Determining the Day-to-Day Occurrence of Low-Latitude Scintillation in Equinoxes at Sanya during High Solar Activities (2012–2013)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dataset
2.1. Ground-Based Observations
2.2. Space-Based Observations
3. Method for Determining Scintillation Activity
3.1. Characteristics of Ionospheric Parameters
3.2. The Simplified Growth Rate of R–T Instability
3.3. The Growth Rate and Equatorial Ionization Anomaly
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogwala, A.; Oyedokun, O.J.; Akala, A.O.; Amaechi, P.O.; Simi, K.G.; Panda, S.K.; Ogabi, C.; Somoye, E.O. Characterization of ionospheric irregularities over the equatorial and low latitude Nigeria region. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2022, 367, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retterer, J.M.; Gentile, L.C. Modeling the climatology of equatorial plasma bubbles observed by DMSP. Radio Sci. 2009, 44, RS0A31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A.; Iyer, K.N.; de Medeiros, R.T.; Batista, I.S.; Sobral, J.H.A. Thermospheric meridional wind control of equatorial spread F and evening prereversal electric field. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.S. Effects of the postsunset vertical plasma drift on the generation of equatorial spread F. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L. Day-to-day variability of prereversal enhancement in the vertical ion drift in response to large-scale forcing from the lower atmosphere. Space Weather 2020, 18, e2019SW002334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasia, C.V.; Jyoti, N.; Viswanathan, K.S.; Subbarao, K.S.V.; Tiwari, D.; Sridharan, R. On the plausible linkage of thermospheric meridional winds with equatorial spread F. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju, G.; Devasia, C.V.; Sridharan, R. On the seasonal variations of the threshold height for the occurrence of equatorial spread F during solar minimum and maximum years. Ann. Geophys. 2007, 25, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ning, B.; Abdu, M.A.; Wan, W.; Hu, L. Precursor signatures and evolution of post-sunset equatorial spread-F observed over Sanya. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, A08321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.N.; Reinisch, B.; Valladare, C.; Chau, J.; Veliz, O. Forecasting the occurrence of ionospheric scintillation activity in the equatorial ionosphere on a day-to-day basis. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2004, 66, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulasi Ram, S.; Rama Rao, P.V.S.; Niranjan, K.; Prasad, D.S.V.V.D.; Sridharan, R.; Devasia, C.V.; Ravindran, S. The role of post-sunset vertical drifts at the equator in predicting the onset of VHF scintillations during high and low sunspot activity years. Ann. Geophys. 2006, 24, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.N.; Redmon, R.J. Forecasting scintillation activity and equatorial spread F. Space Weather 2017, 15, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, R.J.; Anderson, D.; Caton, R.; Bullett, T. A forecasting ionospheric real-time scintillation tool (FIRST). Space Weather 2010, 8, S12003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagiya, M.S.; Sridharan, R.; Sunda, S. Pre-assessment of the “strength” and “latitudinal extent” of L-band scintillation: A case study. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, R.; Bagiya, M.S.; Sunda, S.; Choudhary, R.; Pant, T.K.; Jose, L. First results on forecasting the spatial occurrence pattern of L-band scintillation and its temporal evolution. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2014, 119, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, G.; Xie, H.; Hu, L.; Sun, W.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Ning, B.; Takahashi, H. The prediction of day-to-day occurrence of low latitude ionospheric strong scintillation using gradient boosting algorithm. Space Weather 2021, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A.; Kherani, E.A.; Sousasantos, J. Role of bottom-side density gradient in the development of equatorial plasma bubble/spread F (ESF) irregularities: Solar minimum and maximum conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2020JA027773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olwndo, J.; Cilliers, P.J.; Ming, O. Comparison of ground-based ionospheric scintillation observations with in situ electron density variations as measured by the Swarm satellites. Radio Sci. 2019, 54, 852–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhao, X.; Sun, W.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Xie, H.; Huang, Z.; Ning, B.; Li, G. Statistical characteristics and correlation of low-latitude F region bottom-type irregularity layers and plasma plumes over Sanya. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2020JA027855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ning, B.; Otsuka, Y.; Abdu, M.A.; Abadi, P.; Liu, Z.; Spogli, L.; Wan, W. Challenges to equatorial plasma bubble and ionospheric scintillation short-term forecasting and future aspects in East and Southeast Asia. Surv. Geophys. 2021, 42, 201–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xiong, Y.; Luo, W.; Zhu, Z.; Fan, C. Relationships between ionospheric parameters derived from ionosonde observations and characteristics of post-sunset GHz scintillation during high solar acitivities (2012–2013) at Sanya (18.3° N, 109.6° E), China. Earth Planet. Phys. 2023, 7, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, P.J. Linear theory and modeling of the Rayleigh-Taylor instability leading to the occurrence of the equatorial spread F. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1996, 101, 26875–26891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S. On the linear theory of equatorial plasma instability: Comparison of different descriptions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2002, 107, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retterer, J.M. Physics-based forecasts of equatorial radio scintillation for the Communication and Navigation Outage Forecasting System (C/NOFS). Space Weather 2005, 3, S12C03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Xu, J.S.; Zhu, Z.P. Theoretical modeling of the occurrence of equatorial and low-latitude ionospheric irregularity and scintillation. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 56, 2892–2905. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B.A.; Yizengaw, E.; Retterer, J.M.; Francis, M.; Terkildsen, M.; Marshall, R.; Norman, R.; Zhang, K. An analysis of the quiet time day-to-day variability in the formation of postsunset equatorial plasma bubbles in the Southeast Asian region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 3206–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B.A.; Currie, J.L.; Dao, T.; Yizengaw, E.; Retterer, J.; Terkildsen, M.; Groves, K.; Caton, R. On the assessment of daily equatorial plasma bubble occurrence modeling and forecasting. Space Weather 2020, 18, e2020SW002555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q. Longitudinal and seasonal variation of the equatorial flux tube integrated Rayleigh-Taylor instability growth rate. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 7952–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, H.; Jin, H.; Miyoshi, Y.; Fujiwara, H.; Yokoyama, T.; Otsuka, Y. Daily and seasonal variations in the linear growth rate of the Rayleigh-Taylor instability in the ionosphere obtained with GAIA. Prog. Earth and Planet. Sci. 2018, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Patra, A.K.; Niranjan, K. On the assessment of day-to-day occurrence of equatorial plasma bubble. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2021JA029129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, L.D.; Elvidge, S.; Angling, M.J. Comparison of low-latitude ionospheric scintillation forecasting techniques using a physics-based model. Space Weather 2021, 19, e2020SW002462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thampi, S.V.; Ravindram, S.; Pant, T.K.; Devasia, C.V.; Sreelatha, P.; Sridharan, R. Deterministic prediction of post-sunset ESF based on the strength and asymmetry of EIA from ground based TEC measurements: Preliminary results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, H.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, X.; Chang, S. Linkage of equatorial ionization anomaly with the day-to-day occurrence of postsunset irregularities and scintillation in low-latitude region around 110° E. Space Weather 2022, 20, e2022SW003192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladares, C.E.; Sheehan, R.; Villalobos, J. A latitudinal network of GPS receivers dedicated to studies of equatorial spread-F. Radio Sci. 2004, 39, RS1S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; DasGupta, A. Characteristics of the equatorial ionization anomaly in relation to the day-to-day variability of ionospheric irregularities around the postsunset period. Radio Sci. 2010, 45, RS6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seba, E.B.; Nigussie, M.; Moldwin, M.B. The relationship between equatorial ionization anomaly and nighttime equatorial spread F in East Africa. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 1737–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankadara, R.K.; Panda, S.K.; Amory-Mazaudier, C.; Fleury, R.; Devanadoyina, V.R.; Pant, T.K.; Jamjareegulgarn, P.; Haq, M.A.; Okoh, D.; Seemala, G.K. Signature of equatorial plasma bubbles and ionospheric scintillations from magnetometer and GNSS observations in the Indian Longitudes during the space weather events of early September 2017. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, P.R.; Sahai, Y.; Batista, I.S.; Abdu, M.A.; Bittencourt, J.A.; Takahashi, H. Observations of day-to-day variability in the precursor signatures to equatorial F-region plasma depletions. Ann. Geophys. 1999, 17, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.M.; Rodrigues, F.S.; Fejer, B.G.; Milla, M.A. Coherent and incoherent scatter radar study of the climatology and day-to-day variability of mean F region vertical drifts and equatorial spread F. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 1466–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wan, W.; Li, G.; Liu, L.; Hu, L.; Ning, B.A. comparative study of GPS ionospheric scintillations and ionogram spread F over Sanya. Ann. Geophys. 2015, 33, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Guo, L.; Zhao, Z.; Ding, Z.; Lin, L. Spread-F occurrences and relationships with foF2 and h’F at low- and mid-latitudes in China. Earth Planets Space 2018, 70, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ning, B.; Liu, L.; Zhao, B.; Yue, X.; Su, S.Y.; Venkatraman, S. Correlative study of plasma bubbles, evening equatorial ionization anomaly, and equatorial prereversal E×B drifts at solar maximum. Radio Sci. 2008, 43, RS4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, G.; Ning, B.; Hu, L.; Li, H. Statistical characteristics of low-latitude ionospheric scintillation over China. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, J.A.; Abdu, M.A. A theoretical comparison between apparent and real vertical ionization drift velocities in the equatorial F region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1981, 86, 2451–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkin, I.A.; Kozlov, G.M.; Reinisch, B.W.; Huang, X.; Paznukhov, V.V. The ARTIST 5. AIP Conf. Proc. 2008, 974, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Watkins, M.; Reigber, C. The gravity recovery and climate experiment: Mission overview and early results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L09607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Park, J.; Lühr, H.; Stolle, C.; Ma, S.Y. Comparing plasma bubble occurrence rates at CHAMP and GRACE altitudes during high and low solar activity. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Lühr, H.; Fejer, B.G. Validation of GRACE electron densities by incoherent scatter radar data and estimation of plasma scale height in the topside ionosphere. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Lühr, H.; Ma, S.Y. The magnitude and inter-hemispheric asymmetry of equatorial ionization anomaly- based on CHAMP and GRACE observations. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2013, 105–106, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A.; De Medeiros, R.T.; Sobral, J.H.A. Equatorial spread F instability conditions as determined from ionograms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1982, 9, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayachandran, J.; Balan, N.; Rao, P.B.; Sastri, J.H.; Baliey, G.J. HF Doppler and ionosonde observations on the onset conditions of equatorial spread F. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1993, 98, 13741–13750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, V.L.; Taori, A.; Patra, A.K.; Emperumal, K.; Gurubaran, S. On the importance of wave-like structures in the occurrence of equatorial plasma bubbles: A case study. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, A01306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, R.T.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsugawa, T.; Hong, T.L.; Tulasi Ram, S.; Thampi, S.V.; Chau, H.D.; Nagatsuma, T. On seeding, large-scale wave structure, equatorial spread F, and scintillations over Vietnam. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L20102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Reddy, G.J.; Patra, A.K.; Niranjan, K. Onset condition and features of equatorial F region irregularities: New insight from collocated Digisonde and radar observations from Gadanki. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2022, 127, e2021JA029715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C.; Retterer, J. First successful prediction of a convective equatorial ionospheric storm using solar wind parameters. Space Weather 2008, 6, S08003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, W. Equatorial nighttime thermospheric zonal wind jet response to the temporal oscillation of solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2021JA029345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, L.F.C.; de Paula, E.R.; Stephany, S.; Kantor, I.J.; Muella, M.T.A.H.; de Siqueira, P.M.; Correa, K.S. Survey and prediction of the ionospheric scintillation using data mining techniques. Space Weather 2010, 8, S06D09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taabu, S.D.; Dujanga, F.M.; Ssenyonga, T. Prediction of ionospheric scintillation using neutral network over East African region during ascending phase of sunspot cycle 24. Adv. Space Res. 2016, 57, 1570–1584. [Google Scholar]
- McGranaghan, R.M.L.; Mannucci, A.J.; Wilson, B.; Mattmann, C.A.; Chadwick, R. New capabilities for prediction of high-latitude ionospheric scintillation: A novel approach with machine learning. Space Weather 2018, 16, 1817–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, M.; Ratnam, D.V.; Raju, K.P.; Praharsha, D.S.; Saathvika, K. Ionospheric scintillation forecasting model based on NN-PSO technique. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2017, 362, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.A. The linear dependence of GHz scintillation on electron density observed in the equatorial anomaly. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, R.P.; Manju, G. Equatorial ionization anomaly crest magnitude and its implications on the nocturnal equatorial ionospheric plasma irregularity characteristics. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 4129–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, S.M.; Valladares, C.; Pradipta, R.; Pachero, E.; Condo, P. On the mutual relationship of the equatorial electrojet TEC and scintillation in the Peruvian sector. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
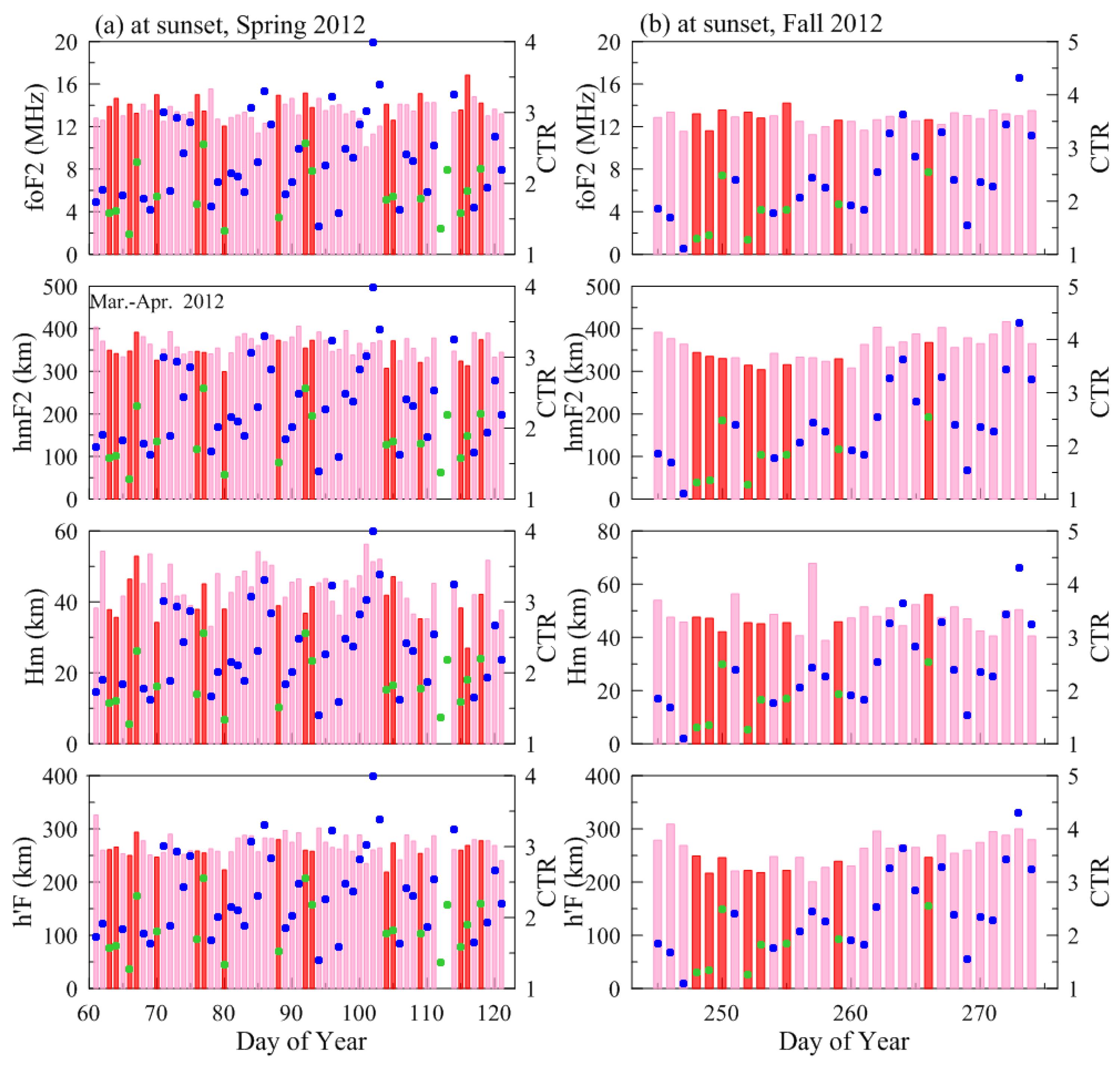
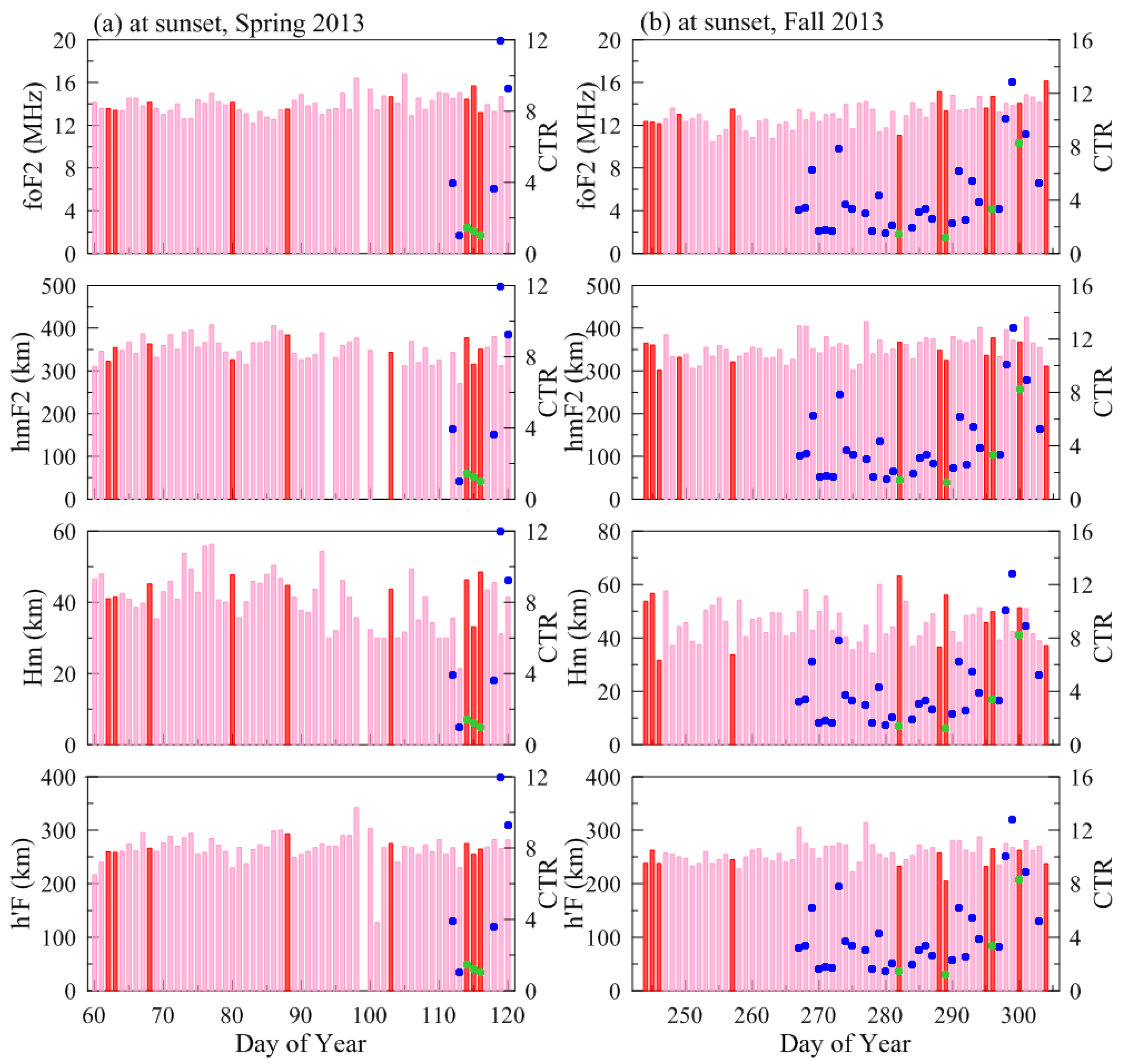
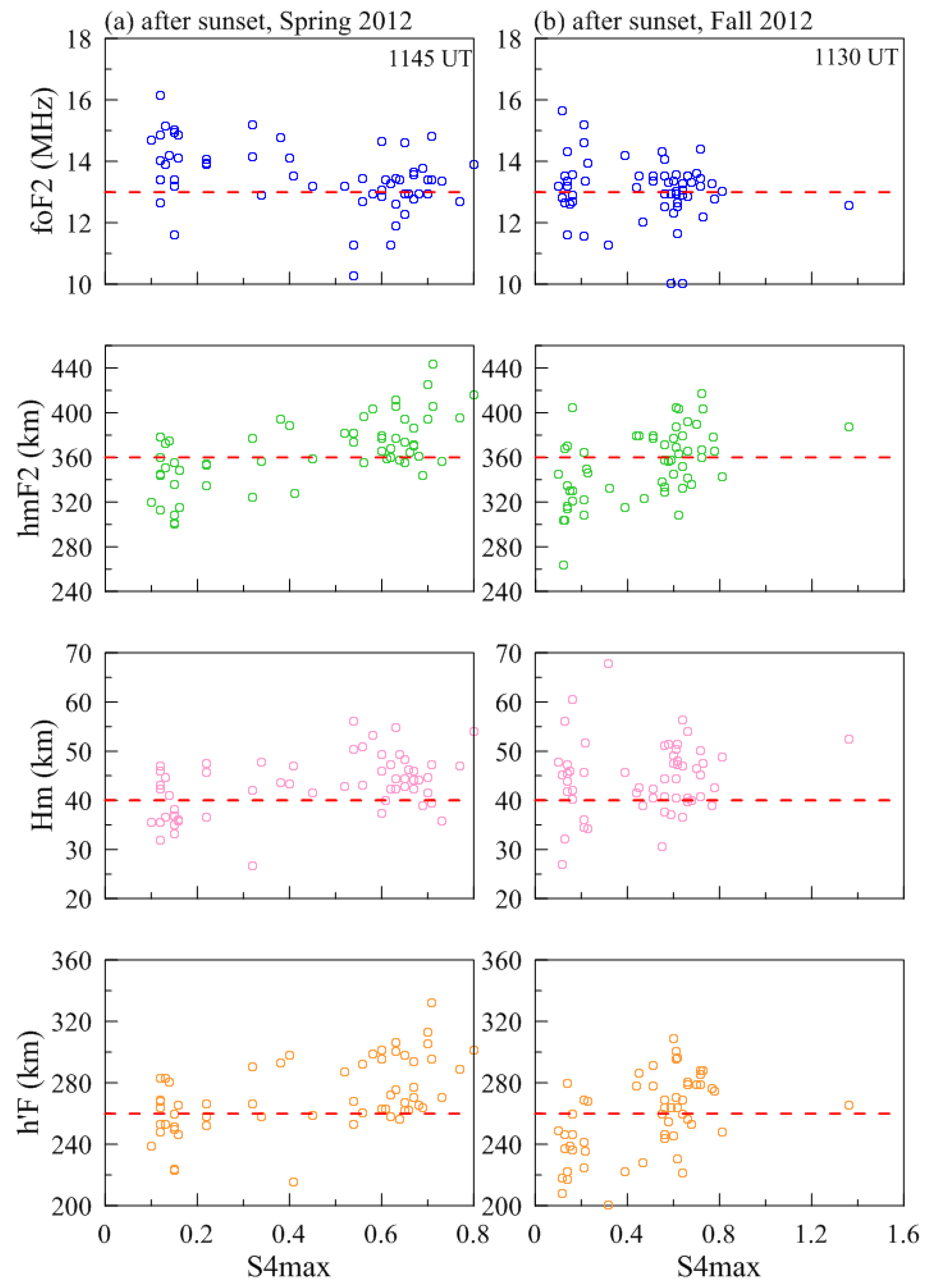
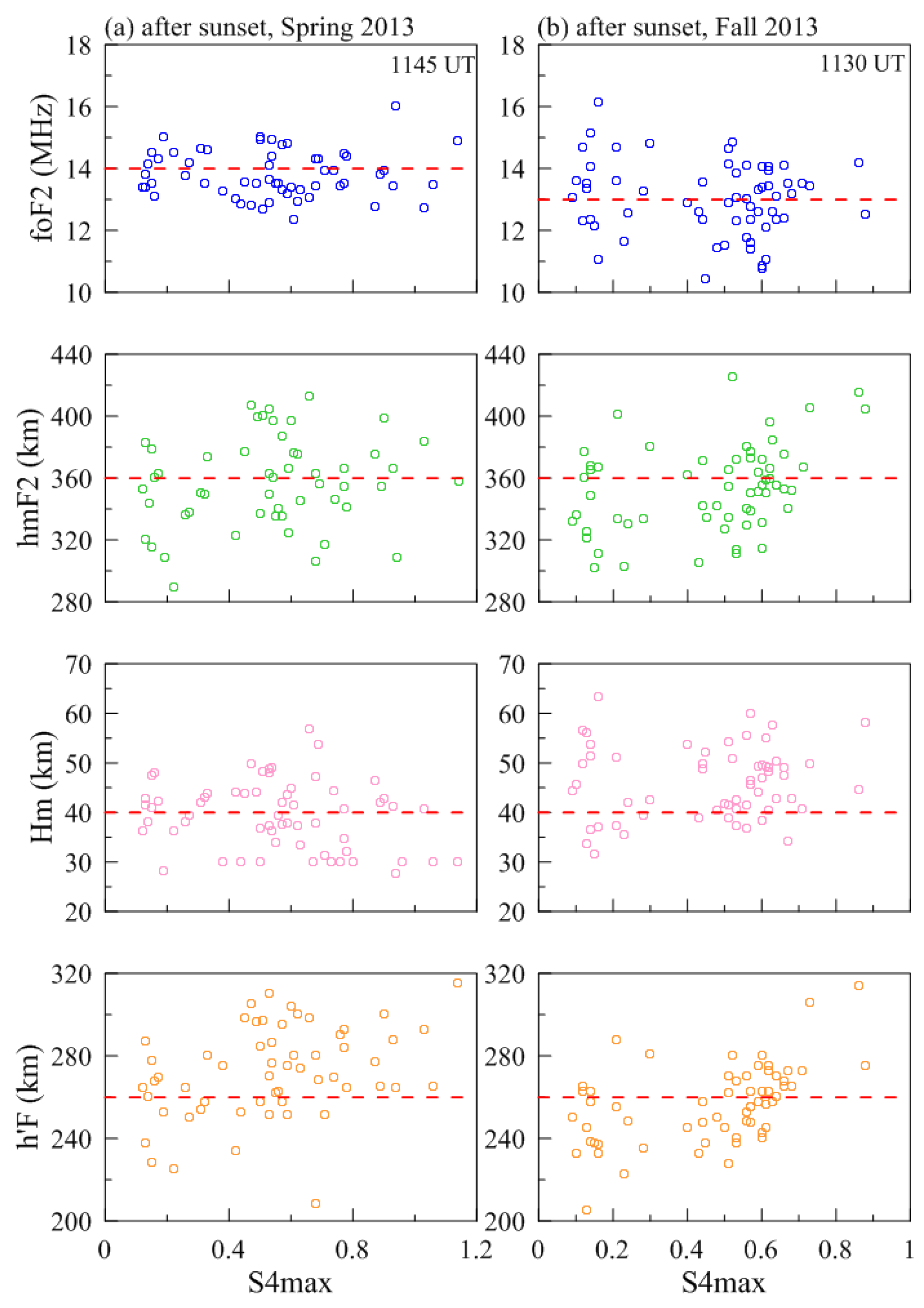
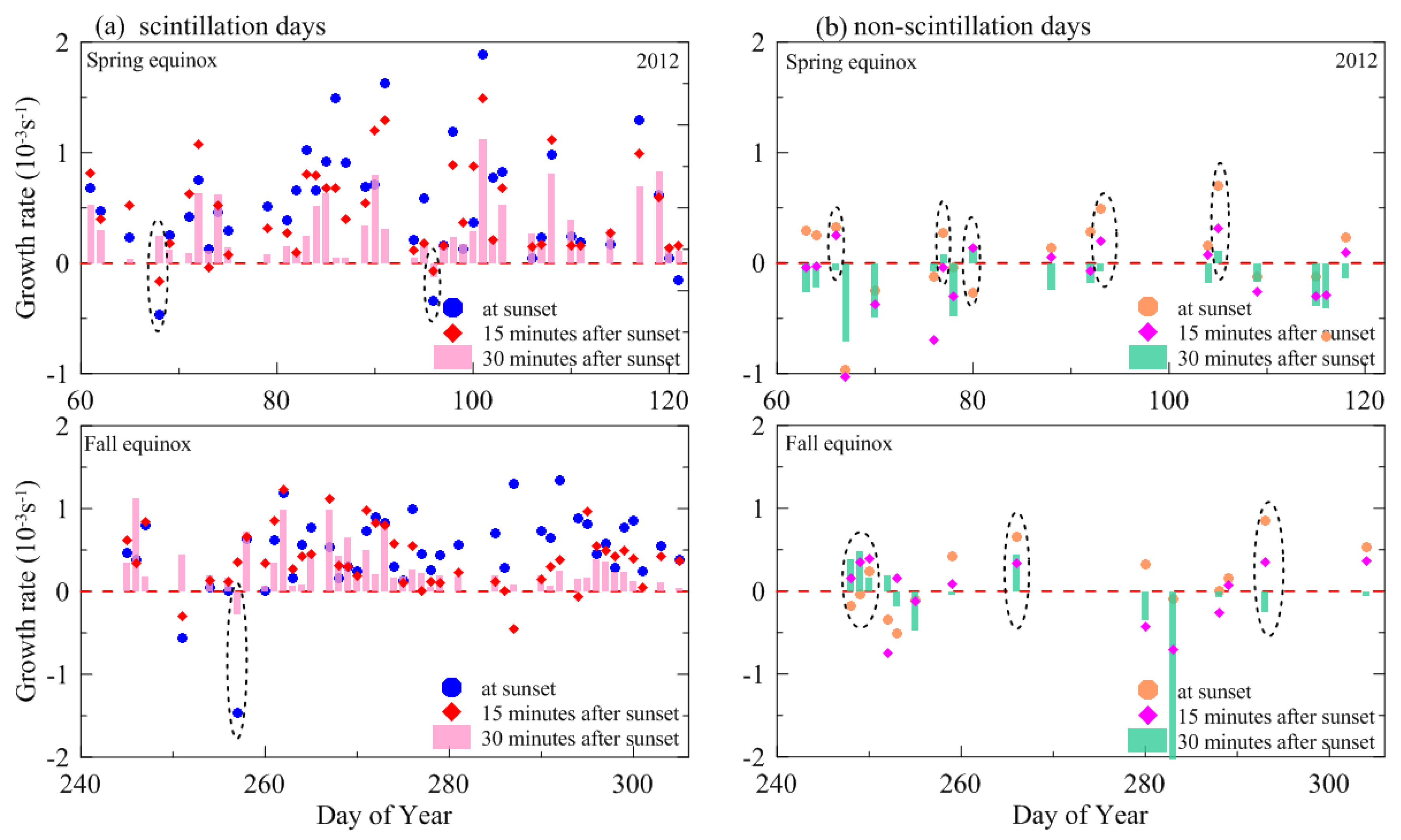

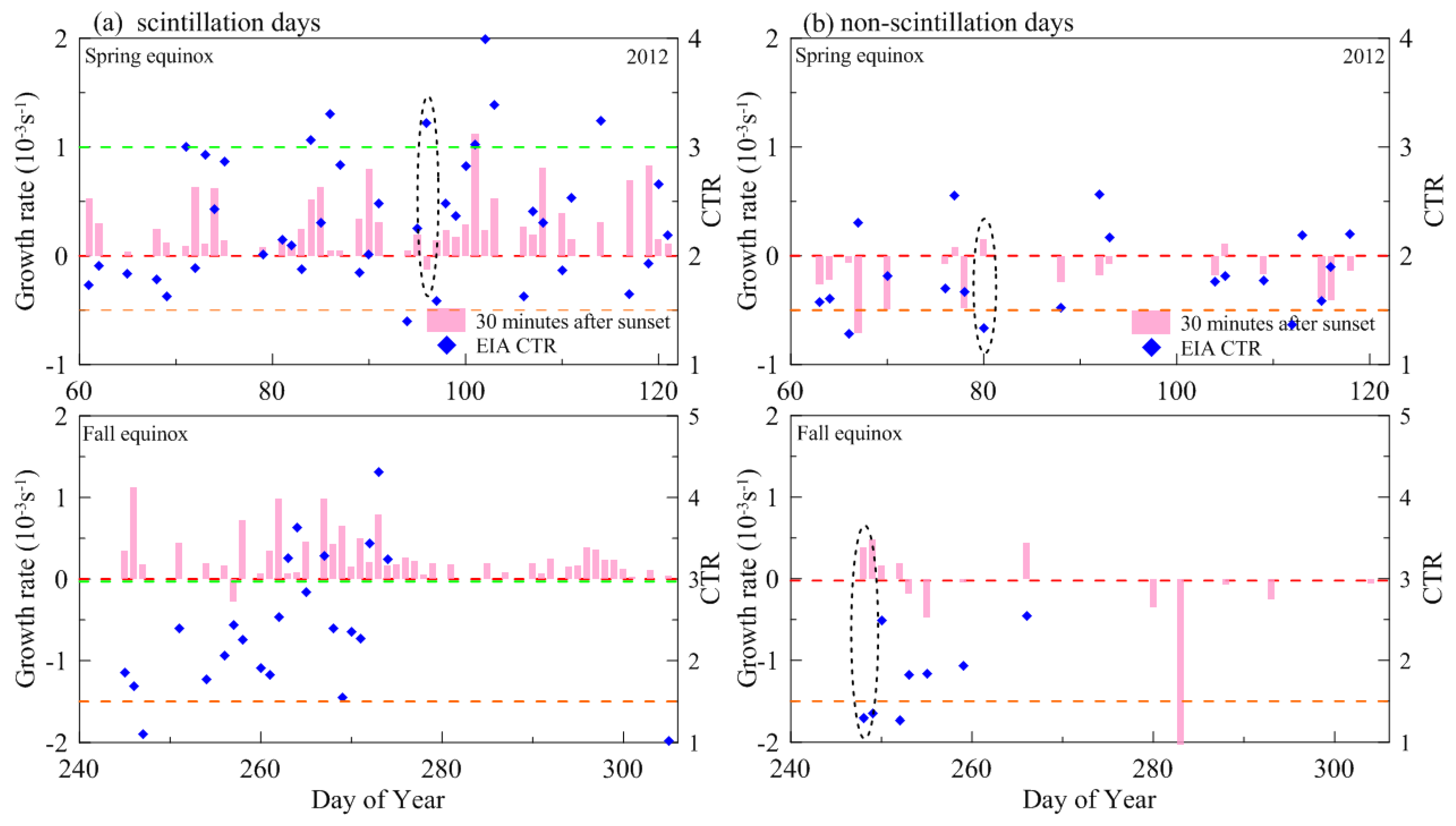
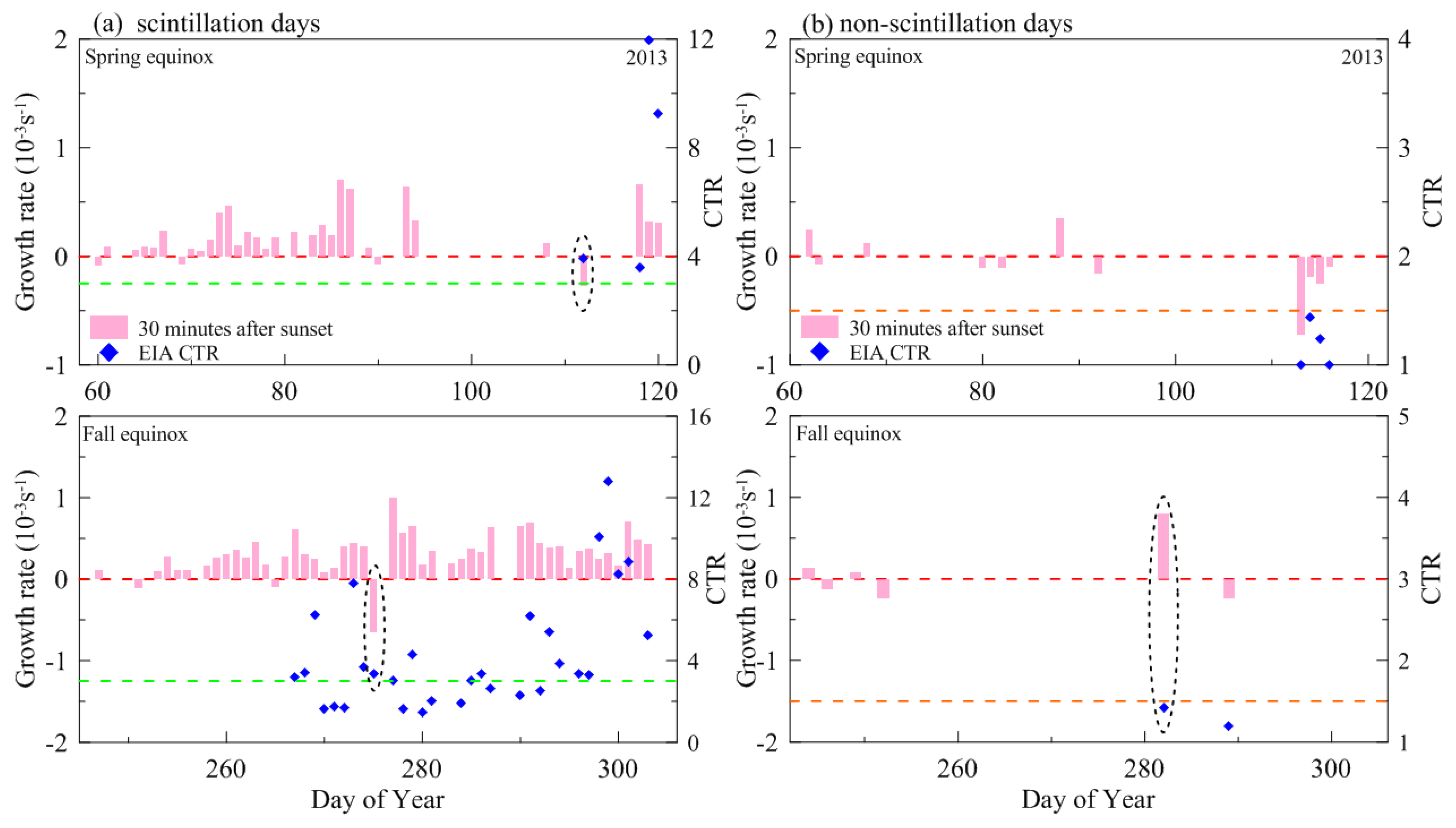
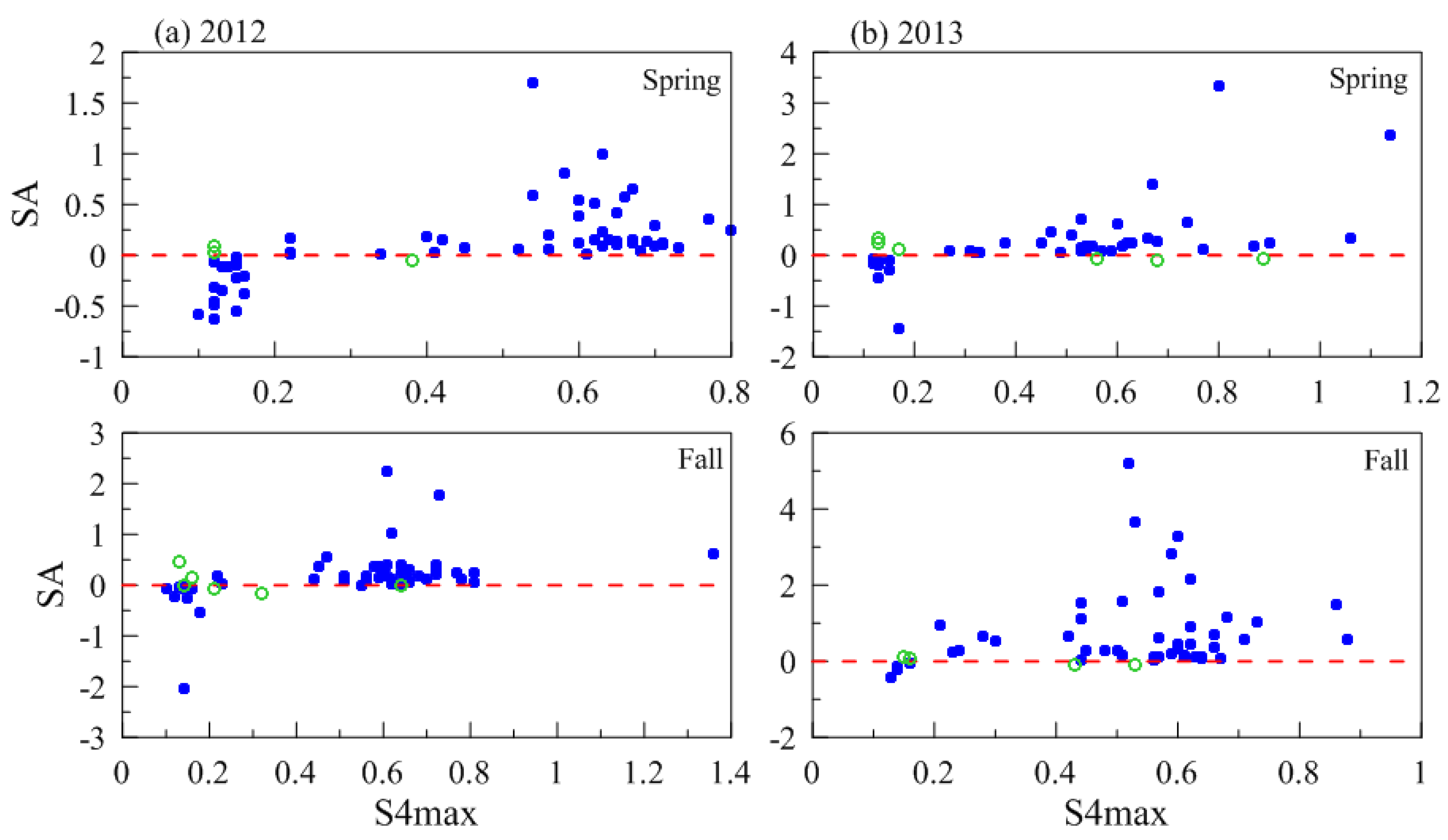
| Spring Equinox (March–April) | Fall Equinox (September–October) | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | |
| Scintillation days | 41 | 33 | 44 | 48 | 85 | 81 |
| Non-scintillation days | 18 | 11 | 13 | 6 | 31 | 17 |
| Total | 59 | 44 | 57 | 54 | 214 | |
| Spring Equinox | Fall Equinox | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | ||
| Scintillation days | True (γ > 0) | 39 | 29 | 42 | 45 | 81 | 74 |
| False (γ < 0) | 2 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 | |
| Non-scintillation days | True (γ < 0) | 13 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 19 | 11 |
| False (γ > 0) | 5 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 12 | 6 | |
| Accuracy rate (%) | 88.1 | 84.1 | 84.2 | 88.9 | 86.2 | 86.7 | |
| Spring Equinox | Fall Equinox | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | ||
| Scintillation days | True (SA > 0) | 40 | 30 | 41 | 46 | 82 | 76 |
| False (SA < 0) | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| Non-scintillation days | True (SA < 0) | 16 | 8 | 10 | 4 | 25 | 12 |
| False (SA > 0) | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 5 | |
| Accuracy rate (%) | 94.9 | 86.4 | 89.5 | 92.6 | 92.2 | 89.8 | |
| Spring Equinox | Fall Equinox | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | |
| Days of successful prediction using | 54 | 37 | 48 | 48 | 102 | 85 |
| Days of successful prediction using SA | 56 | 38 | 51 | 50 | 107 | 88 |
| Total data records | 59 | 44 | 57 | 54 | 116 | 98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, G.; Luo, W.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chang, S. Determining the Day-to-Day Occurrence of Low-Latitude Scintillation in Equinoxes at Sanya during High Solar Activities (2012–2013). Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081242
Jia G, Luo W, Yu X, Zhu Z, Chang S. Determining the Day-to-Day Occurrence of Low-Latitude Scintillation in Equinoxes at Sanya during High Solar Activities (2012–2013). Atmosphere. 2023; 14(8):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081242
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Guodong, Weihua Luo, Xiao Yu, Zhengping Zhu, and Shanshan Chang. 2023. "Determining the Day-to-Day Occurrence of Low-Latitude Scintillation in Equinoxes at Sanya during High Solar Activities (2012–2013)" Atmosphere 14, no. 8: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081242
APA StyleJia, G., Luo, W., Yu, X., Zhu, Z., & Chang, S. (2023). Determining the Day-to-Day Occurrence of Low-Latitude Scintillation in Equinoxes at Sanya during High Solar Activities (2012–2013). Atmosphere, 14(8), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081242








