Influence of Load Condition, Tire Type, and Ambient Temperature on the Emission of Tire–Road Particulate Matter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
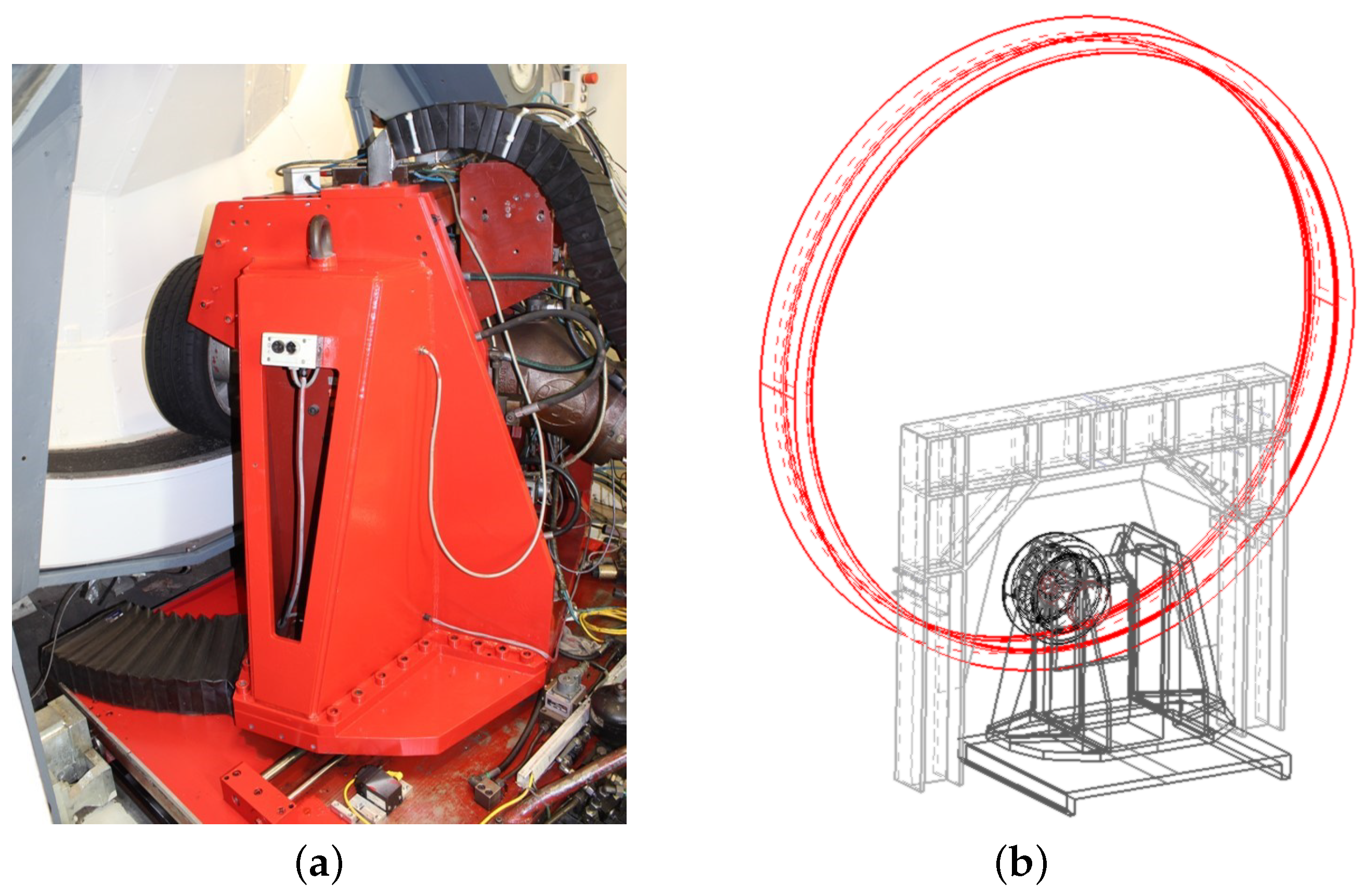
2.1. Internal Drum Test Bench
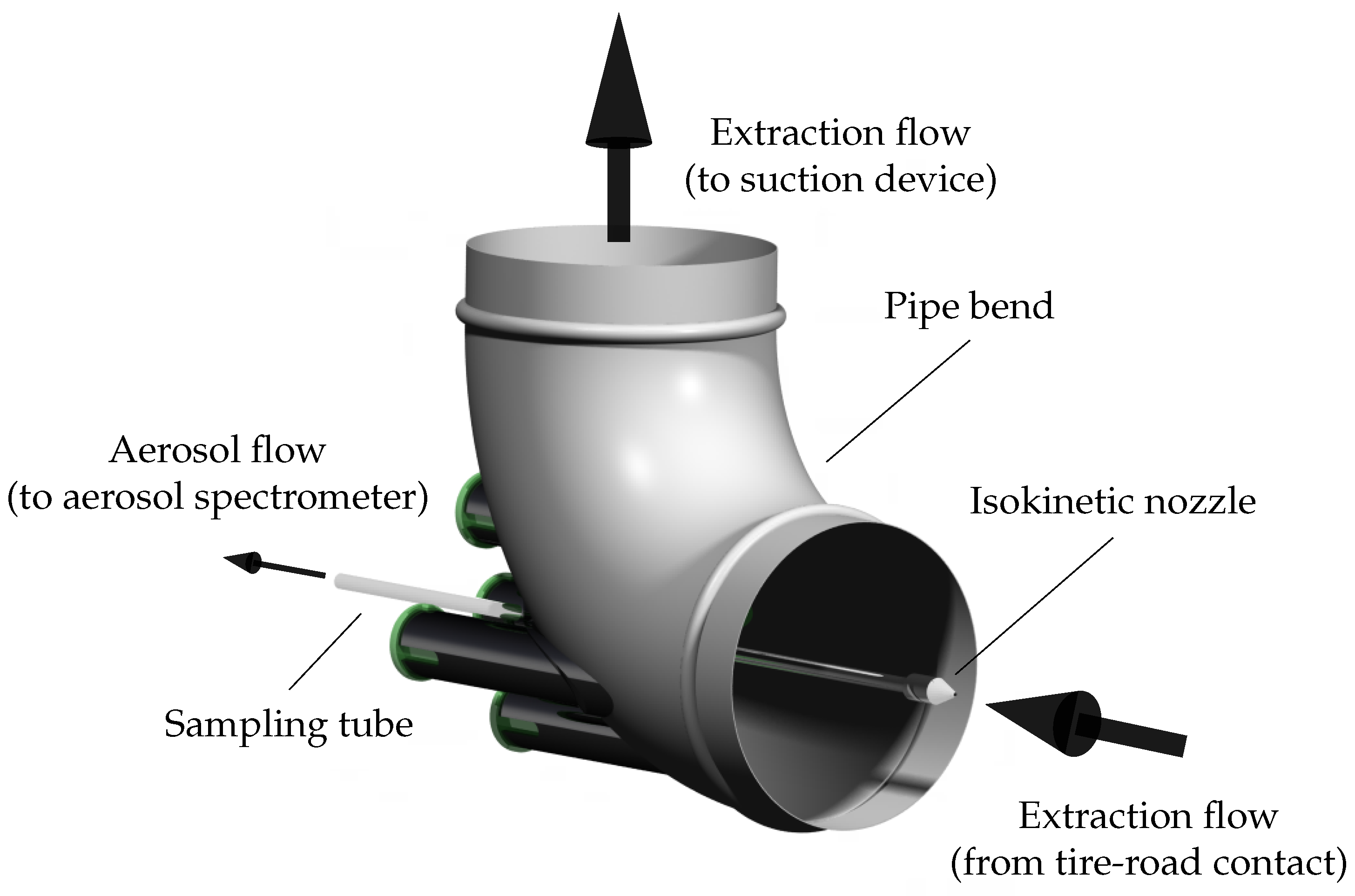
2.2. Measurement System
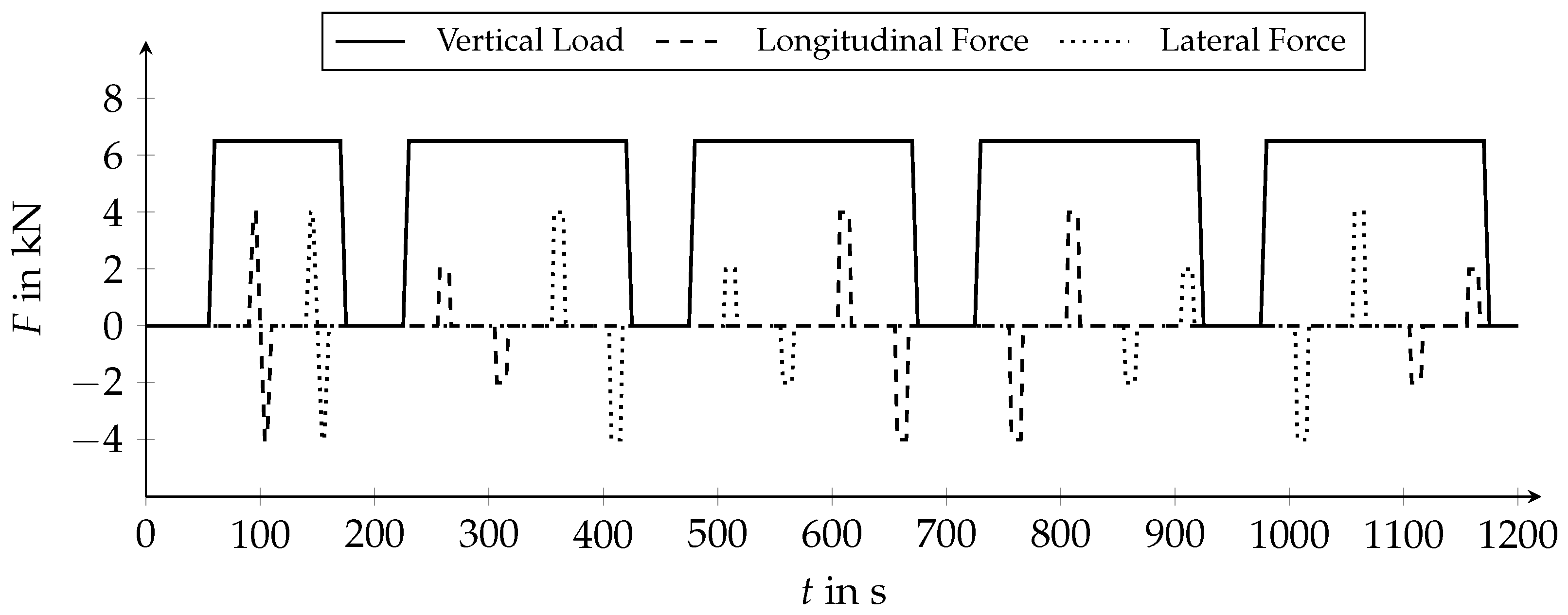
2.3. Varied Parameters
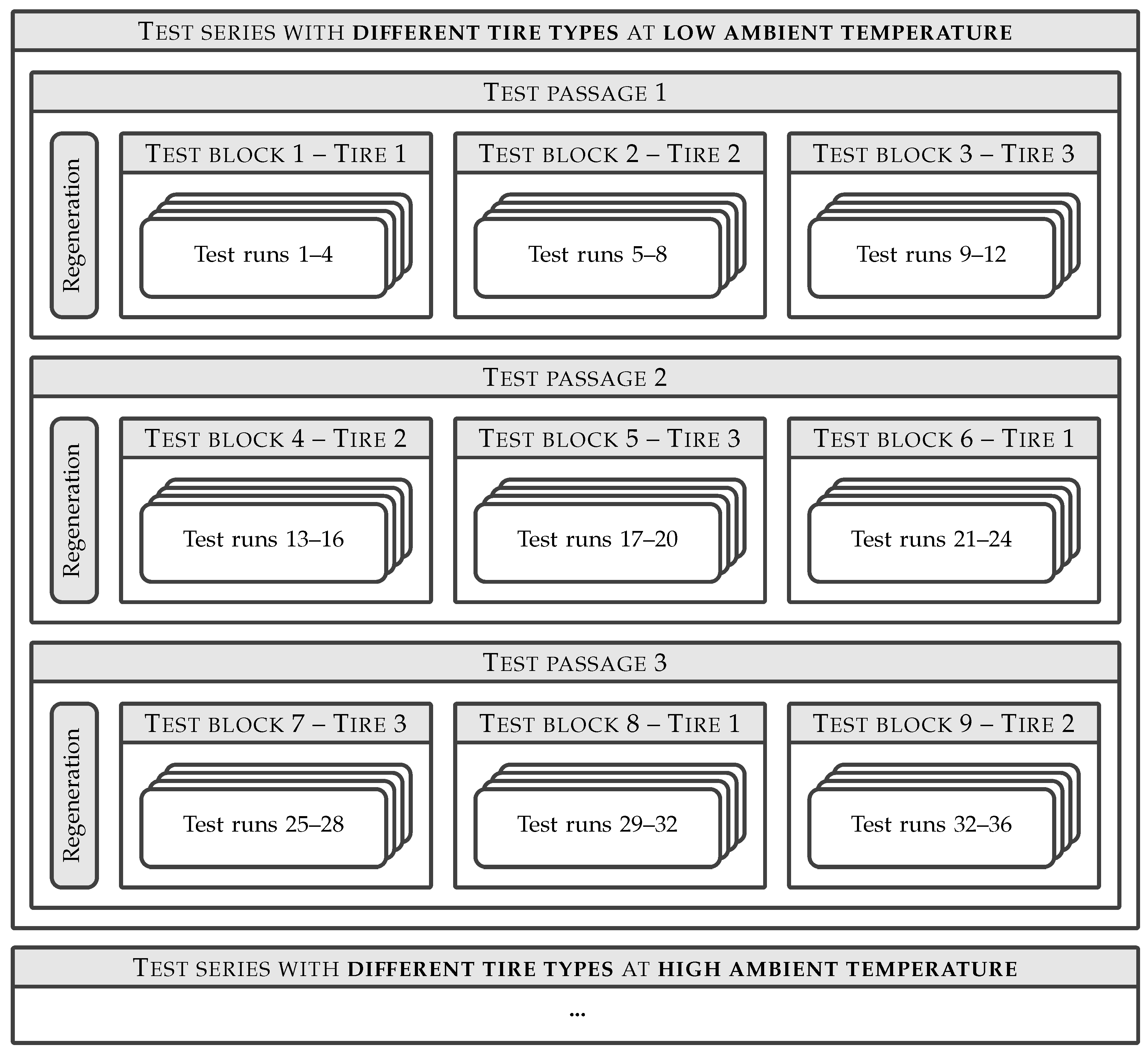
2.4. Experimental Setup and Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Data
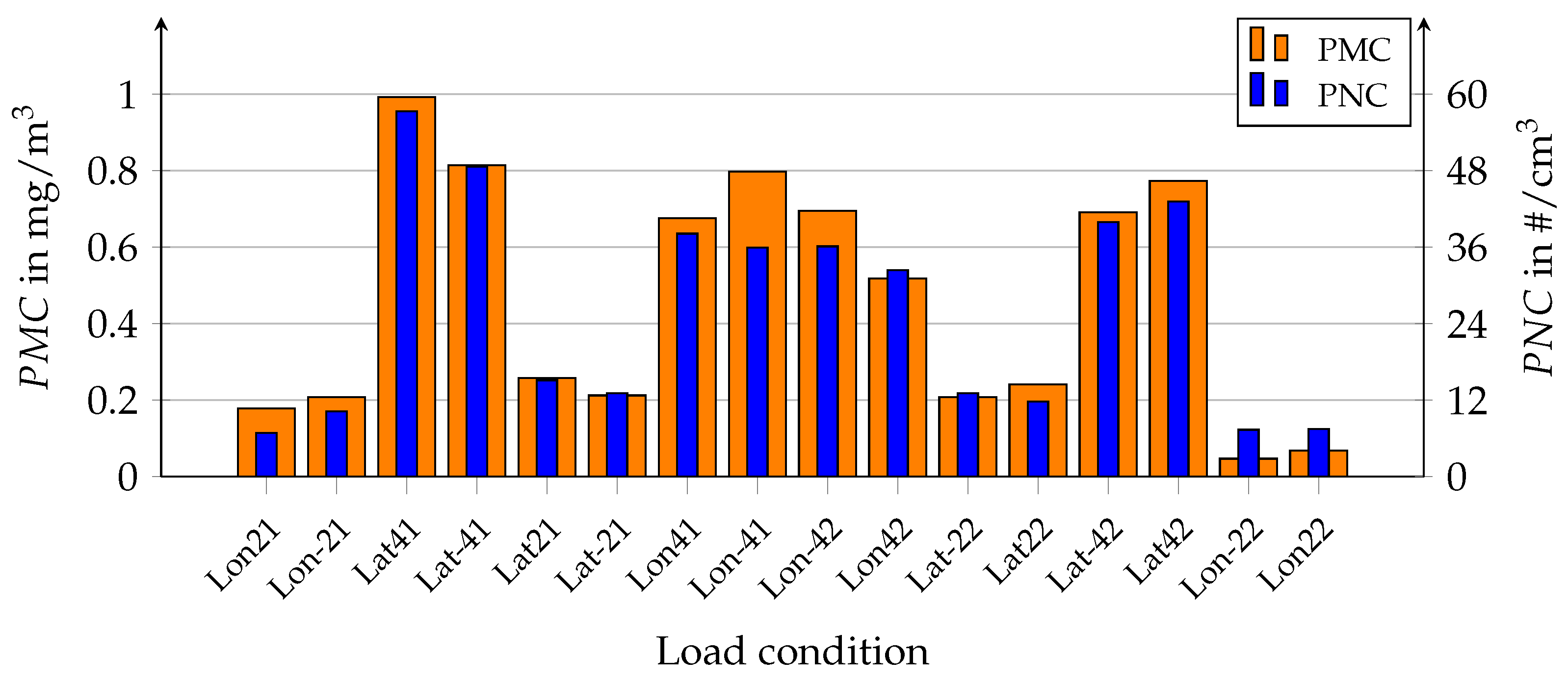
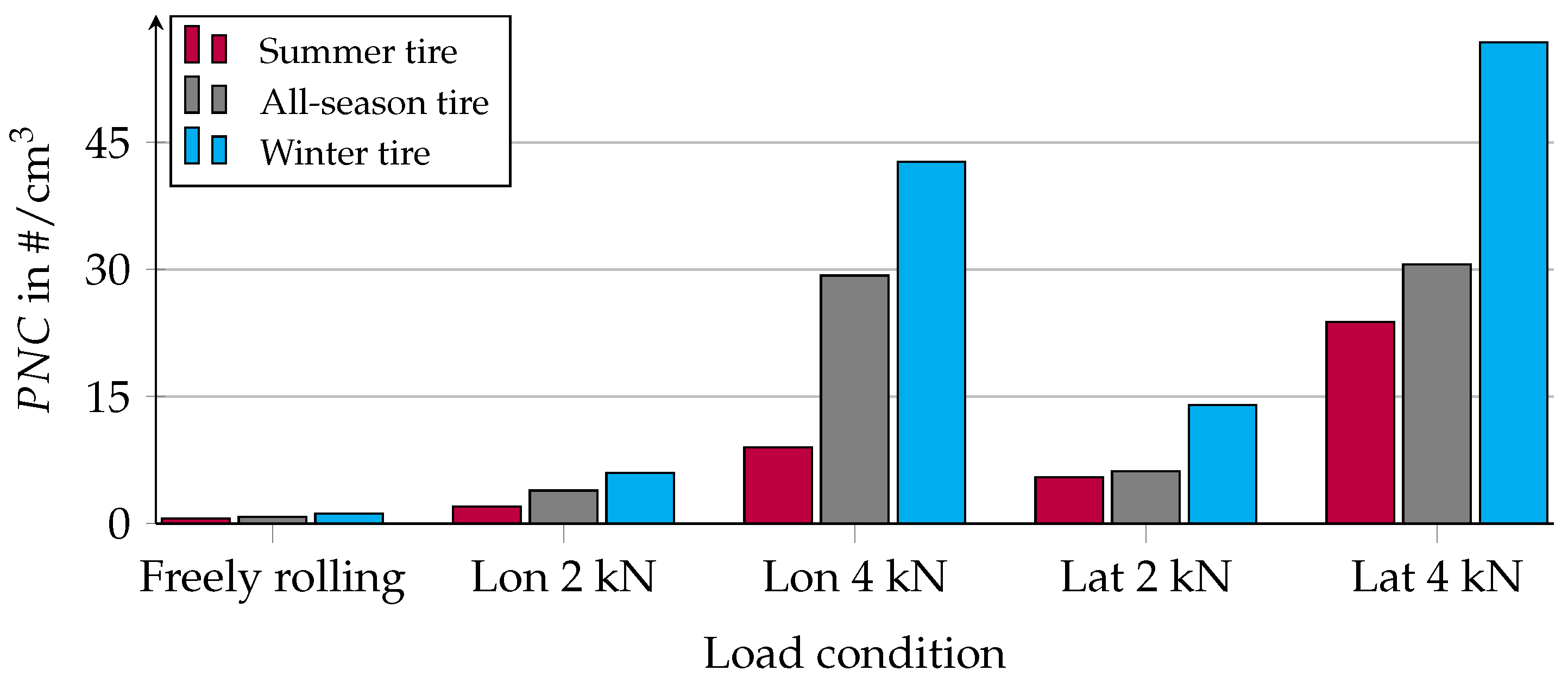
3.2. Influence of Load Condition on PM Emission
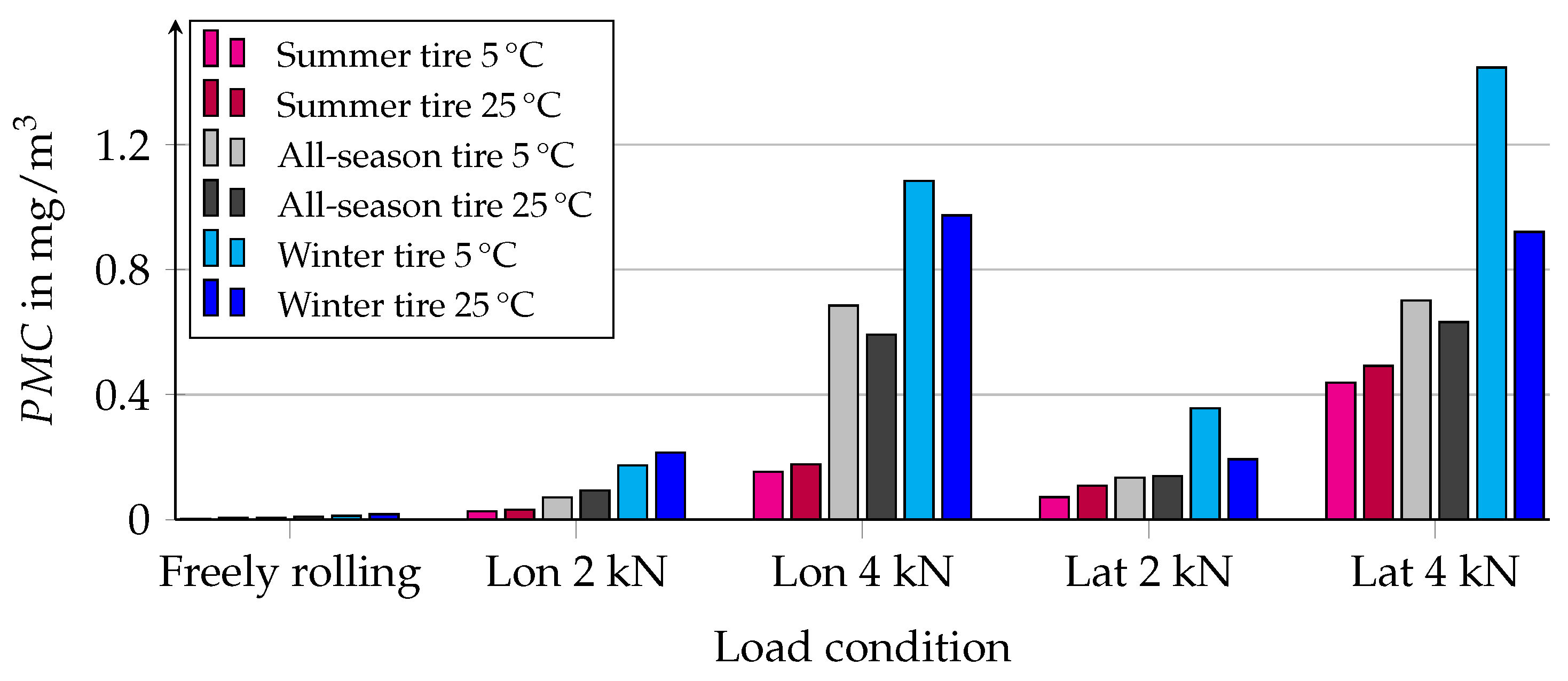
3.3. Influence of Tire Type on PM Emission
3.4. Influence of Ambient Temperature on PM Emission
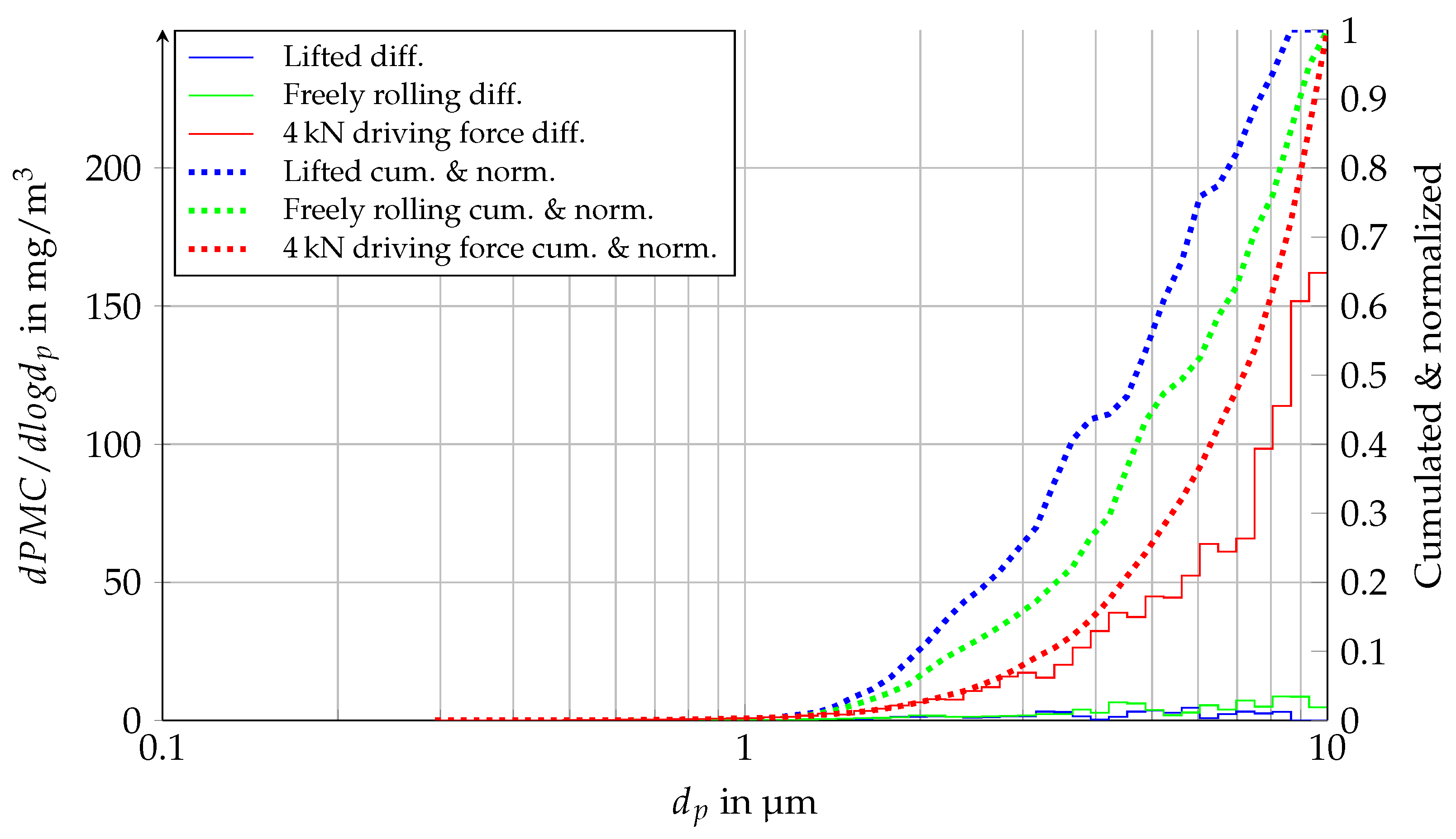
3.5. Influence of Load Condition on Particle Size Distribution
4. Discussion
4.1. Representativeness of the Stated Particle Concentrations
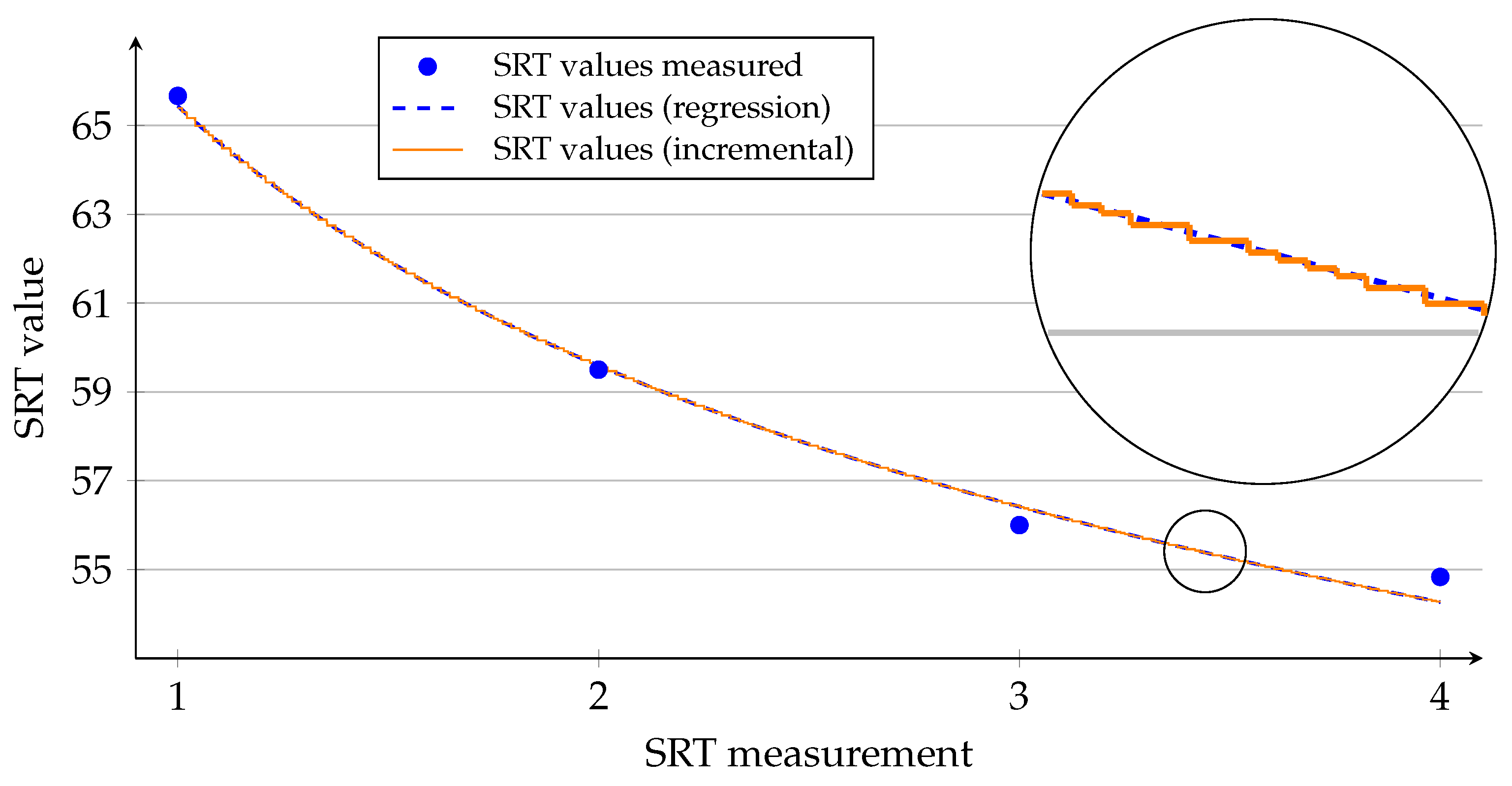
4.2. Procedure for Determination and Influence of the Currently Present SRT Value
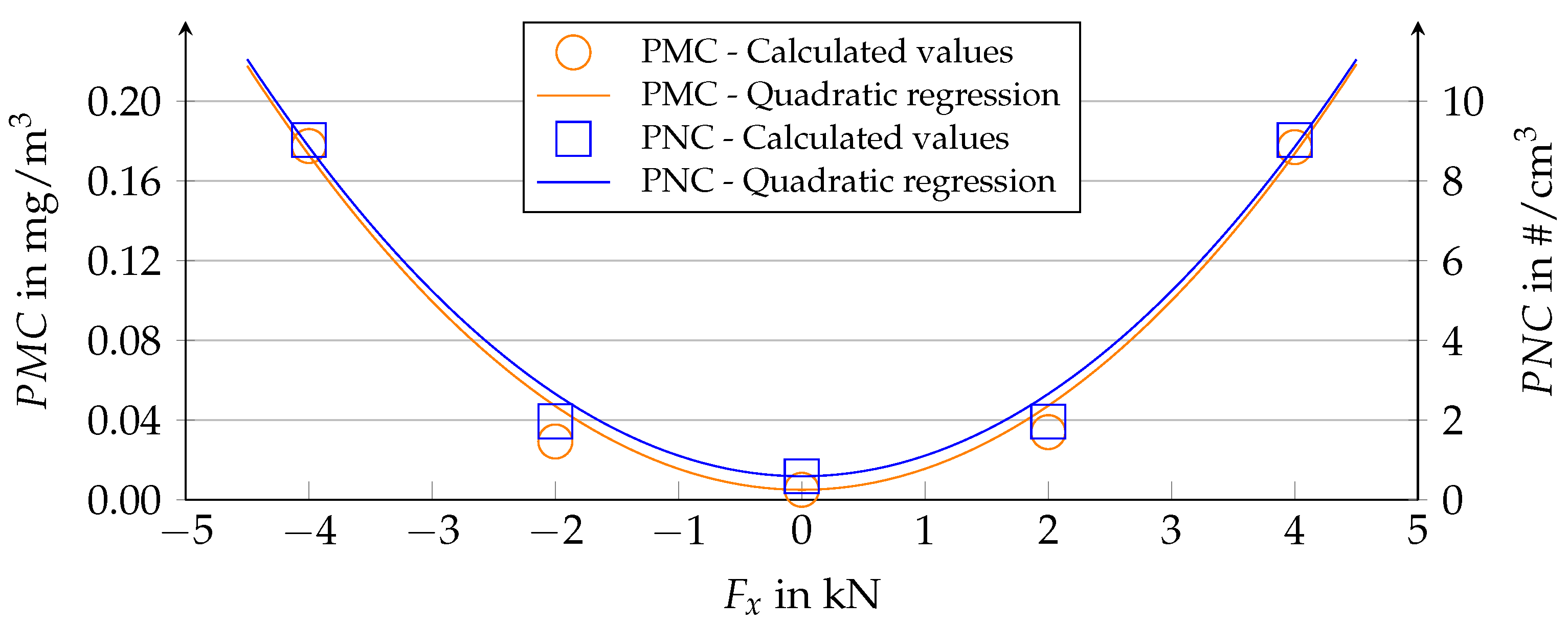
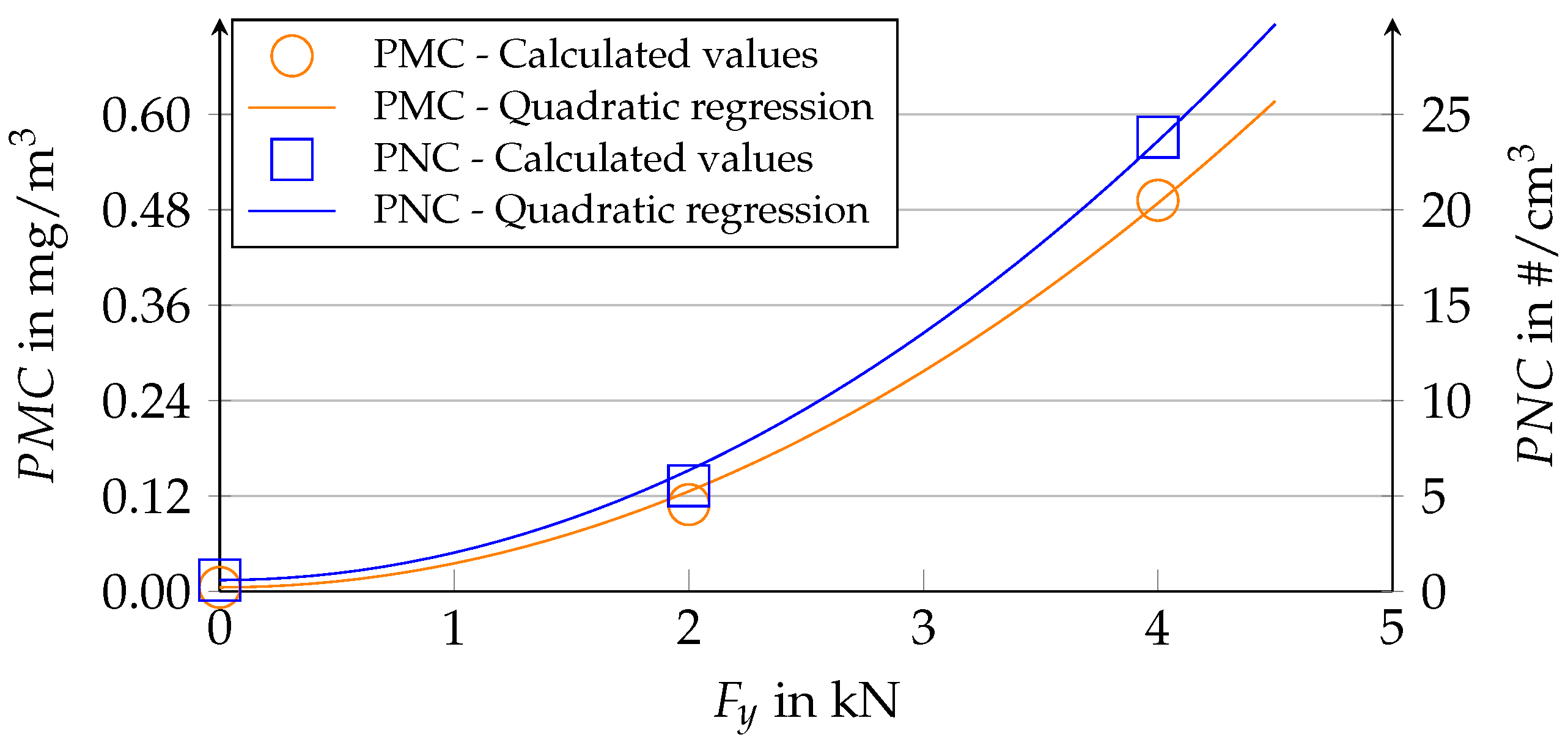
4.3. Quantitative Dependence of the Emission on the Forces
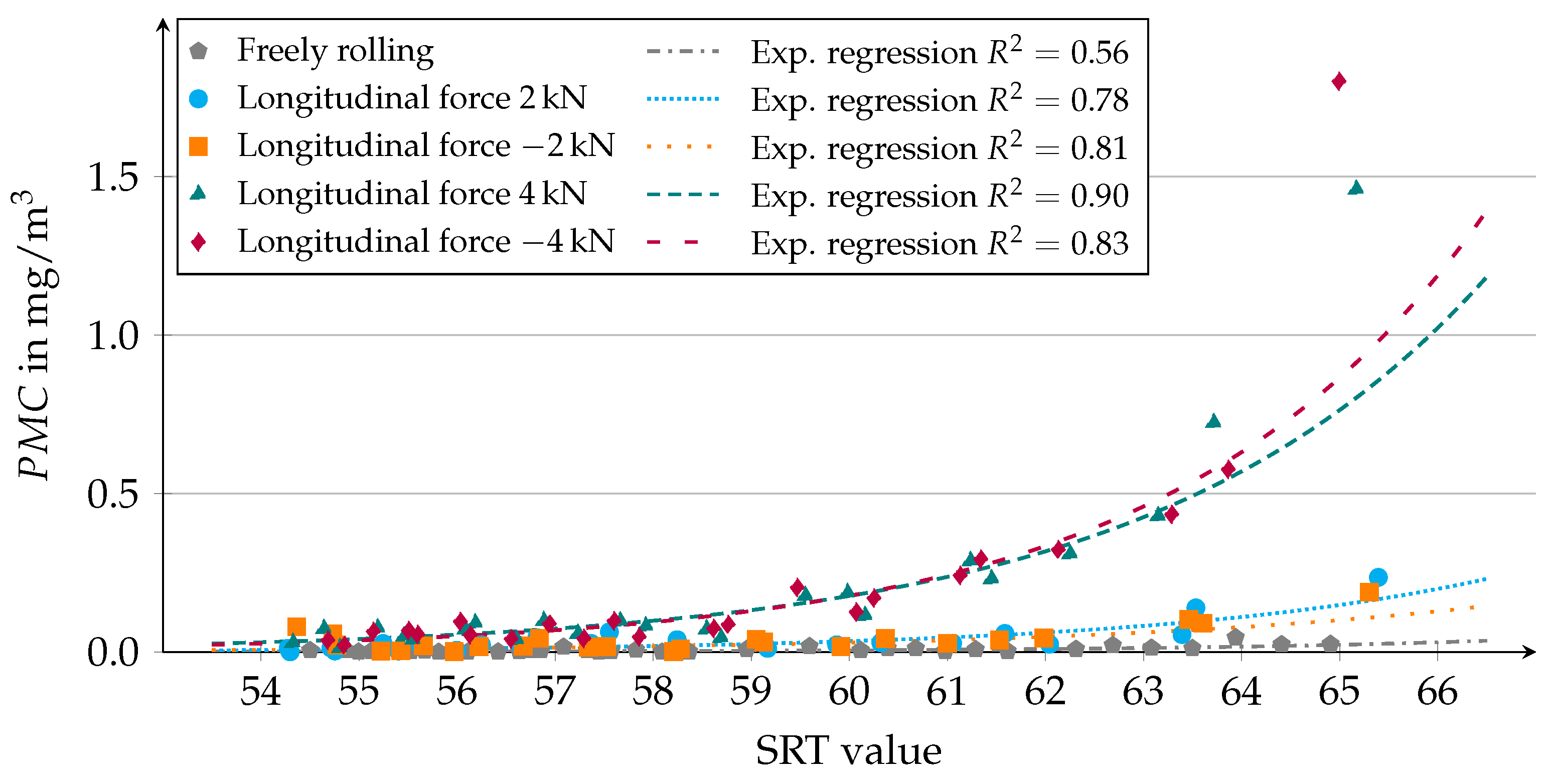
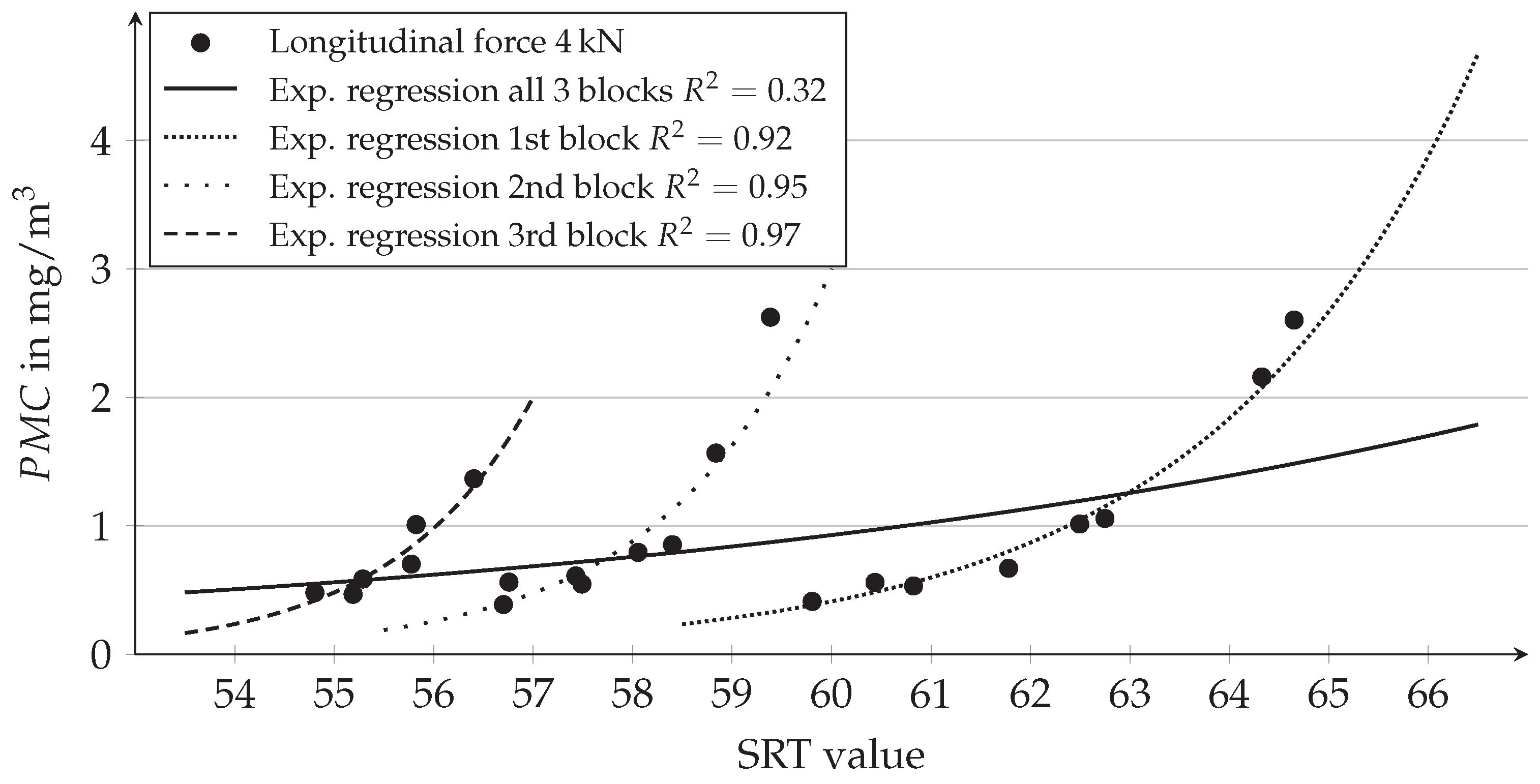
4.4. Use of Regression Curves for Correlation between PMC/PNC and the SRT Value
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BEV | Battery–Electric Vehicle |
| Lat | Lateral Force |
| Lon | Longitudinal Force |
| OECD | Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| PMC | Particle Mass Concentration |
| PMF | Positive Matrix Factorization |
| PNC | Particle Number Concentration |
| SRT | Skid Resistance Tester |
| TRWP | Tire and Road Wear Particles |
| TWP | Tire Wear Particles |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- World Health Organization. Ambient (Outdoor) Air Pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- German Environment Agency. Feinstaub-Jährliche Auswertungen. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/themen/luft/luftschadstoffe-im-ueberblick/feinstaub#feinstaub-jahresmittelwerte (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- OECD. Non-Exhaust Particulate Emissions from Road Transport: An Ignored Environmental Policy Challenge; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhana, L.; Sokhi, R.; Warner, L.; Mao, H.; Boulter, P.; McCrae, I.; Wright, J.; Osborn, D. Measurement of Non-Exhaust Particulate Matter: Characterisation of Exhaust Particulate Emissions from Road Vehicles; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bukowiecki, N.; Lienemann, P.; Hill, M.; Furger, M.; Richard, A.; Amato, F.; Prévôt, A.; Baltensperger, U.; Buchmann, B.; Gehrig, R. PM10 emission factors for non-exhaust particles generated by road traffic in an urban street canyon and along a freeway in Switzerland. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2330–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjödin, Å.; Ferm, M.; Björk, A.; Rahmberg, M.; Gudmundsson, A.; Swietlicki, E.; Johansson, C.; Gustafsson, M.; Blomqvist, G. Wear Particles from Road Traffic: A Field, Laboratory and Modelling Study: Final Report; IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute Ltd.: Göteborg, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Amato, F.; Schaap, M.; van der Denier Gon, H.A.; Pandolfi, M.; Alastuey, A.; Keuken, M.; Querol, X. Effect of rain events on the mobility of road dust load in two Dutch and Spanish roads. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Jones, A.M.; Gietl, J.; Yin, J.; Green, D.C. Estimation of the contributions of brake dust, tire wear, and resuspension to nonexhaust traffic particles derived from atmospheric measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6523–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, W.; Liacos, J.W.; Schauer, J.J.; Delfino, R.J.; Sioutas, C. Size-segregated composition of particulate matter (PM) in major roadways and surface streets. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, F.; Pandolfi, M.; Alastuey, A.; Lozano, A.; Contreras González, J.; Querol, X. Impact of traffic intensity and pavement aggregate size on road dust particles loading. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panko, J.M.; Chu, J.; Kreider, M.L.; Unice, K.M. Measurement of airborne concentrations of tire and road wear particles in urban and rural areas of France, Japan, and the United States. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 72, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.; Sokhi, R.; Ravindra, K. Quantification of vehicle fleet PM10 particulate matter emission factors from exhaust and non-exhaust sources using tunnel measurement techniques. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, F.; Favez, O.; Pandolfi, M.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Moukhtar, S.; Bruge, B.; Verlhac, S.; Orza, J.; Bonnaire, N.; et al. Traffic induced particle resuspension in Paris: Emission factors and source contributions. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etyemezian, V.; Kuhns, H.; Gillies, J.; Chow, J.; Hendrickson, K.; McGown, M.; Pitchford, M. Vehicle-based road dust emission measurement (III): Effect of speed, traffic volume, location, and season on PM10 road dust emissions in the Treasure Valley, ID. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4583–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Johansson, C.; Karlsson, H.; Hansson, H.C. Factors affecting non-tailpipe aerosol particle emissions from paved roads: On-road measurements in Stockholm, Sweden. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathissen, M.; Scheer, V.; Vogt, R.; Benter, T. Investigation on the potential generation of ultrafine particles from the tire–road interface. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6172–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupiainen, K.J.; Pirjola, L. Vehicle non-exhaust emissions from the tyre–road interface–effect of stud properties, traction sanding and resuspension. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4141–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathissen, M.; Scheer, V.; Kirchner, U.; Vogt, R.; Benter, T. Non-exhaust PM emission measurements of a light duty vehicle with a mobile trailer. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, S. On-road and laboratory investigations on non-exhaust ultrafine particles from the interaction between the tire and road pavement under braking conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aatmeeyata; Kaul, D.S.; Sharma, M. Traffic generated non-exhaust particulate emissions from concrete pavement: A mass and particle size study for two-wheelers and small cars. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5691–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Lee, S. Characteristics of Tire Wear Particles Generated by a Tire Simulator under Various Driving Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12153–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Kim, H.; Lee, S. Characteristics of tire wear particles generated in a laboratory simulation of tire/road contact conditions. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 124, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foitzik, M.J.; Unrau, H.J.; Gauterin, F.; Dornhöfer, J.; Koch, T. Investigation of Ultra Fine Particulate Matter Emission of Rubber Tires. Wear 2018, 394–395, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupiainen, K.J.; Tervahattu, H.; Räisänen, M.; Mäkelä, T.; Aurela, M.; Hillamo, R. Size and composition of airborne particles from pavement wear, tires, and traction sanding. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, A.; Gharibi, A.; Swietlicki, E.; Gudmundsson, A.; Bohgard, M.; Ljungman, A.; Blomqvist, G.; Gustafsson, M. Traffic-generated emissions of ultrafine particles from pavement–tire interface. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, M.; Blomqvist, G.; Gudmundsson, A.; Dahl, A.; Swietlicki, E.; Bohgard, M.; Lindbom, J.; Ljungman, A. Properties and toxicological effects of particles from the interaction between tyres, road pavement and winter traction material. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 393, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gustafsson, M.; Blomqvist, G.; Gudmundsson, A.; Dahl, A.; Jonsson, P.; Swietlicki, E. Factors influencing PM10 emissions from road pavement wear. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4699–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panko, J.; McAtee, B.L.; Kreider, M.; Gustafsson, M.; Blomqvist, G.; Gudmundsson, A.; Sweet, L.; Finley, B. Physio-Chemical Analysis of Airborne Tire Wear Particles. Available online: http://docs.wbcsd.org/2010/02/physioChemAnalysisAirborne.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- Schläfle, S.; Gauterin, F.; Lallement, R. Aufbau eines Prüfstands zur Messung von Reifen-Fahrbahn-Feinstaubemissionen auf realen Fahrbahnoberflächen. In Reifen–Fahrwerk–Fahrbahn; VDI Wissensforum GmbH, Ed.; VDI Verlag: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2022; VDI-Berichte 2398; pp. 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PALAS. Datasheet MonoDust 1500. Available online: https://www.palas.de/en/product/download/monodust1500/datasheet/pdf (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- PALAS GmbH. Datasheet Promo 2000. Available online: https://www.palas.de/en/product/download/promo2000/datasheet/pdf (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- PALAS GmbH. Datasheet Aerosol Sensor Welas 2500. Available online: https://www.palas.de/en/product/download/aerosolsensorwelas2500/datasheet/pdf (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- EN 13036; Road and Airfield Surface Characteristics—Test Methods–Part 4: Method for Measurement of Slip/Skid Resistance of a Surface—The Pendulum Test. European Committee for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 2011.
- Forschungsgesellschaft für Straßen- und Verkehrswesen. Zusätzliche Technische Vertragsbedingungen und Richtlinien für den Bau von Verkehrsflächenbefestigungen aus Asphalt: ZTV Asphalt-StB 07/13; FGSV: Cologne, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Parker, J.A.; Oh, S.C.; Lee, J.P.; Xi, L.; Kreider, M.L.; Unice, K.M. Chemical mapping of tire and road wear particles for single particle analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 144085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, J.; Jaramillo-Vogel, D.; Perseguers, S.; Schnidrig, N.; Grobéty, B.; Yajan, P. Automated identification and quantification of tire wear particles (TWP) in airborne dust: SEM/EDX single particle analysis coupled to a machine learning classifier. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP)—A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Parameter Variation | |
|---|---|---|
| Varied | Tire type | Summer; Winter; All-season |
| Ambient temperature | 5 ; 25 | |
| Longitudinal force | 0 kN; kN; kN | |
| Lateral force | 0 kN; kN; kN | |
| Constant | Camber angle | 0° |
| Vertical load | kN | |
| Speed | 80 km/h | |
| Tire inflation pressure | bar |
| Load Condition | SRT Value 55 | SRT Value 60 | SRT Value 65 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMC | Freely rolling | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | mg/m3 |
| Lon 2 kN | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | |
| Lon 4 kN | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | |
| Lat 2 kN | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | |
| Lat 4 kN | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | mg/m3 | |
| PNC | Freely rolling | #/cm3 | #/cm3 | #/cm3 |
| Lon 2 kN | #/cm3 | #/cm3 | #/cm3 | |
| Lon 4 kN | #/cm3 | #/cm3 | #/cm3 | |
| Lat 2 kN | #/cm3 | #/cm3 | #/cm3 | |
| Lat 4 kN | #/cm3 | #/cm3 | #/cm3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schläfle, S.; Unrau, H.-J.; Gauterin, F. Influence of Load Condition, Tire Type, and Ambient Temperature on the Emission of Tire–Road Particulate Matter. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071095
Schläfle S, Unrau H-J, Gauterin F. Influence of Load Condition, Tire Type, and Ambient Temperature on the Emission of Tire–Road Particulate Matter. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(7):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071095
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchläfle, Stefan, Hans-Joachim Unrau, and Frank Gauterin. 2023. "Influence of Load Condition, Tire Type, and Ambient Temperature on the Emission of Tire–Road Particulate Matter" Atmosphere 14, no. 7: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071095
APA StyleSchläfle, S., Unrau, H.-J., & Gauterin, F. (2023). Influence of Load Condition, Tire Type, and Ambient Temperature on the Emission of Tire–Road Particulate Matter. Atmosphere, 14(7), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071095







