Diurnal Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events under Different Synoptic Circulation Patterns in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in Summer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
3. Diurnal Variation Features of Heavy Precipitation under Six Synoptic Circulation Types
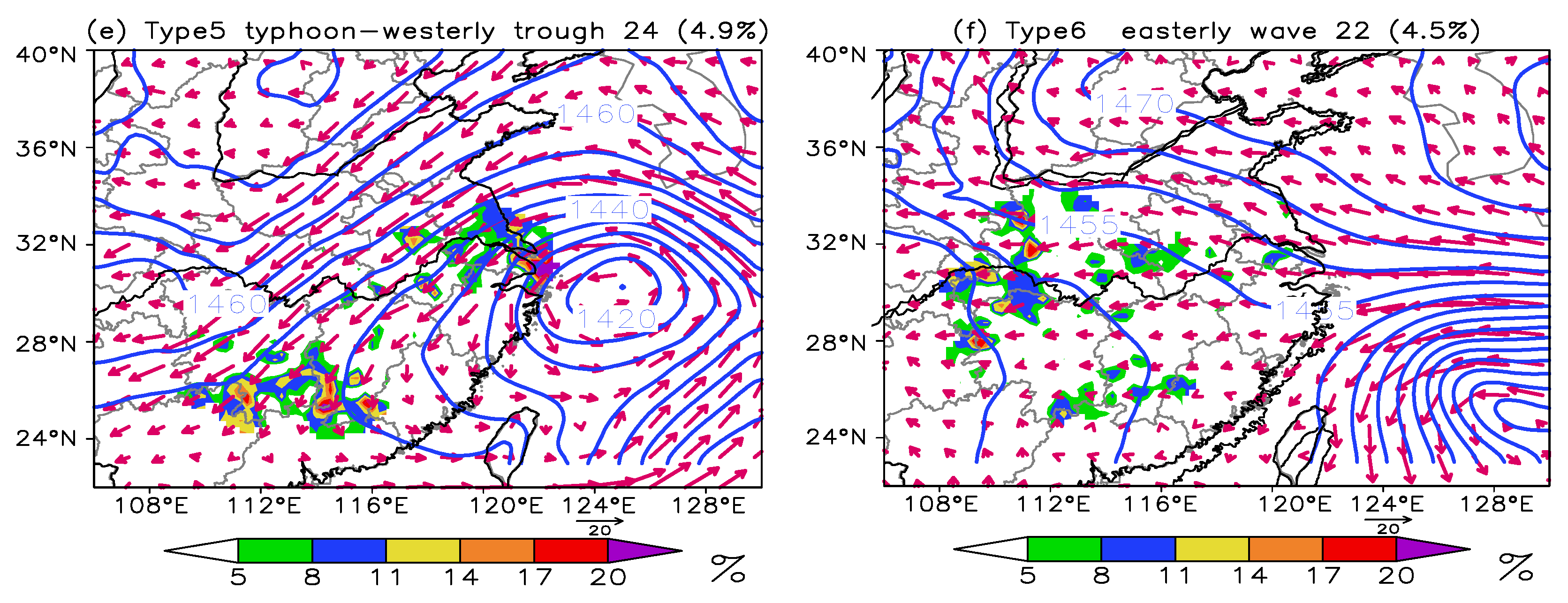
3.1. Objective Circulation Weather Classification of Rainstorm Days
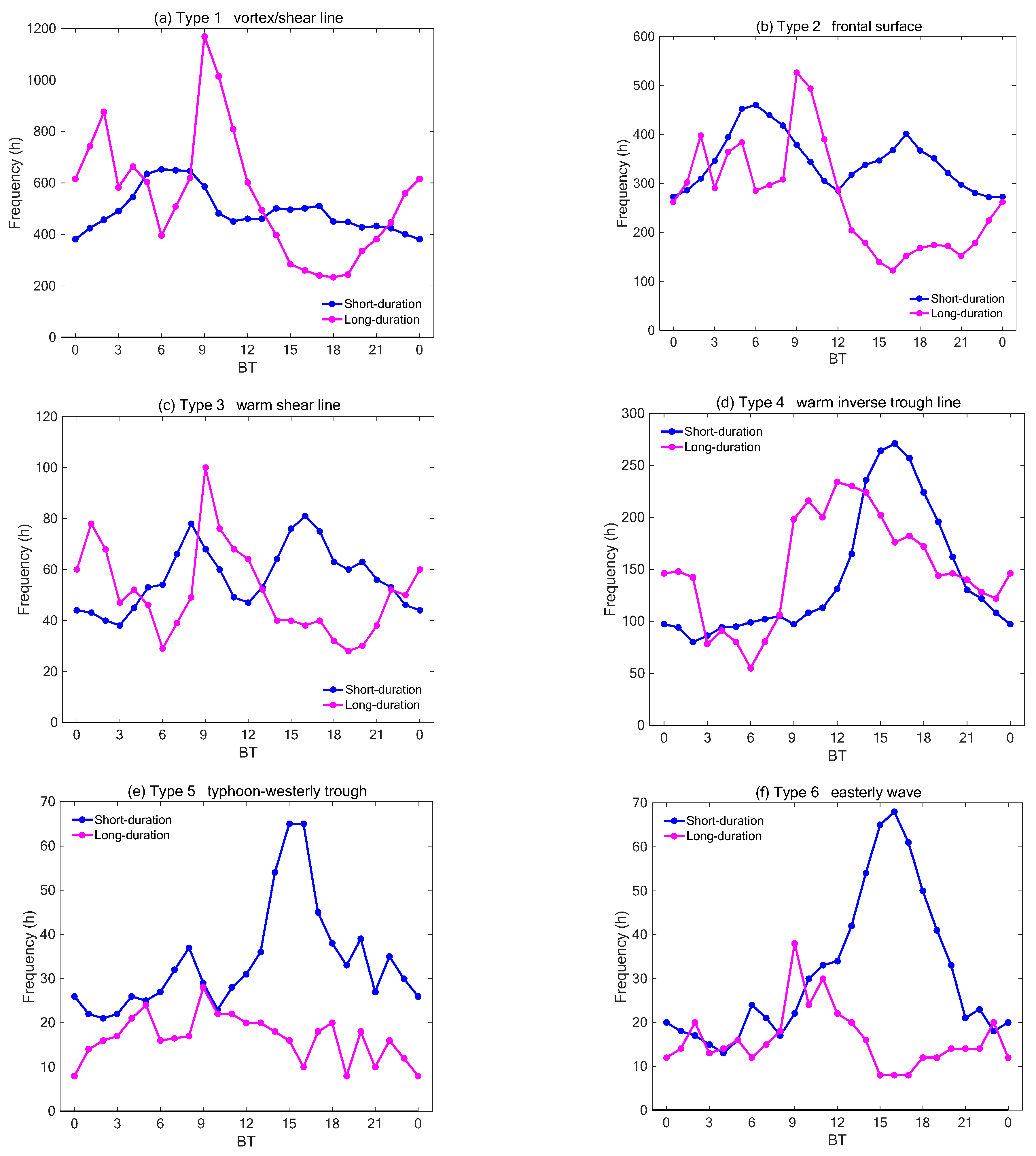
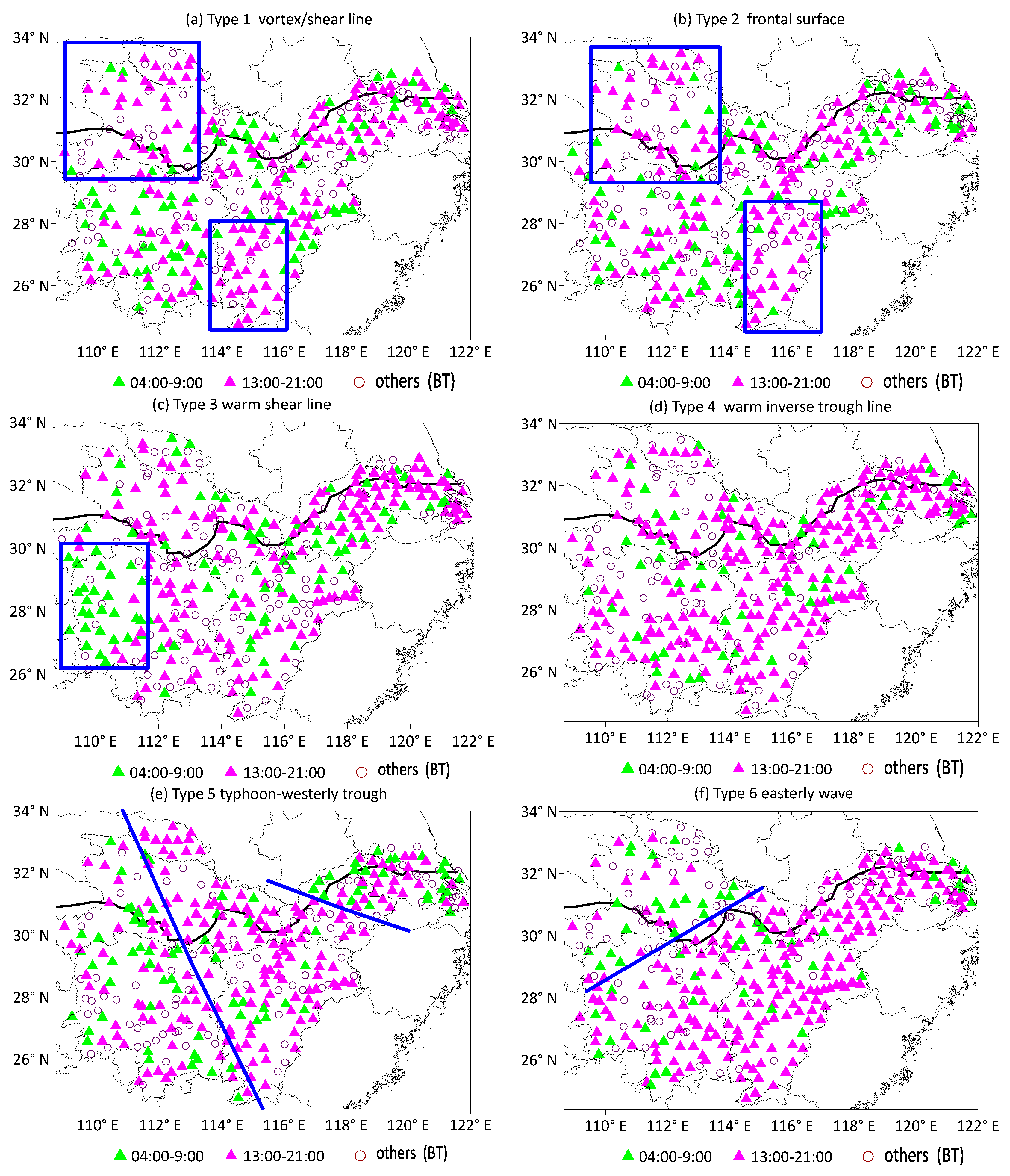
3.2. Differences in Starting Time and Duration of Heavy Precipitation
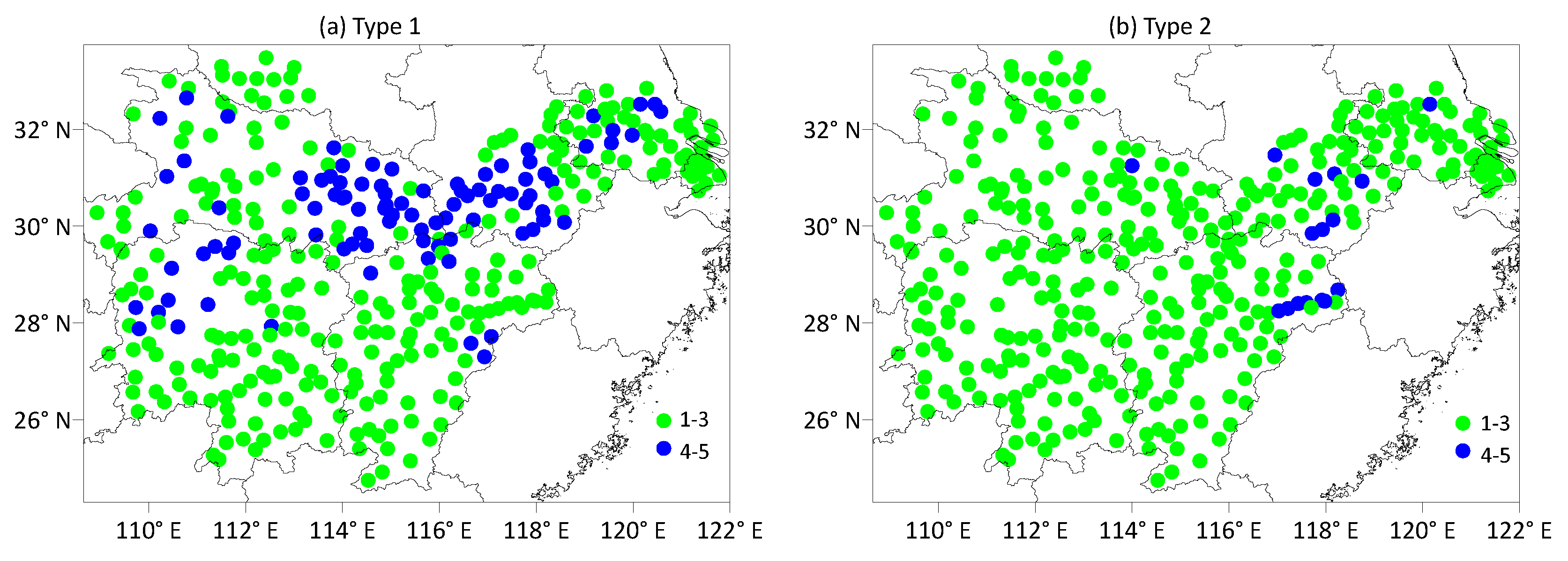
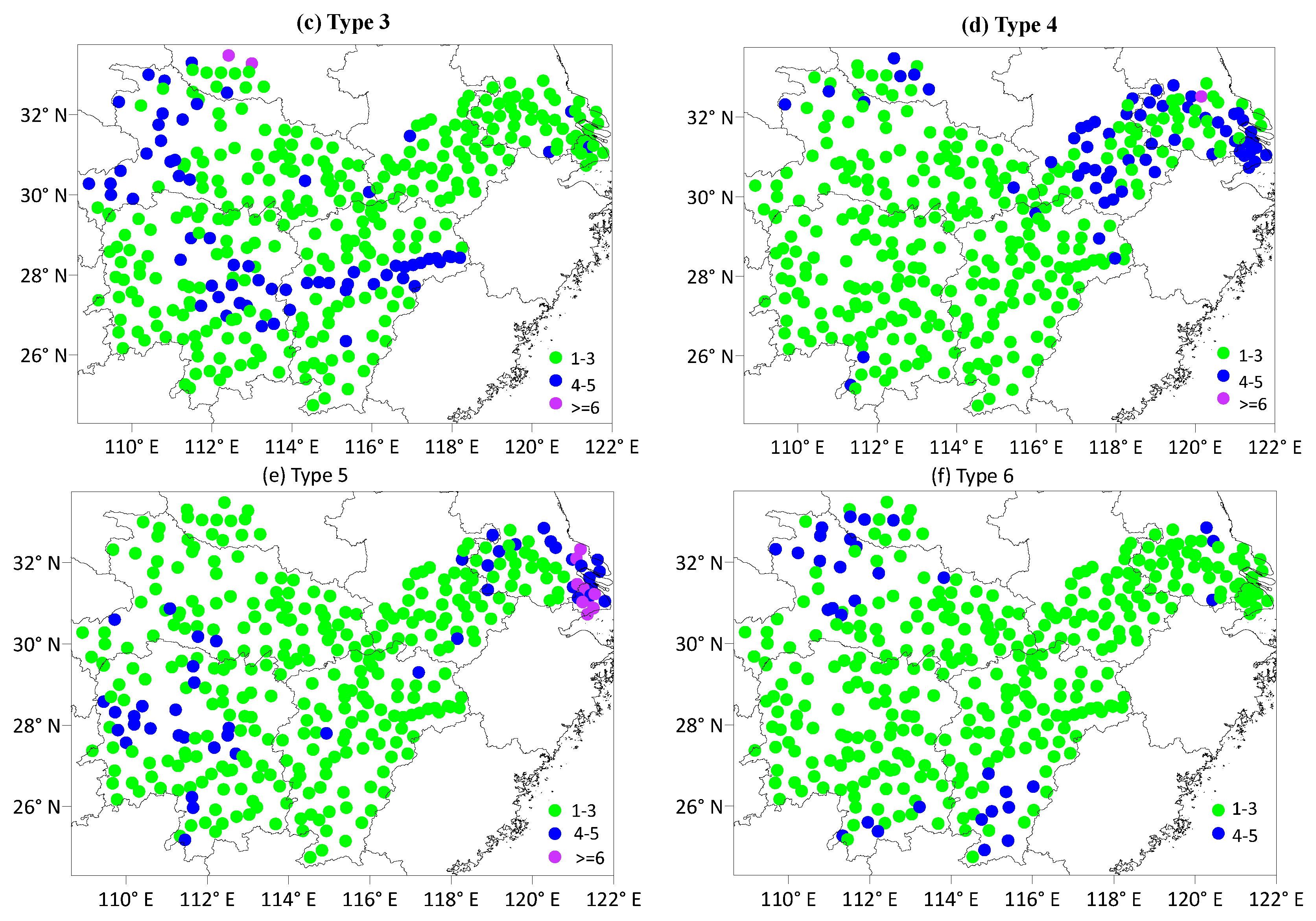
3.3. Distribution Characteristics of Averaged Duration of Heavy Precipitation
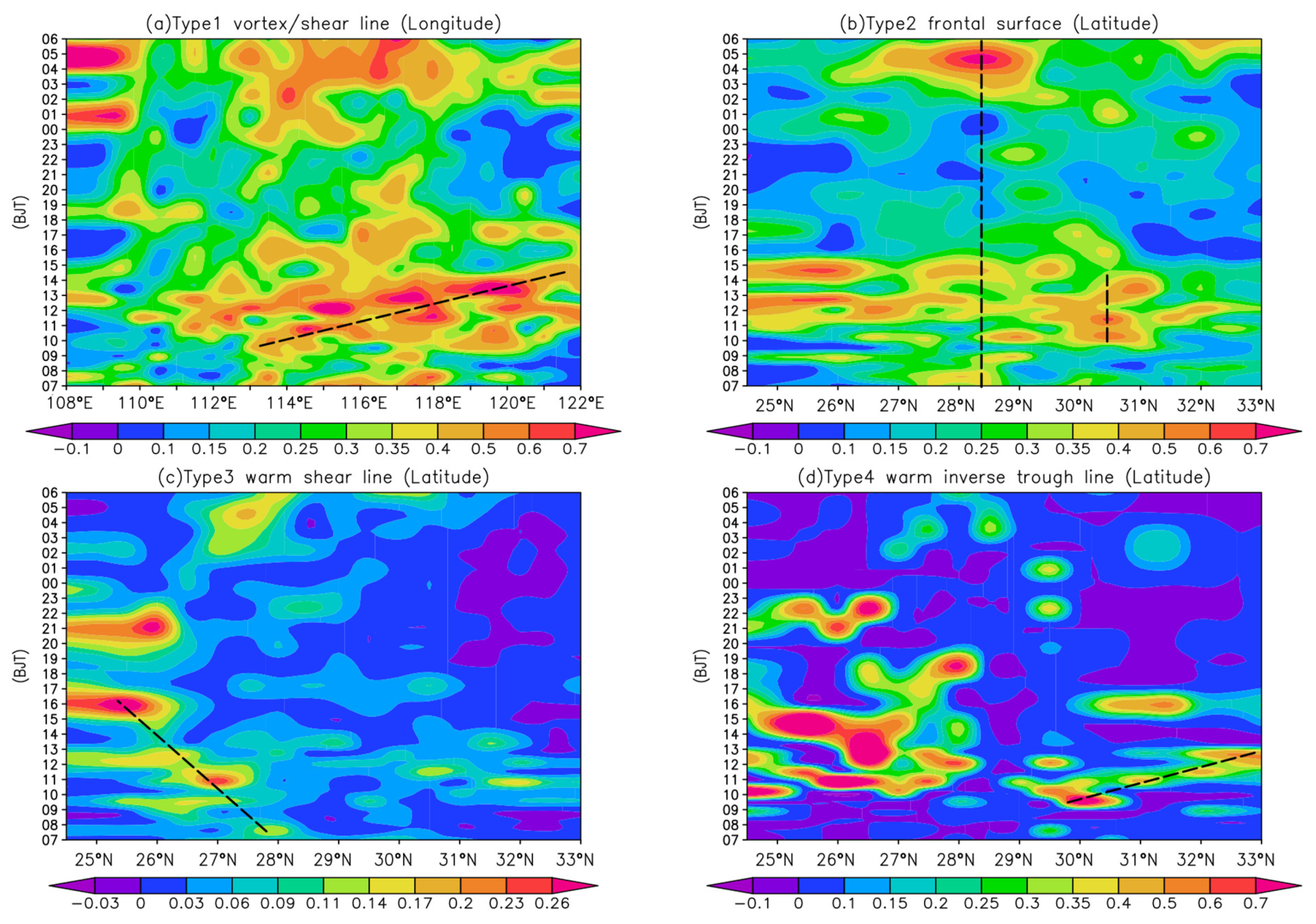
3.4. Propagation Characteristics of Diurnal Variations of Heavy Precipitation
3.5. Temporal Phase Differences of Maximum Precipitation Amount
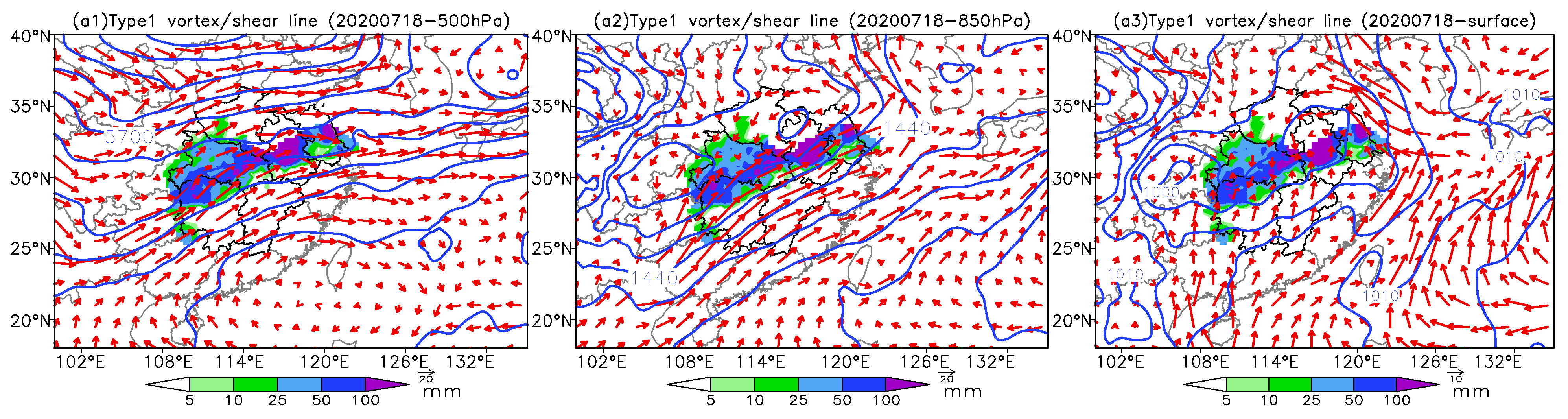
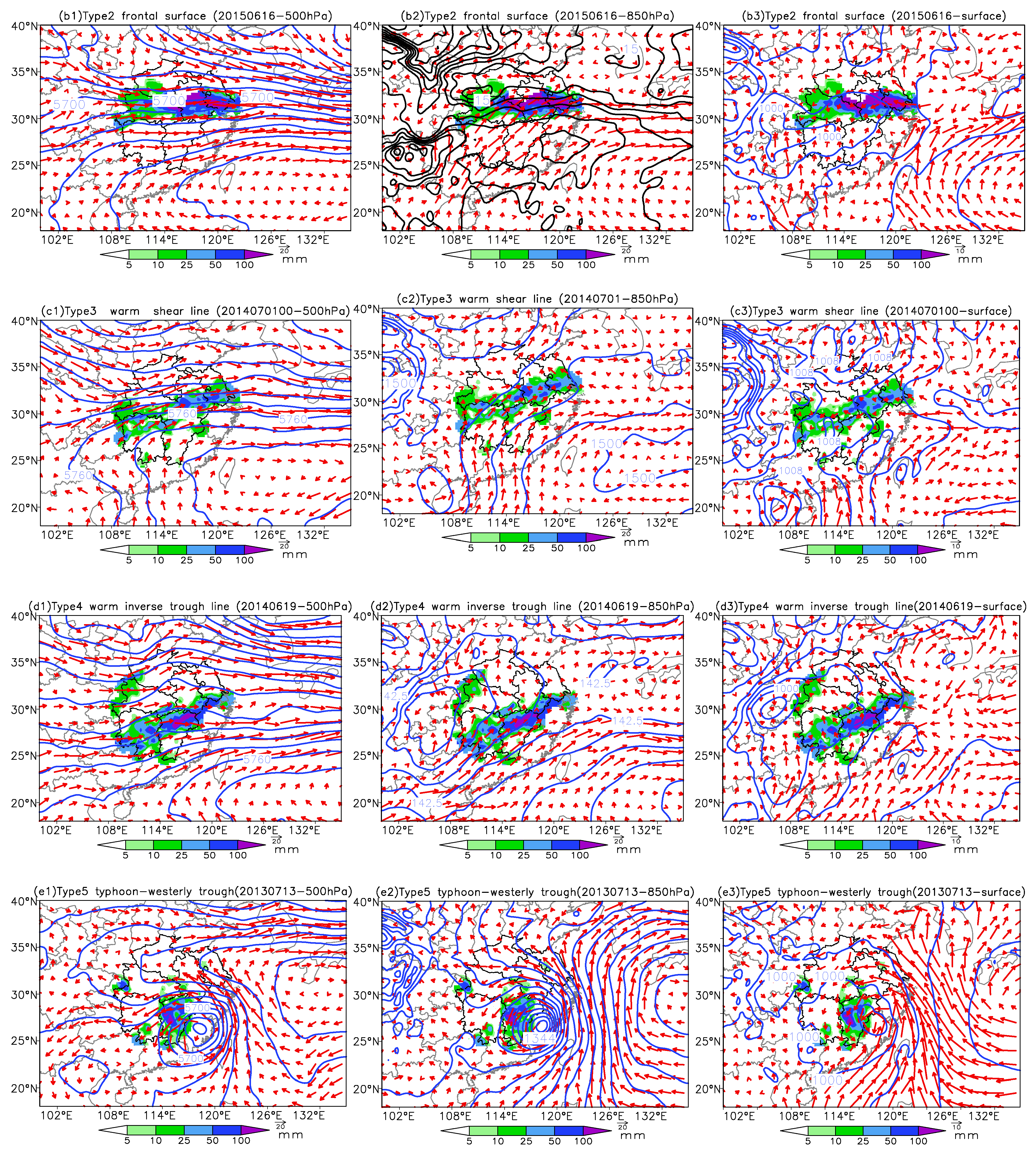
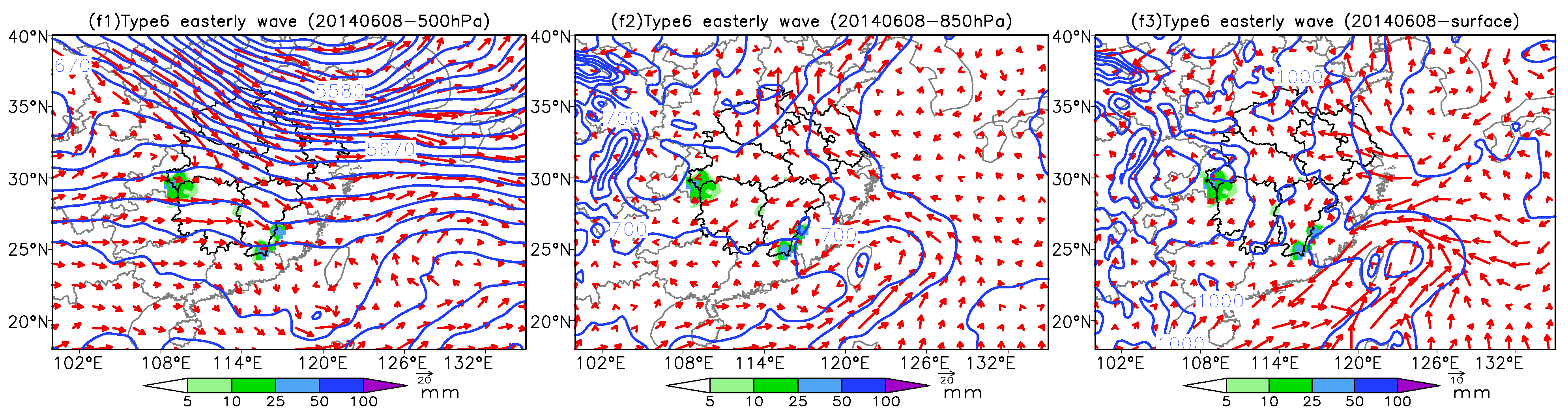
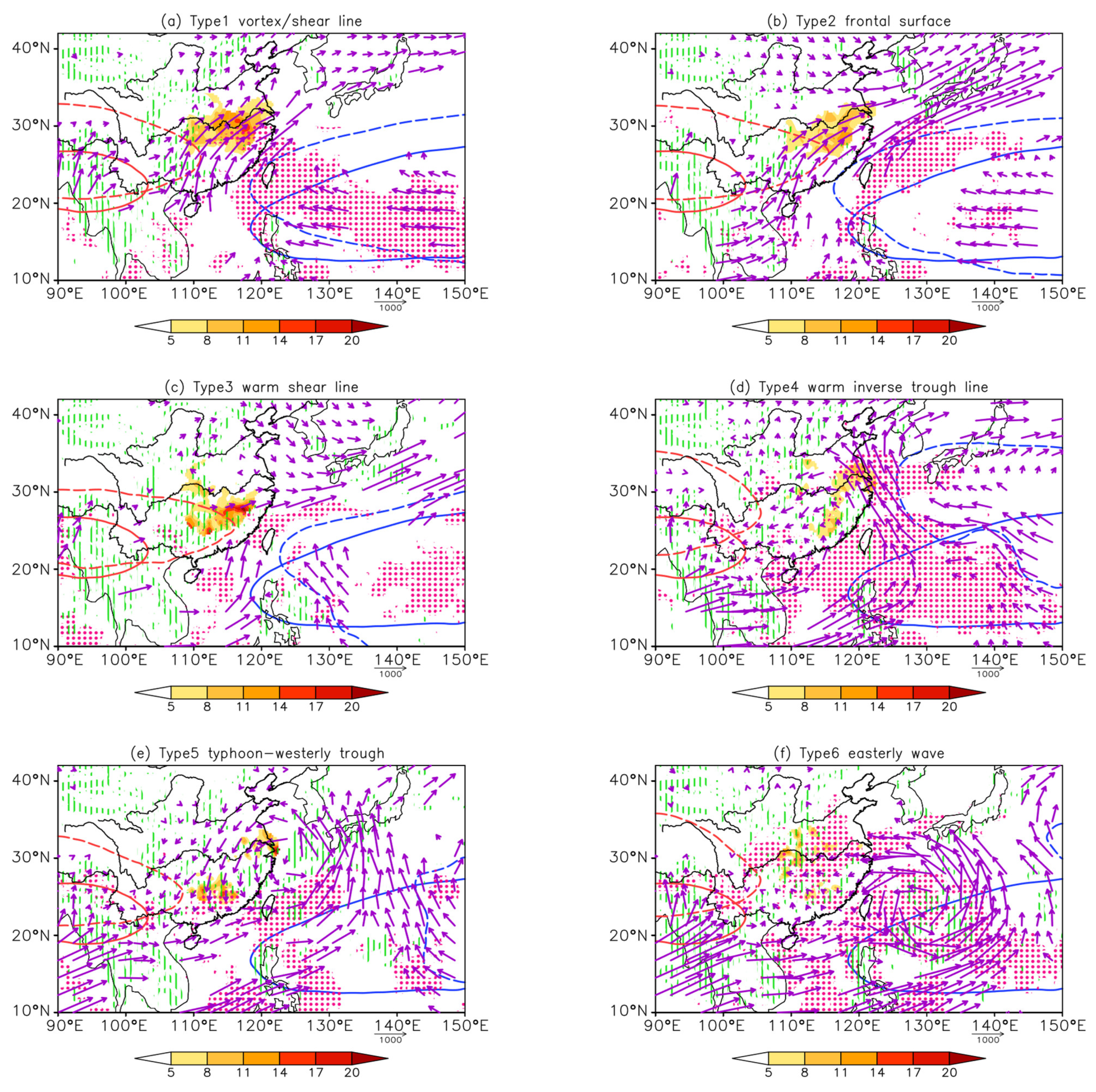
4. Interconfiguration of Multilayer Systems of Six Synoptic Circulation Patterns
5. Long-Term Trends of Six Synoptic Circulation Patterns
6. Summary and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, X.N.; Zhao, K.; Chen, X.C.; Huang, A.N.; Xue, M.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, M.J.M. Influence of synoptic pattern and low-level wind speed on intensity and diurnal variations of orographic convection in summer over Pearl River Delta, South China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 2019, JD030384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.Q.; Chen, D.L.; Xie, Y. Diurnal variations of precipitation during the warm season over China. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1154–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Huang, A.N.; Wu, P.L.; Huang, D.Q.; Xue, D.K.; Wu, Y. Drivers of summer extreme precipitation events over East China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The changing character of precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.M.; Zhang, X.B.; Wan, H.; Pan, X.H. Trends on total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.C.; Xu, Y.P.; Zhou, T.J.; Li, J. Relation between rainfall duration and diurnal variation in the warm season precipitation over central eastern China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.Z.; Zhang, F.Q. Diurnal variations of warm-season precipitation over North China. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.X.; Zipser, E.J.; Liu, C.T. Rainfall characteristics and convective properties of Mei-Yu precipitation systems over South China, Taiwan, and the South China Sea. Part I: TRMM observations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 4261–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañares, E.N.; Narisma, G.T.T.; Simpas, J.B.B.; Cruz, F.T.; Lorenzo, G.R.H.; Cambaliza, M.O.L.; Coronel, R.C. Seasonal and diurnal variations of observed convective rain events in Metro Manila, Philippines. Atmos. Res. 2021, 258, 105646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, T.J. Diurnal cycle of summer rainfall in Shandong of eastern China. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, D.Y.; Zheng, L.L. Characteristics of the diurnal variations flood period precipitation in Anhui during the last 30 years. Torrential Rain Disaster 2017, 36, 53–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.M.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhu, A.X.; Sheng, M.L.; Duan, Z. Spatial distribution of diurnal rainfall variation in summer over China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 19, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, G.T.J.; Carbone, R.E. The role of diurnal solenoidal circulation on propagating rainfall episodes near the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 2975–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Zhang, F.Q. Impacts of mountain-plains solenoid on diurnal variations of rainfalls along the Mei-Yu front over the east China plains. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderholm, B.; Ronalds, B.; Kirshbaum, D.J. The evolution of convective storms initiated by an isolated mountain ridge. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 1430–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, A.; Huang, D.; Chen, F.; Yang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, D.; Zhang, L. Diurnal variations of summer precipitation over the regions east to Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 4287–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhang, F.Q. Hail Day Frequency Trends and Associated Atmospheric Circulation Patterns over China during 1960–2012. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 7027–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Li, J. Hourly rainfall changes in response to surface air temperature over eastern contiguous China. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6851–6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, R.C.; Yuan, W.H.; Chen, H.M. Changes in duration-related characteristics of late-summer precipitation over Eastern China in the past 40 years. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 5683–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.H.; Yu, R.C.; Zhang, M.H.; Lin, W.Y.; Chen, H.M.; Li, J. Regimes of diurnal variation of summer rainfall over subtropical East Asia. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 3307–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.N.; Zhang, D.L.; Xia, R.D.; Qian, T.T. Diurnal variations of presummer rainfall over Southern China. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 755–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottayil, A.; Satheesan, K.; Viju, O.J.; Antony, R. Diurnal variation of deep convective clouds over Indian monsoon region and its association with rainfall. Atmos. Res. 2021, 255, 105540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, R.S.; Johnson, R.H. Organization and environmental properties of extreme-rain-producing mesoscale convective systems. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, R.S.; Clark, A.J.; Xue, M.; Kong, F.Y. Factors influencing the development and maintenance of nocturnal heavy-rain-producing convective systems in a storm-scale ensemble. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 2778–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerns, B.W.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Chang, M.Y. The diurnal cycle of winds, rain, and clouds over Taiwan during the Mei-Yu, summer, and autumn rainfall regimes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppert, K.D.; Cecil, D.J. Tropical cyclone diurnal cycle as observed by TRMM. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 2793–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Chien, F.C.; Paul, S.; Lee, D.I.; Chuang, P.Y. An evaluation of WRF rainfall forecasts in Taiwan during three Mei-Yu seasons from 2008 to 2010. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 1329–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.R.; Cook, K.H.; Vizy, E.K. The role of mesoscale convective systems in the diurnal cycle of rainfall and its seasonality over sub-Saharan Northern Africa. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, S.W.; Zipser, E.J. The diurnal cycle of rainfall and convective intensity according to three years of TRMM measurements. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 1456–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.P.; Hou, S.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Chen, G.T.J. The development of an intense East Asian summer monsoon disturbance with strong vertical coupling. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 2692–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Chan, J.C.L. The East Asian summer monsoon: An overview. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 89, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, L. Observed trends in extreme precipitation events in China during 1961–2001 and the associated changes in large-scale circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L09707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.L.; Wu, M.W.; Ren, F.M.; Li, J.; Wong, W.K. Synoptic situations of extreme hourly precipitation over China. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 8703–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryhal, J.; Huth, R. Classifications of winter Euro-Atlantic circulation patterns: An intercomparison of five atmospheric reanalyses. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 7847–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlaw, L.B.; Cohen, A.E.; Rogers, J.W. Synoptic and mesoscale environment of convection during the north American Monsoon across central and southern Arizona. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.G.; Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhong, M.; Wang, S.S.; Huang, X.Y.; Li, S.; Han, F.; Wang, C. Weather system types of extreme precipitation in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Torrential Rain Disasters 2018, 37, 14–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzung, N.L.; Yamada, T.J. Using weather pattern recognition to classify and predict summertime heavy rainfall occurrence over the upper Nan River basin, northwestern Thailand. Weather Forecast. 2019, 34, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.X.; Sun, J.H.; Chen, B.F. Selection and classification of warm-sector heavy rainfall events over South China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 43, 119–130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, R.; Beck, C.; Philipp, A.; Demuzere, M.; Ustrnul, Z.; Cahynová, M.; Kyselý, J.; Tveito, O.E. Classifications of atmospheric circulation patterns. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1146, 105–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, A.; Bartholy, J.; Beck, C.; Erpicum, M.; Esteban, P.; Fettweis, X.; Huth, R.; James, P.; Jourdain, S.; Kreienkamp, F.; et al. Cost733cat-database of weather and circulation type classifications. Phys. Chem. Earth 2010, 35, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuzere, M.; Kassomenos, P.; Philipp, A. The COST733 circulation type classification software: An example for surface ozone concentrations in Central Europe. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 105, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Yu, R.C.; Li, J.; Yuan, W.H.; Zhou, T.J. Why nocturnal long duration rainfall presents an eastward-delayed diurnal phase of rainfall down the Yangtze River valley. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Deng, L.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, Y.J. Quantitative Attribution of Vertical Motion Responsible for Summer Heavy Rainfall Over North China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.P.; Zhang, H.H.; Ma, J.L.; Shi, D.W.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, G.C. Characteristics of newly formed mesoscale convective systems during the abnormal precipitation over the Yangtze River basin from June to July, 2020. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2022, 23, e1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.C. Study on the formation mechanism of rainstorms associated with surface inverted troughs. J. Mar. 2018, 38, 39–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.J.; LI, L.; Huang, X.Y.; He, B.W.; Ye, R.X. Analysis of mechanism of topographic influence and meso-scale convective characteristics of an extremely severe rainfall affected by typical easterly wave. J. Arid. Meteorol. 2022, 40, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhai, P.M. Temporal and spatial characteristics of extreme hourly precipitation over eastern China in the warm season. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, Z.M.; Cui, C.G.; Dong, X.Q. A statistical and dynamical characterization of large-scale circulation patterns associated with summer extreme precipitation over the middle reaches of Yangtze River. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 6213–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.J.; Huang, G.; Wu, R.G.; Tao, W.C.; Gong, H.N.; Qu, X.; Hu, K. A new upper-level circulation index for the east asian summer monsoon variability. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 9977–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossin, J.P.; Knapp, K.R.; Olander, T.L.; Velden, C.S. Global increase in major tropical cyclone exceedance probability over the past four decades. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11975–11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Ren, F.; Wu, L.; Chen, L.; Ding, C. Characteristics of tropical cyclone extreme precipitation and its preliminary causes in Southeast China. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2019, 131, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yoon, S.K.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Xiong, L.H.; Kim, J.S. Statistical prediction of typhoon-induced total accumulated rainfall in the Western North Pacific using typhoon track similarity indices. Atmos. Res. 2023, 288, 106724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



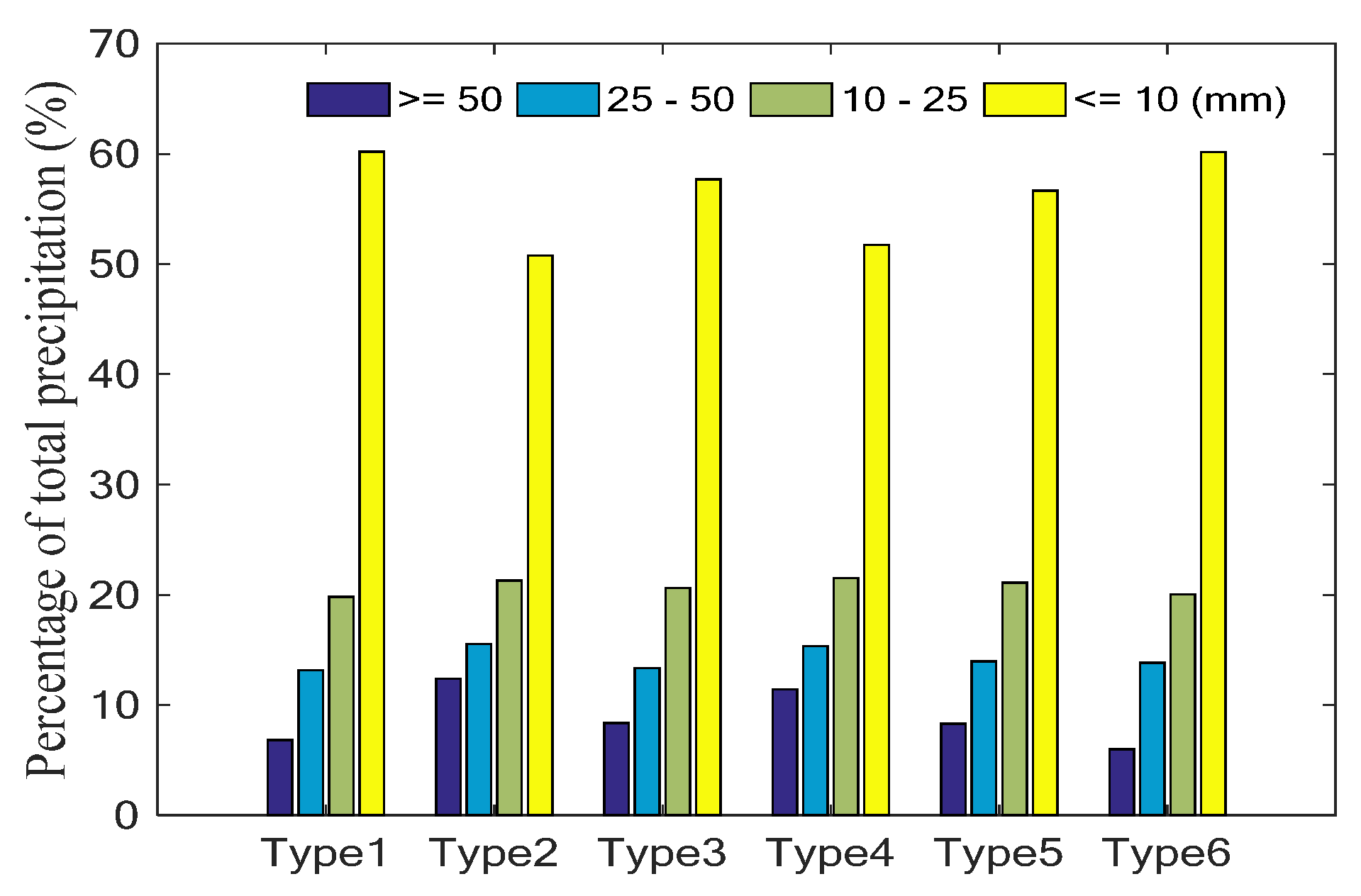



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, H.; Lin, C.; Peng, T.; Zhi, X.; Cui, C.; Chen, W.; Yin, Z.; Shen, T.; Xiang, Y. Diurnal Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events under Different Synoptic Circulation Patterns in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in Summer. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081320
Qi H, Lin C, Peng T, Zhi X, Cui C, Chen W, Yin Z, Shen T, Xiang Y. Diurnal Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events under Different Synoptic Circulation Patterns in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in Summer. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(8):1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081320
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Haixia, Chunze Lin, Tao Peng, Xiefei Zhi, Chunguang Cui, Wen Chen, Zhiyuan Yin, Tieyuan Shen, and Yiheng Xiang. 2023. "Diurnal Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events under Different Synoptic Circulation Patterns in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in Summer" Atmosphere 14, no. 8: 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081320
APA StyleQi, H., Lin, C., Peng, T., Zhi, X., Cui, C., Chen, W., Yin, Z., Shen, T., & Xiang, Y. (2023). Diurnal Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events under Different Synoptic Circulation Patterns in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in Summer. Atmosphere, 14(8), 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081320





