A Novel Reduced Reaction Mechanism for Diesel/2,5-Dimethylfuran Engine Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Kinetic Model Construction
2.1. The Reduced DMF Mechanism
2.2. The Combined Mechanism
2.3. Optimization of the Combined Mechanism
3. Mechanism Validation
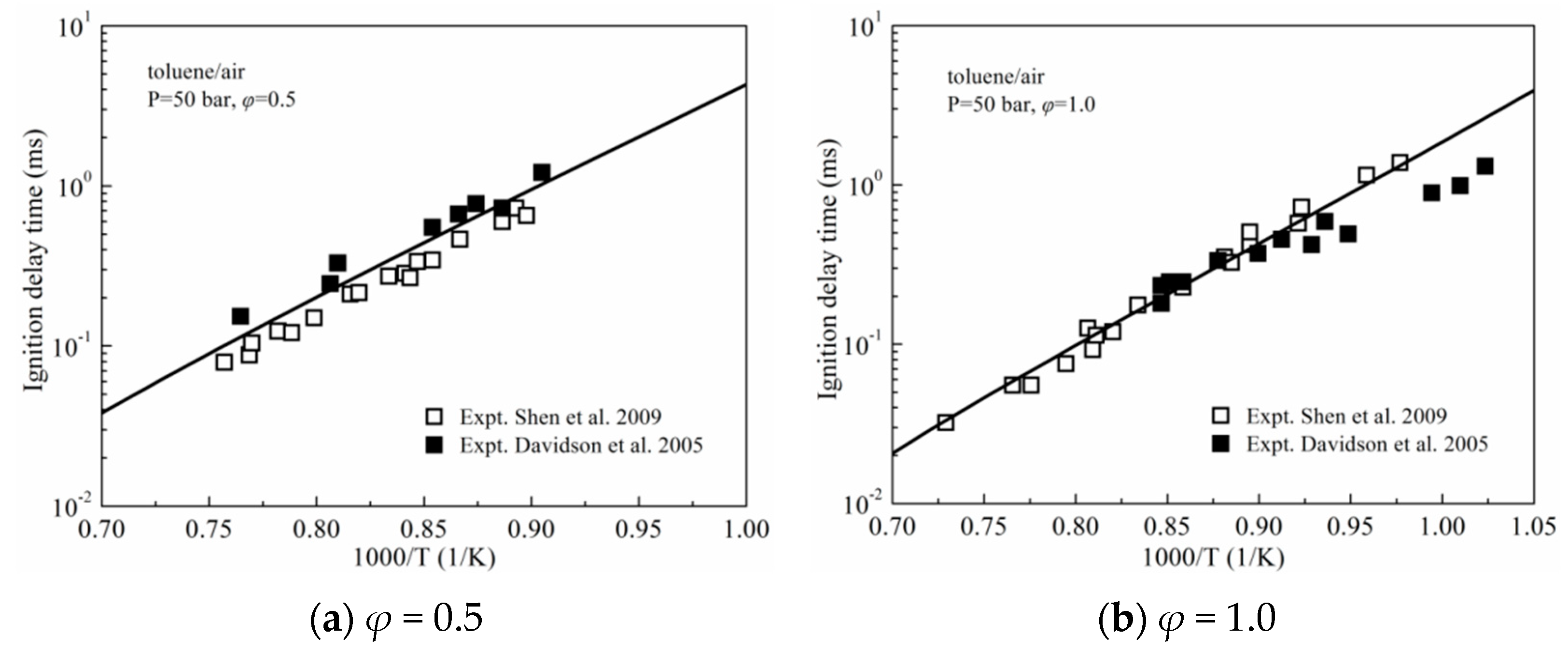
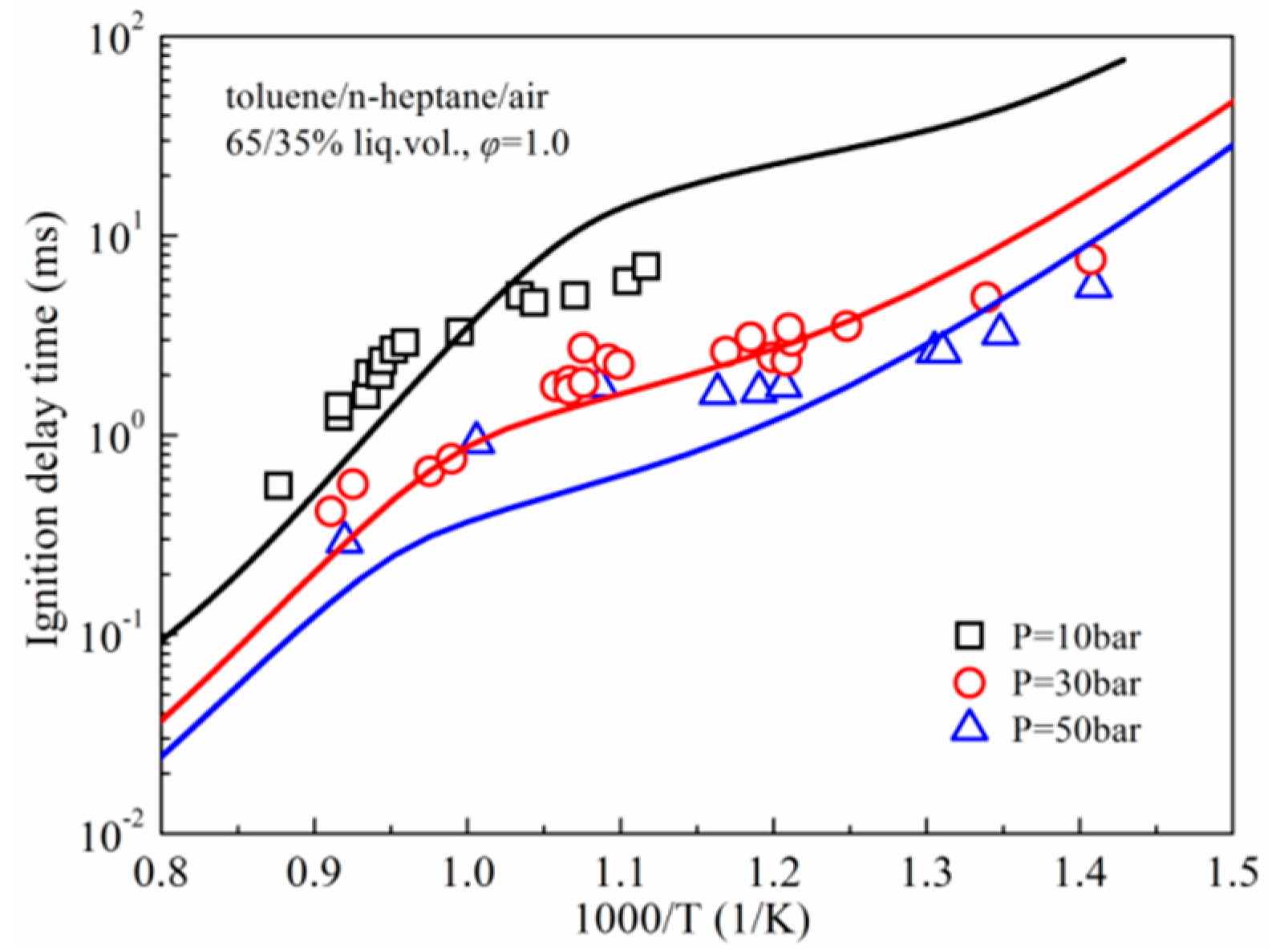
3.1. Ignition Delay Times
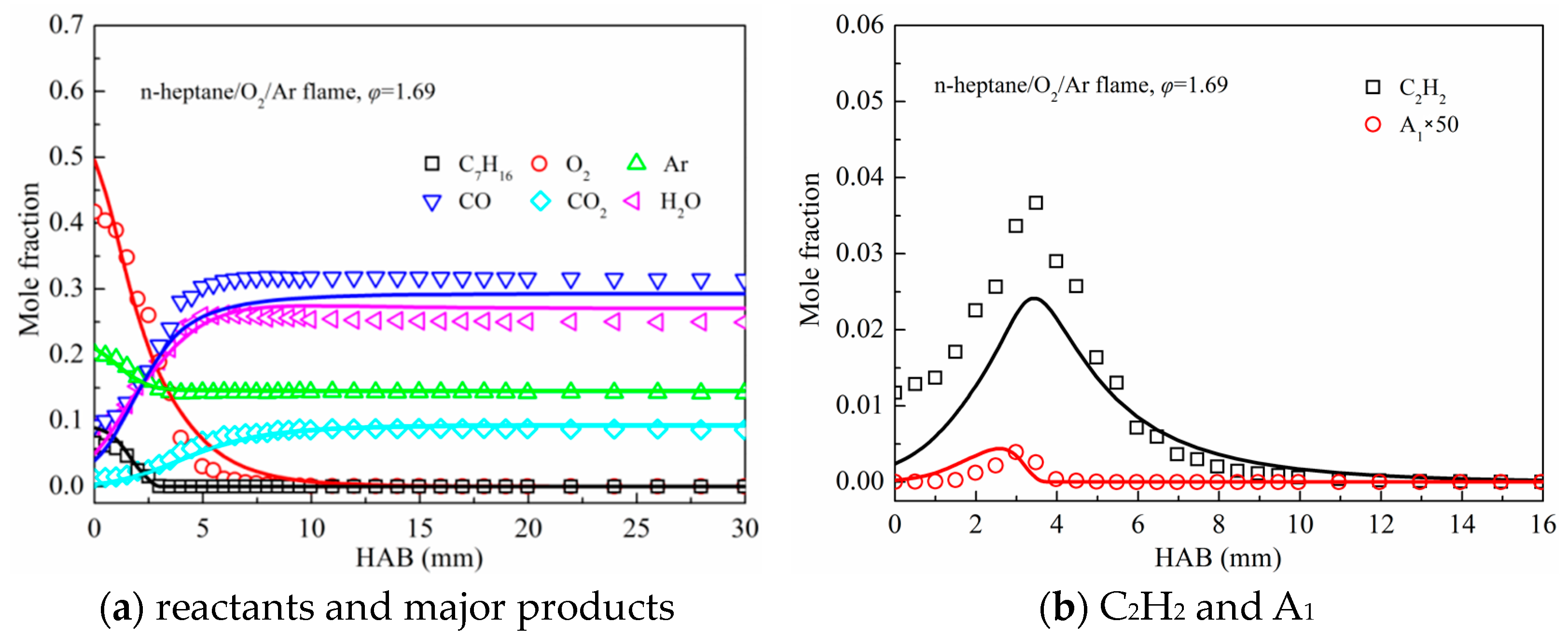
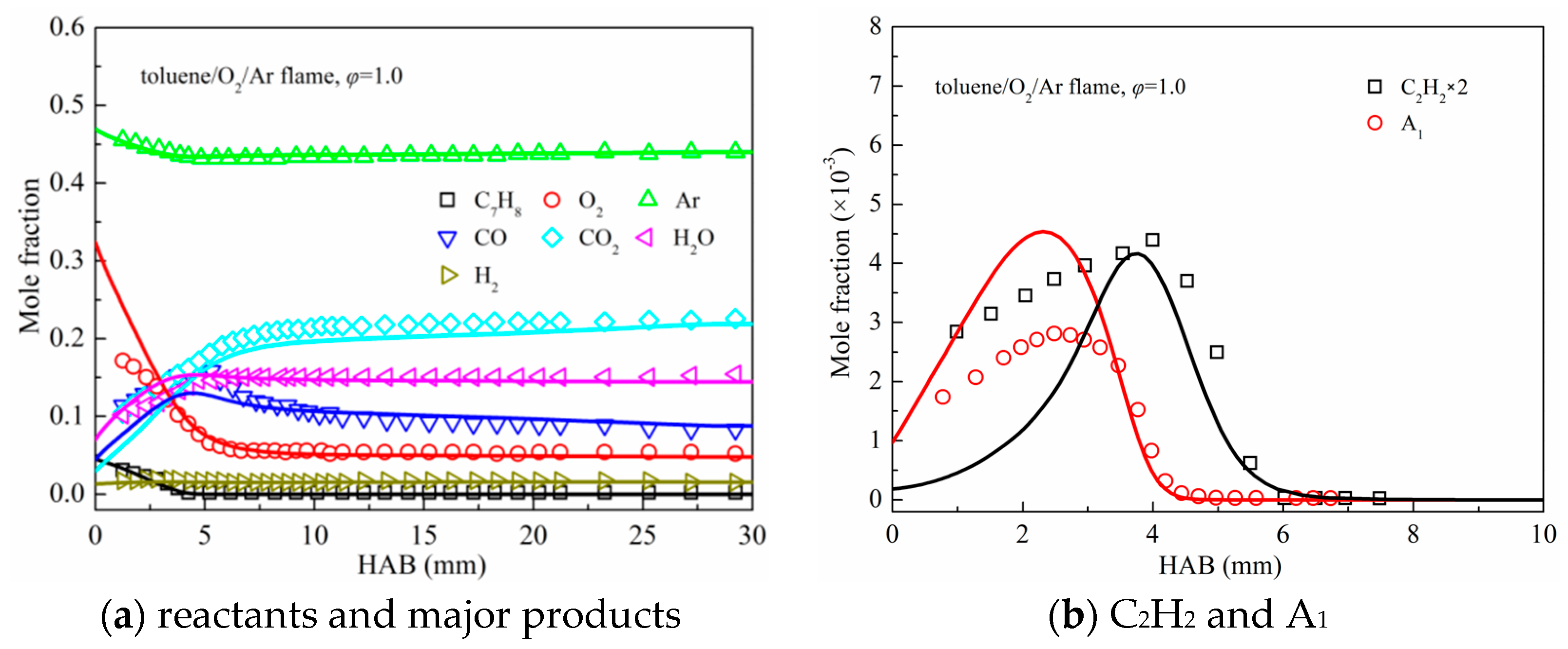
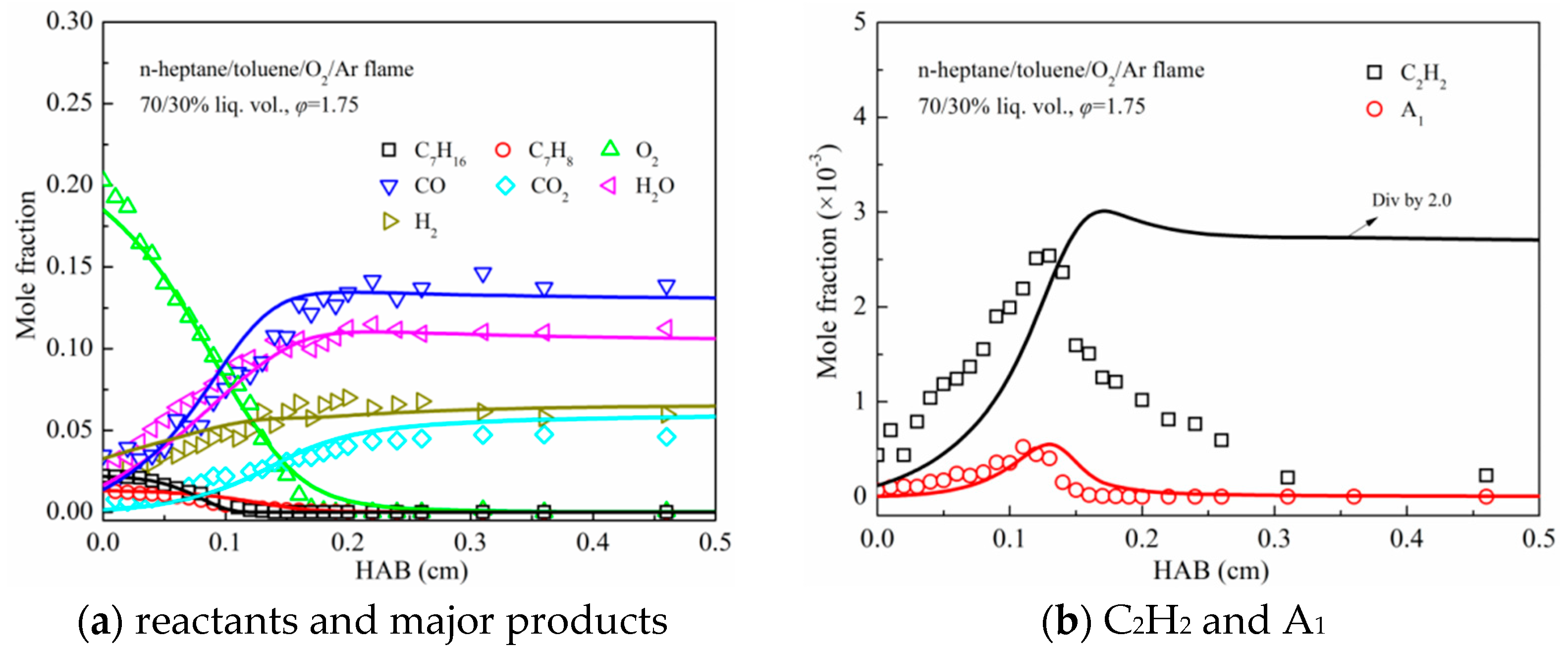
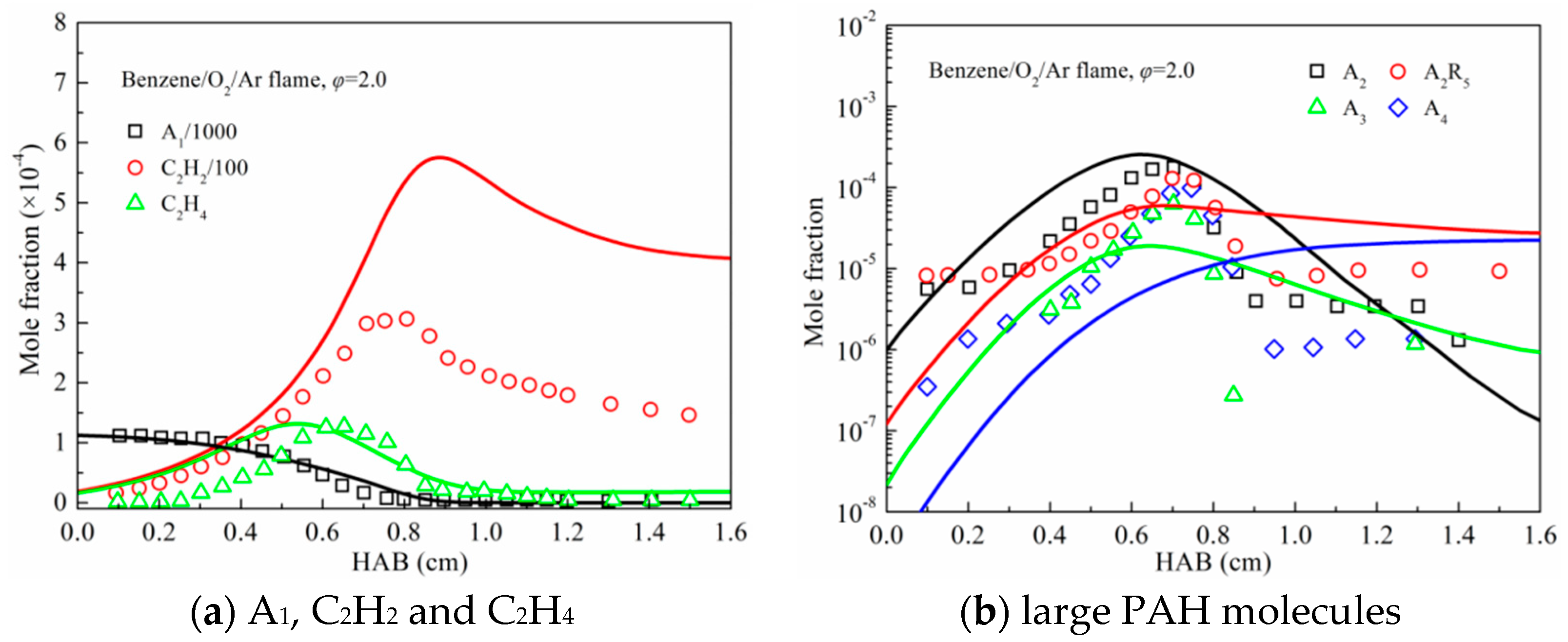
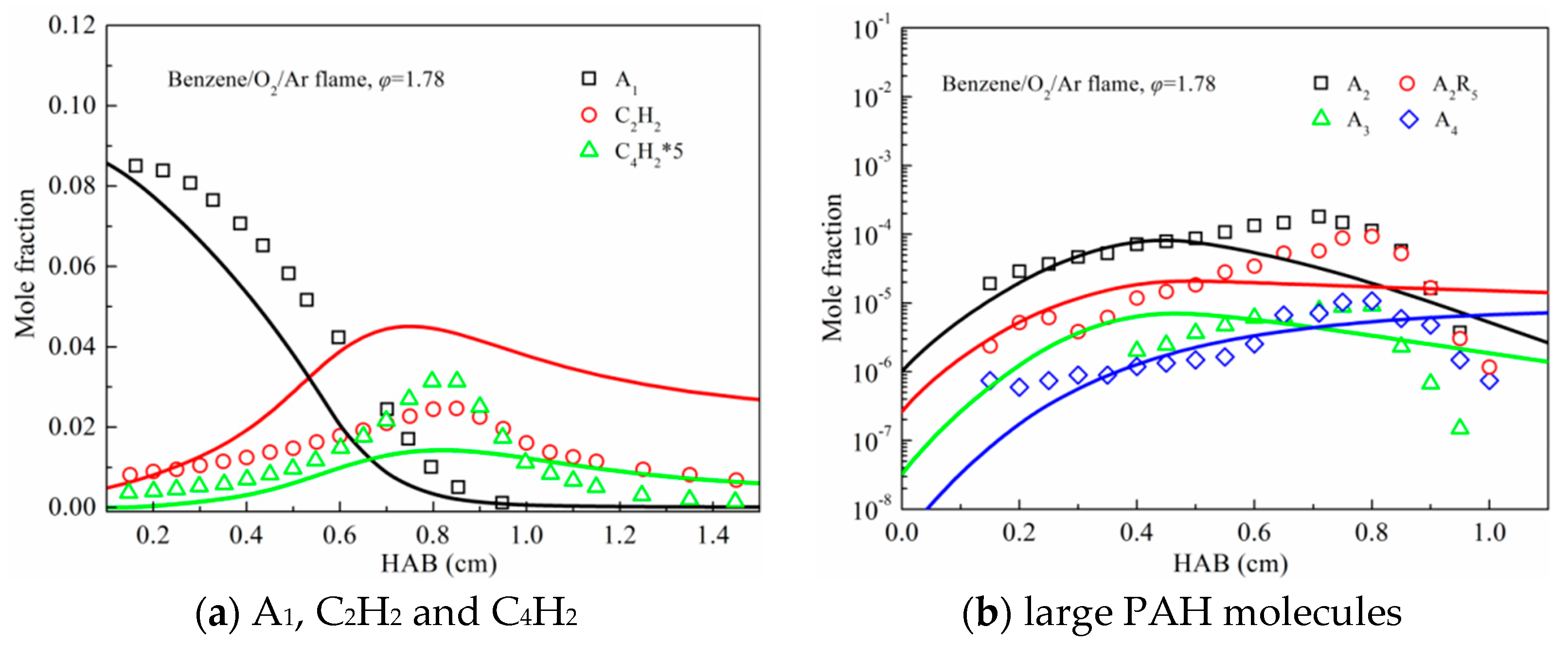
3.2. Premixed Flame Species Profiles
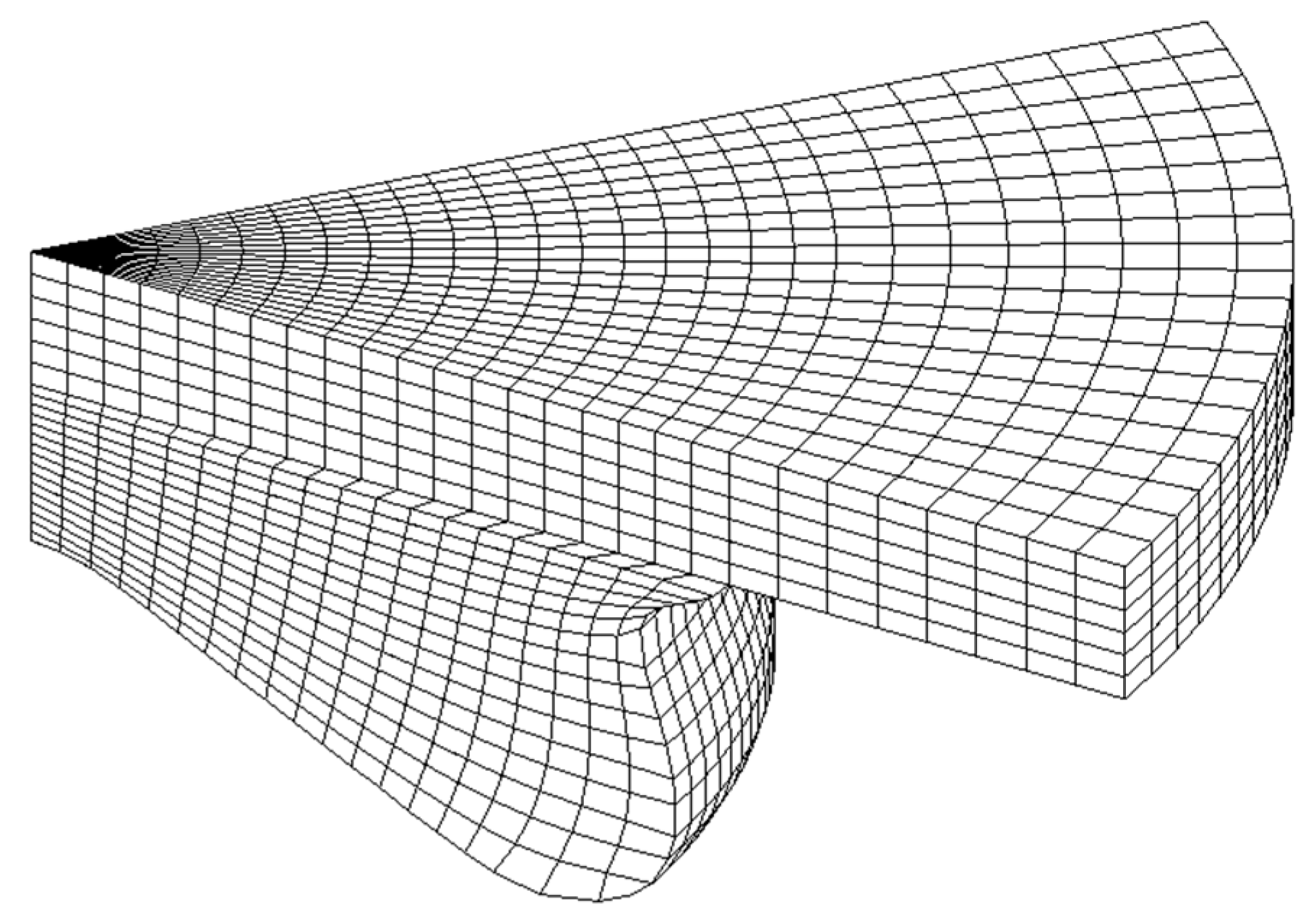
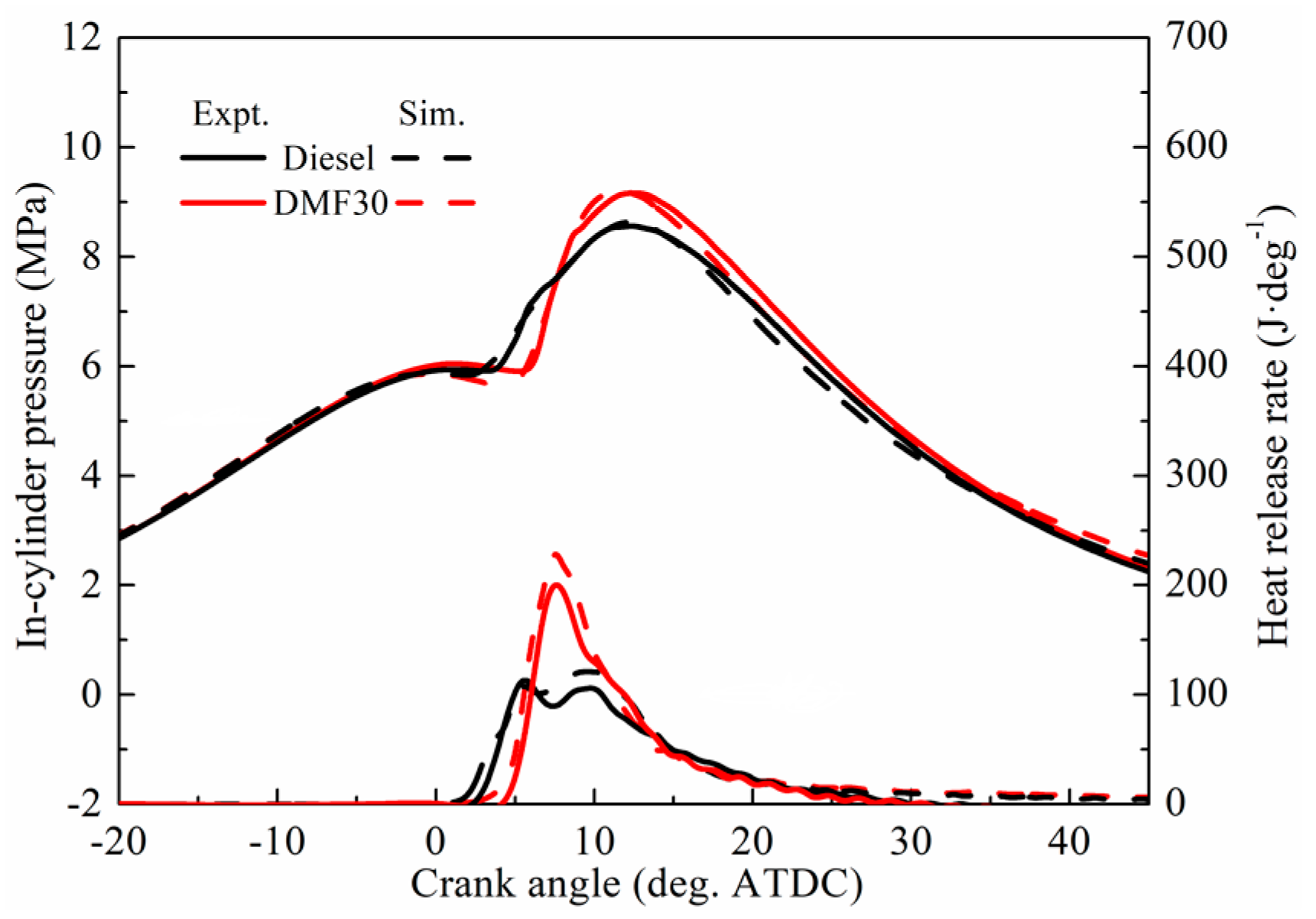
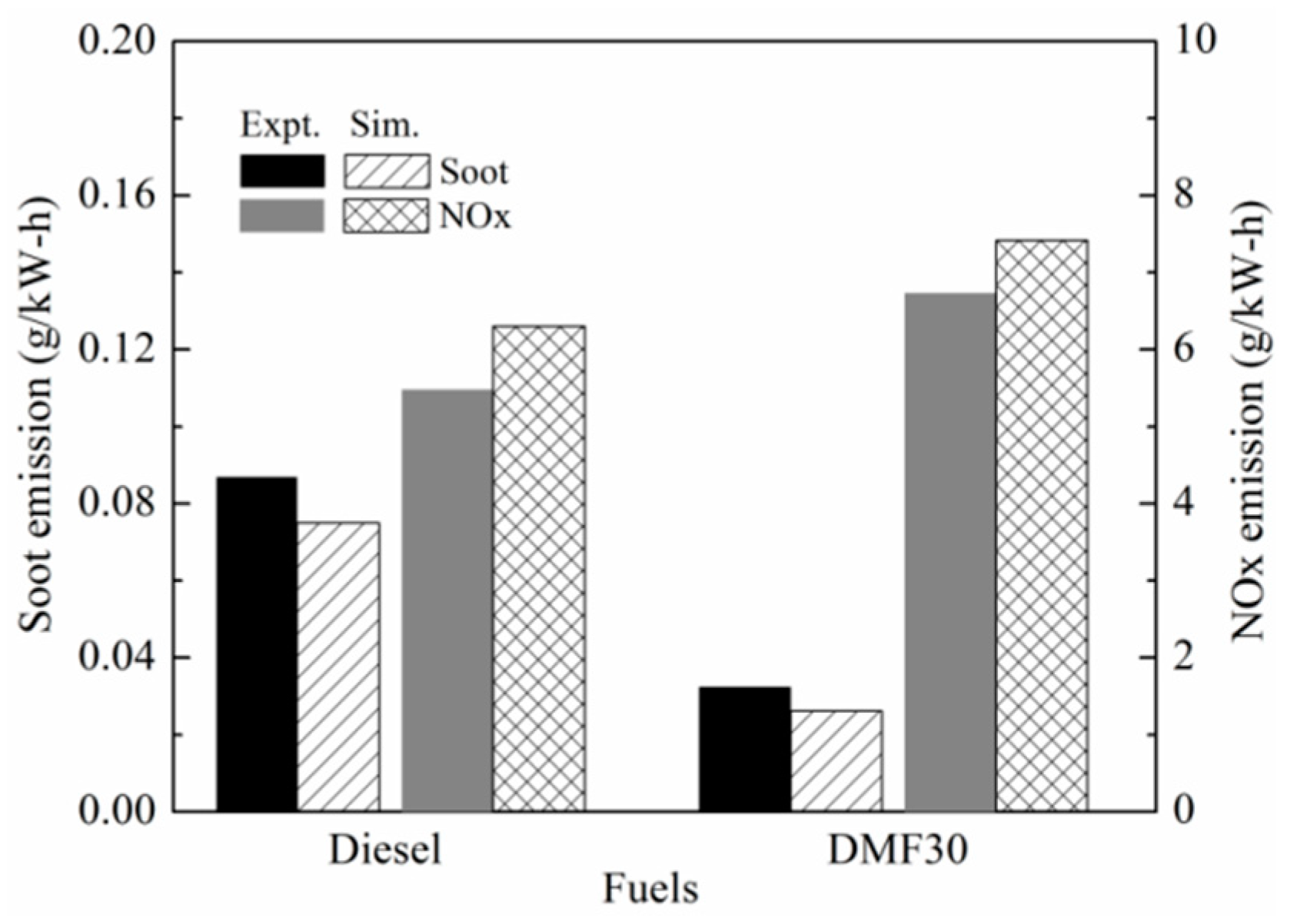
3.3. Engine Combustion Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, R.; Singh, S.; Kumar, M. Impact of n-butanol as an additive with eucalyptus biodiesel-diesel blends on the performance and emission parameters of the diesel engine. Fuel 2020, 277, 118178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay Kumar, M.; Veeresh Babu, A.; Ravi Kumar, P.; Sudhakara Reddy, S. Experimental investigation of the combustion characteristics of mahua oil biodiesel-diesel blend using a di diesel engine modified with egr and nozzle hole orifice diameter. Biofuel Res. J. 2018, 5, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexandrino, K. Comprehensive review of the impact of 2,5-dimethylfuran and 2-methylfuran on soot emissions: Experiments in diesel engines and at laboratory-scale. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 6598–6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channappagoudra, M.; Ramesh, K.; Manavendra, G. Comparative investigation of the effect of hemispherical and toroidal piston bowl geometries on diesel engine combustion characteristics. Biofuel Res. J. 2018, 5, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Deneys Reitz, R.; Yao, M.; Yang, B.; Jiao, Q.; Qiu, L. Development of an n-heptane-n-butanol-pah mechanism and its application for combustion and soot prediction. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 504–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Daniel, R.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Turner, D.; Wyszynski, M.L.; Richards, P. Combustion and emissions of 2, 5-dimethylfuran in a direct-injection spark-ignition engine. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.K.; Singh, E.; Singh, N.; Singal, S.K. Prospects of 2,5-dimethylfuran as a fuel: Physico-chemical and engine performance characteristics evaluation. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Yue, L.; Liu, H.; Yao, M. Effects of six-carbon alcohols, ethers and ketones with chain or ring molecular structures on diesel low temperature combustion. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 124, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Hou, B.; Zeng, P.; Jiang, A.; Hou, X.; Liu, J. Combustion and emission characteristics of diesel engine fueled with 2,5-dimethylfuran and diesel blends. Fuel 2017, 192, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Guo, G.; Sun, Z.; Xiao, H. Effects of injection timing on combustion and emissions in a diesel engine fueled with 2,5-dimethylfuran-diesel blends. Fuel 2017, 192, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Li, S.; Xiao, H.; Guo, G. A comparison study on the combustion and particulate emissions of 2,5-dimethylfuran/diesel and ethanol/diesel in a diesel engine. Therm. Sci. 2018, 22, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Abu-Omar, M.M. Current technologies economics and perspectives for 2,5-dimethylfuran production from biomass-derived intermediates. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, J.; He, A.; Wu, Z.; Xu, J. Chemocatalytic pathways for high-efficiency production of 2,5-dimethylfuran from biomass-derived 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. In Biomass, Biofuels, Biochemicals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 377–394. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Wei, L.; Liu, J.; Reitz, R.D.; Yao, M. Development of a reduced toluene reference fuel (TRF)-2,5-dimethylfuran-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) mechanism for engine applications. Combust. Flame 2016, 165, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhong, X.; Hu, B.; Liu, H.; Yao, M. Experimental study on the combustion and emissions fueling biodiesel/n-butanol, biodiesel/ethanol and biodiesel/2,5-dimethylfuran on a diesel engine. Energy 2016, 115, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, R.; Tian, G.; Xu, H.; Wyszynski, M.L.; Wu, X.; Huang, Z. Effect of spark timing and load on a disi engine fuelled with 2,5-dimethylfuran. Fuel 2011, 90, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, R.; Wei, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Wyszynski, M.L.; Shuai, S. Speciation of hydrocarbon and carbonyl emissions of 2,5-dimethylfuran combustion in a disi engine. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6661–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothamer, D.A.; Jennings, J.H. Study of the knocking propensity of 2,5-dimethylfuran–Gasoline and ethanol–Gasoline blends. Fuel 2012, 98, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Herreros, J.M.; Lattimore, T.; Shuai, S. Fuel effect on particulate matter composition and soot oxidation in a direct-injection spark ignition (DISI) engine. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, G.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Yao, M. Combustion and emissions of 2,5-dimethylfuran addition on a diesel engine with low temperature combustion. Fuel 2013, 103, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, M.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, H. Experimental study on combustion and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with 2,5-dimethylfuran–Diesel, n-butanol–Diesel and gasoline–Diesel blends. Energy 2013, 54, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Di, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, W. Effects of 2,5-dimethylfuran fuel properties coupling with egr (exhaust gas recirculation) on combustion and emission characteristics in common-rail diesel engines. Energy 2015, 93, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, S.; Yao, M. Effects of fuel properties on combustion and emissions under both conventional and low temperature combustion mode fueling 2,5-dimethylfuran/diesel blends. Energy 2013, 62, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zeng, P.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Fu, X. An experimental study of the combusition and emission performances of 2,5-dimethylfuran diesel blends on a diesel engine. Therm. Sci. 2017, 21, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, D.; Guo, F. Effects of 2,5-dimethylfuran addition on morphology, nanostructure and oxidation reactivity of diesel exhaust particles. Fuel 2019, 253, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Won, H.; Peters, N. Experimental Validation of a Surrogate Fuel for Diesel; No. 2007-01-1842, SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, L.S.; Sirjean, B.; Glaude, P.A.; Kohse-Höinghaus, K.; Battin-Leclerc, F. Influence of substituted furans on the formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in flames. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2015, 35, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Meng, W.; Wang, M.; Cao, Y.; Cao, S.; Yao, L.; Zhang, K. Development of a phenomenological soot model integrated with a reduced trf-pah mechanism for diesel engine application. Fuel 2021, 283, 118810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepiot-Desjardins, P.; Pitsch, H. An efficient error-propagation-based reduction method for large chemical kinetic mechanisms. Combust. Flame 2008, 154, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Law, C.K. Strategies for mechanism reduction for large hydrocarbons: N-heptane. Combust. Flame 2008, 154, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, J.; Bergman, M.; Golovitchev, V.I.; Denbratt, I. Modeling the Effect of Injection Schedule Change on Free Piston Engine Operation; No. 2006-01-0449, SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Golovitchev, V.; Calik, A.; Montorsi, L. Analysis of Combustion Regimes in Compression Ignited Engines Using Parametric Φ-T Dynamic Maps; No. 2007-01-1838, SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cancino, L.R.; Fikri, M.; Oliveira, A.A.M.; Schulz, C. Autoignition of gasoline surrogate mixtures at intermediate temperatures and high pressures: Experimental and Numerical Approaches. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Jia, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, M.; Wang, H.; Reitz, R.D. Development of a skeletal mechanism for diesel surrogate fuel by using a decoupling methodology. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 3785–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrae, J.C.G.; Björnbom, P.; Cracknell, R.F.; Kalghatgi, G.T. Autoignition of toluene reference fuels at high pressures modeled with detailed chemical kinetics. Combust. Flame 2007, 149, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, R.J.; Rupley, F.M.; Miller, J.A. CHEMKIN II: A Fortran Chemical Kinetics Package for the Analysis of Gas-Phase Chemical Kinetics; Sandia Laboratories Report, S. 89-8009B; Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1989.
- Ciezki, H.K.; Adomeit, G. Shock-tube investigation of self-ignition of n-heptane-air mixtures under engine relevant conditions. Combust. Flame 1993, 93, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Gushterova, I.; Fikri, M.; Schulz, C.; Schießl, R.; Maas, U. Auto-ignition of toluene-doped n-heptane and iso-octane/air mixtures: High-pressure shock-tube experiments and kinetics modeling. Combust. Flame 2011, 158, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, D.F.; Gauthier, B.M.; Hanson, R.K. Shock tube ignition measurements of iso-octane/air and toluene/air at high pressures. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2005, 30, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.P.S.; Vanderover, J.; Oehlschlaeger, M.A. A shock tube study of the auto-ignition of toluene/air mixtures at high pressures. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzler, J.; Fikri, M.; Hitzbleck, K.; Starke, R.; Schulz, C.; Roth, P.; Kalghatgi, G.T. Shock-tube study of the autoignition of n-heptane/toluene/air mixtures at intermediate temperatures and high pressures. Combust. Flame 2007, 149, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, M.A.; Akih-Kumgeh, B. Reactivity trends in furan and alkyl furan combustion. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 6618–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, K.P.; Simmie, J.M.; Gillespie, F.; Conroy, C.; Black, G.; Metcalfe, W.K.; Battin-Leclerc, F.; Dirrenberger, P.; Herbinet, O.; Glaude, P.A.; et al. A comprehensive experimental and detailed chemical kinetic modelling study of 2,5-dimethylfuran pyrolysis and oxidation. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 2291–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidel, L.; Moshammer, K.; Wang, X.; Zeuch, T.; Kohse-Höinghaus, K.; Mauss, F. Comprehensive kinetic modeling and experimental study of a fuel-rich, premixed n-heptane flame. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 2045–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, K.; Qi, F. Investigation on chemical structures of premixed toluene flames at low pressure. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazkov, D.A.; Slavinskaya, N.A.; Dmitriev, A.M.; Shmakov, A.G.; Korobeinichev, O.P.; Riedel, U. Structure of an n-heptane/toluene flame: Molecular beam mass spectrometry and computer simulation investigations. Combust Explos Shock Waves 2016, 52, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Togbé, C.; Tran, L.S.; Liu, D.; Felsmann, D.; Oßwald, P.; Glaude, P.A.; Sirjean, B.; Fournet, R.; Battin-Leclerc, F.; Kohse-Höinghaus, K. Combustion chemistry and flame structure of furan group biofuels using molecular-beam mass spectrometry and gas chromatography—Part iii: 2,5-dimethylfuran. Combust. Flame 2014, 161, 780–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Defoeux, F.; Dias, V.; Renard, C.; Van Tiggelen, P.J.; Vandooren, J. Experimental investigation of the structure of a sooting premixed benzene/oxygen/argon flame burning at low pressure. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2005, 30, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, Y.; Wei, L.; Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Tian, Z.; Yang, R.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, F. An experimental study of the premixed benzene/oxygen/argon flame with tunable synchrotron photoionization. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, M.; Xiao, H.; Yang, S. Effects of fuel properties on combustion and pollutant emissions of a low temperature combustion mode diesel engine. Fuel 2020, 267, 117123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsden, A.A. KIVA-3V, Release 2: Improvements to KIVA-3V; Los Alamos National Laboratory Report LA-UR-99-915; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 1999.
- Kong, S.C.; Sun, Y.; Rietz, R.D. Modeling diesel spray flame liftoff, sooting tendency, and nox emissions using detailed chemistry with phenomenological soot model. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2007, 129, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Diesel | Gasoline | Biodiesel | Ethanol | DMF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C12–C25 | C4–C12 | C12–C24 | C2H5OH | C6H8O |
| Cetane number | 40–55 | 10–15 | 52 | 8 | – |
| Octane number | – | 90–99 | – | 108 | 119 |
| Oxygen content (wt %) | – | – | 10 | 34.8 | 16.7 |
| Density at 20 °C (g/cm3) | 0.820 | 0.745 | 0.880 | 0.790 | 0.890 |
| Boiling point (°C) | 180–370 | 25–215 | 262–359 | 78.4 | 92–94 |
| Viscosity at 20 °C (mm2/s) | 4.8 | 0.4–0.8 | 8.9 | 1.08 | 0.65 |
| Low heating value (MJ/kg) | 42.5 | 42.7 | 38.0 | 26.8 | 33.7 |
| Latent heating at 25 °C (kJ/kg) | 270–301 | 380–500 | 320 | 904 | 333 |
| Autoignition temperature (°C) | 246 | 420 | 363 | 434 | 285.85 |
| Stoichiometric A/F ratio | 14.3 | 14.7 | 12.5 | 9.02 | 10.79 |
| Reactions | Original A Factor | Adjusted A Factor |
|---|---|---|
| C7H16 + HO2 = C7H15-2 + H2O2 | 1.00 × 1013 | 5.00 × 1013 |
| C7H8 + O2 = C7H7 + HO2 | 3.00 × 1014 | 5.00 × 1014 |
| C7H8 + H = C7H7 + H2 | 1.50 × 1014 | 1.50 × 1013 |
| DMF + O2 = R1C6H7O + HO2 | 4.20 × 1012 | 8.40 × 1013 |
| DMF + H = R1C6H7O + H2 | 3.10 × 105 | 5.10 × 105 |
| DMF + OH => CH3CO + CH3CHO + C2H2 | 7.95 × 1012 | 7.95 × 1010 |
| DMF + H = CH3CO +C4H6 | 1.34 × 1032 | 5.34 × 1032 |
| R1C6H7O + HO2 = M5FCH2O + OH | 5.00 × 1012 | 5.00 × 1013 |
| C4H4 + OH = C4H3 + H2O | 1.00 × 107 | 1.00 × 109 |
| C4H3 + H = C2H2 + C2H2 | 6.30 × 1025 | 8.30 × 1025 |
| C4H4 + C2H3 = A1 + H | 1.90 × 1012 | 1.90 × 1014 |
| C3H3 + C3H3 = A1 | 2.00 × 1012 | 2.00 × 1014 |
| A1- + C4H2 = A2-1 | 5.10 × 1048 | 5.10 × 1050 |
| A2-1 + C2H2 = A2R5 + H | 1.10 × 107 | 1.10 × 106 |
| A1C2H + A1- = A3 + H | 1.10 × 1023 | 3.10 × 1023 |
| O + OH = O2 + H | 2.04 × 1014 | 8.04 × 1013 |
| Engine Name | YC4FA115-40 |
|---|---|
| Cylinders | 4 in-line |
| Capacity | 2.982 L |
| Compression ratio | 17.5:1 |
| Bore × Stroke | 96 mm × 103 mm |
| Connecting rod length | 115 mm |
| Fuel injection system | High-pressure common-rail |
| Number of holes | 7 |
| Inlet valve close | −133 CA ATDC |
| Exhaust valve open | 125 CA ATDC |
| Engine speed | 1800 r/min |
| Brake mean effective pressure | ~0.60 MPa |
| Intake air temperature | 288 K |
| Intake air pressure | 1.25 bar |
| Common-rail pressure | 110 MPa |
| Injection timing | 7.5 CA BTDC |
| EGR | none |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Yu, W.; Yang, C.; Wei, M.; Liu, J. A Novel Reduced Reaction Mechanism for Diesel/2,5-Dimethylfuran Engine Application. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040642
Li S, Yu W, Yang C, Wei M, Liu J. A Novel Reduced Reaction Mechanism for Diesel/2,5-Dimethylfuran Engine Application. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(4):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040642
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Song, Wenbin Yu, Chen Yang, Mingrui Wei, and Jinping Liu. 2023. "A Novel Reduced Reaction Mechanism for Diesel/2,5-Dimethylfuran Engine Application" Atmosphere 14, no. 4: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040642
APA StyleLi, S., Yu, W., Yang, C., Wei, M., & Liu, J. (2023). A Novel Reduced Reaction Mechanism for Diesel/2,5-Dimethylfuran Engine Application. Atmosphere, 14(4), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040642






