Parameterization of Entrainment Rate for Cumulus Clouds with WRF Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simulation Scheme and Method
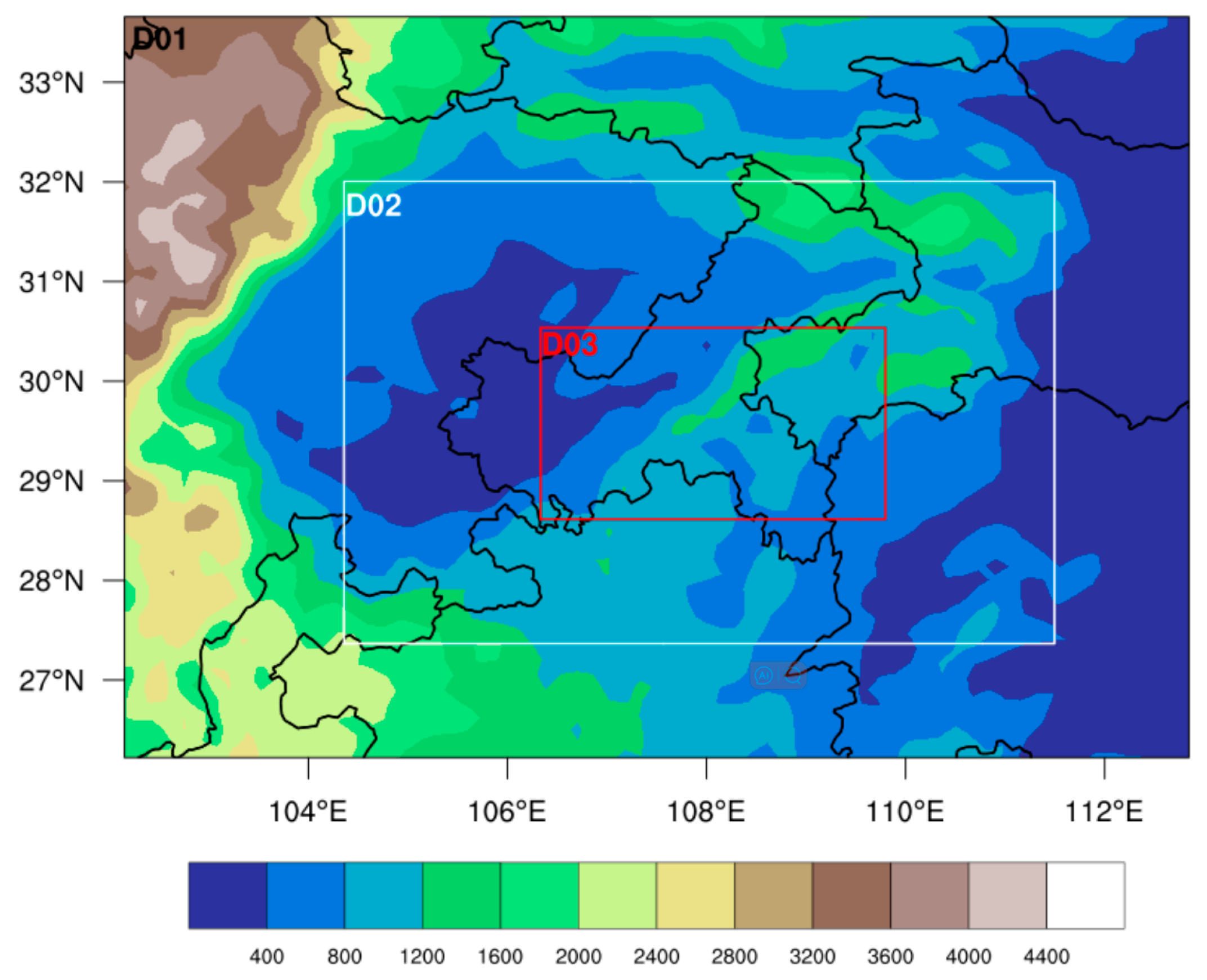
2.1. Simulation Scheme
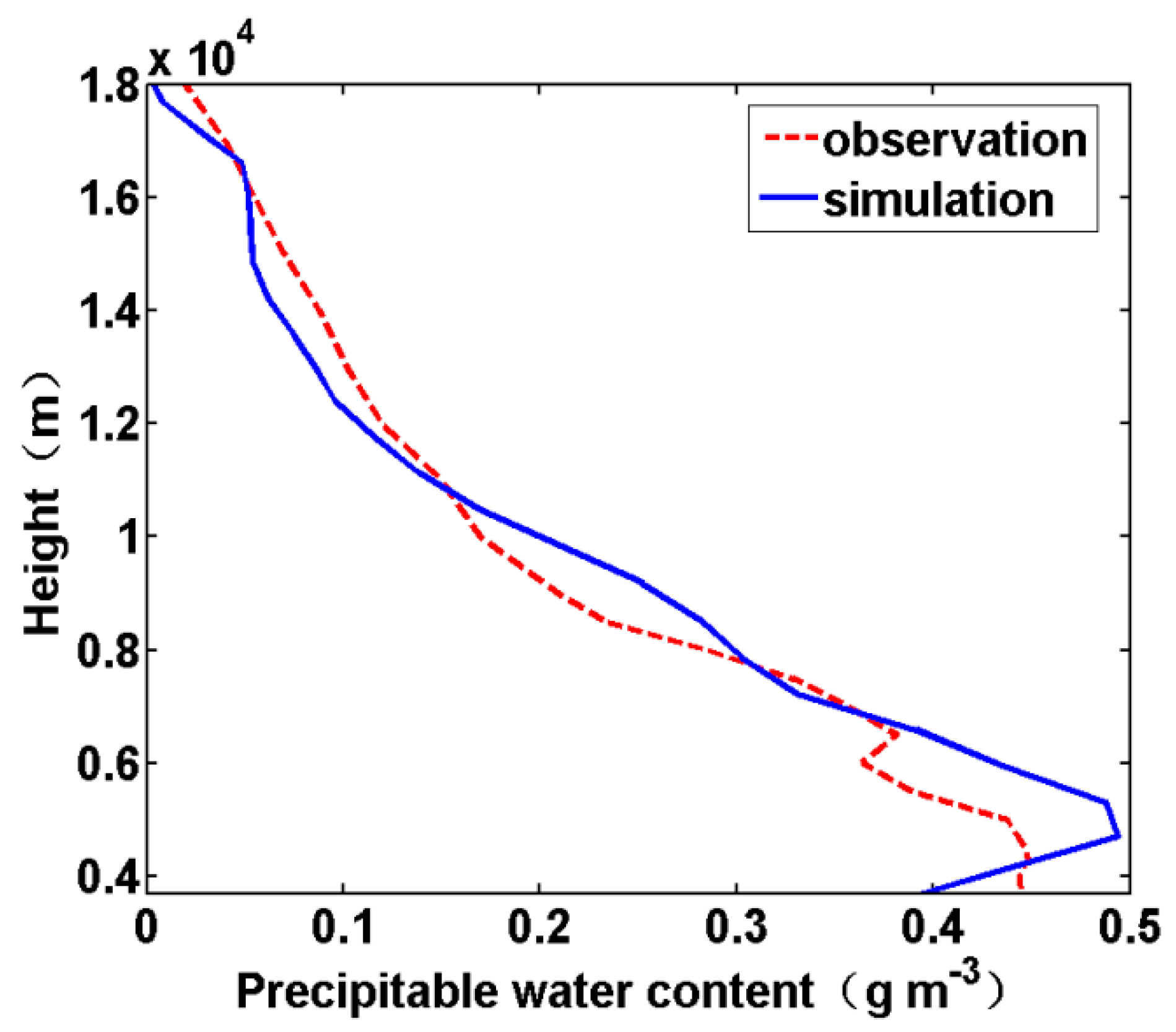
2.2. Method
3. Result
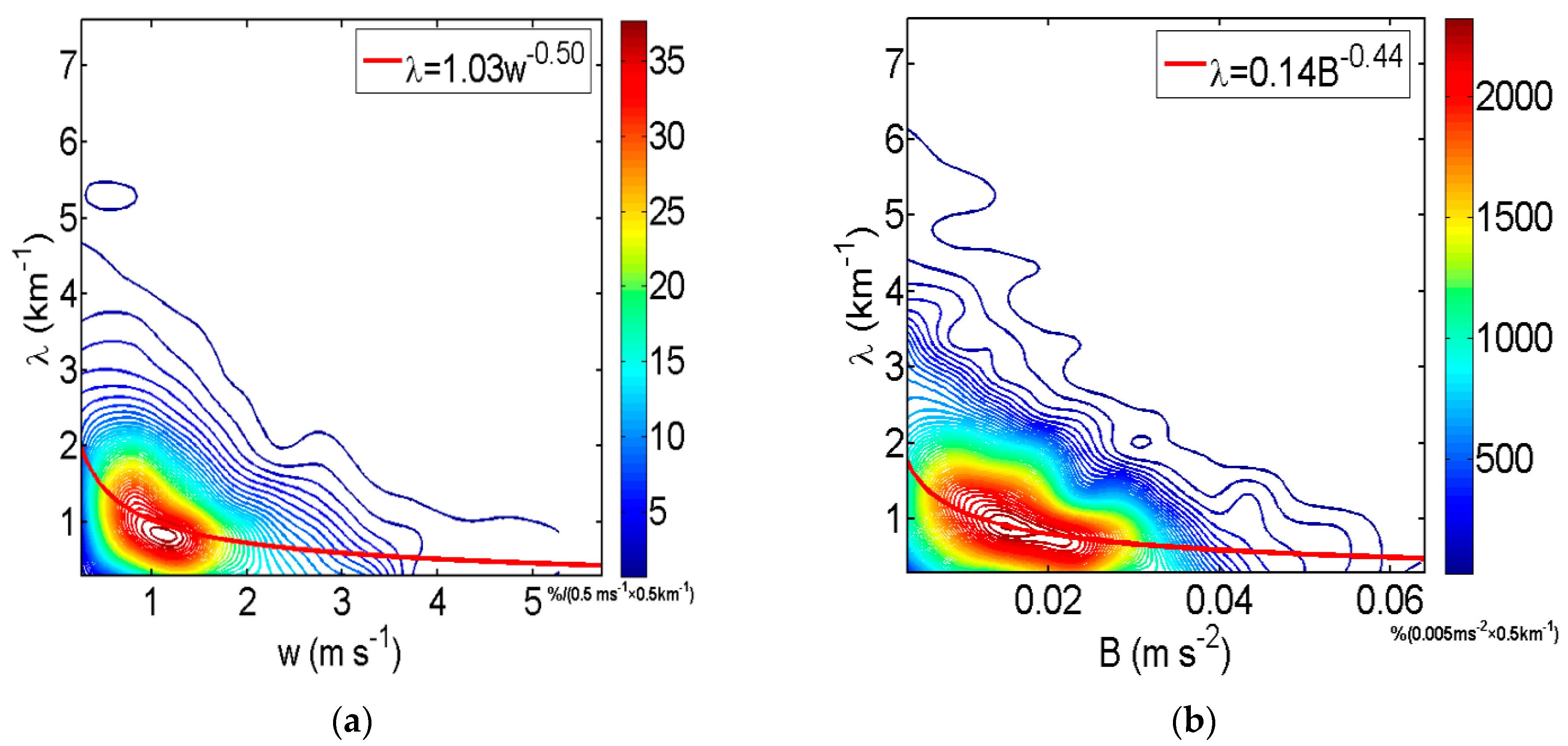
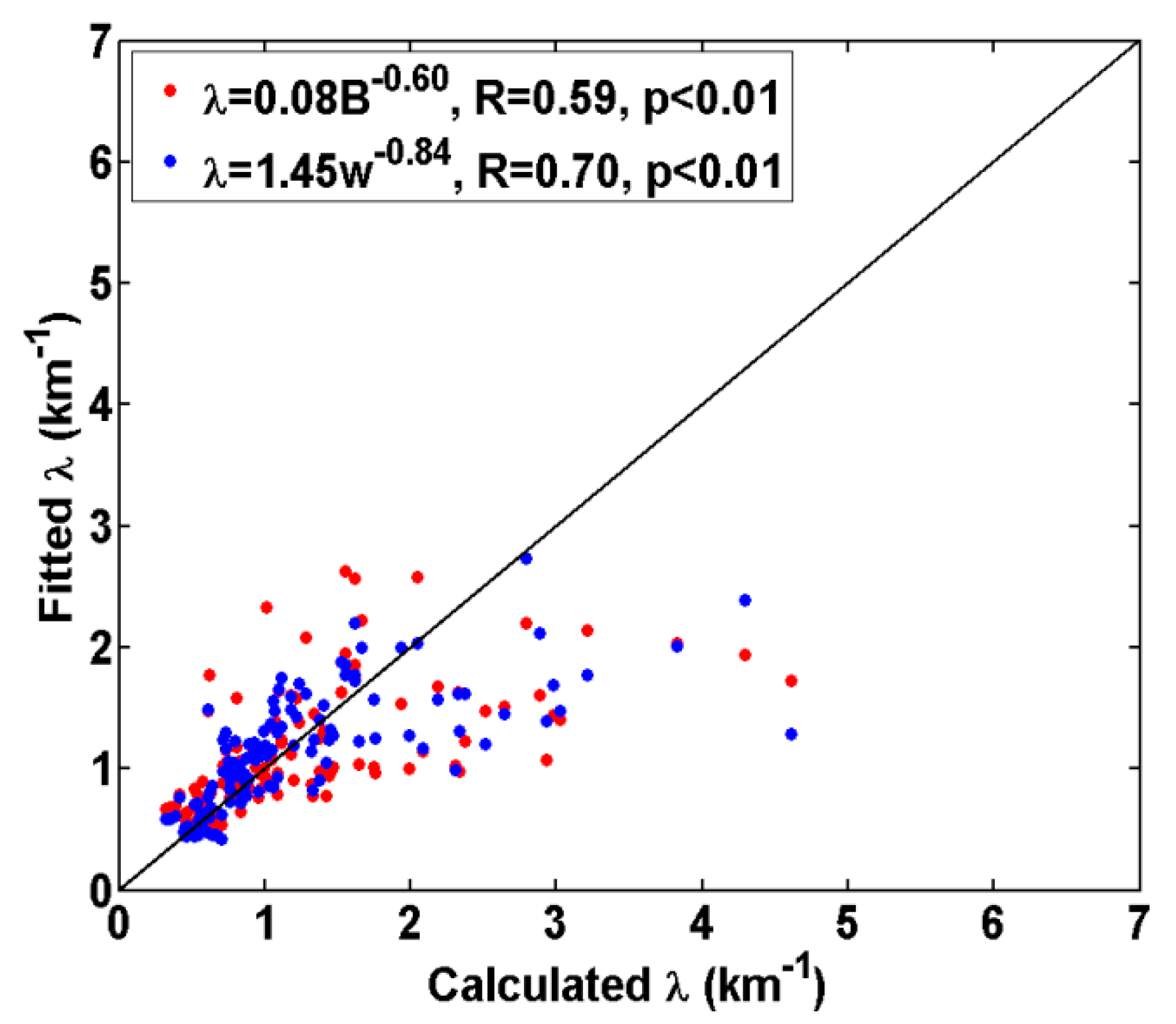
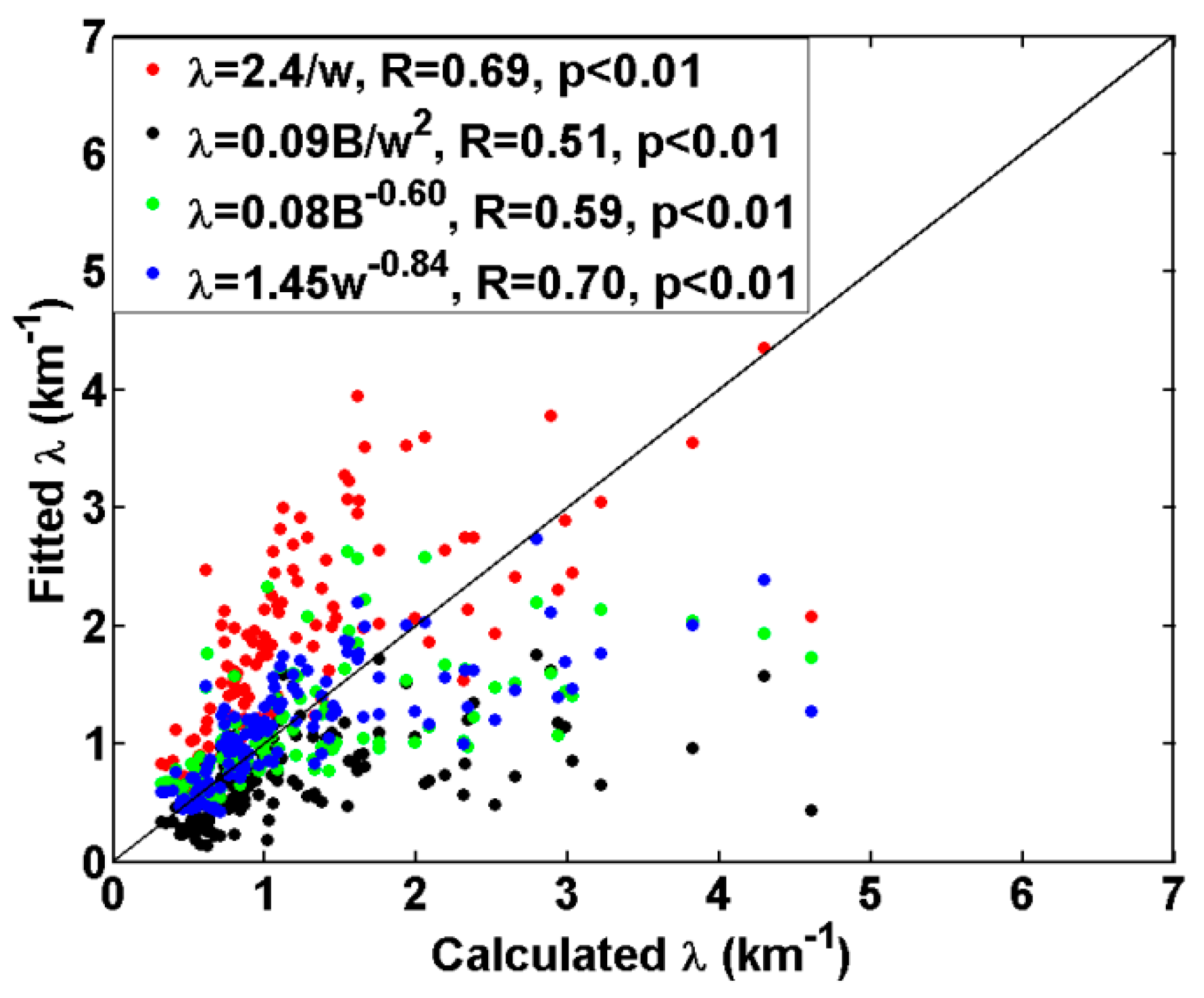
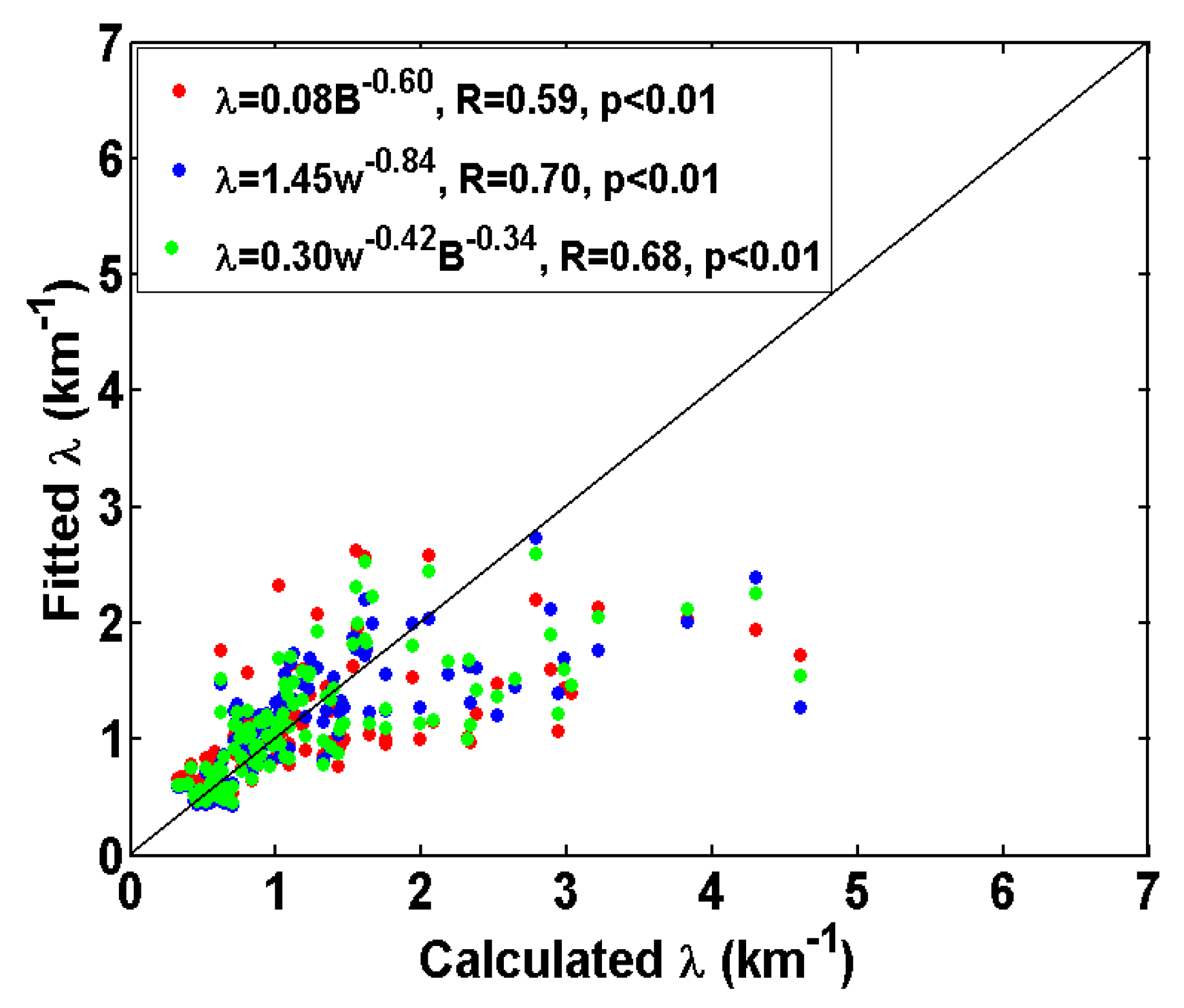
3.1. Fitting of λ Based on PDF
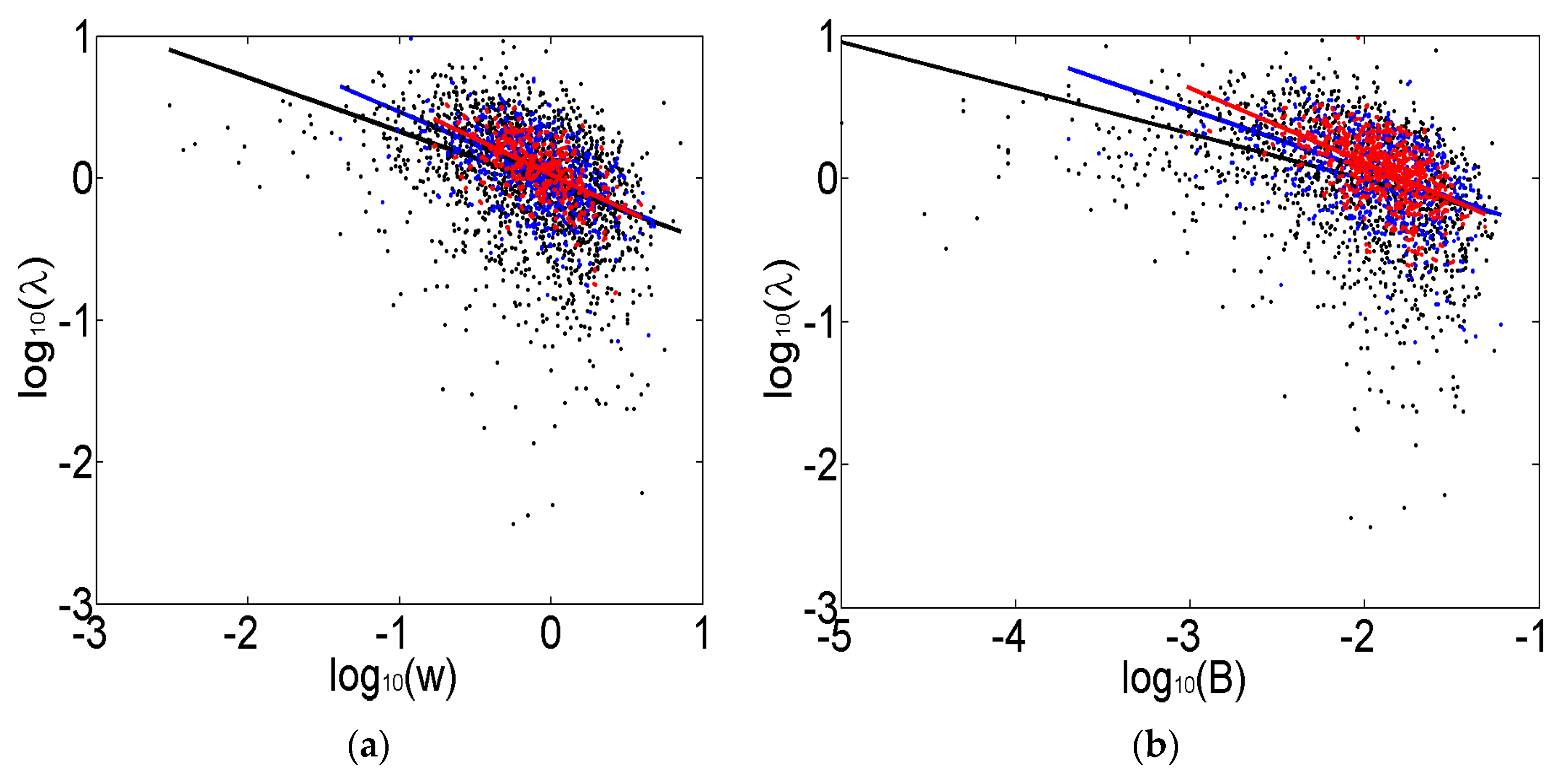
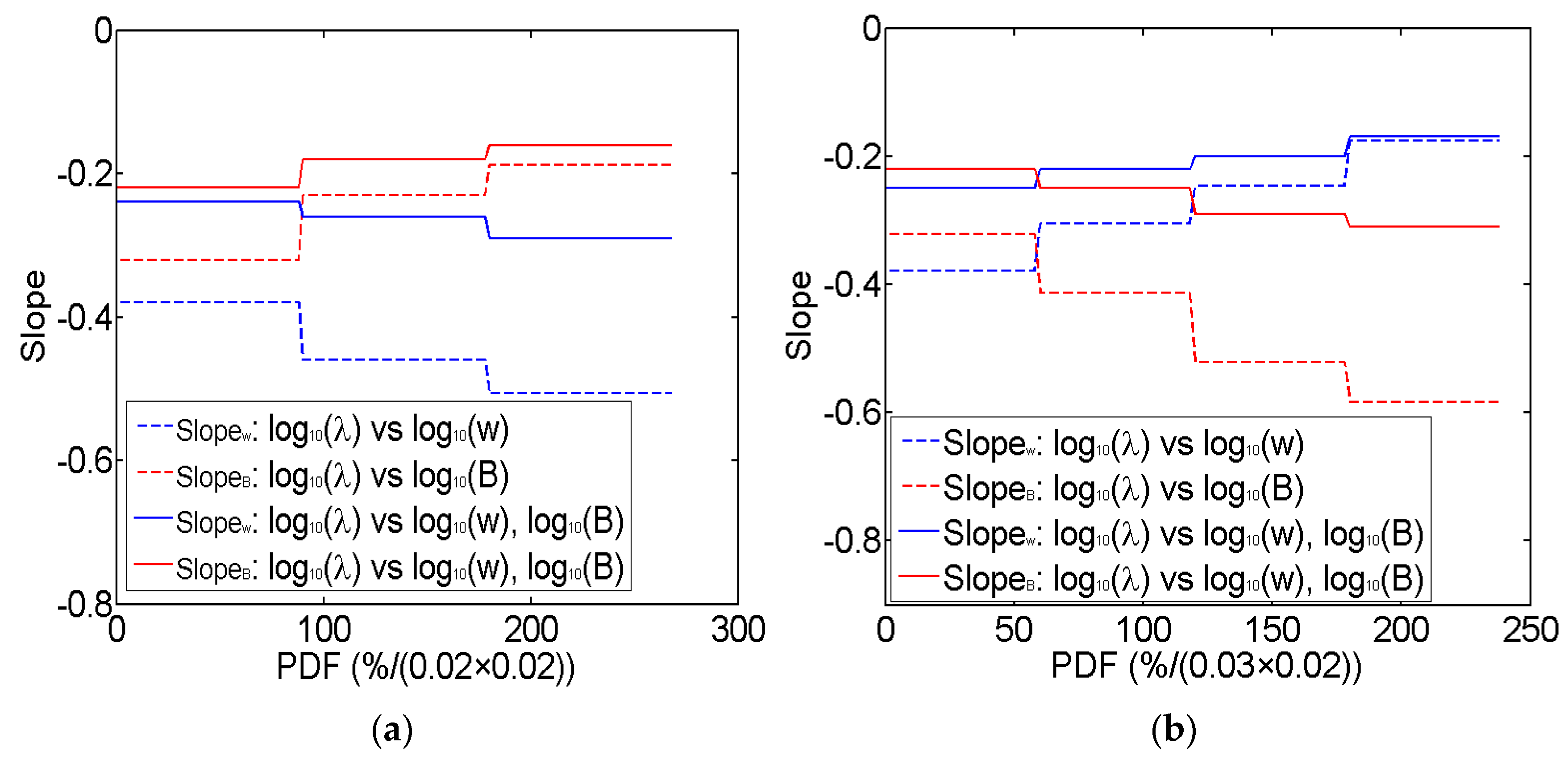
3.2. Variation in Fitting Parameters with PDF
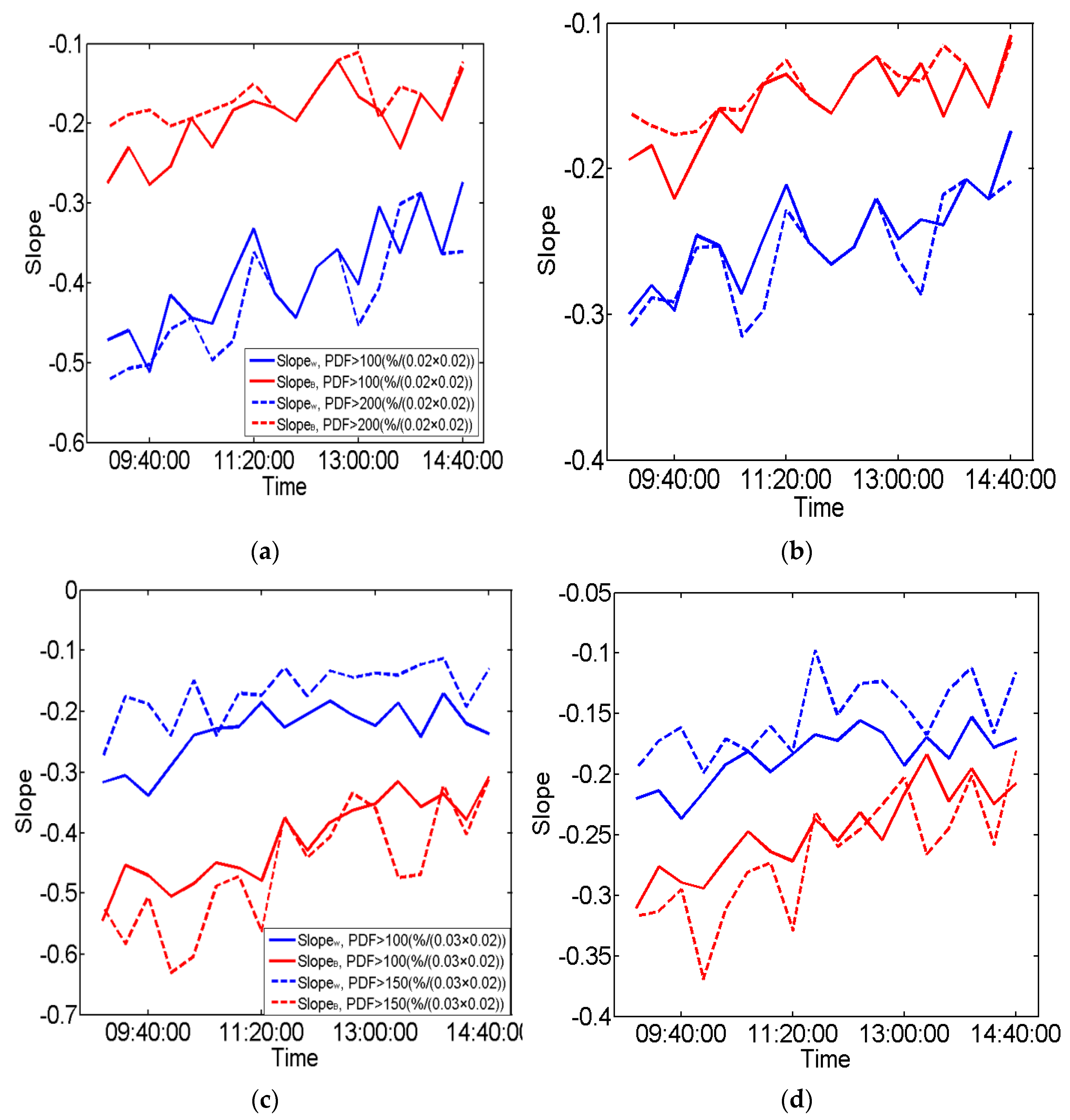
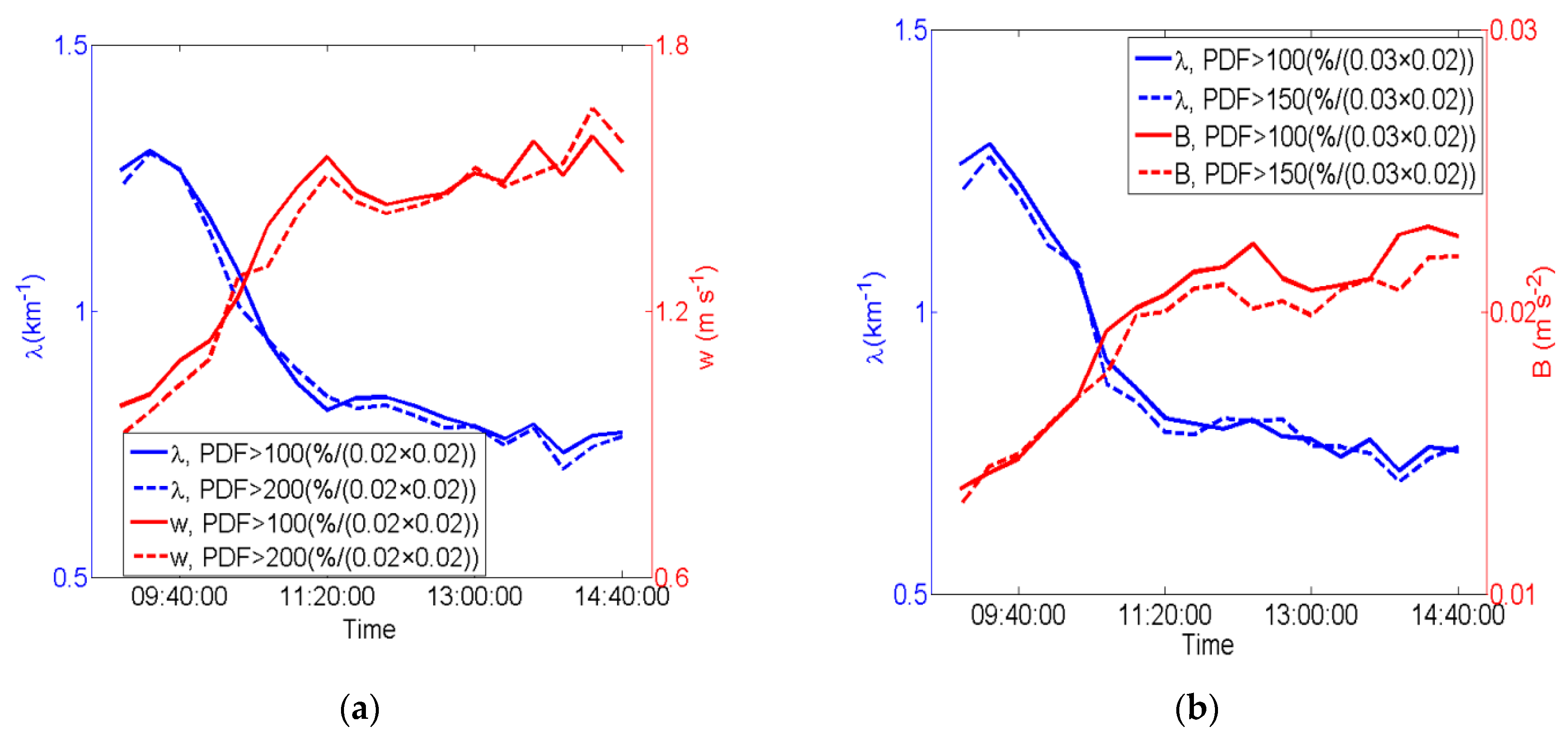
3.3. Variation in Fitting Parameters over Time
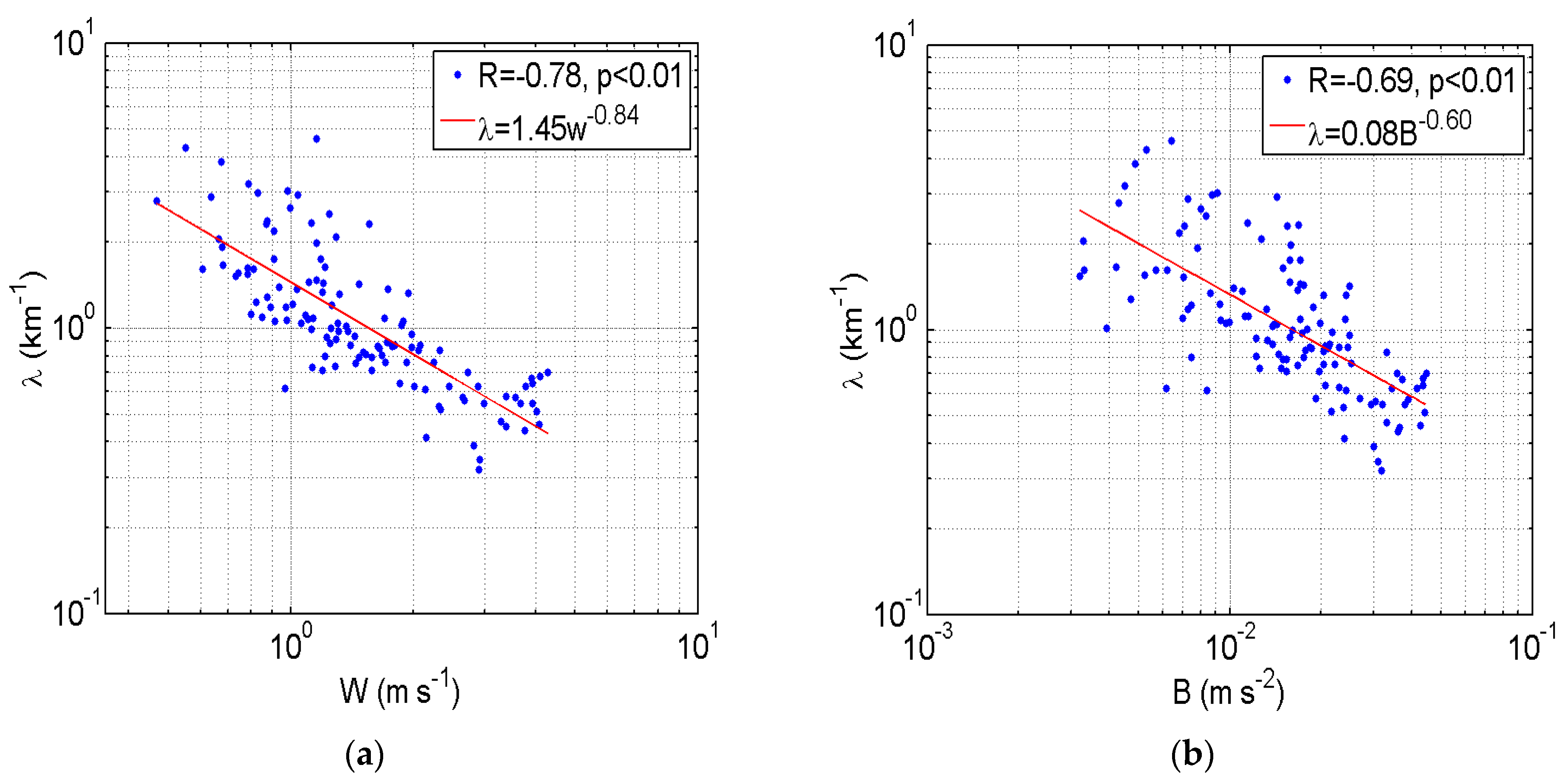
3.4. Fitting of λ Based on Cloud-Averaging
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Hamilton, K. Effect of convective entrainment/detrainment on the simulation of the tropical precipitation diurnal cycle. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 567–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Niu, S.; Vogelmann, A.-M. Empirical relationship between entrainment rate and microphysics in cumulus clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2333–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Mei, F.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Yan, S. Contrasting scale dependence of entrainment-mixing mechanisms in stratocumulus clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL086970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Yum, S.-S.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, L.; Desai, N.; Ma, Y.; Wu, S. Comprehensive quantification of height dependence of entrainment mixing between stratiform cloud top and environment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 11225–11241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.; Mei, F.; Fast, J.-D.; Pekour, M.-S.; Luo, S.; Xu, X.; He, X.; Li, J. Observational study of relationships between entrainment rate, homogeneity of mixing, and cloud droplet relative dispersion. Atmos. Res. 2023, 293, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Guo, X. Consideration of initial cloud droplet size distribution shapes in quantifying different entrainment-mixing mechanisms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.-S.; Del Genio, A.-D. Effects of cumulus entrainment and multiple cloud types on a January global climate model simulation. J. Clim. 1989, 2, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sun, C.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Q. Factors affecting entrainment rate in deep convective clouds and parameterizations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD034881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhou, X.; Endo, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y. Influences of an entrainment–mixing parameterization on numerical simulations of cumulus and stratocumulus clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 5459–5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Bian, J.; Gao, W.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Gao, S.; Yang, S.; Guo, X. Parameterizations of entrainment-mixing mechanisms and their effects on cloud droplet spectral width based on numerical simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.-S. The motion of buoyant elements in turbulent surroundings. J. Fluid Mech. 1963, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedtke, M.-A. Comprehensive Mass Flux Scheme for Cumulus Parameterization in Large-Scale Models. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 1779–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebesma, A.-P.; Cuijpers, J.-W.-M. Evaluation of parametric assumptions for shallow cumulus convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 650–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, P.; Köhler, M.; Jung, T.; Doblas-Reyes, F.; Leutbecher, M.; Rodwell, M.-J.; Vitart, F.; Balsamo, G. Advances in simulating atmospheric variability with the ECMWF model: From synoptic to decadal time-scales. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2008, 134, 1337–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretherton, C.-S.; McCaa, J.-R.; Grenier, H. A new parameterization for shallow cumulus convection and its application to marine subtropical cloud-topped boundary layers. Part I: Description and 1-D results. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 864–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rooy, W.-C.; Siebesma, A.-P. A simple parameterization for detrainment in shallow cumulus. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 560–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stirling, A.-J.; Stratto, R.-A. Entrainment processes in the diurnal cycle of deep convection over land. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2012, 138, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bera, S.; Prabha, T.-V. Parameterization of Entrainment Rate and Mass Flux in Continental Cumulus Clouds: Inference from Large Eddy Simulation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 13127–13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neggers, R.-A.-J.; Siebesma, A.-P.; Jonker, H.-J.-J. A multiparcel model for shallow cumulus convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 1655–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, D. Estimation of entrainment rate in simple models of convective clouds. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2001, 127, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Genio, A.-D.; Wu, J. The role of entrainment in the diurnal cycle of continental convection. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2722–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Salzen, K.; McFarlane, N.A. Parameterization of the bulk effects of lateral and cloud-top entrainment in transient shallow cumulus clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 9, 405–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C. Some bulk properties of cumulus ensembles simulated by a cloud-resolving model. Part II: Entrainment profiles. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 3736–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawe, J.-T.; Austin, P.-H. Direct entrainment and detrainment rate distributions of individual shallow cumulus clouds in an LES. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7795–7811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, X.; Zeng, X.; Mitovski, T. Estimation of convective entrainment properties from a cloud-resolving model simulation during TWP-ICE. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 47, 2177–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wu, X.; Endo, S.; Cao, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, X. Improving Parameterization of Entrainment Rate for Shallow Convection with Aircraft Measurements and Large-Eddy Simulation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romps, D.-M.; Kuang, Z. Nature versus nurture in shallow convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 1655–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.W.; Niu, S.J. The formation and precipitation mechanism of two ordered patterns of embedded convection in stratiform cloud. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, N.-K.; Polcher, J.; Bastin, S.; Pennel, R.; Fita, L. Assessment of the spatio-temporal variability of the added value on precipitation of convection-permitting simulation over the Iberian Peninsula using the RegIPSL regional earth system model. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 59, 471–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, H.-E.; Frick, G.-M.; Jensen, J.-B.; Hudson, J.-G. Entrainment, mixing, and microphysics in trade-wind cumulus. J. Meteor. Res. Jpn. 2008, 86, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Niu, S.; Vogelmann, A.-M. Observed impacts of vertical velocity on cloud microphysics and implications for aerosol indirect effects. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L21808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lu, C.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y. An observational study of entrainment rate in deep convection. Atmosphere 2015, 9, 1362–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gharaati, M.; Xiao, S.; Wei, N.J.; Martínez-Tossas, L.-A.; Dabiri, J.-O.; Yang, D. Large-eddy simulation of helical-and straight-bladed vertical-axis wind turbines in boundary layer turbulence. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy. 2022, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Lin, H.; Zhu, J.; Wei, F. Parameterization of Entrainment Rate for Cumulus Clouds with WRF Simulation. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081285
Guo X, Lin H, Zhu J, Wei F. Parameterization of Entrainment Rate for Cumulus Clouds with WRF Simulation. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(8):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081285
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiaohao, Huijuan Lin, Jinyao Zhu, and Fenfen Wei. 2023. "Parameterization of Entrainment Rate for Cumulus Clouds with WRF Simulation" Atmosphere 14, no. 8: 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081285
APA StyleGuo, X., Lin, H., Zhu, J., & Wei, F. (2023). Parameterization of Entrainment Rate for Cumulus Clouds with WRF Simulation. Atmosphere, 14(8), 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081285




