The WRF-CMAQ Simulation of a Complex Pollution Episode with High-Level O3 and PM2.5 over the North China Plain: Pollution Characteristics and Causes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Observations
2.2. WRF-CMAQ Model Configuration
2.3. The Integrated Process Rate Analysis
2.4. The Integrated Source Apportionment Method
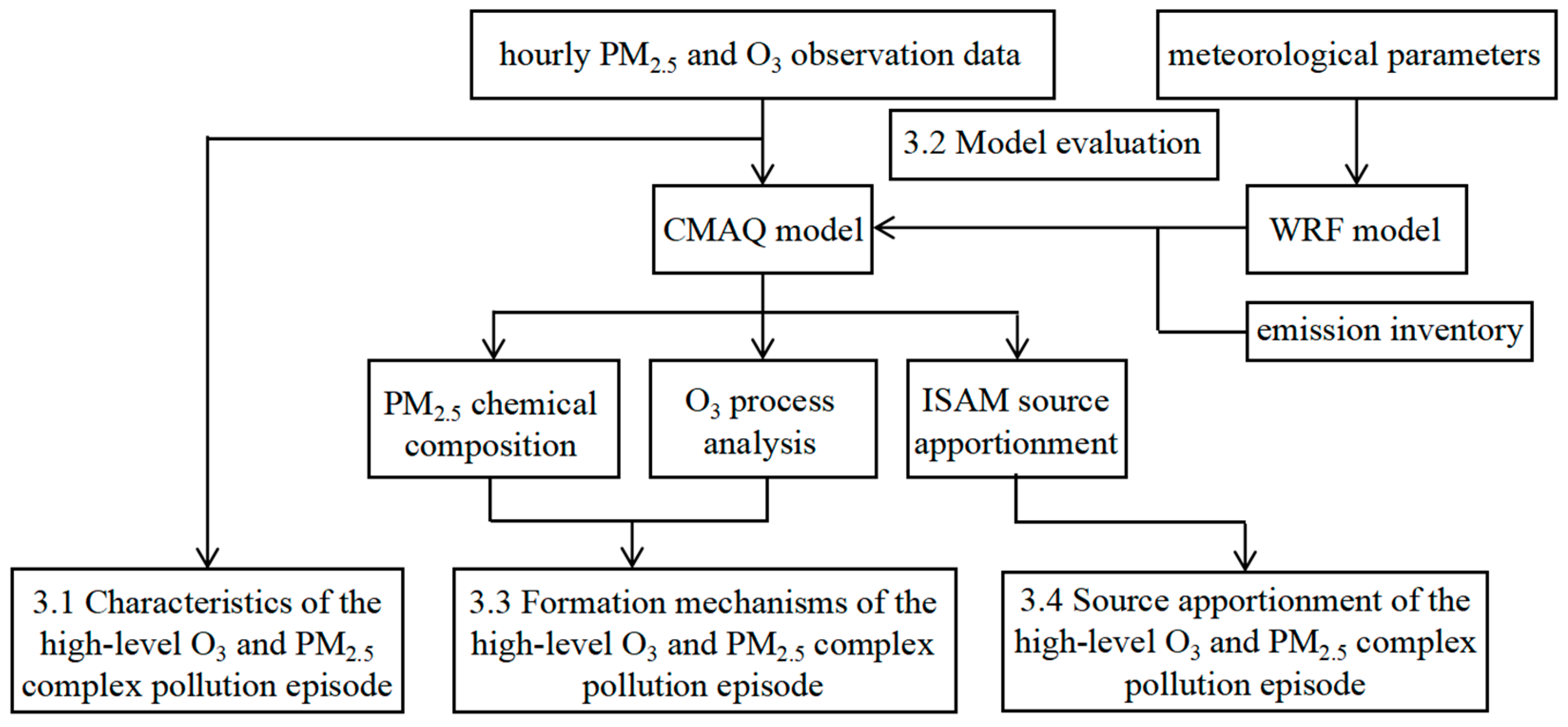
2.5. The Technical Workflow
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the High-Level O3 and PM2.5 Complex Pollution Episode
3.2. Model Evaluation
3.3. Formation Mechanisms of the High-Level O3 and PM2.5 Complex Pollution Episode
3.3.1. Analysis of O3 Formation Mechanisms
3.3.2. Analysis of PM2.5 Formation Mechanisms
3.4. Source Apportionment of the High-Level O3 and PM2.5 Complex Pollution Episode
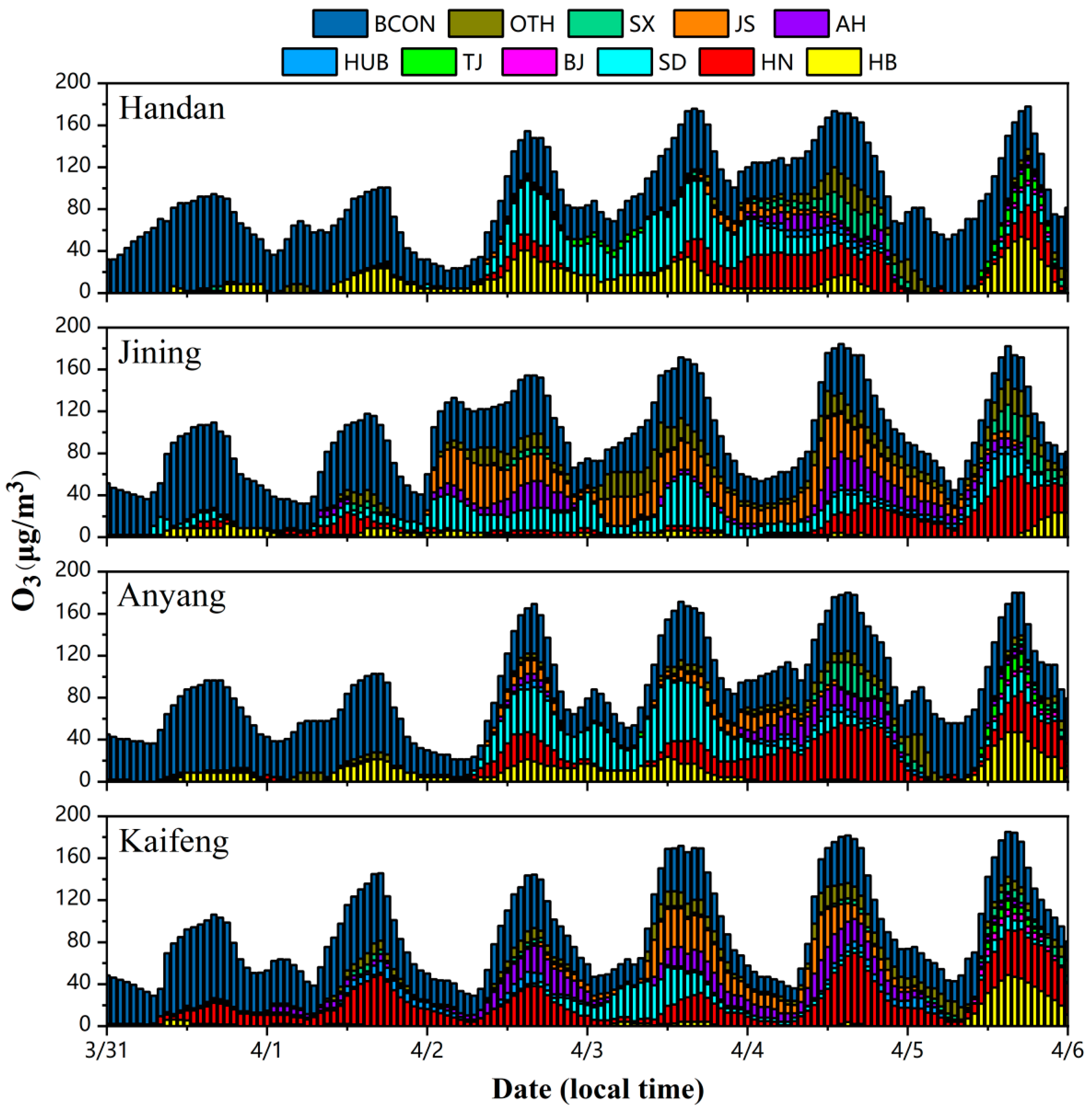
3.4.1. Analysis of O3 Source Apportionment
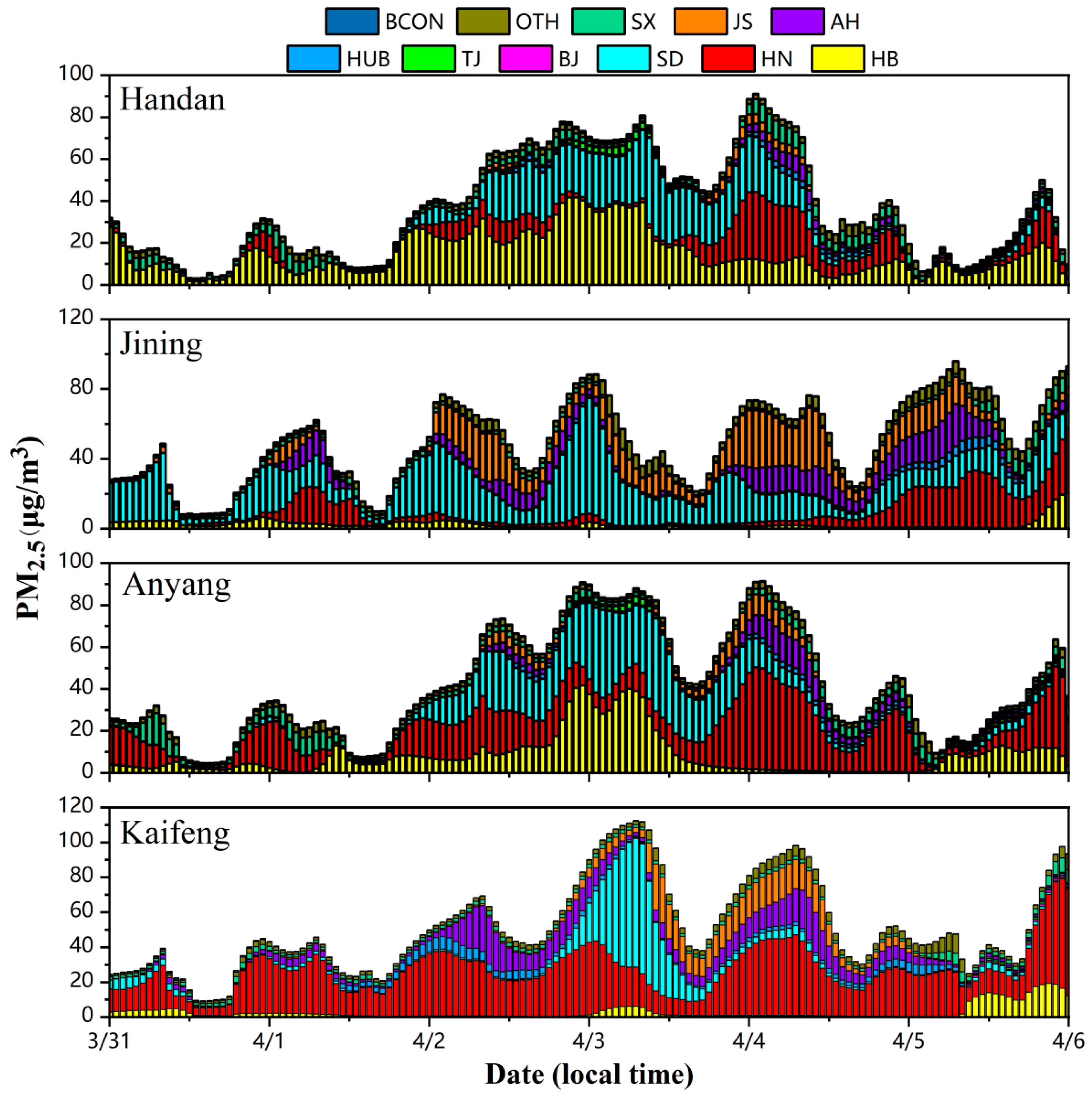
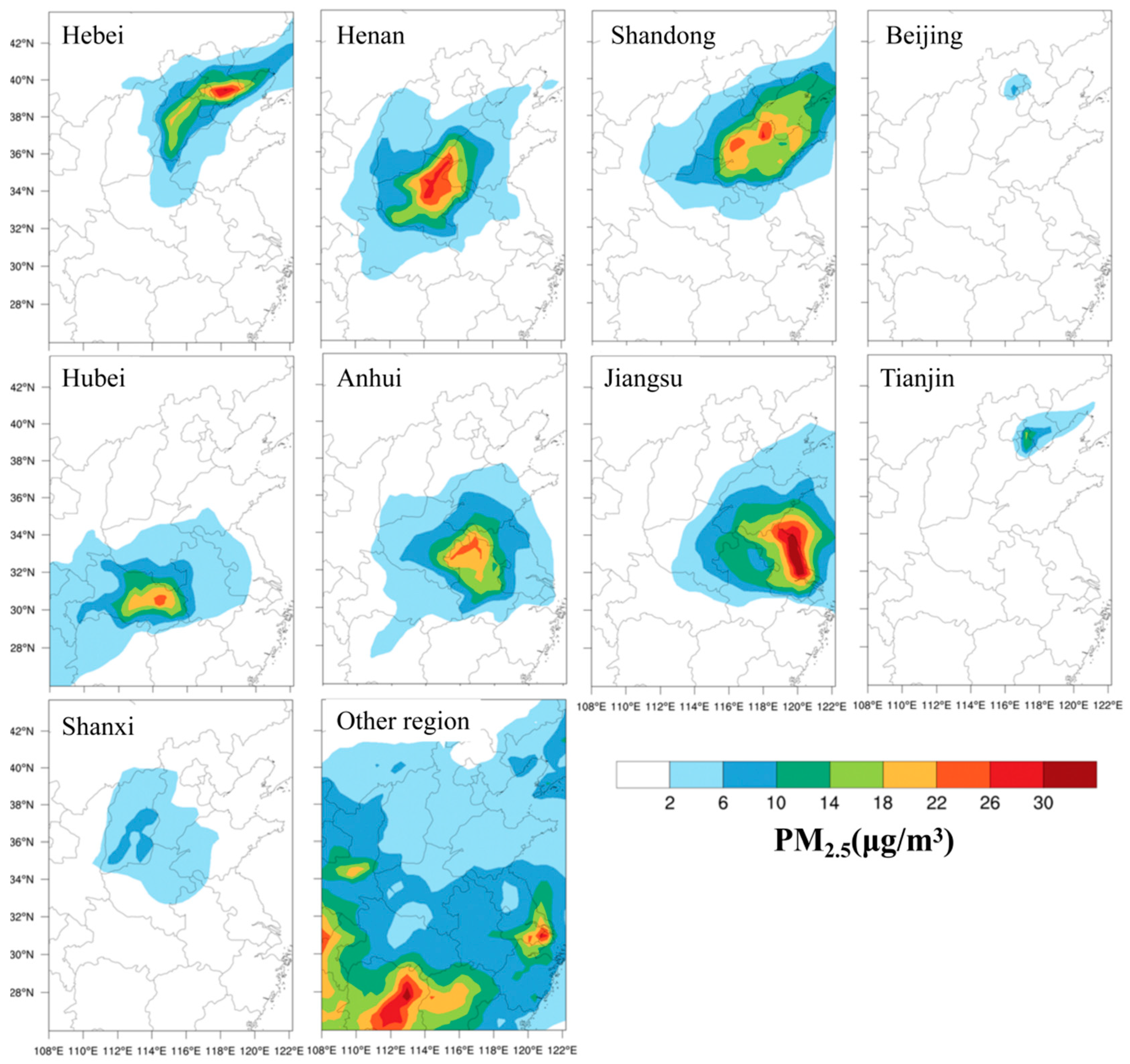
3.4.2. Analysis of PM2.5 Source Apportionment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Zhu, J.; Shah, V.; Shen, L.; Bates, K.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, S. A two-pollutant strategy for improving ozone and particulate air quality in China. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Shen, L.; Lu, X.; De Smedt, I.; Liao, H. Increases in surface ozone pollution in China from 2013 to 2019: Anthropogenic and meteorological influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11423–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yin, D.; Yu, Y.; Kang, S.; Qin, D.; Dong, L. PM2.5 and O3 pollution during 2015–2019 over 367 Chinese cities: Spatiotemporal variations, meteorological and topographical impacts. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Wu, D.; Deng, X.; Tan, H.; Li, F.; Zheng, J.; Liao, B. Simulation of a typical complex pollution process over Pearl River Delta area. China Environ. Sci. 2012, 32, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Kwan, M.-P.; Chen, B.; Gao, B.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, B. The control of anthropogenic emissions contributed to 80 % of the decrease in PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing from 2013 to 2017. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13519–13533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Geng, G.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, D.; Liu, Z.; Guan, D.; Bo, Y.; Zhu, T.; et al. Rapid improvement of PM2.5 pollution and associated health benefits in China during 2013–2017. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Bates, K.H. Anthropogenic drivers of 2013-2017 trends in summer surface ozone in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, F. Application of multivariate geostatistics in environmental epidemiology: Case study from Houston, Texas. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2016, 04, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anderson, F.; Delclos, G.L.; Rao, D.C. The effect of air pollutants and socioeconomic status on asthma in Texas. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2016, 04, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anderson, F.; Carson, A.; Whitehead, L.; Burau, K. Spatiotemporal analysis of the effect of ozone and fine particulate on CVD emergency room visits in Harris County, Texas. Open J. Air Pollut. 2014, 3, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, L.T.; Wei, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.F.; Su, J.; Meng, C.C.; Zhang, Q. The 2013 severe haze over southern Hebei, China: Model evaluation, source apportionment, and policy implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3151–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kang, S.; Ji, Z.; Yin, X.; Tripathee, L. Investigating air pollutant concentrations, impact factors, and emission control strategies in western China by using a regional climate-chemistry model. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ying, Q.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H. Spatial and temporal variations of six criteria air pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities in China during 2013–2014. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Xing, J.; Morawska, L.; Ding, A.; Kulmala, M.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kujansuu, J.; et al. Particulate matter pollution over China and the effects of control policies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 426–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putaud, J.P.; Van Dingenen, R.; Alastuey, A.; Bauer, H.; Birmili, W.; Cyrys, J.; Flentje, H.; Fuzzi, S.; Gehrig, R.; Hansson, H.C.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology—3: Physical and chemical characteristics of particulate matter from 60 rural, urban, and kerbside sites across Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmi, A.; Wiedensohler, A.; Laj, P.; Fjaeraa, A.M.; Sellegri, K.; Birmili, W.; Weingartner, E.; Baltensperger, U.; Zdimal, V.; Zikova, N.; et al. Number size distributions and seasonality of submicron particles in Europe 2008–2009. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5505–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.H.; You, S.; Bae, M.; Kim, E.; Son, K.; Bae, C.; Kim, Y.; Kim, B.U.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, S. The impacts of COVID-19, meteorology, and emission control policies on PM2.5 drops in Northeast Asia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Gao, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yun, Y.; Ren, C. Spatial and temporal variation of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants in 26 cities in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Nielsen, C.P.; Lei, Y.; McElroy, M.B.; Hao, J. Quantifying the uncertainties of a bottom-up emission inventory of anthropogenic atmospheric pollutants in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2295–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danek, T.; Weglinska, E.; Zareba, M. The influence of meteorological factors and terrain on air pollution concentration and migration: A geostatistical case study from Krakow, Poland. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Song, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014–2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ying, Q.; Hu, X.M. Relationships between meteorological parameters and criteria air pollutants in three megacities in China. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Ying, Q. Comparison of the SAPRC07 and SAPRC99 photochemical mechanisms during a high ozone episode in Texas: Differences in concentrations, OH budget and relative response factors. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ying, Q. Contributions of local and regional sources of NOx to ozone concentrations in Southeast Texas. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Ying, Q.; Yu, J.Z.; Wu, D.; Cheng, Y.; He, K.; Jiang, J. Source apportionment of PM2.5 nitrate and sulfate in China using a source-oriented chemical transport model. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Feng, Z.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y. Ground-level ozone pollution in China: A synthesis of recent findings on influencing factors and impacts. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 063003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Hong, J.; Zhang, L.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Severe Surface Ozone Pollution in China: A Global Perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-L.; Petropavlovskikh, I.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Wang, T. Regional trend analysis of surface ozone observations from monitoring networks in eastern North America, Europe and East Asia. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2017, 50, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefohn, A.S.; Malley, C.S.; Smith, L.; Wells, B.; Hazucha, M.; Simon, H.; Naik, V.; Mills, G.; Schultz, M.G.; Paoletti, E.; et al. Tropospheric ozone assessment report Global ozone metrics for climate change, human health and cropecosystem research. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2018, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, J. Lower tropospheric ozone over India and its linkage to the South Asian monsoon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 3101–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, B.S.; Raga, G.B. Variability of winter and summer surface ozone in Mexico City on the intraseasonal timescale. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 15359–15370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Dickerson, R.R.; Pinker, R.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Xue, W.; Cribb, M. Full-coverage mapping and spatiotemporal variations of ground-level ozone (O3) pollution from 2013 to 2020 across China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Liu, J.; Tao, W.; Yi, K.; Xu, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; et al. Control of both PM2.5 and O3 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and the surrounding areas. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Horowitz, L.W.; Payton, R.; Fiore, A.M.; Tonnesen, G. US surface ozone trends and extremes from 1980 to 2014: Quantifying the roles of rising Asian emissions, domestic controls, wildfires, and climate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2943–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.; Yu, Z.; Qu, Y.; Zhou, G. Analysis of characteristics and meteorological causes of PM2.5-O3 compound pollution in Shanghai. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 2730–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Xu, H.; Gao, J.; Cai, Z.; Bi, W.; Li, P.; Yang, N.; Deng, X.; Ji, Y. Characteristics and Sources of PM2.5-O3 Compound Pollution in Tianjin. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikov, D.A.; Schnell, J.L.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Swain, D.L.; Singh, D. Increasing co-occurrence of fine particulate matter and ground-level ozone extremes in the western United States. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabi9386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, N.; Rantala, A.K.; Antikainen, H.; Balogun, H.; Amegah, A.K.; Ryti, N.R.I.; Kukkonen, J.; Sofiev, M.; Jaakkola, M.S.; Jaakkola, J.J.K. Synergistic effects of prenatal exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and ozone (O3) on the risk of preterm birth: A population-based cohort study. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiang, F.; Feng, S.; Cai, Z.; Shen, Y.; Ying, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q. Long-range transport of ozone across the eastern China seas: A case study in coastal cities in southeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Deng, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Yin, C.; Wang, S.; Fan, S. Numerical simulations for the sources apportionment and control strategies of PM2.5 over Pearl River Delta, China, part I: Inventory and PM2.5 sources apportionment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1631–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Yu, S.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Mehmood, K.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Lichtfouse, E.; et al. Residential emissions predicted as a major source of fine particulate matter in winter over the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Kong, L.; Tong, S.; Shen, J.; Chen, L.; Jin, S.; Wang, C.; Sha, F.; Wang, L. Double High-Level Ozone and PM2.5 Co-Pollution Episodes in Shanghai, China: Pollution Characteristics and Significant Role of Daytime HONO. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Fan, Q. Characteristics of complex pollution with high concentrations of PM2.5 and O3 over the Pearl River Delta, China. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2018, 57, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, L.; Qi, M.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. Study on the characteristics and mutual influence of PM2.5-O3 complex pollution in Handan. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2021, 41, 2250–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Sun, R.; Sun, N. Different Air Pollution Situations of O3 and PM2.5 during Summer in Beijing. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Fan, Q. Numerical simulation of a complex pollution episode with high concentrations of PM2.5 and O3 over the Pearl River Delta region, China. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 4022–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareba, M.; Dlugosz, H.; Danek, T.; Weglinska, E. Big-Data-Driven Machine Learning for Enhancing Spatiotemporal Air Pollution Pattern Analysis. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, K.D.; Haidu, I. Modeling NO2 air pollution variation during and after COVID-19-regulation using principal component analysis of satellite imagery. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 342, 122973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 3095–2012; Ambient Air Quality Standard. China Environment Press: Beijing, China, 2012. Available online: http://www.cnemc.cn/jcgf/dqhj/201711/t20171108_647276.shtml (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- HJ630-2011; Technical Guideline on Environmental Monitoring Quality Management. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/other/qt/201109/t20110914_217274.shtml (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. CMAQ User’s Guide; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2022. Available online: https://github.com/USEPA/CMAQ/blob/master/DOCS/Users_Guide/README.md (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Yu, S.; Mathur, R.; Kang, D.; Schere, K.; Eder, B.; Pleim, J. Performance and diagnostic evaluation of ozone predictions by the Eta-Community Multiscale Air Quality Forecast System during the 2002 New England Air Quality Study. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, B.; Yu, S. A performance evaluation of the 2004 release of Models-3 CMAQ. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4811–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Song, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Xie, M.; et al. Evaluation of the WRF-CMAQ Model Performances on Air Quality in China with the Impacts of the Observation Nudging on Meteorology. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 220023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, S.; Xing, J.; Chang, X.; Ding, D.; Zheng, H. Regional transport in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and its changes during 2014–2017: The impacts of meteorology and emission reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Ding, D.; Chang, X.; Liu, K.; Xing, J.; Dong, Z.; Aunan, K.; et al. Transition in source contributions of PM2.5 exposure and associated premature mortality in China during 2005–2015. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.; Schere, K.L. Review of the Governing Equations, Computational Algorithms, and Other Components of the Models-3 Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Modeling System. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Song, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Lichtfouse, E.; et al. Local production, downward and regional transport aggravated surface ozone pollution during the historical orange-alert large-scale ozone episode in eastern China. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.H.F.; Napelenok, S.L.; Baker, K.R. Implementation and evaluation of PM2.5 source contribution analysis in a photochemical model. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, S.; Meng, X.; Zhang, M.; Hu, J. Modeling study of impacts on surface ozone of regional transport and emissions reductions over North China Plain in summer 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 12207–12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.H.F.; Baker, K.R.; Napelenok, S.L.; Tonnesen, G.S. Photochemical grid model implementation and application of VOC, NOx, and O3 source apportionment. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wei, P.; Cheng, S.; Su, F.; Ren, Z.; Bai, J. Analysis of a near earth surface O3 and PM2.5 pollution in combination with its contaminating process in Beijing. J. Saf. Environ. 2017, 17, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Xing, J.; Zhou, H.; Chang, X.; Li, G.; Chen, L.; Li, J. Impacts of land use and land cover change on regional meteorology and air quality over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 189, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA-454/B-07-002; Guidance on the Use of Models and Other Analyses for Demonstrating Attainment of Air Quality Goals for Ozone, PM2.5, and Regional Haze. US-EPA: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2007.
- Shu, L.; Xie, M.; Wang, T.; Gao, D.; Chen, P.; Han, Y.; Li, S.; Zhuang, B.; Li, M. Integrated studies of a regional ozone pollution synthetically affected by subtropical high and typhoon system in the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 15801–15819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, C.H.; Huang, C.; Huang, H.Y.; Zhang, G.F.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, H.L.; Lou, S.R.; Qiao, L.P.; Zhou, M.; et al. Process analysis of regional ozone formation over the Yangtze River Delta, China using the Community Multi-scale Air Quality modeling system. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 10971–10987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, B.; Hu, B.; Wang, L.; Bao, F. What have we missed when studying the impact of aerosols on surface ozone via changing photolysis rates? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 10831–10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.; He, Y. Aerosol effects on ozone concentrations in Beijing: A model sensitivity study. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Mathur, R.; Pleim, J.; Hogrefe, C.; Gan, C.M.; Wong, D.C.; Wei, C.; Wang, J. Air pollution and climate response to aerosol direct radiative effects: A modeling study of decadal trends across the northern hemisphere. J. Geophys. Res.—Atmos. 2015, 120, 12221–12236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Wang, J.; Mathur, R.; Wang, S.; Sarwar, G.; Pleim, J.; Hogrefe, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wong, D.C.; et al. Impacts of aerosol direct effects on tropospheric ozone through changes in atmospheric dynamics and photolysis rates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9869–9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; He, K.; Zhang, Q.; Chai, L. Sulfate-nitrate-ammonium aerosols over China: Response to 2000–2015 emission changes of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and ammonia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2635–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. The Numerical Simulation of Comprehensive Air Pollution Characteristics in a Typical City-Cluster. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China, 30 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kurten, T.; Lane, J.R.; Jorgensen, S.; Kjaergaard, H.G. A computational study of the oxidation of SO2 to SO3 by gas-phase organic oxidants. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 8669–8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.Y.; Zhao, C.S.; Ran, L.; Lin, W.L.; Yan, P.; Xu, X.B. SO2 noontime-peak phenomenon in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 7757–7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Tang, A.; Wang, Y.; An, Z. Chemical Characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 in Haze-Fog Episodes in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3148–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, J. Particulate Nitrate Formation in a Highly Polluted Urban Area: A Case Study by Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry in Shanghai. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3061–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Caihong, X.; Sui, X.; Yao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, T.; et al. Enhanced formation of fine particulate nitrate at a rural site on the North China Plain in summer: The important roles of ammonia and ozone. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chen, H.; Du, J.; Yang, X.; Gao, S.; Chen, J.; Geng, F. Evolution of the mixing state of fine aerosols during haze events in Shanghai. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104–105, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, B.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Duan, Y.; Li, J. Intense secondary aerosol formation due to strong atmospheric photochemical reactions in summer: Observations at a rural site in eastern Yangtze River Delta of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
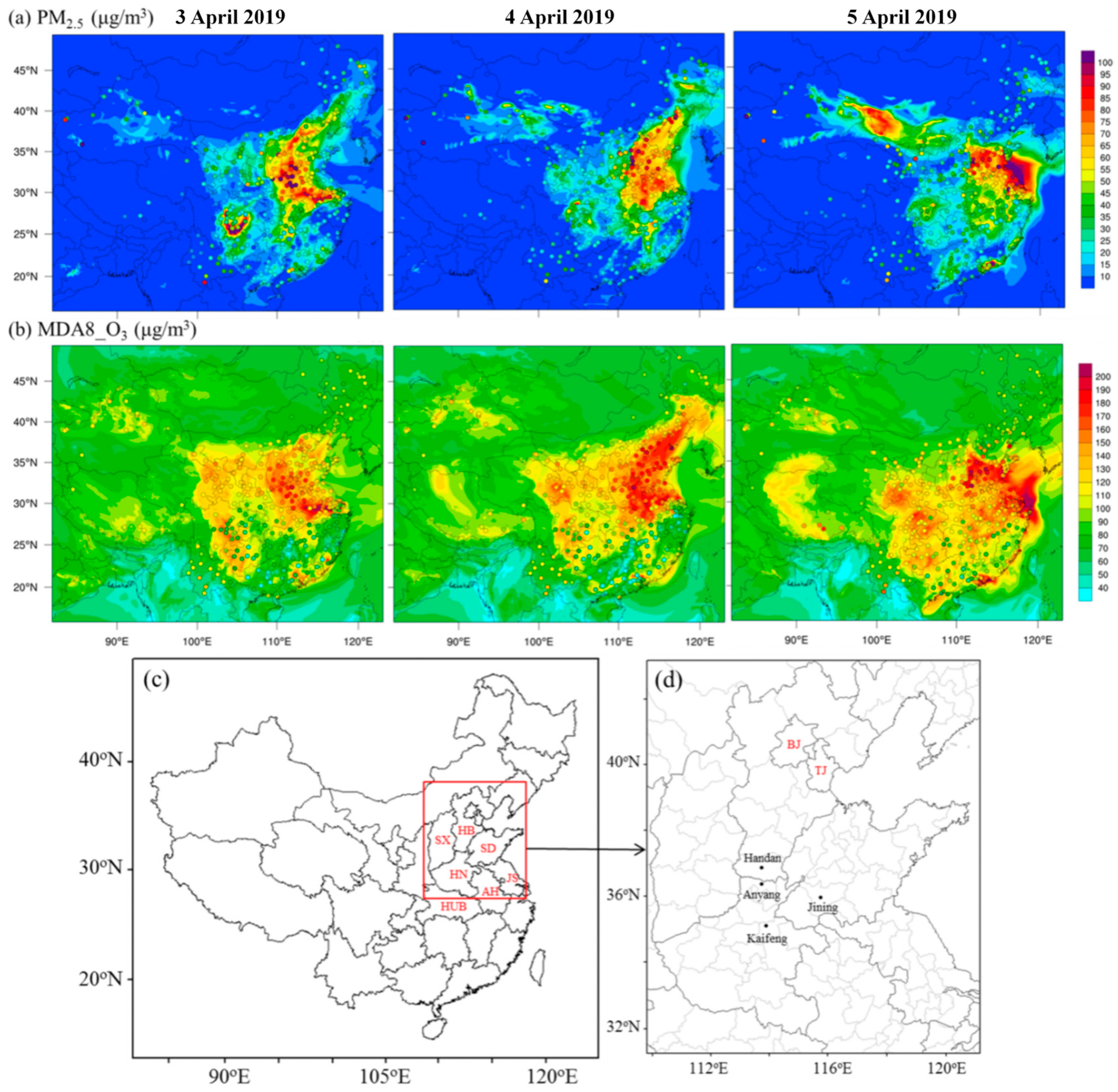

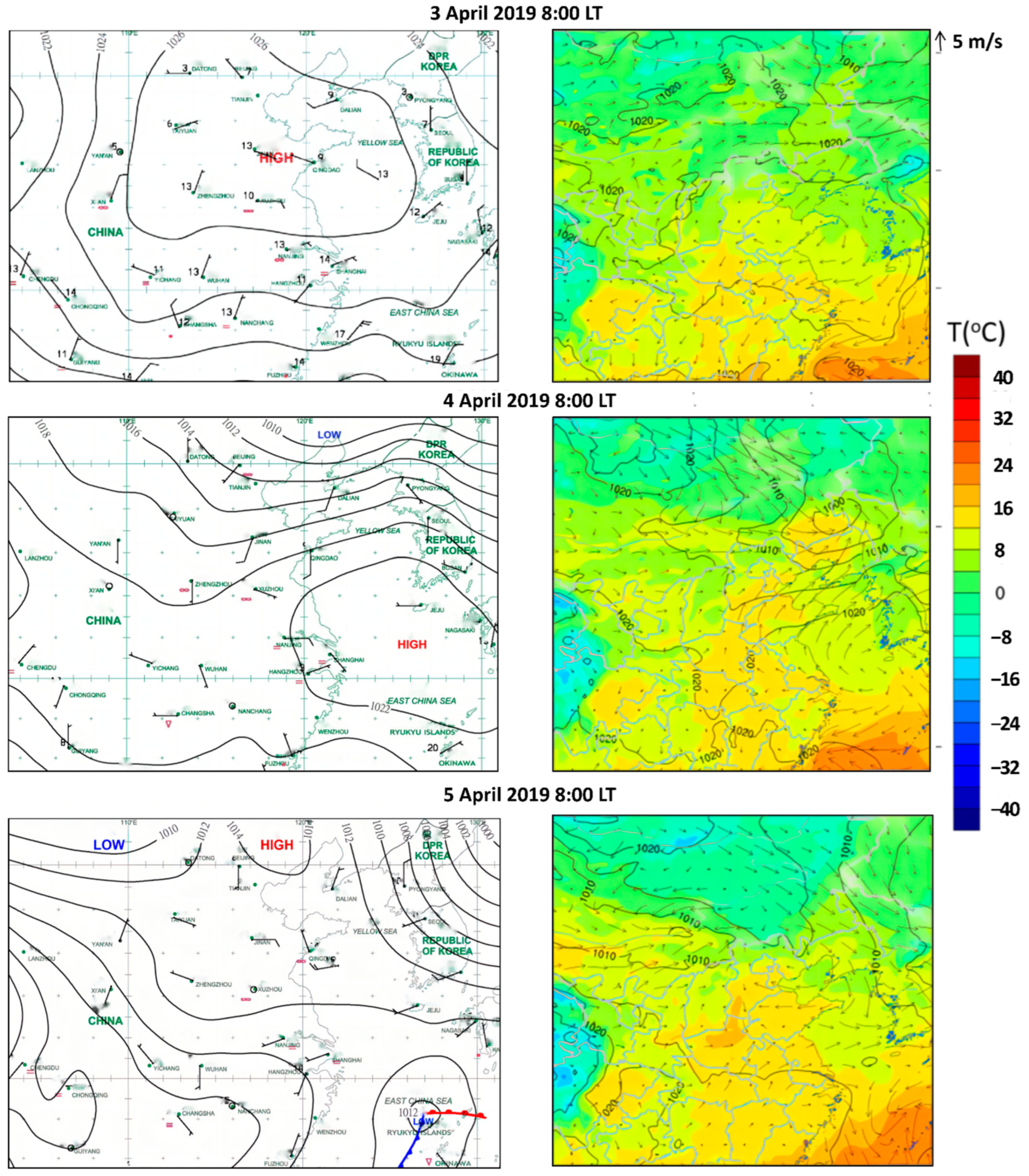
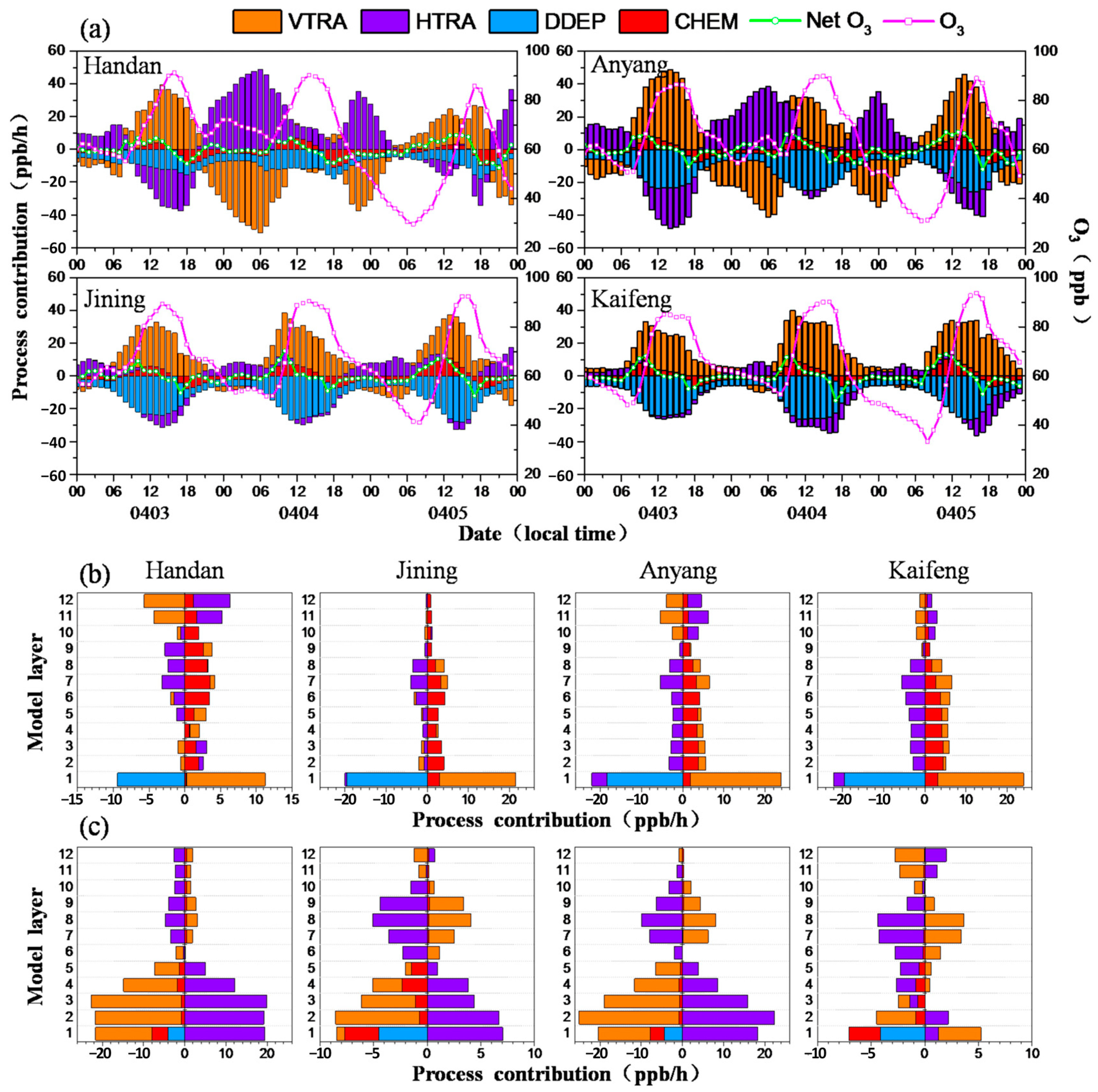


| Pollutants | Complex Pollution Periods | Non-Complex Pollution Periods | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Handan | Jining | Anyang | Kaifeng | Handan | Jining | Anyang | Kaifeng | |
| EC | 3.8 | 2.6 | 3.2 | 2.3 | 2.7 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 2.0 |
| SO42− | 7.8 | 8.3 | 7.5 | 6.7 | 4.4 | 5.2 | 4.7 | 6.0 |
| NO3− | 16.5 | 16.3 | 16.3 | 11.6 | 7.4 | 8.8 | 7.7 | 10.1 |
| NH4+ | 7.0 | 7.1 | 6.8 | 5.2 | 3.2 | 3.8 | 3.4 | 4.4 |
| SOA | 26.9 | 27.0 | 26.7 | 24.8 | 11.7 | 16.1 | 13.7 | 19.6 |
| PM2.5 | 76.6 | 74.7 | 73.9 | 62.5 | 39.0 | 45.9 | 42.3 | 53.2 |
| Secondary proportion 1 | 75.9% | 78.5% | 77.4% | 77.4% | 68.3% | 73.8% | 69.7% | 75.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dou, X.; Yu, S.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Song, Z.; Yao, N.; Li, P. The WRF-CMAQ Simulation of a Complex Pollution Episode with High-Level O3 and PM2.5 over the North China Plain: Pollution Characteristics and Causes. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020198
Dou X, Yu S, Li J, Sun Y, Song Z, Yao N, Li P. The WRF-CMAQ Simulation of a Complex Pollution Episode with High-Level O3 and PM2.5 over the North China Plain: Pollution Characteristics and Causes. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(2):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020198
Chicago/Turabian StyleDou, Xuedan, Shaocai Yu, Jiali Li, Yuhai Sun, Zhe Song, Ningning Yao, and Pengfei Li. 2024. "The WRF-CMAQ Simulation of a Complex Pollution Episode with High-Level O3 and PM2.5 over the North China Plain: Pollution Characteristics and Causes" Atmosphere 15, no. 2: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020198
APA StyleDou, X., Yu, S., Li, J., Sun, Y., Song, Z., Yao, N., & Li, P. (2024). The WRF-CMAQ Simulation of a Complex Pollution Episode with High-Level O3 and PM2.5 over the North China Plain: Pollution Characteristics and Causes. Atmosphere, 15(2), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020198







