes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 420, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Fan, W.; Yang, D.; Xiao, X. Simulation Analyses on a Downburst Event That Caused a Severe Tower Toppling down Accident in Zhejiang (China). Atmosphere 2023, 14, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030427
Li D, Liu J, Liu B, Fan W, Yang D, Xiao X. Simulation Analyses on a Downburst Event That Caused a Severe Tower Toppling down Accident in Zhejiang (China). Atmosphere. 2023; 14(3):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030427
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Danyu, Jinghua Liu, Bin Liu, Wenqi Fan, Dongwen Yang, and Xue Xiao. 2023. "Simulation Analyses on a Downburst Event That Caused a Severe Tower Toppling down Accident in Zhejiang (China)" Atmosphere 14, no. 3: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030427
APA StyleLi, D., Liu, J., Liu, B., Fan, W., Yang, D., & Xiao, X. (2023). Simulation Analyses on a Downburst Event That Caused a Severe Tower Toppling down Accident in Zhejiang (China). Atmosphere, 14(3), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030427





