Comparisons of Spatial and Temporal Variations in PM2.5-Bound Trace Elements in Urban and Rural Areas of South Korea, and Associated Potential Health Risks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Dry Deposition Calculations
2.2.2. Exposure Estimations
2.2.3. Non-Carcinogenic Risk Characterizations
2.2.4. Cancer Risk Characterizations
2.2.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
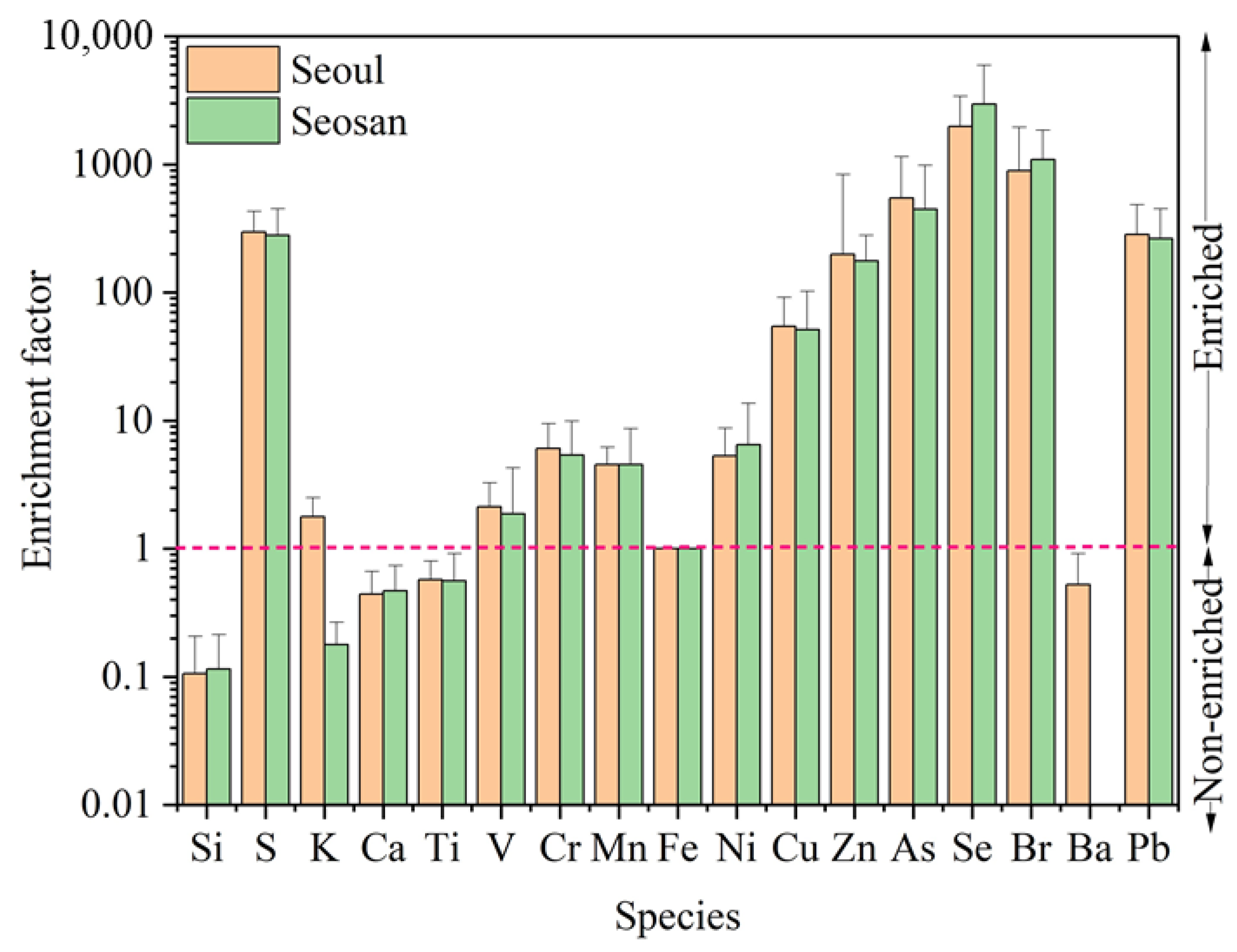
2.2.6. Enrichment Factor
2.2.7. Potential Source Contribution Function (PSCF)
2.2.8. Tukey’s Test and Paired t-Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overview of Trace Elements and PM2.5 in Urban and Rural Areas
3.2. Comparison of Variation in the Trace Elements of PM2.5 in Urban and Rural Areas
3.3. Origins of Trace Elements in PM2.5
3.4. Estimated dry Deposition Fluxes of Elements in PM2.5 in Urban and Rural Areas
3.5. Health Risk Assessments
3.5.1. Exposure Assessments for Trace Elements
3.5.2. Non-Carcinogenic Health Risks
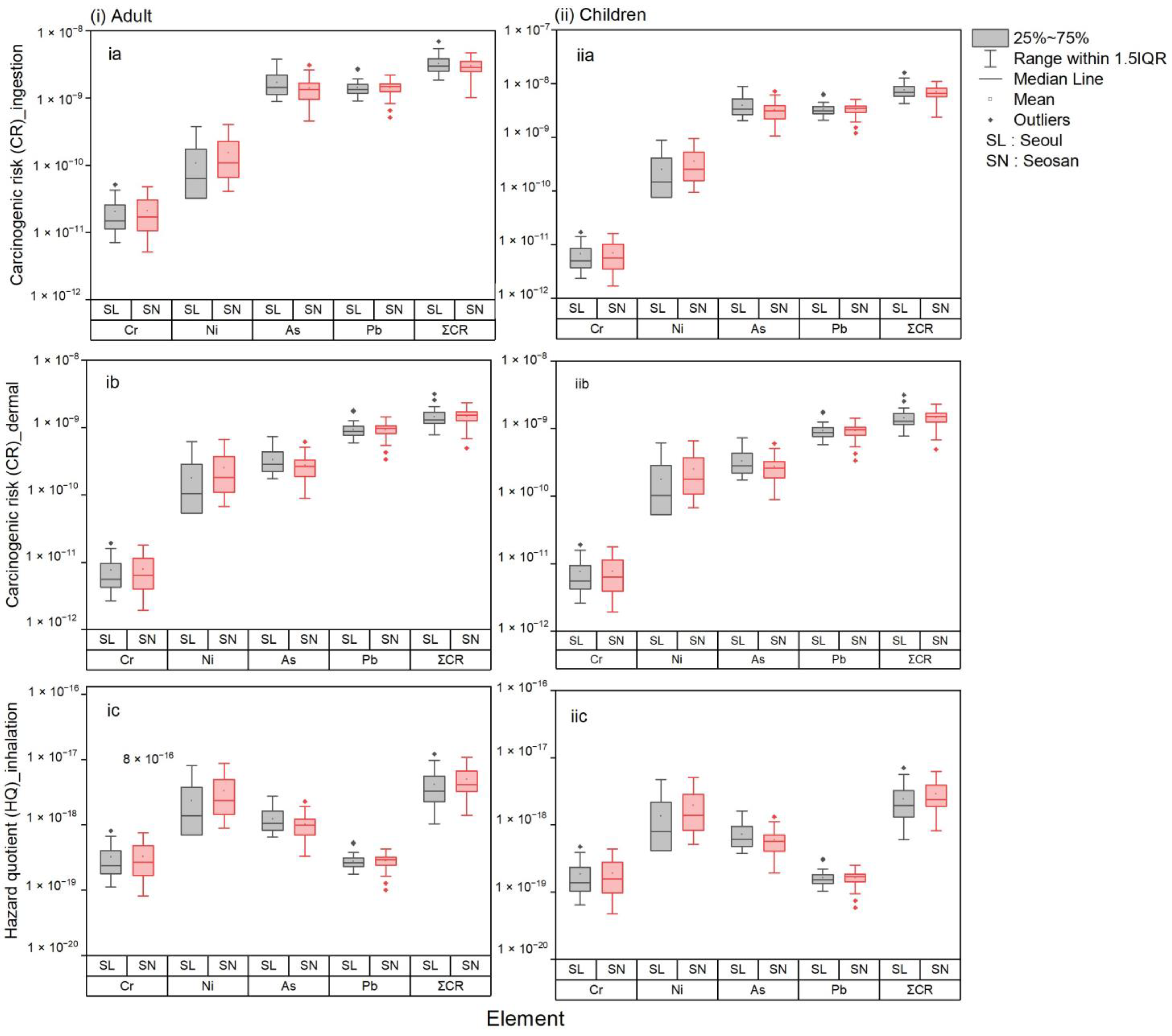
3.5.3. Carcinogenic Risk
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, J.J.; Wang, Q.Y.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Tie, X.X.; Shen, Z.X.; Wang, P.; An, Z.S. Impacts of Aerosol Compositions on Visibility Impairment in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Dobaradaran, S.; Amouei Torkmahalleh, M.; Saeedi, R.; Aibaghi, R.; Faraji Ghasemi, F. Suspended Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5), Microplastics (MPs), and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Air: Their Possible Relationships and Health Implications. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-Year Trends of the Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Ambient Air Pollution: An Analysis of Data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Yan, W.; Elahi, E.; Cao, Y. Air Pollution Risks Human Mental Health: An Implication of Two-Stages Least Squares Estimation of Interaction Effects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 2036–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Spiegelman, D.; Szpiro, A.A.; Sheppard, L.; Kaufman, J.D.; Yanosky, J.D.; Williams, R.; Laden, F.; Hong, B.; Suh, H. Exposure Measurement Error in PM2.5 Health Effects Studies: A Pooled Analysis of Eight Personal Exposure Validation Studies. Environ. Health A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2014, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, M. Toxicological and Epidemiological Studies of Cardiovascular Effects of Ambient Air Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Its Chemical Components: Coherence and Public Health Implications. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 299–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wen, X.; Bian, J.; Lipkind, H.; Hu, H. Associations between the Chemical Composition of PM2.5 and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Environ. Res. 2021, 198, 110470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.S.; Lim, M.N.; Han, Y.J.; Kim, W.J. Epidemiological Study of PM2.5and Risk of COPD-Related Hospital Visits in Association with Particle Constituents in Chuncheon, Korea. Int. J. COPD 2018, 13, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Gong, L.; Liu, S.; Ren, R. Assessment of Trace Elements Characteristics and Human Health Risk of Exposure to Ambient PM2.5 in Hangzhou, China. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 983–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jia, C.; Yu, H.; Xu, H.; Ji, D.; Wang, C.; Xiao, H.; He, J. Characteristics, Sources, and Health Risks of PM2.5-Bound Trace Elements in Representative Areas of Northern Zhejiang Province, China. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Science of the Total Environment Trace Elements in PM 2.5 in Shandong Province: Source Identification and Health Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhou, H.; Fan, Z.; Lin, M.; Wu, D.; Xia, B. Characteristics, Sources and Health Risk Assessment of Toxic Heavy Metals in PM2.5 at a Megacity of Southwest China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.K.; Adar, S.D.; O’Neill, M.S.; Auchincloss, A.H.; Szpiro, A.; Bertoni, A.G.; Navas-Acien, A.; Kaufman, J.D.; Diez-Roux, A.V. Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Multiethnic Cohort. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 181, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moufarrej, L.; Verdin, A.; Cazier, F.; Ledoux, F.; Courcot, D. Oxidative Stress Response in Pulmonary Cells Exposed to Different Fractions of PM2.5-0.3 from Urban, Traffic and Industrial Sites. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Kou, L.; Chai, Y.; Kwan, M.P. Associations of Co-Exposures to Air Pollution and Noise with Psychological Stress in Space and Time: A Case Study in Beijing, China. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorai, A.K.; Tchounwou, P.B.; Biswal, S.S.; Tuluri, F. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Particulate Matter(PM2.5) Concentrations and Its Health Impacts in a Mega City, Delhi in India. Environ. Health Insights 2018, 12, 1178630218792861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.S.; Demerjian, K.L.; Schwab, J.J. Seasonal Estimation of Organic Mass to Organic Carbon in PM2.5 at Rural and Urban Locations in New York State. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 7467–7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Qian, W.B.; Decesari, S.; Facchini, M.C.; Fuzzi, S. Comprehensive Characterization of PM2.5 Aerosols in Singapore. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, D16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Song, I.H.; Park, J.S.; Oh, J.; Moon, K.J.; Shin, H.J.; Ahn, J.Y.; Lee, M.-D.; Kim, J.; Lee, G. Variation of PM2.5 Chemical Compositions and Their Contributions to Light Extinction in Seoul. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.Y.; Chen, H. Assessment of Metals Pollution and Health Risk in Dust from Nursery Schools in Xi’an, China. Environ. Res. 2014, 128, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Soberón, F.; Rovira, J.; Sierra, J.; Mari, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Schuhmacher, M. Seasonal Characterization and Dosimetry-Assisted Risk Assessment of Indoor Particulate Matter (PM10-2.5, PM2.5-0.25, and PM0.25) Collected in Different Schools. Environ. Res. 2019, 175, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natsagdorj, A.; Tugsbayan, B.; Battumur, T.; Oyuntsetseg, B.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.P.; Usuhbayar, B. Seasonal Concentrations of Elements in Both Indoor and Outdoor Housing in PM2.5. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2021, 252, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Yadav, S.; Phuleria, H.C. Chemical Characteristics and Oxidative Potential of Indoor and Outdoor PM2.5 in Densely Populated Urban Slums. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirmalkar, J.; Haswani, D.; Singh, A.; Kumar, S.; Sunder Raman, R. Concentrations, Transport Characteristics, and Health Risks of PM2.5-Bound Trace Elements over a National Park in Central India. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.G.; Kumar, S.; Mandal, P.; Sarangi, B.; Singh, K.; Pokhariyal, J.; Mishra, S.K.; Agarwal, S.; Sinha, D.; Singh, S.; et al. Traceability Issue in PM2.5 and PM10 Measurements. Mapan—J. Metrol. Soc. India 2013, 28, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Gao, Y. Characterization of Trace Elements in PM2.5 Aerosols in the Vicinity of Highways in Northeast New Jersey in the U.S. East Coast. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2011, 2, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, M.; Ding, S.; Wang, S.; Ni, D.; Hu, H. Monitoring and Source Apportionment of Trace Elements in PM2.5: Implications for Local Air Quality Management. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Meng, X.; Yu, X.; Lei, M.; Li, W.; Shi, F.; Yang, W.; Zhang, S.; Xie, S. Characteristics of Trace Elements in PM2.5 and PM10 of Chifeng, Northeast China: Insights into Spatiotemporal Variations and Sources. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.I.; Sopajaree, K.; Kuo, S.C.; Yu, S.P. Potential PM2.5 Impacts of Festival-Related Burning and Other Inputs on Air Quality in an Urban Area of Southern Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reff, A.; Bhave, P.V.; Simon, H.; Pace, T.G.; Pouliot, G.A.; Mobley, J.D.; Houyoux, M. Emissions Inventory of PM2.5 Trace Elements across the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5790–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and Road Wear Particles (TRWP)—A Review of Generation, Properties, Emissions, Human Health Risk, Ecotoxicity, and Fate in the Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicicology Volume 3: Environmental Toxicology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 101, ISBN 978-3-7643-8339-8. [Google Scholar]
- Alavanja, M.; Baron, J.A.; Brownson, R.C.; Buffler, P.A.; DeMarini, D.M.; Djordjevic, M.V.; Doll, R.; Fontham, E.T.H.; Gao, Y.T.; Gray, N.; et al. Tobacco Smoke and Involuntary Smoking. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2004, 83, 1–1413. [Google Scholar]
- Mulware, S.J. Trace Elements and Carcinogenicity: A Subject in Review. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, J.L.; Nadal, M. Domestic Waste Composting Facilities: A Review of Human Health Risks. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Schwartz, J.D.; Weisskopf, M.G.; Melly, S.J.; Wang, Y.; Dominici, F.; Zanobetti, A. Long-Term PM2.5 Exposure and Neurological Hospital Admissions in the Northeastern United States. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Particulate Air Pollution. Ann. Epidemiol. 2009, 19, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wen, W.; Liang, L.; Ma, X.; Jiao, J.; Guo, K. Source Identification of Trace Elements in PM2.5 at a Rural Site in the North China Plain. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.M.; Sunwoo, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, B.W.; Lee, S.K. Atmospheric Concentrations of PM2.5 Trace Elements in the Seoul Urban Area of South Korea. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Han, C.; Ahn, J.; Han, Y.; Lee, A.-h.; Ro, S.; Hong, S. Characterization of Trace Elements and Pb Isotopes in PM2.5 and Isotopic Source Identification during Haze Episodes in Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.R.; Shim, I.K.; Kim, J.; Ah Ji, H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Ghim, Y.S. Pm2.5 and Trace Elements in Underground Shopping Districts in the Seoul Metropolitan Area, Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.K.; Kim, Y.P.; Ghim, Y.S.; Song, M.J.; Kim, C.H.; Jang, K.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Shin, H.J.; Jung, J.S.; Wu, Z.; et al. Spatial Distribution of PM2.5 Chemical Components during Winter at Five Sites in Northeast Asia: High Temporal Resolution Measurement Study. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 290, 119359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.R.; Park, S.; Ju, S.; Lim, Y.-B.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, E.; Kim, S.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, Y.P. Contribution of Liquid Water Content Enhancing Aqueous Phase Reaction Forming Ambient Particulate Nitrosamines. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 303, 119142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, K.A.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, Y.I.; Ulfarsson, G.F. Spatial Regression Analysis of Traffic Crashes in Seoul. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2016, 91, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Son, S.C.; Lee, K.Y. Chemical Characteristics of PM2.5 during Spring and Fall at Two Sites in Chungcheongnam-Do, South Korea; Insight into Fe Solubility and SO42− Formation. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Services, C.E. Xact ® 625i Multi-Metals Monitoring System. Available online: https://www.ecotech.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Cooper-Environmental-Monitoring-625i-Spec-Sheet.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2023).
- Rai, P.; Furger, M.; Slowik, J.G.; Canonaco, F.; Fröhlich, R.; Hüglin, C.; Minguillón, M.C.; Petterson, K.; Baltensperger, U.; Prévôt, A.S.H. Source Apportionment of Highly Time-Resolved Elements during a Firework Episode from a Rural Freeway Site in Switzerland. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1657–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, H.S.; Shukla, A.; Lalchandani, V.; Dave, J.; Rastogi, N.; Kumar, M.; Singh, V.; Tripathi, S.N. Inter-Comparison of Online and Offline Methods for Measuring Ambient Heavy and Trace Elements and Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions (NO3-, SO42-, NH4+, and Cl-) in PM2.5over a Heavily Polluted Megacity, Delhi. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2022, 15, 2667–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furger, M.; Rai, P.; Slowik, J.G.; Cao, J.; Visser, S.; Baltensperger, U.; Prévôt, A.S.H. Automated Alternating Sampling of PM10 and PM2.5 with an Online XRF Spectrometer. Atmos. Environ. X 2020, 5, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariraj Mohan, S. An Overview of Particulate Dry Deposition: Measuring Methods, Deposition Velocity and Controlling Factors. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Paytan, A.; Chase, Z.; Measures, C.; Beck, A.J.; Sañudo-Wilhelmy, S.A.; Post, A.F. Sources and Fluxes of Atmospheric Trace Elements to the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Nelson, E.D.; Field, M.P.; Ding, Q.; Li, H.; Sherrell, R.M.; Gigliotti, C.L.; Van Ry, D.A.; Glenn, T.R.; Eisenreich, S.J. Characterization of Atmospheric Trace Elements on PM2.5 Particulate Matter over the New York-New Jersey Harbor Estuary. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.C.; Wong, G.T.F.; Gong, G.C.; Shiah, F.K.; Huang, Y.T.; Kao, S.J.; Tsai, F.; Candice Lung, S.C.; Lin, F.J.; Lin, I.I.; et al. Sources, Solubility, and Dry Deposition of Aerosol Trace Elements over the East China Sea. Mar. Chem. 2010, 120, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Turco, R.P.; Stolzenbach, K.; Friedlander, S.K.; Xiong, C.; Schiff, K.; Tiefenthaler, L.; Wang, G. Dry Deposition of Airborne Trace Metals on the Los Angeles Basin and Adjacent Coastal Waters. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, D2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Duan, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, B.; Ma, J.; Fan, D.; Sun, C.; He, B.; Wei, F.; Jiang, G. Health Risk Assessment of Various Metal(Loid)s via Multiple Exposure Pathways on Children Living near a Typical Lead-Acid Battery Plant, China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Liang, Z. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Exposure to Street Dust in the Zinc Smelting District, Northeast of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Odman, M.T.; Chang, M.E.; Jackson, W.; Lee, S.; Edgerton, E.S.; Baumann, K.; Russell, A.G. Simulation of Air Quality Impacts from Prescribed Fires on an Urban Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3676–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Environmental Protection Agency Exposure Factors Handbook: 2011 Edition; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 1–1466.
- Guo, F.; Tang, M.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Wei, F.; Zhang, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Chen, Z.; et al. Characteristics, Sources, and Health Risks of Trace Metals in PM2.5. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 289, 119314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wang, T.; Lian, H.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J. Bioaccessibility and Health Risk of Arsenic and Heavy Metals (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn and Mn) in TSP and PM2.5 in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 57, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogianni, E.; Kouras, A.; Samara, C. Indoor Concentrations of PM2.5 and Associated Water-Soluble and Labile Heavy Metal Fractions in Workplaces: Implications for Inhalation Health Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 58983–58993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. Volume I Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1989; Volume I, p. 289.
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.; Seo, Y.K.; Shin, H.J.; Ghim, Y.S.; Song, C.K.; Choi, S.D. Pollution Characteristics of PM2.5 during High Concentration Periods in Summer and Winter in Ulsan, the Largest Industrial City in South Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 292, 119418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.S.; Wong, K.W.; Tseng, Y.L.; Ceng, J.H.; Lee, C.E.; Lin, C. Chemical Significance and Source Apportionment of Fine Particles (PM2.5) in an Industrial Port Area in East Asia. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Eto, Y.; Aikawa, M. Risk Assessment and Management of PM2.5-Bound Heavy Metals in the Urban Area of Kitakyushu, Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The Composition of the Continental Crust. Int. Geophys. 1986, 34, 213–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-k.; Heo, J.B.; Ban, S.J.; Yi, S.M.; Zoh, K.D. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 at the Coastal Area in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Ryoo, J.; Jee, J.; Song, M. Origins and Distributions of Atmospheric Ammonia in Jeonju during 2019~2020. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 36, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Cruz, A.H.; Roca, Y.B.; Suarez-Salas, L.; Pomalaya, J.; Tolentino, D.A.; Gioda, A. Chemical Characterization of PM 2.5 at Rural and Urban Sites around the Metropolitan Area of Huancayo (Central Andes of Peru). Atmosphere 2019, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, S.F. Analysis of Variance: The Fundamental Concepts. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2009, 17, 27E–38E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, I.; Farquhar, J.; Kang, J.; Villa, I.M.; Kim, H. Multi Isotope Systematics of Precipitation to Trace the Sources of Air Pollutants in Seoul, Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, I.; Das, R.; Chua, S.L.; Wang, X. Seasonal Variation of Atmospheric Pb Sources in Singapore—Elemental and Lead Isotopic Compositions of PM10 as Source Tracer. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Q.; Feng, M.; Song, D.; Wu, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Kleeman, M.J.; Li, X. Improve Regional Distribution and Source Apportionment of PM 2.5 Trace Elements in China Using Inventory-Observation Constrained Emission Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayee, J.; Bureekul, S.; Sompongchaiyakul, P.; Wang, X.; Das, R. Sources of Atmospheric Lead (Pb) after Quarter Century of Phasing out of Leaded Gasoline in Bangkok, Thailand. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 253, 118355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Bin Mohamed Mohtar, A.T.; Rakshit, D.; Shome, D.; Wang, X. Sources of Atmospheric Lead (Pb) in and around an Indian Megacity. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 193, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.C.; Huang, K.F. Tracing Local Sources and Long-Range Transport of PM10 in Central Taiwan by Using Chemical Characteristics and Pb Isotope Ratios. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, N.; Fadel, M.; Öztürk, F.; Keleş, M.; Iakovides, M.; Pikridas, M.; Abdallah, C.; Karam, C.; Sciare, J.; Hayes, P.L.; et al. Comprehensive Chemical Characterization of PM2.5 in the Large East Mediterranean-Middle East City of Beirut, Lebanon. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 133, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.J.; Majestic, B.J.; Sheesley, R.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Deminter, J.T.; Mieritz, M. HEI Health Review Committee Improved Source Apportionment and Speciation of Low-Volume Particulate Matter Samples. Res. Rep. Health. Eff. Inst. 2010, 3–75, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Salameh, D.; Detournay, A.; Pey, J.; Pérez, N.; Liguori, F.; Saraga, D.; Bove, M.C.; Brotto, P.; Cassola, F.; Massabò, D.; et al. PM2.5 Chemical Composition in Five European Mediterranean Cities: A 1-Year Study. Atmos. Res. 2015, 155, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoudou, I.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Q.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y. Characteristics of PM2.5 from Ship Emissions and Their Impacts on the Ambient Air: A Case Study in Yangshan Harbor, Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, S.; Che, L.; Yu, Y. Analysis of Temporal Spatial Distribution Characteristics of PM2.5 Pollution and the Influential Meteorological Factors Using Big Data in Harbin, China. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2021, 71, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, G.; Bi, C. Analysis of Long-Range Transport Effects on PM2.5 during a Short Severe Haze in Beijing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 1510–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Wang, T.; Wu, W.S. Nighttime Enhancement of PM2.5 Nitrate in Ammonia-Poor Atmospheric Conditions in Beijing and Shanghai: Plausible Contributions of Heterogeneous Hydrolysis of N2O5 and HNO3 Partitioning. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Jia, B.; Tian, Y.; Feng, Y. Source-Specific Health Risk Assessment of PM2.5-Bound Heavy Metals Based on High Time-Resolved Measurement in a Chinese Megacity: Insights into Seasonal and Diurnal Variations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zheng, N.; Tang, L.; Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Hua, X. Pollution Characteristics, Sources, and Health Risk Assessment of Human Exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb Pollution in Urban Street Dust across China between 2009 and 2018. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, N.; Guan, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhong, J.; Zhu, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Hou, D.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Guan, Y.; Liu, A. Quantitative Source Tracking of Heavy Metals Contained in Urban Road Deposited Sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E. Multielement Contamination of Land in the Margin of Highways. Land 2021, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Heo, J.; Kim, S.W.; Jeon, K.; Yi, S.M.; Hopke, P.K. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Seoul, South Korea and Beijing, China Using Dispersion Normalized PMF. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-B.; Lee, T.J.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, D.S. Enhancing Source Identification of Hourly PM2.5 Data in Seoul Based on a Dataset Segmentation Scheme by Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1042–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charron, A.; Harrison, R.M. Matter on a Heavily Trafficked London Highway: Sources and Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7768–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancras, J.P.; Landis, M.S.; Norris, G.A.; Vedantham, R.; Dvonch, J.T. Source Apportionment of Ambient Fine Particulate Matter in Dearborn, Michigan, Using Hourly Resolved PM Chemical Composition Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 448, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- One, K.H.; Kim, J.; One, Y.K. A Study on the Factors Affecting the Air Environment in Chungnam Province—Focusing on Cheonan, Dangjin, and Seosan. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial. Orthop. 2021, 22, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, X.; Cao, X. In Vitro Bioaccessibility and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Atmospheric Particulate Matters from Three Different Functional Areas of Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Tai, L.; Qiao, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Z.; Fu, K.; Chen, G. Contamination Source Apportionment and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil around Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator: A Case Study in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainka, A.; Zajusz-Zubek, E.; Kaczmarek, K. PM2.5 in Urban and Rural Nursery Schools in Upper Silesia, Poland: Trace Elements Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7990–8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makkonen, U.; Hellén, H.; Anttila, P.; Ferm, M. Size Distribution and Chemical Composition of Airborne Particles in South-Eastern Finland during Different Seasons and Wildfire Episodes in 2006. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez De La Campa, A.M.; De La Rosa, J.; González-Castanedo, Y.; Fernández-Camacho, R.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Stein, A.F.; Ramos, J.L.; Rodríguez, S.; Orellana, I.G.; et al. Levels and Chemical Composition of PM in a City near a Large Cu-Smelter in Spain. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1276–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, P.; Harrison, R.M. Critical Review of Receptor Modelling for Particulate Matter: A Case Study of India. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yoshida, Y.; Turpin, B.J.; Hopke, P.K.; Poirot, R.L.; Lioy, P.J.; Oxley, J.C. Identification of Sources Contributing to Mid-Atlantic Regional Aerosol. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 1186–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Vijayan, N.; Mandal, T.K. Seasonal Characteristics of Aerosols (PM2.5 and PM10) and Their Source Apportionment Using PMF: A Four Year Study over Delhi, India. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo, N.; Yubero, E.; Nicolás, J.F.; Crespo, J.; Varea, M.; Gil-Moltó, J. Regional and Long-Range Transport of Aerosols at Mt. Aitana, Southeastern Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golley, J. Regional Patterns of Industrial Development during China’s Economic Transition. Econ. Transit. 2002, 10, 761–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Tang, A.; Goulding, K.; Collett, J.L. Evolution of Secondary Inorganic Aerosols amidst Improving PM2.5 Air Quality in the North China Plain. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 117027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Engling, G.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Xu, W.; Liu, C.; et al. Biomass Burning Impacts on Ambient Aerosol at a Background Site in East China: Insights from a Yearlong Study. Atmos. Res. 2020, 231, 104660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, M.; Le, H.P.; Wang, F.; Guo, Z.; Iinuma, Y.; Chen, J.; Herrmann, H. Atmospheric Outflow of PM2.5 Saccharides from Megacity Shanghai to East China Sea: Impact of Biological and Biomass Burning Sources. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Song, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. The Distribution, Enrichment and Source of Potential Harmful Elements in Surface Sediments of Bohai Bay, North China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.P.; Wang, Y.S. Atmospheric Wet and Dry Deposition of Trace Elements at 10 Sites in Northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 951–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.M.; Shahin, U.; Sivadechathep, J.; Sofuoglu, S.C.; Holsen, T.M. Overall Elemental Dry Deposition Velocities Measured around Lake Michigan. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir, Y.; Kural, C.; Cindoruk, S.S.; Vardar, N. Assessment of Trace Element Concentrations and Their Estimated Dry Deposition Fluxes in an Urban Atmosphere. Atmos. Res. 2006, 81, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Shi, L.; Guang, A.-l.; Mu, Z.; Zhan, H.; Wu, Y. Contamination Levels and Human Health Risk Assessment of Toxic Heavy Metals in Street Dust in an Industrial City in Northwest China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2007–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; He, J.; Gong, S.; Guo, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Mo, J.; Gui, K.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Effect of Vegetation Seasonal Cycle Alterations to Aerosol Dry Deposition on PM2.5 Concentrations in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Mbululo, Y.; Yang, M.; Yuan, Z.; Nyihirani, F.; Zheng, X. Chemical Composition and Deposition Fluxes of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions on Dry and Wet Deposition Samples in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Hopke, P.K. Chemical Characteristics of PM2.5 during a 2016 Winter Haze Episode in Shijiazhuang, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. Noaa’s Hysplit Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. Human Health Evaluation Manual Part A. 1989. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/risk-assessment-guidance-superfund-rags-part (accessed on 2 April 2023).
- US EPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. In: Part A: Human Health Evaluation Manual; Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment; Part F, Supplemental Guidance for Inhalation Risk Assessment, vol. I. 2011. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/risk-assessment-guidance-superfund-rags-part-f (accessed on 2 April 2023).
- Khanna, I.; Khare, M.; Gargava, P. Health Risks Associated with Heavy Metals in Fine Particulate Matter: A Case Study in Delhi City, India. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2015, 3, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, P.; Peng, C.; Xu, B.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. Mass Concentration and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Size-Segregated Airborne Particulate Matter in Changsha. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 517, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tan, M.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, Z.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y. Characteristics of Trace Elements and Lead Isotope Ratios in PM2.5 from Four Sites in Shanghai. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Seoul | Seosan | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Mean ± SD a | % BDL b | Median | Mean ± SD | %BDL | Median |
| Si | 306 ± 527 | 30 | 101 | 460 ± 761 | 47 | 147 |
| S | 1444 ± 908 | 0.9 | 1168 | 1265 ± 673 | 2.3 | 1153 |
| K | 250 ± 131 | 0.9 | 219 | 294 ± 203 | 2.2 | 239 |
| Ca | 81 ± 113 | 0.9 | 47 | 101 ± 160 | 2.2 | 53.0 |
| Ti | 10.6 ± 10 | 0.9 | 7.8 | 12 ± 15 | 2.2 | 6.6 |
| V | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 33 | 0.5 | 0.7 ± 0.7 | 56 | 0.4 |
| Cr | 1.2 ± 1.0 | 7.7 | 0.9 | 1.3 ± 1.4 | 17 | 0.8 |
| Mn | 13 ± 8.2 | 0.9 | 11 | 16 ± 22 | 2.6 | 10 |
| Fe | 183 ± 135 | 1.0 | 142 | 210 ± 201 | 2.2 | 153 |
| Ni | 0.8 ± 0.7 | 58 | 0.7 | 0.7 ± 0.8 | 12.6 | 0.4 |
| Cu | 4.4 ± 4.0 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 4.1 ± 4.0 | 3.4 | 3.1 |
| Zn | 49 ± 85 | 0.9 | 37 | 51 ± 41 | 2.6 | 39 |
| As | 4.7 ± 3.8 | 0.9 | 3.8 | 3.9 ± 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.1 |
| Se | 1.0 ± 1.0 | 7.4 | 0.5 | 1.4 ± 1.4 | 7.9 | 1.0 |
| Br | 7.3 ± 6.4 | 0.9 | 4.8 | 8.8 ± 6.2 | 2.3 | 7.5 |
| Ba | 2.2 ± 1.8 | 61 | 1.7 | - | −100 | - |
| Pb | 21 ± 11 | 0.9 | 19 | 21.0 ± 11.8 | 4.3 | 19.7 |
| Temperature (°C) | −3.5 ± 6.3 | - | - | −2.64 ± 5.63 | - | - |
| Relative humidity (%) | 56.9 ± 15.7 | - | - | 70.0 ± 17.1 | - | - |
| Wind speed (m/s) | 2.38 ± 1.09 | - | - | 1.79 ± 1.67 | - | - |
| Wind direction (degree) | 205 ± 110.1 | - | - | 146 ± 138 | - | - |
| Rainfall (mm) | 0.76 ± 0.93 | - | - | 0.33 ± 0.25 | - | - |
| Seoul | Seosan | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | |
| Si | 0.01 | 0.98 | −0.09 | 0.98 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.02 |
| S | 0.87 | 0.17 | 0.20 | −0.11 | 0.88 | 0.25 | 0.07 |
| K | 0.55 | 0.68 | 0.34 | 0.58 | 0.64 | 0.31 | 0.10 |
| Ca | 0.03 | 0.98 | −0.09 | 0.94 | 0.06 | 0.12 | −0.09 |
| Ti | 0.09 | 0.98 | −0.03 | 0.97 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.03 |
| V | 0.31 | 0.91 | −0.08 | 0.83 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 0.23 |
| Cr | 0.88 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.44 | −0.20 |
| Mn | 0.72 | 0.56 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.86 | 0.04 |
| Fe | 0.41 | 0.90 | 0.00 | 0.89 | 0.23 | 0.37 | −0.03 |
| Ni | 0.81 | 0.31 | 0.16 | 0.50 | 0.81 | 0.05 | −0.02 |
| Cu | 0.85 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.77 | −0.05 |
| Zn | 0.62 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 0.90 | 0.08 |
| As | 0.02 | −0.13 | 0.95 | 0.05 | −0.18 | 0.00 | 0.93 |
| Se | 0.87 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.88 | 0.21 | −0.17 |
| Br | 0.95 | 0.14 | −0.07 | 0.12 | 0.87 | 0.31 | −0.01 |
| Ba | 0.70 | −0.25 | 0.14 | No data | No data | No data | No data |
| Pb | 0.27 | −0.01 | 0.93 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.61 | 0.59 |
| Variance | 9.05 | 3.76 | 1.69 | 7.94 | 3.02 | 1.78 | 1.16 |
| Percentage of variance (%) | 53.2 | 22.1 | 9.95 | 49.6 | 18.8 | 11.1 | 7.26 |
| Cumulative (%) | 53.2 | 75.3 | 85.3 | 49.6 | 68.5 | 79.6 | 86.8 |
| Element | Dry Deposition Velocity (cm s−1) | Mean ± SD (Seoul) | Mean ± SD (Seosan) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 2.0 | 411.6 ± 689.9 | 530.5 ± 801.8 |
| S | 1.0 | 1253.8 ± 654.0 | 1096.4 ± 451.6 |
| K | 2.0 | 435.2 ± 169.5 | 510.4 ± 194.8 |
| Ca | 2.0 | 144.3 ± 172.6 | 175.2 ± 219.8 |
| Ti | 2.0 | 18.6 ± 16.1 | 20.0 ± 18.7 |
| V | 1.0 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.4 |
| Cr | 0.5 | 1.0 ± 0.6 | 1.0 ± 0.6 |
| Mn | 1.0 | 11.4 ± 5.2 | 13.7 ± 10.4 |
| Fe | 2.0 | 319.9 ± 208.3 | 363.2 ± 242.3 |
| Ni | 0.5 | 0.5 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.4 |
| Cu | 0.5 | 1.9 ± 1.3 | 1.8 ± 0.9 |
| Zn | 0.5 | 21.3 ± 11.9 | 21.9 ± 9.6 |
| As | 0.5 | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 0.7 |
| Se | 0.5 | 0.4 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.4 |
| Br | 0.5 | 3.2 ± 1.8 | 3.8 ± 1.5 |
| Ba | 0.5 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Pb | 0.5 | 9.1 ± 2.7 | 9.1 ± 2.5 |
| Element | Adult | Children | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQing | HQder | HQinh | HQing | HQder | HQinh | |
| Seoul | ||||||
| Cr | 2.8 × 10−07 | 3.7 × 10−05 | 1.3 × 10−13 | 2.6 × 10−06 | 1.5 × 10−04 | 3.1 × 10−13 |
| Mn | 2.0 × 10−07 | 8.3 × 10−06 | 3.0 × 10−12 | 1.9 × 10−06 | 3.3 × 10−05 | 6.9 × 10−12 |
| Ni | 1.7 × 10−08 | 1.1 × 10−07 | 7.7 × 10−17 | 1.6 × 10−07 | 4.2 × 10−07 | 1.8 × 10−16 |
| Cu | 7.8 × 10−08 | 1.7 × 10−08 | 3.6 × 10−16 | 7.3 × 10−07 | 6.8 × 10−08 | 8.4 × 10−16 |
| V | 6.1 × 10−08 | 1.6 × 10−05 | 2.8 × 10−16 | 5.7 × 10−07 | 6.2 × 10−05 | 6.6 × 10−16 |
| Zn | 1.2 × 10−07 | 3.8 × 10−08 | 5.3 × 10−16 | 1.1 × 10−06 | 1.5 × 10−07 | 1.2 × 10−15 |
| As | 1.1 × 10−05 | 5.3 × 10−06 | 5.0 × 10−14 | 1.0 × 10−04 | 2.1 × 10−05 | 1.2 × 10−13 |
| Pb | 4.2 × 10−06 | 1.9 × 10−05 | 1.9 × 10−14 | 3.9 × 10−05 | 7.4 × 10−05 | 4.5 × 10−14 |
| HQ | 1.6 × 10−05 | 8.5 × 10−05 | 3.2 × 10−12 | 1.5 × 10−04 | 3.3 × 10−04 | 7.4 × 10−12 |
| HI = ΣHQ | 1.0 × 10−04 | 4.8 × 10−04 | ||||
| Seosan | ||||||
| Cr | 2.8 × 10−07 | 3.8 × 10−05 | 1.4 × 10−13 | 2.7 × 10−06 | 1.5 × 10−04 | 3.2 × 10−13 |
| Mn | 2.4 × 10−07 | 1.0 × 10−05 | 3.6 × 10−12 | 2.3 × 10−06 | 4.0 × 10−05 | 8.3 × 10−12 |
| Ni | 2.5 × 10−08 | 1.5 × 10−07 | 1.1 × 10−16 | 2.3 × 10−07 | 6.0 × 10−07 | 2.6 × 10−16 |
| Cu | 7.2 × 10−08 | 1.6 × 10−08 | 3.3 × 10−16 | 6.8 × 10−07 | 6.3 × 10−08 | 7.7 × 10−16 |
| V | 5.1 × 10−08 | 1.3 × 10−05 | 2.4 × 10−16 | 4.8 × 10−07 | 5.2 × 10−05 | 5.5 × 10−16 |
| Zn | 1.2 × 10−07 | 3.9 × 10−08 | 5.5 × 10−16 | 1.1 × 10−06 | 1.6 × 10−07 | 1.3 × 10−15 |
| As | 9.0 × 10−06 | 4.4 × 10−06 | 4.1 × 10−14 | 8.4 × 10−05 | 1.7 × 10−05 | 9.6 × 10−14 |
| Pb | 4.2 × 10−06 | 1.9 × 10−05 | 1.9 × 10−14 | 3.9 × 10−05 | 7.4 × 10−05 | 4.5 × 10−14 |
| HQ | 1.4 × 10−05 | 8.4 × 10−05 | 3.8 × 10−12 | 1.3 × 10−04 | 3.3 × 10−04 | 8.8 × 10−12 |
| HI = ΣHQ | 9.8 × 10−05 | 4.6 × 10−04 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nirmalkar, J.; Lee, K.; Ahn, J.; Lee, J.; Song, M. Comparisons of Spatial and Temporal Variations in PM2.5-Bound Trace Elements in Urban and Rural Areas of South Korea, and Associated Potential Health Risks. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040753
Nirmalkar J, Lee K, Ahn J, Lee J, Song M. Comparisons of Spatial and Temporal Variations in PM2.5-Bound Trace Elements in Urban and Rural Areas of South Korea, and Associated Potential Health Risks. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(4):753. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040753
Chicago/Turabian StyleNirmalkar, Jayant, Kwangyul Lee, Junyoung Ahn, Jiyi Lee, and Mijung Song. 2023. "Comparisons of Spatial and Temporal Variations in PM2.5-Bound Trace Elements in Urban and Rural Areas of South Korea, and Associated Potential Health Risks" Atmosphere 14, no. 4: 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040753
APA StyleNirmalkar, J., Lee, K., Ahn, J., Lee, J., & Song, M. (2023). Comparisons of Spatial and Temporal Variations in PM2.5-Bound Trace Elements in Urban and Rural Areas of South Korea, and Associated Potential Health Risks. Atmosphere, 14(4), 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040753










